

植物学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (5): 625-633.DOI: 10.11983/CBB18243 cstr: 32102.14.CBB18243
田怀东1,3,*( ),李菁1,田保华1,牛鹏飞1,李珍1,岳忠孝1,屈雅娟1,姜建芳1,王广元2,岑慧慧1,李南1,闫枫1
),李菁1,田保华1,牛鹏飞1,李珍1,岳忠孝1,屈雅娟1,姜建芳1,王广元2,岑慧慧1,李南1,闫枫1
收稿日期:2018-11-13
接受日期:2019-06-18
出版日期:2019-09-01
发布日期:2020-03-10
通讯作者:
田怀东
基金资助:
Huaidong Tian1,3,*( ),Jing Li1,Baohua Tian1,Pengfei Niu1,Zhen Li1,Zhongxiao Yue1,Yajuan Qu1,Jianfang Jiang1,Guangyuan Wang2,Huihui Cen1,Nan Li1,Feng Yan1
),Jing Li1,Baohua Tian1,Pengfei Niu1,Zhen Li1,Zhongxiao Yue1,Yajuan Qu1,Jianfang Jiang1,Guangyuan Wang2,Huihui Cen1,Nan Li1,Feng Yan1
Received:2018-11-13
Accepted:2019-06-18
Online:2019-09-01
Published:2020-03-10
Contact:
Huaidong Tian
摘要: N-甲基-N-亚硝基脲(MNU)被用于水稻(Oryza sativa)受精卵的诱变。通过水稻辽盐6号成熟生殖器官的MNU体内同步处理及后代群体筛查, 确立了水稻两性生殖细胞的MNU诱变方法。与辽盐6号受精卵的MNU处理相比, 各组条件下两性生殖细胞的MNU处理明显使M1群体生长发育的指标降低及M1-M2群体中突变性状的发生率升高。两性生殖细胞在含有1.5 mmol∙L -1 MNU和10 mmol∙L -1 PO4 3-的缓冲液(pH4.8)中处理60分钟, 突变性状发生率是基于受精卵MNU处理的3倍。进一步筛查M3群体, 获得了包含新型植株和籽粒突变体的纯合突变体系列。研究结果表明, 水稻两性生殖细胞的MNU诱变可显著提高广谱诱变效率。该技术的应用可为水稻的未知功能基因鉴定和育种所需的各种突变体规模化开发提供高效的技术支撑。
田怀东,李菁,田保华,牛鹏飞,李珍,岳忠孝,屈雅娟,姜建芳,王广元,岑慧慧,李南,闫枫. 水稻两性生殖细胞的N-甲基-N-亚硝基脲诱变方法. 植物学报, 2019, 54(5): 625-633.
Huaidong Tian,Jing Li,Baohua Tian,Pengfei Niu,Zhen Li,Zhongxiao Yue,Yajuan Qu,Jianfang Jiang,Guangyuan Wang,Huihui Cen,Nan Li,Feng Yan. Method for N-methyl-N-nitrosourea Mutagenesis on Hermaphroditic Germ Cells of Rice. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(5): 625-633.
| Treatments | MNU (mmol∙L-1) | Time (min) | pH | PO43– (mmol∙L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Germ cells | 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 | 20 40 60 80 | 4.2 4.8 5.4 6.0 | 5 10 20 40 |
| Control | 1.0 | 40 | 4.8 | 10 |
表1 水稻生殖细胞MNU实验设计
Table 1 Design for MNU treatments of germ cells in rice
| Treatments | MNU (mmol∙L-1) | Time (min) | pH | PO43– (mmol∙L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Germ cells | 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 | 20 40 60 80 | 4.2 4.8 5.4 6.0 | 5 10 20 40 |
| Control | 1.0 | 40 | 4.8 | 10 |
| Treatments of germ cells | Setting rate (%) | Seedling rate (%) | Adult plant rate (%) | Fertility rate(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable MNU (mmol∙L-1) | 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 | 86.1 78.6 73.5 62.2 | 82.3 74.5 68.3 59.8 | 82.4 77.1 70.4 61.7 | 89.3 80.4 76.7 68.2 |
| Variable time (min) | 20 40 60 80 | 88.5 78.6 74.7 65.8 | 83.1 74.5 69.3 60.8 | 83.2 77.1 72.3 66.9 | 91.0 80.4 73.8 67.6 |
| Variable pH | 4.2 4.8 5.4 6.0 | 85.3 78.6 74.5 82.9 | 80.3 74.5 79.6 83.7 | 85.3 77.1 81.0 84.9 | 89.6 80.4 85.2 87.9 |
| Variable PO43- (mmol∙L-1) | 5 10 20 40 | 83.7 78.6 82.5 87.4 | 82.4 74.5 78.1 85.0 | 86.3 77.1 70.6 82.8 | 89.7 80.4 85.3 86.9 |
| Control treatment | 89.5 | 87.3 | 90.4 | 92.8 | |
表2 MNU处理因素对辽盐6号水稻生殖细胞M1群体生长发育的影响
Table 2 Effects of MNU-treatment factors on growth and development of M1 populations of germ cells of Liaoyan 6 rice cultivar
| Treatments of germ cells | Setting rate (%) | Seedling rate (%) | Adult plant rate (%) | Fertility rate(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable MNU (mmol∙L-1) | 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 | 86.1 78.6 73.5 62.2 | 82.3 74.5 68.3 59.8 | 82.4 77.1 70.4 61.7 | 89.3 80.4 76.7 68.2 |
| Variable time (min) | 20 40 60 80 | 88.5 78.6 74.7 65.8 | 83.1 74.5 69.3 60.8 | 83.2 77.1 72.3 66.9 | 91.0 80.4 73.8 67.6 |
| Variable pH | 4.2 4.8 5.4 6.0 | 85.3 78.6 74.5 82.9 | 80.3 74.5 79.6 83.7 | 85.3 77.1 81.0 84.9 | 89.6 80.4 85.2 87.9 |
| Variable PO43- (mmol∙L-1) | 5 10 20 40 | 83.7 78.6 82.5 87.4 | 82.4 74.5 78.1 85.0 | 86.3 77.1 70.6 82.8 | 89.7 80.4 85.3 86.9 |
| Control treatment | 89.5 | 87.3 | 90.4 | 92.8 | |
| Treatments of germ cells | Number of mutant characters | Incidences (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seedling | Culm | Leaf | Panicle | Glume | Seed | Total | |||
| Variable MNU (mmol∙L-1) | 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 | 3 4 8 5 | 2 4 6 3 | 3 4 5 2 | 1 2 3 1 | 1 1 2 - | 8 15 15 6 | 18 30 39 17 | 4.6 7.6 9.9 4.3 |
| Variable time (min) | 20 40 60 80 | 3 4 5 5 | 2 4 3 3 | 3 4 5 3 | 2 2 1 2 | - 1 2 1 | 5 15 15 6 | 15 30 31 20 | 3.8 7.6 7.9 5.1 |
| Variable pH | 4.2 4.8 5.4 6.0 | 5 4 5 3 | 3 4 3 3 | 2 4 3 3 | 1 2 1 - | 1 1 1 1 | 9 15 10 6 | 21 30 23 16 | 5.3 7.6 5.9 4.1 |
| Variable PO43- (mmol∙L-1) | 5 10 20 40 | 5 4 6 5 | 2 4 3 3 | 3 4 4 2 | 2 2 1 1 | 1 1 2 1 | 7 15 7 6 | 20 30 23 18 | 5.1 7.6 5.9 4.6 |
| Control treatment | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 13 | 3.3 | |
表3 辽盐6号水稻生殖细胞的MNU处理因素对M1-M2群体中突变性状表达的影响
Table 3 Effects of MNU-treatment factors on mutant-character expression in M1-M2 populations of germ cells of Liaoyan 6 rice cultivar
| Treatments of germ cells | Number of mutant characters | Incidences (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seedling | Culm | Leaf | Panicle | Glume | Seed | Total | |||
| Variable MNU (mmol∙L-1) | 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 | 3 4 8 5 | 2 4 6 3 | 3 4 5 2 | 1 2 3 1 | 1 1 2 - | 8 15 15 6 | 18 30 39 17 | 4.6 7.6 9.9 4.3 |
| Variable time (min) | 20 40 60 80 | 3 4 5 5 | 2 4 3 3 | 3 4 5 3 | 2 2 1 2 | - 1 2 1 | 5 15 15 6 | 15 30 31 20 | 3.8 7.6 7.9 5.1 |
| Variable pH | 4.2 4.8 5.4 6.0 | 5 4 5 3 | 3 4 3 3 | 2 4 3 3 | 1 2 1 - | 1 1 1 1 | 9 15 10 6 | 21 30 23 16 | 5.3 7.6 5.9 4.1 |
| Variable PO43- (mmol∙L-1) | 5 10 20 40 | 5 4 6 5 | 2 4 3 3 | 3 4 4 2 | 2 2 1 1 | 1 1 2 1 | 7 15 7 6 | 20 30 23 18 | 5.1 7.6 5.9 4.6 |
| Control treatment | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 13 | 3.3 | |
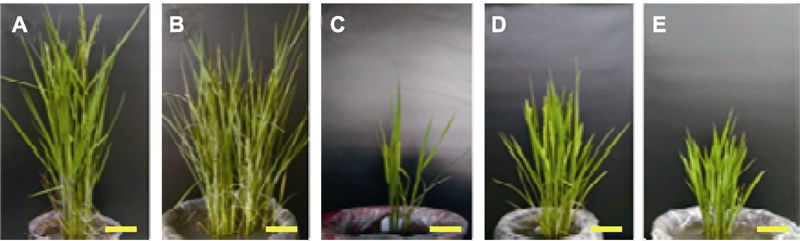
图1 辽盐6号水稻生殖细胞经MNU处理所得的M1-M3群体中的秆形突变性状 (A) 野生型秆; (B) 多分蘖秆; (C) 少分蘖秆; (D), (E) 矮化秆。Bars=10 cm。MNU同表1。
Figure 1 Mutant characters for culm form in M1-M3 populations obtained by the MNU treatments of germ cells of Liaoyan 6 rice cultivar (A) The wild type culm; (B) Multiple-tiller culm; (C) Less-tiller culm; (D), (E) Dwarf culm. Bars=10 cm. MNU see Table 1.

图2 辽盐6号水稻生殖细胞经MNU处理所得M1-M3群体中的叶形与叶色突变性状 (A) 野生型叶; (B) 宽叶; (C) 细卷叶; (D) 竖叶; (E) 深绿叶; (F) 浅绿叶; (G) 黄叶缘; (H) 斑点叶。Bars=5 cm。MNU同表1。
Figure 2 Mutant characters for leaf form and leaf color in M1-M3 populations obtained by the MNU treatments of germ cells of Liaoyan 6 rice cultivar (A) The wild type leaf; (B) Wide leaf; (C) Narrow and rolled leaf; (D) Vertical leaf; (E) Deep-green leaf; (F) Light-green leaf; (G) Yellow margin; (H) Spotted leaf. Bars=5 cm. MNU see Table 1.
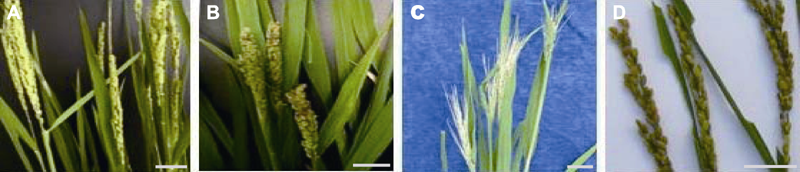
图3 辽盐6号水稻生殖细胞经MNU处理所得M1-M3群体中的穗形与穗色突变性状 (A) 野生型穗; (B) 短穗; (C) 不育穗; (D) 泛红穗。Bars=5 cm。MNU同表1。
Figure 3 Mutant characters for panicle form and panicle color in M1-M3 populations obtained by the MNU treatments of germ cells of Liaoyan 6 rice cultivar (A) The wild type panicle; (B) Short panicle; (C) Sterile panicle; (D) Reddish panicle. Bars=5 cm. MNU see Table 1.

图4 辽盐6号水稻生殖细胞经MNU处理所得M1-M3群体中的颖形与颖色突变性状 (A) 野生型颖; (B) 有芒颖; (C) 紫黑颖; (D) 红棕颖。Bars=5 mm。MNU同表1。
Figure 4 Mutant characters for glume form and glume color in M1-M3 populations obtained by the MNU treatments of germ cells of Liaoyan 6 rice cultivar (A) The wild type glume; (B) Awning glume; (C) Purple-black glume; (D) Reddish-brown glume. Bars=5 mm. MNU see Table 1.

图5 辽盐6号水稻生殖细胞经MNU处理所得M1-M3群体中的种子突变性状 (A) 野生型种子; (B) 细长种子; (C) 皱纹胚乳; (D) 腹部凹陷胚乳; (E) 皱缩胚乳; (F) 蜡质胚乳; (G) 暗浊色胚乳; (H) 粉质胚乳; (I) 心白胚乳; (J) 周白胚乳; (K) 红褐色胚乳; (L) 绿色胚乳。Bars=5 mm。MNU同表1。
Figure 5 Mutant characters of seed in M1-M3 populations obtained by the MNU treatments of germ cells of Liaoyan 6 rice cultivar (A) The wild type seed; (B) Slender seed; (C) Wrinkled endosperm; (D) Abdomen-sunken endosperm; (E) Shrunken endosperm; (F) Waxy endosperm; (G) Dull endosperm; (H) Floury endosperm; (I) Core-white endosperm; (J) Periphery-white endosperm; (K) Reddish-brown endosperm; (L) Green endosperm. Bars=5 mm. MNU see Table 1.
| 1 | 淳雁, 李学勇 (2017). 水稻穗型的遗传调控研究进展. 植物学报 52, 19-29. |
| 2 | 郭丹, 施勇烽, 王惠梅, 张晓波, 宋莉欣, 徐霞, 贺彦, 郭梁, 吴建利 (2016). 一个水稻显性斑点叶突变体的鉴定和基因精细定位. 作物学报 42, 966-975. |
| 3 | 刘艺, 朱小品, 刘喜, 田云录, 刘世家, 王云龙, 张文伟, 江玲, 王益华, 万建民 (2018). 水稻胚乳粉质突变体flo9的表型分析和基因定位. 南京农业大学学报 41, 616-624. |
| 4 | 刘子文, 胡曼曼, 王致远, 张瑜竣, 谷晗, 游佳, 王益华, 江玲, 刘玲珑 (2018). 水稻心白突变体whc的理化性质和基因定位. 南京农业大学学报 41, 231-239. |
| 5 | 涂政军, 邹国兴, 黄李超, 陈龙, 代丽萍, 高易宏, 冷语佳, 朱丽, 张光恒, 胡江, 任德勇, 高振宇, 董国军, 陈光, 郭龙彪, 钱前, 曾大力 (2017). 水稻淡绿叶基因PGL11的鉴定与精细定位. 中国水稻科学 31, 489-499. |
| 6 | 王影, 李相敢, 邱丽娟 (2018). CRISPR/Cas9基因组定点编辑中脱靶现象的研究进展. 植物学报 53, 528-541. |
| 7 | 肖景华, 吴昌银, 袁猛, 王妮丽, 范优荣, 杨猛, 欧阳亦聃, 阮一骏, 张启发 (2015). 中国水稻功能基因组研究进展与展望. 科学通报 60, 1711-1722. |
| 8 | 谢佳, 张孝波, 陶怡然, 熊毓贞, 周倩, 孙莹, 杨正林, 钟秉强, 桑贤春 (2018). 水稻短穗小粒突变体sps1的鉴定与基因精细定位. 中国农业科学 51, 1617-1626. |
| 9 | 张敏娟, 李帅军, 陈琼琼, 景秀清, 陈坤明, 石春海, 李文强 (2018). 水稻矮化少蘖突变体dlt3的基因定位和蛋白质组学分析. 中国水稻科学 32, 529-537. |
| 10 | 周亭亭, 饶玉春, 任德勇 (2018). 水稻卷叶细胞学与分子机制研究进展. 植物学报 53, 848-855. |
| 11 | Cooke MS, Evans MD, Dizdaroglu M, Lunec J (2003). Oxidative DNA damage: mechanisms, mutation, and disease. FASEB J 17, 1195-1214. |
| 12 | Engelbergs J, Thomale J, Rajewsky MF (2000). Role of DNA repair in carcinogen-induced ras mutation. Mutat Res 450, 139-153. |
| 13 | Fukuda M, Kawagoe Y, Murakami T, Washida H, Sugino A, Nagamine A, Okita TW, Ogawa W, Kumamaru T (2016). The dual roles of the Golgi transport 1 (GOT1B): RNA localization to the cortical endoplasmic reticulum and the export of proglutelin and α-globulin from the cortical ER to the golgi. Plant Cell Physiol 57, 2380-2391. |
| 14 | Fukuda M, Satoh-Cruz M, Wen LY, Crofts AJ, Sugino A, Washida H, Okita TW, Ogawa M, Kawagoe Y, Maeshima M, Kumamaru T (2011). The small GTPase Rab5a is essential for intracellular transport of proglutelin from the golgi apparatus to the protein storage vacuole and endosomal membrane organization in developing rice endosperm. Plant Physiol 157, 632-644. |
| 15 | Fukuda M, Wen LY, Satoh-Cruz M, Kawagoe Y, Nagamura Y, Okita TW, Washida H, Sugino A, Ishino S, Ishino Y, Ogawa M, Sunada M, Ueda T, Kumamaru T (2013). A guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Rab5 proteins is essential for intracellular transport of the proglutelin from the golgi apparatus to the protein storage vacuole in rice endosperm. Plant Physiol 162, 663-674. |
| 16 | Goff SA, Ricke D, Lan TH, Presting G, Wang RL, Dunn M, Glazebrook J, Sessions A, Oeller P, Varma H, Hadley D, Hutchison D, Martin C, Katagiri F, Lange BM, Moughamer T, Xia Y, Budworth P, Zhong JP, Miguel T, Paszkowski U, Zhang SP, Colbert M, Sun WL, Chen LL, Cooper B, Park S, Wood TC, Mao L, Quail P, Wing R, Dean R, Yu Y, Zharkikh A, Shen R, Sahasrabudhe S, Thomas A, Cannings R, Gutin A, Pruss D, Reid J, Tavtigian S, Mitchell J, Eldredge G, Scholl T, Miller RM, Bhatnagar S, Adey N, Rubano T, Tusneem N, Robinson R, Feldhaus J, Macalma T, Oliphant A, Briggs S (2002). A draft sequence of the rice genome ( Oryza sativa L. ssp. japonica). Science 296, 92-100. |
| 17 | Itoh JI, Nonomura KI, Ikeda K, Yamaki S, Inukai Y, Yamagishi H, Kitano H, Nagato Y (2005). Rice plant development: from zygote to spikelet. Plant Cell Physiol 46, 23-47. |
| 18 | Jin S, Zong Y, Gao Q, Zhu ZX, Wang YP, Qin P, Liang CZ, Wang DW, Qiu JL, Zhang F, Gao CX (2019). Cytosine, but not adenine, base editors induce genome-wide off- target mutations in rice. Science 364, 292-295. |
| 19 | Kumamaru T, Uemura Y, Inoue Y, Takemoto Y, Siddiqui SU, Ogawa M, Hara-Nishimura I, Satoh H (2010). Vacuolar processing enzyme plays an essential role in the crystalline structure of glutelin in rice seed. Plant Cell Physiol 51, 38-46. |
| 20 | Mao YF, Yang XX, Zhou YT, Zhang ZJ, Botella JR, Zhu JK (2018). Manipulating plant RNA-silencing pathways to improve the gene editing efficiency of CRISPR/Cas9 systems. Genome Biol 19, 149. |
| 21 | Miura S, Crofts N, Saito Y, Hosaka Y, Oitome NF, Watanabe T, Kumamaru T, Fujita N (2018). Starch synthase IIa-deficient mutant rice line produces endosperm starch with lower gelatinization temperature than japonica rice cultivars. Front Plant Sci 9, 645. |
| 22 | Neale S (1976). Mutagenicity of nitrosamides and nitrosamidines in micro-organisms and plants. Mutat Res 32, 229-266. |
| 23 | Nishi A, Nakamura Y, Tanaka N, Satoh H (2001). Biochemical and genetic analysis of the effects of amylose- extender mutation in rice endosperm. Plant Physiol 127, 459-472. |
| 24 | Qu LQ, Wei XL, Satoh H, Kumamaru T, Ogawa M, Takaiwa F (2002). Inheritance of alleles for glutelin α-2 subunit genes in rice and identification of their corresponding cDNA clone. Theor Appl Genet 105, 1099-1108. |
| 25 | Qu LQ, Wei XL, Satoh H, Kumamaru T, Ogawa M, Takaiwa F (2003). Biochemical and molecular characterization of a rice glutelin allele for the GluA-1 gene. Theor Appl Genet 107, 20-25. |
| 26 | Satoh H, Matsusaka H, Kumamaru T (2010). Use of N-methyl-N-nitrosourea treatment of fertilized egg cells for saturation mutagenesis of rice. Breed Sci 60, 475-485. |
| 27 | Satoh H, Shibahara K, Tokunaga T, Nishi A, Tasaki M, Hwang SK, Okita TW, Kaneko N, Fujita N, Yoshida M, Hosaka Y, Sato A, Utsumi Y, Ohdan T, Nakamura Y (2008). Mutation of the plastidial α-glucan phosphorylase gene in rice affects the synthesis and structure of starch in the endosperm. Plant Cell 20, 1833-1849. |
| 28 | Shan QW, Wang YP, Li J, Zhang Y, Chen KL, Liang Z, Zhang K, Liu JX, Xi JJ, Qiu JL, Gao CX (2013). Targeted genome modification of crop plants using a CRISPR-Cas system. Nat Biotechnol 31, 686-688. |
| 29 | Suzuki T, Eiguchi M, Kumamaru T, Satoh H, Matsusaka H, Moriguchi K, Nagato Y, Kurata N (2008). MNUinduced mutant pools and high performance TILLING enable finding of any gene mutation in rice. Mol Genet Genomics 279, 213-223. |
| 30 | Swain CG, Scott CB (1953). Quantitative correlation of relative rates. Comparison of hydroxide ion with other nucleophilic reagents toward alkyl halides, esters, epoxides and acyl halides. J Am Chem Soc 75, 141-147. |
| 31 | Takemoto Y, Coughlan SJ, Okita TW, Satoh H, Ogawa M, Kumamaru T (2002). The rice mutant esp2 greatly accumulates the glutelin precursor and deletes the protein disulfide isomerase. Plant Physiol 128, 1212-1222. |
| 32 | Tian HD, Satoh H, Takemoto Y (2004). Inheritance of novel 57H mutations in rice and their effect on compartmentation of endosperm storage proteins. Int J Plant Sci 165, 537-544. |
| 33 | Wang NL, Long T, Yao W, Xiong LZ, Zhang QF, Wu CY (2013). Mutant resources for the functional analysis of the rice genome. Mol Plant 6, 596-604. |
| 34 | Wu JL, Wu CJ, Lei CL, Baraoidan M, Bordeos A, Madamba MRS, Ramos-Pamplona M, Mauleon R, Portugal A, Ulat VJ, Bruskiewich R, Wang GL, Leach J, Khush G, Leung H (2005). Chemical- and irradiation-induced mutants of indica rice IR64 for forward and reverse genetics. Plant Mol Biol 59, 85-97. |
| 36 | Yu J, Hu SN, Wang J, Wong GKS, Li SG, Liu B, Deng YJ, Dai L, Zhou Y, Zhang XQ, Cao ML, Liu J, Sun JD, Tang JB, Chen YJ, Huang XB, Lin W, Ye C, Tong W, Cong LJ, Geng JN, Han YJ, Li L, Li W, Hu GQ, Huang XG, Li WJ, Li J, Liu ZW, Li L, Liu JP, Qi QH, Liu JS, Li L, Li T, Wang XG, Lu H, Wu TT, Zhu M, Ni PX, Han H, Dong W, Ren XY, Feng XL, Cui P, Li XR, Wang H, Xu X, Zhai WX, Xu Z, Zhang JS, He SJ, Zhang JG, Xu JC, Zhang KL, Zheng XW, Dong JH, Zeng WY, Tao L, Ye J, Tan J, Ren XD, Chen XW, He J, Liu DF, Tian W, Tian CG, Xia HA, Bao QY, Li G, Gao H, Cao T, Wang J, Zhao WM, Li P, Chen W, Wang XD, Zhang Y, Hu JF, Wang J, Liu S, Yang J, Zhang GY, Xiong YQ, Li ZJ, Mao L, Zhou CS, Zhu Z, Chen RS, Hao BL, Zheng WM, Chen SY, Guo W, Li GJ, Liu SQ, Tao M, Wang J, Zhu LH, Yuan LP, Yang HM (2002). A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica). Science 296, 79-92. |
| [1] | 叶灿, 姚林波, 金莹, 高蓉, 谭琪, 李旭映, 张艳军, 陈析丰, 马伯军, 章薇, 张可伟. 水稻水杨酸代谢突变体高通量筛选方法的建立与应用[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | 赵凌, 管菊, 梁文化, 张勇, 路凯, 赵春芳, 李余生, 张亚东. 基于高密度Bin图谱的水稻苗期耐热性QTL定位[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 342-353. |
| [3] | 李新宇, 谷月, 徐非非, 包劲松. 水稻胚乳淀粉合成相关蛋白的翻译后修饰研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 256-270. |
| [4] | 李建国, 张怡, 张文君. 水稻根系铁膜形成及对磷吸收的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 132-143. |
| [5] | 姚瑞枫, 谢道昕. 水稻独脚金内酯信号感知的激活和终止[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 873-877. |
| [6] | 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 张伊诺, 郑佳兴, 朱超宇, 叶语涵, 王跃星, 商文楠, 傅正浩, 徐昕璇, 吴日成, 路梅, 王长春, 饶玉春. 水稻抗氧化性状遗传位点挖掘及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 738-751. |
| [7] | 黄佳慧, 杨惠敏, 陈欣雨, 朱超宇, 江亚楠, 胡程翔, 连锦瑾, 芦涛, 路梅, 张维林, 饶玉春. 水稻突变体pe-1对弱光胁迫的响应机制[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 574-584. |
| [8] | 周俭民. 收放自如的明星战车[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 343-346. |
| [9] | 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 朱哲楠, 张芷宁, 汪理海, 陈钧, 李三峰, 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 钟芊芊, 殷文晶, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻穗部性状QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 217-230. |
| [10] | 夏婧, 饶玉春, 曹丹芸, 王逸, 柳林昕, 徐雅婷, 牟望舒, 薛大伟. 水稻中乙烯生物合成关键酶OsACS和OsACO调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 291-301. |
| [11] | 朱宝, 赵江哲, 张可伟, 黄鹏. 水稻细胞分裂素氧化酶9参与调控水稻叶夹角发育[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 10-21. |
| [12] | 方妍力, 田传玉, 苏如意, 刘亚培, 王春连, 陈析丰, 郭威, 纪志远. 水稻抗细菌性条斑病基因挖掘与初定位[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 1-9. |
| [13] | 贾绮玮, 钟芊芊, 顾育嘉, 陆天麒, 李玮, 杨帅, 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 李三峰, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻茎秆细胞壁相关组分含量QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 882-892. |
| [14] | 戴若惠, 钱心妤, 孙静蕾, 芦涛, 贾绮玮, 陆天麒, 路梅, 饶玉春. 水稻叶色调控机制及相关基因研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 799-812. |
| [15] | 田传玉, 方妍力, 沈晴, 王宏杰, 陈析丰, 郭威, 赵开军, 王春连, 纪志远. 2019-2021年我国南方稻区白叶枯病菌的毒力与遗传多样性调查研究[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 743-749. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||