

植物学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (5): 693-703.DOI: 10.11983/CBB25131 cstr: 32102.14.CBB25131
收稿日期:2025-07-23
接受日期:2025-09-02
出版日期:2025-09-10
发布日期:2025-09-02
通讯作者:
*万里, 中国科学院分子植物科学卓越创新中心研究员, 博士生导师, 入选国家青年千人计划, 获得上海市植物病理学会杰出青年科学家奖。万里课题组专注于植物免疫机制研究和广谱抗性农作物创制, 在植物细胞内免疫受体NLR工作的分子机理方面取得重要进展。相关成果以第一作者(含共同)发表在Science (2014, 2019), 以通讯作者(含共同)发表在Nature、Science、Proc Natl Acad Sci USA、Nature Plants、Science Advances和J Integr Plant Biol等学术期刊。E-mail: lwan@cemps.ac.cn
作者简介:†共同第一作者
基金资助:
Xiao Yinyan,†, Yu Hua,†, Wan Li*( )
)
Received:2025-07-23
Accepted:2025-09-02
Online:2025-09-10
Published:2025-09-02
Contact:
*E-mail: lwan@cemps.ac.cn
About author:†These authors contributed equally to this paper
摘要: 作为抵御病原入侵的核心防线, 植物天然免疫系统的受体识别与信号转导机制已建立较为完善的框架。该文对国内近期植物免疫领域取得的5项关键突破进行了阐述。(1) 发现了真菌染色体非均等分配及卵菌染色体融合驱动毒力进化的新规律; (2) 阐明了豆科植物中激酶MtLICK1/2通过磷酸化修饰MtLYK3精确调控“共生-免疫”转换的分子开关机制; (3) 明确了禾本科作物中串联激酶与NLR免疫受体以“sensor-executor”配对模式协同激活免疫的新范式; (4) 创新性提出“感受型与辅助型NLR共转移”策略以克服物种限制; (5) 开发出基于病原蛋白酶切割的自激活NLR嵌合体工程化改造技术, 赋予了植物广谱抗性。上述研究成果从病原适应性进化、宿主免疫精细调控及受体工程应用3个维度, 深化了对植物-病原-环境互作复杂网络的理解, 成功将基础机制认知转化为作物抗病遗传改良实践, 为设计培育具有持久、广谱抗性的作物新品种提供了坚实的理论基础与可操作的技术路径。
肖银燕, 于华, 万里. 植物免疫研究: 机制突破和应用创新. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 693-703.
Xiao Yinyan, Yu Hua, Wan Li. Plant Immunity Study: Mechanism Breakthroughs and Application Innovations. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(5): 693-703.
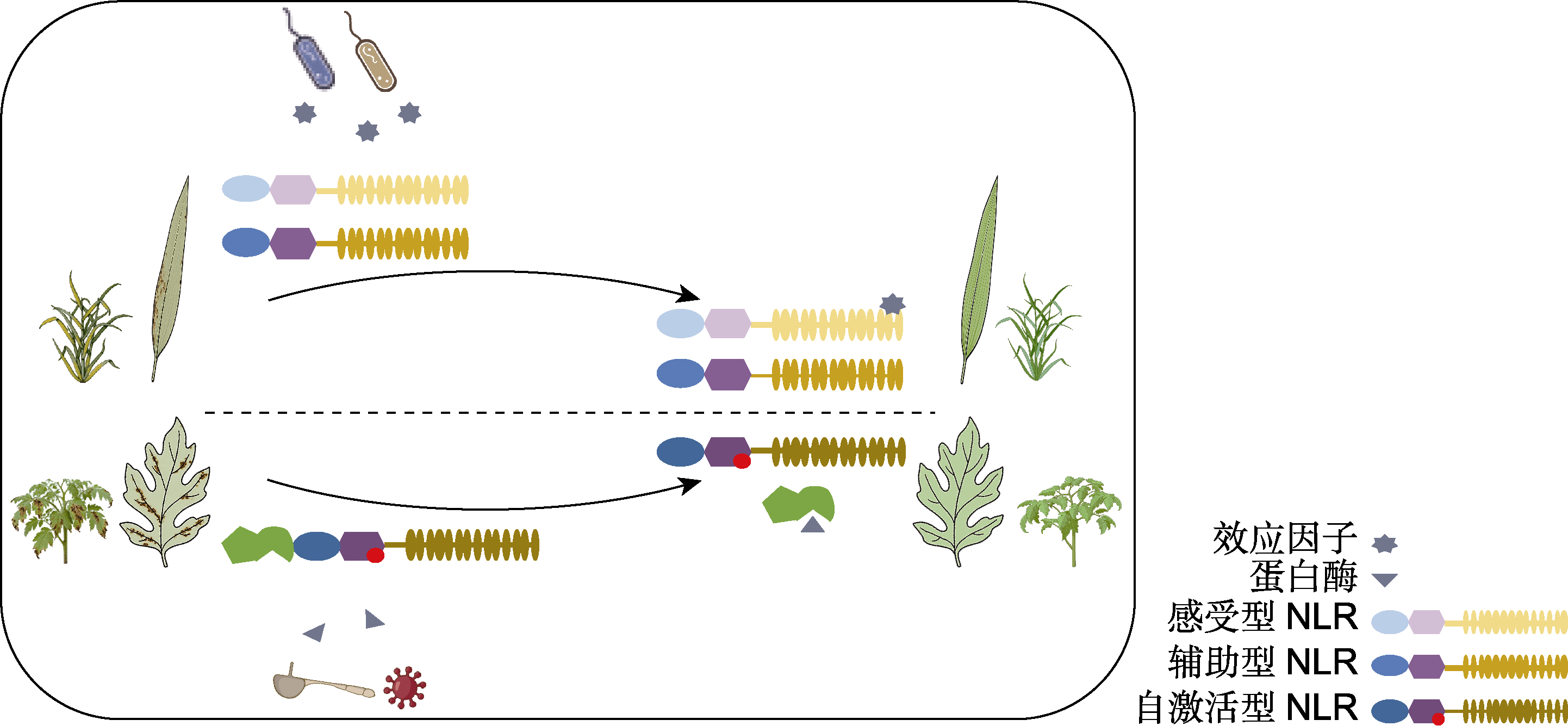
图1 NLR免疫受体改造拓宽植物的抗病性 共转移感受型和辅助型NLR, 实现NLR在被子植物中跨物种调控抗病性(上半部分); 人工设计的自激活NLR被病原菌蛋白酶切割后释放活性, 赋予植物广谱抗病能力(下半部分)。
Figure 1 Engineering NLR immune receptors to broaden plant disease resistance Co-expression of sensor and helper NLRs enables cross-species regulation of disease resistance in angiosperms (upper panel); An artificially designed autoactive NLR, when cleaved by pathogen proteases, releases its activity to confer broad- spectrum disease resistance in plants (lower panel).
| [1] |
Arora S, Steed A, Goddard R, Gaurav K, O’Hara T, Schoen A, Rawat N, Elkot AF, Korolev AV, Chinoy C, Nicholson MH, Asuke S, Antoniou-Kourounioti R, Steuernagel B, Yu GT, Awal R, Forner-Martínez M, Wingen L, Baggs E, Clarke J, Saunders DGO, Krasileva KV, Tosa Y, Jones JDG, Tiwari VK, Wulff BBH, Nicholson P (2023). A wheat kinase and immune receptor form host-specificity barriers against the blast fungus. Nat Plants 9, 385-392.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | Arrighi JF, Barre A, Ben Amor B, Bersoult A, Soriano LC, Mirabella R, de Carvalho-Niebel F, Journet EP, Ghérardi M, Huguet T, Geurts R, Dénarié J, Rougé P, Gough C (2006). The Medicago truncatula lysine motif-receptor-like kinase gene family includes NFP and new nodule-expressed genes. Plant Physiol 142, 265-279. |
| [3] | Cesari S, Bernoux M, Moncuquet P, Kroj T, Dodds PN (2014). A novel conserved mechanism for plant NLR protein pairs: the “integrated decoy” hypothesis. Front Plant Sci 5, 606. |
| [4] | Chen RJ, Chen J, Powell OR, Outram MA, Arndell T, Gajendiran K, Wang YL, Lubega J, Xu Y, Ayliffe MA, Blundell C, Figueroa M, Sperschneider J, Vanhercke T, Kanyuka K, Tang DZ, Zhong GT, Gardener C, Yu GT, Gourdoupis S, Jaremko Ł, Matny O, Steffenson BJ, Boshoff WHP, Meyer WB, Arold ST, Dodds PN, Wulff BBH (2025). A wheat tandem kinase activates an NLR to trigger immunity. Science 387, 1402-1408. |
| [5] | Chen SS, Rouse MN, Zhang WJ, Zhang XQ, Guo Y, Briggs J, Dubcovsky J (2020). Wheat gene Sr60 encodes a protein with two putative kinase domains that confers resistance to stem rust. New Phytol 225, 948-959. |
| [6] |
Dean R, Van Kan JAL, Pretorius ZA, Hammond-Kosack KE, Di Pietro A, Spanu PD, Rudd JJ, Dickman M, Kahmann R, Ellis J, Foster GD (2012). The Top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology. Mol Plant Pathol 13, 414-430.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
DeYoung BJ, Qi D, Kim SH, Burke TP, Innes RW (2012). Activation of a plant nucleotide binding-leucine rich repeat disease resistance protein by a modified self protein. Cell Microbiol 14, 1071-1084.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | Du XF, Alam M, Witek K, Milnes L, Houghton J, Lin X, Ahn HK, Zhang Y, Cui FH, Sun WX, Jones JDG, Guo HL (2025). Interfamily co-transfer of sensor and helper NLRs extends immune receptor functionality between angiosperms. Cell 188, 4505-4516. |
| [9] | Ekins MG (1999). Genetic Diversity in Sclerotinia Species. PhD dissertation. St. Lucia: The University of Queensland. pp. 24-25. |
| [10] | Förderer A, Li ET, Lawson AW, Deng YN, Sun Y, Logemann E, Zhang XX, Wen J, Han ZF, Chang JB, Chen YH, Schulze-Lefert P, Chai JJ (2022). A wheat resistosome defines common principles of immune receptor channels. Nature 610, 532-539. |
| [11] | Gaurav K, Arora S, Silva P, Sánchez-Martín J, Horsnell R, Gao L, Brar GS, Widrig V, John Raupp W, Singh N, Wu S, Kale SM, Chinoy C, Nicholson P, Quiroz-Chávez J, Simmonds J, Hayta S, Smedley MA, Harwood W, Pearce S, Gilbert D, Kangara N, Gardener C, Forner- Martínez M, Liu J, Yu G, Boden SA, Pascucci A, Ghosh S, Hafeez AN, O’Hara T, Waites J, Cheema J, Steuernagel B, Patpour M, Justesen AF, Liu S, Rudd JC, Avni R, Sharon A, Steiner B, Kirana RP, Buerstmayr H, Mehrabi AA, Nasyrova FY, Chayut N, Matny O, Steffenson BJ, Sandhu N, Chhuneja P, Lagudah E, Elkot AF, Tyrrell S, Bian X, Davey RP, Simonsen M, Schauser L, Tiwari VK, Randy Kutcher H, Hucl P, Li A, Liu DC, Mao L, Xu S, Brown-Guedira G, Faris J, Dvorak J, Luo MC, Krasileva K, Lux T, Artmeier S, Mayer KFX, Uauy C, Mascher M, Bentley AR, Keller B, Poland J, Wulff BBH (2022). Population genomic analysis of Aegilops tauschii identifies targets for bread wheat improvement. Nat Biotechnol 40, 422-431. |
| [12] | Gong YH, Tian L, Kontos I, Li J, Li X (2023). Plant immune signaling network mediated by helper NLRs. Curr Opin Plant Biol 73, 102354. |
| [13] | Haney CH, Riely BK, Tricoli DM, Cook DR, Ehrhardt DW, Long SR (2011). Symbiotic rhizobia bacteria trigger a change in localization and dynamics of the Medicago truncatula receptor kinase LYK3. Plant Cell 23, 2774-2787. |
| [14] |
Inoue Y, Vy TTP, Yoshida K, Asano H, Mitsuoka C, Asuke S, Anh VL, Cumagun CJR, Chuma I, Terauchi R, Kato K, Mitchell T, Valent B, Farman M, Tosa Y (2017). Evolution of the wheat blast fungus through functional losses in a host specificity determinant. Science 357, 80-83.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | Jian YN, Gong DM, Wang Z, Liu LJ, He JJ, Han XW, Tsuda K (2023). How plants manage pathogen infection. EMBO Rep 25, 31-44. |
| [16] | Jones JDG, Vance RE, Dangl JL (2016). Intracellular innate immune surveillance devices in plants and animals. Science 354, aaf6395. |
| [17] |
Kamoun S, Furzer O, Jones JDG, Judelson HS, Ali GS, Dalio RJD, Roy SG, Schena L, Zambounis A, Panabières F, Cahill D, Ruocco M, Figueiredo A, Chen XR, Hulvey J, Stam R, Lamour K, Gijzen M, Tyler BM, Grünwald NJ, Mukhtar MS, Tomé DFA, Tör M, Van Den Ackerveken G, McDowell J, Daayf F, Fry WE, Lindqvist-Kreuze H, Meijer HJG, Petre B, Ristaino J, Yoshida K, Birch PRJ, Govers F (2015). The Top 10 oomycete pathogens in molecular plant pathology. Mol Plant Pathol 16, 413-434.
DOI PMID |
| [18] | Klymiuk V, Yaniv E, Huang L, Raats D, Fatiukha A, Chen SS, Feng LH, Frenkel Z, Krugman T, Lidzbarsky G, Chang W, Jääskeläinen MJ, Schudoma C, Paulin L, Laine P, Bariana H, Sela H, Saleem K, Sørensen CK, Hovmøller MS, Distelfeld A, Chalhoub B, Dubcovsky J, Korol AB, Schulman AH, Fahima T (2018). Cloning of the wheat Yr15 resistance gene sheds light on the plant tandem kinase-pseudokinase family. Nat Commun 9, 3735. |
| [19] |
Kourelis J, Marchal C, Posbeyikian A, Harant A, Kamoun S (2023). NLR immune receptor—nanobody fusions confer plant disease resistance. Science 379, 934-939.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Lacombe S, Rougon-Cardoso A, Sherwood E, Peeters N, Dahlbeck D, van Esse HP, Smoker M, Rallapalli G, Thomma BPHJ, Staskawicz B, Jones JDG, Zipfel C (2010). Interfamily transfer of a plant pattern-recognition receptor confers broad-spectrum bacterial resistance. Nat Biotechnol 28, 365-369.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | Li MM, Zhang HZ, Xiao HX, Zhu KY, Shi WQ, Zhang D, Wang Y, Yang LJ, Wu QH, Xie JZ, Chen YX, Qiu D, Guo GH, Lu P, Li BB, Dong L, Li WL, Cui XJ, Li LC, Tian XB, Yuan CG, Li YW, Yu DZ, Nevo E, Fahima T, Li HJ, Dong LL, Zhao YS, Liu ZY (2024). A membrane associated tandem kinase from wild emmer wheat confers broad- spectrum resistance to powdery mildew. Nat Commun 15, 3124. |
| [22] | Li S, Wang YP, Wang SZ, Fang AF, Wang JY, Liu LJ, Zhang K, Mao YL, Sun WX (2015). The type III effector AvrBs2 in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola suppresses rice immunity and promotes disease development. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 28, 869-880. |
| [23] |
Liang Y, Cao YR, Tanaka K, Thibivilliers S, Wan JR, Choi J, Kang CH, Qiu J, Stacey G (2013). Nonlegumes respond to rhizobial Nod factors by suppressing the innate immune response. Science 341, 1384-1387.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
Limpens E, Franken C, Smit P, Willemse J, Bisseling T, Geurts R (2003). LysM domain receptor kinases regulating rhizobial Nod factor-induced infection. Science 302, 630-633.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Lin X, Song TQ, Fairhead S, Witek K, Jouet A, Jupe F, Witek AI, Karki HS, Vleeshouwers VGAA, Hein I, Jones JDG (2020). Identification of Avramr1 from Phytophthora infestans using long read and cDNA pathogen-enrichment sequencing (PenSeq). Mol Plant Pathol 21, 1502-1512. |
| [26] | Liu XX, Wan L (2022). Molecular insights into the biochemical functions and signaling mechanisms of plant NLRs. Mol Plant Pathol 23, 772-780. |
| [27] | Liu Y, Zhang X, Yuan GX, Wang DL, Zheng YY, Ma MQ, Guo LW, Bhadauria V, Peng YL, Liu JF (2021). A designer rice NLR immune receptor confers resistance to the rice blast fungus carrying noncorresponding avirulence effectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 118, e2110751118. |
| [28] |
Lu P, Guo L, Wang ZZ, Li BB, Li J, Li YH, Qiu D, Shi WQ, Yang LJ, Wang N, Guo GH, Xie JZ, Wu QH, Chen YX, Li MM, Zhang HZ, Dong LL, Zhang PP, Zhu KY, Yu DZ, Zhang Y, Deal KR, Huo NX, Liu CM, Luo MC, Dvorak J, Gu YQ, Li HJ, Liu ZY (2020). A rare gain of function mutation in a wheat tandem kinase confers resistance to powdery mildew. Nat Commun 11, 680.
DOI PMID |
| [29] | Lu P, Zhang G, Li J, Gong Z, Wang G, Dong L, Zhang H, G- uo G, Su M, Wang K, Wang Y, Zhu K, Wu Q, Chen Y, Li M, Huang B, Li B, Li W, Dong L, Hou Y, Cui X, Fu H, Qiu D, Yuan C, Li H, Zhou JM, Han GZ, Chen Y, Liu Z (2025). A wheat tandem kinase and NLR pair confers resistance to multiple fungal pathogens. Science 387, 1418-1424. |
| [30] | Madsen EB, Madsen LH, Radutoiu S, Olbryt M, Rakwalska M, Szczyglowski K, Sato S, Kaneko T, Tabata S, Sandal N, Stougaard J (2003). A receptor kinase gene of the LysM type is involved in legumeperception of rhizobial signals. Nature 425, 637-640. |
| [31] | Martin FM, Uroz S, Barker DG (2017). Ancestral alliances: plant mutualistic symbioses with fungi and bacteria. Science 356, eaad4501. |
| [32] | Medina CA, Reyes PA, Trujillo CA, Gonzalez JL, Bejarano DA, Montenegro NA, Jacobs JM, Joe A, Restrepo S, Alfano JR, Bernal A (2018). The role of type III effectors from Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis in virulence and suppression of plant immunity. Mol Plant Pathol 19, 593-606. |
| [33] | Moling S, Pietraszewska-Bogiel A, Postma M, Fedorova E, Hink MA, Limpens E, Gadella TWJ, Bisseling T (2014). Nod factor receptors form heteromeric complexes and are essential for intracellular infection in Medicago nodules. Plant Cell 26, 4188-4199. |
| [34] | Mukhi N, Brown H, Gorenkin D, Ding PT, Bentham AR, Stevenson CEM, Jones JDG, Banfield MJ (2021). Perception of structurally distinct effectors by the integrated WR- KY domain of a plant immune receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 118, e2113996118. |
| [35] | Narusaka M, Hatakeyama K, Shirasu K, Narusaka Y (2014). Arabidopsis dual resistance proteins, both RPS4 and RRS1, are required for resistance to bacterial wilt in transgenic Brassica crops. Plant Signal Behav 9, e29130. |
| [36] | Ngou BPM, Ahn HK, Ding PT, Jones JDG (2021). Mutual potentiation of plant immunity by cell-surface and intracellular receptors. Nature 592, 110-115. |
| [37] | Oh S, Kim MS, Kang HJ, Kim T, Kong J, Choi D (2024). Conserved effector families render Phytophthora species vulnerable to recognition by NLR receptors in nonhost plants. Nat Commun 15, 10070. |
| [38] |
Oldroyd GED (2013). Speak, friend, and enter: signaling systems that promote beneficial symbiotic associations in plants. Nat Rev Microbiol 11, 252-263.
DOI PMID |
| [39] |
Ortiz D, Chen J, Outram MA, Saur IML, Upadhyaya NM, Mago R, Ericsson DJ, Cesari S, Chen CH, Williams SJ, Dodds PN (2022). The stem rust effector protein AvrSr50 escapes Sr50 recognition by a substitution in a single surface-exposed residue. New Phytol 234, 592-606.
DOI PMID |
| [40] |
Poole P, Ramachandran V, Terpolilli J (2018). Rhizobia: from saprophytes to endosymbionts. Nat Rev Microbiol 16, 291-303.
DOI PMID |
| [41] | Radutoiu S, Madsen LH, Madsen EB, Jurkiewicz A, Fukai E, Quistgaard EMH, Albrektsen AS, James EK, Thirup S, Stougaard J (2007). LysM domains mediate lipochitin- oligosaccharide recognition and Nfr genes extend the symbiotic host range. EMBO J 26, 3923-3935. |
| [42] | Schoonbeek HJ, Wang HH, Stefanato FL, Craze M, Bowden S, Wallington E, Zipfel C, Ridout CJ (2015). Arabidopsis EF-Tu receptor enhances bacterial disease resistance in transgenic wheat. New Phytol 206, 606-613. |
| [43] | Schwessinger B, Bahar O, Thomas N, Holton N, Nekrasov V, Ruan DL, Canlas PE, Daudi A, Petzold CJ, Sin- gan VR, Kuo R, Chovatia M, Daum C, Heazlewood JL, Zipfel C, Ronald PC (2015). Transgenic expression of the dicotyledonous pattern recognition receptor EFR in rice leads to ligand-dependent activation of defense responses. PLoS Pathog 11, e1004809. |
| [44] | Segretin ME, Pais M, Franceschetti M, Chaparro-Garcia A, Bos JIB, Banfield MJ, Kamoun S (2014). Single amino acid mutations in the potato immune receptor R3a expand response to Phytophthora effectors. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 27, 624-637. |
| [45] | Steinbrenner AD, Goritschnig S, Staskawicz BJ (2015). Recognition and activation domains contribute to allele- specific responses of an Arabidopsis NLR receptor to an oomycete effector protein. PLoS Pathog 11, e1004665. |
| [46] | Sun YD, Li L, Macho AP, Han ZF, Hu ZH, Zipfel C, Zhou JM, Chai JJ (2013). Structural basis for flg22-induced activation of the Arabidopsis FLS2-BAK1 immune complex. Science 342, 624-628. |
| [47] |
Tai TH, Dahlbeck D, Clark ET, Gajiwala P, Pasion R, Whalen MC, Stall RE, Staskawicz BJ (1999). Expression of the Bs2 pepper gene confers resistance to bacterial spot disease in tomato. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96, 14153-14158.
DOI PMID |
| [48] |
Tamborski J, Krasileva KV (2020). Evolution of plant NLRs: from natural history to precise modifications. Annu Rev Plant Biol 71, 355-378.
DOI PMID |
| [49] | Tamborski J, Seong K, Liu FR, Staskawicz BJ, Krasileva KV (2023). Altering specificity and autoactivity of plant immune receptors Sr33 and Sr50 via a rational engineering approach. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 36, 434-446. |
| [50] |
van Velzen R, Doyle JJ, Geurts R (2019). A resurrected scenario: single gain and massive loss of nitrogen-fixing nodulation. Trends Plant Sci 24, 49-57.
DOI PMID |
| [51] | Wang DP, Jin R, Shi XB, Guo HR, Tan XH, Zhao AC, Lian XH, Dai HL, Li SZ, Xin KX, Tian CF, Yang J, Chen WS, Macho AP, Wang ET (2025a). A kinase mediator of rhizobial symbiosis and immunity in Medicago. Nature 643, 768-775. |
| [52] |
Wang GX, Roux B, Feng F, Guy E, Li L, Li NN, Zhang XJ, Lautier M, Jardinaud MF, Chabannes M, Arlat M, Chen S, He CZ, Noël LD, Zhou JM (2015). The decoy substrate of a pathogen effector and a pseudokinase specify pathogen-induced modified-self recognition and immunity in plants. Cell Host Microbe 18, 285-295.
DOI PMID |
| [53] | Wang JZ, Chen TY, Zhang ZD, Song MJ, Shen TX, Wang X, Zheng XY, Wang Y, Song K, Ge XY, Xu K, Qi TC, Li FG, Hong YG, Liu YL (2025b). Remodelling autoactive NLRs for broad-spectrum immunity in plants. Nature doi: 10.1038/ s41586-025-09252-z. |
| [54] | Wang JZ, Hu MJ, Wang J, Qi JF, Han ZF, Wang GX, Qi YJ, Wang HW, Zhou JM, Chai JJ (2019a). Reconstitution and structure of a plant NLR resistosome conferring immunity. Science 364, eaav5870. |
| [55] | Wang JZ, Wang J, Hu MJ, Wu S, Qi JF, Wang GX, Han ZF, Qi YJ, Gao N, Wang HW, Zhou JM, Chai JJ (2019b). Ligand-triggered allosteric ADP release primes a plant NLR complex. Science 364, eaav5868 |
| [56] | Wang YJ, Abrouk M, Gourdoupis S, Koo DH, Karafiátová M, Molnár I, Holušová K, Doležel J, Athiyannan N, Cavalet-Giorsa E, Jaremko Ł, Poland J, Krattinger SG (2023). An unusual tandem kinase fusion protein confers leaf rust resistance in wheat. Nat Genet 55, 914-920. |
| [57] | Wei YL, Balaceanu A, Rufian JS, Segonzac C, Zhao AC, Morcillo RJL, Macho AP (2020). An immune receptor complex evolved in soybean to perceive a polymorphic bacterial flagellin. Nat Commun 11, 3763. |
| [58] |
Wulff BBH, Thomas CM, Smoker M, Grant M, Jones JDG (2001). Domain swapping and gene shuffling identify sequences required for induction of an Avr-dependent hypersensitive response by the tomato Cf-4 and Cf-9 proteins. Plant Cell 13, 255-272.
DOI PMID |
| [59] | Xu Y, Tian L, Tan JY, Huang WJ, Li J, O'Neil N, Hirst M, Hieter P, Zhang YL, Li X (2025). Distribution of haploid chromosomes into separate nuclei in two pathogenic fungi. Science 388, 784-788. |
| [60] | Yu GT, Matny O, Champouret N, Steuernagel B, Moscou MJ, Hernández-Pinzón I, Green P, Hayta S, Smedley M, Harwood W, Kangara N, Yue YJ, Gardener C, Banfield MJ, Olivera PD, Welchin C, Simmons J, Millet E, Minz-Dub A, Ronen M, Avni R, Sharon A, Patpour M, Justesen AF, Jayakodi M, Himmelbach A, Stein N, Wu SY, Poland J, Ens J, Pozniak C, Karafiátová M, Molnár I, Doležel J, Ward ER, Reuber TL, Jones JDG, Mascher M, Steffenson BJ, Wulff BBH (2022). Aegilops sharonensis genome-assisted identification of stem rust resistance ge- ne Sr62. Nat Commun 13, 1607. |
| [61] | Yuan MH, Jiang ZY, Bi GZ, Nomura K, Liu MH, Wang YP, Cai BY, Zhou JM, He SY, Xin XF (2021). Pattern-recogni- |
| tion receptors are required for NLR-mediated plant immu- | |
| nity. Nature 592, 105-109. | |
| [62] | Zaccaron AZ, Stergiopoulos I (2025). The dynamics of fungal genome organization and its impact on host adaptation and antifungal resistance. J Genet Genomics 52, 628-640. |
| [63] |
Zhang ZC, Zhang XY, Tian Y, Wang LY, Cao JT, Feng H, Li KN, Wang Y, Dong SM, Ye WW, Wang YC (2024). Complete telomere-to-telomere genomes uncover virulence evolution conferred by chromosome fusion in oomycete plant pathogens. Nat Commun 15, 4624.
DOI PMID |
| [64] | Zhao BY, Dahlbeck D, Krasileva KV, Fong RW, Staskawicz BJ (2011). Computational and biochemical analysis of the Xanthomonas effector AvrBs2 and its role in the modulation of Xanthomonas type three effector delivery. PLoS Pathog 7, e1002408. |
| [65] |
Zhao BY, Lin XH, Poland J, Trick H, Leach J, Hulbert S (2005). A maize resistance gene functions against bacterial streak disease in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102, 15383-15388.
DOI PMID |
| [66] | Zhao Y, Dong ZJ, Miao JN, Liu QW, Ma C, Tian XB, He JQ, Bi HH, Yao W, Li T, Gill HS, Zhang ZB, Cao AZ, Liu B, Li HH, Sehgal SK, Liu WX (2024). Pm57 from Aegilops searsii encodes a tandem kinase protein and confers wheat powdery mildew resistance. Nat Commun 15, 4796. |
| [67] | Zhou JM, Zhang YL (2020). Plant immunity: danger perception and signaling. Cell 181, 978-989. |
| [68] | Zipfel C, Oldroyd GED (2017). Plant signaling in symbiosis and immunity. Nature 543, 328-336. |
| [1] | 徐羽丰, 周冕. 植物免疫的转录后调控[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 704-721. |
| [2] | 刘德水, 岳宁, 刘玉乐. 植物免疫机制新突破[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 669-678. |
| [3] | 王笑, 徐昌文, 钱虹萍, 李思博, 林金星, 崔亚宁. 植物细胞壁参与免疫反应的机制及其原位非标记成像方法[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 773-785. |
| [4] | 江亚楠, 徐雨青, 魏毅铤, 陈钧, 张容菀, 赵蓓蓓, 林宇翔, 饶玉春. 水稻抗病调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 734-748. |
| [5] | 覃磊, 彭志红, 夏石头. 植物NLR免疫受体的识别、免疫激活与信号调控[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 12-23. |
| [6] | 周俭民. 免疫信号轴揭示水稻与病原菌斗争的秘密[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(5): 513-515. |
| [7] | 王伟, 唐定中. 两类免疫受体强强联手筑牢植物免疫防线[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(2): 142-146. |
| [8] | 杨程惠子,唐先宇,李威,夏石头. NLR及其在植物抗病中的调控作用[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(4): 497-504. |
| [9] | 崔亚宁, 钱虹萍, 赵艳霞, 李晓娟. 模式识别受体的胞内转运及其在植物免疫中的作用[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(3): 329-339. |
| [10] | 李伟滔, 贺闽, 陈学伟. ZmFBL41 Chang7-2: 玉米抗纹枯病的关键利器[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(5): 547-549. |
| [11] | 夏石头, 李昕. 开启防御之门: 植物抗病小体[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(3): 288-292. |
| [12] | 闫佳, 刘雅琼, 侯岁稳. 植物抗病蛋白研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(2): 250-263. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||