

植物学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (3): 296-314.DOI: 10.11983/CBB20168 cstr: 32102.14.CBB20168
收稿日期:2020-10-12
接受日期:2021-04-22
出版日期:2021-05-01
发布日期:2021-04-30
通讯作者:
李霞
作者简介:*E-mail: jspplx@jaas.ac.cn基金资助:
Jiaxin Li1,2, Xia Li1,2,3,*( ), Yinfeng Xie1
), Yinfeng Xie1
Received:2020-10-12
Accepted:2021-04-22
Online:2021-05-01
Published:2021-04-30
Contact:
Xia Li
摘要: 为揭示海藻糖(Tre)调控转玉米(Zea mays) C4型PEPC基因水稻(Oryza sativa) (PC)的耐旱性机制, 以PC及其野生型Kitaake (WT)为材料, 通过水培试验, 研究了Tre和12% (m/v)聚乙二醇(PEG)单独或联合处理对水稻生理生化特性的影响。结果表明, Tre处理可促进PC和WT水稻幼苗生长, 缓解干旱逆境导致的植株生长抑制, 但对PC的效应更显著。与DS处理相比, Tre+DS联合处理可维持功能叶较高的相对含水量、光化学效率和抗氧化酶活性。在DS处理下, 与WT相比, 外施Tre可使PC的内源Tre和蔗糖含量显著增加, 而葡萄糖含量显著降低, Tre代谢和SnRK1s相关基因表达量增加; 施用Tre也显著促进了ABA合成、信号转导与干旱响应基因的表达, 和维持较稳定的光合能力, 从而使PC表现更强的耐旱性。
李佳馨, 李霞, 谢寅峰. 外源海藻糖增强高表达转玉米C4型PEPC水稻耐旱性的机制. 植物学报, 2021, 56(3): 296-314.
Jiaxin Li, Xia Li, Yinfeng Xie. Mechanism on Drought Tolerance Enhanced by Exogenous Trehalose in C4-PEPC Rice. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(3): 296-314.
| Gene | Forward primer (5′-3′) | Reverse primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Act | CCCTCTTTCATCGGTATGGA | TTGATCTTCATGCTGCTTGG |
| OsTPP1 | CAAATGGATTTGAGCAATAGC | TCACACTGAGTGCTTCTTCCA |
| OsTPP2 | ATGGATTTGAAGACAAGCAAC | TTAAGTGGATTCCTCCTTCCA |
| OsTPP3 | ATGACGAACCACGCCGGC | CTACTTGCCAATCAGCCCTTT |
| OsTPP7 | CCTTCATGAGCGAGACGATG | TCACGAACTCGAACACCTTG |
| OsTre1 | TTGGTACCCCTTACTCCGGCCGATTCA | AAGAGCTCCTGCCTAGCCTAGCCACAT |
| OsTPS1 | AGTTATTATCTGGAAGGAGC | TCAAGAACCTCCTGAATGCC |
| OsTPS2 | ACAAAGATGGGATGAAAGTG | CAGGATTCACAAACAGATTC |
| OsTPS8 | TGAAGAGATAAAATGGCGTG | GAAAAGGTGAATGAATCTGC |
| OsSnR1a | AACCAGAGGTAACAGGCAGG | CATCTGTCAAGGAATGCAGG |
| OsSnRK24 | CGTGTTGGCTTCAGTGAAT | CCTTCTCTATCTAAGGGCCG |
| OsSAPK8 | ATAGATGATAATGTCCAGCGTGAG | GTTCCTACAGTGGATTTTGGTTG |
| OsSAPK9 | CACAGCAACGCCGTCTCC | CACACTTCCACCGCTACCAA |
| OsSAPK10 | TGCTGATGTGTGGTCGTGTG | TGCTGGTATGGTCGCCTCT |
| OsABA8ox2 | CTACTGCTGATGGTGGCTGA | CCCATGGCCTTTGCTTTAT |
| OsABA8ox3 | AGTACAGCCCATTCCCTGTG | ACGCCTAATCAAACCATTGC |
| OsNCED3 | CCCCTCCCAAACCATCCAAACCGA | TGTGAGCATATCCTGGCGTCGTGA |
| OsNCED4 | TCCATCTCCTTCTCCCTCCTCCCA | CCTCGCACCCTGCTTGATCTTGCC |
| OsbZIP23 | CTCTGATCCCTCGTTGCGTTA | CAACACCCCAGCACCAAACT |
| OsMYB2 | GGGCTGAAACGCACAGGCAAGA | GGGCTGAAACGCACAGGCAAGA |
| OsRab16b | CAACAACCACCAGCAGCA | GATCTTGTCCATGAATCCC |
| OsRab21 | AGCAGCAGCATGCCATG | TGGTGCCGGTGGTCAT |
| OsLEA3 | TTCCCACCAGGACCAGGCTA | GTCGCCTCCTTGGTATCCT |
| OsNAC6 | CGCTGTACGAGAAGGAG | ACTCGTGCATGATCCAGTTG |
| C4-PEPC | GTACCGCGAGTGGCCCGAGG | CGTCCATGAGCTTGCGCCAC |
| Osppc2a | CAGCTACTCATGCTTAACGC | GCACAGACTACAGCCTGTAC |
表1 qRT-PCR的基因和引物
Table 1 Genes and primers for qRT-PCR
| Gene | Forward primer (5′-3′) | Reverse primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Act | CCCTCTTTCATCGGTATGGA | TTGATCTTCATGCTGCTTGG |
| OsTPP1 | CAAATGGATTTGAGCAATAGC | TCACACTGAGTGCTTCTTCCA |
| OsTPP2 | ATGGATTTGAAGACAAGCAAC | TTAAGTGGATTCCTCCTTCCA |
| OsTPP3 | ATGACGAACCACGCCGGC | CTACTTGCCAATCAGCCCTTT |
| OsTPP7 | CCTTCATGAGCGAGACGATG | TCACGAACTCGAACACCTTG |
| OsTre1 | TTGGTACCCCTTACTCCGGCCGATTCA | AAGAGCTCCTGCCTAGCCTAGCCACAT |
| OsTPS1 | AGTTATTATCTGGAAGGAGC | TCAAGAACCTCCTGAATGCC |
| OsTPS2 | ACAAAGATGGGATGAAAGTG | CAGGATTCACAAACAGATTC |
| OsTPS8 | TGAAGAGATAAAATGGCGTG | GAAAAGGTGAATGAATCTGC |
| OsSnR1a | AACCAGAGGTAACAGGCAGG | CATCTGTCAAGGAATGCAGG |
| OsSnRK24 | CGTGTTGGCTTCAGTGAAT | CCTTCTCTATCTAAGGGCCG |
| OsSAPK8 | ATAGATGATAATGTCCAGCGTGAG | GTTCCTACAGTGGATTTTGGTTG |
| OsSAPK9 | CACAGCAACGCCGTCTCC | CACACTTCCACCGCTACCAA |
| OsSAPK10 | TGCTGATGTGTGGTCGTGTG | TGCTGGTATGGTCGCCTCT |
| OsABA8ox2 | CTACTGCTGATGGTGGCTGA | CCCATGGCCTTTGCTTTAT |
| OsABA8ox3 | AGTACAGCCCATTCCCTGTG | ACGCCTAATCAAACCATTGC |
| OsNCED3 | CCCCTCCCAAACCATCCAAACCGA | TGTGAGCATATCCTGGCGTCGTGA |
| OsNCED4 | TCCATCTCCTTCTCCCTCCTCCCA | CCTCGCACCCTGCTTGATCTTGCC |
| OsbZIP23 | CTCTGATCCCTCGTTGCGTTA | CAACACCCCAGCACCAAACT |
| OsMYB2 | GGGCTGAAACGCACAGGCAAGA | GGGCTGAAACGCACAGGCAAGA |
| OsRab16b | CAACAACCACCAGCAGCA | GATCTTGTCCATGAATCCC |
| OsRab21 | AGCAGCAGCATGCCATG | TGGTGCCGGTGGTCAT |
| OsLEA3 | TTCCCACCAGGACCAGGCTA | GTCGCCTCCTTGGTATCCT |
| OsNAC6 | CGCTGTACGAGAAGGAG | ACTCGTGCATGATCCAGTTG |
| C4-PEPC | GTACCGCGAGTGGCCCGAGG | CGTCCATGAGCTTGCGCCAC |
| Osppc2a | CAGCTACTCATGCTTAACGC | GCACAGACTACAGCCTGTAC |
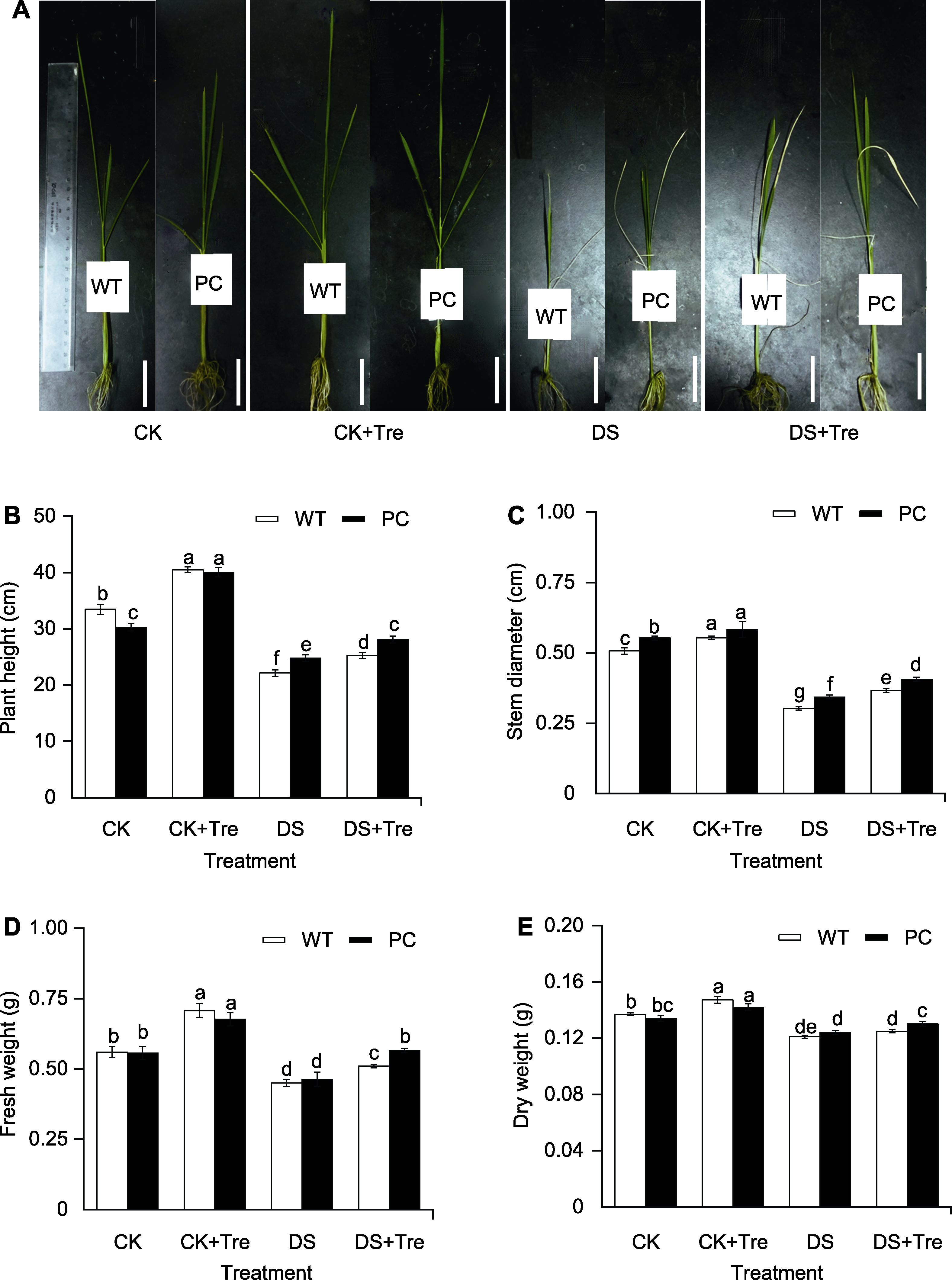
图1 海藻糖处理缓解干旱胁迫对水稻的生长抑制 模拟干旱处理6天后的植株表型(A)、株高(B)、茎粗(C)、鲜重(D)和干重(E)。CK: 正常灌溉; CK+Tre: 正常灌溉+0.5 mmol?L-1海藻糖; DS: 模拟干旱胁迫; DS+Tre: 模拟干旱胁迫+0.5 mmol?L-1海藻糖。图中数值代表来自3个生物学重复的平均值±标准差 (n=9)。不同小写字母的柱值表示差异显著(P<0.05) (Student-Neuman-Keuls)。Bars=1 cm
Figure 1 Trehalose treatments alleviate the growth inhibition of rice under drought stress Plant phenotype (A), plant height (B), stem diameter (C), fresh weight (D) and dry weight (E) after 6 days of simulated drought treatment. CK: Irrigation; CK+Tre: Irrigation and 0.5 mmol?L-1 trehalose; DS: Simulated drought stress; DS+Tre: Simulated drought stress and 0.5 mmol?L-1 trehalose. Values represent means±SD (n=9) from three biological replicates. Bars labeled with different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05) (Student-Neuman-Keuls). Bars=1 cm
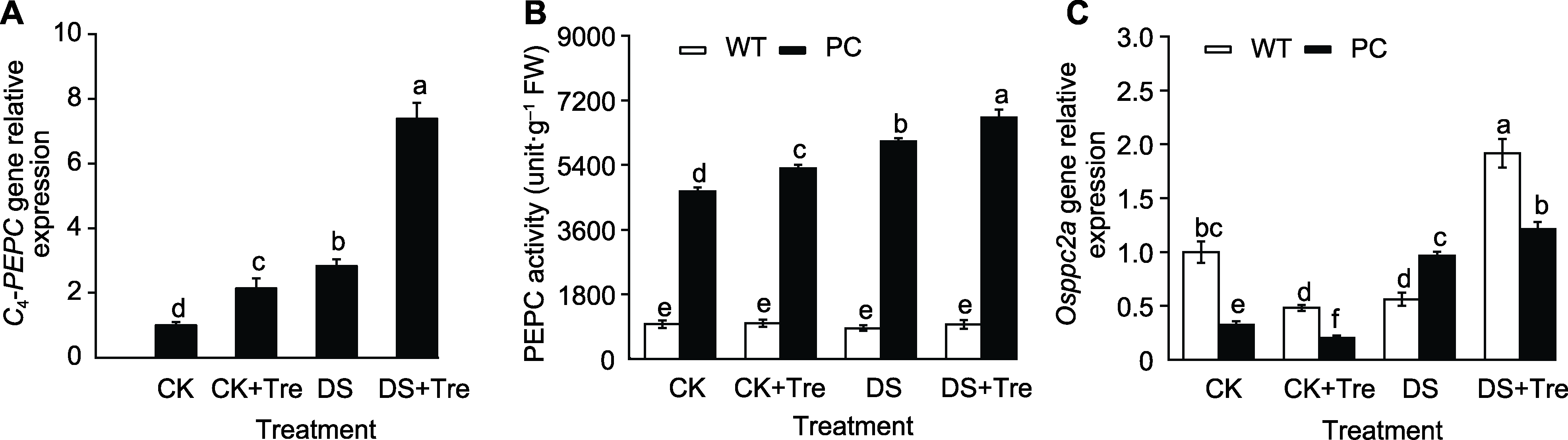
图2 海藻糖处理提高干旱胁迫下水稻叶片内PEPC的转录及翻译水平 模拟干旱处理2小时后C4-PEPC基因的相对表达量(A)、磷酸烯醇式丙酮酸羧化酶(PEPC)活性(B)和Osppc2a基因的相对表达量(C)。缩写同图1。图中数值代表来自3个生物学重复的平均值±标准差(n=6)。不同小写字母的柱值表示差异显著(P<0.05) (Student-Neuman-Keuls)。
Figure 2 Trehalose treatments increase PEPC transcription and translation in rice leaves under drought stress C4-PEPC expression (A), phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC) activity (B) and Osppc2a expression (C) after 2 hours of simulated drought treatment. Abbreviations are the same as those given in Figure 1. Values represent means±SD (n=6) from three biological replicates. Bars labeled with different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05) (Student-Neuman-Keuls).
| Index | WT | PC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | CK+Tre | DS | DS+Tre | CK | CK+Tre | DS | DS+Tre | |
| RWC (%) | 91.09 b | 92.02 ab | 78.05 e | 89.21 c | 89.68 c | 88.30 c | 80.81 d | 93.00 a |
| MDA (nmol·mg-1 prot) | 2.26 d | 2.22 d | 3.39 a | 2.52 c | 2.40 c | 2.18 c | 3.03 b | 1.89 e |
| H2O2 (μmol·g-1 FW) | 6.87 f | 24.84 a | 14.59 c | 5.09 g | 8.01 e | 21.68 b | 11.96 d | 3.63 h |
| SOD (U·mg-1 prot) | 1087.99 d | 1063.79 e | 1101.66 c | 1126.52 b | 1083.80 d | 1059.65 e | 1102.99 c | 1140.24 a |
| CAT (U·mg-1 prot) | 15.74 e | 16.99 c | 16.63 d | 16.65 d | 13.51 f | 18.39 a | 16.25 d | 17.74 b |
| GR (nmol·g-1 prot) | 1.49 e | 2.46 c | 2.17 d | 0.96 g | 1.22 f | 3.26 b | 3.69 a | 2.00 d |
| APX (U·g-1 FW) | 5.26 c | 6.55 b | 6.59 b | 10.14 a | 2.70 f | 4.33 d | 2.32 g | 3.74 e |
表2 海藻糖处理调节干旱胁迫下水稻叶片的氧化损伤
Table 2 Trehalose treatments regulate the oxidative damage of rice leaves under drought stress
| Index | WT | PC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | CK+Tre | DS | DS+Tre | CK | CK+Tre | DS | DS+Tre | |
| RWC (%) | 91.09 b | 92.02 ab | 78.05 e | 89.21 c | 89.68 c | 88.30 c | 80.81 d | 93.00 a |
| MDA (nmol·mg-1 prot) | 2.26 d | 2.22 d | 3.39 a | 2.52 c | 2.40 c | 2.18 c | 3.03 b | 1.89 e |
| H2O2 (μmol·g-1 FW) | 6.87 f | 24.84 a | 14.59 c | 5.09 g | 8.01 e | 21.68 b | 11.96 d | 3.63 h |
| SOD (U·mg-1 prot) | 1087.99 d | 1063.79 e | 1101.66 c | 1126.52 b | 1083.80 d | 1059.65 e | 1102.99 c | 1140.24 a |
| CAT (U·mg-1 prot) | 15.74 e | 16.99 c | 16.63 d | 16.65 d | 13.51 f | 18.39 a | 16.25 d | 17.74 b |
| GR (nmol·g-1 prot) | 1.49 e | 2.46 c | 2.17 d | 0.96 g | 1.22 f | 3.26 b | 3.69 a | 2.00 d |
| APX (U·g-1 FW) | 5.26 c | 6.55 b | 6.59 b | 10.14 a | 2.70 f | 4.33 d | 2.32 g | 3.74 e |
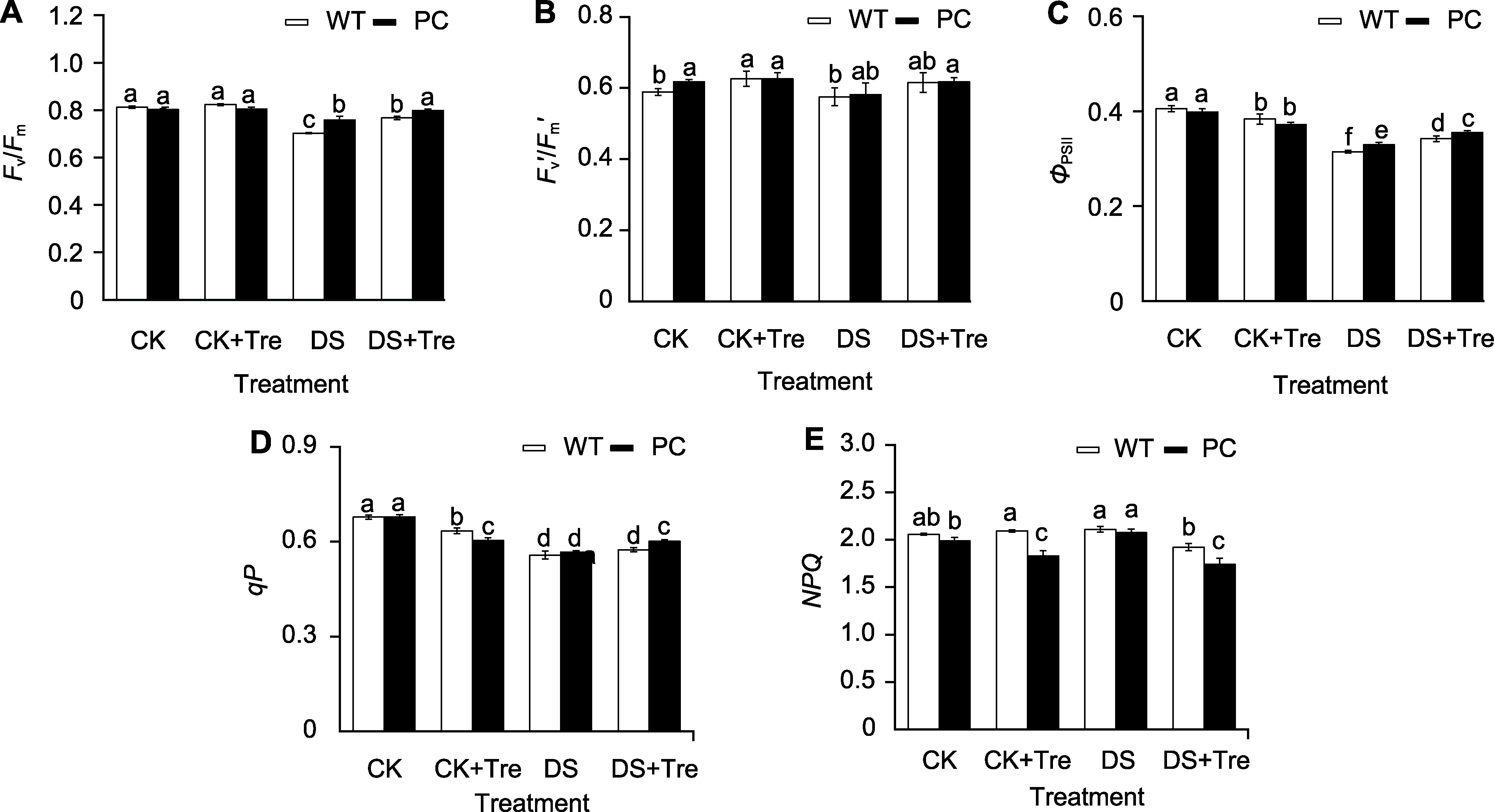
图3 海藻糖处理维持干旱胁迫下水稻叶片的光合性能 模拟干旱处理2小时后PC和WT的最大光化学效率(Fv/Fm) (A)、有效光化学效率(Fv′/Fm′) (B)、实际光化学效率(ΦPSII) (C)、光化学淬灭系数(qP) (D)和非光化学淬灭系数(NPQ) (E)。缩写同图1。图中数值代表来自3个生物学重复的平均值±标准差(n=6)。不同小写字母的柱值表示差异显著(P<0.05) (Student-Neuman-Keuls)。
Figure 3 Trehalose treatment maintain the photosynthetic performance of rice leaves under drought stress Fv/Fm (A), Fv′/Fm′ (B), ΦPSII (C), qP (D) and NPQ (E) of PC and WT after 2 hours of simulated drought treatment. Abbreviations are the same as those given in Figure 1. Values represent means±SD (n=6) from three biological replicates. Bars labeled with different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05) (Student-Neuman-Keuls).
| Index (mg·g-1 FW) | WT | PC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | CK+Tre | DS | DS+Tre | CK | CK+Tre | DS | DS+Tre | |
| Soluble sugar content | 16.10 e | 16.50 e | 29.01 c | 34.32 b | 14.97 f | 19.01 d | 35.31 b | 41.57 a |
| Sucrose content | 9.40 e | 10.78 d | 10.34 d | 12.36 b | 8.51 f | 11.18 c | 11.61 c | 13.81 a |
| Fructose content | 4.01 d | 4.09 d | 4.95 c | 5.81 b | 3.86 e | 3.88 e | 5.49 b | 7.66 a |
| Glucose content | 1.64 b | 1.28 c | 2.35 a | 1.62 b | 0.88 d | 0.78 e | 1.32 c | 0.91 d |
| Trehalose content | 8.22 f | 9.46 e | 10.84 d | 13.60 b | 8.55 f | 10.40 d | 11.23 c | 15.80 a |
表3 海藻糖处理改变干旱胁迫下水稻叶片内可溶性糖的积累与分配
Table 3 Trehalose treatments change the accumulation and distribution of soluble sugars in rice leaves under drought stress
| Index (mg·g-1 FW) | WT | PC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | CK+Tre | DS | DS+Tre | CK | CK+Tre | DS | DS+Tre | |
| Soluble sugar content | 16.10 e | 16.50 e | 29.01 c | 34.32 b | 14.97 f | 19.01 d | 35.31 b | 41.57 a |
| Sucrose content | 9.40 e | 10.78 d | 10.34 d | 12.36 b | 8.51 f | 11.18 c | 11.61 c | 13.81 a |
| Fructose content | 4.01 d | 4.09 d | 4.95 c | 5.81 b | 3.86 e | 3.88 e | 5.49 b | 7.66 a |
| Glucose content | 1.64 b | 1.28 c | 2.35 a | 1.62 b | 0.88 d | 0.78 e | 1.32 c | 0.91 d |
| Trehalose content | 8.22 f | 9.46 e | 10.84 d | 13.60 b | 8.55 f | 10.40 d | 11.23 c | 15.80 a |
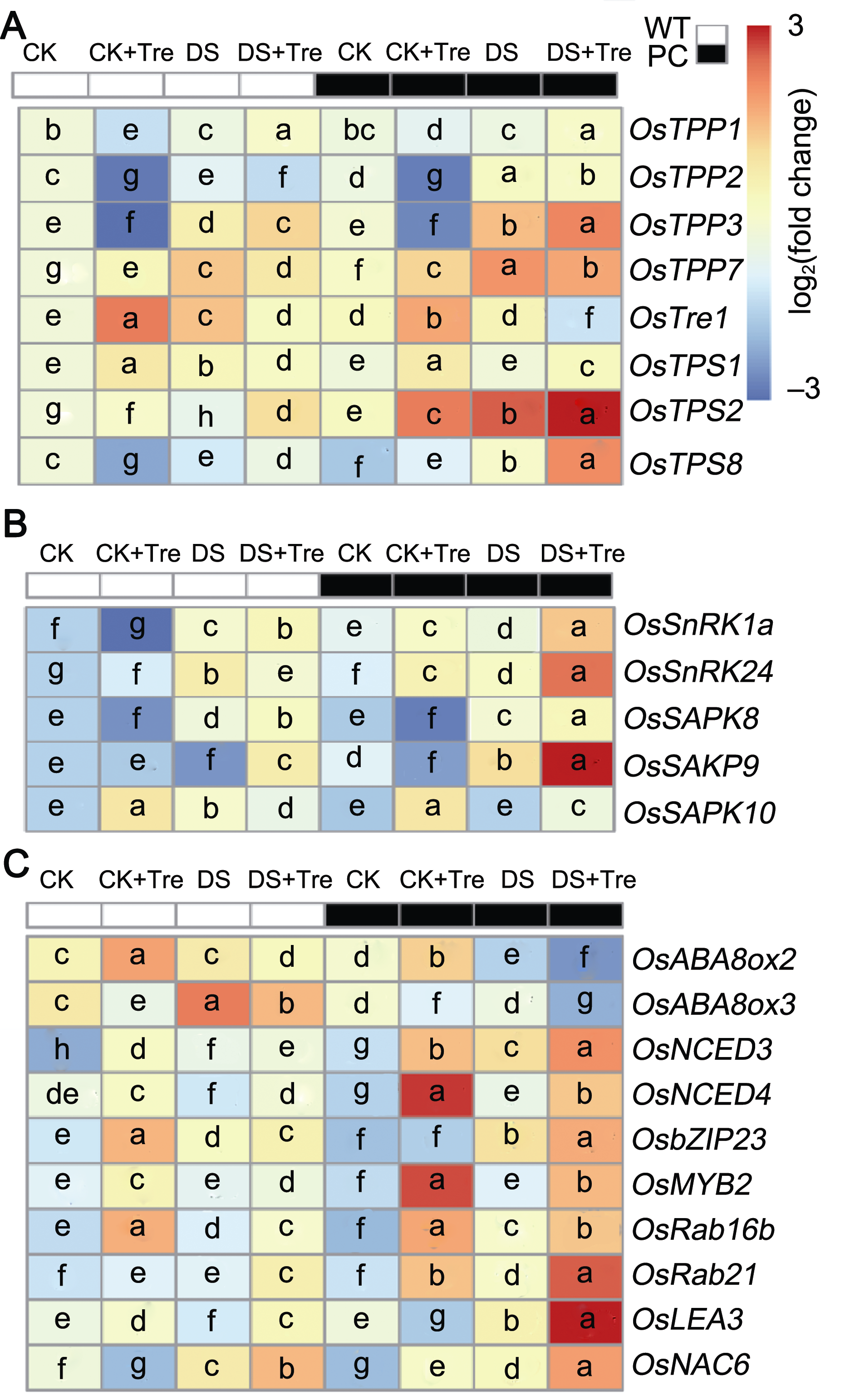
图4 海藻糖处理影响干旱胁迫下水稻叶片内海藻糖、SnRKs及ABA相关基因的表达 (A) 海藻糖合成与代谢相关基因的表达; (B) SnRKs相关基因的表达; (C) ABA代谢相关基因的表达。缩写同图1。热图显示基因相对表达量对数转换均一化值, 显著性分析表示基因相对表达量之间的差异(附表1)。图中不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05) (Student-Neuman-Keuls)。
Figure 4 Trehalose treatments affect the expression of trehalose, SnRKs and ABA-related genes in rice leaves under drought stress (A) The expression of trehalose biosynthesis and metabolism related genes; (B) The expression of SnRKSs-related genes; (C) The expression of ABA metabolism-related genes. Abbreviations are the same as those given in Figure 1. The heat map shows the log-transformed normalized values of relative gene expression, and the significance analysis showed the difference between relative gene expressions (Appendix Table 1). Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05) (Student-Neuman-Keuls).
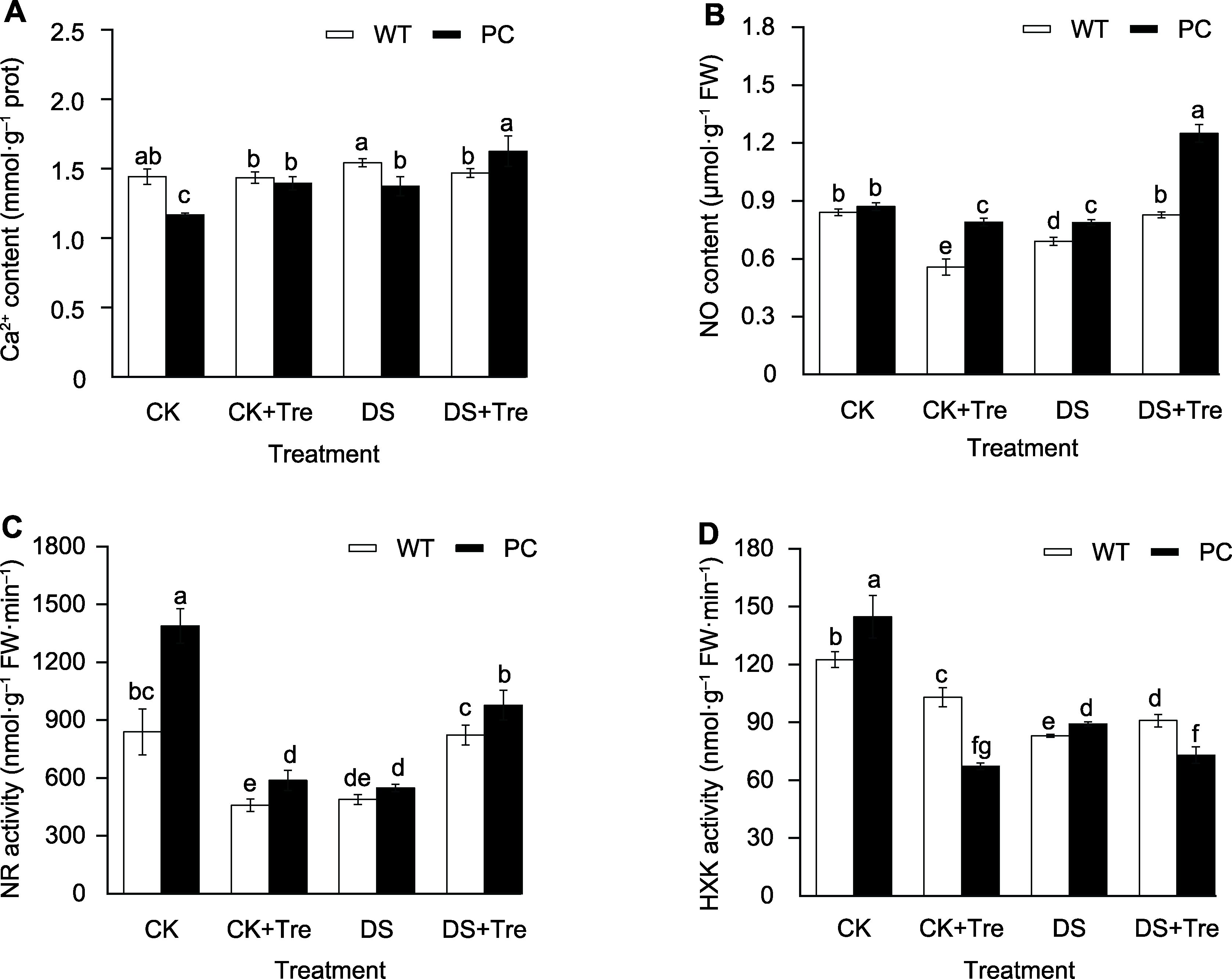
图5 海藻糖处理影响干旱胁迫下水稻叶片内信号分子的含量和相关酶活性 (A) 钙离子含量; (B) 一氧化氮含量; (C) 硝酸还原酶活性; (D) 己糖激酶活性。缩写同图1。图中数值代表来自3个生物学重复的平均值±标准差(n=6)。不同小写字母的柱值表示差异显著(P<0.05) (Student-Neuman-Keuls)。
Figure 5 Trehalose treatments affect the content of signal molecules and the activity of related enzymes in rice leaves under drought stress (A) Ca2+ content; (B) NO content; (C) Nitate reductase (NR) activity; (D) Hexokinase (HXK) activity. Abbreviations are the same as those given in Figure 1. Values represent means±SD (n=6) from three biological replicates. Bars labeled with different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05) (Student-Neuman-Keuls).
| 1 | 何亚飞, 许梦洁, 李霞 (2018). 干旱条件下DCMU对高表达转C4-pepc水稻的花青素合成基因及其相关信号的影响. 中国生态农业学报 26, 409-421. |
| 2 | 李霞, 焦德茂, 戴传超 (2005). 转PEPC基因水稻对光氧化逆境的响应. 作物学报 31, 408-413. |
| 3 | 刘小龙, 李霞, 钱宝云 (2015). 外源Ca 2+对PEG处理下转C4型PEPC基因水稻光合生理的调节 . 植物学报 50, 206-216. |
| 4 | 吴敏怡, 李霞, 何亚飞, 张琛, 严婷 (2017). 脱落酸和己糖激酶抑制剂对高表达C4-PEPC转基因稻苗耐旱性的影响. 植物研究 37, 402-415. |
| 5 | 严婷, 李佳馨, 李霞, 谢寅峰 (2019). 转C4型PEPC基因水稻非生物胁迫耐受性研究进展. 淮阴工学院学报 28, 62-68. |
| 6 | 杨彩琴, 刘伟娜, 赵志弘, 吴海燕 (1998). 血清钙的甲基百里香酚蓝测定法. 光谱学与光谱分析 18, 485-487. |
| 7 | 张金飞, 李霞, 何亚飞, 谢寅峰 (2018). 外源葡萄糖增强高表达转玉米C4型pepc水稻耐旱性的生理机制. 作物学报 44, 82-94. |
| 8 |
张金飞, 李霞, 谢寅峰 (2017). 植物SnRKs家族在胁迫信号通路中的调节作用. 植物学报 52, 346-357.
DOI |
| 9 |
Akram NA, Waseem M, Ameen R, Ashraf M (2016). Trehalose pretreatment induces drought tolerance in radish (Raphanus sativus L.) plants: some key physio-biochemical traits. Acta Physiol Plant 38, 3.
DOI URL |
| 10 | Alam MM, Nahar K, Hasanuzzaman M, Fujita M (2014). Trehalose-induced drought stress tolerance: a comparative study among different brassica species. Plant Omics J 7, 271-283. |
| 11 |
Ambavaram MMR, Basu S, Krishnan A, Ramegowda V, Batlang U, Rahman L, Baisakh N, Pereira A (2014). Coordinated regulation of photosynthesis in rice increases yield and tolerance to environmental stress. Nat Commun 5, 5302.
DOI PMID |
| 12 |
Asami P, Rupasinghe T, Moghaddam L, Njaci I, Roessner U, Mundree S, Williams B (2019). Roots of the resurrection plant tripogon loliiformis survive desiccation without the activation of autophagy pathways by maintaining energy reserves. Front Plant Sci 10, 459.
DOI URL |
| 13 |
Baena-González E, Lunn JE (2020). SnRK1 and trehalose 6-phosphate: two ancient pathways converge to regulate plant metabolism and growth. Curr Opin Plant Biol 55, 52-59.
DOI URL |
| 14 |
Bandyopadhyay A, Datta K, Zhang J, Yang W, Raychaudhuri S, Miyao M, Datta SK (2007). Enhanced photosynthesis rate in genetically engineered indica rice expressing pepc gene cloned from maize. Plant Sci 172, 1204-1209.
DOI URL |
| 15 |
Blázquez MA, Lagunas R, Gancedo C, Gancedo JM (1993). Trehalose-6-phosphate, a new regulator of yeast glycolysis that inhibits hexokinases. FEBS Lett 329, 51-54.
PMID |
| 16 |
Chen PB, Li X, Huo K, Wei XD, Dai CC, Lu CG (2014). Promotion of photosynthesis in transgenic rice over-expressing of maize C4 phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene by nitric oxide donors. J Plant Physiol 171, 458-466.
DOI URL |
| 17 |
Claeys H, Vi SL, Xu XS, Satoh-Nagasawa N, Eveland AL, Goldshmidt A, Feil R, Beggs GA, Sakai H, Brennan RG, Lunn JE, Jackson D (2019). Control of meristem determinacy by trehalose 6-phosphate phosphatases is uncoupled from enzymatic activity. Nat Plants 5, 352-357.
DOI URL |
| 18 | Corpas FJ, Barroso JB (2018). Peroxisomal plant metabolism: an update on nitric oxide, Ca 2+ and the NADPH recycling network . J Cell Sci 131, jcs202978. |
| 19 |
Delorge I, Janiak M, Carpentier S, van Dijck F (2014). Fine tuning of trehalose biosynthesis and hydrolysis as novel tools for the generation of abiotic stress tolerant plants. Front Plant Sci 5, 147.
DOI PMID |
| 20 |
Dey A, Samanta MK, Gayen S, Sen SK, Maiti MK (2016). Enhanced gene expression rather than natural polymorphism in coding sequence of the OsbZIP23 determines drought tolerance and yield improvement in rice genotypes. PLoS One 11, e0150763.
DOI URL |
| 21 |
Ding ZS, Huang SH, Zhou BY, Sun XF, Zhao M (2013). Over-expression of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase cDNA from C4 millet ( Seteria italica) increase rice photosynthesis and yield under upland condition but not in wetland fields. Plant Biotechnol Rep 7, 155-163.
DOI URL |
| 22 | Ding ZS, Zhou BY, Sun XF, Zhao M (2012). High light tolerance is enhanced by overexpressed PEPC in rice under drought stress. Acta Agron Sin 38, 285-292. |
| 23 |
Duan JL, Cai WM (2012). OsLEA3-2, an abiotic stress induced gene of rice plays a key role in salt and drought tolerance. PLoS One 7, e45117.
DOI URL |
| 24 |
Durand M, Mainson D, Porcheron B, Maurousset L, Lemoine R, Pourtau N (2018). Carbon source-sink relationship in Arabidopsis thaliana: the role of sucrose transporters. Planta 247, 587-611.
DOI URL |
| 25 |
Ermakova M, Danila FR, Furbank RT, Caemmerer S (2020). On the road to C4 rice: advances and perspectives. Plant J 101, 940-950.
DOI |
| 26 |
Feng YC, Chen XY, He YL, Kou XH, Xue ZH (2019). Effects of exogenous trehalose on the metabolism of sugar and abscisic acid in tomato seedlings under salt stress. Trans Tianjin Univ 25, 451-471.
DOI URL |
| 27 | Fichtner F, Lunn JE (2021). The role of trehalose 6-phosphate (Tre6P) in plant metabolism and development. Annu Rev Plant Biol 72, 187-220. |
| 28 |
Figueroa CM, Feil R, Ishihara H, Watanabe M, Kölling K, Krause U, Höhne M, Encke B, Plaxton WC, Zeeman SC, Li Z, Schu WX, Hoefgen R, Stitt M, Lunn JE (2016). Trehalose 6-phosphate coordinates organic and amino acid metabolism with carbon availability. Plant J 85, 410-423.
DOI URL |
| 29 | Figueroa CM, Lunn JE (2016). A tale of two sugars: trehalose 6-phosphate and sucrose. Plant Physiol 172, 7-27. |
| 30 |
Foyer CH, Halliwell B (1976). The presence of glutathione and glutathione reductase in chloroplasts: a proposed role in ascorbic acid metabolism. Planta 133, 21-25.
DOI PMID |
| 31 |
Ge LF, Chao DY, Shi M, Zhu MZ, Gao JP, Lin HX (2008). Overexpression of the trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase gene OsTPP1 confers stress tolerance in rice and results in the activation of stress responsive genes. Planta 228, 191-201.
DOI URL |
| 32 |
Giannopolitis CN, Ries SK (1977). Superoxide dismutases I: occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiol 59, 309-314.
PMID |
| 33 |
Giglioli-Guivarc'h G, Pierre JN, Brown S, Chollet R, Vidal J, Gadal P (1996). The light-dependent transduction pathway controlling the regulatory phosphorylation of C4 phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in protoplasts from digitaria sanguinalis. Plant Cell 8, 573-586.
DOI URL |
| 34 | Gómez LD, Gilday A, Feil R, Lunn JE, Graham IA (2010). AtTPS1-mediated trehalose 6-phosphate synthesis is essential for embryogenic and vegetative growth and responsiveness to ABA in germinating seeds and stomatal guard cells. Plant J 64, 1-13. |
| 35 |
Han BY, Fu LL, Zhang D, He XQ, Chen Q, Peng M, Zhang JM (2016). Interspecies and intraspecies analysis of trehalose contents and the biosynthesis pathway gene family reveals crucial roles of trehalose in osmotic-stress tolerance in cassava. Int J Mol Sci 17, 1077.
DOI URL |
| 36 |
He YF, Xie YF, Li X, Yang J (2020). Drought tolerance of transgenic rice overexpressing maize C4-PEPC gene related to increased anthocyanin synthesis regulated by sucrose and calcium. Biol Plantarum 64, 136-149.
DOI URL |
| 37 |
Hong CY, Chao YY, Yang MY, Cheng SY, Cho SC, Kao CH (2009). NaCl-induced expression of glutathione reductase in roots of rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings is mediated through hydrogen peroxide but not abscisic acid. Plant Soil 320, 103-115.
DOI URL |
| 38 | Hong YB, Zhang HJ, Huang L, Li DY, Song FM (2016). Overexpression of a stress-responsive NAC transcription factor gene ONAC022 improves drought and salt tolerance in rice. Front Plant Sci 7, 4. |
| 39 |
Huo K, Li X, He YF, Wei XD, Lu W, Zhao CF, Wang CL (2017). Exogenous ATP enhance signal response of suspension cells of transgenic rice ( Oryza sativa L.) expressing maize C4-pepc encoded phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase under PEG treatment. Plant Growth Regul 82, 55-67.
DOI URL |
| 40 |
Ilhan S, Ozdemir F, Bor M (2015). Contribution of trehalose biosynthetic pathway to drought stress tolerance of Capparis ovata desf. Plant Biol 17, 402-407.
DOI URL |
| 41 |
Islam MO, Kato H, Shima S, Tezuka D, Matsui H, Imai R (2019). Functional identification of a rice trehalose gene involved in salt stress tolerance. Gene 685, 42-49.
DOI URL |
| 42 |
Izui K, Matsumura H, Furumoto, Kai Y (2004). Phospho enol pyruvate carboxylase: a new era of structural biology. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55, 69-84.
DOI URL |
| 43 |
Jiang DG, Chen WT, Gao J, Yang F, Zhuang CX (2019). Overexpression of the trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase OsTPP3 increases drought tolerance in rice. Plant Biotechnol Rep 13, 285-292.
DOI URL |
| 44 |
Jiao DM, Ji BH, Li X (2003). Characteristics of chlorophyll fluorescence and membrane-lipid peroxidation during senescence of flag leaf in different cultivars of rice. Photosynthetica 41, 33-41.
DOI URL |
| 45 | John R, Raja V, Ahmad M, Jan N, Majeed U, Ahmad S, Yaqoob U, Kaul T (2017). Trehalose: metabolism and role in stress signaling in plants. In: Sarwat M, Ahmad A, Abdin M, Ibrahim M, eds. Stress Signaling in Plants: Genomics and Proteomics Perspective, Volume 2. Cham: Springer International Publishing. pp. 261-275. |
| 46 |
Karki S, Rizal G, Quick WP (2013). Improvement of photosynthesis in rice (Oryza sativa L.) by inserting the C4 pathway. Rice 6, 28.
DOI URL |
| 47 |
Kim YM, Heinzel N, Giese JO, Koeber J, Melzer M, Rutten T, von Wirén N, Sonnewald U, Hajirezaei MR (2013). A dual role of tobacco hexokinase 1 in primary metabolism and sugar sensing. Plant Cell Environ 36, 1311-1327.
DOI URL |
| 48 |
Kosar F, Akram NA, Sadiq M, Al-Qurainy F, Ashraf M (2019). Trehalose: a key organic osmolyte effectively involved in plant abiotic stress tolerance. J Plant Growth Regul 38, 606-618.
DOI URL |
| 49 |
Kretzschmar T, Pelayo MAF, Trijatmiko KR, Gabunada LFM, Alam R, Jimenez R, Mendioro MS, Slamet- Loedin IH, Sreenivasulu N, Bailey-Serres J, Ismail AM, Mackill DJ, Septiningsih EM (2015). A trehalose-6- phosphate phosphatase enhances anaerobic germination tolerance in rice. Nat Plants 1, 15124.
DOI PMID |
| 50 |
Ku MSB, Agarie S, Nomura M, Fukayama H, Tsuchida H, Ono K, Hirose S, Toki S, Miyao M, Matsuoka M (1999). High-level expression of maize phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in transgenic rice plants. Nat Biotechnol 17, 76-80.
PMID |
| 51 | Latzko E, Kelly GJ (1983). The many-faceted function of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in C3 plants. Physiol Végét 21, 805-815. |
| 52 |
Li CX, Shen HY, Wang T, Wang XL (2015). ABA regulates subcellular redistribution of OsABI-LIKE2, a negative regulator in ABA signaling, to control root architecture and drought resistance in Oryza sativa. Plant Cell Physiol 56, 2396-2408.
DOI URL |
| 53 | Li X, Wang C, Ren CG (2011). Effects of 1-butanol, neomycin and calcium on the photosynthetic characteristics of pepc transgenic rice. Afr J Biotechnol 10, 17466-17476. |
| 54 |
Li ZW, Zhao Q, Cheng FM (2020). Sugar starvation enhances leaf senescence and genes involved in sugar signaling pathways regulate early leaf senescence in mutant rice. Rice Sci 27, 201-204.
DOI URL |
| 55 |
Liu T, Ye XL, Li M, Li JM, Qi HY, Hu XH (2020). H2O2 and NO are involved in trehalose-regulated oxidative stress tolerance in cold-stressed tomato plants. Environ Exp Bot 171, 103961.
DOI URL |
| 56 |
Liu XL, Li X, Dai CC, Zhou JY, Yan T, Zhang JF (2017a). Improved short-term drought response of transgenic rice over-expressing maize C4 phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase via calcium signal cascade. J Plant Physiol 218, 206-221.
DOI URL |
| 57 |
Liu XL, Li X, Zhang C, Dai CC, Zhou JY, Ren CG, Zhang JF (2017b). Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase regulation in C4-PEPC expressing transgenic rice during early responses to drought stress. Physiol Plantarum 159, 178-200.
DOI URL |
| 58 |
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2002). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR. Methods 25, 402-408.
DOI URL |
| 59 |
Lunn JE, Delorge I, Figueroa CM, van Dijck P, Stitt M (2014). Trehalose metabolism in plants. Plant J 79, 544-567.
DOI URL |
| 60 |
Mamedov TG, Moellering ER, Chollet R (2005). Identification and expression analysis of two inorganic C- and N- responsive genes encoding novel and distinct molecular forms of eukaryotic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in the green microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant J 42, 832-843.
PMID |
| 61 |
Matsuoka M, Minami EI (1989). Complete structure of the gene for phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from maize. Eur J Biochem 181, 593-598.
PMID |
| 62 |
Morales F, Ancín M, Fakhet D, González-Torralba J, Gámez AL, Seminario A, Soba D, Ben Mariem S, Garriga M, Aranjuelo I (2020). Photosynthetic metabolism under stressful growth conditions as a bases for crop breeding and yield improvement. Plants 9, 88.
DOI URL |
| 63 |
Murphy ME, Noack E (1994). Nitric oxide assay using hemoglobin method. Method Enzymol 233, 240.
PMID |
| 64 | Nakano Y, Asada K (1981). Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22, 867-880. |
| 65 |
Noctor G, Reichheld JP, Foyer CH (2018). ROS-related redox regulation and signaling in plants. Semin Cell Dev Biol 80, 3-12.
DOI URL |
| 66 |
Oladosu Y, Rafii MY, Samuel C, Fatai A, Magaji U, Kareem I, Kamarudin ZS, Muhammad I, Kolapo K (2019). Drought resistance in rice from conventional to molecular breeding: a review. Intl J Mol Sci 20, 3519.
DOI URL |
| 67 |
Pramanik MHR, Imai R (2005). Functional identification of a trehalose 6-phosphate phosphatase gene that is involved in transient induction of trehalose biosynthesis during chilling stress in rice. Plant Mol Biol 58, 751-762.
DOI PMID |
| 68 |
Qian BY, Li X, Liu XL, Chen PB, Ren CG, Dai CC (2015a). Enhanced drought tolerance in transgenic rice over-expressing of maize C4 phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene via NO and Ca 2+ . J Plant Physiol 175, 9-20.
DOI URL |
| 69 |
Qian BY, Li X, Liu XL, Wang M (2015b). Improved oxidative tolerance in suspension-cultured cells of C4-pepc transgenic rice by H2O2 and Ca 2+ under PEG-6000. J Integr Plant Biol 57, 534-539.
DOI URL |
| 70 |
Ren CG, Li X, Liu XL, Wei XD, Dai CC (2014). Hydrogen peroxide regulated photosynthesis in C4-pepc transgenic rice. Plant Physiol Biochem 74, 218-229.
DOI URL |
| 71 | Sadak MS (2016). Mitigation of drought stress on fenugreek plant by foliar application of trehalose. Int J ChemTech Res 9, 147-155. |
| 72 |
Samadi S, Habibi G, Vaziri A (2019). Exogenous trehalose alleviates the inhibitory effects of salt stress in strawberry plants. Acta Physiol Plant 41, 112.
DOI URL |
| 73 |
Schaffer AA, Petreikov M (1997). Sucrose-to-starch metabolism in tomato fruit undergoing transient starch accumulation. Plant Physiol 113, 739-746.
DOI URL |
| 74 |
Shahbaz M, Abid A, Masood A, Waraich EA (2017). Foliar-applied trehalose modulates growth, mineral nutrition, photosynthetic ability, and oxidative defense system of rice (Oryza sativa L.) under saline stress. J Plant Nutr 40, 584-599.
DOI URL |
| 75 |
Shi JH, Yi KK, Liu Y, Xie L, Zhou ZJ, Chen Y, Hu ZH, Zheng T, Liu RH, Chen YL, Chen JQ (2015). Phospho enol pyruvate carboxylase in Arabidopsis leaves plays a crucial role in carbon and nitrogen metabolism. Plant Physiol 167, 671-681.
DOI URL |
| 76 |
Simon NML, Kusakina J, Fernández-López Á, Chembath A, Belbin FE, Dodd AN (2018). The energy-signaling hub SnRK1 is important for sucrose-induced hypocotyl elongation. Plant Physiol 176, 1299-1310.
DOI URL |
| 77 |
Smart RE, Bingham GE (1974). Rapid estimates of relative water content. Plant Physiol 53, 258-260.
PMID |
| 78 |
Sun SJ, Qi GN, Gao QF, Wang HQ, Yao FY, Hussain J, Wang YF (2016). Protein kinase OsSAPK8 functions as an essential activator of S-type anion channel OsSLAC1, which is nitrate-selective in rice. Planta 243, 489-500.
DOI URL |
| 79 |
Tachibaana S, Konishi N, Kanda H (1991). Diurnal variation of in vivo and in vitro nitrate reductase activity in cucumber plants. J Jap Soc Hortic Sci 60, 593-599.
DOI URL |
| 80 |
Tang YT, Li X, Lu W, Wei XD, Zhang QJ, Lv CG, Song NX (2018). Enhanced photorespiration in transgenic rice over-expressing maize C4 phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene contributes to alleviating low nitrogen stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 130, 577-588.
DOI URL |
| 81 |
Theerakulp P, Phongngarm S (2013). Alleviation of adverse effects of salt stress on rice seedlings by exogenous trehalose. Asian J Crop Sci 5, 405-415.
DOI URL |
| 82 |
Tian LF, Xie ZJ, Lu CQ, Hao XH, Wu S, Huang Y, Li DP, Chen LB (2019). The trehalose-6-phosphate synthase TPS5 negatively regulates ABA signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Rep 38, 869-882.
DOI URL |
| 83 |
Uzilday B, Turkan I, Ozgur R, Sekmen AH (2014). Strategies of ROS regulation and antioxidant defense during transition from C3 to C4 photosynthesis in the genus Flaveria under PEG-induced osmotic stress. J Plant Physiol 171, 65-75.
DOI URL |
| 84 |
Velikova V, Yordanov I, Edreva A (2000). Oxidative stress and some antioxidant systems in acid rain-treated bean plants. Plant Sci 151, 59-66.
DOI URL |
| 85 |
Vishal B, Krishnamurthy P, Ramamoorthy R, Kumar PP (2019). OsTPS8 controls yield-related traits and confers salt stress tolerance in rice by enhancing suberin deposition. New Phytol 221, 1369-1386.
DOI URL |
| 86 |
Wang PC, Zhu JK, Lang ZB (2015). Nitric oxide suppresses the inhibitory effect of abscisic acid on seed germination by S-nitrosylation of SnRK2 proteins. Plant Signal Behav 10, e1031939.
DOI URL |
| 87 |
Wang WJ, Chen QB, Xu SM, Liu WC, Zhu XH, Song CP (2020a). Trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase E modulates ABA-controlled root growth and stomatal movement inArabidopsis. J Integr Plant Biol 62, 1518-1534.
DOI URL |
| 88 | Wang Y, Wang LP, Micallef BJ, Tetlow IJ, Mullen RT, Feil R, Lunn JE, Emes MJ (2020b). AKINβ1, a subunit of SnRK1, regulates organic acid metabolism and acts as a global modulator of genes involved in carbon, lipid, and nitrogen metabolism. J Exp Bot 71, 1010-1028. |
| 89 |
Wingler A (2018). Transitioning to the next phase: the role of sugar signaling throughout the plant life cycle. Plant Physiol 176, 1075-1084.
DOI URL |
| 90 |
Yang A, Dai XY, Zhang WH (2012). A R2R3-type MYB gene, OsMYB2, is involved in salt, cold, and dehydration tolerance in rice. J Exp Bot 63, 2541-2556.
DOI URL |
| 91 | Yoshida S, Forno DA, Cock J (1971). Laboratory Manual for Physiological Studies of Rice. Los Banos: International Rice Research Institute. pp. 62. |
| 92 |
Yu WQ, Zhao RR, Wang L, Zhang SJ, Li R, Sheng JP, Shen L (2019). ABA signaling rather than ABA metabolism is involved in trehalose-induced drought tolerance in tomato plants. Planta 250, 643-655.
DOI URL |
| 93 |
Zang BS, Li HW, Li WJ, Deng XW, Wang XP (2011). Analysis of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase (TPS) gene family suggests the formation of TPS complexes in rice. Plant Mol Biol 76, 507-522.
DOI URL |
| 94 |
Zhai ZY, Keereetaweep J, Liu H, Feil R, Lunn JE, Shanklin J (2018). Trehalose 6-phosphate positively regulates fatty acid synthesis by stabilizing WRINKLED. Plant Cell 30, 2616-2627.
DOI URL |
| 95 |
Zhang C, Li X, He YF, Zhang JF, Yan T, Liu XL (2017). Physiological investigation of C4-phosphoenolpyruvate-carboxylase-introduced rice line shows that sucrose metabolism is involved in the improved drought tolerance. Plant Physiol Biochem 115, 328-342.
DOI URL |
| 96 |
Zhang C, Peng X, Guo XF, Tang GJ, Sun FL, Liu SD, Xi YJ (2018). Transcriptional and physiological data reveal the dehydration memory behavior in switchgrass ( Panicum virgatum L.). Biotechnol Biofuels 11, 91.
DOI PMID |
| 97 |
Zhao RQ (2019). Expression, purification and characterization of the plant Snf1-related protein kinase 1 from Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 162, 24-31.
DOI URL |
| 98 |
Zhong RL, Wang YX, Gai RN, Xi DD, Mao CJ, Feng M (2020). Rice SnRK protein kinase OsSAPK8 acts as a positive regulator in abiotic stress responses. Plant Sci 292, 110373.
DOI URL |
| 99 |
Zhu G, Ye N, Zhang J (2009). Glucose-induced delay of seed germination in rice is mediated by the suppression of ABA catabolism rather than an enhancement of ABA biosynthesis. Plant Cell Physiol 50, 644-651.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 叶灿, 姚林波, 金莹, 高蓉, 谭琪, 李旭映, 张艳军, 陈析丰, 马伯军, 章薇, 张可伟. 水稻水杨酸代谢突变体高通量筛选方法的建立与应用[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | 赵凌, 管菊, 梁文化, 张勇, 路凯, 赵春芳, 李余生, 张亚东. 基于高密度Bin图谱的水稻苗期耐热性QTL定位[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 342-353. |
| [3] | 李新宇, 谷月, 徐非非, 包劲松. 水稻胚乳淀粉合成相关蛋白的翻译后修饰研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 256-270. |
| [4] | 樊蓓, 任敏, 王延峰, 党峰峰, 陈国梁, 程国亭, 杨金雨, 孙会茹. 番茄SlWRKY45转录因子在响应低温和干旱胁迫中的功能(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 186-203. |
| [5] | 曹婕, 卢秋连, 翟健平, 刘宝辉, 方超, 李世晨, 苏彤. 大豆TPS基因家族在盐胁迫下的表达变化及单倍型选择规律分析(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 172-185. |
| [6] | 李建国, 张怡, 张文君. 水稻根系铁膜形成及对磷吸收的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 132-143. |
| [7] | 龙吉兰, 蒋铮, 刘定琴, 缪宇轩, 周灵燕, 冯颖, 裴佳宁, 刘瑞强, 周旭辉, 伏玉玲. 干旱下植物根系分泌物及其介导的根际激发效应研究进展[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(7): 817-827. |
| [8] | 姚瑞枫, 谢道昕. 水稻独脚金内酯信号感知的激活和终止[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 873-877. |
| [9] | 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 张伊诺, 郑佳兴, 朱超宇, 叶语涵, 王跃星, 商文楠, 傅正浩, 徐昕璇, 吴日成, 路梅, 王长春, 饶玉春. 水稻抗氧化性状遗传位点挖掘及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 738-751. |
| [10] | 黄佳慧, 杨惠敏, 陈欣雨, 朱超宇, 江亚楠, 胡程翔, 连锦瑾, 芦涛, 路梅, 张维林, 饶玉春. 水稻突变体pe-1对弱光胁迫的响应机制[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 574-584. |
| [11] | 赵来鹏, 王柏柯, 杨涛, 李宁, 杨海涛, 王娟, 闫会转. SlHVA22l基因调节番茄耐旱性[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 558-573. |
| [12] | 周俭民. 收放自如的明星战车[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 343-346. |
| [13] | 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 朱哲楠, 张芷宁, 汪理海, 陈钧, 李三峰, 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 钟芊芊, 殷文晶, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻穗部性状QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 217-230. |
| [14] | 夏婧, 饶玉春, 曹丹芸, 王逸, 柳林昕, 徐雅婷, 牟望舒, 薛大伟. 水稻中乙烯生物合成关键酶OsACS和OsACO调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 291-301. |
| [15] | 方妍力, 田传玉, 苏如意, 刘亚培, 王春连, 陈析丰, 郭威, 纪志远. 水稻抗细菌性条斑病基因挖掘与初定位[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 1-9. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||