

植物学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (2): 194-207.DOI: 10.11983/CBB18184 cstr: 32102.14.CBB18184
所属专题: 逆境生物学专辑 (2019年54卷2期)
收稿日期:2018-08-28
接受日期:2019-01-11
出版日期:2019-03-01
发布日期:2019-09-01
通讯作者:
丁艳锋
基金资助:
Lin Chen,Yan Lin,Pengfei Chen,Shaohua Wang,Yanfeng Ding( )
)
Received:2018-08-28
Accepted:2019-01-11
Online:2019-03-01
Published:2019-09-01
Contact:
Yanfeng Ding
摘要: 为鉴定水稻(Oryza sativa)响应缺铁的根冠长距离信号转导物质, 采用TMT标记技术分析了不同浓度铁处理下水稻韧皮部汁液的蛋白质组学变化, 共鉴定出206个差异蛋白, 其中54个蛋白表达丰度上调, 152个蛋白表达丰度下调。差异蛋白的KEGG通路分类主要包括激素信号代谢、谷胱甘肽代谢、碳代谢以及mRNA转运等代谢途径。此外, 对差异蛋白对应的生理指标进行测定, 发现激素、蔗糖、谷胱甘肽和转运蛋白等在缺铁条件下变化显著, 后续对这些差异蛋白的功能研究有助于揭示水稻响应铁素营养的长距离信号途径。
陈琳,林焱,陈鹏飞,王绍华,丁艳锋. 水稻响应缺铁的韧皮部汁液蛋白质组学分析. 植物学报, 2019, 54(2): 194-207.
Lin Chen,Yan Lin,Pengfei Chen,Shaohua Wang,Yanfeng Ding. Effect of Iron Deficiency on the Protein Profile of Rice (Oryza sativa) Phloem Sap. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(2): 194-207.
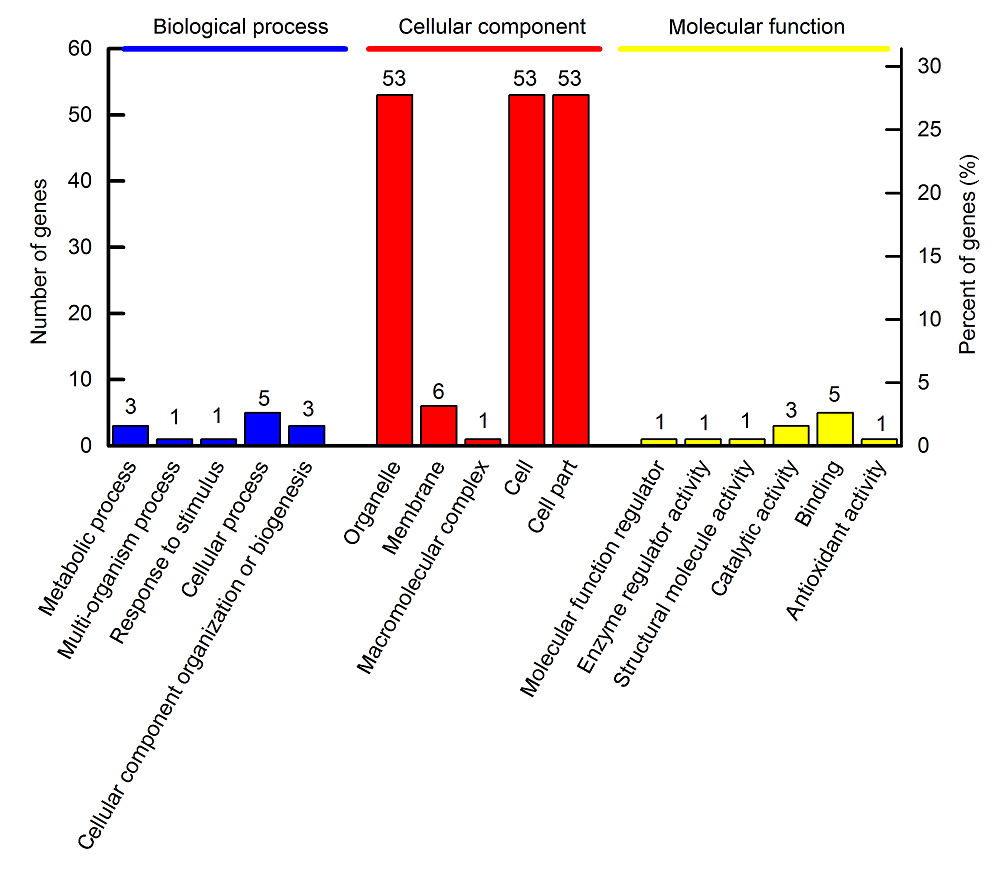
图1 水稻韧皮部汁液差异表达蛋白GO功能分类
Figure 1 Functional classification of the differentially expressed proteins of rice phloem sap via the Gene Ontology (GO) database
| Gene ID | Protein name | Unique peptides | FC (-Fe/+Fe) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant hormone signal transduction | ||||
| 4332374 | Probable protein phosphatase 2C 30 | 1 | 0.81 | 0.01 |
| 4333666 | Regulatory protein NPR3 isoform X2 | 1 | 1.45 | 0.01 |
| 4337780 | Probable indole-3-acetic acid-amido synthetase GH3.6 | 1 | 0.83 | 0.03 |
| 4340712 | Gibberellin-regulated protein 5 | 1 | 1.22 | 0.00 |
| Carbon metabolism | ||||
| 9268154 | Malate synthase | 12 | 0.77 | 0.03 |
| 4349723 | Phosphoglycerate mutase-like protein 4 | 2 | 0.75 | 0.01 |
| 4345814 | Alpha-amylase isozyme 3D | 14 | 0.72 | 0.00 |
| Stress and defense | ||||
| 4332474 | L-ascorbate peroxidase 1, cytosolic | 10 | 0.64 | 0.00 |
| 4336627 | Probable phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase | 2 | 0.75 | 0.00 |
| 4330235 | Probable phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase | 2 | 0.82 | 0.00 |
| 4349585 | Cationic peroxidase 1 | 2 | 0.52 | 0.00 |
| 4347962 | Peroxidase A2 isoform X2 | 8 | 0.80 | 0.00 |
| 4337232 | Peroxidase 4 | 2 | 0.68 | 0.02 |
| 4332928 | Peroxidase 2 | 1 | 0.58 | 0.00 |
| 4332175 | Peroxidase A2 | 2 | 0.76 | 0.01 |
| 4344277 | Peroxidase 2-like | 5 | 0.82 | 0.00 |
| 4328425 | 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase | 5 | 0.82 | 0.02 |
| Biosynthesis of amino acids | ||||
| 4342571 | Tryptophan synthase alpha chain | 1 | 0.79 | 0.05 |
| Ribosome | ||||
| 4325555 | 50S ribosomal protein L13, chloroplastic | 2 | 1.26 | 0.00 |
| 4324671 | 40S ribosomal protein S24-1 | 1 | 1.21 | 0.04 |
| 4334651 | 50S ribosomal protein L18, chloroplastic | 2 | 1.21 | 0.04 |
| 3131445 | Ribosomal protein S7 (plastid) | 2 | 1.21 | 0.00 |
| 4342697 | 40S ribosomal protein S15a-1 | 1 | 1.28 | 0.02 |
| 3131440 | Ribosomal protein S18 (plastid) | 1 | 0.74 | 0.01 |
| mRNA surveillance pathway | ||||
| 4347878 | Polyadenylation and cleavage factor homolog 4 | 2 | 0.77 | 0.01 |
| RNA transport | ||||
| 4329091 | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 1A | 3 | 0.79 | 0.01 |
| 4345498 | ABC transporter A family member 7 | 1 | 1.40 | 0.00 |
表1 缺铁处理下水稻韧皮部汁液差异表达蛋白KEGG通路分类
Table 1 Differentially expressed proteins in phloem exudates of rice under iron deficiency in KEGG pathway
| Gene ID | Protein name | Unique peptides | FC (-Fe/+Fe) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant hormone signal transduction | ||||
| 4332374 | Probable protein phosphatase 2C 30 | 1 | 0.81 | 0.01 |
| 4333666 | Regulatory protein NPR3 isoform X2 | 1 | 1.45 | 0.01 |
| 4337780 | Probable indole-3-acetic acid-amido synthetase GH3.6 | 1 | 0.83 | 0.03 |
| 4340712 | Gibberellin-regulated protein 5 | 1 | 1.22 | 0.00 |
| Carbon metabolism | ||||
| 9268154 | Malate synthase | 12 | 0.77 | 0.03 |
| 4349723 | Phosphoglycerate mutase-like protein 4 | 2 | 0.75 | 0.01 |
| 4345814 | Alpha-amylase isozyme 3D | 14 | 0.72 | 0.00 |
| Stress and defense | ||||
| 4332474 | L-ascorbate peroxidase 1, cytosolic | 10 | 0.64 | 0.00 |
| 4336627 | Probable phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase | 2 | 0.75 | 0.00 |
| 4330235 | Probable phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase | 2 | 0.82 | 0.00 |
| 4349585 | Cationic peroxidase 1 | 2 | 0.52 | 0.00 |
| 4347962 | Peroxidase A2 isoform X2 | 8 | 0.80 | 0.00 |
| 4337232 | Peroxidase 4 | 2 | 0.68 | 0.02 |
| 4332928 | Peroxidase 2 | 1 | 0.58 | 0.00 |
| 4332175 | Peroxidase A2 | 2 | 0.76 | 0.01 |
| 4344277 | Peroxidase 2-like | 5 | 0.82 | 0.00 |
| 4328425 | 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase | 5 | 0.82 | 0.02 |
| Biosynthesis of amino acids | ||||
| 4342571 | Tryptophan synthase alpha chain | 1 | 0.79 | 0.05 |
| Ribosome | ||||
| 4325555 | 50S ribosomal protein L13, chloroplastic | 2 | 1.26 | 0.00 |
| 4324671 | 40S ribosomal protein S24-1 | 1 | 1.21 | 0.04 |
| 4334651 | 50S ribosomal protein L18, chloroplastic | 2 | 1.21 | 0.04 |
| 3131445 | Ribosomal protein S7 (plastid) | 2 | 1.21 | 0.00 |
| 4342697 | 40S ribosomal protein S15a-1 | 1 | 1.28 | 0.02 |
| 3131440 | Ribosomal protein S18 (plastid) | 1 | 0.74 | 0.01 |
| mRNA surveillance pathway | ||||
| 4347878 | Polyadenylation and cleavage factor homolog 4 | 2 | 0.77 | 0.01 |
| RNA transport | ||||
| 4329091 | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 1A | 3 | 0.79 | 0.01 |
| 4345498 | ABC transporter A family member 7 | 1 | 1.40 | 0.00 |
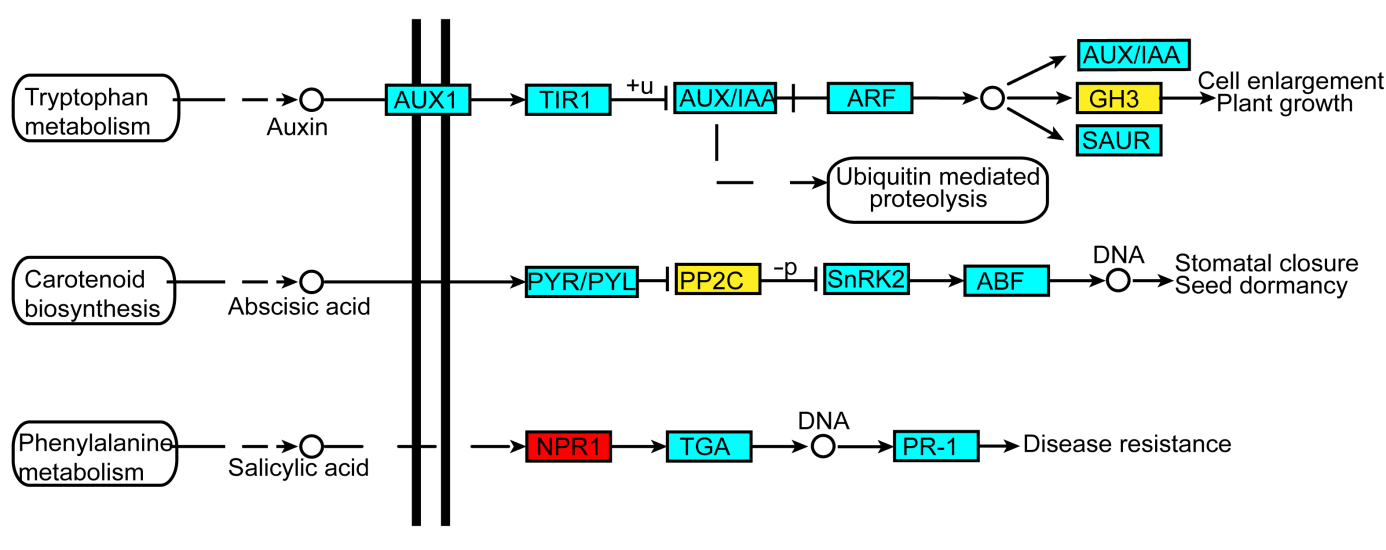
图2 缺铁条件下水稻韧皮部激素信号转导变化示意图红色表示蛋白丰度上调, 黄色表示蛋白丰度下调。实线表示直接作用, 虚线表示中间有省略过程。箭头表示促进作用(正效应), 短竖线表示抑制作用(负效应)。
Figure 2 Schematic representation of plant hormone signal transduction in phloem of rice under iron deficiencyRed represents an increase of protein expression abundance, and yellow represents a decrease. The solid lines indicate direct action and the dotted lines indicate omission process. The arrows mean a positive effect and the short vertical lines mean inhibited effect.
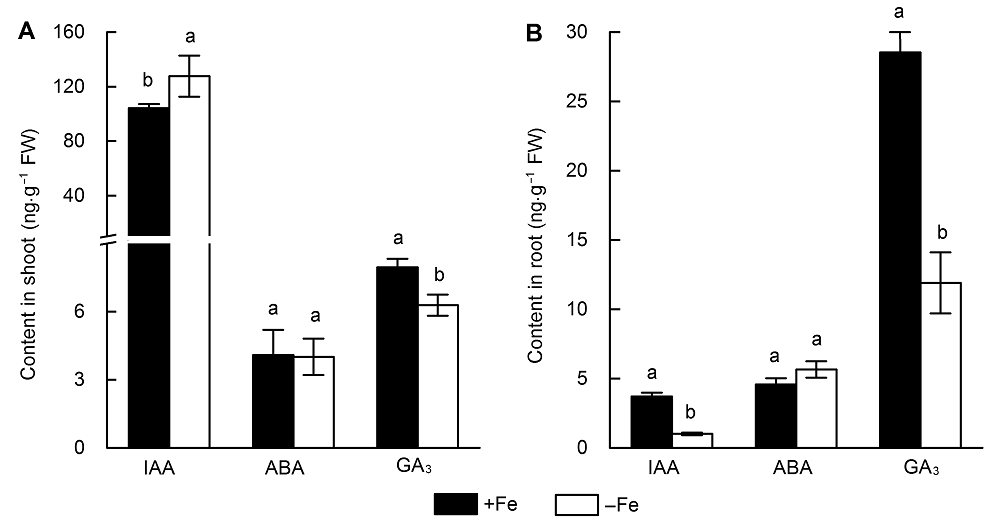
图3 缺铁处理3天后水稻地上部(A)和根系(B)激素含量变化不同小写字母表示缺铁(-Fe)和对照(+Fe)之间差异显著。
Figure 3 The hormone content in rice shoots (A) and roots (B) after three days of iron deficiency treatmentDifferent lowercase letters indicate significant differences between iron deficiency (-Fe) and the control (+Fe).
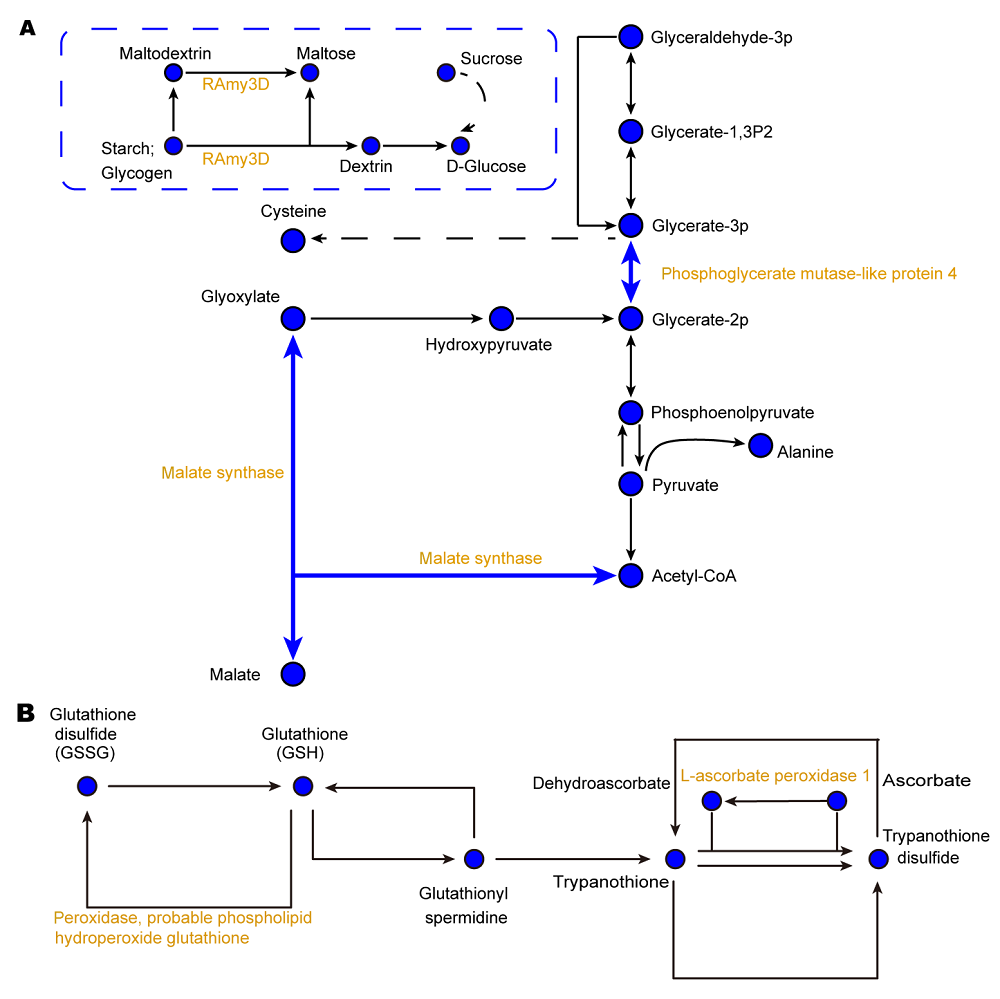
图4 缺铁条件下水稻韧皮部汁液碳代谢(A)和谷胱甘肽代谢(B)相关蛋白质丰度变化示意图黄色表示蛋白丰度下调。实线表示直接作用, 虚线表示中间有省略过程。箭头表示促进作用(正效应)。
Figure 4 Metabolic pathways of carbon (A) and glutathione (B) related proteins in phloem exudates of rice under iron deficiencyYellow represents a decrease of protein expression abundance. The solid lines indicate direct action and the dotted lines indicate omission process. The arrows mean a positive effect.
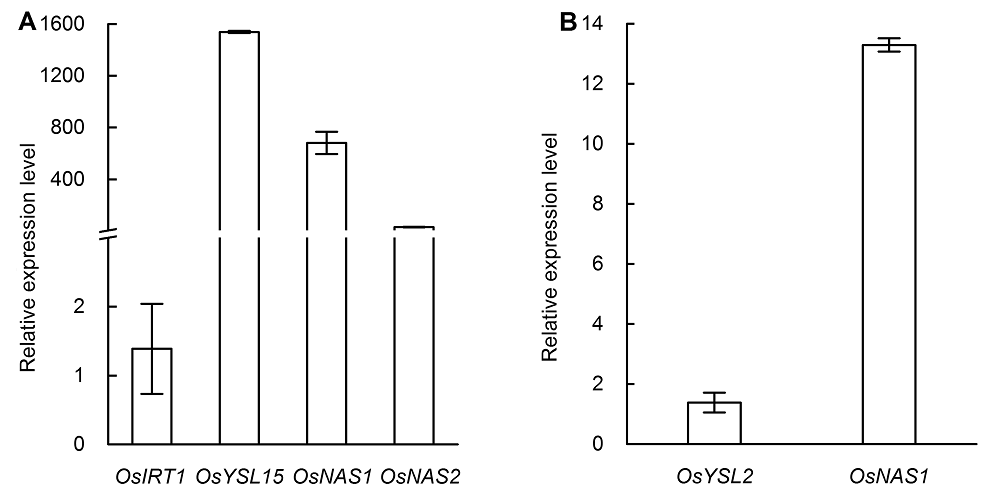
图5 水稻缺铁处理3天后根系OsIRT1、OsYSL15、OsNAS1和OsNAS2 (A)以及地上部OsYSL2和OsNAS1 (B)相对表达水平柱形图代表缺铁与对照基因相对表达量的比值。
Figure 5 The relative expression levels of OsIRT1, OsYSL15, OsNAS1 and OsNAS2 in root (A) and the relative expression levels of OsYSL2 and OsNAS1 in shoot (B) after three days of iron deficiency treatmentThe column diagram represents the relative gene expression level ratio of iron deficiency induced to the control.
| [54] |
Thimm O, Essigmann B, Kloska S, Altmann T, Buckhout TJ ( 2001). Response of Arabidopsis to iron deficiency stress as revealed by microarray analysis. Plant Physiol 127, 1030-1043.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
Tiffin LO ( 1966). Iron translocation II. Citrate/iron ratios in plant stem exudates. Plant Physiol 41, 515-518.
DOI URL |
| [56] | Tougane K, Komatsu K, Bhyan SB, Sakata Y, Ishizaki K, Yamato KT, Kohchi T, Takezawa D ( 2010). Evolutionarily conserved regulatory mechanisms of abscisic acid signa- ling in land plants: characterization of ABSCISIC ACID INSENSITIVE1-like type 2C protein phosphatase in the liverwort Marchantia polymorpha. Plant Physiol 152, 1529-1543. |
| [57] | Vasiliou V, Vasiliou K, Nebert DW ( 2009). Human ATP- binding cassette (ABC) transporter family. Hum Genomics 3, 281-290. |
| [58] |
Vert GA, Briat JF, Curie C ( 2003). Dual regulation of the Arabidopsis high-affinity root iron uptake system by local and long-distance signals. Plant Physiol 132, 796-804.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
von Wirén N, Klair S, Bansal S, Briat JF, Khodr H, Shioiri T, Leigh RA, Hider RC ( 1999). Nicotianamine chelates both Fe III and Fe II. Implications for metal transport in plants . Plant Physiol 119, 1107-1114.
DOI URL |
| [60] | Wang BL, Wei HF, Xue Z, Zhang WH ( 2017). Gibberellins regulate iron deficiency-response by influencing iron trans- port and translocation in rice seedlings (Oryza sativa). Ann Bot 119, 945-956. |
| [61] |
Yokosho K, Yamaji N, Ueno D, Mitani N, Ma JF ( 2009). OsFRDL1 is a citrate transporter required for efficient translocation of iron in rice. Plant Physiol 149, 297-305.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 傅友强, 梁建平, 于智卫, 吴道铭, 蔡昆争, 沈宏 ( 2011). 不同铁形态对水稻根表铁膜及铁吸收的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报 17, 1050-1057. |
| [2] | 吴慧兰, 王宁, 凌宏清 ( 2007). 植物铁吸收、转运和调控的分子机制研究进展. 植物学通报 24, 779-788. |
| [3] | 熊长明, 王晔, 田晓莉 ( 2014). 植物矿质养分吸收的长距离反馈调节研究进展. 植物营养与肥料学报 20, 737-746. |
| [4] | 邹春琴, 陈新平, 张福锁, 毛达如 ( 1998). 活性铁作为植物铁营养状况诊断指标的相关研究. 植物营养与肥料学报 4, 399-406. |
| [5] |
Agarwala SC, Sharma CP ( 1961). The relation of iron supply to the tissue concentration of iron, chlorophyll and catalase in barley plants grown in sand culture. Physiol Plant 14, 275-283.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Aoyama T, Kobayashi T, Takahashi M, Nagasaka S, Usuda K, Kakei Y, Ishimaru Y, Nakanishi H, Mori S, Nishizawa NK ( 2009). OsYSL18 is a rice iron(III)-deoxy- mugineic acid transporter specifically expressed in reproductive organs and phloem of lamina joints. Plant Mol Biol 70, 681-692.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Bao F, Li JY ( 2002). Evidence that the auxin signaling path- way interacts with plant stress response. Acta Bot Sin 44, 532-536. |
| [8] |
Bashir K, Nagasaka S, Itai RN, Kobayashi T, Takahashi M, Nakanishi H, Mori S, Nishizawa NK ( 2007). Expres- sion and enzyme activity of glutathione reductase is upregulated by Fe-deficiency in graminaceous plants. Plant Mol Biol 65, 277-284.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Brown JC, Chaney RL ( 1971). Effect of iron on the transport of citrate into the xylem of soybeans and tomatoes. Plant Physiol 47, 836-840.
DOI URL |
| [10] | Chen L, Ding CQ, Zhao XF, Xu JX, Mohammad AA, Wang SH, Ding YF ( 2015). Differential regulation of proteins in rice ( Oryza sativa L.) under iron deficiency. Plant Cell Rep 34, 83-96. |
| [11] | Chen L, Wang GP, Chen PF, Zhu HL, Wang SH, Ding YF ( 2018a). Shoot-root communication plays a key role in physiological alterations of rice (Oryza sativa) under iron deficiency. Front Plant Sci 9, 757. |
| [12] | Chen PF, Chen L, Jiang ZR, Wang GP, Wang SH, Ding YF ( 2018b). Sucrose is involved in the regulation of iron deficiency responses in rice ( Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Rep 37, 789-798. |
| [13] |
Cheng LJ, Wang F, Shou HX, Huang FL, Zheng LQ, He F, Li JH, Zhao FJ, Ueno D, Ma JF, Wu P ( 2007). Mutation in nicotianamine aminotransferase stimulated the Fe(II) acquisition system and led to iron accumulation in rice. Plant Physiol 145, 1647-1657.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Connolly EL, Campbell N, Grotz N, Prichard CL, Guerinot ML ( 2003). Overexpression of the FRO2 iron reductase confers tolerance to growth on low iron and uncovers post-transcriptional control. Plant Physiol 133, 1102-1110.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Curie C, Cassin G, Counch D, Divol F, Higuchi K, Jean ML, Misson J, Schikora A, Czernic P, Mari S ( 2009). Metal movement within the plant: contribution of nico- tianamine and yellow stripe 1-like transporters. Ann Bot 103, 1-11.
DOI URL |
| [16] | Curie C, Panaviene Z, Loulergue C, Dellaporta SL, Briat JF, Walker EL ( 2001). Maize yellow stripe1 encodes a membrane protein directly involved in Fe(III) uptake. Nature 409, 346-349. |
| [17] | Dean M, Hamon Y, Chimini G ( 2001). The human ATP- binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily. J Lipid Res 42, 1007-1017. |
| [18] |
Dong J, Piñeros MA, Li X, Yang H, Liu Y, Murphy AS, Kochian LV, Liu D ( 2017). An Arabidopsis ABC trans- porter mediates phosphate deficiency-induced remodeling of root architecture by modulating iron homeostasis in roots. Mol Plant 10, 244-259.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Eide D, Broderius M, Fett J, Guerinot ML ( 1996). A novel iron-regulated metal transporter from plants identified by functional expression in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93, 5624-5628.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Enomoto Y, Hodoshima H, Shimada H, Shoji K, Yoshi- hara T, Goto F ( 2007). Long-distance signals positively regulate the expression of iron uptake genes in tobacco roots. Planta 227, 81-89.
DOI URL |
| [21] | Espen L, Dell'Orto M, Nisi PD, Zocchi G ( 2000). Metabolic responses in cucumber ( Cucumis sativus L.) roots under Fe-deficiency: a 31P-nuclear magnetic resonance in-vivo study. Planta 210, 985-992. |
| [22] |
Falka J, Andersena G, Kernebeckb B, Krupinskaa K ( 2003). Constitutive overexpression of barley 4-hydroxyp henylpyruvate dioxygenase in tobacco results in elevation of the vitamin E content in seeds but not in leaves. FEBS Lett 540, 35-40.
DOI URL |
| [23] | Forde BG ( 2002). The role of long-distance signaling in plant responses to nitrate and other nutrients. J Exp Bot 53, 39-43. |
| [24] |
García MJ, Romera FJ, Stacey MG, Stacey G, Villar E, Alcántara E, Pérez-Vicente R ( 2013). Shoot to root com- munication is necessary to control the expression of iron- acquisition genes in Strategy I plants. Planta 237, 65-75.
DOI URL |
| [25] | Green LS, Rogers EE ( 2004). FRD3 controls iron localiza- tion in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 136, 2523-2531. |
| [26] | Hagen G, Uhrhammer N, Guilfoyle TJ ( 1988). Regulation of expression of an auxin-induced soybean sequence by cadmium. J Biol Chem 263, 6442-6446. |
| [27] |
Haydon MJ, Cobbett CS ( 2007). Transporters of ligands for essential metal ions in plants. New Phytol 174, 499-506.
DOI URL |
| [28] | Hell R, Stephan UW ( 2003). Iron uptake, trafficking and homeostasis in plants. Planta 216, 541-551. |
| [29] |
Hindt MN, Guerinot ML ( 2012). Getting a sense for signals: regulation of the plant iron deficiency response. Biochim Biophys Acta 1823, 1521-1530.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Inoue H, Kobayashi T, Nozoye T, Takahashi M, Kakei Y, Suzuki K, Nakazono M, Nakanishi H, Mori S, Nishizawa NK ( 2009). Rice OsYSL15 is an iron-regulated iron(III)- deoxymugineic acid transporter expressed in the roots and is essential for iron uptake in early growth of the seedlings. J Biol Chem 284, 3470-3479.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Ishimaru Y, Kim SA, Tsukamoto T, Oki H, Kobayashi T, Watanabe S, Matsuhashi S, Takahashi M, Nakanishi H, Mori S, Nishizawa NK ( 2007). Mutational reconstructed ferric chelate reductase confers enhanced tolerance in rice to iron deficiency in calcareous soil. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104, 7373-7378.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Ishimaru Y, Suzuki M, Tsukamoto T, Suzuki K, Nakazono M, Kobayashi T, Wada Y, Watanabe S, Matsuhashi S, Takahashi M, Nakanishi H, Mori S, Nishizawa NK ( 2006). Rice plants take up iron as an Fe 3+-phytosidero- phore and as Fe 2+ . Plant J 45, 335-346.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Jiang CF, Gao XH, Liao LL, Harberd NP, Fu XD ( 2007). Phosphate starvation root architecture and anthocyanin accumulation responses are modulated by the gibberellin- DELLA signaling pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 145, 1460-1470.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Kakei Y, Yamaguchi I, Kobayashi T, Takahashi M, Naka- nishi H, Yamakawa T, Nishizawa NK ( 2009). A highly sensitive, quick and simple quantification method for nicotianamine and 2’-deoxymugineic acid from minimum samp- les using LC/ESI-TOF-MS achieves functional analysis of these components in plants. Plant Cell Physiol 50, 1988-1993.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Kerk D, Bulgrien J, Smith DW, Barsam B, Veretnik S, Gribskov M ( 2002). The complement of protein phos- phatase catalytic subunits encoded in the genome of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 129, 908-925.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Lee S, Chiecko JC, Kim SA, Walker EL, Lee Y, Guerinot ML, An G ( 2009). Disruption of OsYSL15 leads to iron inefficiency in rice plants. Plant Physiol 150, 786-800.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Lei GJ, Zhu XF, Wang ZW, Dong F, Dong NY, Zheng SJ ( 2014). Abscisic acid alleviates iron deficiency by promo- ting root iron reutilization and transport from root to shoot in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ 37, 852-863.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Li J, Wu XD, Hao ST, Wang XJ, Ling HQ ( 2008). Proteomic response to iron deficiency in tomato root. Proteomics 8, 2299-2311.
DOI URL |
| [39] | Liu KD, Yue RQ, Yuan CC, Liu JX, Zhang L, Sun T, Yang YJ, Tie SG, Shen CJ ( 2015). Auxin signaling is involved in iron deficiency-induced photosynthetic inhibition and shoot growth defect in rice ( Oryza sativa L.). J Plant Biol 58, 391-401. |
| [40] |
López-Millán AF, Morales F, Andaluz S, Gogorcena Y, Abadía A, De Las Rivas J, Abadía J ( 2000). Responses of sugar beet roots to iron deficiency. Changes in carbon assimilation and oxygen use. Plant Physiol 124, 885-897.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Lucas WJ, Groover A, Lichtenberger R, Furuta K, Yadav SR, Helariutta Y, He XQ, Fukuda H, Kang JL, Brady SM, Patrick JW, Sperry J, Yoshida A, López-Millán AF, Grusak MA, Kachroo P ( 2013). The plant vascular sys- tem: evolution, development and functions. J Integr Plant Biol 55, 294-388.
DOI URL |
| [42] | Lucas WJ, Yoo BC, Kragler F ( 2001). RNA as a long- distance information macromolecule in plants. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2, 849-857. |
| [43] | Majerus V, Bertin P, Lutts S ( 2009). Abscisic acid and oxidative stress implications in overall ferritin synthesis by African rice ( Oryza glaberrima Steud.) seedlings exposed to short term iron toxicity. Plant Soil 324, 253-265. |
| [44] |
Matsuoka K, Furukawa J, Bidadi H, Asahina M, Yama- guchi S, Satoh S ( 2014). Gibberellin-induced expression of Fe uptake-related genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Phy- siol 55, 87-98.
DOI URL |
| [45] | Mol PC, Park HM, Mullins JT, Cabib E ( 1994). A GTP- binding protein regulates the activity of (1→3)-β-glucan synthase, an enzyme directly involved in yeast cell wall morphogenesis. J Biol Chem 269, 31267-31274. |
| [46] |
Negishi T, Nakanishi H, Yazaki J, Kishimoto N, Fujii F, Shimbo K, Yamamoto K, Sakata K, Sasaki T, Kikuchi S, Mori S, Nishizawa NK ( 2002). cDNA microarray analysis of gene expression during Fe-deficiency stress in barley suggests that polar transport of vesicles is implicated in phytosiderophore secretion in Fe-deficient barley roots. Plant J 30, 83-94.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Nguyen VNT, Moon S, Jung KH ( 2014). Genome-wide expression analysis of rice ABC transporter family across spatio-temporal samples and in response to abiotic stress- ses. J Plant Physiol 171, 1276-1288.
DOI URL |
| [48] | Qi YH, Wang SK, Shen CJ, Zhang SN, Chen Y, Xu YX, Liu Y, Wu YR, Jiang DA ( 2012). OsARF12, a transcription activator on auxin response gene, regulates root elonga- tion and affects iron accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa). New Phytol 193, 109-120. |
| [49] |
Robinson NJ, Procter CM, Connolly EL, Guerinot ML ( 1999). A ferric-chelate reductase for iron uptake from soils. Nature 397, 694-697.
DOI |
| [50] |
Shanmugam V, Wang YW, Tsednee M, Karunakaran K, Yeh KC ( 2015). Glutathione plays an essential role in nitric oxide-mediated iron-deficiency signaling and iron-defi- ciency tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant J 84, 464-477.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Soon FF, Ng LM, Zhou XE, West GM, Kovach A, Tan MHE, Suino-Powell KM, He YZ, Xu Y, Chalmers MJ, Brun- zelle JS, Zhang HM, Yang HY, Jiang HL, Li J, Yong EL, Cutler S, Zhu JK, Griffin PR, Melcher K, Xu HE ( 2012). Molecular mimicry regulates ABA signaling by SnRK2 kinases and PP2C phosphatases. Science 335, 85-88.
DOI URL |
| [52] | Takahashi M, Terada Y, Nakai I, Nakanishi H, Yoshimura E, Mori S, Nishizawa NK ( 2003). Role of nicotianamine in the intracellular delivery of metals and plant reproductive development. Plant Cell 15, 1263-1280. |
| [62] | Yoseph T, David KS, Dean DP ( 2002). Overexpression of the enzyme p -hydroxyphenolpyruvate dioxygenase in Ara- bidopsis and its relation to tocopherol biosynthesis. Plant Physiol Biochem 40, 913-920. |
| [53] |
Tanaka N, Abe-Dohmae S, Iwamoto N, Fitzgerald ML, Yokoyama S ( 2010). Helical apolipoproteins of high- density lipoprotein enhance phagocytosis by stabilizing ATP-binding cassette transporter A7. J Lipid Res 51, 2591-2599.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 叶灿, 姚林波, 金莹, 高蓉, 谭琪, 李旭映, 张艳军, 陈析丰, 马伯军, 章薇, 张可伟. 水稻水杨酸代谢突变体高通量筛选方法的建立与应用[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | 赵凌, 管菊, 梁文化, 张勇, 路凯, 赵春芳, 李余生, 张亚东. 基于高密度Bin图谱的水稻苗期耐热性QTL定位[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 342-353. |
| [3] | 李新宇, 谷月, 徐非非, 包劲松. 水稻胚乳淀粉合成相关蛋白的翻译后修饰研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 256-270. |
| [4] | 李建国, 张怡, 张文君. 水稻根系铁膜形成及对磷吸收的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 132-143. |
| [5] | 张富崇, 于明含, 张建玲, 王平, 丁国栋, 何莹莹, 孙慧媛. 黑沙蒿应对降水变化的木质部与韧皮部协同响应机制[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(7): 903-914. |
| [6] | 姚瑞枫, 谢道昕. 水稻独脚金内酯信号感知的激活和终止[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 873-877. |
| [7] | 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 张伊诺, 郑佳兴, 朱超宇, 叶语涵, 王跃星, 商文楠, 傅正浩, 徐昕璇, 吴日成, 路梅, 王长春, 饶玉春. 水稻抗氧化性状遗传位点挖掘及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 738-751. |
| [8] | 黄佳慧, 杨惠敏, 陈欣雨, 朱超宇, 江亚楠, 胡程翔, 连锦瑾, 芦涛, 路梅, 张维林, 饶玉春. 水稻突变体pe-1对弱光胁迫的响应机制[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 574-584. |
| [9] | 周俭民. 收放自如的明星战车[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 343-346. |
| [10] | 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 朱哲楠, 张芷宁, 汪理海, 陈钧, 李三峰, 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 钟芊芊, 殷文晶, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻穗部性状QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 217-230. |
| [11] | 夏婧, 饶玉春, 曹丹芸, 王逸, 柳林昕, 徐雅婷, 牟望舒, 薛大伟. 水稻中乙烯生物合成关键酶OsACS和OsACO调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 291-301. |
| [12] | 朱宝, 赵江哲, 张可伟, 黄鹏. 水稻细胞分裂素氧化酶9参与调控水稻叶夹角发育[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 10-21. |
| [13] | 方妍力, 田传玉, 苏如意, 刘亚培, 王春连, 陈析丰, 郭威, 纪志远. 水稻抗细菌性条斑病基因挖掘与初定位[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 1-9. |
| [14] | 贾绮玮, 钟芊芊, 顾育嘉, 陆天麒, 李玮, 杨帅, 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 李三峰, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻茎秆细胞壁相关组分含量QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 882-892. |
| [15] | 戴若惠, 钱心妤, 孙静蕾, 芦涛, 贾绮玮, 陆天麒, 路梅, 饶玉春. 水稻叶色调控机制及相关基因研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 799-812. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||