

植物学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (1): 25-32.DOI: 10.11983/CBB20148 cstr: 32102.14.CBB20148
潘晨阳1, 叶涵斐1, 周维永3, 王盛1, 李梦佳1, 路梅1, 李三峰2, 朱旭东2, 王跃星2, 饶玉春1,*( ), 戴高兴3,*(
), 戴高兴3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-08-26
接受日期:2020-11-11
出版日期:2021-01-01
发布日期:2021-01-15
通讯作者:
饶玉春,戴高兴
作者简介:2526620@qq.com基金资助:
Chenyang Pan1, Hanfei Ye1, Weiyong Zhou3, Sheng Wang1, Mengjia Li1, Mei Lu1, Sanfeng Li2, Xudong Zhu2, Yuexing Wang2, Yuchun Rao1,*( ), Gaoxing Dai3,*(
), Gaoxing Dai3,*( )
)
Received:2020-08-26
Accepted:2020-11-11
Online:2021-01-01
Published:2021-01-15
Contact:
Yuchun Rao,Gaoxing Dai
摘要: 水稻(Oryza sativa)是全世界重要的经济作物之一, 稻田镉(Cd)污染和镉积累问题严重威胁世界水稻的产量和品质以及人类健康, 如何降低水稻中镉积累已成为热点问题。以籼稻品种华占(HZ)为父本、粳稻品种热研2号(Nekken2)为母本, 连续自交多代后得到120个重组自交系群体, 对其镉积累进行检测和分析, 同时利用遗传图谱进行QTL作图。结果共检测到7个QTLs, 分别位于水稻第2、3、9和12号染色体上, 其中1个LOD值高达4.97。对这些QTL区间内与耐金属离子胁迫相关的候选基因进行定量分析, 发现LOC_Os02g50240、LOC_Os02g52780、LOC_Os09g31200、LOC_Os09g35030和LOC_Os09g37949这5个基因在双亲间的表达量差异显著, 结合亲本对不同金属离子的浓度积累数据, 推测LOC_ Os02g50240、LOC_Os09g31200及LOC_Os09g35030的高表达可能极大地提高了水稻对镉离子的吸收和胁迫耐受能力。通过QTL挖掘和分析, 发现这些基因与水稻籽粒的镉积累有关, 可能影响水稻耐镉胁迫的能力。研究结果为进一步筛选和培育耐镉胁迫的水稻品种创造了条件, 为阐明水稻镉积累的分子调控机制奠定了基础。
潘晨阳, 叶涵斐, 周维永, 王盛, 李梦佳, 路梅, 李三峰, 朱旭东, 王跃星, 饶玉春, 戴高兴. 水稻籽粒镉积累QTL定位及候选基因分析. 植物学报, 2021, 56(1): 25-32.
Chenyang Pan, Hanfei Ye, Weiyong Zhou, Sheng Wang, Mengjia Li, Mei Lu, Sanfeng Li, Xudong Zhu, Yuexing Wang, Yuchun Rao, Gaoxing Dai. QTL Mapping of Candidate Genes Involved in Cd Accumulation in Rice Grain. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(1): 25-32.
| Primer name | Sequence (5'-3') | Tm (°C) | Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LOC_Os02g50240-F-qrt | CTTCAAGGACCCATTCAGGA | 60.04 | 113 |
| LOC_Os02g50240-R-qrt | TGAAGATCTTGGCAGCATTG | 59.95 | |
| LOC_Os02g52780-F-qrt | GTTTTCAAAGGTGGGCTGAG | 59.71 | 148 |
| LOC_Os02g52780-R-qrt | CCTCAGCTTCCAATTCCATC | 59.68 | |
| LOC_Os09g31200-F-qrt | GCGACAAGAAGGATCAGGAG | 59.95 | 117 |
| LOC_Os09g31200-R-qrt | AGAAGCAGTTCTGGCAGAGG | 59.75 | |
| LOC_Os09g35030-F-qrt | GGATCAAGCAGGAGATGAGC | 59.92 | 135 |
| LOC_Os09g35030-R-qrt | GCCTCGTCTCCCTGAACTT | 59.39 | |
| LOC_Os09g37949-F-qrt | GGAAATCTGCCGATCAGTGT | 60.08 | 123 |
| LOC_Os09g37949-R-qrt | GGGTCCTTCGATGGGTTTAT | 60.02 |
表1 qRT-PCR所用引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences for qRT-PCR
| Primer name | Sequence (5'-3') | Tm (°C) | Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LOC_Os02g50240-F-qrt | CTTCAAGGACCCATTCAGGA | 60.04 | 113 |
| LOC_Os02g50240-R-qrt | TGAAGATCTTGGCAGCATTG | 59.95 | |
| LOC_Os02g52780-F-qrt | GTTTTCAAAGGTGGGCTGAG | 59.71 | 148 |
| LOC_Os02g52780-R-qrt | CCTCAGCTTCCAATTCCATC | 59.68 | |
| LOC_Os09g31200-F-qrt | GCGACAAGAAGGATCAGGAG | 59.95 | 117 |
| LOC_Os09g31200-R-qrt | AGAAGCAGTTCTGGCAGAGG | 59.75 | |
| LOC_Os09g35030-F-qrt | GGATCAAGCAGGAGATGAGC | 59.92 | 135 |
| LOC_Os09g35030-R-qrt | GCCTCGTCTCCCTGAACTT | 59.39 | |
| LOC_Os09g37949-F-qrt | GGAAATCTGCCGATCAGTGT | 60.08 | 123 |
| LOC_Os09g37949-R-qrt | GGGTCCTTCGATGGGTTTAT | 60.02 |
| QTL | Chromosome | Physical distance (bp) | Position of support (cM) | Limit of detection |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| qRCd-1 | 2 | 30302111-35902152 | 129.90-153.90 | 4.48 |
| qRCd-2 | 3 | 5112031-5335542 | 21.91-22.87 | 2.51 |
| qRCd-3 | 3 | 6338887-6654517 | 27.17-28.53 | 2.61 |
| qRCd-4 | 9 | 13883217-15424344 | 59.51-66.12 | 4.32 |
| qRCd-5 | 9 | 16779765-22230863 | 71.93-95.30 | 4.97 |
| qRCd-6 | 9 | 22748818-22938953 | 97.52-98.33 | 2.60 |
| qRCd-7 | 12 | 21976412-22336740 | 94.21-95.75 | 2.66 |
表2 水稻重组自交系(RIL)群体籽粒中镉含量的QTL分析
Table 2 QTL analysis of Cd contents in rice grains of the recombinant inbred line (RIL)
| QTL | Chromosome | Physical distance (bp) | Position of support (cM) | Limit of detection |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| qRCd-1 | 2 | 30302111-35902152 | 129.90-153.90 | 4.48 |
| qRCd-2 | 3 | 5112031-5335542 | 21.91-22.87 | 2.51 |
| qRCd-3 | 3 | 6338887-6654517 | 27.17-28.53 | 2.61 |
| qRCd-4 | 9 | 13883217-15424344 | 59.51-66.12 | 4.32 |
| qRCd-5 | 9 | 16779765-22230863 | 71.93-95.30 | 4.97 |
| qRCd-6 | 9 | 22748818-22938953 | 97.52-98.33 | 2.60 |
| qRCd-7 | 12 | 21976412-22336740 | 94.21-95.75 | 2.66 |
| Chromosome | Gene | Function | Object |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | LOC_Os02g50240 | It participates in the regulation of various biological processes and stress response | Cytoplasmic glutamine synthetase |
| 2 | LOC_Os02g52780 | It regulates ABA-dependent stress-related gene expression to enhance the plant tolerance of drought and salt | Transcription factors bZIP |
| 9 | LOC_Os09g31200 | A major determinant of plant response to stress | Zinc finger protein |
| 9 | LOC_Os09g35030 | It specifically combines with drought response elements and controls many stress-induced genes | Transcription factors AP2/EREBP |
| 9 | LOC_Os09g37949 | It plays an important role in salt stress response | Receptor protein kinase |
表3 水稻镉积累候选基因的功能
Table 3 The function of candidate genes related to the accumulation of cadmium in rice
| Chromosome | Gene | Function | Object |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | LOC_Os02g50240 | It participates in the regulation of various biological processes and stress response | Cytoplasmic glutamine synthetase |
| 2 | LOC_Os02g52780 | It regulates ABA-dependent stress-related gene expression to enhance the plant tolerance of drought and salt | Transcription factors bZIP |
| 9 | LOC_Os09g31200 | A major determinant of plant response to stress | Zinc finger protein |
| 9 | LOC_Os09g35030 | It specifically combines with drought response elements and controls many stress-induced genes | Transcription factors AP2/EREBP |
| 9 | LOC_Os09g37949 | It plays an important role in salt stress response | Receptor protein kinase |
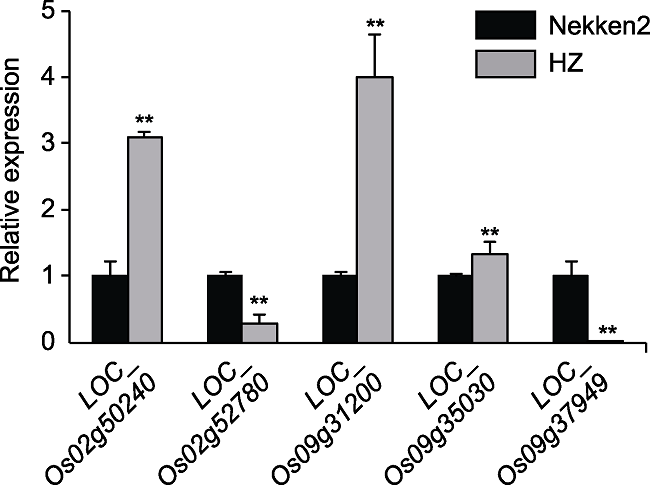
图4 水稻镉积累候选基因表达量差异 ** 表示差异极显著(P<0.01)。
Figure 4 Differences in the expression level of candidate genes involved in cadmium accumulation in rice ** indicate extremely significant differences (P<0.01).
| [1] | 黄新元, 赵方杰 (2018). 植物防御素调控水稻镉积累的新机制. 植物学报 53, 451-455. |
| [2] | 王兰, 黄李超, 代丽萍, 杨窑龙, 徐杰, 冷语佳, 张光恒, 胡江, 朱丽, 高振宇, 董国军, 郭龙彪, 钱前, 曾大力 (2014). 利用日本晴/9311重组自交系群体定位水稻成熟期叶形相关性状QTL. 中国水稻科学 28, 589-597. |
| [3] |
Abe T, Nonoue Y, Ono N, Omoteno M, Kuramata M, Fukuoka S, Yamamoto T, Yano M, Ishikawa S (2013). Detection of QTLs to reduce cadmium content in rice grains using LAC23/Koshihikari chromosome segment substitution lines. Breed Sci 63, 284-291.
URL PMID |
| [4] |
Arisawa K, Uemura H, Hiyoshi M, Takeda H, Saito H, Soda M (2007). Cadmium-induced renal dysfunction and mortality in two cohorts: disappearance of the association in a generation born later. Toxicol Lett 169, 214-221.
URL PMID |
| [5] | Cheng YW, Qi YC, Zhu Q, Chen X, Wang N, Zhao X, Chen HY, Cui XJ, Xu LL, Zhang W (2009). New changes in the plasma-membrane-associated proteome of rice roots under salt stress. Proteomics 9, 3100-3114. |
| [6] | Dubouzet JG, Sakuma Y, Ito Y, Kasuga M, Dubouzet EG, Miura S, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2003). OsDREB genes in rice, Oryza sativa L., encode transcription activators that function in drought-, high-salt- and cold-responsive gene expression. Plant J 33, 751-763. |
| [7] | Florijn PJ, van Beusichem ML (1993). Uptake and distribution of cadmium in maize inbred lines. Plant Soil 150, 25-32. |
| [8] | Fujimaki S, Suzui N, Ishioka NS, Kawachi N, Ito S, Chino M, Nakamura S (2010). Tracing cadmium from culture to spikelet: noninvasive imaging and quantitative characterization of absorption, transport, and accumulation of cadmium in an intact rice plant. Plant Physiol 152, 1796-1806. |
| [9] |
Horiguchi H, Teranishi H, Niiya K, Aoshima K, Katoh K, Sakuragawa N, Kasuya M (1994). Hypoproduction of erythropoietin contributes to anemia in chronic cadmium intoxication: clinical study on Itai-itai disease in Japan. Arch Toxicol 68, 632-636.
URL PMID |
| [10] | Hu DW, Sheng ZH, Li QL, Chen W, Wei XJ, Xie LH, Jiao GA, Shao GN, Wang JL, Tang SQ, Hu PS (2018). Identification of QTLs associated with cadmium concentration in rice grains. J Integr Agric 17, 1563-1573. |
| [11] |
Ishikawa S, Abe T, Kuramata M, Yamaguchi M, Ando T, Yamamoto T, Yano M (2010). A major quantitative trait locus for increasing cadmium-specific concentration in rice grain is located on the short arm of chromosome 7. J Exp Bot 61, 923-934.
URL PMID |
| [12] | Liu WQ, Pan XW, Li YC, Duan YH, Min J, Liu SX, Liu LC, Sheng XN, Li XX (2019). Identification of QTLs and validation of qCd-2 associated with grain cadmium concentrations in rice. Rice Sci 26, 42-49. |
| [13] |
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2‒ΔΔCT method. Methods 25, 402-408.
URL PMID |
| [14] | Mao CP, Song YX, Chen LX, Ji JF, Li JZ, Yuan XY, Yang ZF, Ayoko GA, Frost RL, Theiss F (2019). Human health risks of heavy metals in paddy rice based on transfer characteristics of heavy metals from soil to rice. Catena 175, 339-348. |
| [15] | McCouch SR, Cho YG, Yano M, Paul E, Blinstrub M, Morishima H, Kinoshita T (1997). Report on QTL nomenclature. Rice Genet Newsl 14, 11-13. |
| [16] |
Miyadate H, Adachi S, Hiraizumi A, Tezuka K, Nakazawa N, Kawamoto T, Katou K, Kodama I, Sakurai K, Takahashi H, Satoh-Nagasawa N, Watanabe A, Fujimura T, Akagi H (2011). OsHMA3, a P1B-type of ATPase affects root-to-shoot cadmium translocation in rice by mediating efflux into vacuoles. New Phytol 189, 190-199.
DOI URL PMID |
| [17] |
Mukhopadhyay A, Vij S, Tyagi AK (2004). Overexpression of a zinc-finger protein gene from rice confers tolerance to cold, dehydration, and salt stress in transgenic tobacco. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101, 6309-6314.
URL PMID |
| [18] | Nakanishi H, Ogawa I, Ishimaru Y, Mori S, Nishizawa NK (2006). Iron deficiency enhances cadmium uptake and translocation mediated by the Fe2+ transporters OsIRT1 and OsIRT2 in rice. Soil Sci Plant Nut 52, 464-469. |
| [19] |
Satarug S, Garrett SH, Sens MA, Sens DA (2010). Cadmium, environmental exposure, and health outcomes. Environ Health Perspect 118, 182-190.
DOI URL PMID |
| [20] | Satoh-Nagasawa N, Mori M, Nakazawa N, Kawamoto T, Nagato Y, Sakurai K, Takahashi H, Watanabe A, Akagi H (2012). Mutations in rice (Oryza sativa) heavy metal ATPase 2 (OsHMA2) restrict the translocation of zinc and cadmium. Plant Cell Physiol 53, 213-224. |
| [21] |
Shi JC, Yu XL, Zhang MK, Lu SG, Wu WH, Wu JJ, Xu JM (2011). Potential risks of copper, zinc, and cadmium pollution due to pig manure application in a soil-rice system under intensive farming: a case study of Nanhu, China. J Environ Qual 40, 1695-1704.
DOI URL PMID |
| [22] | Singh KK, Ghosh S (2013). Regulation of glutamine synthetase isoforms in two differentially drought-tolerant rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars under water deficit conditions. Plant Cell Rep 32, 183-193. |
| [23] |
Takahashi A, Agrawal GK, Yamazaki M, Onosato K, Miyao A, Kawasaki T, Shimamoto K, Hirochika H (2007). Rice Pti1a negatively regulates RAR1-dependent defense responses. Plant Cell 19, 2940-2951.
URL PMID |
| [24] |
Ueno D, Kono I, Yokosho K, Ando T, Yano M, Ma JF (2009a). A major quantitative trait locus controlling cadmium translocation in rice (Oryza sativa). New Phytol 182, 644-653.
URL PMID |
| [25] | Ueno D, Koyama E, Kono I, Ando T, Yano M, Ma JF (2009b). Identification of a novel major quantitative trait locus controlling distribution of Cd between roots and shoots in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 50, 2223-2233. |
| [26] |
Uraguchi S, Kamiya T, Sakamoto T, Kasai K, Sato Y, Nagamura Y, Yoshida A, Kyozuka J, Ishikawa S, Fujiwara T (2011). Low-affinity cation transporter (OsLCT1) regulates cadmium transport into rice grains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108, 20959-20964.
DOI URL PMID |
| [27] | Wang FJ, Wang M, Liu ZB, Shi Y, Han TQ, Ye YY, Gong N, Sun JW, Zhu C (2015). Different responses of low grain-Cd-accumulating and high grain-Cd-accumulating rice cultivars to Cd stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 96, 261-269. |
| [28] |
Yu H, Wang JL, Fang W, Yuan JG, Yang ZY (2006). Cadmium accumulation in different rice cultivars and screening for pollution-safe cultivars of rice. Sci Total Environ 370, 302-309.
DOI URL PMID |
| [29] | Zhang XQ, Zhang GP, Guo LB, Wang HZ, Zeng DL, Dong GJ, Qian Q, Xue DW (2011). Identification of quantitative trait loci for Cd and Zn concentrations of brown rice grown in Cd-polluted soils. Euphytica 180, 173-179. |
| [30] | Zong W, Tang N, Yang J, Peng L, Ma SQ, Xu Y, Li GL, Xiong LZ (2016). Feedback regulation of ABA signaling and biosynthesis by a bZIP transcription factor targets drought-resistance-related genes. Plant Physiol 171, 2810-2825. |
| [1] | 叶灿, 姚林波, 金莹, 高蓉, 谭琪, 李旭映, 张艳军, 陈析丰, 马伯军, 章薇, 张可伟. 水稻水杨酸代谢突变体高通量筛选方法的建立与应用[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | 赵凌, 管菊, 梁文化, 张勇, 路凯, 赵春芳, 李余生, 张亚东. 基于高密度Bin图谱的水稻苗期耐热性QTL定位[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 342-353. |
| [3] | 李新宇, 谷月, 徐非非, 包劲松. 水稻胚乳淀粉合成相关蛋白的翻译后修饰研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 256-270. |
| [4] | 李建国, 张怡, 张文君. 水稻根系铁膜形成及对磷吸收的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 132-143. |
| [5] | 姚瑞枫, 谢道昕. 水稻独脚金内酯信号感知的激活和终止[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 873-877. |
| [6] | 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 张伊诺, 郑佳兴, 朱超宇, 叶语涵, 王跃星, 商文楠, 傅正浩, 徐昕璇, 吴日成, 路梅, 王长春, 饶玉春. 水稻抗氧化性状遗传位点挖掘及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 738-751. |
| [7] | 黄佳慧, 杨惠敏, 陈欣雨, 朱超宇, 江亚楠, 胡程翔, 连锦瑾, 芦涛, 路梅, 张维林, 饶玉春. 水稻突变体pe-1对弱光胁迫的响应机制[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 574-584. |
| [8] | 周俭民. 收放自如的明星战车[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 343-346. |
| [9] | 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 朱哲楠, 张芷宁, 汪理海, 陈钧, 李三峰, 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 钟芊芊, 殷文晶, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻穗部性状QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 217-230. |
| [10] | 夏婧, 饶玉春, 曹丹芸, 王逸, 柳林昕, 徐雅婷, 牟望舒, 薛大伟. 水稻中乙烯生物合成关键酶OsACS和OsACO调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 291-301. |
| [11] | 方妍力, 田传玉, 苏如意, 刘亚培, 王春连, 陈析丰, 郭威, 纪志远. 水稻抗细菌性条斑病基因挖掘与初定位[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 1-9. |
| [12] | 朱宝, 赵江哲, 张可伟, 黄鹏. 水稻细胞分裂素氧化酶9参与调控水稻叶夹角发育[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 10-21. |
| [13] | 贾绮玮, 钟芊芊, 顾育嘉, 陆天麒, 李玮, 杨帅, 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 李三峰, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻茎秆细胞壁相关组分含量QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 882-892. |
| [14] | 戴若惠, 钱心妤, 孙静蕾, 芦涛, 贾绮玮, 陆天麒, 路梅, 饶玉春. 水稻叶色调控机制及相关基因研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 799-812. |
| [15] | 田传玉, 方妍力, 沈晴, 王宏杰, 陈析丰, 郭威, 赵开军, 王春连, 纪志远. 2019-2021年我国南方稻区白叶枯病菌的毒力与遗传多样性调查研究[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 743-749. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||