

植物学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (5): 726-737.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24010 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24010
陈婷欣1, 符敏3, 李娜2, 杨蕾蕾2, 李凌飞2,*( ), 钟春梅1,*(
), 钟春梅1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-01-22
接受日期:2024-05-07
出版日期:2024-09-10
发布日期:2024-08-19
通讯作者:
李凌飞,钟春梅
基金资助:
Tingxin Chen1, Min Fu3, Na Li2, Leilei Yang2, Lingfei Li2,*( ), Chunmei Zhong1,*(
), Chunmei Zhong1,*( )
)
Received:2024-01-22
Accepted:2024-05-07
Online:2024-09-10
Published:2024-08-19
Contact:
Lingfei Li, Chunmei Zhong
摘要: DNA甲基化是重要的表观遗传修饰之一, 参与调控植物基因组稳定性、发育及胁迫响应等过程。DNA甲基转移酶是DNA甲基化的关键酶。为了解铁甲秋海棠(Begonia masoniana) DNA甲基转移酶的功能, 采用生物信息学方法从铁甲秋海棠基因组中鉴定出5个编码DNA甲基转移酶的基因。根据序列特征将其分为CMT、MET和DRM三类。不同类别成员的基因序列长度和内含子数量存在明显差异, 但同类成员的基因结构和保守结构域具有高度保守性。这些蛋白均定位于细胞核, 且基因启动子含有大量的光响应、MYB结合及植物激素响应等元件。激素响应模式分析表明, CMT3类在GA、SA和NAA处理下基因表达显著降低, CMT2类在MeJA和NAA处理下基因表达显著降低, 而MET类和DRM类分别在GA和ABA处理下基因表达显著升高。此外, 组织特异性分析发现, 叶片中BmaCMT2-5和BmaDRM2-2的表达量明显高于其它组织器官, 且这2个酶的编码基因与BmaMET1-15在叶片红色部分的表达高于绿叶部分, 推测这3个DNA甲基转移酶可能在叶斑形成过程中发挥重要作用。
陈婷欣, 符敏, 李娜, 杨蕾蕾, 李凌飞, 钟春梅. 铁甲秋海棠DNA甲基转移酶全基因组鉴定及表达分析(长英文摘要). 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 726-737.
Tingxin Chen, Min Fu, Na Li, Leilei Yang, Lingfei Li, Chunmei Zhong. Identification and Expression Analysis of DNA Methyltransferase in Begonia masoniana . Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(5): 726-737.
| Gene name | Gene ID | Primer sequence (5′-3′) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BmaCMT2-5 | Bma021768.1 | F: CTGCTGGCTGCTATGGTCTT | R: ACATCATGTGTGGGTAGCGG |
| BmaCMT3-11 | Bma005730.1 | F: CCAACAGTAGTTACACGCGCGG | R: CCGGAAAACCTTGCAGTCTCGC |
| BmaCMT3-14 | Bma011172.1 | F: TGCCGAGCAAACGTCAAGCG | R: ACTTCAGGCGCCGAAGAAGC |
| BmaMET1-15 | Bma013045.1 | F: CGGCTAACGCTTGCATCGCT | R: AGGAGCAGCCGCCCATATGA |
| BmaDRM2-2 | Bma014831.1 | F: CTGCCGCAAGAAAGAGAGGT | R: GAAGGCCACCACTTCCTTGT |
表1 铁甲秋海棠DNA甲基转移酶qRT-PCR引物
Table 1 DNA methyltransferase qRT-PCR primers for Begonia masoniana
| Gene name | Gene ID | Primer sequence (5′-3′) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BmaCMT2-5 | Bma021768.1 | F: CTGCTGGCTGCTATGGTCTT | R: ACATCATGTGTGGGTAGCGG |
| BmaCMT3-11 | Bma005730.1 | F: CCAACAGTAGTTACACGCGCGG | R: CCGGAAAACCTTGCAGTCTCGC |
| BmaCMT3-14 | Bma011172.1 | F: TGCCGAGCAAACGTCAAGCG | R: ACTTCAGGCGCCGAAGAAGC |
| BmaMET1-15 | Bma013045.1 | F: CGGCTAACGCTTGCATCGCT | R: AGGAGCAGCCGCCCATATGA |
| BmaDRM2-2 | Bma014831.1 | F: CTGCCGCAAGAAAGAGAGGT | R: GAAGGCCACCACTTCCTTGT |

图1 拟南芥(At)、甘蓝型油菜(Bna)、水稻(Os)和铁甲秋海棠(Bma) DNA甲基转移酶系统发育树(A)与蛋白结构域分布图(B) 采用MEGA7, 邻接法。Bootstrap值为1 000。数字表示自展值。CMT: 染色质甲基化酶; MET: 甲基转移酶; DNMT: 从头DNA甲基转移酶; DRM: 结构域重排甲基化酶; aa: 氨基酸
Figure 1 DNA methyltransferase phylogenetic tree (A) and protein domain map (B) of Arabidopsis thaliana (At), Brassica napus (Bna), Oryza sativa (Os) and Begonia masoniana (Bma) Using the Neighbor-joining method in MEGA 7 software. The value of bootstrap is 1 000. Numbers indicate bootstrap values. CMT: Chromomethylases; MET: Methyltransferase; DNMT: de novo DNA methyltransferase; DRM: Domains rearranged methylase; aa: Amino acid
| Gene name | CDS (bp) | Protein | Chr. | N-glycosyl-sites | Subcellular localization | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amino acid (aa) | pI | Molecular weight (Da) | |||||
| BmaCMT2-5 | 2547 | 848 | 6.3013 | 97206.68 | Chr.5 | 4 | Nucleus |
| BmaCMT3-11 | 2892 | 963 | 6.0700 | 109079.09 | Chr.11 | 4 | Nucleus |
| BmaCMT3-14 | 2511 | 836 | 4.7815 | 94618.65 | Chr.14 | 4 | Nucleus |
| BmaMET1-15 | 3645 | 1214 | 6.3066 | 136797.74 | Chr.15 | 6 | Nucleus |
| BmaDRM2-2 | 1773 | 590 | 4.8922 | 66506.45 | Chr.2 | 2 | Nucleus |
表2 铁甲秋海棠DNA甲基转移酶基本理化性质分析
Table 2 Analysis on the physical and chemical properties of DNA methyltransferase in Begonia masoniana
| Gene name | CDS (bp) | Protein | Chr. | N-glycosyl-sites | Subcellular localization | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amino acid (aa) | pI | Molecular weight (Da) | |||||
| BmaCMT2-5 | 2547 | 848 | 6.3013 | 97206.68 | Chr.5 | 4 | Nucleus |
| BmaCMT3-11 | 2892 | 963 | 6.0700 | 109079.09 | Chr.11 | 4 | Nucleus |
| BmaCMT3-14 | 2511 | 836 | 4.7815 | 94618.65 | Chr.14 | 4 | Nucleus |
| BmaMET1-15 | 3645 | 1214 | 6.3066 | 136797.74 | Chr.15 | 6 | Nucleus |
| BmaDRM2-2 | 1773 | 590 | 4.8922 | 66506.45 | Chr.2 | 2 | Nucleus |

图2 铁甲秋海棠(Bma) DNA甲基转移酶基因结构(A)和保守基序分布图(B) CDS同表2。
Figure 2 Gene structure of DNA methyltransferase (A) and distribution map of conserved motif (B) of Begonia masoniana CDS is the same as shown in Table 2.

图3 铁甲秋海棠DNA甲基转移酶基因启动子序列顺式元件数量(A)和分布(B) MeJA: 茉莉酸甲酯
Figure 3 Number (A) and distribution (B) of cis-elements in DNA methyltransferase gene promoter sequence of Begonia masoniana MeJA: Methyl jasmonate
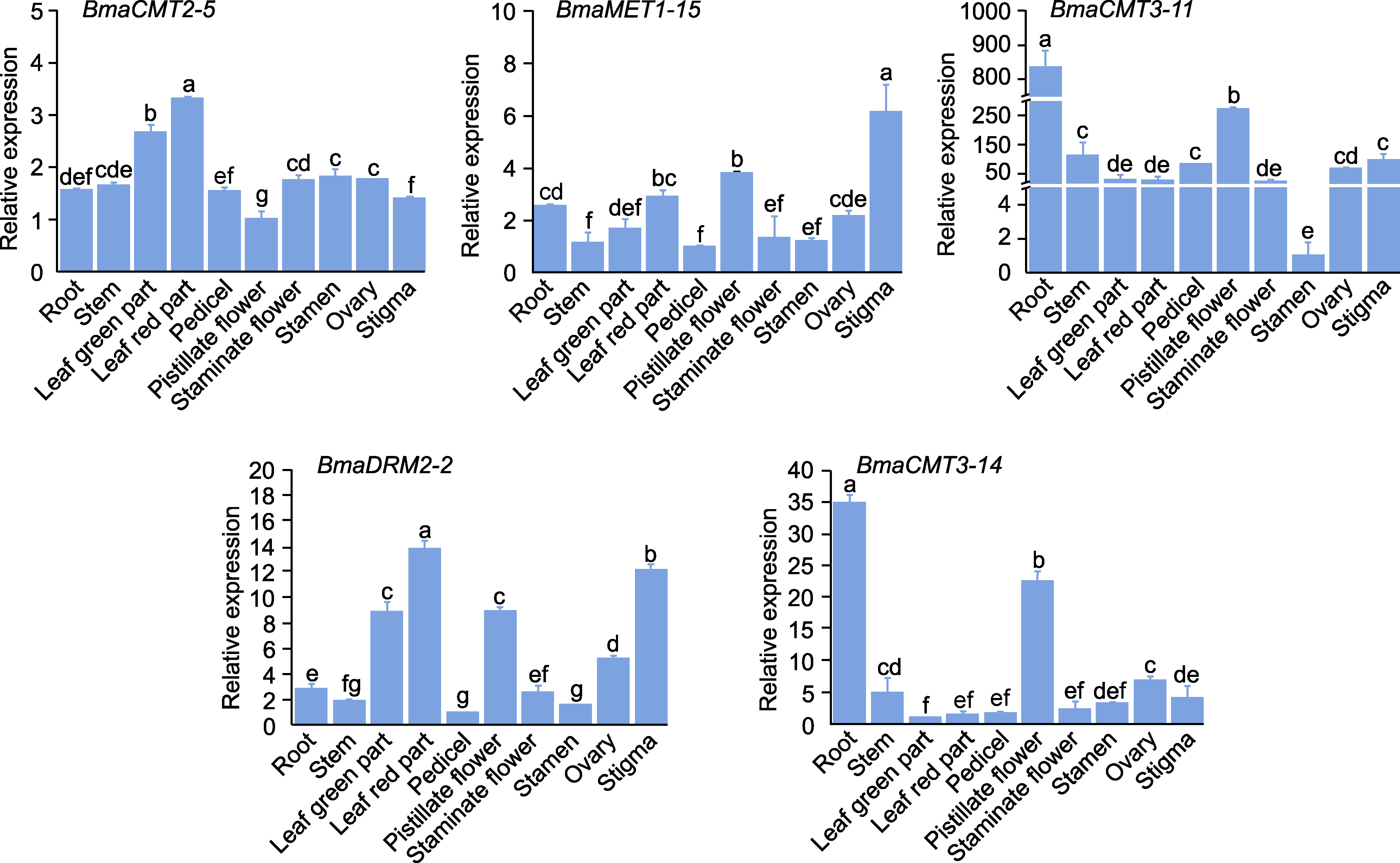
图4 铁甲秋海棠DNA甲基转移酶基因在不同组织器官中的相对表达量 ACT7为内参基因, 基因相对表达量为平均值±标准差。DNA甲基转移酶在不同组织中的最小表达量视为“1”。不同小写字母表示各处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 4 Relative expression levels of DNA methyltransferase genes in different tissues and organs of Begonia masoniana ACT7 was the internal reference gene and the relative gene expression was means±SD. The minimum expression of DNA methyltransferase in different tissues is regarded as “1”. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05).
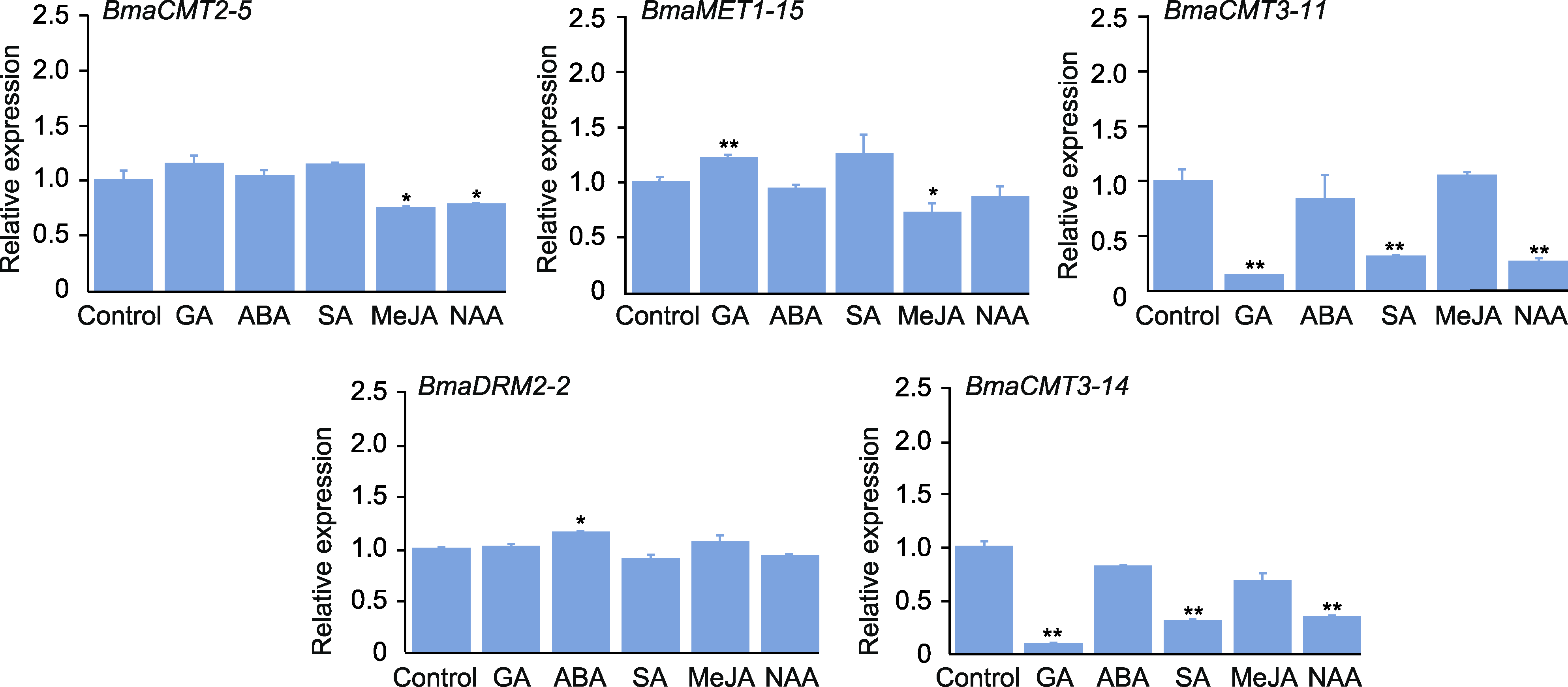
图5 铁甲秋海棠DNA甲基转移酶基因在GA、ABA、SA、MeJA和NAA处理(6小时)下的相对表达量 将对照组的相对表达量视为“1”。GA: 赤霉素; ABA: 脱落酸; SA: 水杨酸; MeJA: 茉莉酸甲酯; NAA: 萘乙酸。*表示处理组与对照组差异显著(P<0.05); **表示处理组与对照组差异极显著(P<0.01)。
Figure 5 Relative expression levels of DNA methyltransferase genes in Begonia masoniana treated with GA, ABA, SA, MeJA and NAA (6 h) The relative expression of control is regarded as “1”. GA: Gibberellin; ABA: Abscisic acid; SA: Salicylic acid; MeJA: Methyl jasmonate; NAA: 1-naphthalene acetic acid. * indicate that the difference between treatment group and control group is significant (P<0.05); ** indicate that the difference between treatment group and control group is extremely significant (P<0.01).
| [1] | 崔卫华, 管开云 (2013). 中国秋海棠属植物叶片斑纹多样性研究. 植物分类与资源学报 35, 119-127. |
| [2] | 戴若惠, 钱心妤, 孙静蕾, 芦涛, 贾绮玮, 陆天麒, 路梅, 饶玉春 (2023). 水稻叶色调控机制及相关基因研究进展. 植物学报 58, 799-812. |
| [3] | 杜文文, 段青, 马璐琳, 瞿素萍, 贾文杰, 王祥宁, 崔光芬 (2018). 7种秋海棠叶片斑纹结构及遗传特性分析. 西北植物学报 38, 2045-2052. |
| [4] | 关峰, 韦正乙, 王云鹏, 林春晶, 邢少辰, 马景勇 (2011). 内含子数量改变GUS基因的瞬时表达调控. 基因组学与应用生物学 30, 571-576. |
| [5] | 黎家, 李传友 (2019). 新中国成立70年来植物激素研究进展. 中国科学: 生命科学 49, 1227-1281. |
| [6] | 李景秀, 管开云, 孔繁才, 李爱荣 (2021). 中国秋海棠属植物资源概述. 中国野生植物资源 40(12), 35-44. |
| [7] | 李立奇, 万瑛 (2009). 蛋白质的亚细胞定位预测研究进展. 免疫学杂志 25, 602-604. |
| [8] | 冉浩然, 张毓, 陈简村, 于超, 张启翔, 罗乐 (2024). 观赏植物叶斑的研究进展. 植物遗传资源学报 25, 704-717. |
| [9] | 夏晗, 刘美芹, 尹伟伦, 卢存福, 夏新莉 (2008). 植物DNA甲基化调控因子研究进展. 遗传 30, 426-432. |
| [10] | 杨凯如, 贾绮玮, 金佳怡, 叶涵斐, 王盛, 陈芊羽, 管易安, 潘晨阳, 辛德东, 方媛, 王跃星, 饶玉春 (2022). 水稻黄绿叶调控基因YGL18的克隆与功能解析. 植物学报 57, 276- 287. |
| [11] | 杨婷, 薛珍珍, 李娜, 郎校安, 李凌飞, 钟春梅 (2021). 铁十字秋海棠斑叶发育过程内参基因筛选及验证. 园艺学报 48, 2251-2261. |
| [12] | 周陈平, 杨敏, 郭金菊, 邝瑞彬, 杨护, 黄炳雄, 魏岳荣 (2022). 番木瓜成熟过程中全基因组DNA甲基化和转录组变化分析. 园艺学报 49, 519-532. |
| [13] | Ahmad F, Huang X, Lan HX, Huma T, Bao YM, Huang J, Zhang HS (2014). Comprehensive gene expression analysis of the DNA (cytosine-5) methyltransferase family in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Genet Mol Res 13, 5159-5172. |
| [14] | Bennett M, Cleaves K, Hewezi T (2021). Expression patterns of DNA methylation and demethylation genes during plant development and in response to phytohormones. Int J Mol Sci 22, 9681. |
| [15] | Cao DY, Ju Z, Gao C, Mei XH, Fu DQ, Zhu HL, Luo YB, Zhu BZ (2014). Genome-wide identification of cytosine-5 DNA methyltransferases and demethylases in Solanum lycopersicum. Gene 550, 230-237. |
| [16] | Carey NS, Krogan NT (2017). The role of AUXIN RESPONSE FACTORs in the development and differential growth of inflorescence stems. Plant Signal Behav 12, e130-7492. |
| [17] | Chiu LW, Li L (2012). Characterization of the regulatory network of BoMYB2 in controlling anthocyanin biosynthesis in purple cauliflower. Planta 236, 1153-1164. |
| [18] | Fan SH, Liu HF, Liu J, Hua W, Xu SM, Li J (2020). Systematic analysis of the DNA methylase and demethylase gene families in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) and their expression variations after salt and heat stresses. Int J Mol Sci 21, 953. |
| [19] | Furner IJ, Matzke M (2011). Methylation and demethylation of the Arabidopsis genome. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14, 137-141. |
| [20] | Gahlaut V, Samtani H, Khurana P (2020). Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of cytosine-5 DNA methyltransferases during drought and heat stress in wheat (Triticum aestivum). Genomics 112, 4796-4807. |
| [21] | Gianoglio S, Moglia A, Acquadro A, Comino C, Portis E (2017). The genome-wide identification and transcriptional levels of DNA methyltransferases and demethylases in globe artichoke. PLoS One 12, e0181669. |
| [22] | Gu TT, Ren S, Wang YH, Han YH, Li Y (2016). Characterization of DNA methyltransferase and demethylase genes in Fragaria vesca. Mol Genet Genomics 291, 1333- 1345. |
| [23] | Hong X, Scofield DG, Lynch M (2006). Intron size, abundance, and distribution within untranslated regions of genes. Mol Biol Evol 23, 2392-2404. |
| [24] | Jiang S, Guo YC (2020). Epigenetic clock: DNA methylation in aging. Stem Cells Int 2020, 1047896. |
| [25] | Li LF, Chen XL, Fang DM, Dong SS, Guo X, Li N, Campos-Dominguez L, Wang WG, Liu Y, Lang XA, Peng Y, Tian DK, Thomas DC, Mu WX, Liu M, Wu CY, Yang T, Zhang SZ, Yang LL, Yang JF, Liu ZJ, Zhang LS, Zhang XT, Chen F, Jiao YN, Guo YL, Hughes M, Wang W, Liu XF, Zhong CM, Li AR, Sahu SK, Yang HM, Wu E, Sharbrough J, Lisby M, Liu X, Xu X, Soltis DE, Van de Peer Y, Kidner C, Zhang SZ, Liu H (2022). Genomes shed light on the evolution of Begonia, a mega-diverse genus. New Phytol 234, 295-310. |
| [26] | Ma J, Li Q, Zhang L, Cai S, Liu YY, Lin JC, Huang RF, Yu YQ, Wen MZ, Xu TD (2022). High auxin stimulates callus through SDG8-mediated histone H3K36 methylation in Arabidopsis. J Integr Plant Biol 64, 2425-2437. |
| [27] | Parra G, Bradnam K, Rose AB, Korf I (2011). Comparative and functional analysis of intron-mediated enhancement signals reveals conserved features among plants. Nucleic Acids Res 39, 5328-5337. |
| [28] | Parrilla-Doblas JT, Roldán-Arjona T, Ariza RR, Córdoba- Cañero D (2019). Active DNA demethylation in plants. Int J Mol Sci 20, 4683. |
| [29] | Tian J, Li KT, Zhang S, Zhang J, Song TT, Zhu YJ, Yao YC (2017). The structure and methylation level of the McMYB10 promoter determine the leaf color of Malus crabapple. HortScience 52, 520-526. |
| [30] | Wang QM, Wang L, Zhou YB, Cui JG, Wang YZ, Zhao CM (2016). Leaf patterning of Clivia miniata var. variegata is associated with differential DNA methylation. Plant Cell Rep 35, 167-184. |
| [31] | Wang Y, Liu S, Tian X, Fu Y, Jiang X, Li Y, Wang G (2018). Influence of light intensity on chloroplast development and pigment accumulation in wild-type and etiolated mutant plants of Anthurium andraeanum ‘Sonate’. Plant Signal Behav 13, e1482174. |
| [32] | Wu XX, Zhou Y, Yao D, Iqbal S, Gao ZH, Zhang Z (2020). DNA methylation of LDOX gene contributes to the floral colour variegation in peach. J Plant Physiol 246-247, 153116. |
| [33] | Xiao K, Chen J, He QXM, Wang YX, Shen HL, Sun L (2020). DNA methylation is involved in the regulation of pepper fruit ripening and interacts with phytohormones. J Exp Bot 71, 1928-1942. |
| [34] | Xu P, Su H, Jin R, Mao YX, Xu AN, Cheng HY, Wang YF, Meng Q (2020). Shading effects on leaf color conversion and biosynthesis of the major secondary metabolites in the albino tea cultivar ‘Yujinxiang’. J Agric Food Chem 68, 2528-2538. |
| [35] | Yan M, Yan Y, Wang P, Wang YP, Piao XM, Di P, Yang DC (2023). Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of auxin response factor (ARF) gene family in Panax ginseng indicates its possible roles in root development. Plants 12, 3943. |
| [36] | Yao MQ, Chen WW, Kong JH, Zhang XL, Shi NN, Zhong SL, Ma P, Gallusci P, Jackson S, Liu YL, Hong YG (2020). METHYLTRANSFERASE1 and ripening modulate vivipary during tomato fruit development. Plant Physiol 183, 1883-1897. |
| [37] | Yu H, Cui N, Guo K, Xu W, Wang HF (2023). Epigenetic changes in the regulation of carotenoid metabolism during honeysuckle flower development. Hortic Plant J 9, 577- 588. |
| [38] | Yue PT, Lu Q, Liu Z, Lv TX, Li XY, Bu HD, Liu WT, Xu YX, Yuan H, Wang AD (2020). Auxin-activated MdARF5 induces the expression of ethylene biosynthetic genes to initiate apple fruit ripening. New Phytol 226, 1781-1795. |
| [39] | Zhang Y, Zhao GY, Li YS, Mo N, Zhang J, Liang Y (2017). Transcriptomic analysis implies that GA regulates sex expression via ethylene-dependent and ethylene-indepen- dent pathways in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Front Plant Sci 8, 10. |
| [40] | Zheng J, Wu H, Zhu HB, Huang CY, Liu C, Chang YS, Kong ZC, Zhou ZH, Wang GW, Lin YJ, Chen H (2019). Determining factors, regulation system, and domestication of anthocyanin biosynthesis in rice leaves. New Phytol 223, 705-721. |
| [1] | 刘旭鹏, 王敏, 韩守安, 朱学慧, 王艳蒙, 潘明启, 张雯. 植物器官脱落调控因素及分子机理研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 472-482. |
| [2] | 张悦婧, 桑鹤天, 王涵琦, 石珍珍, 李丽, 王馨, 孙坤, 张继, 冯汉青. 植物对非生物胁迫系统性反应中信号传递的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 122-133. |
| [3] | 李季蔓, 靳楠, 胥毛刚, 霍举颂, 陈小云, 胡锋, 刘满强. 不同干旱水平下蚯蚓对番茄抗旱能力的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21488-. |
| [4] | 李月, 胡德升, 谭金芳, 梅浩, 王祎, 李慧, 李芳, 韩燕来. 单列毛壳菌通过促进秸秆降解并调控激素响应基因表达促进玉米生长[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(4): 422-433. |
| [5] | 戴琛, 汪瑾, 卢亚萍. 衍生化UPLC-MS法测定酸性植物激素[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(4): 500-507. |
| [6] | 孟彦彦, 张楠, 熊延. 植物TOR激酶响应上游信号的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 1-11. |
| [7] | 赵晓亭, 毛凯涛, 徐佳慧, 郑钏, 罗晓峰, 舒凯. 蛋白质磷酸化修饰与种子休眠及萌发调控[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(4): 488-499. |
| [8] | 俞启璐, 赵江哲, 朱晓仙, 张可伟. 水稻根分泌激素调节生长速度[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(2): 175-182. |
| [9] | 谢露露, 崔青青, 董春娟, 尚庆茂. 植物嫁接愈合分子机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(5): 634-643. |
| [10] | 姚瑞枫,谢道昕. 独脚金内酯信号途径的新发现——抑制子也是转录因子[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(4): 397-402. |
| [11] | 徐佳慧, 代宇佳, 罗晓峰, 舒凯, 谭伟明. 植物激素研究中的化学生物学思路与应用[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(3): 369-381. |
| [12] | 肖燕,王振兴,李东明,齐艳华,恩和巴雅尔. 羊草成熟胚诱导愈伤组织及植株再生系统的优化[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(2): 192-198. |
| [13] | 郭佳,李衍素,贺超兴,闫妍,于贤昌. 南瓜高效再生体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(4): 539-546. |
| [14] | 范业赓,丘立杭,黄杏,周慧文,甘崇琨,李杨瑞,杨荣仲,吴建明,陈荣发. 甘蔗节间伸长过程赤霉素生物合成关键基因的表达及相关植物激素动态变化[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(4): 486-496. |
| [15] | 刘铭, 刘霞, 孙然, 李玉灵, 杜克久. 多氯联苯促进毛白杨不定根分化的效应[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(6): 764-772. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||