

植物学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (6): 993-1004.DOI: 10.11983/CBB25064 cstr: 32102.14.CBB25064
收稿日期:2025-04-11
接受日期:2025-07-29
出版日期:2025-11-10
发布日期:2025-07-30
通讯作者:
刘勇波
基金资助:Received:2025-04-11
Accepted:2025-07-29
Online:2025-11-10
Published:2025-07-30
Contact:
Yongbo Liu
摘要: 植物卷须是一种特化的攀缘器官, 在植物的生存与环境适应中发挥关键作用。通过提供结构支撑、增强光能捕获能力以及降低地面资源竞争, 卷须显著提升了植物的生态适应性。卷须由花序、叶片和枝茎等器官衍生而来, 由TCP、HD-ZIP和MADS-box等基因家族调控, 并受到生长素、赤霉素、细胞分裂素和茉莉酸等植物激素的影响。卷须在功能、形态及分子机制上表现出趋同进化现象, 并呈现独立演化特征, 这反映了植物对生存环境的适应策略。该文系统综述了植物卷须的生物学特性和发育的分子机制, 展望了未来卷须形成与调控机制研究应关注跨物种的演化机制、环境信号与植物激素的相互调控等方面。
罗号东, 刘勇波. 植物卷须发生及调控机制研究进展. 植物学报, 2025, 60(6): 993-1004.
Haodong Luo, Yongbo Liu. Research Progress in the Development and Regulatory Mechanisms of Plant Tendrils. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(6): 993-1004.
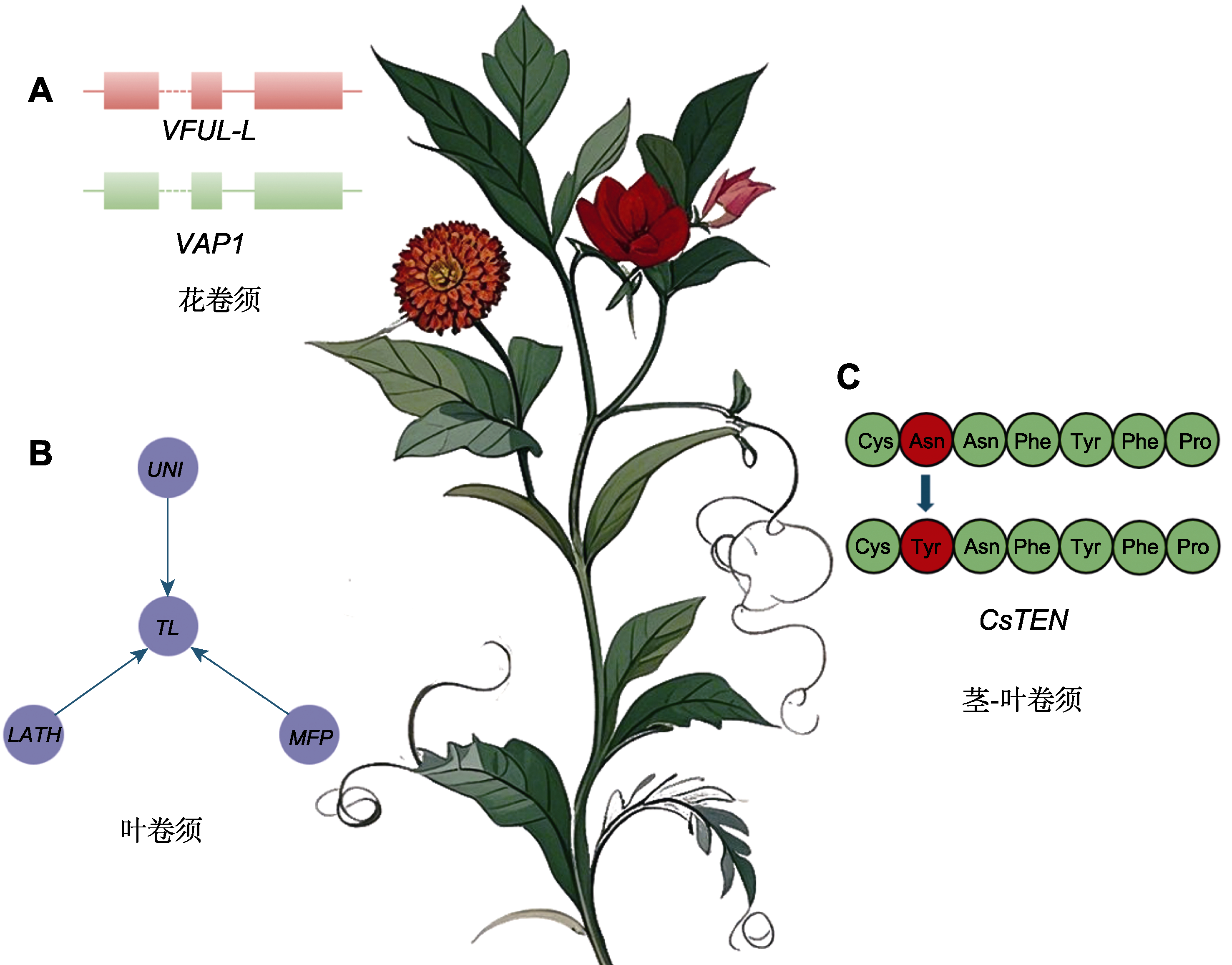
图1 植物卷须发育的部分调控基因 (A) 参与花起源卷须的调控基因VFUL-L与VAP1; (B) 参与叶起源卷须的调控基因TL及调控TL的UNI、LATH和MFP基因; (C) 参与茎-叶起源卷须的调控基因CsTEN及其无卷须突变体N338Y (由Asn突变成Tyr)。图片植物仅展示卷须的器官来源, 无真实对应物种。
Figure 1 Partial genes regulating tendril development in plants (A) Tendril regulatory genes VFUL-L and VAP1 participate in floral-derived tendril formation; (B) Tendril regulatory gene TL and its upstream regulators UNI, LATH, and MFP participate in leaf-derived tendril formation; (C) Tendril regulatory gene CsTEN and its tendril-less mutant N338Y (Asn mutating to Tyr) participate in shoot-leaf transitional area tendril regulation. The plant in the image shows only the organ origin of tendrils and does not correspond to any real species.
| 基因家族 | 基因 | 物种 | 功能 | 机制 | 来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCP | CmTCP1和CsTEN | Cucumis melo和C. sativus | 调控细胞分裂分化与叶片形态 | 调控细胞周期基因, 促进细胞增殖, 优化叶片与分枝的生长 | Mizuno et al., |
| GNAT | CsGCN5 | C. sativus | 调控染色质开放状态, 调节基因表达 | 通过组蛋白乙酰化松散染色质结构, 促进目标基因的表达 | Chen et al., |
| PEBP | ClTFL1 | C. lanatus | 延长顶端分生组织的营养生长阶段 | 抑制开花基因的过早激活, 维持分生组织未分化状态, 平衡营养生长与生殖生长 | Yi et al., |
| F-box | CsUFO | C. sativus | 调控花与卷须发育 | 受TCP/GRAS同源基因激活, 调控花与卷须发育 | Chen et al., |
| GRAS | ClLS和CsTL | C. lanatus和 C. sativus | 调控卷须发育 | 与TCP同源基因形成复合物, 激活下游UFO基因表达, 调节花与卷须发育 | Jiang et al., |
| SPL | SPL | C. sativus | 调控卷须发育的潜在功能 | miR156/157作用于SPL, 调控下游基因的表达 | 汪淑雯等, |
表1 茎-叶结构起源的卷须调控基因
Table 1 Regulatory genes of tendrils of stem-leaf origin
| 基因家族 | 基因 | 物种 | 功能 | 机制 | 来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCP | CmTCP1和CsTEN | Cucumis melo和C. sativus | 调控细胞分裂分化与叶片形态 | 调控细胞周期基因, 促进细胞增殖, 优化叶片与分枝的生长 | Mizuno et al., |
| GNAT | CsGCN5 | C. sativus | 调控染色质开放状态, 调节基因表达 | 通过组蛋白乙酰化松散染色质结构, 促进目标基因的表达 | Chen et al., |
| PEBP | ClTFL1 | C. lanatus | 延长顶端分生组织的营养生长阶段 | 抑制开花基因的过早激活, 维持分生组织未分化状态, 平衡营养生长与生殖生长 | Yi et al., |
| F-box | CsUFO | C. sativus | 调控花与卷须发育 | 受TCP/GRAS同源基因激活, 调控花与卷须发育 | Chen et al., |
| GRAS | ClLS和CsTL | C. lanatus和 C. sativus | 调控卷须发育 | 与TCP同源基因形成复合物, 激活下游UFO基因表达, 调节花与卷须发育 | Jiang et al., |
| SPL | SPL | C. sativus | 调控卷须发育的潜在功能 | miR156/157作用于SPL, 调控下游基因的表达 | 汪淑雯等, |
| 基因家族 | 基因 | 物种 | 功能 | 机制 | 来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEBP | VvTFL1A和VvFT | Vitis vinifera | 在卷须发育的早期阶段维持分生组织的活性, 并调控花序分化 | 抑制开花促进基因表达, 维持分生组织未分化状态, 并通过调控开花时间平衡营养生长与生殖生长 | Carmona et al., |
| MADS-box | PeFU、VFUL-L、PeAP1、VAP1和PeSEP3 | Passiflora edulis和V. vinifera | 调控果实发育、花序分化和开花时间, 确保卷须发育正常进行 | 通过与LFY和CAL等基因形成复合体控制植物开花进程, 协调卷须发育 | Calonje et al., |
| None | PeLF和PsLFY | P. edulis和 P. suberosa | 调控开花时间和花器官发育的核心功能 | LFY基因整合内外信号, 精准调控花器官发育基因表达, 与其它因子协作决定花的形态与功能 | Cutri, |
| YABBY | YAB1 | Arabidopsis thaliana | 调控叶片背腹轴分化与边缘扩展, 并在花器官发育中发挥关键作用 | 通过特异性表达调控叶片背腹轴发育, 与植物激素信号协作确保花器官形态特化 | Eshed et al., |
| CIPK | VvCIPK14 | V. vinifera | 可能参与卷须发育 | 未知 | 闫朝辉等, |
表2 花起源的卷须调控基因
Table 2 Regulatory genes of tendrils of floral origin
| 基因家族 | 基因 | 物种 | 功能 | 机制 | 来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEBP | VvTFL1A和VvFT | Vitis vinifera | 在卷须发育的早期阶段维持分生组织的活性, 并调控花序分化 | 抑制开花促进基因表达, 维持分生组织未分化状态, 并通过调控开花时间平衡营养生长与生殖生长 | Carmona et al., |
| MADS-box | PeFU、VFUL-L、PeAP1、VAP1和PeSEP3 | Passiflora edulis和V. vinifera | 调控果实发育、花序分化和开花时间, 确保卷须发育正常进行 | 通过与LFY和CAL等基因形成复合体控制植物开花进程, 协调卷须发育 | Calonje et al., |
| None | PeLF和PsLFY | P. edulis和 P. suberosa | 调控开花时间和花器官发育的核心功能 | LFY基因整合内外信号, 精准调控花器官发育基因表达, 与其它因子协作决定花的形态与功能 | Cutri, |
| YABBY | YAB1 | Arabidopsis thaliana | 调控叶片背腹轴分化与边缘扩展, 并在花器官发育中发挥关键作用 | 通过特异性表达调控叶片背腹轴发育, 与植物激素信号协作确保花器官形态特化 | Eshed et al., |
| CIPK | VvCIPK14 | V. vinifera | 可能参与卷须发育 | 未知 | 闫朝辉等, |
| 基因家族 | 基因 | 物种 | 功能 | 机制 | 来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HD-ZIP | TL | Pisum sativum、Lathyrus odoratus、Vicia sativa、V. narbonensis和Lens culinaris | 调控卷须和叶片的分化, 优化植物攀缘能力 | 整合植物激素信号, 调控卷须和叶片的分化比例, 确保结构和功能适应性 | Hofer et al., |
| None | UNI和MFP | P. sativum | UNI促进小叶和卷须发育; MFP调控复叶结构, 促进卷须发育 | UNI调控复叶原基芽生区; MFP蛋白通过START结构域与TL蛋白互作, 调控卷须发育 | Weigel et al., |
| WOX | LATH | P. sativum | 调控叶片与卷须的分化, 平衡两者发育, 增强攀缘能力并提高资源利用效率 | 调控卷须与叶片特化基因表达, 协调分化以适应复杂环境 | Tadege et al., |
| KNOX | STM | Arabidopsis thaliana、Bignonia callistegioides、Dolichandra unguis-cati和Amphilophium buccinatorium | 调控植物器官和攀缘结构发育 | STM基因通过维持分生组织未分化状态, 调控细胞分裂以适应植物发育需求 | Sousa-Baena et al., |
| ARP | BcPHAN和PHAN | B. callistegioides、D. unguis- cati和A. buccinatorium | 通过调控叶片背腹性和卷须形成支持植物攀缘功能 | 通过调控目标基因, 促进叶片背腹极性和卷须形成 | Waites and Hudson, |
表3 叶起源的卷须调控基因
Table 3 Regulatory genes of tendrils of leaf origin
| 基因家族 | 基因 | 物种 | 功能 | 机制 | 来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HD-ZIP | TL | Pisum sativum、Lathyrus odoratus、Vicia sativa、V. narbonensis和Lens culinaris | 调控卷须和叶片的分化, 优化植物攀缘能力 | 整合植物激素信号, 调控卷须和叶片的分化比例, 确保结构和功能适应性 | Hofer et al., |
| None | UNI和MFP | P. sativum | UNI促进小叶和卷须发育; MFP调控复叶结构, 促进卷须发育 | UNI调控复叶原基芽生区; MFP蛋白通过START结构域与TL蛋白互作, 调控卷须发育 | Weigel et al., |
| WOX | LATH | P. sativum | 调控叶片与卷须的分化, 平衡两者发育, 增强攀缘能力并提高资源利用效率 | 调控卷须与叶片特化基因表达, 协调分化以适应复杂环境 | Tadege et al., |
| KNOX | STM | Arabidopsis thaliana、Bignonia callistegioides、Dolichandra unguis-cati和Amphilophium buccinatorium | 调控植物器官和攀缘结构发育 | STM基因通过维持分生组织未分化状态, 调控细胞分裂以适应植物发育需求 | Sousa-Baena et al., |
| ARP | BcPHAN和PHAN | B. callistegioides、D. unguis- cati和A. buccinatorium | 通过调控叶片背腹性和卷须形成支持植物攀缘功能 | 通过调控目标基因, 促进叶片背腹极性和卷须形成 | Waites and Hudson, |
| [1] |
Allfrey VG, Faulkner R, Mirsky AE (1964). Acetylation and methylation of histones and their possible role in the regulation of RNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 51, 786-794.
PMID |
| [2] |
Ameha M, Skirvin RM, Mitiku G, Bullock D, Hofmann P (1998). In vitro tendril and flower development in cucumber (Cucumis sativus) may be regulated by gibberellins. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 73, 159-163.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Bai F, DeMason DA (2006). Hormone interactions and regulation of Unifoliata, PsPK2, PsPIN1 and LE gene expression in pea (Pisum sativum) shoot tips. Plant Cell Physiol 47, 935-948.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Bharathan G, Goliber TE, Moore C, Kessler S, Pham T, Sinha NR (2002). Homologies in leaf form inferred from KNOXI gene expression during development. Science 296, 1858-1860.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
Boss PK, Thomas MR (2002). Association of dwarfism and floral induction with a grape ‘green revolution’ mutation. Nature 416, 847-850.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Bucher P (1990). Weight matrix descriptions of four eukaryotic RNA polymerase II promoter elements derived from 502 unrelated promoter sequences. J Mol Biol 212, 563-578.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
Calonje M, Cubas P, Martínez-Zapater JM, Carmona MJ (2004). Floral meristem identity genes are expressed during tendril development in grapevine. Plant Physiol 135, 1491-1501.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
Carmona MJ, Cubas P, Calonje M, Martínez-Zapater JM (2007). Flowering transition in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.). Can J Bot 85, 701-711.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Chen FF, Fu BB, Pan YP, Zhang CW, Wen HF, Weng YQ, Chen P, Li YH (2017). Fine mapping identifies CsGCN5 encoding a histone acetyltransferase as putative candidate gene for tendril-less1 mutation (td-1) in cucumber. Theor Appl Genet 130, 1549-1558.
DOI URL |
| [10] | Chen JY, Wang WQ, Luo SY, Yang LX, Wang HJ, Wu TY, Zhu QK (2025). Expression pattern and metabolic correlation analysis of TCP gene family in Bergenia purpurascens. Chin Bull Bot doi: 10.11983/CBB25008. (in Chinese) |
| 陈靖彧, 王文庆, 罗诗语, 杨路祥, 汪慧骏, 吴天宇, 朱乾坤 (2025). 岩白菜TCP基因家族的表达模式及代谢关联分析. 植物学报 doi: 10.11983/CBB25008. | |
| [11] |
Chen Y, Wen HF, Pan J, Du H, Zhang KY, Zhang LY, Yu Y, He HL, Cai R, Pan JS, Wang G (2021). CsUFO is involved in the formation of flowers and tendrils in cucumber. Theor Appl Genet 134, 2141-2150.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | Cutri L (2009). Estudo da Função do Gene LEAFY (LFY) em Duas Especies de Passiflora. Master’s thesis. Campinas, SP: Universidade Estadual de Campinas. |
| [13] | Cutri L, Dornelas MC (2012). PASSIOMA: exploring expressed sequence tags during flower development in Passiflora spp. Comp Funct Genomics 2012, 510549. |
| [14] | Dai YJ, Luo XF, Zhou WG, Chen F, Shuai HY, Yang WY, Shu K (2019). Plant systemic signaling under biotic and abiotic stresses conditions. Chin Bull Bot 54, 255-264. (in Chinese) |
|
代宇佳, 罗晓峰, 周文冠, 陈锋, 帅海威, 杨文钰, 舒凯 (2019). 生物和非生物逆境胁迫下的植物系统信号. 植物学报 54, 255-264.
DOI |
|
| [15] |
DeMason DA, Chetty V, Barkawi LS, Liu X, Cohen JD (2013). Unifoliata-Afila interactions in pea leaf morphogenesis. Am J Bot 100, 478-495.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
DeMason DA, Chetty VJ (2011). Interactions between GA, auxin, and UNI expression controlling shoot ontogeny, leaf morphogenesis, and auxin response in Pisum sativum (Fabaceae): or how the uni-tac mutant is rescued. Am J Bot 98, 775-791.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Eshed Y, Baum SF, Perea JV, Bowman JL (2001). Establishment of polarity in lateral organs of plants. Curr Biol 11, 1251-1260.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Gélinas-Marion A, Eléouët MP, Cook SD, Vander Schoor JK, Abel SAG, Nichols DS, Smith JA, Hofer JMI, Ross JJ (2023). Plant development in the garden pea as revealed by mutations in the Crd/PsYUC1 gene. Genes 14, 2115.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Gourlay CW, Hofer JM, Ellis TH (2000). Pea compound leaf architecture is regulated by interactions among the genes UNIFOLIATA, COCHLEATA, AFILA, and TENDRIL-LESS. Plant Cell 12, 1279-1294.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Guo J, Xu WB, Hu Y, Huang J, Zhao YY, Zhang L, Huang CH, Ma H (2020). Phylotranscriptomics in Cucurbitaceae reveal multiple whole-genome duplications and key morphological and molecular innovations. Mol Plant 13, 1117-1133.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | Han XR, Yuan X, Gao J, Wang LS, Wang XH, Jia WQ, Fu ZZ, Zhang HC (2025). Identification of TCP gene family and functional analysis of TCP15a of tree peony. Chin Bull Bot doi: 10.11983/CBB25005. (in Chinese) |
| 韩新蕊, 袁欣, 高杰, 王亮生, 王晓晖, 贾文庆, 符真珠, 张和臣 (2025). 牡丹TCP基因家族鉴定及TCP15a功能分析. 植物学报 doi: 10.11983/CBB25005. | |
| [22] |
Hofer J, Turner L, Hellens R, Ambrose M, Matthews P, Michael A, Ellis N (1997). UNIFOLIATA regulates leaf and flower morphogenesis in pea. Curr Biol 7, 581-587.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
Hofer J, Turner L, Moreau C, Ambrose M, Isaac P, Butcher S, Weller J, Dupin A, Dalmais M, Le Signor C, Bendahmane A, Ellis N (2009). Tendril-less regulates tendril formation in pea leaves. Plant Cell 21, 420-428.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Hong ZZ, Wang XR, Fan ZP, Wang JH, Yang AY, Yan GC, He Y, Wang HS, Zhu ZJ, Xu YM (2024). The intrinsic developmental age signal defines an age-dependent climbing behavior in cucumber. Hortic Plant J 10, 797-808. |
| [25] |
Hong ZZ, Wang XR, Yang AY, Yan GC, He Y, Zhu ZJ, Xu YM (2023). Tendril morphogenesis is regulated by a CsaTEN-CsaUFO module in cucumber. New Phytol 239, 364-373.
DOI URL |
| [26] | Immink RG, Tonaco IA, De Folter S, Shchennikova A, Van Dijk AD, Busscher-Lange J, Borst JW, Angenent GC (2009). SEPALLATA3: the ‘glue’ for MADS box transcription factor complex formation. Genome Biol 10, R24. |
| [27] | Jaffe MJ, Galston AW (1968). The physiology of tendrils. Annu Rev Plant Biol 19, 417-434. |
| [28] |
Jiang YX, Zhang AR, He WJ, Li QQ, Zhao BS, Zhao HJ, Ke XB, Guo YL, Sun PY, Yang TW, Wang Z, Jiang B, Shen JJ, Li Z (2023). GRAS family member LATERAL SUPPRESSOR regulates the initiation and morphogenesis of watermelon lateral organs. Plant Physiol 193, 2592-2604.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
Kim M, Pham T, Hamidi A, McCormick S, Kuzoff RK, Sinha N (2003). Reduced leaf complexity in tomato wiry mutants suggests a role for PHAN and KNOX genes in generating compound leaves. Development 130, 4405-4415.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Kosugi S, Ohashi Y (2002). DNA binding and dimerization specificity and potential targets for the TCP protein family. Plant J 30, 337-348.
DOI PMID |
| [31] | Kotoda N, Wada M, Komori S, Kidou S, Abe K, Masuda T, Soejima J (2000). Expression pattern of homologues of floral meristem identity genes LFY and AP1 during flower development in apple. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 125, 398-403. |
| [32] |
Krings M, Kerp H, Taylor TN, Taylor EL (2003). How Paleozoic vines and lianas got off the ground: on scrambling and climbing carboniferous-early permian pteridosperms. Bot Rev 69, 204-224.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Kumar S, Kumar Rai S, Pandey-Rai S, Srivastava S, Singh D (2004). Regulation of unipinnate character in the distal tendrilled domain of compound leaf-blade by the gene MULTIFOLIATE PINNA (MFP) in pea Pisum sativum. Plant Sci 166, 929-940.
DOI URL |
| [34] | Lescot M (2002). PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 30, 325-327. |
| [35] | Li BQ, Yan JH, Li H, Xin W, Tian YH, Yang ZB, Tang WX (2022). Changes of small GTPases activity during cucumber tendril Winding. Chin Bull Bot 57, 299-307. (in Chinese) |
|
李彬琪, 闫佳慧, 李豪, 辛伟, 田云鹤, 杨贞标, 唐文鑫 (2022). 黄瓜卷须缠绕过程中小G蛋白活性变化. 植物学报 57, 299-307.
DOI |
|
| [36] |
Li CJ, Bangerth F (2003). Stimulatory effect of cytokinins and interaction with IAA on the release of lateral buds of pea plants from apical dominance. J Plant Physiol 160, 1059-1063.
DOI URL |
| [37] | Li YY, Qi YH (2022). Advances in biological functions of Aux/IAA gene family in plants. Chin Bull Bot 57, 30-41. (in Chinese) |
|
李艳艳, 齐艳华 (2022). 植物Aux/IAA基因家族生物学功能研究进展. 植物学报 57, 30-41.
DOI |
|
| [38] |
Lin H, Niu LF, McHale NA, Ohme-Takagi M, Mysore KS, Tadege M (2013). Evolutionarily conserved repressive activity of WOX proteins mediates leaf blade outgrowth and floral organ development in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110, 366-371.
DOI PMID |
| [39] |
Liu XF, Hao N, Li HY, Ge DF, Du YL, Liu RY, Wen CL, Li YH, Zhang XL, Wu T (2019). PINOID is required for lateral organ morphogenesis and ovule development in cucumber. J Exp Bot 70, 5715-5730.
DOI PMID |
| [40] |
López-Juez E, Buurmeijer WF, Heeringa GH, Kendrick RE, Wesselius JC (1990). Response of light-grown wild- type and long-hypocotyl mutant cucumber plants to end- of-day far-red light. Photochem Photobiol 52, 143-149.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Mishra RK, Chaudhary S, Kumar A, Kumar S (2009). Effects of MULTIFOLIATE-PINNA, AFILA, TENDRIL-LESS and UNIFOLIATA genes on leafblade architecture in Pisum sativum. Planta 230, 177-190.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Mizuno S, Sonoda M, Tamura Y, Nishino E, Suzuki H, Sato T, Oizumi T (2015). Chiba Tendril-Less locus determines tendril organ identity in melon (Cucumis melo L.) and potentially encodes a tendril-specific TCP homolog. J Plant Res 128, 941-951.
DOI URL |
| [43] | Narasimhan S (2024). Ultrastructural studies on tendrils of plant climbers reveals a hierarchical tissue organization: a microscopic investigation. J Integr Sci Technol 12, 760. |
| [44] | Nicolas M, Cubas P (2015). The role of TCP transcription factors in shaping flower structure, leaf morphology, and plant architecture. In: Gonzalez DH, ed. Plant Transcription Factors: Evolutionary, Structural and Functional Aspects, Amsterdam: Academic Press. pp. 249-267. |
| [45] |
Pajoro A, Biewers S, Dougali E, Leal Valentim F, Mendes MA, Porri A, Coupland G, Van de Peer Y, van Dijk ADJ, Colombo L, Davies B, Angenent GC (2014). The (r)evolution of gene regulatory networks controlling Arabidopsis plant reproduction: a two-decade history. J Exp Bot 65, 4731-4745.
DOI PMID |
| [46] |
Pratt C (1974). Vegetative anatomy of cultivated grapes—a review. Am J Enol Vitic 25, 131-150.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Prenner G (2014). Floral ontogeny in Passiflora lobata (Malpighiales, Passifloraceae) reveals a rare pattern in petal formation and provides new evidence for interpretation of the tendril and corona. Plant Syst Evol 300, 1285-1297.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
Scorza LCT, Hernandes-Lopes J, Melo-de-Pinna GFA, Dornelas MC (2017). Expression patterns of Passiflora edulis APETALA1/FRUITFULL homologues shed light onto tendril and corona identities. EvoDevo 8, 3.
DOI PMID |
| [49] |
Shen JJ, Jiang YX, Pan J, Sun LH, Li QQ, He WJ, Sun PY, Zhao BS, Zhao HJ, Ke XB, Guo YL, Yang TW, Li Z (2024). The GRAS transcription factor CsTL regulates tendril formation in cucumber. Plant Cell 36, 2818-2833.
DOI URL |
| [50] | Shuai HY, Meng YJ, Chen F, Zhou WG, Luo XF, Yang WY, Shu K (2018). Phytohormone-mediated plant shade responses. Chin Bull Bot 53, 139-148. (in Chinese) |
|
帅海威, 孟永杰, 陈锋, 周文冠, 罗晓峰, 杨文钰, 舒凯 (2018). 植物荫蔽胁迫的激素信号响应. 植物学报 53, 139-148.
DOI |
|
| [51] |
Song MF, Zha GH, Chen JF, Lou QF (2022). Research progress on molecular basis of plant architecture related traits in cucumber. Acta Hortic Sin 49, 2683-2702. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
宋蒙飞, 查高辉, 陈劲枫, 娄群峰 (2022). 黄瓜株型性状分子基础研究进展. 园艺学报 49, 2683-2702.
DOI |
|
| [52] |
Sousa-Baena MS, Lohmann LG, Hernandes-Lopes J, Sinha NR (2018a). The molecular control of tendril development in angiosperms. New Phytol 218, 944-958.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
Sousa-Baena MS, Lohmann LG, Rossi M, Sinha NR (2014a). Acquisition and diversification of tendrilled leaves in Bignonieae (Bignoniaceae) involved changes in expression patterns of SHOOTMERISTEMLESS (STM), LEAFY/ FLORICAULA (LFY/FLO), and PHANTASTICA (PHAN). New Phytol 201, 993-1008.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
Sousa-Baena MS, Sinha NR, Hernandes-Lopes J, Lohmann LG (2018b). Convergent evolution and the diverse ontogenetic origins of tendrils in angiosperms. Front Plant Sci 9, 403.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
Sousa-Baena MS, Sinha NR, Lohmann LG (2014b). Evolution and development of tendrils in Bignonieae (Lamiales, Bignoniaceae). Ann Mo Bot Gard 99, 323-347.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
Srinivasan C, Mullins MG (1976). Reproductive anatomy of the grape-vine (Vitis vinifera L.): origin and development of the anlage and its derivatives. Ann Bot 40, 1079-1084.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
Srinivasan C, Mullins MG (1978). Control of flowering in the grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.): formation of inflorescences in vitro by isolated tendrils. Plant Physiol 61, 127-130.
DOI PMID |
| [58] |
Sung SK, Yu GH, An G (1999). Characterization of MdMADS2, a member of the SQUAMOSA subfamily of genes, in apple. Plant Physiol 120, 969-978.
DOI PMID |
| [59] |
Tadege M, Lin H, Bedair M, Berbel A, Wen JQ, Rojas CM, Niu LF, Tang YH, Sumner L, Ratet P, McHale NA, Madueño F, Mysore KS (2011). STENOFOLIA regulates blade outgrowth and leaf vascular patterning in Medicago truncatula and Nicotiana sylvestris. Plant Cell 23, 2125-2142.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
Tian L, Chen ZJ (2001). Blocking histone deacetylation in Arabidopsis induces pleiotropic effects on plant gene regulation and development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98, 200-205.
DOI PMID |
| [61] |
Turner BM (1991). Histone acetylation and control of gene expression. J Cell Sci 99, 13-20.
DOI URL |
| [62] | Vaughn KC, Bowling AJ (2010). Biology and physiology of vines. In: Janick J, ed. Horticultural Reviews. NJ: John Wiley & Sons Inc. pp. 1-21. |
| [63] |
Viola IL, Reinheimer R, Ripoll R, Manassero NGU, Gonzalez DH (2012). Determinants of the DNA binding specificity of class I and class II TCP transcription factors. J Biol Chem 287, 347-356.
DOI PMID |
| [64] |
Waites R, Hudson A (1995). Phantastica: a gene required for dorsoventrality of leaves in Antirrhinum majus. Development 121, 2143-2154.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
Walton EF, Podivinsky E, Wu RM (2001). Bimodal patterns of floral gene expression over the two seasons that kiwifruit flowers develop. Physiol Plant 111, 396-404.
PMID |
| [66] |
Wang SH, Yang XY, Xu MN, Lin XZ, Lin T, Qi JJ, Shao GJ, Tian NN, Yang Q, Zhang ZH, Huang SW (2015). A rare SNP identified a TCP transcription factor essential for tendril development in cucumber. Mol Plant 8, 1795-1808.
DOI PMID |
| [67] |
Wang SW, Yang AY, Wang HS, Xu YM (2021). Identification and expression analysis of miR156/157-SPL pathway genes in cucumber. Acta Hortic Sin 48, 2227-2238. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
汪淑雯, 杨爱怡, 王华森, 徐云敏 (2021). 黄瓜miR156/ 157-SPL途径基因鉴定和表达分析. 园艺学报 48, 2227-2238.
DOI |
|
| [68] |
Weigel D, Alvarez J, Smyth DR, Yanofsky MF, Meyerowitz EM (1992). LEAFY controls floral meristem identity in Arabidopsis. Cell 69, 843-859.
DOI PMID |
| [69] |
Weiler EW, Albrecht T, Groth B, Xia ZQ, Luxem M, Liß H, Andert L, Spengler P (1993). Evidence for the involvement of jasmonates and their octadecanoid precursors in the tendril coiling response of Bryonia dioica. Phytochemistry 32, 591-600.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
Yan CH, Li GR, Hu YS, Zhou RJ, Hu HL, Miao WD, Zhu ZG (2017). Cloning and expression analysis of CIPK genes in grapevine. Acta Hortic Sin 44, 1463-1476. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
闫朝辉, 李桂荣, 扈岩松, 周瑞金, 扈惠灵, 苗卫东, 朱自果 (2017). 欧洲葡萄中CIPK基因的克隆及表达分析. 园艺学报 44, 1463-1476.
DOI |
|
| [71] |
Yang XY, Yan JB, Zhang Z, Lin T, Xin TX, Wang BW, Wang SH, Zhao JC, Zhang ZH, Lucas WJ, Li GH, Huang SW (2020). Regulation of plant architecture by a new histone acetyltransferase targeting gene bodies. Nat Plants 6, 809-822.
DOI PMID |
| [72] |
Yi LC, Zhou W, Zhou QL, Chen ZB, Zhang Y, Dai ZY, Wang YQ (2023). Fine mapping identifies ClTFL1 encodes a TERMINAL FLOWER 1 protein as putative candidate gene for inflorescence architecture and tendril development and in watermelon. J Plant Growth Regul 42, 4150-4160.
DOI |
| [73] | Yuan Y, Enhebayaer, Qi YH (2023). Research advances in biological functions of GH3 gene family in plants. Chin Bull Bot 58, 770-782. (in Chinese) |
|
园园, 恩和巴雅尔, 齐艳华 (2023). 植物GH3基因家族生物学功能研究进展. 植物学报 58, 770-782.
DOI |
|
| [74] | Zeng K, Wang SW, Zhou BY, Wang HS, Xu YM (2020). Research progress on tendril formation in Cucurbitaceae horticultural crops. J Zhejiang A F Univ 37, 1216-1223. (in Chinese) |
| 曾康, 汪淑雯, 周冰莹, 王华森, 徐云敏 (2020). 葫芦科园艺作物卷须发生的研究进展. 浙江农林大学学报 37, 1216-1223. | |
| [75] | Zhang SY, Qi Q, Li XH, Gai Y, Jiang XN (2017). Simultaneous determination of jasmonic acid and 12-oxo-phytodienoic acid in different plant materials by HPLC-MS/ MS. Chin Bull Bot 52, 631-636. (in Chinese) |
|
张双玉, 齐芪, 李晓慧, 盖颖, 蒋湘宁 (2017). 茉莉酸及其前体12-氧-植物二烯酸的HPLC-MS/MS检测方法. 植物学报 52, 631-636.
DOI |
|
| [76] | Zhang Y, Zhang YC, Li B, Tan X, Zhu CP, Wu T, Feng SY, Yang QH, Shen SQ, Yu T, Liu Z, Song XM (2022). Polyploidy events shaped the expansion of transcription factors in Cucurbitaceae and exploitation of genes for tendril development. Hortic Plant J 8, 562-574. |
| [77] | Zhang YP, Mu Q, Li XP, Wang C, Song CN, Fang JG (2013). Advances of studies on grape tendrils. Plant Phys J 49, 234-240. (in Chinese) |
| 张彦苹, 慕茜, 李晓鹏, 王晨, 宋长年, 房经贵 (2013). 葡萄卷须及其相关研究. 植物生理学报 49, 234-240. | |
| [78] | Zhuang D, Ding F, Wu J, Gan DF (2014). Expression of CsaIAAs gene in cucumber induced by 6-BA treatment. J Anhui Agric Univ 41, 260-264. (in Chinese) |
| 庄丹, 丁飞, 吴娇, 甘德芳 (2014). 6-BA诱导黄瓜CsaIAAs基因的表达研究. 安徽农业大学学报 41, 260-264. | |
| [79] |
Zhuang LL, Ambrose M, Rameau C, Weng L, Yang J, Hu XH, Luo D, Li X (2012). LATHYROIDES, encoding a WUSCHEL-related homeobox1 transcription factor, controls organ lateral growth, and regulates tendril and dorsal petal identities in garden pea (Pisum sativum L.). Mol Plant 5, 1333-1345.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 林淼. 玉米雄穗分枝数的激素“密码”[J]. 植物学报, 2026, 61(1): 1-0. |
| [2] | 赵洁, 李静, 李雨欣, 黄奕, 杨杰, 李霞. 活性氧在植物种子休眠释放和萌发中的作用研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(6): 978-992. |
| [3] | 刘旭鹏, 王敏, 韩守安, 朱学慧, 王艳蒙, 潘明启, 张雯. 植物器官脱落调控因素及分子机理研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 472-482. |
| [4] | 罗燕, 刘奇源, 吕元兵, 吴越, 田耀宇, 安田, 李振华. 拟南芥光敏色素突变体种子萌发的光温敏感性[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 752-762. |
| [5] | 陈婷欣, 符敏, 李娜, 杨蕾蕾, 李凌飞, 钟春梅. 铁甲秋海棠DNA甲基转移酶全基因组鉴定及表达分析(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 726-737. |
| [6] | 何璐梅, 马伯军, 陈析丰. 植物执行者抗病基因研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 671-680. |
| [7] | 车佳航, 李纬楠, 秦英之, 陈金焕. 木本植物叶色变异机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 319-328. |
| [8] | 杨智, 杨永. 重要林木樟科植物全基因组测序研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 302-318. |
| [9] | 张悦婧, 桑鹤天, 王涵琦, 石珍珍, 李丽, 王馨, 孙坤, 张继, 冯汉青. 植物对非生物胁迫系统性反应中信号传递的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 122-133. |
| [10] | 黄慧梅, 高永康, 台玉莹, 刘超, 曲德杰, 汤锐恒, 王幼宁. 硝酸盐转运蛋白NRT2在植物中的功能及分子机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 783-798. |
| [11] | 戴琛, 汪瑾, 卢亚萍. 衍生化UPLC-MS法测定酸性植物激素[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(4): 500-507. |
| [12] | 李月, 胡德升, 谭金芳, 梅浩, 王祎, 李慧, 李芳, 韩燕来. 单列毛壳菌通过促进秸秆降解并调控激素响应基因表达促进玉米生长[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(4): 422-433. |
| [13] | 王璐瑶, 陈謇, 赵守清, 闫慧莉, 许文秀, 刘若溪, 麻密, 虞轶俊, 何振艳. 水稻镉积累特性的生理和分子机制研究概述[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(2): 236-249. |
| [14] | 孟彦彦, 张楠, 熊延. 植物TOR激酶响应上游信号的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 1-11. |
| [15] | 赵晓亭, 毛凯涛, 徐佳慧, 郑钏, 罗晓峰, 舒凯. 蛋白质磷酸化修饰与种子休眠及萌发调控[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(4): 488-499. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
