

植物学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (3): 315-329.DOI: 10.11983/CBB20143 cstr: 32102.14.CBB20143
康凯程1,2, 牛西强2, 黄先忠2,*( ), 胡能兵2, 隋益虎2, 张开京2, 艾昊2
), 胡能兵2, 隋益虎2, 张开京2, 艾昊2
收稿日期:2020-08-10
接受日期:2021-02-01
出版日期:2021-05-01
发布日期:2021-04-30
通讯作者:
黄先忠
作者简介:*huangxz@ahstu.edu.cn基金资助:
Kaicheng Kang1,2, Xiqiang Niu2, Xianzhong Huang2,*( ), Nengbing Hu2, Yihu Sui2, Kaijing Zhang2, Hao Ai2
), Nengbing Hu2, Yihu Sui2, Kaijing Zhang2, Hao Ai2
Received:2020-08-10
Accepted:2021-02-01
Online:2021-05-01
Published:2021-04-30
Contact:
Xianzhong Huang
摘要: MYB转录因子作为植物中最大的转录因子家族之一, 参与植物的生长、代谢、抵御生物和非生物胁迫等多种生理生化过程。R2R3-MYB是MYB转录因子家族的主要存在形式。辣椒是具有重要经济价值的蔬菜作物, 其R2R3-MYB转录因子缺乏系统的研究。从一年生辣椒(Capsicum annuum)、浆果状辣椒(C. baccatum)和中国辣椒(C. chinense)基因组中分别鉴定出94、92和94个R2R3-MYB基因, 基于系统发育关系将其分为28个亚族。共线性分析表明, 3种辣椒间存在73组直系同源R2R3-MYB基因, 一年生辣椒、浆果状辣椒和中国辣椒分别存在5、4和2个特有的R2R3-MYB基因。鉴定出12对重复基因, 其中8对是串联重复基因, 它们在3种辣椒分化前就已经存在。比较基因组学分析表明, 在辣椒进化过程中同源R2R3-MYB转录因子发生了功能分化。组织表达分析表明, 辣椒R2R3-MYB基因主要有3种表达特征: 在根、叶、茎和花中均高表达, 如CaMYB13/CbMYB12/CcMYB13; 仅在花中高表达, 如CaMYB93/CbMYB86/CcMYB12; 仅在根中高表达, 如CaMYB48/CbMYB47/CcMYB51。研究结果为深入揭示R2R3-MYB转录因子在辣椒生长发育中的生物学功能奠定了基础。
康凯程, 牛西强, 黄先忠, 胡能兵, 隋益虎, 张开京, 艾昊. 辣椒R2R3-MYB转录因子家族的全基因组鉴定与比较进化分析. 植物学报, 2021, 56(3): 315-329.
Kaicheng Kang, Xiqiang Niu, Xianzhong Huang, Nengbing Hu, Yihu Sui, Kaijing Zhang, Hao Ai. Genome-wide Identification and Comparative Evolutionary Analysis of the R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor Gene Family in Pepper. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(3): 315-329.
| Gene name | Primer sequences (5′→3′) | Use |
|---|---|---|
| CaMYB62 | ATCGCAGCGTATGAACACAC | qRT-PCR |
| TTGTTACCGTGTTTGGCCTG | ||
| CaMYB35 | GGCGGTGAATGTGATGATCC | qRT-PCR |
| GGAAACCCCGTAGAAGCAAC | ||
| CaMYB92 | TGATCCAACAACACACAGGC | qRT-PCR |
| TTGTTCTCGAAATGGGCTGC | ||
| CaMYB39 | TGGGGCAATCGTTGGTCTAA | qRT-PCR |
| TGGATGTAAGTGGTGGTGGG | ||
| CaMYB25 | AACCACCTACCTCGGCATTT | qRT-PCR |
| TCACTTTTGTTTGAGCCTGCA | ||
| CaMYB2 | CATCATCACCAGCAGTCACA | qRT-PCR |
| GATCGACTTGCCAGCAGAAC | ||
| CaMYB8 | CAGATCCTAGGGCTCTCGTG | qRT-PCR |
| GGCCCGACTAATCCTGAGAT | ||
| CaMYB80 | TCTTGGCAATAGGTGGTCGA | qRT-PCR |
| TGCTGCTCTCGTGGATAATCT | ||
| CaMYB19 | GGACACAACATGGACAGCAG | qRT-PCR |
| CTGAATCAGATGGGGAAGGA | ||
| CaUBI-3 | TGTCCATCTGCTCTCTGTTG | Internal reference gene |
| CACCCCAAGCACAATAAGAC |
表1 本研究使用的引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences used in this study
| Gene name | Primer sequences (5′→3′) | Use |
|---|---|---|
| CaMYB62 | ATCGCAGCGTATGAACACAC | qRT-PCR |
| TTGTTACCGTGTTTGGCCTG | ||
| CaMYB35 | GGCGGTGAATGTGATGATCC | qRT-PCR |
| GGAAACCCCGTAGAAGCAAC | ||
| CaMYB92 | TGATCCAACAACACACAGGC | qRT-PCR |
| TTGTTCTCGAAATGGGCTGC | ||
| CaMYB39 | TGGGGCAATCGTTGGTCTAA | qRT-PCR |
| TGGATGTAAGTGGTGGTGGG | ||
| CaMYB25 | AACCACCTACCTCGGCATTT | qRT-PCR |
| TCACTTTTGTTTGAGCCTGCA | ||
| CaMYB2 | CATCATCACCAGCAGTCACA | qRT-PCR |
| GATCGACTTGCCAGCAGAAC | ||
| CaMYB8 | CAGATCCTAGGGCTCTCGTG | qRT-PCR |
| GGCCCGACTAATCCTGAGAT | ||
| CaMYB80 | TCTTGGCAATAGGTGGTCGA | qRT-PCR |
| TGCTGCTCTCGTGGATAATCT | ||
| CaMYB19 | GGACACAACATGGACAGCAG | qRT-PCR |
| CTGAATCAGATGGGGAAGGA | ||
| CaUBI-3 | TGTCCATCTGCTCTCTGTTG | Internal reference gene |
| CACCCCAAGCACAATAAGAC |

图1 3种辣椒R2 (A)和R3 (B) MYB结构域的seqlogo图 氨基酸的得分(Bits)表示它在这个位点出现的频率。
Figure 1 Sequence logos of the R2 (A) and R3 (B) MYB domains from three Capsicum species The score of an amino acid (Bits) indicates the frequency of its occurrence at this site.
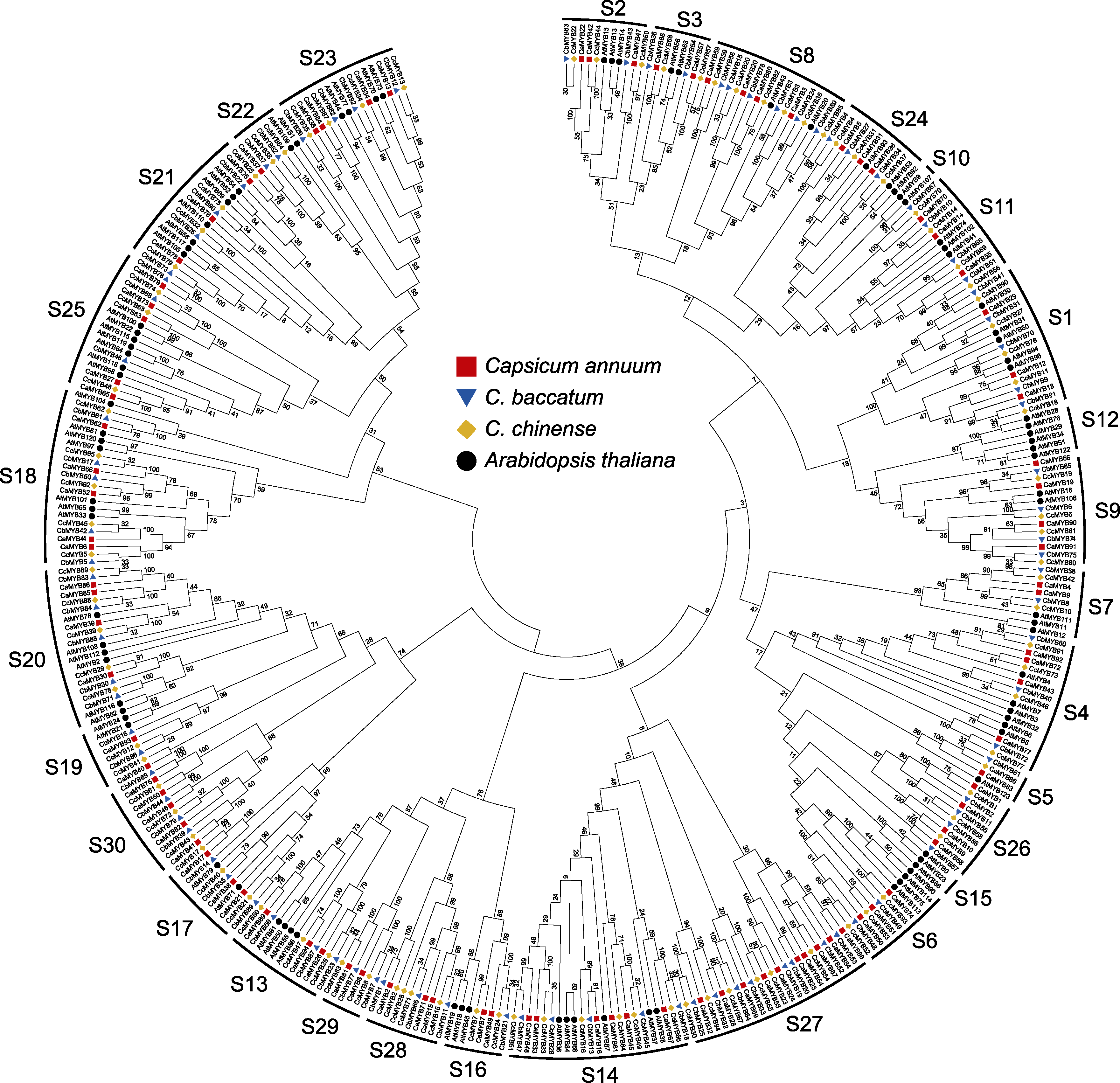
图2 3种辣椒和拟南芥R2R3-MYB转录因子家族的系统进化树 S1-S30分别代表30个亚组。
Figure 2 Phylogenetic tree of the R2R3-MYB transcription factor family from three Capsicum species and Arabidopsis thaliana S1-S30 represent 30 subgroups.
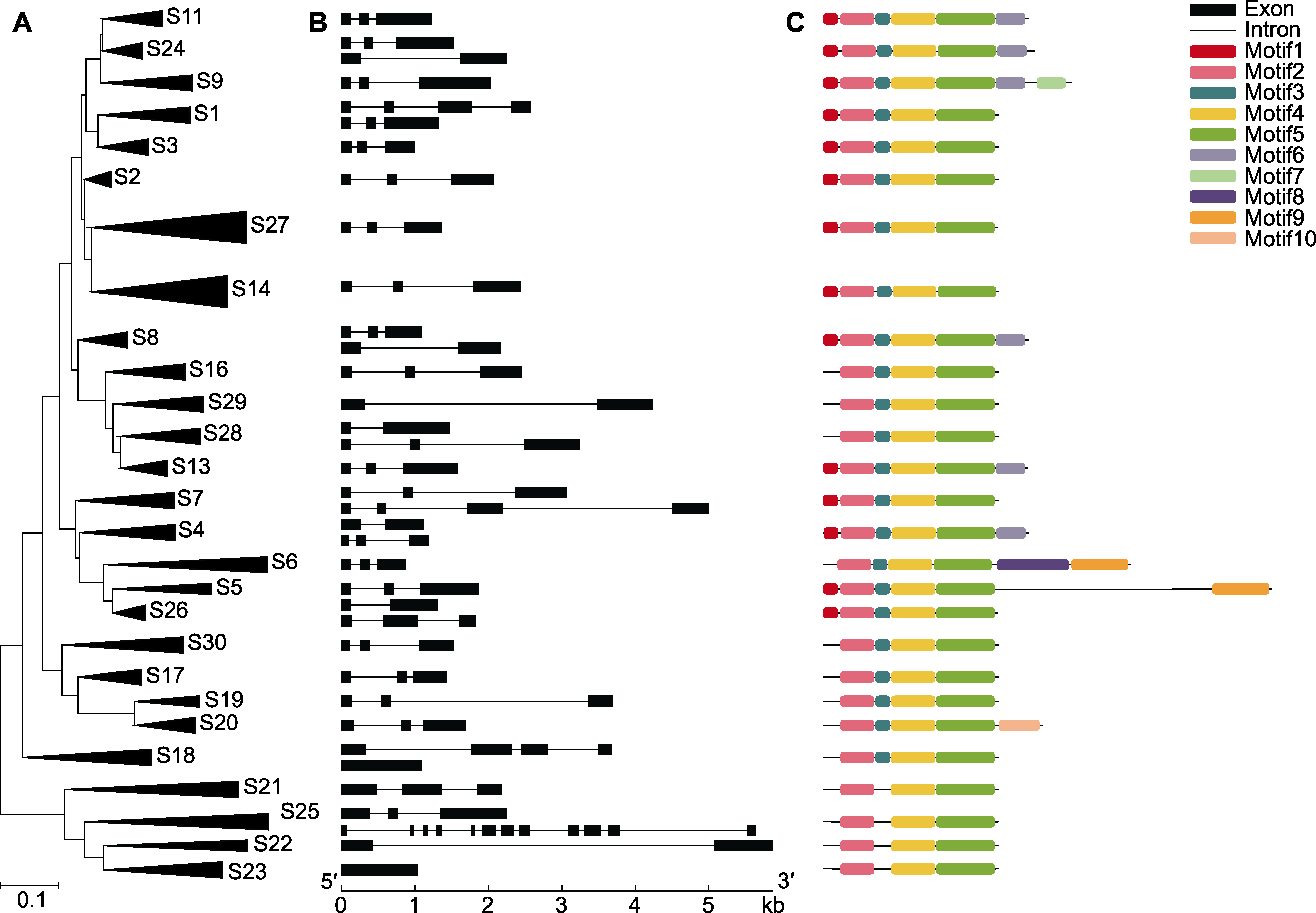
图3 3种辣椒R2R3-MYB转录因子家族的系统进化、基因外显子-内含子结构和motif分析 (A) 27个亚家族的系统进化树; (B) 27个亚家族的外显子-内含子结构(黑色方框表示外显子, 黑色线条表示内含子); (C) 27个亚家族的motif分布(不同颜色的方框表示不同的motif)
Figure 3 Phylogenetic tree, gene exon-intron structure and motif analysis of R2R3-MYB transcription factor family in three Capsicum species (A) Phylogenetic tree of the 27 subfamilies; (B) Exon-intron structure of the 27 subfamilies (Black boxes indicate exons and black lines indicate introns); (C) The motif distribution of the 27 subfamilies (The boxes with different colors indicate different motifs)
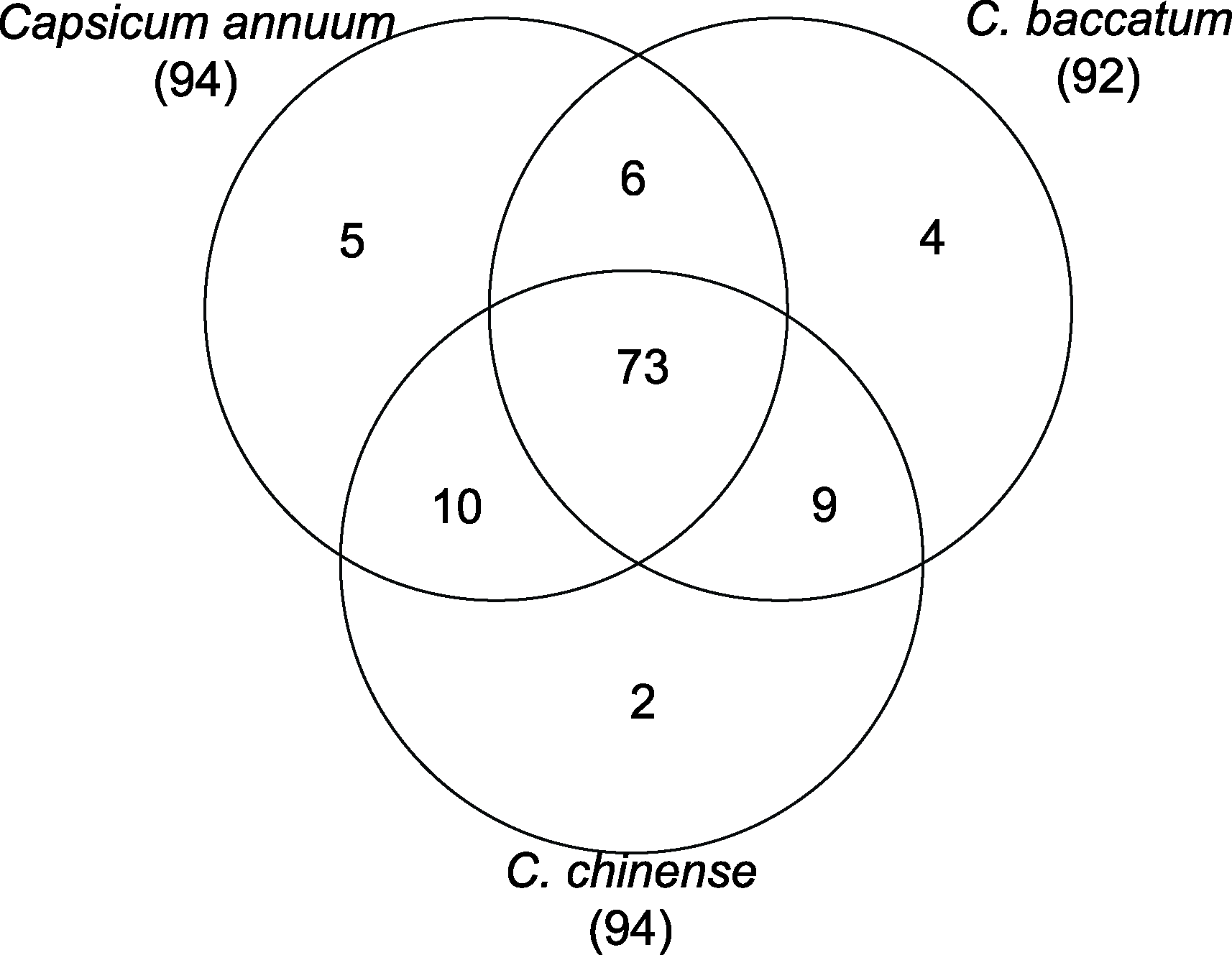
图4 一年生辣椒、浆果状辣椒和中国辣椒中R2R3-MYB转录因子直系同源基因的数量
Figure 4 The number of R2R3-MYB transcription factor orthologous genes in Capsicum annuum, C. baccatum, and C. chinense
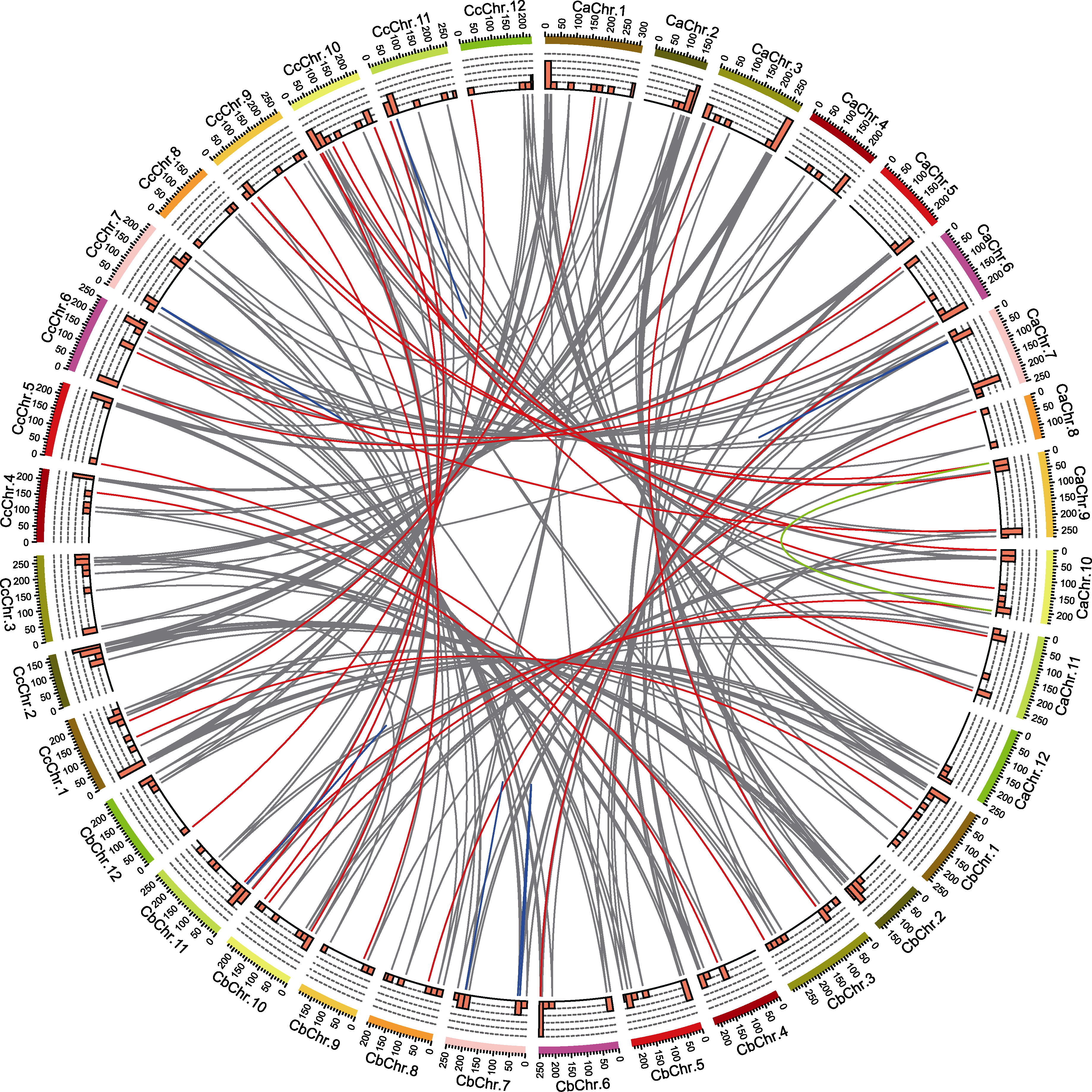
图5 一年生辣椒(Ca)、浆果状辣椒(Cb)和中国辣椒(Cc)中R2R3-MYB转录因子的同源基因对 从外向内依次是3种辣椒的染色体数目、20 Mb窗口统计R2R3-MYB基因的数量(0-5)和3种辣椒中R2R3-MYB同源基因对。灰色线连接3种辣椒中都存在的同源基因对; 红色线连接只在两种辣椒中存在的同源基因对; 绿色线连接重复基因; 蓝色线连接串联重复基因。
Figure 5 Homologous R2R3-MYB transcription factor gene pairs in Capsicum annuum (Ca), C. baccatum (Cb), and C. chinense (Cc) Tracks from outside to inside are the number of chromosomes, number of R2R3-MYB genes (0-5) (20 Mb windows), and homologous gene pairs among three Capsicum species. The gray lines connect the homologous gene pairs that exist in three Capsicum species; the red lines connect the homologous gene pairs in two species; the green lines connect the replicated genes; and the blue lines connect the tandem repeated genes.
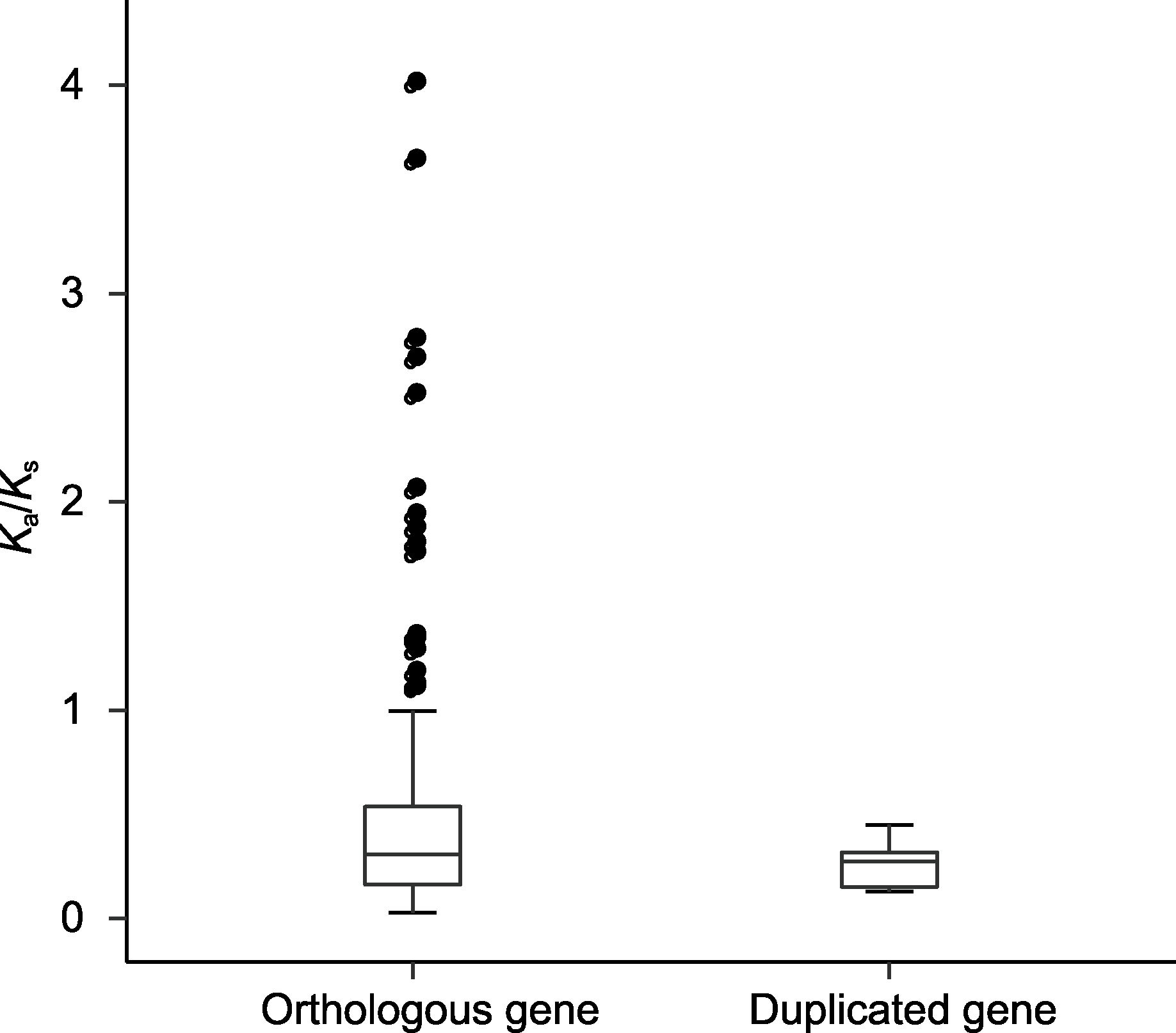
图6 一年生辣椒、浆果状辣椒和中国辣椒中R2R3-MYB转录因子直系同源和重复基因对的Ka/Ks比率 黑色点表示非同义替换率(Ka)/同义替换率(Ks)>1的基因对。
Figure 6 The Ka/Ks ratios for the orthologous and duplicated gene pairs of R2R3-MYB transcription factor in Capsicum annuum, C. baccatum, and C. chinense The black dots represent gene pairs with non-synonymous substitution rate (Ka)/synonymous substitution rate (Ks)>1.
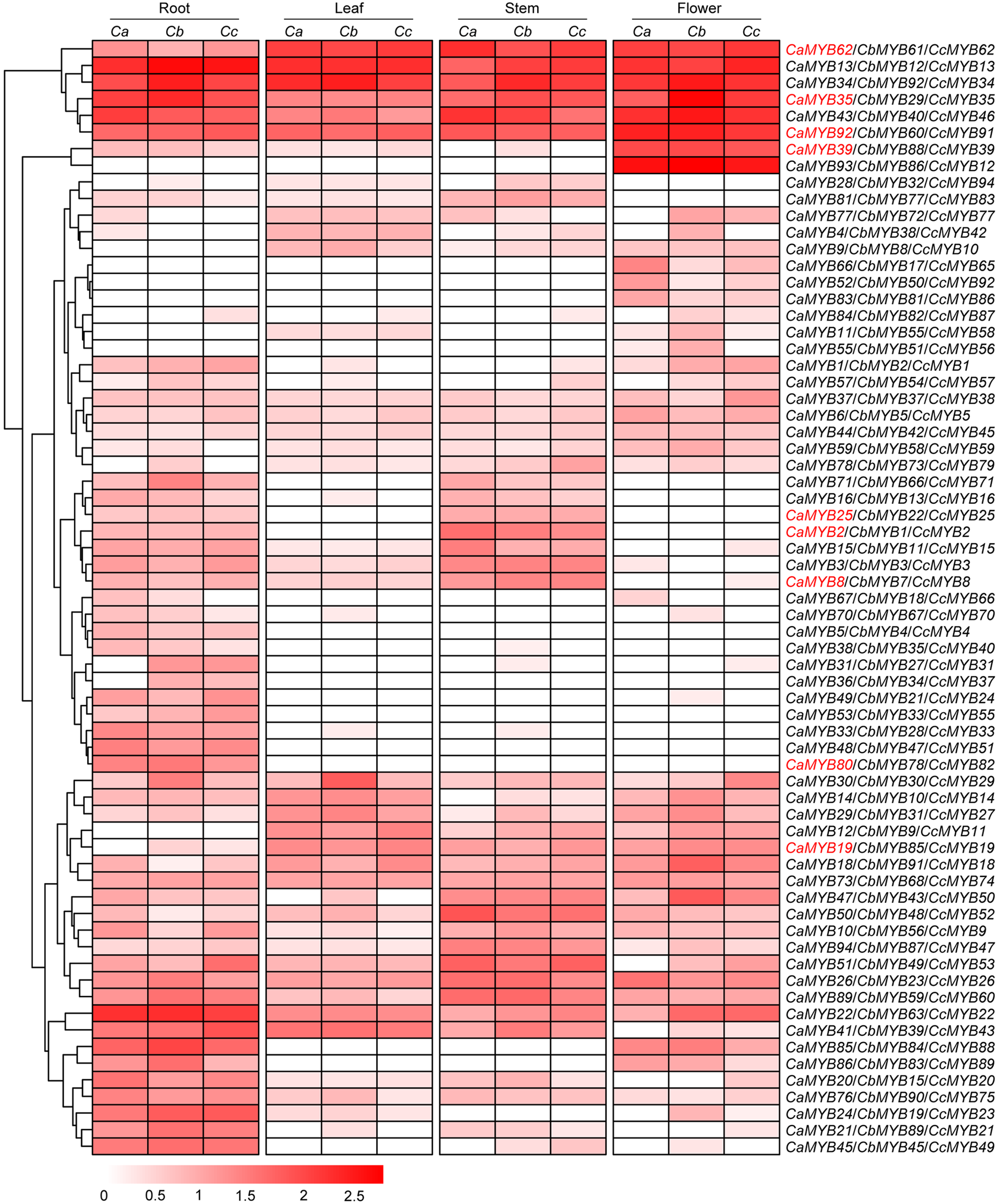
图7 一年生辣椒(Ca)、浆果状辣椒(Cb)和中国辣椒(Cc) R2R3-MYB基因的组织表达特征颜色条表示R2R3-MYB基因在不同组织中log10(FPKM+1)值的变化范围。红色字体的基因进行了qRT-PCR验证。
Figure 7 Expression profile of R2R3-MYB genes in different tissues from Capsicum annuum (Ca), C. baccatum (Cb), and C. chinense (Cc) The color bars indicate the variation range of log10(FPKM+1) values of R2R3-MYB genes in different tissues. The expression of the genes in red was verified by qRT-PCR.
| 1 | 居利香, 雷欣, 赵成志, 舒黄英, 汪志伟, 成善汉 (2020). 辣椒MYB基因家族的鉴定及与辣味关系分析. 园艺学报 47, 875-892. |
| 2 |
李格, 孟小庆, 李宗芸, 朱明库 (2020). 甘薯盐胁迫响应基因IbMYB3的表达特征及生物信息学分析. 植物学报 55, 38-48.
DOI |
| 3 | 隋益虎, 陈劲枫 (2009). 辣椒属种间远缘杂交育种研究进展. 热带作物学报 30, 557-563. |
| 4 |
唐嘉瓅, 邱杰, 黄学辉 (2020). 基因组学技术大发展助力园艺植物研究取得新进展. 植物学报 55, 1-4.
DOI |
| 5 | 魏家香, 俞佳虹, 程远, 叶青静, 王荣青, 阮美颖, 李志邈, 姚祝平, 周国治, 杨悦俭, 万红建 (2018). 辣椒种间杂交的现状及其研究进展. 分子植物育种 16, 5474-5482. |
| 6 |
Blanc G, Wolfe KH (2004). Widespread paleopolyploidy in model plant species inferred from age distributions of duplicate genes. Plant Cell 16, 1667-1678.
DOI URL |
| 7 |
Cannon SB, Mitra A, Baumgarten A, Young ND, May G (2004). The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families inArabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol 4, 10.
DOI URL |
| 8 |
Chalhoub B, Denoeud F, Liu SY, Parkin IAP, Tang HB, Wang XY, Chiquet J, Belcram H, Tong CB, Samans B, Corréa M, Da Silva C, Just J, Falentin C, Koh CS, Le Clainche I, Bernard M, Bento P, Noel B, Labadie K, Alberti A, Charles M, Arnaud D, Guo H, Daviaud C, Alamery S, Jabbari K, Zhao MX, Edger PP, Chelaifa H, Tack D, Lassalle G, Mestiri I, Schnel N, Le Paslier MC, Fan GY, Renault V, Bayer PE, Golicz AA, Manoli S, Lee TH, Thi VHD, Chalabi S, Hu Q, Fan CC, Tollenaere R, Lu YH, Battail C, Shen JX, Sidebottom CHD, Wang XF, Canaguier A, Chauveau A, Bérard A, Deniot G, Guan M, Liu ZS, Sun FM, Lim YP, Lyons E, Town CD, Bancroft I, Wang XW, Meng JL, Ma JX, Pires JC, King GJ, Brunel D, Delourme R, Renard M, Aury JM, Adams KL, Batley J, Snowdon RJ, Tost J, Edwards D, Zhou YM, Hua W, Sharpe AG, Paterson AH, Guan CY, Wincker P (2014). Early allopolyploid evolution in the post-Neolithic Brassica napus oilseed genome. Science 345, 950-953.
DOI URL |
| 9 |
Chen SF, Zhou YQ, Chen YR, Gu J (2018). Fastp: an ultra- fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 34, i884-i890.
DOI URL |
| 10 |
Chen YH, Yang XY, He K, Liu MH, Li JG, Gao ZF, Lin ZQ, Zhang YF, Wang XX, Qiu XM, Shen YP, Zhang L, Deng XH, Luo JC, Deng XW, Chen ZL, Gu HY, Qu LJ (2006). The MYB transcription factor superfamily of Arabidopsis: expression analysis and phylogenetic comparison with the rice MYB family. Plant Mol Biol 60, 107-124.
DOI URL |
| 11 |
Crooks GE, Hon G, Chandonia JM, Brenner SE (2004). WebLogo: a sequence logo generator. Genome Res 14, 1188-1190.
PMID |
| 12 |
Dias AP, Braun EL, McMullen MD, Grotewold E (2003). Recently duplicated maize R2R3 Myb genes provide evidence for distinct mechanisms of evolutionary divergence after duplication. Plant Physiol 131, 610-620.
DOI URL |
| 13 |
Dossa K, Mmadi MA, Zhou R, Liu AL, Yang YX, Diouf D, You J, Zhang XR (2020). Ectopic expression of the sesame MYB transcription factor SiMYB305 promotes root growth and modulates ABA-mediated tolerance to drought and salt stresses in Arabidopsis. AoB Plants 12, plz081.
DOI URL |
| 14 |
Du H, Yang SS, Liang Z, Feng BR, Liu L, Huang YB, Tang YX (2012). Genome-wide analysis of the MYB transcription factor superfamily in soybean. BMC Plant Biol 12, 106.
DOI URL |
| 15 |
Dubos C, Stracke R, Grotewold E, Weisshaar B, Martin C, Lepiniec L (2010). MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci 15, 573-581.
DOI URL |
| 16 |
Geng P, Zhang S, Liu JY, Zhao CH, Wu J, Cao YP, Fu CX, Han X, He H, Zhao Q (2020). MYB20, MYB42, MYB43, and MYB85 regulate phenylalanine and lignin biosynthesis during secondary cell wall formation. Plant Physiol 182, 1272-1283.
DOI URL |
| 17 |
Haga N, Kato K, Murase M, Araki S, Kubo M, Demura T, Suzuki K, Muller I, Voß U, Jürgens G, Ito M (2007). R1R2R3-Myb proteins positively regulate cytokinesis through activation of KNOLLE transcription in Arabidopsis thaliana. Development 134, 1101-1110.
DOI URL |
| 18 |
Hajiebrahimi A, Owji H, Hemmati S (2017). Genome-wide identification, functional prediction, and evolutionary analysis of the R2R3-MYB superfamily in Brassica napus. Genome 60, 797-814.
DOI PMID |
| 19 |
Heberle H, Meirelles GV, da Silva FR, Telles GP, Minghim R (2015). InteractiVenn: a web-based tool for the analysis of sets through Venn diagrams. BMC Bioinformatics 16, 169.
DOI PMID |
| 20 |
Hu B, Jin JP, Guo AY, Zhang H, Luo JC, Gao G (2015). GSDS 2.0: an upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 31, 1296-1297.
DOI URL |
| 21 |
Ibiza VP, Blanca J, Cañizares J, Nuez F (2012). Taxonomy and genetic diversity of domesticated Capsicum species in the Andean region. Genet Resour Crop Evol 59, 1077-1088.
DOI URL |
| 22 |
Jia L, Clegg MT, Jiang T (2004). Evolutionary dynamics of the DNA-binding domains in putative R2R3-MYB genes identified from rice subspecies indica and japonica genomes. Plant Physiol 134, 575-585.
PMID |
| 23 |
Jiang CZ, Gu JY, Chopra S, Gu X, Peterson T (2004). Ordered origin of the typical two- and three-repeat MYB genes. Gene 326, 13-22.
DOI URL |
| 24 |
Kasuga M, Liu Q, Miura S, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (1999). Improving plant drought, salt, and freezing tolerance by gene transfer of a single stress-inducible transcription factor. Nat Biotechnol 17, 287-291.
PMID |
| 25 |
Kim S, Park J, Yeom SI, Kim YM, Seo E, Kim KT, Kim MS, Lee JM, Cheong K, Shin HS, Kim SB, Han K, Lee J, Park M, Lee HA, Lee HY, Lee Y, Oh S, Lee JH, Choi E, Choi E, Lee SE, Jeon J, Kim H, Choi G, Song H, Lee J, Lee SC, Kwon JK, Lee HY, Koo N, Hong YJ, Kim RW, Kang WH, Huh JH, Kang BC, Yang TJ, Lee YH, Bennetzen JL, Choi D (2017). New reference genome sequences of hot pepper reveal the massive evolution of plant disease-resistance genes by retroduplication. Genome Biol 18, 210.
DOI URL |
| 26 |
Krzywinski M, Schein J, Birol I, Connors J, Gascoyne R, Horsman D, Jones SJ, Marra MA (2009). Circos: an information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res 19, 1639-1645.
DOI URL |
| 27 |
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016). MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33, 1870-1874.
DOI URL |
| 28 |
Langmead B, Salzberg SL (2012). Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods 9, 357-359.
DOI URL |
| 29 |
Li B, Dewey CN (2011). RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinformatics 12, 323.
DOI URL |
| 30 |
Li XX, Guo C, Ahmad S, Wang Q, Yu J, Liu C, Guo YF (2019). Systematic analysis of MYB family genes in potato and their multiple roles in development and stress responses. Biomolecules 9, 317.
DOI URL |
| 31 |
Liu YH, Kui LW, Espley RV, Wang L, Li YM, Liu Z, Zhou P, Zeng LH, Zhang XJ, Zhang JL, Allan AC (2019). StMYB44 negatively regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis at high temperatures in tuber flesh of potato. J Exp Bot 70, 3809-3824.
DOI URL |
| 32 |
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2 ‒ΔΔCT method . Methods 25, 402-408.
PMID |
| 33 | Lotkowska ME, Tohge T, Fernie AR, Xue GP, Balazadeh S, Mueller-Roeber B (2015). The Arabidopsis transcription factor MYB112 promotes anthocyanin formation during salinity and under high light stress. Plant Physiol 169, 1862-1880. |
| 34 |
Matus JT, Aquea F, Arce-Johnson P (2008). Analysis of the grape MYB R2R3 subfamily reveals expanded wine quality-related clades and conserved gene structure organization across Vitis and Arabidopsis genomes. BMC Plant Biol 8, 83.
DOI URL |
| 35 |
Ogata K, Kanei-Ishii C, Sasaki M, Hatanaka H, Nagadoi A, Enari M, Nakamura H, Nishimura Y, Ishii S, Sarai A (1996). The cavity in the hydrophobic core of Myb DNA- binding domain is reserved for DNA recognition and trans- activation. Nat Struct Biol 3, 178-187.
PMID |
| 36 |
Pabo CO, Sauer RT (1992). Transcription factors: structural families and principles of DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem 61, 1053-1095.
PMID |
| 37 |
Paz-Ares J, Ghosal D, Wienand U, Peterson PA, Saedler H (1987). The regulatory c1 locus of Zea mays encodes a protein with homology to myb proto-oncogene products and with structural similarities to transcriptional activators. EMBO J 6, 3553-3558.
PMID |
| 38 |
Qi XW, Fang HL, Chen ZQ, Liu ZQ, Yu X, Liang CY (2019). Ectopic expression of a R2R3-MYB transcription factor gene LjaMYB12 from Lonicera japonica increases flavonoid accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Int J Mol Sci 20, 4494.
DOI URL |
| 39 |
Riechmann JL, Heard J, Martin G, Reuber L, Jiang CZ, Keddie J, Adam L, Pineda O, Ratcliffe OJ, Samaha RR, Creelman R, Pilgrim M, Broun P, Zhang JZ, Ghandehari D, Sherman BK, Yu GL (2000). Arabidopsis transcription factors: genome-wide comparative analysis among eukaryotes. Science 290, 2105-2110.
DOI URL |
| 40 |
Rosinski JA, Atchley WR (1998). Molecular evolution of the MYB family of transcription factors: evidence for polyphyletic origin. J Mol Evol 46, 74-83.
PMID |
| 41 |
Schmutz J, Cannon SB, Schlueter J, Ma JX, Mitros T, Nelson W, Hyten DL, Song QJ, Thelen JJ, Cheng JL, Xu D, Hellsten U, May GD, Yu Y, Sakurai T, Umezawa T, Bhattacharyya MK, Sandhu D, Valliyodan B, Lindquist E, Peto M, Grant D, Shu SQ, Goodstein D, Barry K, Futrell-Griggs M, Abernathy B, Du JC, Tian ZX, Zhu LC, Gill N, Joshi T, Libault M, Sethuraman A, Zhang XC, Shinozaki K, Nguyen HT, Wing RA, Cregan P, Specht J, Grimwood J, Rokhsar D, Stacey G, Shoema- ker RC, Jackson SA (2010). Genome sequence of the palaeopolyploid soybean. Nature 463, 178-183.
DOI PMID |
| 42 |
Stracke R, Ishihara H, Huep G, Barsch A, Mehrtens F, Niehaus K, Weisshaar B (2007). Differential regulation of closely related R2R3-MYB transcription factors controls flavonol accumulation in different parts of the Arabidopsis thaliana seedling. Plant J 50, 660-677.
PMID |
| 43 |
Stracke R, Werber M, Weisshaar B (2001). The R2R3- MYB gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4, 447-456.
PMID |
| 44 |
Sun WJ, Ma ZT, Chen H, Liu MY (2019). MYB gene family in potato ( Solanum tuberosum L.): genome-wide identification of hormone-responsive reveals their potential functions in growth and development. Int J Mol Sci 20, 4847.
DOI URL |
| 45 |
The Potato Genome Sequencing Consortium (2011). Genome sequence and analysis of the tuber crop potato. Nature 475, 189-195.
DOI URL |
| 46 |
The Tomato Genome Consortium (2012). The tomato genome sequence provides insights into fleshy fruit evolution. Nature 485, 635-641.
DOI URL |
| 47 |
Ullah A, Ul Qamar MT, Nisar M, Hazrat A, Rahim G, Khan AH, Hayat K, Ahmed S, Ali W, Khan A, Yang XY (2020). Characterization of a novel cotton MYB gene, GhMYB108- like responsive to abiotic stresses. Mol Biol Rep 47, 1573-1581.
DOI URL |
| 48 |
Valliyodan B, Nguyen HT (2006). Understanding regulatory networks and engineering for enhanced drought tolerance in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 9, 189-195.
PMID |
| 49 |
Wang DP, Wan HL, Zhang S, Yu J (2009). γ-MYN: a new algorithm for estimating Ka and Ks with consideration of variable substitution rates. Biol Direct 4, 20.
DOI URL |
| 50 |
Wang DP, Zhang YB, Zhang Z, Zhu J, Yu J (2010). KaKs_Calculator 2.0: a toolkit incorporating gamma-series methods and sliding window strategies. Genom Proteom Bioinf 8, 77-80.
DOI URL |
| 51 |
Wang YC, Liu WJ, Jiang HY, Mao ZL, Wang N, Jiang SH, Xu HF, Yang GX, Zhang ZY, Chen XS (2019). The R2R3-MYB transcription factor MdMYB24-like is involved in methyl jasmonate-induced anthocyanin biosynthesis in apple. Plant Physiol Biochem 139, 273-282.
DOI URL |
| 52 |
Wang YP, Tang HB, Debarry JD, Tan X, Li JP, Wang XY, Lee TH, Jin HZ, Marler B, Guo H, Kissinger JC, Paterson AH (2012). MCScanX: a toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res 40, e49.
DOI URL |
| 53 |
Yadav CB, Bonthala VS, Muthamilarasan M, Pandey G, Khan Y, Prasad M (2015). Genome-wide development of transposable elements-based markers in foxtail millet and construction of an integrated database. DNA Res 22, 79-90.
DOI URL |
| 54 |
Zapata L, Ding J, Willing EM, Hartwig B, Bezdan D, Jiao WB, Patel V, Velikkakam James G, Koornneef M, Ossowski S, Schneeberger K (2016). Chromosome-level assembly of Arabidopsis thaliana Ler reveals the extent of translocation and inversion polymorphisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113, E4052-E4060.
DOI URL |
| 55 |
Zhang YL, Zhang CL, Wang GL, Wang YX, Qi CH, Zhao Q, You CX, Li YY, Hao YJ (2019). The R2R3 MYB transcription factor MdMYB30 modulates plant resistance against pathogens by regulating cuticular wax biosynthesis. BMC Plant Biol 19, 362.
DOI URL |
| 56 |
Zhang Z, Xiao JF, Wu JY, Zhang HY, Liu GM, Wang XM, Dai L (2012). ParaAT: a parallel tool for constructing multiple protein-coding DNA alignments. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 419, 779-781.
DOI URL |
| 57 |
Zhao PP, Li Q, Li J, Wang LN, Ren ZH (2014). Genome- wide identification and characterization of R2R3MYB family in Solanum lycopersicum. Mol Genet Genomics 289, 1183-1207.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 李安, 徐桂霞, 孔宏智. F-box基因拷贝数目变异的机制研究:以12种果蝇为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2011, 19(1): 3-16. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||