

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (5): 831-845.DOI: 10.11983/CBB25059 cstr: 32102.14.CBB25059
• RESEARCH ARTICLES • Previous Articles Next Articles
Chen Jun1,†, Xu Jiangmin1,†, Zhou Yinan1, Jiang Yanan1, Hu Chengxiang1, Jin Qianyun1, Zhao Beibei1, Zhu Zhenan1, Xu Yuqing1, Zhang Luyi1, Liu Xiaoyan1, Liu Jun1, Li Sanfeng2, Wang Yuexing2,*( ), Rao Yuchun1,*(
), Rao Yuchun1,*( )
)
Received:2025-04-08
Accepted:2025-06-03
Online:2025-09-10
Published:2025-06-10
Contact:
*E-mail: About author:†These authors contributed equally to this paper
Chen Jun, Xu Jiangmin, Zhou Yinan, Jiang Yanan, Hu Chengxiang, Jin Qianyun, Zhao Beibei, Zhu Zhenan, Xu Yuqing, Zhang Luyi, Liu Xiaoyan, Liu Jun, Li Sanfeng, Wang Yuexing, Rao Yuchun. Identification of Candidate Genes for Rice Resistance to Bacterial Blight via QTL Mapping and Gene Expression Analysis[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(5): 831-845.
| Primer name | Forward primer (5'-3') | Reverse primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| OsActin | TGGCATCTCAGCACATTCC | TGCACAATGGATGGGTCAGA |
| LOC_Os02g13270 | TGGCCATTTCCTCCATAAAG | TTGGTATCCTTCTTCCCTTTGA |
| LOC_Os02g13350 | AATGTCCATCGCACTGTTCA | GCTGCTTCAATCTCGGACTC |
| LOC_Os02g13410 | TCAATTATCCGGCAGACTCC | TGCCTGTGCTACTGATCCTG |
| LOC_Os02g13420 | TGCTCAGCTTTGGAGTTCCT | CCCAACGATAGCCTGTCAAT |
| LOC_Os02g13430 | CCGATGAGTGATGTTCTCCA | CGCTATGTGTTCCGCTATGA |
| LOC_Os04g01310 | TAATGGTACCAAGGGGGTGA | GAAGGCGATTCGTTGGATAA |
| LOC_Os04g01320 | AGCCCGACTTCAAGCTAACA | ATGGATTCATTGGCATGGTT |
| LOC_Os01g12130 | AATGGTGCTACCCGTTCTTG | CCGTGCGTATGAAACAGAAA |
| LOC_Os01g12160 | CATCGCCTACTTCGAGTTCA | CATGCATGATGAGGACGAAC |
| LOC_Os01g12320 | AGGTCCCGGAAAATACCACT | ATGGCATGAAGCCAATCATC |
| LOC_Os05g10690 | TGGTGAAGGAGGAGGTTGTC | TAGCTCCAGGTCAGGCATCT |
Table 1 Primer sequences for qRT-PCR
| Primer name | Forward primer (5'-3') | Reverse primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| OsActin | TGGCATCTCAGCACATTCC | TGCACAATGGATGGGTCAGA |
| LOC_Os02g13270 | TGGCCATTTCCTCCATAAAG | TTGGTATCCTTCTTCCCTTTGA |
| LOC_Os02g13350 | AATGTCCATCGCACTGTTCA | GCTGCTTCAATCTCGGACTC |
| LOC_Os02g13410 | TCAATTATCCGGCAGACTCC | TGCCTGTGCTACTGATCCTG |
| LOC_Os02g13420 | TGCTCAGCTTTGGAGTTCCT | CCCAACGATAGCCTGTCAAT |
| LOC_Os02g13430 | CCGATGAGTGATGTTCTCCA | CGCTATGTGTTCCGCTATGA |
| LOC_Os04g01310 | TAATGGTACCAAGGGGGTGA | GAAGGCGATTCGTTGGATAA |
| LOC_Os04g01320 | AGCCCGACTTCAAGCTAACA | ATGGATTCATTGGCATGGTT |
| LOC_Os01g12130 | AATGGTGCTACCCGTTCTTG | CCGTGCGTATGAAACAGAAA |
| LOC_Os01g12160 | CATCGCCTACTTCGAGTTCA | CATGCATGATGAGGACGAAC |
| LOC_Os01g12320 | AGGTCCCGGAAAATACCACT | ATGGCATGAAGCCAATCATC |
| LOC_Os05g10690 | TGGTGAAGGAGGAGGTTGTC | TAGCTCCAGGTCAGGCATCT |
| Race | Significance test for all traits between their parents (t-test) | Variation for all traits tested in the RILs population | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HZ | Nekken2 | P value | Means±SD | Range | Skewness | Kurtosis | |
| P6 | 32.57±1.92 | 19.25±1.78 | 5.66E-08 | 22.01±7.71 | 0.50-46.83 | 0.33 | 1.54 |
| P10 | 4.08±0.58 | 2.92±0.38 | 2.11E-03 | 4.43±2.47 | 0.50-17.08 | 2.27 | 7.93 |
| C5 | 21.50±2.49 | 10.63±2.59 | 1.59E-04 | 14.89±5.98 | 0.45-32.40 | 0.19 | 0.62 |
| T1 | 11.83±1.29 | 15.25±1.51 | 1.78E-03 | 12.03±6.61 | 0.60-30.25 | 0.47 | -0.42 |
Table 2 Presentation of pathogenicity of pathogenic races in parents and recombinant inbred lines (RILs) population of rice
| Race | Significance test for all traits between their parents (t-test) | Variation for all traits tested in the RILs population | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HZ | Nekken2 | P value | Means±SD | Range | Skewness | Kurtosis | |
| P6 | 32.57±1.92 | 19.25±1.78 | 5.66E-08 | 22.01±7.71 | 0.50-46.83 | 0.33 | 1.54 |
| P10 | 4.08±0.58 | 2.92±0.38 | 2.11E-03 | 4.43±2.47 | 0.50-17.08 | 2.27 | 7.93 |
| C5 | 21.50±2.49 | 10.63±2.59 | 1.59E-04 | 14.89±5.98 | 0.45-32.40 | 0.19 | 0.62 |
| T1 | 11.83±1.29 | 15.25±1.51 | 1.78E-03 | 12.03±6.61 | 0.60-30.25 | 0.47 | -0.42 |
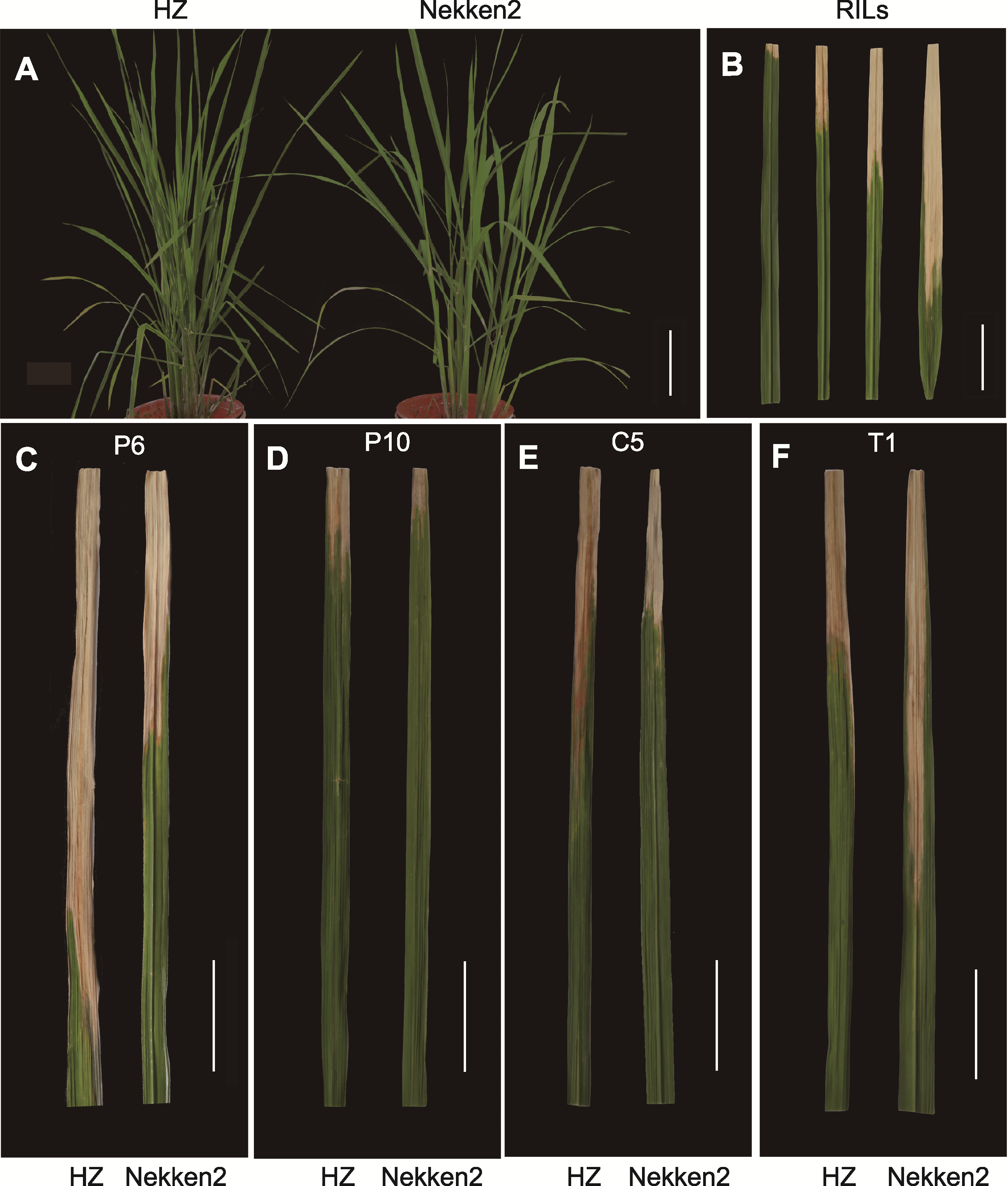

Figure 2 Phenotypes of rice parents and their recombinant inbred lines (RILs) population (A) The phenotypes of male parent HZ and maternal Nekken2 at full tillering stage (bar=10 cm); (B) Comparison of resistance levels of white leaf blight in RILs population (spot length less than 5 cm was high disease resistance, spot length between 5 cm and 10 cm was medium disease resistance, spot length between 10 cm and 15 cm was medium disease susceptibility, and more than 15 cm was susceptible, bar=5 cm); (C)-(F) Spot phenotypes of HZ and Nekken2 at the peak of tilling stage after infection by 4 types of bacterial leaf blight races (P6, P10, C5, and T1) (bars=5 cm)
| Race | QTL locus | Chromo- some | Physical distance (bp) | Position of support (cM) | Limit of detection | Overlapped with known genes/QTL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P6 | qP6-2 | 2 | 6987519-7215671 | 29.95-30.93 | 2.82 | Novel |
| qP6-6 | 6 | 22540408-24198880 | 96.62-103.73 | 2.10 | Xa27 (Gu et al., | |
| P10 | qP10-4.1 | 4 | 46622-253174 | 0.20-1.09 | 4.09 | Novel |
| qP10-4.2 | 4 | 21662809-22843728 | 92.86-97.92 | 4.12 | OsABA1 (Zhang et al., | |
| qP10-4.3 | 4 | 26889242-31662274 | 115.27-135.73 | 5.49 | Xa1 (Yoshimura et al., | |
| qP10-5 | 5 | 5860546-5932385 | 25.12-25.43 | 2.17 | Novel | |
| qP10-8 | 8 | 27210008-27435407 | 116.64-117.66 | 2.34 | OsPDR1 (Zhang et al., | |
| qP10-9 | 9 | 11237877-11654883 | 48.17-49.96 | 2.50 | Novel | |
| qP10-11 | 11 | 4880924-5893190 | 20.92-25.26 | 3.23 | Novel | |
| qP10-12.1 | 12 | 3541703-5035843 | 15.18-21.59 | 3.52 | OsSGS3a (Gu et al., | |
| qP10-12.2 | 12 | 9212254-11302449 | 39.49-48.45 | 3.47 | ELL1 (Tian et al., | |
| C5 | qC5-1 | 1 | 6568005-6737416 | 28.16-28.88 | 2.41 | Novel |
| qC5-8 | 8 | 26765295-26912750 | 114.74-115.37 | 2.58 | Xa-45(t) (Neelam et al., | |
| T1 | qT1-1.1 | 1 | 2317764-2649258 | 9.94-11.36 | 2.25 | Novel |
| qT1-1.2 | 1 | 5747788-6006625 | 24.64-25.75 | 2.17 | TUT1 (Zhang et al., | |
| qT1-3 | 3 | 28465343-29876347 | 122.02-128.07 | 2.24 | Xa11 (Goto et al., | |
| qT1-4 | 4 | 23759183-23831009 | 101.85-102.16 | 2.48 | Novel | |
| qT1-5 | 5 | 5860546-5932385 | 25.12-25.43 | 2.51 | Novel | |
| qT1-12 | 12 | 19717421-19889567 | 84.52-85.26 | 2.12 | OsPR10a (Huang et al., |
Table 3 QTL analysis of rice resistance to bacterial blight
| Race | QTL locus | Chromo- some | Physical distance (bp) | Position of support (cM) | Limit of detection | Overlapped with known genes/QTL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P6 | qP6-2 | 2 | 6987519-7215671 | 29.95-30.93 | 2.82 | Novel |
| qP6-6 | 6 | 22540408-24198880 | 96.62-103.73 | 2.10 | Xa27 (Gu et al., | |
| P10 | qP10-4.1 | 4 | 46622-253174 | 0.20-1.09 | 4.09 | Novel |
| qP10-4.2 | 4 | 21662809-22843728 | 92.86-97.92 | 4.12 | OsABA1 (Zhang et al., | |
| qP10-4.3 | 4 | 26889242-31662274 | 115.27-135.73 | 5.49 | Xa1 (Yoshimura et al., | |
| qP10-5 | 5 | 5860546-5932385 | 25.12-25.43 | 2.17 | Novel | |
| qP10-8 | 8 | 27210008-27435407 | 116.64-117.66 | 2.34 | OsPDR1 (Zhang et al., | |
| qP10-9 | 9 | 11237877-11654883 | 48.17-49.96 | 2.50 | Novel | |
| qP10-11 | 11 | 4880924-5893190 | 20.92-25.26 | 3.23 | Novel | |
| qP10-12.1 | 12 | 3541703-5035843 | 15.18-21.59 | 3.52 | OsSGS3a (Gu et al., | |
| qP10-12.2 | 12 | 9212254-11302449 | 39.49-48.45 | 3.47 | ELL1 (Tian et al., | |
| C5 | qC5-1 | 1 | 6568005-6737416 | 28.16-28.88 | 2.41 | Novel |
| qC5-8 | 8 | 26765295-26912750 | 114.74-115.37 | 2.58 | Xa-45(t) (Neelam et al., | |
| T1 | qT1-1.1 | 1 | 2317764-2649258 | 9.94-11.36 | 2.25 | Novel |
| qT1-1.2 | 1 | 5747788-6006625 | 24.64-25.75 | 2.17 | TUT1 (Zhang et al., | |
| qT1-3 | 3 | 28465343-29876347 | 122.02-128.07 | 2.24 | Xa11 (Goto et al., | |
| qT1-4 | 4 | 23759183-23831009 | 101.85-102.16 | 2.48 | Novel | |
| qT1-5 | 5 | 5860546-5932385 | 25.12-25.43 | 2.51 | Novel | |
| qT1-12 | 12 | 19717421-19889567 | 84.52-85.26 | 2.12 | OsPR10a (Huang et al., |
| QTL locus | Chromosome | Gene ID | Functional annotation |
|---|---|---|---|
| qP6-2 | 2 | LOC_Os02g13270 | Mpv17/PMP22 family domain containing protein |
| LOC_Os02g13350 | NUDIX family | ||
| LOC_Os02g13410 | Leucine-rich repeat family protein | ||
| LOC_Os02g13420 | Leucine-rich repeat receptor protein kinase EXS precursor | ||
| LOC_Os02g13430 | Receptor-like protein kinase 5 precursor | ||
| qP10-4.1 | 4 | LOC_Os04g01310 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase receptor precursor |
| LOC_Os04g01320 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase receptor precursor | ||
| qC5-1 | 1 | LOC_Os01g12130 | Enodulin MtN3 family protein |
| LOC_Os01g12160 | Ndole-3-acetic acid-amido synthetase | ||
| LOC_Os01g12320 | GDSL-like lipase/acylhydrolase | ||
| qT1-5 | 5 | LOC_Os05g10690 | Myb transcription factor |
Table 4 The function of candidate genes associated with resistance of rice bacterial blight
| QTL locus | Chromosome | Gene ID | Functional annotation |
|---|---|---|---|
| qP6-2 | 2 | LOC_Os02g13270 | Mpv17/PMP22 family domain containing protein |
| LOC_Os02g13350 | NUDIX family | ||
| LOC_Os02g13410 | Leucine-rich repeat family protein | ||
| LOC_Os02g13420 | Leucine-rich repeat receptor protein kinase EXS precursor | ||
| LOC_Os02g13430 | Receptor-like protein kinase 5 precursor | ||
| qP10-4.1 | 4 | LOC_Os04g01310 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase receptor precursor |
| LOC_Os04g01320 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase receptor precursor | ||
| qC5-1 | 1 | LOC_Os01g12130 | Enodulin MtN3 family protein |
| LOC_Os01g12160 | Ndole-3-acetic acid-amido synthetase | ||
| LOC_Os01g12320 | GDSL-like lipase/acylhydrolase | ||
| qT1-5 | 5 | LOC_Os05g10690 | Myb transcription factor |
| Gene ID | Length (bp) | Number of amino acids (aa) | Molecular weight (kDa) | Theoretical pI | Instabiliy index | Grand average of hydropathicity | Subcellular location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOC_Os02g13270 | 3105 | 205 | 23.61 | 10.47 | 55.17 | -0.063 | Cytoplasmic |
| LOC_Os02g13350 | 2612 | 297 | 32.69 | 5.47 | 44.45 | 0.056 | Nuclear |
| LOC_Os02g13410 | 2761 | 508 | 57.34 | 8.05 | 51.52 | -0.406 | Nuclear |
| LOC_Os02g13420 | 3070 | 611 | 66.79 | 5.75 | 29.68 | 0.077 | Extracellular |
| LOC_Os02g13430 | 3541 | 1004 | 110.39 | 5.21 | 38.88 | -0.049 | Nuclear |
| LOC_Os04g01310 | 2758 | 828 | 91.62 | 6.01 | 40.39 | -0.016 | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| LOC_Os04g01320 | 2927 | 813 | 90.71 | 6.15 | 43.94 | -0.170 | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| LOC_Os01g12130 | 1563 | 252 | 28.17 | 9.25 | 36.00 | 0.538 | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| LOC_Os01g12160 | 5501 | 591 | 64.19 | 5.90 | 39.85 | -0.059 | Cytoplasmic |
| LOC_Os01g12320 | 3688 | 379 | 40.97 | 5.13 | 41.35 | 0.061 | Cytoplasmic |
| LOC_Os05g10690 | 3818 | 287 | 30.46 | 9.35 | 64.91 | -0.298 | Mitochondrial |
Table 5 Information of candidate genes associated with resistance of rice bacterial blight
| Gene ID | Length (bp) | Number of amino acids (aa) | Molecular weight (kDa) | Theoretical pI | Instabiliy index | Grand average of hydropathicity | Subcellular location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOC_Os02g13270 | 3105 | 205 | 23.61 | 10.47 | 55.17 | -0.063 | Cytoplasmic |
| LOC_Os02g13350 | 2612 | 297 | 32.69 | 5.47 | 44.45 | 0.056 | Nuclear |
| LOC_Os02g13410 | 2761 | 508 | 57.34 | 8.05 | 51.52 | -0.406 | Nuclear |
| LOC_Os02g13420 | 3070 | 611 | 66.79 | 5.75 | 29.68 | 0.077 | Extracellular |
| LOC_Os02g13430 | 3541 | 1004 | 110.39 | 5.21 | 38.88 | -0.049 | Nuclear |
| LOC_Os04g01310 | 2758 | 828 | 91.62 | 6.01 | 40.39 | -0.016 | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| LOC_Os04g01320 | 2927 | 813 | 90.71 | 6.15 | 43.94 | -0.170 | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| LOC_Os01g12130 | 1563 | 252 | 28.17 | 9.25 | 36.00 | 0.538 | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| LOC_Os01g12160 | 5501 | 591 | 64.19 | 5.90 | 39.85 | -0.059 | Cytoplasmic |
| LOC_Os01g12320 | 3688 | 379 | 40.97 | 5.13 | 41.35 | 0.061 | Cytoplasmic |
| LOC_Os05g10690 | 3818 | 287 | 30.46 | 9.35 | 64.91 | -0.298 | Mitochondrial |
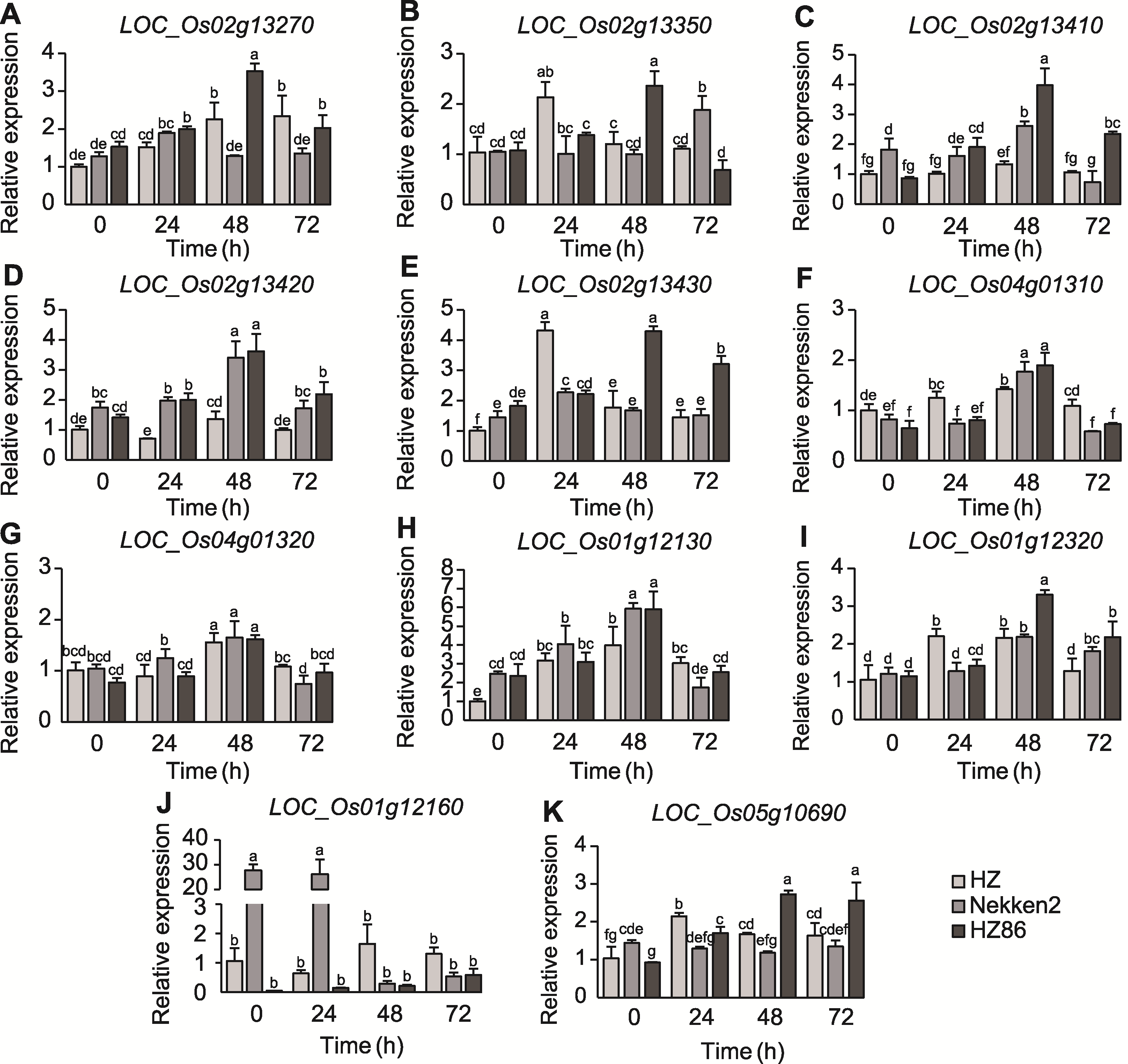
Figure 5 Differences in the expression of candidate genes for resistance to bacterial blight Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in gene expression at the 0.05 level.
| [1] | Antony G, Zhou JH, Huang S, Li T, Liu B, White F, Yang B (2010). Rice xa13 recessive resistance to bacterial blight is defeated by induction of the disease susceptibility gene Os-11N3. Plant Cell 22, 3864-3876. |
| [2] | Bao SY, Tan MP, Lin XH (2010). Genetic mapping of a bacterial blight resistance gene Xa14 in rice. Acta Agron Sin 36, 422-427. (in Chinese) |
|
鲍思元, 谭明谱, 林兴华 (2010). 水稻抗白叶枯病基因Xa14的遗传定位. 作物学报 36, 422-427.
DOI |
|
| [3] | Bhasin H, Bhatia D, Raghuvanshi S, Lore JS, Sahi GK, Kaur B, Vikal Y, Singh K (2012). New PCR-based sequence-tagged site marker for bacterial blight resistance gene Xa38 of rice. Mol Breeding 30, 607-611. |
| [4] |
Bogdanove AJ, Schornack S, Lahaye T (2010). TAL effectors: finding plant genes for disease and defense. Curr Opin Plant Biol 13, 394-401.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | Chen XF, Liu PC, Mei L, He XL, Chen L, Liu H, Shen SR, Ji ZD, Zheng XX, Zhang YC, Gao ZY, Zeng DL, Qian Q, Ma BJ (2021). Xa7, a new executor R gene that confers durable and broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight disease in rice. Plant Commun 2, 100143. |
| [6] |
De Vleesschauwer D, Seifi HS, Filipe O, Haeck A, Huu SN, Demeestere K, Höfte M (2016). The DELLA protein SLR1 integrates and amplifies salicylic acid- and jasmonic acid-dependent innate immunity in rice. Plant Physiol 170, 1831-1847.
DOI PMID |
| [7] | Goto T, Matsumoto T, Furuya N, Tsuchiya K, Yoshimura A (2009). Mapping of bacterial blight resistance gene Xa11 on rice chromosome 3. Japan Agric Res Quart 43, 221-225. |
| [8] |
Gu K, Tian D, Yang F, Wu L, Sreekala C, Wang D, Wang GL, Yin Z (2004). High-resolution genetic mapping of Xa27(t), a new bacterial blight resistance gene in rice, Oryza sativa L. Theor Appl Genet 108, 800-807.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | Gu KY, Yang B, Tian DS, Wu LF, Wang DJ, Sreekala C, Yang F, Chu ZQ, Wang GL, White FF, Yin ZC (2005). R gene expression induced by a type-III effector triggers disease resistance in rice. Nature 435, 1122-1125. |
| [10] | Gu XT, Si FY, Feng ZX, Li SJ, Liang D, Yang P, Yang C, Yan B, Tang J, Yang Y, Li T, Li L, Zhou JL, Li J, Feng LL, Liu JY, Yang YZ, Deng YW, Wu XN, Zhao ZG, Wan JM, Cao XF, Song XW, He ZH, Liu JZ (2023). The OsSGS3-tasiRNA-OsARF3 module orchestrates abiotic- biotic stress response trade-off in rice. Nat Commun 14, 4441. |
| [11] | Han YL, Cai MH, Zhang SQ, Chai JW, Sun MZ, Wang YW, Xie QY, Chen YH, Wang HZ, Chen T (2022). Genome-wide identification of AP2/ERF transcription factor family and functional analysis of DcAP2/ERF#96 associated with abiotic stress in Dendrobium catenatum. Int J Mol Sci 23, 13603. |
| [12] | He Q, Li DB, Zhu YS, Tan MP, Zhang DP, Lin XH (2006). Fine mapping of Xa2, a bacterial blight resistance gene in rice. Mol Breeding 17, 1-6. |
| [13] |
Hu KM, Cao JB, Zhang J, Xia F, Ke YG, Zhang HT, Xie WY, Liu HB, Cui Y, Cao YL, Sun XL, Xiao JH, Li XH, Zhang QL, Wang SP (2017). Improvement of multiple agronomic traits by a disease resistance gene via cell wall reinforcement. Nat Plants 3, 17009.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | Huang LF, Lin KH, He SL, Chen JL, Jiang JZ, Chen BH, Hou YS, Chen RS, Hong CY, Ho SL (2016). Multiple patterns of regulation and overexpression of a ribonuclease-like pathogenesis-related protein gene, OsPR10a, conferring disease resistance in rice and Arabidopsis. PLoS One 11, e0156414. |
| [15] |
Iyer-Pascuzzi AS, Jiang H, Huang L, Mccouch SR (2008). Genetic and functional characterization of the rice bacterial blight disease resistance gene xa5. Phytopathology 98, 289-295.
DOI PMID |
| [16] | Ji CH, Ji ZY, Liu B, Cheng H, Liu H, Liu SZ, Yang B, Chen GY (2020). Xa1 allelic R genes activate rice blight resistance suppressed by interfering TAL effectors. Plant Commun 1, 100087. |
| [17] | Ji ZY, Guo W, Chen XF, Wang CL, Zhao KJ (2022). Plant executor genes. Int J Mol Sci 23, 1524. |
| [18] | Jia QW, Zhong QQ, Gu YJ, Lu TQ, Li W, Yang S, Zhu CY, Hu CX, Li SF, Wang YX, Rao YC (2023). Mapping of QTL for cell wall related components in rice stem and analysis of candidate genes. Chin Bull Bot 58, 882-892. (in Chinese) |
|
贾绮玮, 钟芊芊, 顾育嘉, 陆天麒, 李玮, 杨帅, 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 李三峰, 王跃星, 饶玉春 (2023). 水稻茎秆细胞壁相关组分含量QTL定位及候选基因分析. 植物学报 58, 882-892.
DOI |
|
| [19] | Jiang GH, Liu DF, Yin DD, Zhou ZZ, Shi Y, Li CR, Zhu LH, Zhai WX (2020). A rice NBS-ARC gene conferring quantitative resistance to bacterial blight is regulated by a pathogen effector-inducible miRNA. Mol Plant 13, 1752-1767. |
| [20] | Jin JY, Luo YT, Yang HM, Lu T, Ye HF, Xie JY, Wang KX, Chen QY, Fang Y, Wang YX, Rao YC (2023). QTL mapping and expression analysis on candidate genes related to chlorophyll content in rice. Chin Bull Bot 58, 394-403. (in Chinese) |
|
金佳怡, 罗怿婷, 杨惠敏, 芦涛, 叶涵斐, 谢继毅, 王珂欣, 陈芊羽, 方媛, 王跃星, 饶玉春 (2023). 水稻叶绿素含量QTL定位与候选基因表达分析. 植物学报 58, 394-403.
DOI |
|
| [21] | Li XR, He XY, Chen H, Lu ZH, Wang XF, Wang SG, Fang ZQ, Wu HX, Liu W (2022). Mechanism and breeding application of bacterial blight gene in rice. Guangdong Agric Sci 49, 31-41. (in Chinese) |
| 李香荣, 何秀英, 陈浩, 陆展华, 王晓飞, 王石光, 方志强, 巫浩翔, 刘维 (2022). 水稻白叶枯病基因的作用机制与育种应用. 广东农业科学 49, 31-41. | |
| [22] |
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-∆∆CT method. Methods 25, 402-408.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | Lu YD, Zhong QF, Xiao SQ, Wang B, Ke X, Zhang Y, Yin FY, Zhang DY, Jiang C, Liu L, Li JL, Yu TQ, Wang LX, Cheng ZQ, Chen L (2022). A new NLR disease resistance gene Xa47confers durable and broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight in rice. Front Plant Sci 13, 1037901. |
| [24] |
Luu DD, Joe A, Chen Y, Parys K, Bahar O, Pruitt R, Chan LJG, Petzold CJ, Long K, Adamchak C, Stewart V, Belkhadir Y, Ronald PC (2019). Biosynthesis and secretion of the microbial sulfated peptide RaxX and binding to the rice XA21 immune receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116, 8525-8534.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | McCouch SR, Cho YG, Yano M, Paul E, Blinstrub M, Morishima H, Kinoshita T (1997). Report on QTL nomenclature. Rice Genet Newsl 14, 11-13. |
| [26] | Neelam K, Mahajan R, Gupta V, Bhatia D, Gill BK, Komal R, Lore JS, Mangat GS, Singh K (2020). High-resolution genetic mapping of a novel bacterial blight resistance gene xa-45(t) identified from Oryza glaberrima and transferred to Oryza sativa. Theor Appl Genet 133, 689-705. |
| [27] |
Oliva R, Ji CH, Atienza-Grande G, Huguet-Tapia JC, Perez-Quintero A, Li T, Eom JS, Li CH, Nguyen H, Liu B, Auguy F, Sciallano C, Luu VT, Dossa GS, Cunnac S, Schmidt SM, Slamet-Loedin IH, Vera Cruz C, Szurek B, Frommer WB, White FF, Yang B (2019). Broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight in rice using genome editing. Nat Biotechnol 37, 1344-1350.
DOI PMID |
| [28] | Pan BH, Yin JJ, Wang S, Huang H, Gao P, Zhong W, Hu CR, He DP (2024). Research hotspots and evolution trends of rice bran oil. China Oils Fats 1-21. (in Chinese) |
| 潘保辉, 殷娇娇, 王澍, 黄何, 高盼, 钟武, 胡传荣, 何东平 (2024). 稻米油研究热点和演变趋势的分析. 中国油脂. 1-21. | |
| [29] | Peng XQ, Wang ML (2022). Research advances on resistance genes to bacterial blight disease in rice. Plant Physiol J 58, 472-482. (in Chinese) |
| 彭小群, 王梦龙 (2022). 水稻白叶枯病抗性基因研究进展. 植物生理学报 58, 472-482. | |
| [30] |
Pradhan SK, Barik SR, Nayak DK, Pradhan A, Pandit E, Nayak P, Das SR, Pathak H (2020). Genetics, molecular mechanisms and deployment of bacterial blight resistance genes in rice. Crit Rev Plant Sci 39, 360-385.
DOI |
| [31] | Pundir S, Singh R, Singh VK, Sharma S, Balyan HS, Gupta PK, Sharma S (2023). Mapping of QTLs and meta-QTLs for Heterodera avenae Woll. resistance in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). BMC Plant Biol 23, 529. |
| [32] | Rao YC, Wu RC, Liu FY, Dai RH (2024). On research progress of RNAi application in prevention and control of rice pests and diseases. J Zhejiang Normal Univ (Nat Sci) 47, 361-369. (in Chinese) |
| 饶玉春, 吴日成, 刘富远, 戴若惠 (2024). RNAi在水稻病虫害防控中的应用研究进展. 浙江师范大学学报(自然科学版) 47, 361-369. | |
| [33] | Sun XL, Cao YL, Yang ZF, Xu CG, Li XH, Wang SP, Zhang QF (2004). Xa26, a gene conferring resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in rice, encodes an LRR receptor kinase-like protein. Plant J 37, 517-527. |
| [34] | Tian DG, Yang F, Niu YQ, Lin Y, Chen ZJ, Li G, Luo Q, Wang F, Wang M (2020). Loss function of SL (sekiguchi lesion) in the rice cultivar Minghui 86 leads to enhanced resistance to (hemi) biotrophic pathogens. BMC Plant Biol 20, 507. |
| [35] | Tian DS, Wang JX, Zeng X, Gu KY, Qiu CX, Yang XB, Zhou ZY, Goh M, Luo YC, Murata-Hori M, White FF, Yin ZC (2014). The rice TAL effector-dependent resistance protein XA10 triggers cell death and calcium depletion in the endoplasmic reticulum. Plant Cell 26, 497-515. |
| [36] | Wu T, Bi YY, Yu Y, Zhou Z, Yuan B, Ding XH, Zhang QX, Chen XS, Yang H, Liu HF, Chu ZH (2023). Activated expression of rice DMR6-like gene OsS3H partially explores the susceptibility to bacterial leaf streak mediated by knock-out OsF3H04g. Int J Mol Sci 24, 13263. |
| [37] | Wu XJ, Zhang XY, Xu M, Bu QY, Wang ZY (2024). Research advances on MYB transcription factor in rice stress response. J Northeast Agric Univ 55, 83-96. (in Chinese) |
| 吴秀菊, 张新颖, 许敏, 卜庆云, 王臻昱 (2024). MYB转录因子在水稻胁迫响应中的研究进展. 东北农业大学学报 55, 83-96. | |
| [38] | Xu ZY, Xu XM, Li Y, Liu LL, Wang Q, Wang YJ, Wang Y, Yan JL, Cheng GY, Zou LF, Zhu B, Chen GY (2023). Tal6b/AvrXa27A, a hidden TALE targeting the susceptibility gene OsSWEET11a and the resistance gene Xa27 in rice. Plant Commun 5, 100721. |
| [39] |
Yoshimura S, Yamanouchi U, Katayose Y, Toki S, Wang ZX, Kono I, Kurata N, Yano M, Iwata N, Sasaki T (1998). Expression of Xa1, a bacterial blight-resistance gene in rice, is induced by bacterial inoculation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95, 1663-1668.
DOI PMID |
| [40] | Zhang DD, Tian CJ, Yin KQ, Wang WY, Qiu JL (2019). Postinvasive bacterial resistance conferred by open stomata in rice. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 32, 255-266. |
| [41] | Zhang HS, Jing W, Zheng JM, Jin YY, Wu D, Cao CJ, Dong YM, Shi XY, Zhang WH (2020). The ATP-binding cassette transporter OsPDR1 regulates plant growth and pathogen resistance by affecting jasmonates biosynthesis in rice. Plant Sci 298, 110582. |
| [42] | Zhang Q (2009). Genetics and improvement of resistance to bacterial blight in hybrid rice in China. Chin J Rice Sci 23, 111-119. (in Chinese) |
| 章琦 (2009). 中国杂交水稻白叶枯病抗性的遗传改良. 中国水稻科学 23, 111-119. | |
| [43] | Zhong QQ, Huang JH, Yin WJ, Lu T, Gu YJ, Chen ZG, Ye HF, Rao YC (2023). QTLs mapping and expression analysis of candidate genes for root traits in rice. J Zhejiang Normal Univ (Nat Sci) 46, 425-432. (in Chinese) |
| 钟芊芊, 黄佳慧, 殷文晶, 芦涛, 顾育嘉, 陈振概, 叶涵斐, 饶玉春 (2023). 水稻种子耐储藏性状QTLs挖掘及候选基因分析. 浙江师范大学学报(自然科学版) 46, 425-432. | |
| [44] | Zhu CY, Hu CX, Zhu ZN, Zhang ZN, Wang LH, Chen J, Li SF, Lian JJ, Tang LY, Zhong QQ, Yin WJ, Wang YX, Rao YC (2024). Mapping of QTLs associated with rice panicle traits and candidate gene analysis. Chin Bull Bot 59, 217-230. (in Chinese) |
|
朱超宇, 胡程翔, 朱哲楠, 张芷宁, 汪理海, 陈钧, 李三峰, 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 钟芊芊, 殷文晶, 王跃星, 饶玉春 (2024). 水稻穗部性状QTL定位及候选基因分析. 植物学报 59, 217-230.
DOI |
| [1] | Zhao Ling, Guan Ju, Liang Wenhua, Zhang Yong, Lu Kai, Zhao Chunfang, Li Yusheng, Zhang Yadong. Mapping of QTLs for Heat Tolerance at the Seedling Stage in Rice Based on a High-density Bin Map [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(3): 342-353. |
| [2] | Jinjin Lian, Luyao Tang, Yinuo Zhang, Jiaxing Zheng, Chaoyu Zhu, Yuhan Ye, Yuexing Wang, Wennan Shang, Zhenghao Fu, Xinxuan Xu, Richeng Wu, Mei Lu, Changchun Wang, Yuchun Rao. Genetic Locus Mining and Candidate Gene Analysis of Antioxidant Traits in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(5): 738-751. |
| [3] | Jing Xia, Yuchun Rao, Danyun Cao, Yi Wang, Linxin Liu, Yating Xu, Wangshu Mou, Dawei Xue. Research Progress on the Regulatory Mechanisms of OsACS and OsACO in Rice Ethylene Biosynthesis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(2): 291-301. |
| [4] | Chaoyu Zhu, Chengxiang Hu, Zhenan Zhu, Zhining Zhang, Lihai Wang, Jun Chen, Sanfeng Li, Jinjin Lian, Luyao Tang, Qianqian Zhong, Wenjing Yin, Yuexing Wang, Yuchun Rao. Mapping of QTLs Associated with Rice Panicle Traits and Candidate Gene Analysis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(2): 217-230. |
| [5] | Qiwei Jia, Qianqian Zhong, Yujia Gu, Tianqi Lu, Wei Li, Shuai Yang, Chaoyu Zhu, Chengxiang Hu, Sanfeng Li, Yuexing Wang, Yuchun Rao. Mapping of QTL for Cell Wall Related Components in Rice Stem and Analysis of Candidate Genes [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(6): 882-892. |
| [6] | Tian Chuanyu, Fang Yanli, Shen Qing, Wang Hongjie, Chen Xifeng, Guo Wei, Zhao Kaijun, Wang Chunlian, Ji Zhiyuan. Genotypic Diversity and Pathogenisity of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae Isolated from Southern China in 2019-2021 [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(5): 743-749. |
| [7] | Jiayi Jin, Yiting Luo, Huimin Yang, Tao Lu, Hanfei Ye, Jiyi Xie, Kexin Wang, Qianyu Chen, Yuan Fang, Yuexing Wang, Yuchun Rao. QTL Mapping and Expression Analysis on Candidate Genes Related to Chlorophyll Content in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(3): 394-403. |
| [8] | Weijun Ye, Yin Zhang, Peiran Wang, Lingling Zhang, Dongfeng Tian, Zejiang Wu, Bin Zhou. QTLs Analysis for Five Yield-related Traits in Mungbean [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(1): 150-158. |
| [9] | Wei Heping, Lu Tao, Jia Qiwei, Deng Fei, Zhu Hao, Qi Zehua, Wang Yuxi, Ye Hanfei, Yin Wenjing, Fang Yuan, Mu Dan, Rao Yuchun. QTL Mapping of Candidate Genes for Heading Date in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(5): 588-595. |
| [10] | Liu Xiaolong, Ji Ping, Yang Hongtao, Ding Yongdian, Fu Jialing, Liang Jiangxia, Yu Congcong. Priming Effect of Abscisic Acid on High Temperature Stress During Rice Heading-flowering Stage [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(5): 596-610. |
| [11] | Kairu Yang, Qiwei Jia, Jiayi Jin, Hanfei Ye, Sheng Wang, Qianyu Chen, Yian Guan, Chenyang Pan, Dedong Xin, Yuan Fang, Yuexing Wang, Yuchun Rao. Cloning and Functional Analysis of Rice Yellow Green Leaf Regulatory Gene YGL18 [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(3): 276-287. |
| [12] | Hong Yu, Jiayang Li. The Gold Will Glitter Wherever it is: Convergent Selection in Maize and Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(2): 153-156. |
| [13] | Hanfei Ye, Wenjing Yin, Yian Guan, Kairu Yang, Qianyu Chen, Shuying Yu, Xudong Zhu, Dedong Xin, Wei Zhang, Yuexing Wang, Yuchun Rao. QTL Mapping and Candidate Gene Analysis of Vitamin E in Rice Grain [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(2): 157-170. |
| [14] | Jiaxin Li, Xia Li, Yinfeng Xie. Mechanism on Drought Tolerance Enhanced by Exogenous Trehalose in C4-PEPC Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(3): 296-314. |
| [15] | Chenyang Pan, Yue Zhang, Han Lin, Qianyu Chen, Kairu Yang, Jiaji Jiang, Mengjia Li, Tao Lu, Kexin Wang, Mei Lu, Sheng Wang, Hanfei Ye, Yuchun Rao, Haitao Hu. QTL Mapping and Candidate Gene Analysis on Rice Leaf Water Potential [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(3): 275-283. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||