

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2021, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (4): 443-450.DOI: 10.11983/CBB20195 cstr: 32102.14.CBB20195
• TECHNIQUES AND METHODS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yanmin Li, Hui Jiang, Zhenzhu Fu, Jing Zhang, Xin Yuan, Huijuan Wang, Jie Gao, Xiaoyu Dong, Limin Wang, Hechen Zhang*( )
)
Received:2020-12-01
Accepted:2021-05-27
Online:2021-07-01
Published:2021-06-30
Contact:
Hechen Zhang
Yanmin Li, Hui Jiang, Zhenzhu Fu, Jing Zhang, Xin Yuan, Huijuan Wang, Jie Gao, Xiaoyu Dong, Limin Wang, Hechen Zhang. Callus Induction and Somatic Embryogenesis in Anther Culture of Paeonia lactiflora[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(4): 443-450.
| Medium number | 2,4-D (mg·L-1) | NAA (mg·L-1) | KT (mg·L-1) | Callus induction rate (%) | Callus state |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 1 | 1 | 0.1 | 14.7±3.64 a | Light brown, loose |
| M2 | 1.5 | 1 | 0.1 | 16.7±2.33 a | Light brown, loose |
| M3 | 2 | 1 | 0.1 | 14. 8±3.70 a | Brown, loose |
Table 1 Effects of 2,4-D concentration on anther callus induction (means±SD)
| Medium number | 2,4-D (mg·L-1) | NAA (mg·L-1) | KT (mg·L-1) | Callus induction rate (%) | Callus state |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 1 | 1 | 0.1 | 14.7±3.64 a | Light brown, loose |
| M2 | 1.5 | 1 | 0.1 | 16.7±2.33 a | Light brown, loose |
| M3 | 2 | 1 | 0.1 | 14. 8±3.70 a | Brown, loose |
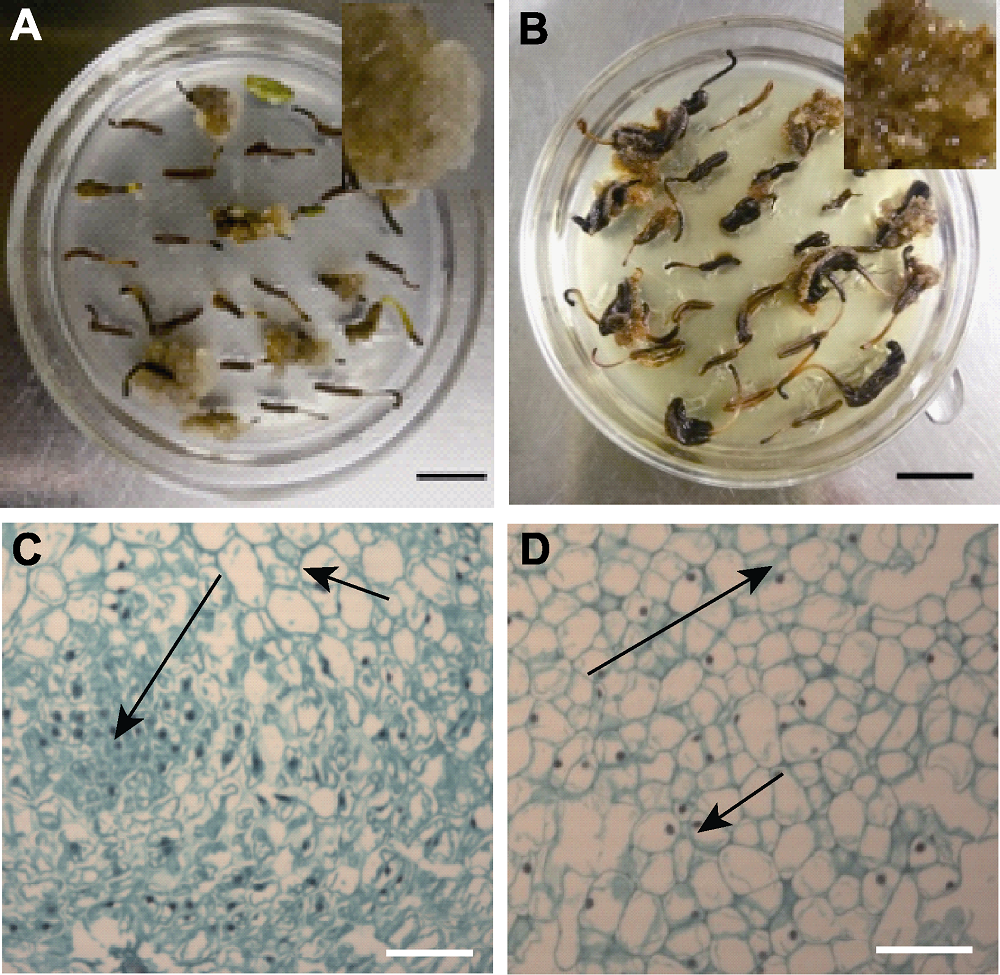
Figure 1 Types of Paeonia lactiflora anther callus (A) Light brown loose callus (type I); (B) Brown loose callus (type II); (C) The microstructure of type I; (D) The microstructure of type II. Short arrows refer to non-embryonic cells (type a) and long arrows refer to embryonic cells (type b); (A), (B) Bars=1 cm; (C), (D) Bars=100 μm
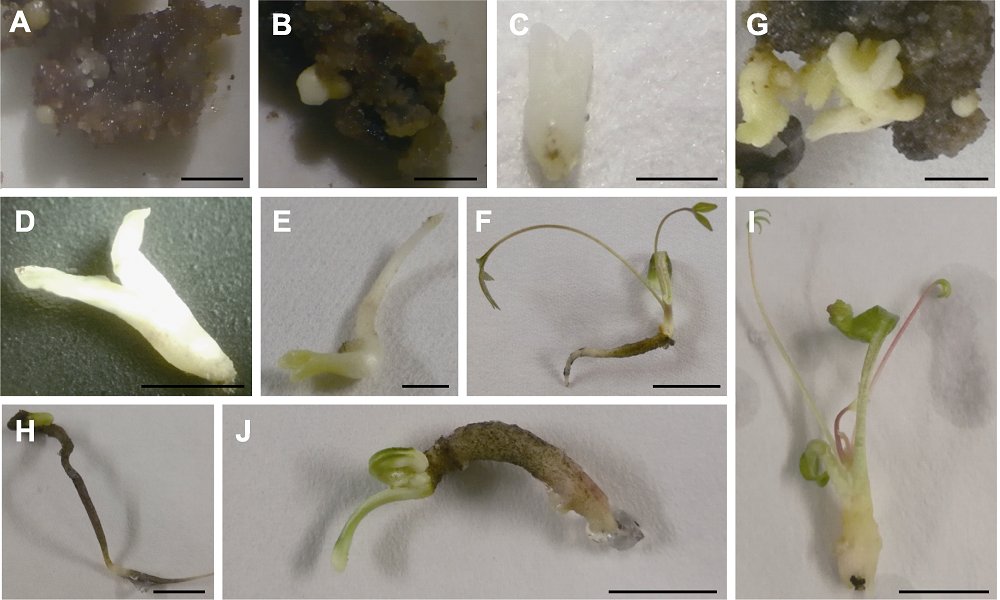

Figure 2 Anther somatic embryo development process of Paeonia lactiflora (A) Spherical embryo; (B) Heart-shaped embryo; (C) Torpedo embryo; (D) Cotyledon embryo; (E) Mature embryo; (F) Regenerating plants; (G) Somatic embryos with unsynchronized development; (H) Radicle elongation; (I) Germ germination; (J) Malformed cotyledon embryo; (A)-(D) Bars=2 mm; (E)-(J) Bars=1 cm
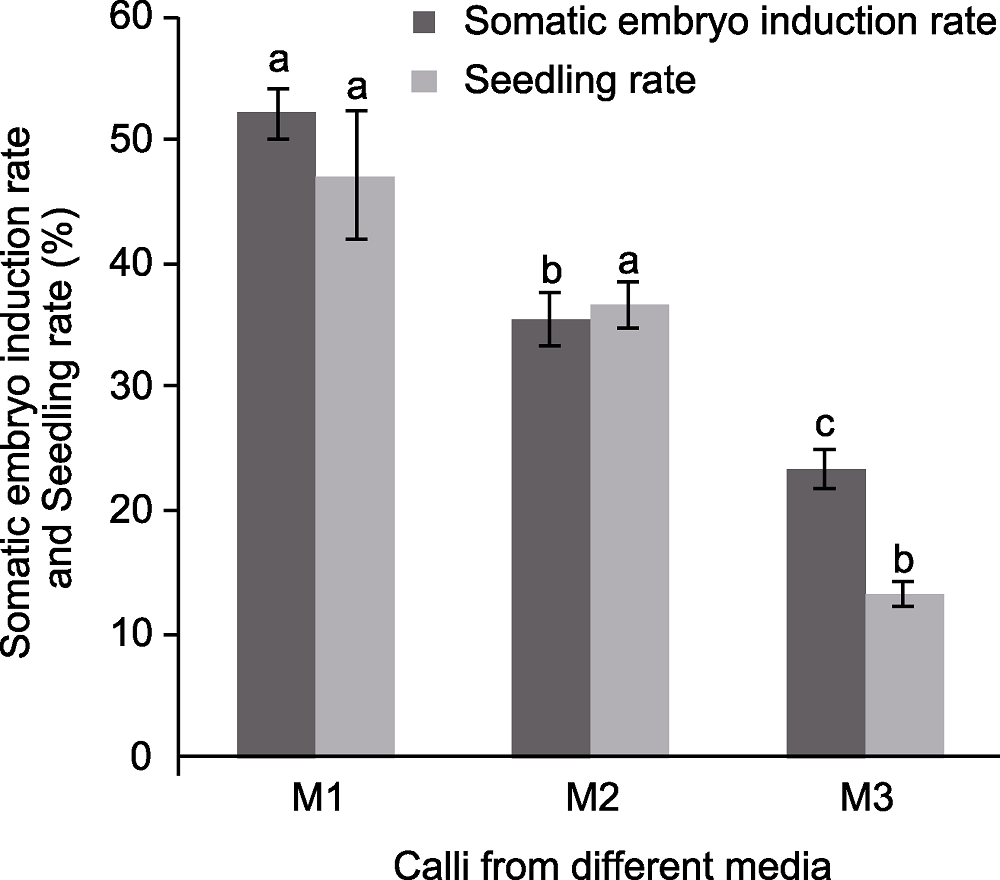
Figure 3 Somatic embryo induction rate and seedling rate of Paeonia lactiflora calli from different sources Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at P<0.05 level.
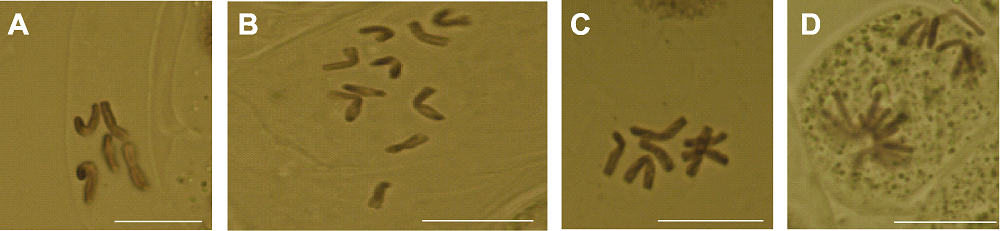
Figure 4 Chromosome observation of root tip cells from plant regeneration of Paeonia lactiflora (A) Haploid; (B) Diploid; (C) Aneuploid; (D) Asymmetric chromosome division. Bars=2 μm
| [1] | 卜华虎, 任志强, 王晓清, 肖建红 (2017). 植物单倍体育种研究进展. 山西农业科学 45, 2032-2037. |
| [2] | 陈怡平, 丁兰, 赵敏桂 (2001). 用紫斑牡丹不同外植体诱导愈伤组织的研究. 西北师范大学学报(自然科学版) 37(3), 66-69. |
| [3] | 成仿云, 陈德忠 (1998). 紫斑牡丹新品种选育及牡丹品种分类研究. 北京林业大学学报 20(2), 27-32. |
| [4] | 褚云霞, 陈龙清, 黄燕文, 张永春 (2001). 百合的花药培养研究. 园艺学报 32, 472-474. |
| [5] | 崔凯荣, 邢更生, 周功克, 刘新民, 王亚馥 (2000). 植物激素对体细胞胚胎发生的诱导与调节. 遗传 22, 349-354. |
| [6] | 冯大领, 李伟, 张洁, 李鹏涛, 李明, 赵书岗, 史宝胜, 彭伟秀 (2009). 黄山栾树体细胞胚的发生和组织学观察. 植物生理学通讯 45, 855-858. |
| [7] | 何业华, 方少秋, 马均, 胡中沂, 卢敏, 彭兵 (2010). 菠萝愈伤组织中体细胞胚起源过程的组织细胞学观察. 园艺学报 37, 689-696. |
| [8] | 金飚, 丁玲, 何小弟, 贾妮, 李娜, 向其柏 (2006). 芍药种子露地播种和低温贮藏过程中内源激素含量的变化. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) 30, 45-48. |
| [9] | 荆茹月, 霍坤, 李志辉 (2020). 香樟胚性与非胚性愈伤组织间的差异研究. 中南林业科技大学学报 40(10), 70-78. |
| [10] | 李懋学, 陈定慧 (1980). 栽培芍药染色体的Giemsa C-带及体细胞染色体联合的观察. 遗传学报 7, 271-275. |
| [11] | 李杉, 邢更妹, 崔凯荣, 王亚馥 (2001). 植物体细胞胚发生中ATP酶活性时空分布动态与内源激素的变化. 植物学通报 18, 308-317. |
| [12] | 李允菲, 孙宇涵, 李云 (2016). 植物单倍体育种及其在林木育种中的应用. 世界林业研究 26, 41-46. |
| [13] | 卢洁, 徐金光, 杲承荣, 窦霄, 于华冰, 姜楠南 (2017). 芍药切花优良品种筛选. 山东林业科技 47(3), 13-17. |
| [14] | 田丹青, 葛亚英, 潘晓韵, 金亮, 周媛, 朱强, 万晓 (2020). 红掌花药培养及单倍体植株的鉴定. 分子植物育种 18, 7149-7154. |
| [15] | 魏冬霞, 张滕, 郑严仪, 于晓南 (2018). 芍药愈伤组织中体细胞胚发育过程的组织细胞学观察. 植物研究 38, 56-63. |
| [16] | 文书生, 何绒绒, 郑佳康, 田如男 (2018). 牡丹组织培养技术研究进展. 林业科学 54(10), 143-155. |
| [17] | 吴健, 王鸿昌, 罗弦, 钟雄辉, 高明伟, 吴泽, 义鸣放 (2012). 唐菖蒲体细胞胚起源、发育的形态与组织细胞学观察. 园艺学报 39, 2413-2420. |
| [18] | 苑庆磊 (2011). 中国芍药花文化研究. 硕士论文. 北京: 北京林业大学. pp. 7-11. |
| [19] | 张建军, 陈莉祺, 李建光, 孙苗, 范永明, 于晓南 (2020). 芍药根茎解剖结构特征及生长轮分析. 北京林业大学学报 42(5), 124-134. |
| [20] | 张捷, 谢军, 孙辑凯, 沙伟 (2018). 芍药播种繁殖中种子破眠技术的研究进展. 分子植物育种 16, 4380-4386. |
| [21] |
张文婷, 何燕红, 舒宁, 邢景景, 刘宝骏, 包满珠, 刘国锋 (2019). 金黄花滇百合植株再生与离体快繁技术体系的建立. 植物学报 54, 773-778.
DOI |
| [22] | 郑相穆, 周阮宝, 谷丽萍, 茆敦俊, 周嘉槐 (1995). 凤丹种子的休眠和萌发特性. 植物生理学通讯 31, 260-262. |
| [23] | 周秀梅, 成仿云, 钟原, 齐力旺 (2009). 紫斑牡丹‘书生捧墨’的体胚诱导与发生. 北京林业大学学报 31, 151-154. |
| [24] | 朱向涛, 王雁, 彭镇华, 律春燕 (2010a). 牡丹花药诱导愈伤组织. 东北林业大学学报 38, 34-36. |
| [25] | 朱向涛, 王雁, 彭镇华, 律春燕, 郑宝强, 高云瑞 (2010b). 牡丹花蕾大小对花药组培诱导率的影响. 湖南农业科学 (11), 102-104. |
| [26] |
Buchheim JAT, Burkhart LF, Meyer MM Jr (1994). Effect of exogenous gibberellic acid, abscisic acid, and benzylaminopurine on epicotyl dormancy of cultured herbaceous peony embryos. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 36, 35-43.
DOI URL |
| [27] | Roberts M, Sunderland N (1977). Pollen culture in Paeonia. John Innes Annu Rep 68, 60-61. |
| [28] | Sunderland N, Dunwell JM, Robert M (1975). Anther culture in the genus Paeonia. John Innes Annu Rep 66, 57-60. |
| [29] |
von Arnold S, Sabala I, Bozhkov P, Dyachok J, Filonova L (2002). Developmental pathways of somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 69, 233-249.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Yang Y, Sun M, Li SS, Chen QH, da Silva JAT, Wang AJ, Yu XN, Wang LS (2020). Germplasm resources and genetic breeding of Paeonia: a systematic review. Hortic Res 7, 107.
DOI URL |
| [1] | Zheng Guo, Xiangjun Shao, Haiwen Lu, Dan Hou, Simeng Kong, Xiangyu Li, Huaqian Liu, Xinchun Lin. Efficient Induction and Identification of Polyploids in Dendrocalamus asper [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(2): 246-255. |
| [2] | Yuchen Li, Haixia Zhao, Xiping Jiang, Xintian Huang, Yaling Liu, Zhenying Wu, Yan Zhao, Chunxiang Fu. Establishment of Agrobacterium-mediated Transformation System for Agropyron mongolicum [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(4): 600-612. |
| [3] | Xuping Tian, Kangjie Yue, Jiali Wang, Huixin Liu, Ziyin Shi, Hongwei Kang. Callus Induction and Plant Regeneration of Dracocephalum rupestre [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(4): 613-625. |
| [4] | Hao Zeng, Peifang Li, Zhihui Guo, Chunlin Liu, Ying Ruan. Establishment of a Regeneration System for Lunaria annua [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(3): 433-440. |
| [5] | Shangwen Zhang, Shiyu Huang, Tianwei Yang, Ting Li, Xiangjun Zhang, Manrong Gao. Establishment of a Tissue Culture and Rapid Propagation System for Erythropalum scandens Based on Orthogonal Test [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(1): 99-109. |
| [6] | Yefei Liu, Haixia Zhao, Xiping Jiang, Rui Qiu, Xinyue Zhou, Yan Zhao, Chunxiang Fu. Establishment of Highly Efficient Tissue Culture and Agrobacterium-mediated Callus Infection Systems for Hordeum brevisubulatum [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(3): 440-448. |
| [7] | Jinchun Lu, Lina Cao, Guanjie Tong, Xinying Wang, Liying Zhang, Xin Yu, Huifang Li, Yanhui Li. Establishment of Callus Induction and Regeneration System of Anemone silvestris [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(2): 217-226. |
| [8] | Churan Li, Ling Fu, Yun Liu, Xiaoqin Yang, Guolei Zhu, Sida Xie, Huancheng Ma, Ping Zhao. Optimization of Cell Suspension Culture Conditions of Vaccinium dunalianum [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(2): 227-235. |
| [9] | Qian Luo, Yansha Zhang, Jing Ou. Callus Induction and Plant Regeneration of Cerasus serrulata var. lannesiana cv. ‘Grandiflora’ [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(4): 451-461. |
| [10] | Pengfei Du, Yu Wang, Yingping Cao, Song Yang, Zhichao Sun, Decai Mao, Jiajun Yan, Daxu Li, Meizhen Sun, Chunxiang Fu, Shiqie Bai. Establishment of Biolistic Mediated Transformation System for Elymus sibiricus [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(1): 62-70. |
| [11] | Dongrui Zhang, Zhigang Bu, Lingling Chen, Ying Chang. Establishment of a Tissue Culture and Rapid Propagation System of Dryopteris fragrans [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(6): 760-767. |
| [12] | Jianfei Liu, Yan Liu, Kejian Liu, Yang Chi, Zhifa Huo, Yonghong Huo, Xiangling You. Optimization of the Regeneration System from Somatic Embryogenesis in Larix olgensis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(5): 605-612. |
| [13] | Yan Xiao,Zhenxing Wang,Dongming Li,Yanhua Qi, Enhebayaer. Optimization of Tissue Culture and Plant Regeneration System of Mature Embryo of Leymus chinensis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(2): 192-198. |
| [14] | Ying Feng,Lianwen Qian,Qingliang Lin. The Effect of Different Hormones on Explant Browning and Callus Browning in Cyclocarya paliurus [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(5): 634-641. |
| [15] | Xiaomei Liu,Lili Sun,Xiangdong Fu,Hong Liao. An Effective Method for the Rooting of Tea Cuttings [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(4): 531-538. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||