

植物学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (2): 217-226.DOI: 10.11983/CBB18222 cstr: 32102.14.CBB18222
所属专题: 逆境生物学专辑 (2019年54卷2期)
化文平1,2,陈尘3,4,智媛2,刘莉1,王喆之2,李翠芹2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2018-10-22
接受日期:2019-02-19
出版日期:2019-03-01
发布日期:2019-09-01
通讯作者:
李翠芹
基金资助:
Wenping Hua1,2,Chen Chen3,4,Yuan Zhi2,Li Liu1,Zhezhi Wang2,Cuiqin Li2,*( )
)
Received:2018-10-22
Accepted:2019-02-19
Online:2019-03-01
Published:2019-09-01
Contact:
Cuiqin Li
摘要: 香叶基香叶基焦磷酸合酶(GGPPS)是植物二萜类次生代谢物合成过程中的重要调控位点。在药用模式植物丹参(Salvia miltiorrhiza)中, GGPPS基因家族成员SmGGPPS2的生物学功能及其在丹参酮有效成分合成过程中的作用尚不明确。分别在丹参植株中过表达和RNA干涉SmGGPPS2基因, 并对转基因丹参中丹参酮含量和丹参酮合成相关基因表达量 以及转基因植物生理指标进行检测, 结果表明, 过表达SmGGPPS2株系中的丹参酮IIA和铁锈醇等脂溶性成分含量高于野生型; RNA干涉SmGGPPS2株系中的丹参酮IIA和铁锈醇等脂溶性成分含量均低于野生型。调节表达SmGGPPS2后, 丹参株系中SmHMGR1和SmCPS1等多个关键酶基因的表达都呈现明显的变化。此外, 调节表达SmGGPPS2还影响丹参植株抗性。以上结果表明, SmGGPPS2在丹参酮等萜类物质的合成中起重要的调控作用。
化文平,陈尘,智媛,刘莉,王喆之,李翠芹. SmGGPPS2对丹参酮合成的影响. 植物学报, 2019, 54(2): 217-226.
Wenping Hua,Chen Chen,Yuan Zhi,Li Liu,Zhezhi Wang,Cuiqin Li. Effect of SmGGPPS2 Expression on Tanshinones Biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(2): 217-226.
| Primer name | Sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|
| OG2S (KpnI) | GGGGTACCGCGAAGAGCGTGGAAGC- AGA |
| OG2R (BamHI) | CGGGATCC GGCAATAGCAATCAAGGGAGCA |
| G2i1S (EcoRI) | CGGAATTC CTCCTCTCAACCTCTGTCAAAACTC |
| G2i1R (KpnI) | GGGGTACCTCATCTGGACCACTGCC- TCC |
| G2i2S (BamHI) | CGGGATCC CTCCTCTCAACCTCTGTCAAAACTC |
| G2i2R (HindIII) | CCCAAGCTTTCATCTGGACCACTGCC- TCC |
| 35SF | GCCGTGAAGACTGGCGAACA |
| 35SR | AGGAAGGGTCTTGCGAAGGATAGT |
表1 本研究中载体构建及检测所用引物
Table 1 Primers used for vector construction and detection in this study
| Primer name | Sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|
| OG2S (KpnI) | GGGGTACCGCGAAGAGCGTGGAAGC- AGA |
| OG2R (BamHI) | CGGGATCC GGCAATAGCAATCAAGGGAGCA |
| G2i1S (EcoRI) | CGGAATTC CTCCTCTCAACCTCTGTCAAAACTC |
| G2i1R (KpnI) | GGGGTACCTCATCTGGACCACTGCC- TCC |
| G2i2S (BamHI) | CGGGATCC CTCCTCTCAACCTCTGTCAAAACTC |
| G2i2R (HindIII) | CCCAAGCTTTCATCTGGACCACTGCC- TCC |
| 35SF | GCCGTGAAGACTGGCGAACA |
| 35SR | AGGAAGGGTCTTGCGAAGGATAGT |
| Primer name | Sequence (5′→3′) | Primer name | Sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ActinS | AGGAACCACCGATCCAGACA | SmDXS1S | TGAGAGCGACTACGACTGCTTTGG |
| ActinR | GGTGCCCTGAGGTCCTGTT | SmDXS1R | CCCATCCAGATTGGCAGTAGGC |
| SmHMGR1S | GCAACCATCTACTCTCGTCCCA | SmDXS2S | GGTCGAGGAACTGGAGGGATTG |
| SmHMGR1R | GTGCTCCATGAGCTGCATCAG | SmDXS2R | CGTCAGGATTTCGTGCGGATA |
| SmHMGR2S | GGGTTCAACTACGAGGCCATACTG | SmDXS3S | CACGAATGGGCTGCCAAAAT |
| SmHMGR2R | TGTTTGTGCTCGCCACCAGG | SmDXS3R | CCATCGAATCCAATGAAGCCAC |
| SmHMGR3S | AGTCTCGTGATGTCCCTGCTCG | SmGGPPS1S | GGGGCTATTTTGGGAGGTGGAA |
| SmHMGR3R | GCCTCAACCTGCTTGGCGTA | SmGGPPS1R | CAGCAGCTTGGGATACGTGGTC |
| SmIPI1S | AGCGTGCATCCAAATCCAGAC | SmGGPPS2S | CGGTCTCCTCTCAACCTCTGTCAA |
| SmIPI1R | GATAGCTTCAAGCCCCCCTCA | SmGGPPS2R | CTCCTTCATCTGGACCACTGCCT |
| SmCPS1S | ATGGATGGGCAGCAGCAGTAAA | SmGGPPS3S | GGCCAGTGCTCTGCTGTCTGTG |
| SmCPS1R | CGTCCTCAACAACGTCCTGATGTATT | SmGGPPS3R | TCGGCCACCTCCATCGCTT |
表2 本研究中qPCR检测所用引物
Table 2 Primers used for qPCR in this study
| Primer name | Sequence (5′→3′) | Primer name | Sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ActinS | AGGAACCACCGATCCAGACA | SmDXS1S | TGAGAGCGACTACGACTGCTTTGG |
| ActinR | GGTGCCCTGAGGTCCTGTT | SmDXS1R | CCCATCCAGATTGGCAGTAGGC |
| SmHMGR1S | GCAACCATCTACTCTCGTCCCA | SmDXS2S | GGTCGAGGAACTGGAGGGATTG |
| SmHMGR1R | GTGCTCCATGAGCTGCATCAG | SmDXS2R | CGTCAGGATTTCGTGCGGATA |
| SmHMGR2S | GGGTTCAACTACGAGGCCATACTG | SmDXS3S | CACGAATGGGCTGCCAAAAT |
| SmHMGR2R | TGTTTGTGCTCGCCACCAGG | SmDXS3R | CCATCGAATCCAATGAAGCCAC |
| SmHMGR3S | AGTCTCGTGATGTCCCTGCTCG | SmGGPPS1S | GGGGCTATTTTGGGAGGTGGAA |
| SmHMGR3R | GCCTCAACCTGCTTGGCGTA | SmGGPPS1R | CAGCAGCTTGGGATACGTGGTC |
| SmIPI1S | AGCGTGCATCCAAATCCAGAC | SmGGPPS2S | CGGTCTCCTCTCAACCTCTGTCAA |
| SmIPI1R | GATAGCTTCAAGCCCCCCTCA | SmGGPPS2R | CTCCTTCATCTGGACCACTGCCT |
| SmCPS1S | ATGGATGGGCAGCAGCAGTAAA | SmGGPPS3S | GGCCAGTGCTCTGCTGTCTGTG |
| SmCPS1R | CGTCCTCAACAACGTCCTGATGTATT | SmGGPPS3R | TCGGCCACCTCCATCGCTT |
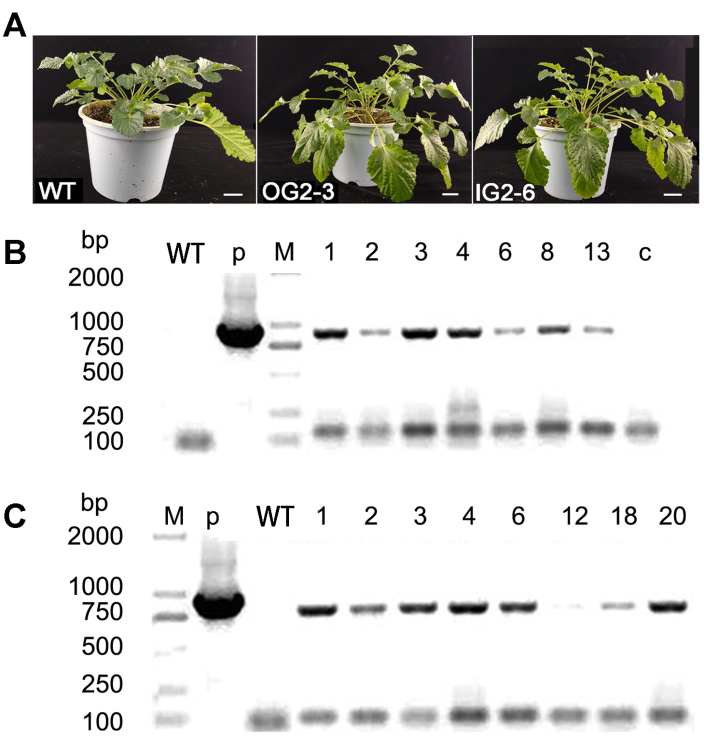

图1 丹参转基因株系及其DNA水平的PCR检测 (A) SmGGPPS2过表达代表性株系(OG2-3)、SmGGPPS2 RNA干涉表达代表性株系(IG2-6)及野生型对照(Bar=2 cm); (B) SmGGPPS2过表达转基因株系(1-13); (C) SmGGPPS2- RNAi转基因株系(1-20)。M: DNA标准量DL2000; WT: 野生型; c: 阴性对照; p: 阳性对照
Figure 1 Phenotypes and PCR-screening of the transgenic lines of Salvia miltiorrhiza (A) SmGGPPS2-overexpression transgenic line (OG2-3), SmGGPPS2-RNAi transgenic line (IG2-6), and wild type (Bar= 2 cm); (B) SmGGPPS2-overexpression transgenic lines (1-13); (B) SmGGPPS2-RNAi transgenic lines (1-20). M: DNA marker DL2000; WT: Wild type; c: Negative control; p: Positive control
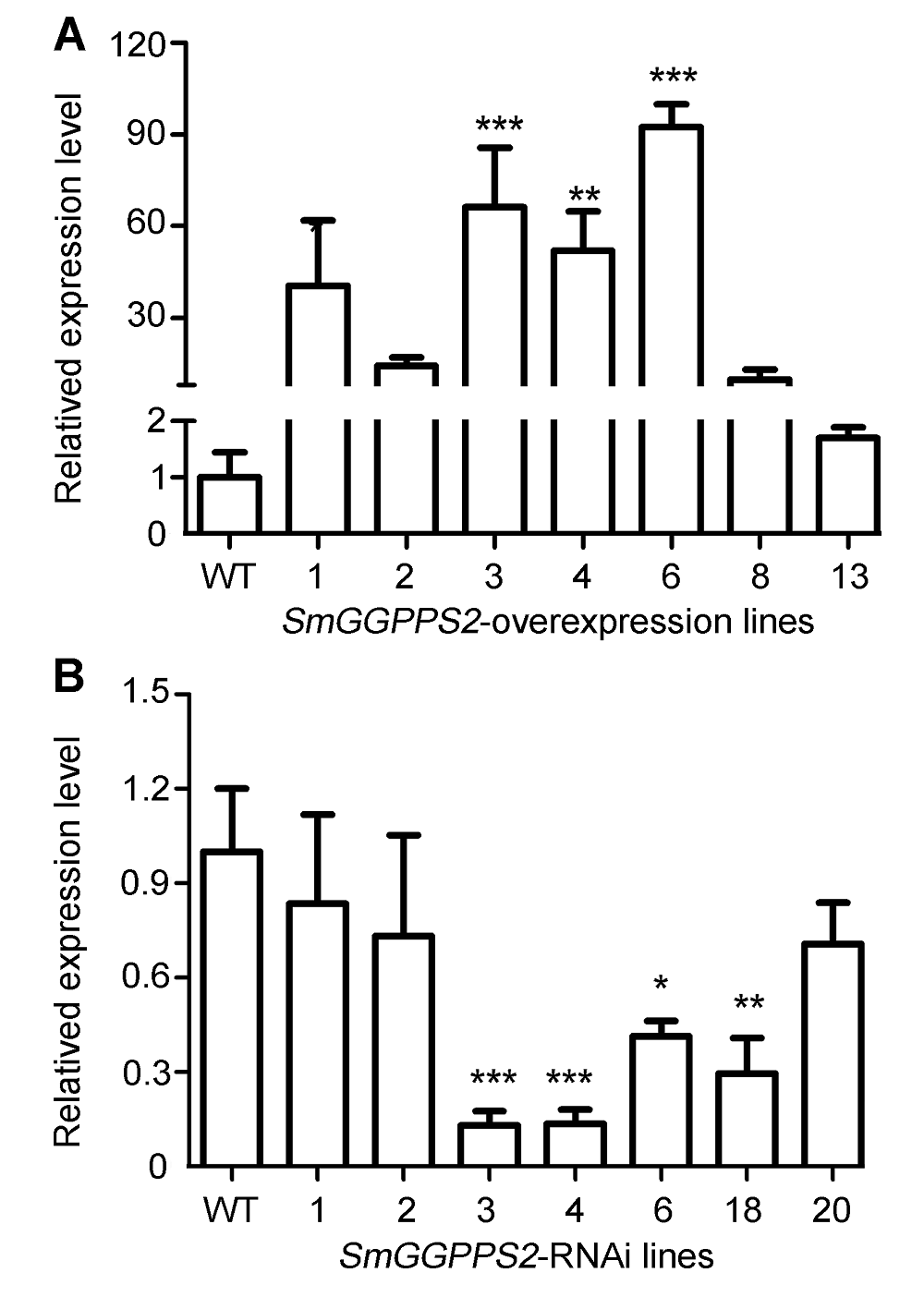
图2 SmGGPPS2在丹参过表达(A)和RNA干涉(B)株系中的表达WT: 野生型。* 差异显著(P?0.05); ** 差异显著(P?0.01); *** 差异显著(P? 0.001)。数据均进行归一化处理。
Figure 2 Expression of SmGGPPS2 in overexpression (A) and RNAi (B) Salvia miltiorrhiza transgenic linesWT: Wild type. * Significant differences (P?0.05); ** Significant differences (P?0.01); *** Significant differences (P? 0.001). The data are normalized.
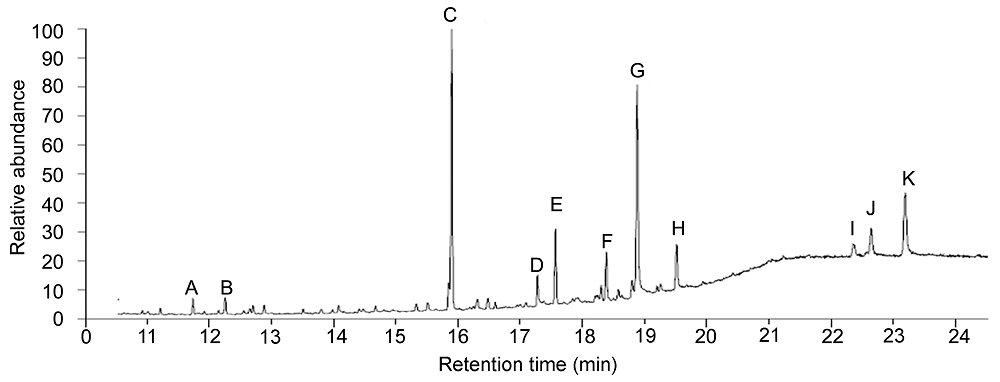
图3 GC-MS检测转基因丹参提取物总离子流色谱峰A: 邻苯二甲酸二异丁酯; B: 7,9-Di-tert-butyl-1-oxaspiro(4,5)deca-6,9-diene-2,8-dione; C: 铁锈醇; D: 单棕榈酸甘油; E: 邻苯二甲酸二异辛酯; F: 羟基陶塔酚; G: 丹参酮IIA; H: 隐丹参酮; I: 菜油甾醇; J: 豆甾醇; K: β-谷甾醇
Figure 3 GC-MS chromatogram of Salvia miltiorrhiza transgenic linesA: Phthalic acid diisobutyl ester; B: 7,9-Di-tert-butyl-1-oxaspiro(4,5)deca-6,9-diene-2,8-dione; C: Ferruginol; D: b-monopalmitin; E: Diisooctyl phthalate; F: 7β-hydroxytotarol; G: Tanshinone IIA; H: Cryptotanshinone; I: Campesterol; J: Stigmasterol; K: β- sitosterol
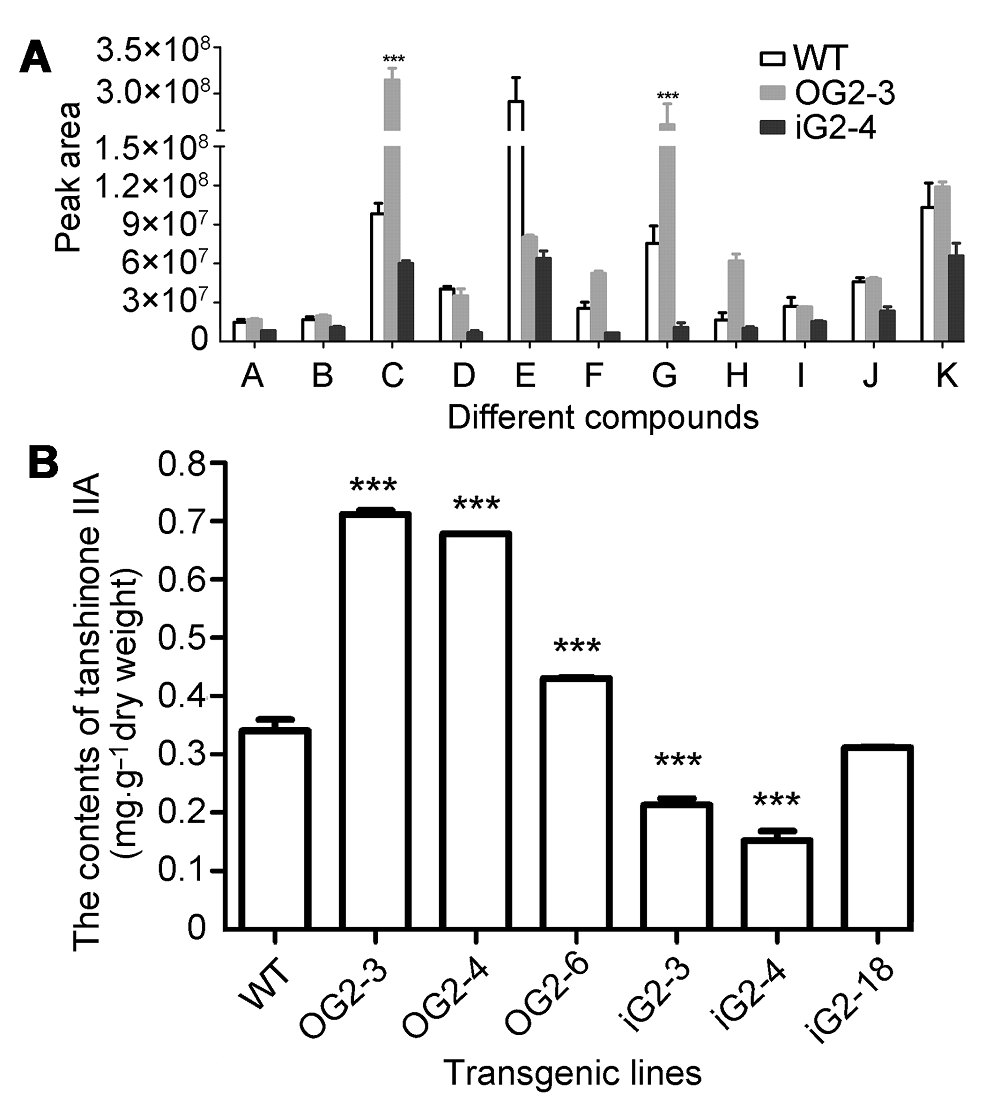
图4 转基因丹参株系脂溶性提取物中不同成分含量比较(A)及不同转基因丹参株系中丹参酮IIA含量(B) A–K同图3。WT: 野生型。*** 差异显著(P<0.001)
Figure 4 Contents of different ingredients from fat-soluble extract in transgenic lines (A) and contents oftanshinone IIA in different transgenic lines (B) of Salvia miltiorrhizaA–K see Figure 3. WT: Wild type. *** Significant differences (P<0.001)
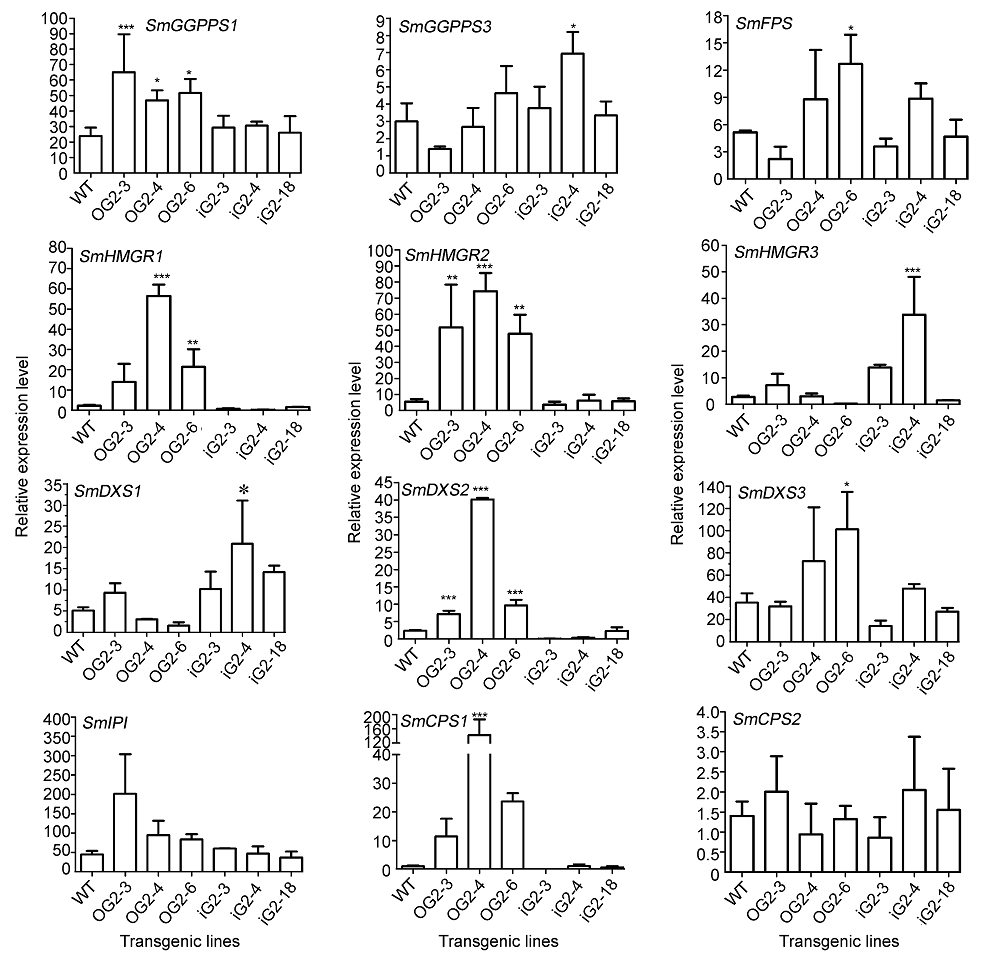
图5 转基因丹参株系中丹参酮合成途径相关基因的表达水平WT: 野生型。* 差异显著(P<0.05); ** 差异显著(P<0.01); *** 差异显著(P<0.001)
Figure 5 Relative expression levels of genes involved in tanshinones biosynthesis of Salvia miltiorrhiza transgenic lines WT: Wild type. * Significant differences (P<0.05); ** Significant differences (P<0.01); *** Significant differences (P<0.001)
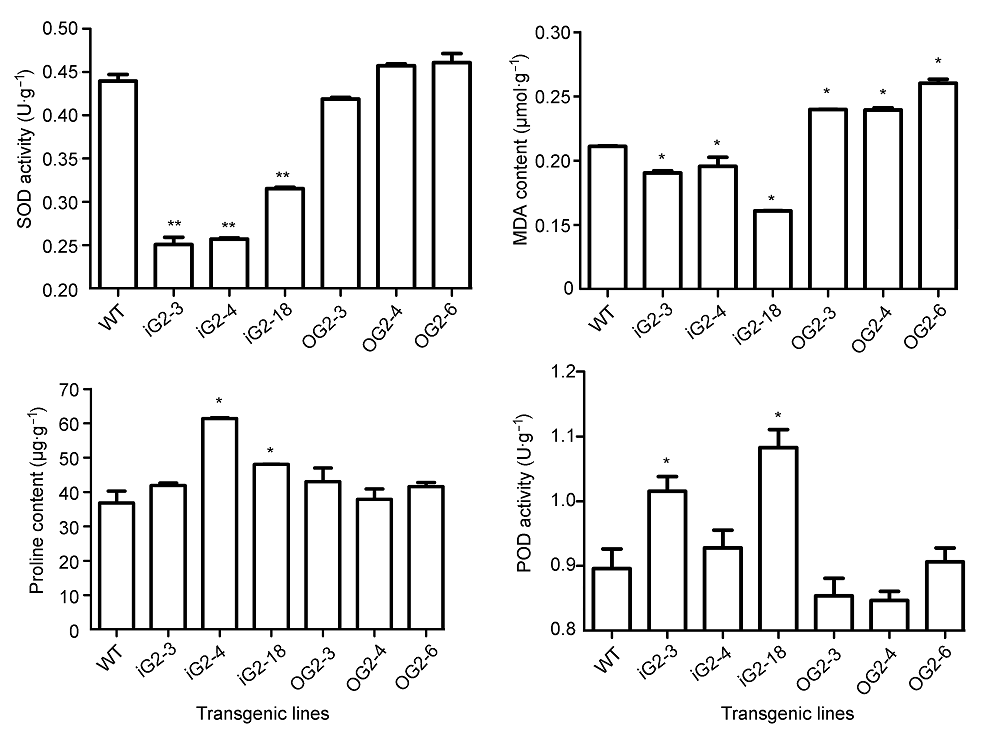
图6 不同丹参转基因株系抗逆生理指标SOD: 超氧化物歧化酶; MDA: 丙二醛; POD: 过氧化物酶; WT: 野生型。* 差异显著(P<0.05); ** 差异显著(P<0.01)
Figure 6 The resistance physiological indexes of different Salvia miltiorrhiza transgenic linesSOD: Superoxide dismutase; MDA: Malondialdehyde; POD: Peroxidase; WT: Wild type. * Significant differences (P<0.05); ** Significant differences (P<0.01)
| [1] | 化文平, 刘文超, 王喆之, 李翠芹 ( 2016). 干涉丹参SmORA1对植物抗病和丹参酮类次生代谢的影响. 中国农业科学 49, 491-502. |
| [2] | 化文平, 宋双红, 智媛, 王喆之 ( 2014). 丹参SmGGPPS3基因的克隆及表达分析. 植物科学学报 32, 50-57. |
| [3] | 王海燕, 李玉琴, 王广旭 ( 2011). 白花丹参脂溶性成分超临界二氧化碳流体萃取与气相色谱-质谱分析. 医药导报 30, 978-981. |
| [4] | 张蕾 ( 2009). 丹参牻牛儿基牻牛儿基焦磷酸合酶基因的克隆与功能研究. 博士论文. 北京: 中国人民解放军军事医学科学院. pp. 27-40. |
| [5] |
Aharoni A, Giri AP, Deuerlein S, Griepink F, de Kogel WJ, Verstappen FWA, Verhoeven HA, Jongsma MA, Schwab W, Bouwmeester HJ ( 2003). Terpenoid metabolism in wild-type and transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Plant Cell 15, 2866-2884.
DOI URL |
| [6] | Chang TH, Guo RT, Ko TP, Wang AHJ, Liang PH ( 2006). Crystal structure of type-III geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the mecha- nism of product chain length determination. J Biol Chem 281, 14991-15000. |
| [7] | Chen C, Zhang Y, Qiakefu K, Zhang X, Han LM, Hua WP, Yan YP, Wang ZZ ( 2016). Overexpression of tomato Prosystemin (LePS) enhances pest resistance and the production of tanshinones in Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge. J Agric Food Chem 64, 7760-7769. |
| [8] | Chen W, He SZ, Liu DG, Patil GB, Zhai H, Wang FB, Stephenson TJ, Wang YN, Wang B, Valliyodan B, Nguyen HT, Liu QC ( 2015). A sweetpotato geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase gene, IbGGPS, increases carotenoid content and enhances osmotic stress tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS One 10, e0137623. |
| [9] | Cheng QQ, Su P, Hu YT, He YF, Gao W, Huang LQ ( 2014). RNA interference-mediated repression of SmCPS (Copalyldiphosphate synthase) expression in hairy roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza causes a decrease of tanshinones and sheds light on the functional role of SmCPS. Biotechnol Lett 36, 363-369. |
| [10] | Cui GH, Duan LX, Jin BL, Qian J, Xue ZY, Shen GA, Snyder JH, Song JY, Chen SL, Huang LQ, Peters RJ, Qi XQ ( 2015). Functional divergence of diterpene syntheses in the medicinal plant Salvia miltiorrhiza . Plant Physiol 169, 1607-1618. |
| [11] | Han JL, Liu BY, Ye HC, Wang H, Li ZQ, Li GF ( 2006). Effects of overexpression of the endogenous farnesyl diphosphate synthase on the artemisinin content in Artemisia annua L. J Integr Plant Biol 48, 482-487. |
| [12] | Hua WP, Song J, Li CQ, Wang ZZ ( 2012). Molecular cloning and characterization of the promoter of SmGGPPs and its expression pattern in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Mol Biol Rep 39, 5775-5783. |
| [13] | Hua WP, Zhang Y, Song J, Zhao LJ, Wang ZZ ( 2011). De novo transcriptome sequencing in Salvia miltiorrhiza to identify genes involved in the biosynthesis of active ingredients. Genomics 98, 272-279. |
| [14] | Kai GY, Liao P, Zhang T, Zhou W, Wang J, Xu H, Liu YY, Zhang L ( 2010). Characterization, expression profiling, and functional identification of a gene encoding geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase from Salvia miltiorrhiza . Bio- technol Bioproc Eng 15, 236-245. |
| [15] | Kai GY, Xu H, Zhou CC, Liao P, Xiao JB, Luo XQ, You LJ, Zhang L ( 2011). Metabolic engineering tanshinone biosynthetic pathway in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root cultures. Metab Eng 13, 319-327. |
| [16] | Lin TH, Hsieh CL ( 2010). Pharmacological effects of Salvia miltiorrhiza( Danshen) on cerebral infarction. Chin Med 5, 22. |
| [17] | Ma XH, Ma Y, Tang JF, He YL, Liu YC, Ma XJ, Shen Y, Cui GH, Lin HX, Rong QX, Guo J, Huang LQ ( 2015). The biosynthetic pathways of tanshinones and phenolic acids in Salvia miltiorrhiza . Molecules 20, 16235-16254. |
| [18] | Ma YM, Yuan LC, Wu B, Li XE, Chen SL, Lu SF ( 2012). Genome-wide identification and characterization of novel genes involved in terpenoid biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza . J Exp Bot 63, 2809-2823. |
| [19] | Shi M, Luo XQ, Ju GH, Li LL, Huang SX, Zhang T, Wang HZ, Kai GY ( 2016). Enhanced diterpene tanshinone accumulation and bioactivity of transgenic Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots by pathway engineering. J Agric Food Chem 64, 2523-2530. |
| [20] | Shi M, Luo XQ, Ju GH, Yu XH, Hao XL, Huang Q, Xiao JB, Cui LJ, Kai GY ( 2014). Increased accumulation of the cardio-cerebrovascular disease treatment drug tanshinone in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots by the enzymes 3-hy- droxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA reductase and 1-deoxy-Dxylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase. Funct Integr Genom 14, 603-615. |
| [21] |
Tata SK, Jung J, Kim YH, Choi JY, Jung JY, Lee IJ, Shin JS, Ryu SB ( 2016). Heterologous expression of chloroplast-localized geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase confers fast plant growth, early flowering and increased seed yield. Plant Biotechnol J 14, 29-39.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F ( 2002). Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3, research0034. |
| [23] | Yan YP, Wang ZZ ( 2007). Genetic transformation of the medicinal plant Salvia miltiorrhiza by Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated method. Plant Cell Tiss Org 88, 175-184. |
| [24] |
Young AJ, Lowe GM ( 2001). Antioxidant and prooxidant properties of carotenoids. Arch Biochem Biophys 385, 20-27.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 王子韵, 吕燕文, 肖钰, 吴超, 胡新生. 植物基因表达调控与进化机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | 赵来鹏, 王柏柯, 杨涛, 李宁, 杨海涛, 王娟, 闫会转. SlHVA22l基因调节番茄耐旱性[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 558-573. |
| [3] | 段政勇, 丁敏, 王宇卓, 丁艺冰, 陈凌, 王瑞云, 乔治军. 糜子SBP基因家族全基因组鉴定及表达分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 231-244. |
| [4] | 吴楠, 覃磊, 崔看, 李海鸥, 刘忠松, 夏石头. 甘蓝型油菜EXA1的克隆及其对植物抗病的调控作用[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 385-393. |
| [5] | 王菲菲, 周振祥, 洪益, 谷洋洋, 吕超, 郭宝健, 朱娟, 许如根. 大麦NF-YC基因鉴定及在盐胁迫下的表达分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 140-149. |
| [6] | 范凯, 叶方婷, 毛志君, 潘鑫峰, 李兆伟, 林文雄. 被子植物小热激蛋白家族的比较基因组学分析[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(3): 245-261. |
| [7] | 谢露露, 崔青青, 董春娟, 尚庆茂. 植物嫁接愈合分子机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(5): 634-643. |
| [8] | 王小龙,刘凤之,史祥宾,王孝娣,冀晓昊,王志强,王宝亮,郑晓翠,王海波. 葡萄NCED基因家族进化及表达分析[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(4): 474-485. |
| [9] | 范业赓,丘立杭,黄杏,周慧文,甘崇琨,李杨瑞,杨荣仲,吴建明,陈荣发. 甘蔗节间伸长过程赤霉素生物合成关键基因的表达及相关植物激素动态变化[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(4): 486-496. |
| [10] | 刘铭, 刘霞, 孙然, 李玉灵, 杜克久. 多氯联苯促进毛白杨不定根分化的效应[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(6): 764-772. |
| [11] | 孙万梅, 王晓珠, 韩二琴, 韩丽, 孙丽萍, 彭再慧, 王邦俊. 亲免素在植物体内的功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2017, 52(6): 808-819. |
| [12] | 景丹龙, 夏燕, 张守攻, 王军辉. 黄金树B类MADS-box基因表达特征分析[J]. 植物学报, 2016, 51(2): 210-217. |
| [13] | 包颖, 杜家潇, 景翔, 徐思. 药用野生稻叶中淀粉合成酶基因家族的序列分化和特异表达[J]. 植物学报, 2015, 50(6): 683-690. |
| [14] | 王涛, 陈孟龙, 刘玲, 宁传丽, 蔡斌华, 章镇, 乔玉山. 植物多倍体化中基因组和基因表达的变化[J]. 植物学报, 2015, 50(4): 504-515. |
| [15] | 蔡元保, 杨祥燕, 孙光明, 黄强, 刘业强, 李绍鹏, 张治礼. 菠萝花发育相关基因AcMADS1的克隆与组织表达特性分析[J]. 植物学报, 2014, 49(6): 692-703. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||