

植物学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (2): 185-193.DOI: 10.11983/CBB19013 cstr: 32102.14.CBB19013
所属专题: 逆境生物学专辑 (2019年54卷2期)
收稿日期:2019-01-18
接受日期:2019-03-19
出版日期:2019-03-01
发布日期:2019-09-01
通讯作者:
童红宁
基金资助:
Lulu Li,Wenchao Yin,Mei Niu,Wenjing Meng,Xiaoxing Zhang,Hongning Tong( )
)
Received:2019-01-18
Accepted:2019-03-19
Online:2019-03-01
Published:2019-09-01
Contact:
Hongning Tong
摘要: 油菜素甾醇(BR)作为植物内源激素, 广泛参与植物的生长发育过程及逆境应答。虽然BR调控生长发育的分子机制目前已相对清楚, 但在水稻(Oryza sativa)中, BR在逆境反应中的功能还鲜有报道。该研究系统分析了BR在高盐胁迫过程中的作用, 表明盐胁迫和逆境激素脱落酸可抑制BR合成基因D2和D11的表达, 典型的BR缺陷突变体(如d2-2和d61-1)则表现出对盐胁迫敏感性增强。此外, 通过对BR核心转录因子OsBZR1的过表达株系进行分析, 发现BR可显著诱导OsBZR1的去磷酸化, 盐胁迫对OsBZR1蛋白的积累水平和磷酸化状态均有调控作用。转录组数据分析表明, BR处理前后差异表达基因中有38.4%同时受到盐胁迫调控, 其中91.5%受到BR和高盐一致调控, 并显著富集在应激反应过程中。研究结果表明, BR正调控水稻的耐盐性, 而盐胁迫通过抑制BR合成来限制水稻的生长。
栗露露,殷文超,牛梅,孟文静,张晓星,童红宁. 油菜素甾醇调控水稻盐胁迫应答的作用研究. 植物学报, 2019, 54(2): 185-193.
Lulu Li,Wenchao Yin,Mei Niu,Wenjing Meng,Xiaoxing Zhang,Hongning Tong. Functional Analysis of Brassinosteroids in Salt Stress Responses in Rice. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(2): 185-193.
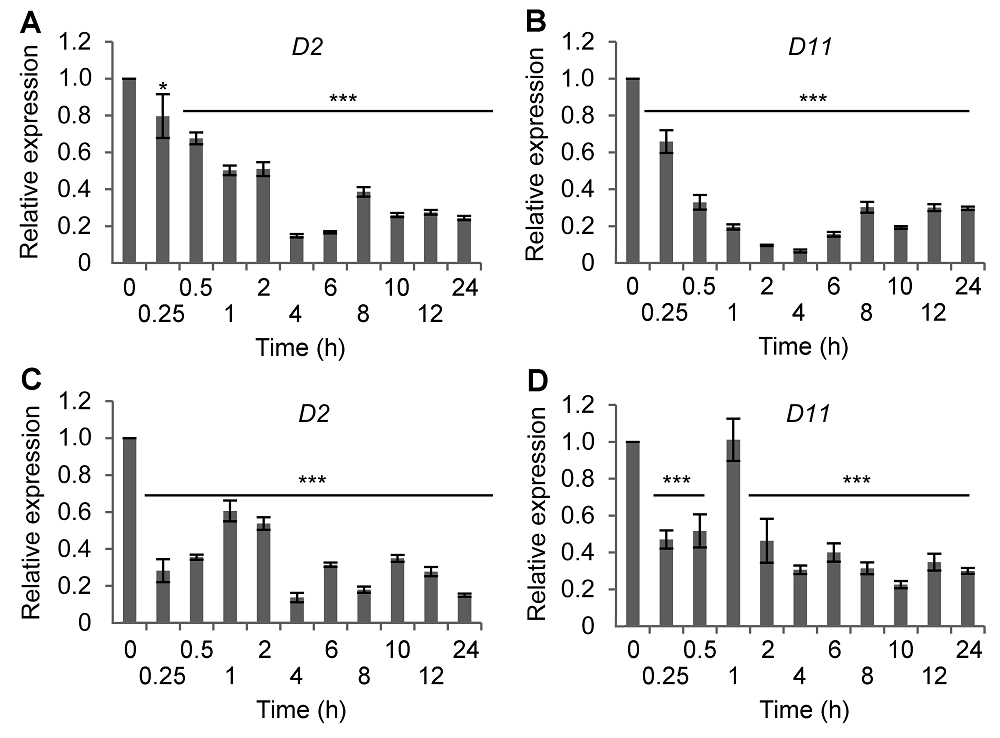
图1 不同时间高盐和ABA处理对水稻BR合成基因表达的影响(A) 盐处理后D2基因的表达; (B) 盐处理后D11基因的表达; (C) ABA处理后D2基因的表达; (D) ABA处理后D11基因的表达。* P< 0.05; *** P<0.001
Figure 1 Time-course expression of BR synthetic genes in rice following salt or ABA treatment(A) D2 expression after NaCl treatment; (B) D11 expression after NaCl treatment; (C) D2 expression after ABA treatment; (D) D11 expression after ABA treatment. * P<0.05; *** P<0.001
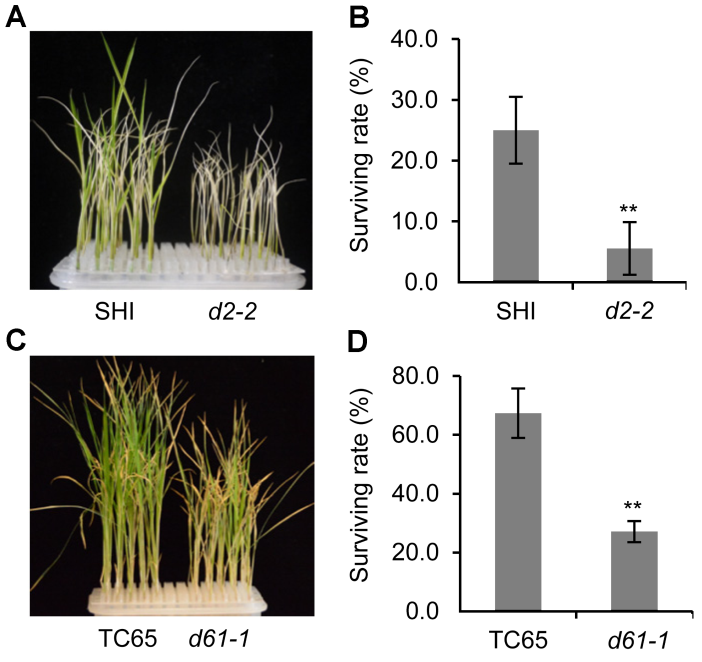
图2 盐胁迫下水稻BR缺陷突变体及其野生型的存活率(A) 盐处理后d2-2突变体及其野生型的生长情况; (B) 盐处理后d2-2突变体及其野生型的存活率统计; (C) 盐处理后d61-1突变体及其野生型的生长情况; (D) 盐处理后d61-1突变体及其野生型的存活率统计。** P<0.01
Figure 2 Survival rate of rice BR defective mutants and the wild type under salt stress(A) Growth status of d2-2 mutant and the wild type after salt treatment; (B) Statistic data of the survival rate of d2-2 and the wild type after salt treatment; (C) Growth status of d61-1 mutant and the wild type after salt treatment; (D) Statistic data of the survival rate of d61-1 and the wild type after salt treatment. ** P<0.01
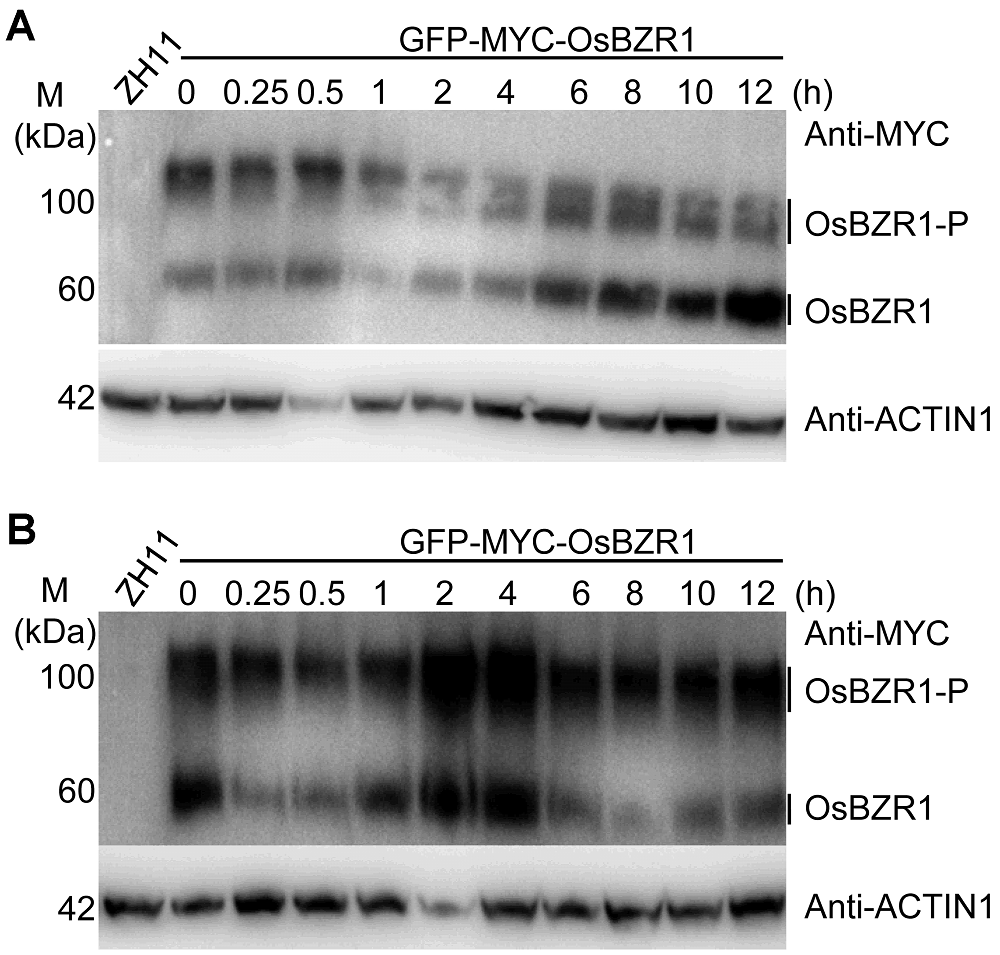
图3 不同时间BR和盐处理对水稻OsBZR1蛋白的影响(A) BR处理对OsBZR1蛋白的影响; (B) 盐处理对OsBZR1蛋白的影响
Figure 3 Effects of BR and salt stress on OsBZR1 proteins in rice(A) Effect of BR treatment on OsBZR1 proteins; (B) Effect of salt treatment on OsBZR1 proteins
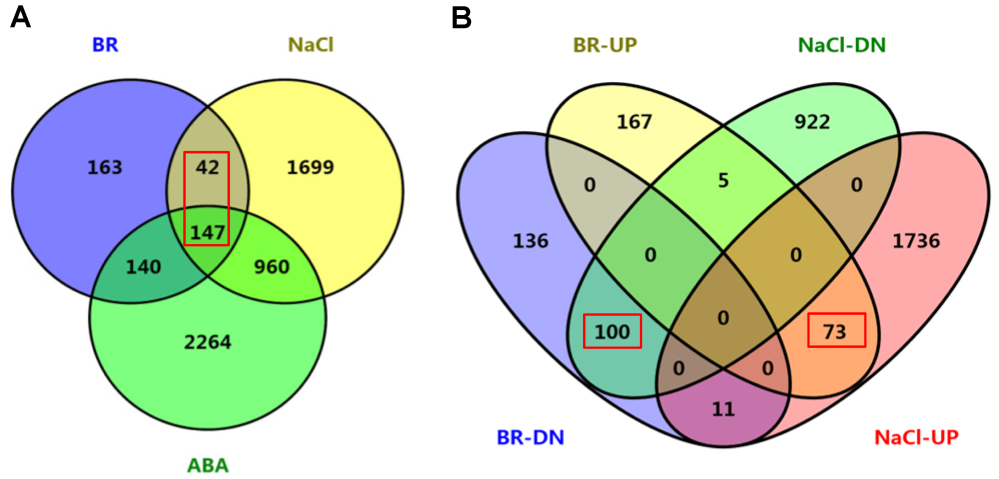
图4 BR、ABA和盐处理后水稻差异基因共调控分析(A) BR和ABA与盐差异调控基因的共调控分析; (B) BR上调(BR-UP)和下调(BR-DN)以及NaCl上调(NaCl-UP)和下调(NaCl-DN)基因的共调控分析。图中显示差异基因的分布及数目。
Figure 4 Co-regulation analyses of BR-, ABA- and NaCl-regulated genes of rice(A) Co-regulated gene numbers between BR-, ABA- and NaCl-regulated different expression genes (DEGs); (B) Co-regulation analyses among BR-upregulated (BR-UP), BR-downregulated (BR-DN), NaCl-upregulated (NaCl-UP) and NaCl-downregulated (NaCl-DN) genes. Distribution of the gene numbers was indicated.
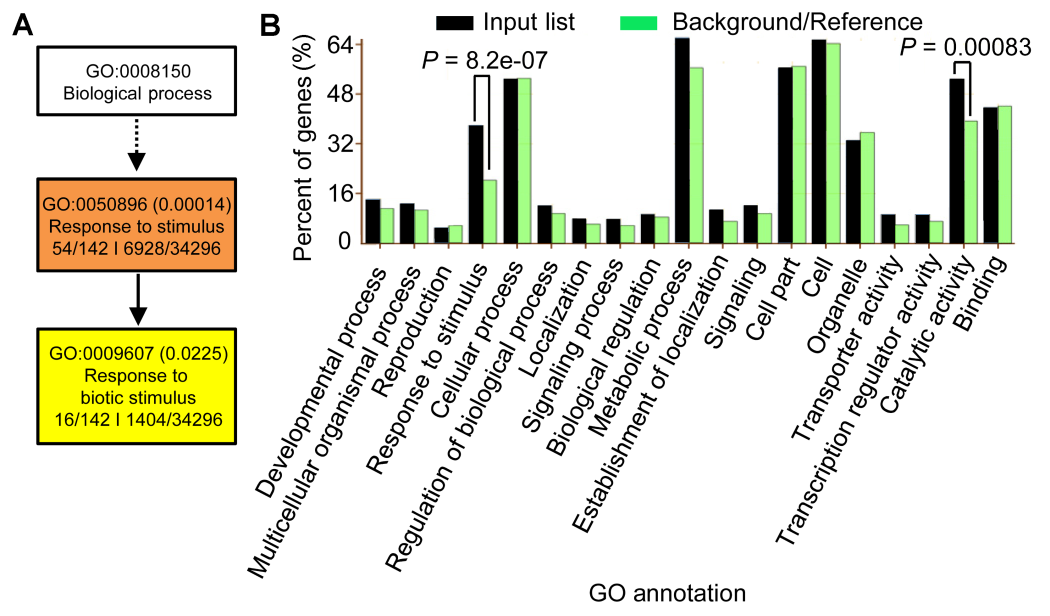
图5 水稻189个BR和盐共调控基因的聚类分析(A) 生物学途径聚类分析; (B) 生物学途径、细胞组分及分子功能的聚类分析
Figure 5 Gene Ontology analyses of the 189 BR-NaCl co-regulated genes of rice(A) GO analyses in term of the biological process; (B) GO analyses in terms of biological process, cellular component, and molecular function
| [1] | 李钱峰, 鲁军, 余佳雯, 张昌泉, 刘巧泉 ( 2018). 油菜素内酯与脱落酸互作调控植物生长与抗逆的分子机制研究进展. 植物生理学报 54, 370-378. |
| [2] | 王沛雅, 周剑平, 王治业, 张军, 强维亚, 杨涛, 郭琪, 杨晖 ( 2014). 油菜素内酯合成酶基因DAS5促进杨树生长及提高抗旱性的作用. 植物学报 49, 407-416. |
| [3] | 吴家富, 杨博文, 向珣朝, 许亮, 颜李梅 ( 2017). 不同水稻种质在不同生育期耐盐鉴定的差异. 植物学报 52, 77-88. |
| [4] | 俞仁培, 陈德明 ( 1999). 我国盐渍土资源及其开发利用. 土壤通报 30, 158-159. |
| [5] |
Choe S ( 2006). Brassinosteroid biosynthesis and inactiva- tion. Physiol Plant 126, 539-548.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Divi UK, Krishna P ( 2009). Brassinosteroid: a biotechno- logical target for enhancing crop yield and stress tole- rance. N Biotechnol 26, 131-136.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Feng Y, Yin YH, Fei SZ ( 2015). Down-regulation of BdBRI1, a putative brassinosteroid receptor gene produces a dwarf phenotype with enhanced drought tolerance in Brachy- podium distachyon. Plant Sci 234, 163-173. |
| [8] | Grove MD, Spencer GF, Rohwedder WK, Mandava N, Worley JF, Warthen JD Jr, Steffens GL, Flippen- Anderson JL, Cook JC Jr ( 1979). Brassinolide, a plant growth-promoting steroid isolated from Brassica napus pollen. Nature 281, 216-217. |
| [9] |
Ha YM, Shang Y, Nam KH ( 2016). Brassinosteroids modu- late ABA-induced stomatal closure in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 67, 6297-6308.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
He JX, Gendron JM, Sun Y, Gampala SSL, Gendron N, Sun CQ, Wang ZY ( 2005). BZR1 is a transcriptional repressor with dual roles in brassinosteroid homeostasis and growth responses. Science 307, 1634-1638.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
He JX, Gendron JM, Yang YL, Li JM, Wang ZY ( 2002). The GSK3-like kinase BIN2 phosphorylates and destabilizes BZR1, a positive regulator of the brassinosteroid signaling pathway in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99, 10185-10190.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Hong Z, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Matsuoka M ( 2004). Bras- sinosteroids and rice architecture. J Pestic Sci 29, 184-188.
DOI URL |
| [13] | Hong Z, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Umemura K, Uozu S, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M ( 2003). A rice brassinosteroid-deficient mutant, ebisu dwarf (d2), is caused by a loss of function of a new member of cytochrome P450. Plant Cell 15, 2900-2910. |
| [14] |
Khripach V, Zhabinskii V, De Groot A ( 2000). Twenty years of brassinosteroids: steroidal plant hormones warrant better crops for the XXI century. Ann Bot 86, 441-447.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Kim TW, Wang ZY ( 2010). Brassinosteroid signal transduc- tion from receptor kinases to transcription factors. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61, 681-704.
DOI URL |
| [16] | Krishna P, Prasad BD, Rahman T ( 2017). Brassinosteroid action in plant abiotic stress tolerance. In: Russinova E, Caño-Delgado AI, eds. Brassinosteroids. New York: Hum- ana Press. pp. 193-202. |
| [17] |
Morinaka Y, Sakamoto T, Inukai Y, Agetsuma M, Kitano H, Ashikari M, Matsuoka M ( 2006). Morphological alteration caused by brassinosteroid insensitivity increases the biomass and grain production of rice. Plant Physiol 141, 924-931.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Nakashima K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K ( 2013). ABA signaling in stress-response and seed development. Plant Cell Rep 32, 959-970.
DOI URL |
| [19] | Nolan TM, Brennan B, Yang MR, Chen JN, Zhang MC, Li ZH, Wang XL, Bassham DC, Walley J, Yin YH ( 2017). Selective autophagy of BES1 mediated by DSK2 balances plant growth and survival. Dev Cell 41, 33-46.e7. |
| [20] |
Peleg Z, Blumwald E ( 2011). Hormone balance and abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14, 290-295.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Ryu H, Kim K, Cho H, Park J, Choe S, Hwang I ( 2007). Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of BZR1 mediated by phos- phorylation is essential in Arabidopsis brassinosteroid signaling. Plant Cell 19, 2749-2762.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Sakamoto T, Morinaka Y, Ohnishi T, Sunohara H, Fujioka S, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Mizutani M, Sakata K, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Tanaka H, Kitano H, Matsuoka M ( 2006). Erect leaves caused by brassinosteroid deficiency inc- rease biomass production and grain yield in rice. Nat Bio- technol 24, 105-109.
DOI |
| [23] |
Singh AP, Savaldi-Goldstein S ( 2015). Growth control: brassinosteroid activity gets context. J Exp Bot 66, 1123-1132.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Sun Y, Fan XY, Cao DM, Tang WQ, He K, Zhu JY, He JX, Bai MY, Zhu SW, Oh E, Patil S, Kim TW, Ji HK, Wong WH, Rhee SY, Wang ZY ( 2010). Integration of bras- sinosteroid signal transduction with the transcription network for plant growth regulation in Arabidopsis. Dev Cell 19, 765-777.
DOI URL |
| [25] | Tong HN, Chu CC ( 2016). Reply: brassinosteroid regulates gibberellin synthesis to promote cell elongation in rice: critical comments on ross and quittenden's letter. Plant Cell 28, 833-835. |
| [26] | Tong HN, Chu CC ( 2018). Functional specificities of bras- sinosteroid and potential utilization for crop improvement. Trends Plant Sci 23, 1016-1028. |
| [27] |
Tong HN, Liu LC, Jin Y, Du L, Yin YH, Qian Q, Zhu LH, Chu CC ( 2012). DWARF AND LOW-TILLERING acts as a direct downstream target of a GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase to mediate brassinosteroid responses in rice. Plant Cell 24, 2562-2577.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Tong HN, Xiao YH, Liu DP, Gao SP, Liu LC, Yin YH, Jin Y, Qian Q, Chu CC ( 2014). Brassinosteroid regulates cell elongation by modulating gibberellin metabolism in rice. Plant Cell 26, 4376-4393.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Wang ZY, Nakano T, Gendron J, He JX, Chen M, Vafeados D, Yang YL, Fujioka S, Yoshida S, Asami T, Chory J ( 2002). Nuclear-localized BZR1 mediates bras- sinosteroid-induced growth and feedback suppression of brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Dev Cell 2, 505-513.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Wu CY, Trieu A, Radhakrishnan P, Kwok SF, Harris S, Zhang K, Wang JL, Wan JM, Zhai HQ, Takatsuto S, Matsumoto S, Fujioka S, Feldmann KA, Pennell RI ( 2008). Brassinosteroids regulate grain filling in rice. Plant Cell 20, 2130-2145.
DOI URL |
| [31] | Yamamuro C, Ihara Y, Wu X, Noguchi T, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M ( 2000). Loss of function of a rice brassinosteroid insensitive 1 homolog prevents internode elongation and bending of the lamina joint. Plant Cell 12, 1591-1606. |
| [32] | Yang MR, Li CX, Cai ZY, Hu YM, Nolan T, Yu FF, Yin YH, Xie Q, Tang GL, Wang XL ( 2017). SINAT E3 ligases control the light-mediated stability of the brassinosteroid- activated transcription factor BES1 in Arabidopsis. Dev Cell 41, 47-58.e4. |
| [33] | Yin WC, Dong NN, Niu M, Zhang XX, Li LL, Liu J, Liu B, Tong HN ( 2018). Brassinosteroid-regulated plant growth and development and gene expression in soybean. Crop J. DOI: 10.1016/j.cj.2018.10.003. |
| [34] |
Yin YH, Wang ZY, Mora-Garcia S, Li JM, Yoshida S, Asami T, Chory J ( 2002). BES1 accumulates in the nucleus in response to brassinosteroids to regulate gene expression and promote stem elongation. Cell 109, 181-191.
DOI URL |
| [35] | Yu XF, Li L, Zola J, Aluru M, Ye HX, Foudree A, Guo HQ, Anderson S, Aluru S, Liu P, Rodermel S, Yin YH ( 2011). A brassinosteroid transcriptional network revealed by genome-wide identification of BESI target genes in Ara- bidopsis thaliana . Plant J 65, 634-646. |
| [36] |
Zhao X, Dou LR, Gong ZZ, Wang XF, Mao TL ( 2019). BES1 hinders ABSCISIC ACID INSENSITIVE5 and promotes seed germination in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 221, 908-918.
DOI URL |
| [37] | Zhu JK ( 2001). Plant salt tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 6, 66-71. |
| [1] | 叶灿, 姚林波, 金莹, 高蓉, 谭琪, 李旭映, 张艳军, 陈析丰, 马伯军, 章薇, 张可伟. 水稻水杨酸代谢突变体高通量筛选方法的建立与应用[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | 徐田甜, 杨培建, 周晓茜, 曹怡, 陈艳红, 刘国元, 张健, 魏辉. 紫薇GolS家族基因的理化特性与表达特征[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 393-406. |
| [3] | 赵凌, 管菊, 梁文化, 张勇, 路凯, 赵春芳, 李余生, 张亚东. 基于高密度Bin图谱的水稻苗期耐热性QTL定位[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 342-353. |
| [4] | 李新宇, 谷月, 徐非非, 包劲松. 水稻胚乳淀粉合成相关蛋白的翻译后修饰研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 256-270. |
| [5] | 李建国, 张怡, 张文君. 水稻根系铁膜形成及对磷吸收的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 132-143. |
| [6] | 姚瑞枫, 谢道昕. 水稻独脚金内酯信号感知的激活和终止[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 873-877. |
| [7] | 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 张伊诺, 郑佳兴, 朱超宇, 叶语涵, 王跃星, 商文楠, 傅正浩, 徐昕璇, 吴日成, 路梅, 王长春, 饶玉春. 水稻抗氧化性状遗传位点挖掘及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 738-751. |
| [8] | 黄佳慧, 杨惠敏, 陈欣雨, 朱超宇, 江亚楠, 胡程翔, 连锦瑾, 芦涛, 路梅, 张维林, 饶玉春. 水稻突变体pe-1对弱光胁迫的响应机制[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 574-584. |
| [9] | 周俭民. 收放自如的明星战车[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 343-346. |
| [10] | 杜锦瑜, 孙震, 苏彦龙, 王贺萍, 刘亚玲, 吴振映, 何峰, 赵彦, 付春祥. 蒙古冰草咖啡酸氧甲基转移酶基因AmCOMT1的鉴定及功能分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 383-396. |
| [11] | 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 朱哲楠, 张芷宁, 汪理海, 陈钧, 李三峰, 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 钟芊芊, 殷文晶, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻穗部性状QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 217-230. |
| [12] | 夏婧, 饶玉春, 曹丹芸, 王逸, 柳林昕, 徐雅婷, 牟望舒, 薛大伟. 水稻中乙烯生物合成关键酶OsACS和OsACO调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 291-301. |
| [13] | 方妍力, 田传玉, 苏如意, 刘亚培, 王春连, 陈析丰, 郭威, 纪志远. 水稻抗细菌性条斑病基因挖掘与初定位[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 1-9. |
| [14] | 朱宝, 赵江哲, 张可伟, 黄鹏. 水稻细胞分裂素氧化酶9参与调控水稻叶夹角发育[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 10-21. |
| [15] | 贾绮玮, 钟芊芊, 顾育嘉, 陆天麒, 李玮, 杨帅, 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 李三峰, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻茎秆细胞壁相关组分含量QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 882-892. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||