

植物学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (4): 489-498.DOI: 10.11983/CBB25021 cstr: 32102.14.CBB25021
• 热点评述 • 下一篇
收稿日期:2025-02-11
接受日期:2025-05-07
出版日期:2025-07-10
发布日期:2025-05-14
通讯作者:
*郭岩, 博士, 教授, 中国农业大学生物学院、未来技术学院院长。1999年获德国科隆大学遗传学系博士。2009年起在中国农业大学生物学院工作。2010年获得“国家杰出青年科学基金”资助, 同年被聘为教育部“长江学者”特聘教授, 2012年获聘科技部973“作物应答盐碱胁迫的分子调控机理”项目首席科学家, 2013年入选“国家百千万人才工程”。兼任Plant Cell Physiology、Journal of Genetics and Genomics和Journal of Integrative Plant Biology等期刊编委。郭岩教授团队围绕植物盐碱胁迫应答的分子机制及调控网络开展系统性研究工作, 取得了一系列重要研究进展, 先后在Developmental Cell、Nature Communications、Proc Natl Acad Sci USA、Plant Cell、Molecular Plant及EMBO Journal等国际知名期刊发表论文60余篇。E-mail: guoyan@cau.edu.cn
基金资助:
Liang Ma, Yongqing Yang, Yan Guo*( )
)
Received:2025-02-11
Accepted:2025-05-07
Online:2025-07-10
Published:2025-05-14
Contact:
*E-mail: guoyan@cau.edu.cn
摘要: 近年来, 植物逆境生物学领域在极端温度与盐碱胁迫响应机制研究方面取得了重要进展, 不仅拓宽了我们对植物抗逆性的理解, 还为分子育种提供了丰富的靶点, 为培育顺境高产、逆境稳产的“气候智能”作物品种开辟了新途径。该文简要总结了植物感知和转导极端温度与盐碱胁迫信号的分子机制, 讨论了植物生长发育与胁迫耐受的平衡调控, 着重介绍了我国科学家近期在协同提高作物耐逆与产量的关键基因挖掘和机制解析方面的突破性成果, 并提出了未来的育种策略。
马亮, 杨永青, 郭岩. “后绿色革命”基因——助力培育“气候智能”作物新品种. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 489-498.
Liang Ma, Yongqing Yang, Yan Guo. “Next-generation Green Revolution” Genes: Toward New “Climate-Smart” Crop Breeding. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(4): 489-498.
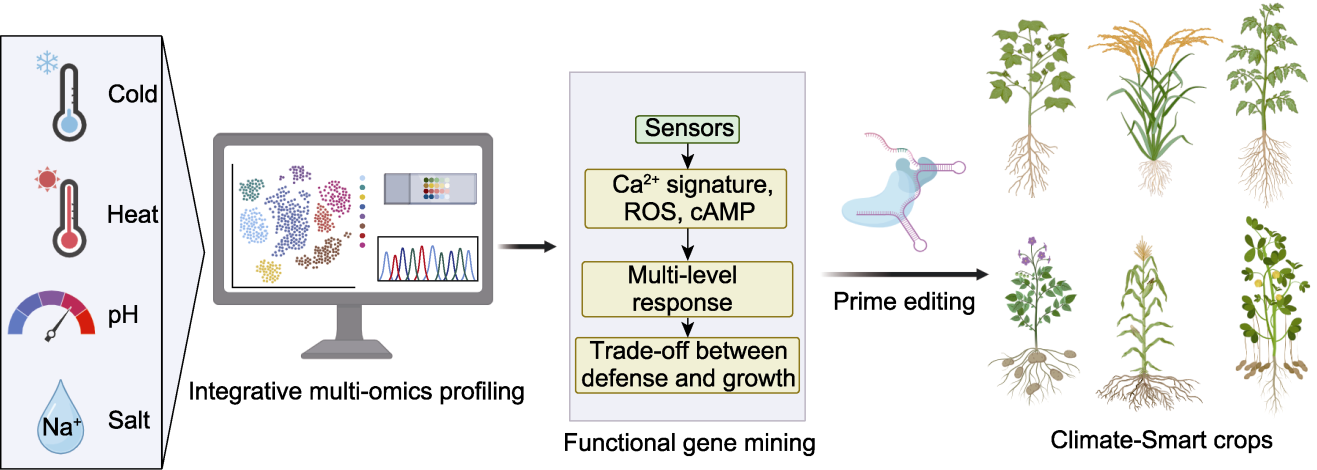
图1 生长与非生物胁迫平衡调控机制及抗逆模块挖掘: 面向“气候智能”作物育种的解决方案
Figure 1 Regulation of growth-stress trade-offs and exploration of abiotic resilience modules: a roadmap for “Climate-Smart” crops breeding
| [1] |
Allen DJ, Ort DR (2001). Impacts of chilling temperatures on photosynthesis in warm-climate plants. Trends Plant Sci 6, 36-42.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | Banani SF, Lee HO, Hyman AA, Rosen MK (2017). Biomolecular condensates: organizers of cellular biochemistry. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 18, 285-298. |
| [3] | Bohn L, Huang J, Weidig S, Yang ZY, Heidersberger C, Genty B, Falter-Braun P, Christmann A, Grill E (2024). The temperature sensor TWA1 is required for thermotolerance in Arabidopsis. Nature 629, 1126-1132. |
| [4] | Chen K, Gao JH, Sun SJ, Zhang ZJ, Yu B, Li J, Xie CG, Li GJ, Wang PC, Song CP, Bressan RA, Hua J, Zhu JK, Zhao Y (2020). BONZAI proteins control global osmotic stress responses in plants. Curr Biol 30, 4815-4825. |
| [5] | Chen LP, Zhao Y, Xu SJ, Zhang ZY, Xu YY, Zhang JY, Chong K (2018). OsMADS57 together with OsTB1 coordinates transcription of its target OsWRKY94 and D14 to switch its organogenesis to defense for cold adaptation in rice. New Phytol 218, 219-231. |
| [6] | Choi WG, Toyota M, Kim SH, Hilleary R, Gilroy S (2014). Salt stress-induced Ca2+ waves are associated with rapid, long-distance root-to-shoot signaling in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, 6497-6502. |
| [7] | Chung BYW, Balcerowicz M, Di Antonio M, Jaeger KE, Geng F, Franaszek K, Marriott P, Brierley I, Firth AE, Wigge PA (2020). An RNA thermoswitch regulates daytime growth in Arabidopsis. Nat Plants 6, 522-532. |
| [8] |
Ding YL, Shi YT, Yang SH (2024). Regulatory networks underlying plant responses and adaptation to cold stress. Annu Rev Genet 58, 43-65.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | Doherty CJ, Van Buskirk HA, Myers SJ, Thomashow MF (2009). Roles for Arabidopsis CAMTA transcription factors in cold-regulated gene expression and freezing tolerance. Plant Cell 21, 972-984. |
| [10] |
Feng W, Kita D, Peaucelle A, Cartwright HN, Doan V, Duan QH, Liu MC, Maman J, Steinhorst L, Schmitz- Thom I, Yvon R, Kudla J, Wu HM, Cheung AY, Dinneny JR (2018). The FERONIA receptor kinase maintains cell- wall integrity during salt stress through Ca2+ signaling. Curr Biol 28, 666-675.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | Gao L, Jiang HF, Li MZ, Wang DF, Xiang HT, Zeng R, Chen LM, Zhang XY, Zuo JR, Yang SH, Shi YT (2024a). Genetic and lipidomic analyses reveal the key role of lipid metabolism for cold tolerance in maize. J Genet Genomics 51, 326-337 |
| [12] | Gao L, Pan LL, Shi YT, Zeng R, Li MZ, Li ZY, Zhang X, Zhao XM, Gong XR, Huang W, Yang XH, Lai JS, Zuo JR, Gong ZZ, Wang XQ, Jin WW, Dong ZB, Yang SH (2024b). Genetic variation in a heat shock transcription factor modulates cold tolerance in maize. Mol Plant 17, 1423-1438. |
| [13] | Guo SQ, Chen YX, Ju YL, Pan CY, Shan JX, Ye WW, Dong NQ, Kan Y, Yang YB, Zhao HY, Yu HX, Lu ZQ, Lei JJ, Liao B, Mu XR, Cao YJ, Guo LX, Gao J, Zhou JF, Yang KY, Lin HX, Lin YS (2025). Fine-tuning gibberellin improves rice alkali-thermal tolerance and yield. Nature 639, 162-171. |
| [14] | Guo SY, Xu YY, Liu HH, Mao ZW, Zhang C, Ma Y, Zhang QR, Meng Z, Chong K (2013). The interaction between OsMADS57 and OsTB1 modulates rice tillering via DWARF- 14. Nat Commun 4, 1566. |
| [15] | Guo XY, Zhang DJ, Wang ZL, Xu SJ, Batistič O, Steinhorst L, Li H, Weng YX, Ren DT, Kudla J, Xu YY, Chong K (2023). Cold-induced calreticulin OsCRT3 conformational changes promote OsCIPK7 binding and temperature sensing in rice. EMBO J 42, e110518. |
| [16] |
Jiang HF, Shi YT, Liu JY, Li Z, Fu DY, Wu SF, Li MZ, Yang ZJ, Shi YL, Lai JS, Yang XH, Gong ZZ, Hua J, Yang SH (2022). Natural polymorphism of ZmICE1 contributes to amino acid metabolism that impacts cold tolerance in maize. Nat Plants 8, 1176-1190.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | Jiang ZH, Zhou XP, Tao M, Yuan F, Liu LL, Wu FH, Wu XM, Xiang Y, Niu Y, Liu F, Li CJ, Ye R, Byeon B, Xue Y, Zhao HY, Wang HN, Crawford BM, Johnson DM, Hu CX, Pei C, Zhou WM, Swift GB, Zhang H, Vo-Dinh T, Hu ZL, Siedow JN, Pei ZM (2019). Plant cell-surface GIPC sphingolipids sense salt to trigger Ca2+ influx. Nature 572, 341-346. |
| [18] | Jung JH, Barbosa AD, Hutin S, Kumita JR, Gao MJ, Derwort D, Silva CS, Lai XL, Pierre E, Geng F, Kim SB, Baek S, Zubieta C, Jaeger KE, Wigge PA (2020). A prion-like domain in ELF3 functions as a thermosensor in Arabidopsis. Nature 585, 256-260. |
| [19] |
Jung JH, Domijan M, Klose C, Biswas S, Ezer D, Gao MJ, Khattak AK, Box MS, Charoensawan V, Cortijo S, Kumar M, Grant A, Locke JCW, Schäfer E, Jaeger KE, Wigge PA (2016). Phytochromes function as thermosensors in Arabidopsis. Science 354, 886-889.
PMID |
| [20] |
Kan Y, Mu XR, Zhang H, Gao J, Shan JX, Ye WW, Lin HX (2022). TT2 controls rice thermotolerance through SCT1- dependent alteration of wax biosynthesis. Nat Plants 8, 53-67.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Kiegle E, Moore CA, Haseloff J, Tester MA, Knight MR (2000). Cell-type-specific calcium responses to drought, salt and cold in the Arabidopsis root. Plant J 23, 267-278.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | Kim Y, Park S, Gilmour SJ, Thomashow MF (2013). Roles of CAMTA transcription factors and salicylic acid in configuring the low-temperature transcriptome and freezing tolerance of Arabidopsis. Plant J 75, 364-376. |
| [23] |
Knight H, Trewavas AJ, Knight MR (1997). Calcium signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana responding to drought and salinity. Plant J 12, 1067-1078.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
Laohavisit A, Richards SL, Shabala L, Chen C, Colaço RDDR, Swarbreck SM, Shaw E, Dark A, Shabala S, Shang ZL, Davies JM (2013). Salinity-induced calcium signaling and root adaptation in Arabidopsis require the calcium regulatory protein annexin1. Plant Physiol 163, 253-262.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Legris M, Klose C, Burgie ES, Rojas CCB, Neme M, Hiltbrunner A, Wigge PA, Schäfer E, Vierstra RD, Casal JJ (2016). Phytochrome B integrates light and temperature signals in Arabidopsis. Science 354, 897-900. |
| [26] | Li ZY, Fu DY, Wang X, Zeng R, Zhang X, Tian JG, Zhang SS, Yang XH, Tian F, Lai JS, Shi YT, Yang SH (2022). The transcription factor bZIP68 negatively regulates cold tolerance in maize. Plant Cell 34, 2833-2851. |
| [27] |
Liu ZY, Jia YX, Ding YL, Shi YT, Li Z, Guo Y, Gong ZZ, Yang SH (2017). Plasma membrane CRPK1-mediated phosphorylation of 14-3-3 proteins induces their nuclear import to fine-tune CBF signaling during cold response. Mol Cell 66, 117-128.
DOI PMID |
| [28] |
Lou HC, Li SJ, Shi ZH, Zou YP, Zhang YQ, Huang XZ, Yang DD, Yang YF, Li ZY, Xu C (2025). Engineering source-sink relations by prime editing confers heat-stress resilience in tomato and rice. Cell 188, 530-549.
DOI PMID |
| [29] | Luo W, Xu YY, Cao J, Guo XY, Han JD, Zhang YY, Niu YD, Zhang ML, Wang Y, Liang GH, Qian Q, Ge S, Chong K (2024). COLD6-OSM1 module senses chilling for cold tolerance via 2',3'-cAMP signaling in rice. Mol Cell 84, 4224-4238. |
| [30] | Ma L, Liu XH, Lv WJ, Yang YQ (2022). Molecular mechanisms of plant responses to salt stress. Front Plant Sci 13, 934877. |
| [31] |
Ma L, Ye JM, Yang YQ, Lin HX, Yue LL, Luo J, Long Y, Fu HQ, Liu XN, Zhang YL, Wang Y, Chen LY, Kudla J, Wang YJ, Han SC, Song CP, Guo Y (2019). The SOS2-SCaBP8 complex generates and fine-tunes an AtANN4-dependent calcium signature under salt stress. Dev Cell 48, 697-709.
DOI PMID |
| [32] | Ma Y, Dai XY, Xu YY, Luo W, Zheng XM, Zeng DL, Pan YJ, Lin XL, Liu HH, Zhang DJ, Xiao J, Guo XY, Xu SJ, Niu YD, Jin JB, Zhang H, Xu X, Li LG, Wang W, Qian Q, Ge S, Chong K (2015). COLD1 confers chilling tolerance in rice. Cell 160, 1209-1221. |
| [33] | Mason TG, Maskell EJ (1928). Studies on the transport of carbohydrates in the cotton plant: II. The factors determining the rate and the direction of movement of sugars. Ann Bot 42, 571-636. |
| [34] |
Matsuoka Y, Vigouroux Y, Goodman MM, Sanchez GJ, Buckler E, Doebley J (2002). A single domestication for maize shown by multilocus microsatellite genotyping. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99, 6080-6084.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
Reindl A, Schöffl F, Schell J, Koncz C, Bakó L (1997). Phosphorylation by a cyclin-dependent kinase modulates DNA binding of the Arabidopsis heat-shock transcription factor HSF1 in vitro. Plant Physiol 115, 93-100.
PMID |
| [36] |
Steinhorst L, He GF, Moore LK, Schültke S, Schmitz- Thom I, Cao YB, Hashimoto K, Andrés Z, Piepenburg K, Ragel P, Behera S, Almutairi BO, Batistič O, Wyganowski T, Köster P, Edel KH, Zhang CX, Krebs M, Jiang CF, Guo Y, Quintero FJ, Bock R, Kudla J (2022). A Ca2+-sensor switch for tolerance to elevated salt stress in Arabidopsis. Dev Cell 57, 2081-2094.
DOI PMID |
| [37] | Tracy FE, Gilliham M, Dodd AN, Webb AAR, Tester M (2008). NaCl-induced changes in cytosolic free Ca2+ in Arabidopsis thaliana are heterogeneous and modified by external ionic composition. Plant Cell Environ 31, 1063-1073. |
| [38] | van Dijk M, Morley T, Rau ML, Saghai Y (2021). A meta- analysis of projected global food demand and population at risk of hunger for the period 2010-2050. Nat Food 2, 494-501. |
| [39] | Wang BY, Zhang HH, Huai JL, Peng FY, Wu J, Lin RC, Fang XF (2022). Condensation of SEUSS promotes hyperosmotic stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Nat Chem Biol 18, 1361-1369. |
| [40] | Wang XH, Zhao C, Müller C, Wang CZ, Ciais P, Janssens I, Peñuelas J, Asseng S, Li T, Elliott J, Huang Y, Li L, Piao S (2020). Emergent constraint on crop yield response to warmer temperature from field experiments. Nat Sustain 3, 908-916. |
| [41] | Wang ZY, Yang QH, Zhang D, Lu YY, Wang YC, Pan YJ, Qiu YP, Men Y, Yan W, Xiao ZN, Sun RX, Li WY, Huang HD, Guo HW (2024). A cytoplasmic osmosensing mechanism mediated by molecular crowding-sensitive DCP5. Science 386, eadk9067. |
| [42] |
Wheeler T, Von Braun J (2013). Climate change impacts on global food security. Science 341, 508-513.
DOI PMID |
| [43] | Wu Y, Wang Y, Mi XF, Shan JX, Li XM, Xu JL, Lin HX (2016). The QTL GNP1 encodes GA20ox1, which increases grain number and yield by increasing cytokinin activity in rice panicle meristems. PLoS Genet 12, e1006386. |
| [44] | Xia CX, Liang GH, Chong K, Xu YY (2023). The COG1- OsSERL2 complex senses cold to trigger signaling network for chilling tolerance in japonica rice. Nat Commun 14, 3104. |
| [45] | Xiang YH, Yu JJ, Liao B, Shan JX, Ye WW, Dong NQ, Guo T, Kan Y, Zhang H, Yang YB, Li YC, Zhao HY, Yu HX, Lu ZQ, Lin HX (2022). An α/β hydrolase family member negatively regulates salt tolerance but promotes flowering through three distinct functions in rice. Mol Plant 15, 1908-1930. |
| [46] |
Yang YQ, Guo Y (2018). Unraveling salt stress signaling in plants. J Integr Plant Biol 60, 796-804.
DOI |
| [47] | Yang ZR, Cao YB, Shi YT, Qin F, Jiang CF, Yang SH (2023). Genetic and molecular exploration of maize environmental stress resilience: toward sustainable agriculture. Mol Plant 16, 1496-1517. |
| [48] | Yin WC, Xiao YH, Niu M, Meng WJ, Li LL, Zhang XX, Liu DP, Zhang GX, Qian YW, Sun ZT, Huang RY, Wang SP, Liu CM, Chu CC, Tong HN (2020). ARGONAUTE2 enhances grain length and salt tolerance by activating BIG GRAIN3 to modulate cytokinin distribution in rice. Plant Cell 32, 2292-2306. |
| [49] | Yuan F, Yang HM, Xue Y, Kong DD, Ye R, Li CJ, Zhang JY, Theprungsirikul L, Shrift T, Krichilsky B, Johnson DM, Swift GB, He YK, Siedow JN, Pei ZM (2014). OSCA1 mediates osmotic-stress-evoked Ca2+ increases vital for osmosensing in Arabidopsis. Nature 514, 367-371. |
| [50] |
Zeng R, Li ZY, Shi YT, Fu DY, Yin P, Cheng JK, Jiang CF, Yang SH (2021). Natural variation in a type-A response regulator confers maize chilling tolerance. Nat Commun 12, 4713.
DOI PMID |
| [51] | Zeng R, Shi YT, Guo L, Fu DY, Li MZ, Zhang XY, Li ZY, Zhuang JH, Yang XH, Zuo JR, Gong ZZ, Tian F, Yang SH (2025). A natural variant of COOL1 gene enhances cold tolerance for high-latitude adaptation in maize. Cell 188, 1315-1329. |
| [52] |
Zhang DJ, Guo XY, Xu YY, Li H, Ma L, Yao XF, Weng YX, Guo Y, Liu CM, Chong K (2019). OsCIPK7 point-mutation leads to conformation and kinase-activity change for sensing cold response. J Integr Plant Biol 61, 1194-1200.
DOI |
| [53] |
Zhang H, Zhang JY, Xu QY, Wang DD, Di H, Huang J, Yang XW, Wang ZF, Zhang L, Dong L, Wang ZH, Zhou Y (2020). Identification of candidate tolerance genes to low-temperature during maize germination by GWAS and RNA-seq approaches. BMC Plant Biol 20, 333.
DOI PMID |
| [54] |
Zhang H, Zhou JF, Kan Y, Shan JX, Ye WW, Dong NQ, Guo T, Xiang YH, Yang YB, Li YC, Zhao HY, Yu HX, Lu ZQ, Guo SQ, Lei JJ, Liao B, Mu XR, Cao YJ, Yu JJ, Lin YS, Lin HX (2022). A genetic module at one locus in rice protects chloroplasts to enhance thermotolerance. Science 376, 1293-1300.
DOI PMID |
| [55] | Zhou XM, Muhammad I, Lan H, Xia C (2022). Recent advances in the analysis of cold tolerance in maize. Front Plant Sci 13, 866034. |
| [1] | 吴玉俊, 李英菊, 罗巧玉, 马永贵. 光控植物免疫:从光信号通路到免疫应答的调控网络[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 1-0. |
| [2] | 周玉滢, 陈辉, 刘斯穆. 植物非典型Aux/IAA蛋白应答生长素研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 651-658. |
| [3] | 李聪, 齐立娟, 谷晓峰, 李继刚. 植物光信号途径重要新调控因子TZP的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(5): 579-587. |
| [4] | 贾利霞, 齐艳华. 生长素代谢、运输及信号转导调控水稻粒型研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(3): 263-275. |
| [5] | 支添添, 周舟, 韩成云, 任春梅. PAD4突变加速拟南芥酪氨酸降解缺陷突变体sscd1的程序性细胞死亡[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(3): 288-298. |
| [6] | 崔晓敏, 季东超, 陈彤, 田世平. 类受体激酶FER调节植物与病原菌相互作用的分子机制[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(3): 339-346. |
| [7] | 宋松泉, 刘军, 杨华, 张文虎, 张琪, 高家东. 细胞分裂素调控种子发育、休眠与萌发的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(2): 218-231. |
| [8] | 杨程惠子,唐先宇,李威,夏石头. NLR及其在植物抗病中的调控作用[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(4): 497-504. |
| [9] | 张娜,刘秀霞,陈学森,吴树敬. 基于转录组分析鉴定苹果茉莉素响应基因[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(6): 733-743. |
| [10] | 胡孔琴, 丁兆军. 非TIR1受体依赖型激活生长素信号的新机制[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(3): 293-295. |
| [11] | 王雅静,张欣莹,黄桂荣,刘晓英,郭瑞,顾峰雪,钟秀丽,梅旭荣. 植物磷脂酸的特性及其在ABA诱导气孔运动中的作用[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(2): 245-154. |
| [12] | 牛艳丽, 柏胜龙, 王麒云, 刘凌云. 单细胞组学技术及其在植物保卫细胞研究中的应用[J]. 植物学报, 2017, 52(6): 788-796. |
| [13] | 张玲玲, 吴丹, 赵子捷, 赵立群. 植物一氧化氮信号分子的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2017, 52(3): 337-345. |
| [14] | 景艳军, 林荣呈. 我国植物光信号转导研究进展概述[J]. 植物学报, 2017, 52(3): 257-270. |
| [15] | 曾后清, 张亚仙, 汪尚, 张夏俊, 王慧中, 杜立群. 植物钙/钙调素介导的信号转导系统[J]. 植物学报, 2016, 51(5): 705-723. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||