

植物学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (3): 279-286.DOI: 10.11983/CBB19239 cstr: 32102.14.CBB19239
管柳蓉1,2,刘祖培2,3,徐冉2,段朋根2,张国政2,3,于海跃2,3,李静2,3,罗越华1,*( ),李云海2,*(
),李云海2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2019-12-25
接受日期:2020-03-23
出版日期:2020-05-01
发布日期:2020-07-06
通讯作者:
罗越华,李云海
基金资助:
Liurong Guan1,2,Zupei Liu2,3,Ran Xu2,Penggen Duan2,Guozheng Zhang2,3,Haiyue Yu2,3,Jing Li2,3,Yuehua Luo1,*( ),Yunhai Li2,*(
),Yunhai Li2,*( )
)
Received:2019-12-25
Accepted:2020-03-23
Online:2020-05-01
Published:2020-07-06
Contact:
Yuehua Luo,Yunhai Li
摘要: 水稻(Oryza sativa)籽粒大小是影响其产量的关键农艺性状, 克隆并研究水稻籽粒大小相关基因对于提高水稻产量具有重要意义。为深入探究水稻籽粒大小的调控机制, 通过EMS诱变品种宽叶粳(KYJ), 分离了一系列水稻籽粒大小改变的突变体, 其中smg12表现为籽粒变小, 株高变矮, 一级枝梗数和二级枝梗数减少。遗传分析表明, 该小粒突变体受隐性单基因控制。细胞学分析显示, 该突变体颖壳纵向细胞长度显著变短, 表明SMG12主要影响细胞扩展。利用Mutmap方法对候选基因进行克隆, 筛选出SMG12的候选基因OsBRI1, 该基因编码油菜素内酯受体激酶。OsBRI1外显子上的第2 074个碱基发生了由C到T的置换, 产生非同义突变, 使得该位置编码的脯氨酸变为丝氨酸, 从而影响OsBRI1的功能。综上, 该研究鉴定了OsBRI1基因的1个新等位变异, 揭示了油菜素内酯途径调控水稻籽粒大小的细胞和分子基础。
管柳蓉, 刘祖培, 徐冉, 段朋根, 张国政, 于海跃, 李静, 罗越华, 李云海. 一个新的OsBRI1弱等位突变体的鉴定及其调控种子大小的功能研究. 植物学报, 2020, 55(3): 279-286.
Liurong Guan, Zupei Liu, Ran Xu, Penggen Duan, Guozheng Zhang, Haiyue Yu, Jing Li, Yuehua Luo, Yunhai Li. Identification of a New OsBRI1 Weak Allele and Analysis of its Function in Grain Size Control. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(3): 279-286.
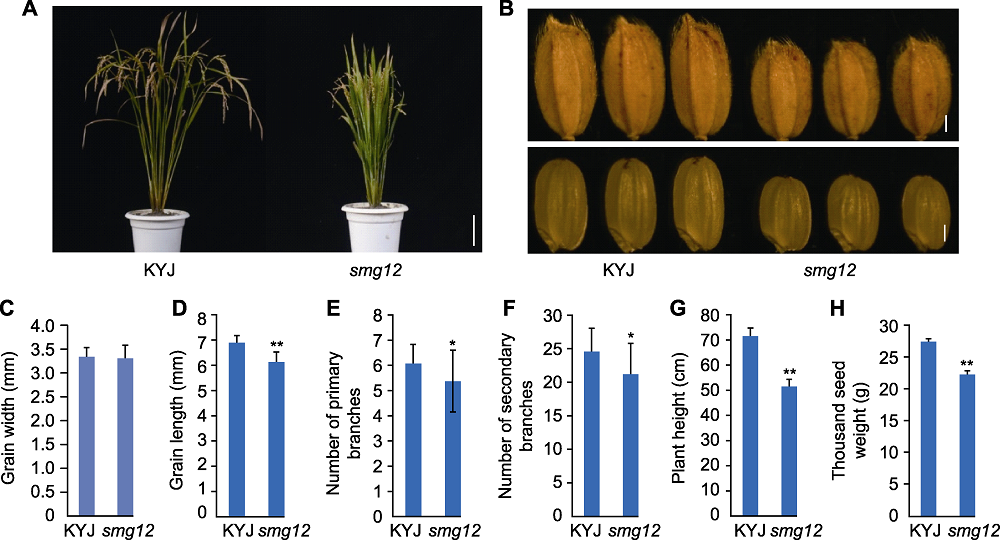
图1 水稻突变体smg12的表型分析 (A) KYJ (野生型)和smg12突变体表型(Bar=10 cm); (B) KYJ和smg12的籽粒(Bars=1 cm); (C) 粒宽; (D) 粒长; (E) 一级枝梗数; (F) 二级枝梗数; (G) 株高; (H) 千粒重。显著性分析采用t检验, * 表示差异显著(P<0.05), ** 表示差异极显著(P<0.01)。
Figure 1 Analysis of rice smg12 mutant phenotypes (A) KYJ (wild type) and smg12 mutant phenotype (Bar=10 cm); (B) Grains of KYJ and smg12 (Bars=1 cm); (C) Grain width; (D) Grain length; (E) Number of primary branches; (F) Number of secondary branches; (G) Plant height; (H) Thousand seed weight. Significance is determined using t-test, * indicates significant differences at P<0.05, ** indicates significant differences at P<0.01.
| Primer name | Primer sequence (5'→3') | DNA fragment length (bp) | Enzyme |
|---|---|---|---|
| smg12-1 | CTTTCTCGGCACTTTCCTTG | 154 | HphI |
| CTATGGTCACATGGTGGCGGTG |
表1 用于dCAPS分析的引物和酶
Table 1 Primer and enzyme for dCAPS analysis
| Primer name | Primer sequence (5'→3') | DNA fragment length (bp) | Enzyme |
|---|---|---|---|
| smg12-1 | CTTTCTCGGCACTTTCCTTG | 154 | HphI |
| CTATGGTCACATGGTGGCGGTG |
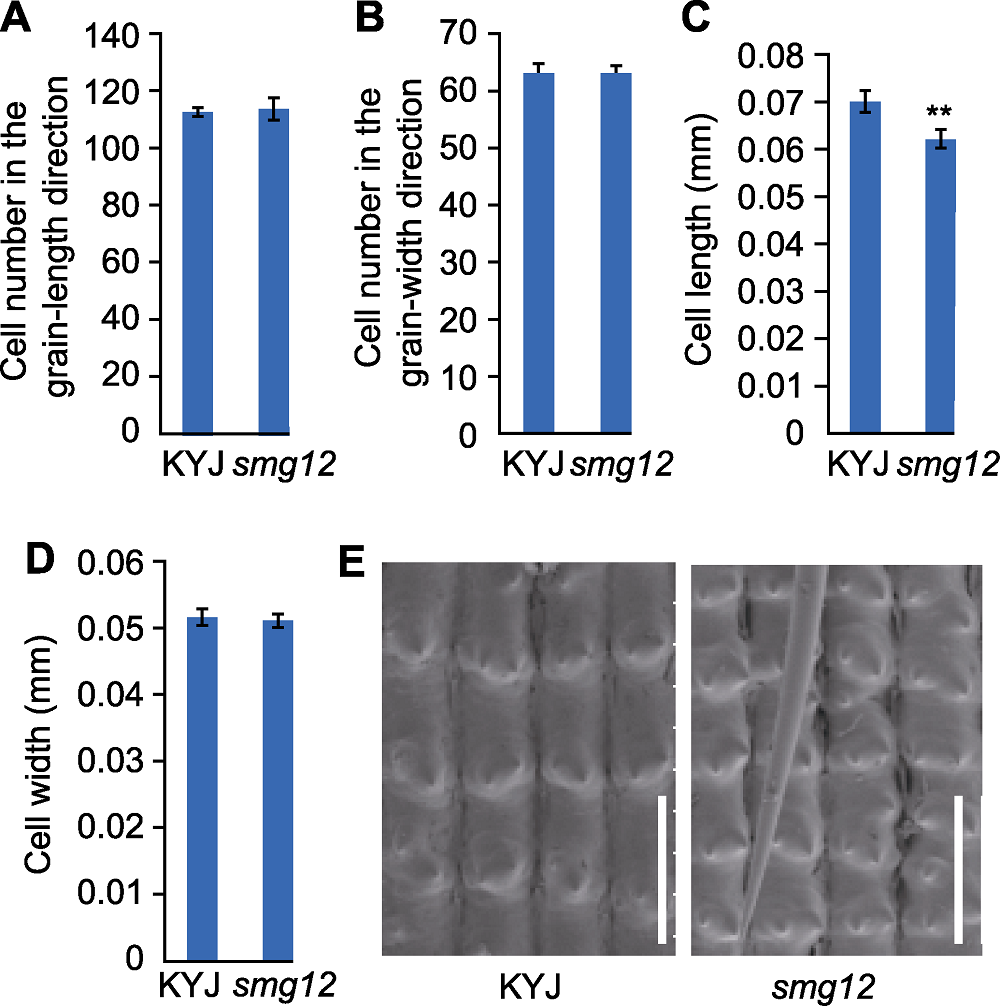
图2 SMG12调控水稻颖壳细胞大小 (A) 颖壳纵向细胞数目; (B) 颖壳横向细胞数目; (C) 颖壳单个细胞纵向长度; (D) 颖壳单个细胞横向宽度; (E) 细胞学分析图(Bars=0.1 mm)。** 表示突变体与野生型之间差异极显著(P< 0.01)。
Figure 2 SMG12 regulates cell size in grain hulls of rice (A) Outer epidermal cell number in the grain-length direction of the glume; (B) Outer epidermal cell number in the grain-width direction of the glume; (C) The longitudinal length of a single cell in the glume; (D) Transverse width of a single cell in the glume; (E) Cytological analysis diagram (Bars= 0.1 mm). ** indicates extremely significant difference between the mutant and the wild type (P<0.01).
| Hybrid combinations | Phenotype of F1 | F2 generation | χ23:1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wild-phenotypic plant number | Mutant-phenotypic plant number | Total number | |||
| smg12/KYJ | Wild type | 168 | 52 | 220 | 0.151 |
表2 水稻突变体smg12的遗传分析
Table 2 Genetic analysis of the rice mutant smg12
| Hybrid combinations | Phenotype of F1 | F2 generation | χ23:1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wild-phenotypic plant number | Mutant-phenotypic plant number | Total number | |||
| smg12/KYJ | Wild type | 168 | 52 | 220 | 0.151 |
| Chromosomal position | Physical location (bp) | Genotype (KYJ/smg12) | Gene location | Gene locus name | Frequency of sequencing (KYJ/smg12) | Mutation type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chr. 1 | 15686971 | G/A | Upstream of the gene | LOC_Os01g28040 | 0/6 | / |
| Chr. 1 | 27750517 | G/A | In the gene compartment | LOC_Os01g48420; LOC_Os01g48430 | 0/12 | / |
| Chr. 1 | 28534819 | G/A | Upstream and downstream of the gene | LOC_Os01g49630; LOC_Os01g49614 | 0/14 | / |
| Chr. 1 | 29397508 | G/A | In the gene compartment | LOC_Os01g51140; LOC_Os01g51154 | 0/12 | / |
| Chr. 1 | 29788896 | G/A | Upstream of the gene | LOC_Os01g51810 | 0/17 | / |
| Chr. 1 | 29929259 | G/A | Exon | LOC_Os01g52050 | 0/19 | Changes in amino acids |
| Chr. 1 | 33892012 | T/A | Upstream of the gene | LOC_Os01g58620 | 0/1 | / |
| Chr. 1 | 39503252 | G/A | Downstream of the gene | LOC_Os01g67980 | 0/11 | / |
| Chr. 1 | 30392222 | G/A | Upstream of the gene | LOC_Os01g52840; LOC_Os01g52851 | 0/5 | / |
| Chr. 1 | 33745383 | G/A | Intron | LOC_Os01g58400 | 0/8 | / |
| Chr. 3 | 19627588 | C/A | Upstream of the gene | LOC_Os03g35390 | 0/6 | / |
| Chr. 6 | 17710551 | G/A | Intron | LOC_Os06g30610 | 0/8 | / |
表3 smg12突变体的候选SNPs分析
Table 3 Analysis of the candidate SNPs for the smg12 mutant
| Chromosomal position | Physical location (bp) | Genotype (KYJ/smg12) | Gene location | Gene locus name | Frequency of sequencing (KYJ/smg12) | Mutation type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chr. 1 | 15686971 | G/A | Upstream of the gene | LOC_Os01g28040 | 0/6 | / |
| Chr. 1 | 27750517 | G/A | In the gene compartment | LOC_Os01g48420; LOC_Os01g48430 | 0/12 | / |
| Chr. 1 | 28534819 | G/A | Upstream and downstream of the gene | LOC_Os01g49630; LOC_Os01g49614 | 0/14 | / |
| Chr. 1 | 29397508 | G/A | In the gene compartment | LOC_Os01g51140; LOC_Os01g51154 | 0/12 | / |
| Chr. 1 | 29788896 | G/A | Upstream of the gene | LOC_Os01g51810 | 0/17 | / |
| Chr. 1 | 29929259 | G/A | Exon | LOC_Os01g52050 | 0/19 | Changes in amino acids |
| Chr. 1 | 33892012 | T/A | Upstream of the gene | LOC_Os01g58620 | 0/1 | / |
| Chr. 1 | 39503252 | G/A | Downstream of the gene | LOC_Os01g67980 | 0/11 | / |
| Chr. 1 | 30392222 | G/A | Upstream of the gene | LOC_Os01g52840; LOC_Os01g52851 | 0/5 | / |
| Chr. 1 | 33745383 | G/A | Intron | LOC_Os01g58400 | 0/8 | / |
| Chr. 3 | 19627588 | C/A | Upstream of the gene | LOC_Os03g35390 | 0/6 | / |
| Chr. 6 | 17710551 | G/A | Intron | LOC_Os06g30610 | 0/8 | / |
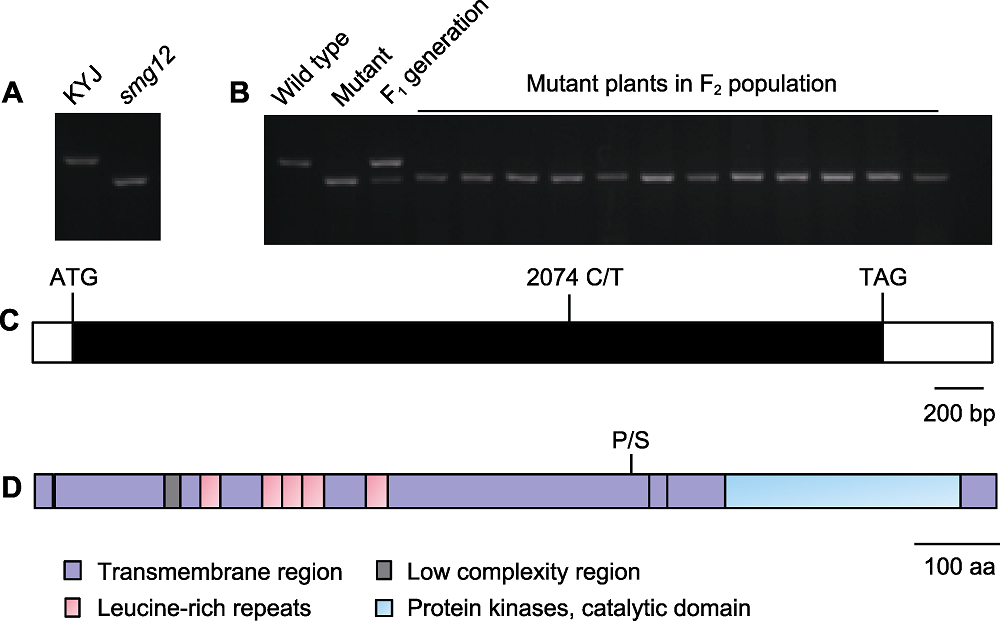
图3 候选基因的鉴定 (A) smg12突变的dCAPS标记验证; (B) 候选基因LOC_Os01g52050的群体连锁分析; (C) LOC_Os01g52050的基因结构图, 开放的方框表示基因5'和3'端的未翻译区, 封闭的方框表示编码区, 且图中标注起始密码子(ATG)和终止密码子(TAG)以及LOC_Os01g52050中的突变位点(C/T); (D) LOC_Os01g52050的蛋白结构域。P/S表示LOC_Os01g52050编码蛋白结构域中的突变位点。
Figure 3 Identification of candidate genes (A) The dCAPS marker was developed to detect the smg12 mutation; (B) Population linkage analysis of the candidate gene LOC_Os01g52050; (C) The LOC_Os01g52050 gene structure, open boxes show the 5' and 3' untranslated regions, the closed box shows the coding sequence, and the start codon (ATG), the stop codon (TAG) and the LOC_Os01g52050 mutation site (C/T) are indicated; (D) Schematic of the LOC_Os01g52050 protein. P/S indicated the LOC_Os01g52050 mutation site.
| [1] | 宫李辉, 高振宇, 马伯军, 钱前 (2011). 水稻粒形遗传的研究进展. 植物学报 46, 597-605. |
| [2] | 侯雷平, 李梅兰 (2001). 油菜素内酯(BR)促进植物生长机理研究进展. 植物学通报 18, 560-566. |
| [3] |
Abe A, Kosugi S, Yoshida K, Natsume S, Takagi H, Kanzaki H, Matsumura H, Yoshida K, Mitsuoka C, Tamiru M, Innan H, Canno L, Kamoun S, Terauchi R (2012). Genome sequencing reveals agronomically important loci in rice using Mutmap. Nat Biotechnol 30, 174-178.
URL PMID |
| [4] |
Fan CC, Xing YZ, Mao HL, Lu TT, Han B, Xu CG, Li XH, Zhang QF (2006). GS3, a major QTL for grain length and weight and minor QTL for grain width and thickness in rice, encodes a putative transmembrane protein. Theor Appl Genet 112, 1164-1171.
URL PMID |
| [5] | James MG, Denyer K, Myers AM (2003). Starch synthesis in the cereal endosperm. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6, 215-222. |
| [6] | Li N, Xu R, Duan PG, Li YH (2018). Control of grain size in rice. Plant Reprod 31, 237-251. |
| [7] |
Li N, Xu R, Li YH (2019). Molecular networks of seed size control in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 70, 435-463.
URL PMID |
| [8] |
Liu LC, Tong HN, Xiao YH, Che RH, Xu F, Hu B, Liang CZ, Chu JF, Li JY, Chu CC (2015a). Activation of Big Grain1 significantly improves grain size by regulating auxin transport in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112, 11102-11107.
URL PMID |
| [9] |
Liu SY, Hua L, Dong SJ, Chen HQ, Zhu XD, Jiang JE, Zhang F, Li YH, Fang XH, Chen F (2015b). OsMAPK6, a mitogen-activated protein kinase, influences rice grain size and biomass production. Plant J 84, 672-681.
DOI URL PMID |
| [10] | Mao HL, Sun SY, Yao JL, Wang CR, Yu SB, Xu CG, Li XH, Zhang QF (2010). Linking differential domain functions of the GS3 protein to natural variation of grain size in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107, 19579-19584. |
| [11] |
Meng XZ, Zhang SQ (2013). MAPK cascades in plant disease resistance signaling. Annu Rev Phytopathol 51, 245-266.
URL PMID |
| [12] |
Miura K, Ashikari M, Matsuoka M (2011). The role of QTLs in the breeding of high-yielding rice. Trends Plant Sci 16, 319-326.
URL PMID |
| [13] | Morinaka Y, Sakamoto T, Inukai Y, Agetsuma M, Kitano H, Ashikari M, Matsuoka M (2006). Morphological alteration caused by brassinosteroid insensitivity increases the biomass and grain production of rice. Plant Physiol 141, 924-931. |
| [14] |
Nakamura A, Fujioka S, Sunohara H, Kamiya N, Hong Z, Inukai Y, Miura K, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Ueguchi- Tanaka M, Hasegawa Y, Kitano H, Matsuoka M (2006). The role of OsBRI1 and its homologous genes, OsBRL1 and OsBRL3, in rice. Plant Physiol 140, 580-590.
DOI URL PMID |
| [15] |
Sakamoto T, Matsuoka M (2008). Identifying and exploiting grain yield genes in rice. Curr Opin Plant Biol 11, 209-214.
DOI URL PMID |
| [16] |
Shomura A, Izawa T, Ebana K, Ebitani T, Kanegae H, Konishi S, Yano M (2008). Deletion in a gene associated with grain size increased yields during rice domestication. Nat Genet 40, 1023-1028.
URL PMID |
| [17] | Si LZ, Chen JY, Huang XH, Gong H, Luo JH, Hou QQ, Zhou TY, Lu TT, Zhu JJ, Shangguan YY, Chen EW, Gong CX, Zhao Q, Jing YF, Zhao Y, Li Y, Cui LL, Fan DL, Lu YQ, Weng QJ, Wang YC, Zhan QL, Liu KY, Wei XH, An K, An G, Han B (2016). OsSPL13 controls grain size in cultivated rice. Nat Genet 48, 447-456. |
| [18] |
Song XJ, Huang W, Shi M, Zhu MZ, Lin HX (2007). A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nat Genet 39, 623-630.
DOI URL PMID |
| [19] |
Takagi H, Tamiru M, Abe A, Yoshida K, Uemura A, Yaegashi H, Obara T, Oikawa K, Utsushi H, Kanzaki E, Mitsuoka C, Natsume S, Kosugi S, Kanzaki H, Matsumura H, Urasaki N, Kamoun S, Terauchi R (2015). Mutmap accelerates breeding of a salt-tolerant rice cultivar. Nat Biotechnol 33, 445-449.
URL PMID |
| [20] |
Tanabe S, Ashikari M, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Yano M, Yoshimura A, Kotano H, Matsuoka M, Fujisawa Y, Kato H, Lwasaki Y (2005). A novel cytochrome P450 is implicated in brassinosteroid biosynthesis via the characterization of a rice dwarf mutant, dwarf11, with reduced seed length. Plant Cell 17, 776-790.
DOI URL PMID |
| [21] |
Tanaka A, Nakagawa H, Tomita C, Shimatani Z, Ohtake M, Nomura T, Jiang CJ, Dubozet JG, Kikuchi S, Sekimoto H, Yokota T, Asami T, Kamakura T, Mori M (2009). BRASSINOSTEROID UPREGULATED1, encoding a helix-loop-helix protein, is a novel gene involved in brassinosteroid signaling and controls bending of the lamina joint in rice. Plant Physiol 151, 669-680.
DOI URL PMID |
| [22] |
Tong HN, Liu LC, Jin Y, Du L, Yin YH, Qian Q, Zhu LH, Chu CC (2012). DWARF AND LOW-TILLERING acts as a direct downstream target of a GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase to mediate brassinosteroid responses in rice. Plant Cell 24, 2562-2577.
URL PMID |
| [23] |
Wang SK, Wu K, Yuan QB, Liu XY, Liu ZB, Lin XY, Zeng RZ, Zhu HT, Dong GJ, Qian Q, Zhang GQ, Fu XD (2012). Control of grain size, shape and quality by OsSPL16 in rice. Nat Genet 44, 950-954.
DOI URL PMID |
| [24] | Xing YZ, Zhang QF (2010). Genetic and molecular bases of rice yield. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61, 421-442. |
| [25] | Xu R, Duan PG, Yu HY, Zhou ZK, Zhang BL, Wang RC, Li J, Zhang GZ, Zhuang SS, Lyu J, Li N, Chai TY, Tian ZX, Yao SG, Li YH (2018a). Control of grain size and weight by the OsMKKK10-OsMKK4-OsMAPK6 signaling pathway in rice. Mol Plant 11, 860-873. |
| [26] |
Xu R, Yu HY, Wang JM, Duan PG, Zhang BL, Li J, Li Y, Xu JS, Lyu J, Li N, Chai TY, Li YH (2018b). A mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase influences grain size and weight in rice. Plant J 95, 937-946.
DOI URL PMID |
| [27] | Zhang C, Bai MY, Chong K (2014). Brassinosteroid-mediated regulation of agronomic traits in rice. Plant Cell Rep 33, 683-696. |
| [28] |
Zhao JF, Wu CX, Yuan SJ, Yin L, Sun W, Zhao QL, Zhao BH, Li XY (2013). Kinase activity of OsBRI1 is essential for brassinosteroids to regulate rice growth and development. Plant Sci 199-200, 113-120.
DOI URL PMID |
| [29] |
Zhou SR, Yin LL, Xue HW (2013). Functional genomics based understanding of rice endosperm development. Curr Opin Plant Biol 16, 236-246.
URL PMID |
| [30] | Zuo JR, Li JY (2014). Molecular genetic dissection of quantitative trait loci regulating rice grain size. Annu Rev Genet 48, 99-118. |
| [1] | 叶灿, 姚林波, 金莹, 高蓉, 谭琪, 李旭映, 张艳军, 陈析丰, 马伯军, 章薇, 张可伟. 水稻水杨酸代谢突变体高通量筛选方法的建立与应用[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | 赵凌, 管菊, 梁文化, 张勇, 路凯, 赵春芳, 李余生, 张亚东. 基于高密度Bin图谱的水稻苗期耐热性QTL定位[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 342-353. |
| [3] | 李新宇, 谷月, 徐非非, 包劲松. 水稻胚乳淀粉合成相关蛋白的翻译后修饰研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 256-270. |
| [4] | 李建国, 张怡, 张文君. 水稻根系铁膜形成及对磷吸收的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 132-143. |
| [5] | 姚瑞枫, 谢道昕. 水稻独脚金内酯信号感知的激活和终止[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 873-877. |
| [6] | 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 张伊诺, 郑佳兴, 朱超宇, 叶语涵, 王跃星, 商文楠, 傅正浩, 徐昕璇, 吴日成, 路梅, 王长春, 饶玉春. 水稻抗氧化性状遗传位点挖掘及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 738-751. |
| [7] | 黄佳慧, 杨惠敏, 陈欣雨, 朱超宇, 江亚楠, 胡程翔, 连锦瑾, 芦涛, 路梅, 张维林, 饶玉春. 水稻突变体pe-1对弱光胁迫的响应机制[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 574-584. |
| [8] | 周俭民. 收放自如的明星战车[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 343-346. |
| [9] | 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 朱哲楠, 张芷宁, 汪理海, 陈钧, 李三峰, 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 钟芊芊, 殷文晶, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻穗部性状QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 217-230. |
| [10] | 夏婧, 饶玉春, 曹丹芸, 王逸, 柳林昕, 徐雅婷, 牟望舒, 薛大伟. 水稻中乙烯生物合成关键酶OsACS和OsACO调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 291-301. |
| [11] | 方妍力, 田传玉, 苏如意, 刘亚培, 王春连, 陈析丰, 郭威, 纪志远. 水稻抗细菌性条斑病基因挖掘与初定位[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 1-9. |
| [12] | 朱宝, 赵江哲, 张可伟, 黄鹏. 水稻细胞分裂素氧化酶9参与调控水稻叶夹角发育[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 10-21. |
| [13] | 贾绮玮, 钟芊芊, 顾育嘉, 陆天麒, 李玮, 杨帅, 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 李三峰, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻茎秆细胞壁相关组分含量QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 882-892. |
| [14] | 戴若惠, 钱心妤, 孙静蕾, 芦涛, 贾绮玮, 陆天麒, 路梅, 饶玉春. 水稻叶色调控机制及相关基因研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 799-812. |
| [15] | 田传玉, 方妍力, 沈晴, 王宏杰, 陈析丰, 郭威, 赵开军, 王春连, 纪志远. 2019-2021年我国南方稻区白叶枯病菌的毒力与遗传多样性调查研究[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 743-749. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||