

植物学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (6): 723-732.DOI: 10.11983/CBB19037 cstr: 32102.14.CBB19037
何杰丽1,石甜甜2,陈凌3,王海岗3,高志军4,杨美红1,王瑞云2,3,*( ),乔治军3,*(
),乔治军3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2019-02-24
接受日期:2019-06-18
出版日期:2019-11-01
发布日期:2020-07-09
通讯作者:
王瑞云,乔治军
基金资助:
Jieli He1,Tiantian Shi2,Ling Chen3,Haigang Wang3,Zhijun Gao4,Meihong Yang1,Ruiyun Wang2,3,*( ),Zhijun Qiao3,*(
),Zhijun Qiao3,*( )
)
Received:2019-02-24
Accepted:2019-06-18
Online:2019-11-01
Published:2020-07-09
Contact:
Ruiyun Wang,Zhijun Qiao
摘要: 基于前期高通量测序结果设计EST-SSR引物, 用于评估国内外不同生态区144份糜子(Panicum miliaceum)种质资源的遗传差异。结果表明, 200对引物中80对呈多态性, 开发效率为40%; 引物分辨率(Rp)为0.67-4.67 (平均值为2.00), 扩增产物大小为50-500 bp。144份材料在80个位点共检测到206个等位变异, 每个位点为2-3个; 多样性指数(I)为0.659 3 (RYW108)-1.087 2 (RYW124), 平均为0.859 9; 多态性信息含量(PIC)为0.222 9 (RYW98)-0.717 2 (RYW124), 平均为0.457 3。基于UPGMA将144份资源划分为3个群组, 其中2个群组主要为北方春糜子区材料, 另一个群组主要为黄土高原春夏糜子区材料。基于Structure (K=4)将材料划分为4个类群, 即2个代表北方资源基因库以及代表黄土高原和国外资源基因库各1个。基于主成分分析将材料聚为7个类群, 划分结果与材料的地理来源一致。
何杰丽,石甜甜,陈凌,王海岗,高志军,杨美红,王瑞云,乔治军. 糜子EST-SSR分子标记的开发及种质资源遗传多样性分析. 植物学报, 2019, 54(6): 723-732.
Jieli He,Tiantian Shi,Ling Chen,Haigang Wang,Zhijun Gao,Meihong Yang,Ruiyun Wang,Zhijun Qiao. The Genetic Diversity of Common Millet (Panicum miliaceum) Germplasm Resources Based on the EST-SSR Markers. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(6): 723-732.
| Ecotope/abroad | Origin | Number of accession | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Northwest spring and summer-sowing ecotope (NWSS) | Xinjiang | 4 | 4 |
| Northern spring-sowing ecotope (NSP) | Qinghai | 13 | 48 |
| Gansu | 11 | ||
| Inner Mongolia | 14 | ||
| Shanxi | 10 | ||
| Loess Plateau spring and summer-sowing ecotope (LPSS) | Shanxi | 18 | 37 |
| Shaanxi | 8 | ||
| Ningxia | 11 | ||
| Northeast spring-sowing ecotope (NES) | Heilongjiang | 5 | 9 |
| Jilin | 3 | ||
| Liaoning | 1 | ||
| Northern summer-sowing ecotope (NSU) | Hebei | 9 | 13 |
| Shandong | 2 | ||
| Anhui | 1 | ||
| Henan | 1 | ||
| Southern autumn and winter-sowing ecotope (SAW) | Hainan | 2 | 2 |
| Abroad | Former Soviet Union | 2 | 31 |
| Poland | 2 | ||
| India | 27 | ||
| Total | 144 | ||
表1 国内各生态区和国外糜子资源的分布
Table 1 Distribution of common millet accessions in different ecotopes of China and abroad
| Ecotope/abroad | Origin | Number of accession | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Northwest spring and summer-sowing ecotope (NWSS) | Xinjiang | 4 | 4 |
| Northern spring-sowing ecotope (NSP) | Qinghai | 13 | 48 |
| Gansu | 11 | ||
| Inner Mongolia | 14 | ||
| Shanxi | 10 | ||
| Loess Plateau spring and summer-sowing ecotope (LPSS) | Shanxi | 18 | 37 |
| Shaanxi | 8 | ||
| Ningxia | 11 | ||
| Northeast spring-sowing ecotope (NES) | Heilongjiang | 5 | 9 |
| Jilin | 3 | ||
| Liaoning | 1 | ||
| Northern summer-sowing ecotope (NSU) | Hebei | 9 | 13 |
| Shandong | 2 | ||
| Anhui | 1 | ||
| Henan | 1 | ||
| Southern autumn and winter-sowing ecotope (SAW) | Hainan | 2 | 2 |
| Abroad | Former Soviet Union | 2 | 31 |
| Poland | 2 | ||
| India | 27 | ||
| Total | 144 | ||
| Number | Unicode | Accession name | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 00000177 | Hongmizi | Ningan, Heilongjiang |
| 2 | 00000750 | Baimizi | Shawan, Xinjiang |
| 3 | 00006653 | Jinshu | Hainan |
| 4 | 00007238 | Dahongmizi | Bameng, Inner Mongolia |
| 5 | 00007478 | Baigedami | Huangzhong, Qinghai |
| 6 | No unicode | Hongshuzi | Anyang, Henan |
表2 糜子SSR引物筛选
Table 2 Screening of SSR primers for common millet
| Number | Unicode | Accession name | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 00000177 | Hongmizi | Ningan, Heilongjiang |
| 2 | 00000750 | Baimizi | Shawan, Xinjiang |
| 3 | 00006653 | Jinshu | Hainan |
| 4 | 00007238 | Dahongmizi | Bameng, Inner Mongolia |
| 5 | 00007478 | Baigedami | Huangzhong, Qinghai |
| 6 | No unicode | Hongshuzi | Anyang, Henan |
| Ecotope/ abroad | Accessions | Na | Ne | I | Ho | He | PIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NWSS | 4 | 2.3375±0.5017 | 2.1517±0.4194 | 0.7644±0.2178 | 0.8042±0.2688 | 0.5944±0.1193 | 0.3551 |
| NSP | 48 | 2.5750±0.4975 | 2.3106±0.3211 | 0.8604±0.1576 | 0.8228±0.1308 | 0.5655±0.0604 | 0.4536 |
| LPSS | 37 | 2.5750±0.4975 | 2.2803±0.3110 | 0.8506±0.1534 | 0.8384±0.1166 | 0.5615±0.0595 | 0.4203 |
| NES | 9 | 2.5125±0.5030 | 2.2435±0.3929 | 0.8289±0.1823 | 0.7937±0.1732 | 0.5737±0.0909 | 0.4212 |
| NSU | 13 | 2.5625±0.4992 | 2.2815±0.3527 | 0.8496±0.1632 | 0.7946±0.1608 | 0.5712±0.0667 | 0.4304 |
| SAW | 2 | 2.2375±0.5092 | 2.0608±0.4387 | 0.7347±0.2316 | 0.7812±0.3265 | 0.6813±0.2006 | 0.2156 |
| Domestic | 113 | 2.5750 ±0.4975 | 2.3122±0.3086 | 0.8628±0.1554 | 0.8200±0.1188 | 0.5625±0.0584 | 0.4651 |
| Abroad | 31 | 2.5750±0.4975 | 2.2464±0.2909 | 0.8387±0.1449 | 0.8540±0.1193 | 0.5571±0.0561 | 0.3896 |
表3 不同生态区糜子的遗传多样性参数
Table 3 Parameters of genetic diversity in different ecotope of common millet
| Ecotope/ abroad | Accessions | Na | Ne | I | Ho | He | PIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NWSS | 4 | 2.3375±0.5017 | 2.1517±0.4194 | 0.7644±0.2178 | 0.8042±0.2688 | 0.5944±0.1193 | 0.3551 |
| NSP | 48 | 2.5750±0.4975 | 2.3106±0.3211 | 0.8604±0.1576 | 0.8228±0.1308 | 0.5655±0.0604 | 0.4536 |
| LPSS | 37 | 2.5750±0.4975 | 2.2803±0.3110 | 0.8506±0.1534 | 0.8384±0.1166 | 0.5615±0.0595 | 0.4203 |
| NES | 9 | 2.5125±0.5030 | 2.2435±0.3929 | 0.8289±0.1823 | 0.7937±0.1732 | 0.5737±0.0909 | 0.4212 |
| NSU | 13 | 2.5625±0.4992 | 2.2815±0.3527 | 0.8496±0.1632 | 0.7946±0.1608 | 0.5712±0.0667 | 0.4304 |
| SAW | 2 | 2.2375±0.5092 | 2.0608±0.4387 | 0.7347±0.2316 | 0.7812±0.3265 | 0.6813±0.2006 | 0.2156 |
| Domestic | 113 | 2.5750 ±0.4975 | 2.3122±0.3086 | 0.8628±0.1554 | 0.8200±0.1188 | 0.5625±0.0584 | 0.4651 |
| Abroad | 31 | 2.5750±0.4975 | 2.2464±0.2909 | 0.8387±0.1449 | 0.8540±0.1193 | 0.5571±0.0561 | 0.3896 |
| Population | NWSS | NSP | LPSS | NES | NSU | SAW | Abroad |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NWSS | 0.9560 | 0.9614 | 0.9487 | 0.9380 | 0.8694 | 0.9477 | |
| NSP | 0.0449 | 0.9884 | 0.9678 | 0.9794 | 0.9110 | 0.9864 | |
| LPSS | 0.0394 | 0.0117 | 0.9716 | 0.9830 | 0.9116 | 0.9865 | |
| NES | 0.0527 | 0.0327 | 0.0288 | 0.9675 | 0.8974 | 0.9587 | |
| NSU | 0.0640 | 0.0208 | 0.0171 | 0.0331 | 0.9023 | 0.9762 | |
| SAW | 0.1400 | 0.0932 | 0.0926 | 0.1083 | 0.1029 | 0.9102 | |
| Abroad | 0.0537 | 0.0137 | 0.0136 | 0.0422 | 0.0240 | 0.0941 |
表4 各糜子群体间的Nei氏遗传距离与遗传一致度
Table 4 Parameters of Nei’s genetic distance and Nei’s genetic agreement in common millet populations
| Population | NWSS | NSP | LPSS | NES | NSU | SAW | Abroad |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NWSS | 0.9560 | 0.9614 | 0.9487 | 0.9380 | 0.8694 | 0.9477 | |
| NSP | 0.0449 | 0.9884 | 0.9678 | 0.9794 | 0.9110 | 0.9864 | |
| LPSS | 0.0394 | 0.0117 | 0.9716 | 0.9830 | 0.9116 | 0.9865 | |
| NES | 0.0527 | 0.0327 | 0.0288 | 0.9675 | 0.8974 | 0.9587 | |
| NSU | 0.0640 | 0.0208 | 0.0171 | 0.0331 | 0.9023 | 0.9762 | |
| SAW | 0.1400 | 0.0932 | 0.0926 | 0.1083 | 0.1029 | 0.9102 | |
| Abroad | 0.0537 | 0.0137 | 0.0136 | 0.0422 | 0.0240 | 0.0941 |
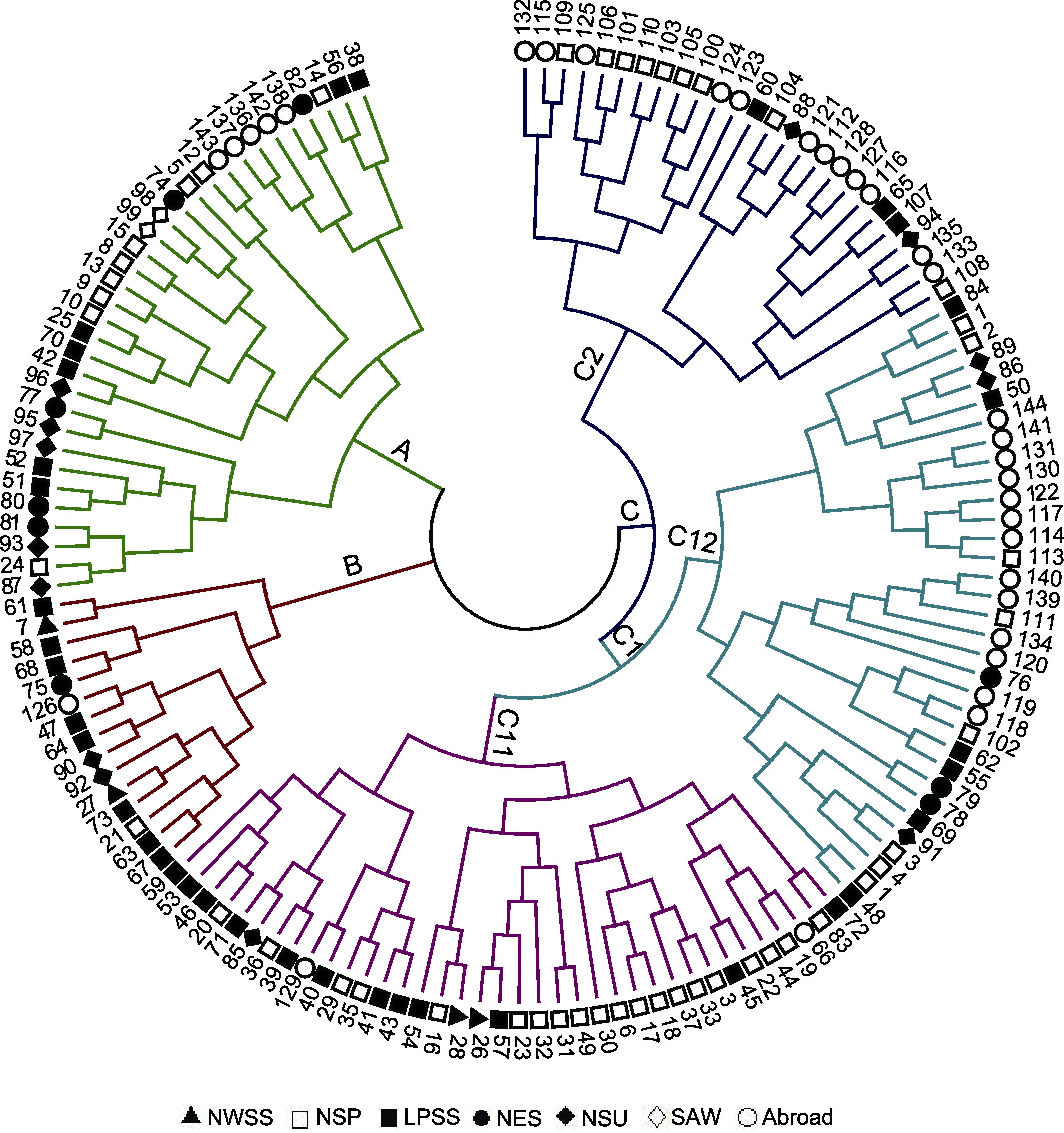
图2 基于UPGMA的糜子资源聚类分析 NWSS、NSP、LPSS、NES、NSU和SAW同表1。
Figure 2 Cluster analysis chart of common millet accessions based on UPGMA NWSS, NSP, LPSS, NES, NSU and SAW are the same as Table 1.
| Group | Accessions | Na | Ne | I | Ho | He | PIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 33 | 2.5750±0.4975 | 2.3226±0.3374 | 0.8654±0.1620 | 0.8055±0.1417 | 0.5696±0.0636 | 0.4716 |
| B | 15 | 2.5125±0.5030 | 2.2471±0.3383 | 0.8330±0.1627 | 0.8153±0.1530 | 0.5651±0.0686 | 0.3993 |
| C | 96 | 2.5750±0.4975 | 2.2922±0.2894 | 0.8571±0.1495 | 0.8363±0.1111 | 0.5599±0.0553 | 0.4380 |
| C1 | 70 | 2.5750±0.4975 | 2.3136±0.3098 | 0.8635±0.1551 | 0.8291±0.1199 | 0.5643±0.0584 | 0.4531 |
| C2 | 26 | 2.5625±0.4992 | 2.1912±0.2797 | 0.8163±0.1391 | 0.8555 ±0.1212 | 0.5477±0.0558 | 0.3420 |
| C11 | 37 | 2.5750±0.4975 | 2.3014±0.3143 | 0.8589±0.1561 | 0.8332±0.1182 | 0.5664±0.0603 | 0.4382 |
| C12 | 33 | 2.5750±0.4975 | 2.3028±0.3224 | 0.8583±0.1571 | 0.8255±0.1383 | 0.5654±0.0610 | 0.4348 |
表5 基于UPGMA聚类分析糜子各类群的遗传多样性
Table 5 Genetic diversity of common millet groups based on UPGMA cluster analysis
| Group | Accessions | Na | Ne | I | Ho | He | PIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 33 | 2.5750±0.4975 | 2.3226±0.3374 | 0.8654±0.1620 | 0.8055±0.1417 | 0.5696±0.0636 | 0.4716 |
| B | 15 | 2.5125±0.5030 | 2.2471±0.3383 | 0.8330±0.1627 | 0.8153±0.1530 | 0.5651±0.0686 | 0.3993 |
| C | 96 | 2.5750±0.4975 | 2.2922±0.2894 | 0.8571±0.1495 | 0.8363±0.1111 | 0.5599±0.0553 | 0.4380 |
| C1 | 70 | 2.5750±0.4975 | 2.3136±0.3098 | 0.8635±0.1551 | 0.8291±0.1199 | 0.5643±0.0584 | 0.4531 |
| C2 | 26 | 2.5625±0.4992 | 2.1912±0.2797 | 0.8163±0.1391 | 0.8555 ±0.1212 | 0.5477±0.0558 | 0.3420 |
| C11 | 37 | 2.5750±0.4975 | 2.3014±0.3143 | 0.8589±0.1561 | 0.8332±0.1182 | 0.5664±0.0603 | 0.4382 |
| C12 | 33 | 2.5750±0.4975 | 2.3028±0.3224 | 0.8583±0.1571 | 0.8255±0.1383 | 0.5654±0.0610 | 0.4348 |
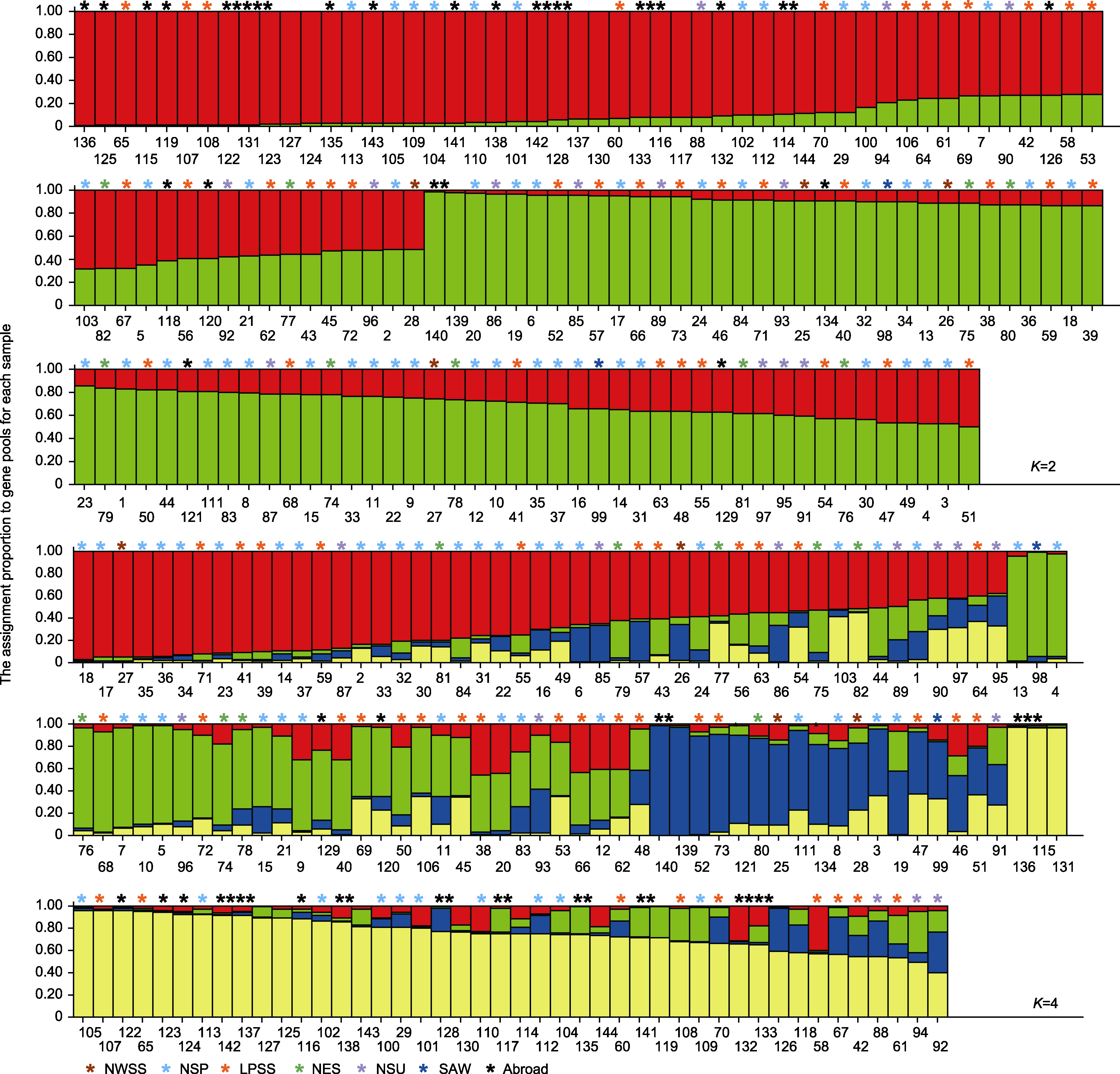
图4 基于Structure的糜子资源遗传结构 颜色代表类群; 条形和横坐标数字分别表示资源及其编号。
Figure 4 Genetic structure of common millet based on Structure Color represents group; bar and the horizontal coordinate represent origin and its serial number, respectively.
| Cluster | Accessions | Na | Ne | I | Ho | He | PIC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K=2 | Red | 68 | 2.5750±0.4975 | 2.2446±0.2626 | 0.8407±0.1403 | 0.8602±0.1056 | 0.5528±0.0520 | 0.3773 |
| Green | 76 | 2.5750±0.4975 | 2.3396±0.3329 | 0.8711±0.1620 | 0.7975±0.1315 | 0.5679±0.0619 | 0.5031 | |
| K=4 | Red | 47 | 2.5750± 0.4975 | 2.3496±0.3944 | 0.8745±0.1768 | 0.7439±0.1668 | 0.5785±0.0743 | 0.5296 |
| Green | 31 | 2.5750± 0.4975 | 2.2844±0.3202 | 0.8516± 0.1549 | 0.8225±0.1399 | 0.5635±0.0607 | 0.4414 | |
| Blue | 19 | 2.5750±0.4975 | 2.2973±0.3199 | 0.8575±0.1568 | 0.8190±0.1311 | 0.5628±0.0608 | 0.4450 | |
| Yellow | 47 | 2.5750±0.4975 | 2.2238±0.2723 | 0.8312±0.1387 | 0.3634±0.2702 | 0.4984±0.1050 | 0.3543 | |
表6 遗传结构图中K=2和K=4各类群的遗传多样性分析
Table 6 Genetic diversity analysis of different cluster based on genetic structure (K=2 and K=4)
| Cluster | Accessions | Na | Ne | I | Ho | He | PIC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K=2 | Red | 68 | 2.5750±0.4975 | 2.2446±0.2626 | 0.8407±0.1403 | 0.8602±0.1056 | 0.5528±0.0520 | 0.3773 |
| Green | 76 | 2.5750±0.4975 | 2.3396±0.3329 | 0.8711±0.1620 | 0.7975±0.1315 | 0.5679±0.0619 | 0.5031 | |
| K=4 | Red | 47 | 2.5750± 0.4975 | 2.3496±0.3944 | 0.8745±0.1768 | 0.7439±0.1668 | 0.5785±0.0743 | 0.5296 |
| Green | 31 | 2.5750± 0.4975 | 2.2844±0.3202 | 0.8516± 0.1549 | 0.8225±0.1399 | 0.5635±0.0607 | 0.4414 | |
| Blue | 19 | 2.5750±0.4975 | 2.2973±0.3199 | 0.8575±0.1568 | 0.8190±0.1311 | 0.5628±0.0608 | 0.4450 | |
| Yellow | 47 | 2.5750±0.4975 | 2.2238±0.2723 | 0.8312±0.1387 | 0.3634±0.2702 | 0.4984±0.1050 | 0.3543 | |
| [1] | 董俊丽, 王海岗, 陈凌, 王君杰, 曹晓宁, 王纶, 乔治军 ( 2015). 糜子骨干种质遗传多样性和遗传结构分析. 中国农业科学 48, 3121-3131. |
| [2] | 国家谷子糜子产业技术体系 ( 2018). 中国现代农业产业可持续发展战略研究·谷子糜子分册. 北京: 中国农业出版社. pp. 3-22. |
| [3] | 郭琪, 郭大龙, 郭丽丽, 张琳, 侯小改 ( 2015). SSR分子标记在牡丹亲缘关系研究中的应用与研究进展. 植物学报 50, 652-664. |
| [4] | 连帅, 陆平, 乔治军, 张琦, 张茜, 刘敏轩, 王瑞云 ( 2016). 利用SSR分子标记研究国内外黍稷地方品种和野生资源的遗传多样性. 中国农业科学 49, 3264-3275. |
| [5] | 刘笑瑜 ( 2017). 利用高基元SSR分析中国糜子资源的遗传多样性. 硕士论文. 太谷: 山西农业大学. pp. 22-41. |
| [6] | 刘笑瑜, 王瑞云, 刘敏轩, 邱岩岩, 季煦, 连帅, 乔治军, 王纶, 王海岗 ( 2016). 利用SSR标记分析40份糜子资源的遗传多样性. 分子植物育种 14, 1624-1630. |
| [7] | 王璐琳, 王瑞云, 何杰丽, 薛延桃, 陈凌, 王海岗, 乔治军 ( 2018). 糜子特异性SSR标记的开发. 山西农业科学 46, 1-4, 86. |
| [8] | 王瑞云 (2017). 糜子遗传多样性及进化研究进展. 北京: 中国农业出版社. pp. 20-92. |
| [9] | 王瑞云, 季煦, 陆平, 刘敏轩, 许月, 王纶, 王海岗, 乔治军 ( 2017a). 利用荧光SSR分析中国糜子遗传多样性. 作物学报 43, 530-548. |
| [10] | 王瑞云, 刘笑瑜, 王海岗, 陆平, 刘敏轩, 陈凌, 乔治军 ( 2017b). 用高基元微卫星标记分析中国糜子遗传多样性. 中国农业科学 50, 3848-3859. |
| [11] | 王舒婷, 何杰丽, 石甜甜, 陈凌, 王海岗, 王瑞云, 乔治军 ( 2019). 利用微卫星标记分析山西糜子的遗传多样性. 植物遗传资源学报 20, 69-78. |
| [12] | 王银月, 刘敏轩, 陆平, 乔治军, 杨天育, 李海, 崔喜艳 ( 2014). 构建黍稷分子遗传图谱SSR引物的筛选. 作物杂志 ( 4), 32-38. |
| [13] | 薛延桃, 陆平, 乔治军, 刘敏轩, 王瑞云 ( 2018). 基于SSR标记的黍稷种质资源遗传多样性及亲缘关系研究. 中国农业科学 51, 2846-2859. |
| [14] | 朱宇佳, 焦凯丽, 罗秀俊, 冯尚国, 王慧中 ( 2018). 基于SSR分子标记的酸浆属植物亲缘关系研究. 植物学报 53, 305-312. |
| [15] | Azevedo ALS, Costa PP, Machado JC, Machado MA, Pereira AV, da Silva Lédo FJ ( 2012). Cross species amplification of Pennisetum glaucum microsatellite markers in Pennisetum purpureum and genetic diversity of napier grass accessions. Crop Sci 52, 1776-1785. |
| [16] | Bonman JM, Babiker EM, Cuesta-Marcos A, Esvelt-Klos K, Brown-Guedira G, Chao SM, See D, Chen JL, Akhunov E, Zhang JL, Bockelman HE, Gordon TC ( 2015). Genetic diversity among wheat accessions from the USDA national small grains collection. Crop Sci 55, 1243-1253. |
| [17] | Changmei S, Dorothy J ( 2014). Millet—the frugal grain. Int J Sci Res Rev 3(4), 75-90. |
| [18] | Cho Yl, Chung JW, Lee GA, Ma KH, Dixit A, Gwag JG, Park YJ ( 2010). Development and characterization of twenty-five new polymorphic microsatellite markers in proso millet ( Panicum miliaceum L.). Genes Genomics 32, 267-273. |
| [19] | Courtois B, Frouin J, Greco R, Bruschi G, Droc G, Hamelin C, Ruiz M, Clément G, Evrard JC, Van Coppenole S, Katsantonis D, Oliveira M, Negrão S, Matos C, Cavigiolo S, Lupotto E, Piffanelli P, Ahmadi N ( 2012). Genetic diversity and population structure in a European collection of rice. Crop Sci 52, 1663-1675. |
| [20] | Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J ( 2005). Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software structure: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14, 2611-2620. |
| [21] | Falush D, Stephens M, Pritchard JK ( 2003). Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: linked loci and correlated allele frequencies. Genetics 164, 1567-1587. |
| [22] | Habiyaremye C, Matanguihan JB, Guedes JD, Ganjyal GM, Whiteman MR, Kidwell KK, Murphy KM ( 2017). Proso millet ( Panicum miliaceum L.) and its potential for cultivation in the pacific northwest, U.S: a review. Front Plant Sci 7, 1961. |
| [23] | Hu XY, Wang JF, Lu P, Zhang HS ( 2009). Assessment of genetic diversity in broomcorn millet ( Panicum miliaceum L.) using SSR markers. J Genet Genomics 36, 491-500. |
| [24] | Hunt HV, Campana MG, Lawes MC, Park YJ, Bower MA, Howe CJ, Jones MK ( 2011). Genetic diversity and phylogeography of broomcorn millet ( Panicum miliaceum L.) across Eurasia. Mol Ecol 20, 4756-4771. |
| [25] | Liu KJ, Muse SV ( 2005). PowerMarker: an integrated analysis environment for genetic marker analysis. Bioinformatics 21, 2128-2129. |
| [26] | Liu MX, Xu Y, He JH, Zhang S, Wang YY, Lu P ( 2016). Genetic diversity and population structure of broomcorn millet ( Panicum miliaceum L.) cultivars and landraces in China based on microsatellite markers. Int J Mol Sci 17, 370. |
| [27] | Lu HY, Zhang JP, Liu KB, Wu NQ, Li YM, Zhou KS, Ye ML, Zhang TY, Zhang HJ, Yang XY, Shen LC, Xu DK, Li Q ( 2009). Earliest domestication of common millet ( Panicum miliaceum ) in East Asia extended to 10, 000 years ago. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106, 7367-7372. |
| [28] | Murray MG, Thompson WF ( 1980). Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8, 4321-4325. |
| [29] | Prevost A, Wilkinson MJ ( 1999). A new system of comparing PCR primers applied to ISSR fingerprinting of potato cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 98, 107-112. |
| [30] | Rajput SG, Plyler-Harveson T, Santra DK ( 2014). Development and characterization of SSR markers in proso millet based on switchgrass genomics. Am J Plant Sci 5, 175-186. |
| [31] | Rajput SG, Santra DK ( 2016). Evaluation of genetic diversity of proso millet germplasm available in the United States using simple-sequence repeat markers. Crop Sci 56, 2401-2409. |
| [32] | Rohlf FJ (2002). NTSYS-pc: Numerical Taxonomy and Multivariate Analysis System, Version 2.10. New York: Exter Publishing Ltd. Setauket. |
| [33] | Saha D, Channabyre Gowda MV, Arya L, Verma M, Bansal KC ( 2016). Genetic and genomic resources of small millets. Crit Rev Plant Sci 35, 56-79. |
| [34] | Satya P, Karan M, Jana S, Mitra S, Sharma A, Karmakar PG, Ray DP ( 2015). Start codon targeted (SCoT) polymorphism reveals genetic diversity in wild and domesticated populations of ramie ( Boehmeria nivea L. Gaudich.), a premium textile fiber producing species. Meta Gene 3, 62-70. |
| [35] | Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S ( 2011). MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 665, 2731-2739. |
| [36] | Tiwar G, Singh R, Singh N, Choudhury DR, Paliwal R, Kumar A, Gupta V ( 2016). Study of arbitrarily amplified (RAPD and ISSR) and gene targeted (SCoT and CBDP) markers for genetic diversity and population structure in kalmegh [Andrographis paniculata(Burm. f.) Nees]. Ind Crops Prod 86, 1-11. |
| [37] | Van Inghelandt D, Melchinger AE, Lebreton C, Stich B ( 2010). Population structure and genetic diversity in a commercial maize breeding program assessed with SSR and SNP markers. Theor Appl Genet 120, 1289-1299. |
| [38] | Wang RY, Hunt HV, Qiao ZJ, Wang L, Han YH ( 2016). Diversity and cultivation of broomcorn millet ( Panicum miliaceum L.) in China: a review. Econ Bot 70, 332-342. |
| [39] | Wang RY, Wang HG, Liu XY, Ji X, Chen L, Lu P, Liu MX, Teng B, Qiao ZJ ( 2018). Waxy allelic diversity in common millet(Panicum miliaceum L.) in China. Crop J 6, 377-385. |
| [40] | Yeh FC, Boyle TJB ( 1997). Population genetic analysis of codominant and dominant markers and quantitative traits. Belg J Bot 129, 157-163. |
| [1] | 黄承玲, 黎荣瀚, 覃红玲, 杨胜雄, 田晓玲, 夏国威, 陈正仁, 周玮. 基于SNP分子标记的极小种群野生植物荔波杜鹃保护遗传学研究[J]. , 2025, 49(濒危植物的保护与恢复): 0-. |
| [2] | 崔娟, 于晓玉, 于跃娇, 梁铖玮, 孙健, 陈温福. 影响中国东北和日本粳稻食味品质差异的质构因素及其遗传基础解析[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [3] | 张如礼, 李德铢, 张玉霄. 短穗竹居群遗传结构及气候适应性分析[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 407-424. |
| [4] | 杨志刚, 张鹏程, 常海文, 康立茹, 左毅, 向浩鑫, 韩凤英. 基于形态学性状和SSR标记的辣椒种质资源遗传多样性分析(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 218-234. |
| [5] | 王嘉陈, 徐汤俊, 许唯, 张高季, 尤艺瑾, 阮宏华, 刘宏毅. 城市景观格局对大蚰蜒种群遗传结构的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24251-. |
| [6] | 张锋, Richard Dormatey, 刘寅笃, 李成举, 王云姣, 张春利, 张莹, 范又方, 姚攀锋, 毕真真, 刘玉汇, 白江平, 孙超. 耐亚磷酸盐马铃薯的筛选与评价[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 544-557. |
| [7] | 段政勇, 丁敏, 王宇卓, 丁艺冰, 陈凌, 王瑞云, 乔治军. 糜子SBP基因家族全基因组鉴定及表达分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 231-244. |
| [8] | 李庆多, 栗冬梅. 全球蝙蝠巴尔通体流行状况分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23166-. |
| [9] | 冯晨, 张洁, 黄宏文. 统筹植物就地保护与迁地保护的解决方案: 植物并地保护(parallel situ conservation)[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23184-. |
| [10] | 齐海玲, 樊鹏振, 王跃华, 刘杰. 中国北方六省区胡桃的遗传多样性和群体结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23120-. |
| [11] | 熊飞, 刘红艳, 翟东东, 段辛斌, 田辉伍, 陈大庆. 基于基因组重测序的长江上游瓦氏黄颡鱼群体遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22391-. |
| [12] | 蒲佳佳, 杨平俊, 戴洋, 陶可欣, 高磊, 杜予州, 曹俊, 俞晓平, 杨倩倩. 长江下游外来生物福寿螺的种类及其种群遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22346-. |
| [13] | 何艺玥, 刘玉莹, 张富斌, 秦强, 曾燏, 吕振宇, 杨坤. 梯级水利工程背景下的嘉陵江干流蛇鮈群体遗传多样性和遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23160-. |
| [14] | 刘佳佳, 张大众, 张渊博, 张楚楚, 周佳玥, 熊亚红, 卓振生, 饶煜健, 冯佰利. 硒和碲对缓解糜子镉毒害及减少籽粒镉积累的调控效应[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 62-76. |
| [15] | 王宇卓, 林元香, 薛亚鹏, 段政勇, 王晓丹, 陈凌, 曹晓宁, 王瑞云, 乔治军. 山西糜子核心种质分子身份证构建[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 159-168. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||