

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2021, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (2): 151-165.DOI: 10.11983/CBB20198 cstr: 32102.14.CBB20198
• INVITED REVIEW • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2020-12-03
Accepted:2021-01-18
Online:2021-03-01
Published:2021-03-17
Contact:
Yanhua Qi
Yuqing Lin, Yanhua Qi. Advances in Auxin Efflux Carrier PIN Proteins[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(2): 151-165.
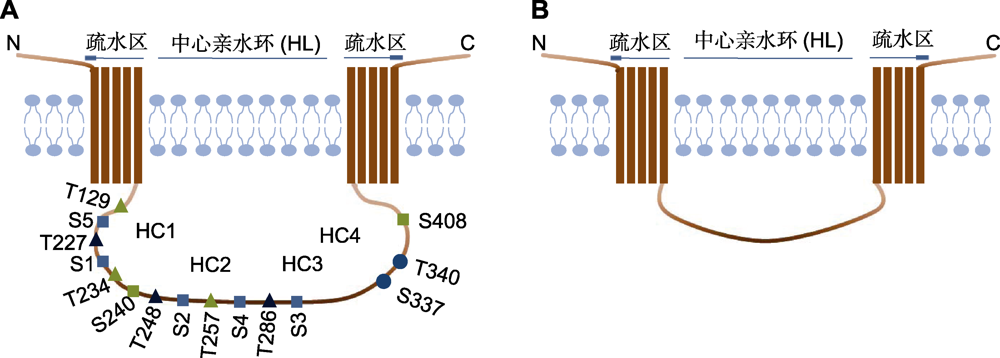
Figure 1 Structural model of PIN proteins (A)Structural model of PIN protein with a long hydrophilic loop (HL) and the phosphorylation sites on the HL (with AtPIN1 as an example); (B)Structural model of PIN protein with a short HL.
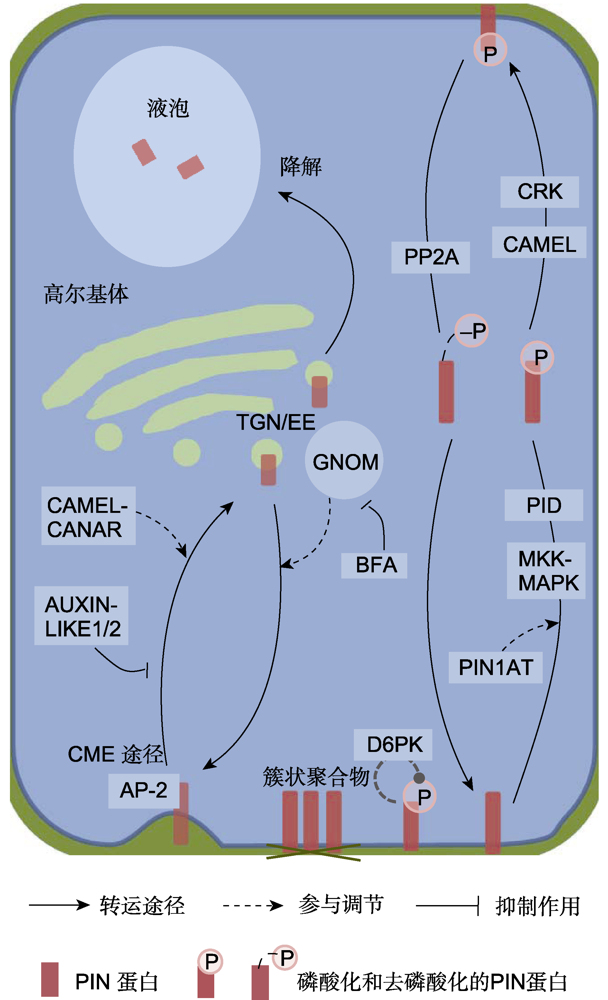
Figure 2 Regulation of PIN polarity and subcellular trafficking TGN/EE: Trans Golgi network/early endosome; GNOM: ADP- ribosylation factor guanine-nucleotide exchange factors; CME: Clathrin-mediated endocytosis; CRK: CDPK-related kinase; CAMEL: Canalization-related auxin-regulated Malectin- type RLK; PP2A: Protein phosphatase 2A; BFA: Brefeldin A; PIDs: PINOID; MKK/MAPK: MAPK kinase/mitogen activated protein kinases; CANAR: Canalization-related receptor-like kinase; AP-2: Adaptor protein-2
| 基因名称 | 功能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| OsPIN1 | 调控不定根发育、分蘖及地下部和地上部的比例; OsPIN1a和OsPIN1b参与根和茎的发育; OsPIN1c和OsPIN1d参与穗的形成; OsPIN1a也在根的负趋光性调控中起作用 | Xu et al. |
| OsPIN2 | 介导生长素从地上部向根茎结合部的转运; 调控分蘖、分蘖角度和株高 | Chen et al. |
| OsPIN5b | 定位于内质网上参与胞内生长素转运, 调控株型和产量 | Lu et al. |
| OsPIN9 | 调控分蘖数 | Hou et al. |
| OsPIN10a/OsPIN3t/OsPIN3a | 参与抗旱响应过程 | Zhang et al. |
Table 1 Biofunctions of PIN genes in rice
| 基因名称 | 功能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| OsPIN1 | 调控不定根发育、分蘖及地下部和地上部的比例; OsPIN1a和OsPIN1b参与根和茎的发育; OsPIN1c和OsPIN1d参与穗的形成; OsPIN1a也在根的负趋光性调控中起作用 | Xu et al. |
| OsPIN2 | 介导生长素从地上部向根茎结合部的转运; 调控分蘖、分蘖角度和株高 | Chen et al. |
| OsPIN5b | 定位于内质网上参与胞内生长素转运, 调控株型和产量 | Lu et al. |
| OsPIN9 | 调控分蘖数 | Hou et al. |
| OsPIN10a/OsPIN3t/OsPIN3a | 参与抗旱响应过程 | Zhang et al. |
| [1] | 贺祯媚, 李东明, 齐艳华 (2019). 植物ABCB亚家族生物学功能研究进展. 植物学报 54,688-698. |
| [2] | 潘建伟, 张晨燕, 周哉材 (2018). 生长素极性输出载体PIN的研究进展. 浙江师范大学学报(自然科学版) 41,436-443. |
| [3] | 邹纯雪, 门淑珍 (2013). 生长素的外输载体PIN蛋白家族研究进展. 中国细胞生物学学报 35,574-582. |
| [4] | Adamowski M, Narasimhan M, Kania U, Glanc M, De Jaeger G, Friml J (2018). A functional study of AUXILIN-LIKE1 and 2, two putative clathrin uncoating factors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 30,700-716. |
| [5] | Barbez E, Kubeš M, Rolčík J, Béziat C, Pěnčík A, Wang BJ, Rosquete MR, Zhu JS, Dobrev PI, Lee Y, Zaží-malovà E, Petrášek J, Geisler M, Friml J, Kleine-Vehn J (2012). A novel putative auxin carrier family regulates intracellular auxin homeostasis in plants. Nature 485,119- 122. |
| [6] | Barbosa ICR, Hammes UZ, Schwechheimer C (2018). Activation and polarity control of PIN-FORMED auxin transporters by phosphorylation. Trends Plant Sci 23,523- 538. |
| [7] |
Bell CJ, Maher EP (1990). Mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana with abnormal gravitropic responses. Mol Gen Genet 220,289-293.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Benková E, Michniewicz M, Sauer M, Teichmann T, Seifertová D, Jürgens G, Friml J (2003). Local, efflux-dependent auxin gradients as a common module for plant organ formation. Cell 115,591-602.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Bennett T, Brockington SF, Rothfels C, Graham SW, Stevenson D, Kutchan T, Rolf M, Thomas P, Wong GKS, Leyser O, Glover BJ, Harrison CJ (2014). Para- logous radiations of PIN proteins with multiple origins of noncanonical PIN structure. Mol Biol Evol 31,2042-2060.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Bennett MJ, Marchant A, Green HG, May ST, Ward SP, Millner PA, Walker AR, Schulz B, Feldmann KA (1996). Arabidopsis AUX1 gene: a permease-like regulator of root gravitropism. Science 273,948-950.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Blakeslee JJ, Bandyopadhyay A, Lee OR, Mravec J, Titapiwatanakun B, Sauer M, Makam SN, Cheng Y, Bouchard R, Adamec J, Geisler M, Nagashima A, Sakai T, Martinoia E, Friml J, Peer WA, Murphy AS (2007). Interactions among PIN-FORMED and P-Glycoprotein auxin transporters in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 19,131-147.
PMID |
| [12] |
Blilou I, Xu J, Wildwater M, Willemsen V, Paponov I, Friml J, Heidstra R, Aida M, Palme K, Scheres B (2005). The PIN auxin efflux facilitator network controls growth and patterning in Arabidopsis roots. Nature 433,39-44.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Bögre L, Okrész L, Henriques R, Anthony RG (2003). Growth signaling pathways in Arabidopsis and the AGC protein kinases. Trends Plant Sci 8,424-431.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Carraro N, Forestan C, Canova S, Traas J, Varotto S (2006). ZmPIN1a and ZmPIN1b encode two novel putative candidates for polar auxin transport and plant architecture determination of maize. Plant Physiol 142,254- 264.
PMID |
| [15] |
Chen Q, Liu Y, Maere S, Lee E, Van Isterdael G, Xie ZD, Xuan W, Lucas J, Vassileva V, Kitakura S, Marhavý P, Wabnik K, Geldner N, Benková E, Le J, Fukaki H, Grotewold E, Li CY, Friml J, Sack F, Beeckman T, Vanneste S (2015). A coherent transcriptional feed-forward motif model for mediating auxin-sensitive PIN3 expression during lateral root development. Nat Commun 6,8821.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Chen R, Hilson P, Sedbrook J, Rosen E, Caspar T, Masson PH (1998). The Arabidopsis thaliana AGRAVITROPIC 1 gene encodes a component of the polar-auxin- transport efflux carrier. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95,15112- 15117.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Chen YN, Fan XR, Song WJ, Zhang YL, Xu GH (2012). Over-expression of OsPIN2 leads to increased tiller num- bers, angle and shorter plant height through suppression of OsLAZY1. Plant Biotechnol J 10,139-149.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Dai MQ, Zhang C, Kania U, Chen F, Xue Q, McCray T, Li G, Qin GJ, Wakeley M, Terzaghi W, Wan JM, Zhao YD, Xu J, Friml J, Deng XW, Wang HY (2012). A PP6-type phosphatase holoenzyme directly regulates PIN phosphorylation and auxin efflux in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24,2497-2514.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Ding ZJ, Wang BJ, Moreno I, Dupláková N, Simon S, Carraro N, Reemmer J, Pěnčík A, Chen X, Tejos R, Skůpa P, Pollmann S, Mravec J, Petrášek J, Zažímalová E, Honys D, Rolčík J, Murphy A, Orellana A, Geisler M, Friml J (2012). ER-localized auxin transporter PIN8 regulates auxin homeostasis and male gametophyte development in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun 3, 941.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Ditengou FA, Gomes D, Nziengui H, Kochersperger P, Lasok H, Medeiros V, Paponov IA, Nagy SK, Nádai TV, Mészáros T, Barnabás B, Ditengou BI, Rapp K, Qi LL, Li XG, Becker C, Li CY, Dóczi R, Palme K (2018). Characterization of auxin transporter PIN6 plasma membrane targeting reveals a function for PIN6 in plant bolting. New Phytol 217,1610-1624.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Dory M, Hatzimasoura E, Kállai BM, Nagy SK, Jäger K, Darula Z, Nádai TV, Mészáros T, López-Juez E, Barnabás B, Palme K, Bögre L, Ditengou FA, Dóczi R (2018). Coevolving MAPK and PID phosphosites indicate an ancient environmental control of PIN auxin transpor- ters in land plants. FEBS Lett 592,89-102.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Enders TA, Strader LC (2015). Auxin activity: past, present, and future. Am J Bot 102,180-196.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Feraru E, Feraru MI, Kleine-Vehn J, Martinière A, Mouille G, Vanneste S, Vernhettes S, Runions J, Friml J (2011). PIN polarity maintenance by the cell wall in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol 21,338-343.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Forestan C, Farinati S, Varotto S (2012). The maize PIN gene family of auxin transporters. Front Plant Sci 3,16. |
| [25] |
Forestan C, Varotto S (2012). The role of PIN auxin efflux carriers in polar auxin transport and accumulation and their effect on shaping maize development. Mol Plant 5,787-798.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Friml J (2010). Subcellular trafficking of PIN auxin efflux carriers in auxin transport. Eur J Cell Biol 89,231-235.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Friml J, Benková E, Blilou I, Wisniewska J, Hamann T, Ljung K, Woody S, Sandberg G, Scheres B, Jürgens G, Palme K (2002). AtPIN4 mediates sink-driven auxin gradients and root patterning in Arabidopsis. Cell 108,661-673.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Friml J, Yang X, Michniewicz M, Weijers D, Quint A, Tietz O, Benjamins R, Ouwerkerk PBF, Ljung K, Sandberg G, Hooykaas PJJ, Palme K, Offringa R (2004). A PINOID-dependent binary switch in apical-basal PIN polar targeting directs auxin efflux. Science 306,862-865.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Galván-Ampudia CS, Offringa R (2007). Plant evolution: AGC kinases tell the auxin tale. Trends Plant Sci 12,541- 547.
DOI URL |
| [30] | Gälweiler L, Guan CH, Müller A, Wisman E, Mendgen K, Yephremov A, Palme K (1998). Regulation of polar auxin transport by AtPIN1 in Arabidopsis vascular tissue. S- cience 282,2226-2230. |
| [31] |
Ganguly A, Park M, Kesawat MS, Cho HT (2014). Functional analysis of the hydrophilic loop in intracellular trafficking of Arabidopsis PIN-FORMED proteins. Plant Cell 26,1570-1585.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Ganguly A, Sasayama D, Cho HT (2012). Regulation of the polarity of protein trafficking by phosphorylation. Mol Cells 33,423-430.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Geisler M, Aryal B, Di Donato M, Hao PC (2017). A critical view on ABC transporters and their interacting partners in auxin transport. Plant Cell Physiol 58,1601-1614.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Geldner N, Anders N, Wolters H, Keicher J, Kornberger W, Muller P, Delbarre A, Ueda T, Nakano A, Jürgens G (2003). The Arabidopsis GNOM ARF-GEF mediates endosomal recycling, auxin transport, and auxin-dependent plant growth. Cell 112,219-230.
DOI URL |
| [35] | Geldner N, Richter S, Vieten A, Marquardt S, Torres-Ruiz RA, Mayer U, Jürgens G (2004). Partial loss-of-function alleles reveal a role for GNOM in auxin transport-related, post-embryonic development of Arabidopsis. Development 131,389-400. |
| [36] | Goto N, Starke M, Kranz AR (1987). Effect of gibberellins on flower development of the pin-formed mutant of Ara- bidopsis thaliana. Arabidopsis Inf Serv 23,66-71. |
| [37] | Haga K, Frank L, Kimura T, Schwechheimer C, Sakai T (2018). Roles of AGCVIII kinases in the hypocotyl phototropism of Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant Cell Physiol 59,1060-1071. |
| [38] |
Hajný J, Prát T, Rydza N, Rodriguez L, Tan ST, Verstraeten I, Domjan D, Mazur E, Smakowska-Luzan E, Smet W, Mor E, Nolf J, Yang BJ, Grunewald W, Molnár G, Belkhadir Y, De Rybel B, Friml J (2020). Receptor kinase module targets PIN-dependent auxin transport during canalization. Science 370,550-557.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Hou MM, Luo FF, Wu DX, Zhang XH, Lou MM, Shen DF, Yan M, Mao CZ, Fan XR, Xu GH, Zhang YL (2021). OsPIN9, an auxin efflux carrier, is required for the regulation of rice tiller bud outgrowth by ammonium. New Phytol 229,935-949.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Huang F, Zago MK, Abas L, Van Marion A, Galván-Am- pudia CS, Offringa R (2010). Phosphorylation of conserved PIN motifs directs Arabidopsis PIN1 polarity and auxin transport. Plant Cell 22,1129-1142.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Huang X, Bai XH, Guo TY, Xie ZL, Laimer M, Du DX, Gbokie T Jr, Zhang ZR, He CP, Lu Y, Wu WH, Yi K (2020). Genome-wide analysis of the PIN auxin efflux carrier gene family in coffee. Plants 9,1061.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Jang G, Yoon Y, Choi YD (2019). Jasmonic acid modulates xylem development by controlling expression of PIN-FOR- MED 7. Plant Signal Behav 14,1637664.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Jia WY, Li BH, Li SJ, Liang Y, Wu XW, Ma M, Wang JY, Gao J, Cai YY, Zhang YY, Wang YC, Li JY, Wang YH (2016). Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade MKK7- MPK6 plays important roles in plant development and regulates shoot branching by phosphorylating PIN1 in Arabidopsis. PLoS Biol 14,e1002550.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Keuskamp DH, Pollmann S, Voesenek LACJ, Peeters AJ, Pierik R (2010). Auxin transport through PIN-FORMED 3 (PIN3) controls shade avoidance and fitness during com- petition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107,22740-22744.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Kitakura S, Vanneste S, Robert S, Löfke C, Teichmann T, Tanaka H, Friml J (2011). Clathrin mediates endocytosis and polar distribution of PIN auxin transporters in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 23, 1920-1931.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Kleine-Vehn J, Wabnik K, Martinière A, Łangowski Ł, Willig K, Naramoto S, Leitner J, Tanaka H, Jakobs S, Robert S, Luschnig C, Govaerts W, Hell SW, Runions J, Friml J (2011). Recycling, clustering, and endocytosis jointly maintain PIN auxin carrier polarity at the plasma membrane. Mol Syst Biol 7,540.
DOI PMID |
| [47] |
Kong Q, Ma W, Yang HB, Ma GJ, Mantyla JJ, Benning C (2017). The Arabidopsis WRINKLED1 transcription factor affects auxin homeostasis in roots. J Exp Bot 68,4627- 4634.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
Kong XZ, Huang GQ, Xiong YL, Zhao CY, Wang J, Song XY, Giri J, Zuo KJ (2019). IBR5 regulates leaf serrations development via modulation of the expression of PIN1. Int J Mol Sci 20,4429.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Křeček P, Skůpa P, Libus J, Naramoto S, Tejos R, Friml J, Zažímalová E (2009). The PIN-FORMED (PIN) protein family of auxin transporters. Genome Biol 10,249.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Krouk G, Lacombe B, Bielach A, Perrine-Walker F, Malinska K, Mounier E, Hoyerova K, Tillard P, Leon S, Ljung K, Zazimalova E, Benkova E, Nacry P, Gojon A (2010). Nitrate-regulated auxin transport by NRT1.1 defines a mechanism for nutrient sensing in plants. Dev Cell 18,927-937.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Lee H, Ganguly A, Lee RD, Park M, Cho HT (2020). Intracellularly localized PIN-FORMED8 promotes lateral root emergence in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 10, 1808.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Leyser O (2006). Dynamic integration of auxin transport and signaling. Curr Biol 16,R424-R433.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
Li G, Liang WQ, Zhang XQ, Ren HY, Hu JP, Bennett MJ, Zhang DB (2014). Rice actin-binding protein RMD is a key link in the auxin-actin regulatory loop that controls cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111,10377-10382.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
Li HJ, Lin DS, Dhonukshe P, Nagawa S, Chen DD, Friml J, Scheres B, Guo HW, Yang ZB (2011). Phosphorylation switch modulates the interdigitated pattern of PIN1 localization and cell expansion in Arabidopsis leaf epidermis. Cell Res 21,970-978.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
Li L, Xu J, Xu ZH, Xue HW (2005). Brassinosteroids stimulate plant tropisms through modulation of polar auxin transport in Brassica and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 17, 2738- 2753.
PMID |
| [56] |
Li T, Yan A, Bhatia N, Altinok A, Afik E, Durand-Smet P, Tarr PT, Schroeder JI, Heisler MG, Meyerowitz EM (2019a). Calcium signals are necessary to establish auxin transporter polarity in a plant stem cell niche. Nat Commun 10,726.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
Li Y, Zhu JS, Wu LL, Shao YL, Wu YR, Mao CZ (2019b). Functional divergence of PIN1 paralogous genes in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 60,2720-2732.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
Lin DL, Yao HY, Jia LH, Tan JF, Xu ZH, Zheng WM, Xue HW (2020). Phospholipase D-derived phosphatidic acid promotes root hair development under phosphorus deficiency by suppressing vacuolar degradation of PINFOR- MED2. New Phytol 226,142-155.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
Liu SP, Wang JR, Wang L, Wang XF, Xue YH, Wu P, Shou HX (2009). Adventitious root formation in rice requires OsGNOM1 and is mediated by the OsPINs family. Cell Res 19,1110-1119.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
Löfke C, Luschnig C, Kleine-Vehn J (2013). Posttranslational modification and trafficking of PIN auxin efflux carriers. Mech Dev 130,82-94.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
Lu GW, Coneva V, Casaretto JA, Ying S, Mahmood K, Liu F, Nambara E, Bi YM, Rothstein SJ (2015). OsPIN5b modulates rice ( Oryza sativa) plant architecture and yield by changing auxin homeostasis, transport and distribution. Plant J 83,913-925.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
Luschnig C, Gaxiola RA, Grisafi P, Fink GR (1998). EIR1, a root-specific protein involved in auxin transport, is required for gravitropism in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genes Dev 12, 2175-2187.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
Marhava P, Bassukas AEL, Zourelidou M, Kolb M, Moret B, Fastner A, Schulze WX, Cattaneo P, Hammes UZ, Schwechheimer C, Hardtke CS (2018). A molecular rheostat adjusts auxin flux to promote root protophloem differentiation. Nature 558,297-300.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
Marhavý P, Bielach A, Abas L, Abuzeineh A, Duclercq J, Tanaka H, Pařezová M, Petrášek J, Friml J, Kleine- Vehn J, Benková E (2011). Cytokinin modulates endocytic trafficking of PIN1 auxin efflux carrier to control plant organogenesis. Dev Cell 21,796-804.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
Marquès-Bueno MM, Armengot L, Noack LC, Bareille J, Rodriguez L, Platre MP, Bayle V, Liu MY, Opdenacker D, Vanneste S, Möller BK, Nimchuk ZL, Beeckman T, Caño-Delgado AI, Friml J, Jaillais Y (2021). Auxin- regulated reversible inhibition of TMK1 signaling by MAKR2 modulates the dynamics of root gravitropism. Curr Biol 31,228-237.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
Martinière A, Lavagi I, Nageswaran G, Rolfe DJ, Maneta- Peyret L, Luu DT, Botchway SW, Webb SED, Mon- grand S, Maurel C, Martin-Fernandez ML, Kleine-Vehn J, Friml J, Moreau P, Runions J (2012). Cell wall constrains lateral diffusion of plant plasma-membrane proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109,12805-12810.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
Mattsson J, Ckurshumova W, Berleth T (2003). Auxin signaling in Arabidopsis leaf vascular development. Plant Physiol 131,1327-1339.
PMID |
| [68] |
Men SZ, Boutté Y, Ikeda Y, Li XG, Palme K, Stierhof YD, Hartmann MA, Moritz T, Grebe M (2008). Sterol-dependent endocytosis mediates post-cytokinetic acquisition of PIN2 auxin efflux carrier polarity. Nat Cell Biol 10,237-244.
DOI URL |
| [69] |
Miyashita Y, Takasugi T, Ito Y (2010). Identification and expression analysis of PIN genes in rice. Plant Sci 178,424-428.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
Mravec J, Skůpa P, Bailly A, Hoyerová K, Křeček P, Bielach A, Petrášek J, Zhang J, Gaykova V, Stierhof YD, Dobrev PI, Schwarzerová K, Rolčík J, Seifertová D, Luschnig C, Benková E, Zažímalová E, Geisler M, Friml J (2009). Subcellular homeostasis of phytohormone auxin is mediated by the ER-localized PIN5 transporter. Nature 459,1136-1140.
DOI URL |
| [71] |
Müller A, Guan C, Gälweiler L, Tänzler P, Huijser P, Marchant A, Parry G, Bennett M, Wisman E, Palme K (1998). AtPIN2 defines a locus of Arabidopsis for root gravitropism control. EMBO J 17,6903-6911.
DOI URL |
| [72] | Okada K, Shimura Y (1990). Reversible root tip rotation in Arabidopsis seedlings induced by obstacle-touching stimu- lus. Science 250,274-276. |
| [73] | Okada K, Ueda J, Komaki MK, Bell CJ, Shimura Y (1991). Requirement of the auxin polar transport system in early stages of Arabidopsis floral bud formation. Plant Cell 3,677-684. |
| [74] |
Pan JW, Fujioka S, Peng JL, Chen JH, Li GM, Chen RJ (2009). The E3 ubiquitin ligase SCFTIR1/AFB and membrane sterols play key roles in auxin regulation of endocytosis, recycling, and plasma membrane accumulation of the auxin efflux transporter PIN2 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 21,568-580.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
Paponov IA, Budnyk V, Paponov M, Teale W, Palme K (2020). Butylated Hydroxytoluene (BHT) inhibits PIN1 exocytosis from BFA compartments in Arabidopsis roots. Front Plant Sci 11,393.
DOI PMID |
| [76] |
Peer WA, Blakeslee JJ, Yang HB, Murphy AS (2011). Seven things we think we know about auxin transport. Mol Plant 4,487-504.
DOI URL |
| [77] |
Péret B, Swarup K, Ferguson A, Seth M, Yang YD, Dhondt S, James N, Casimiro I, Perry P, Syed A, Yang HB, Reemmer J, Venison E, Howells C, Perez-Amador MA, Yun J, Alonso J, Beemster GTS, Laplaze L, Murphy A, Bennett MJ, Nielsen E, Swarup R (2012). AUX/ LAX genes encode a family of auxin influx transporters that perform distinct functions during Arabidopsis development. Plant Cell 24,2874-2885.
DOI URL |
| [78] |
Petrášek J, Friml J (2009). Auxin transport routes in plant development. Development 136,2675-2688.
DOI URL |
| [79] |
Petrásek J, Mravec J, Bouchard R, Blakeslee JJ, Abas M, Seifertová D, Wisniewska J, Tadele Z, Kubeš M, Čovanová M, Dhonukshe P, Skůpa P, Benková E, Perry L, Křeček P, Lee OR, Fink GR, Geisler M, Murphy AS, Luschnig C, Zažímalová E, Friml J (2006). PIN proteins perform a rate-limiting function in cellular auxin efflux. Science 312,914-918.
DOI URL |
| [80] |
Ranocha P, Dima O, Nagy R, Felten J, Corratgé-Faillie C, Novák O, Morreel K, Lacombe B, Martinez Y, Pfrunder S, Jin X, Renou JP, Thibaud JB, Ljung K, Fischer U, Martinoia E, Boerjan W, Goffner D (2013). Arabidopsis WAT1 is a vacuolar auxin transport facilitator required for auxin homoeostasis. Nat Commun 4,2625.
DOI URL |
| [81] |
Rigó G, Ayaydin F, Tietz O, Zsigmond L, Kovács H, Páy A, Salchert K, Darula Z, Medzihradszky KF, Szabados L, Palme K, Koncz C, Cséplő Á (2013). Inactivation of plasma membrane-localized CDPK-RELATED KINASE5 decelerates PIN2 exocytosis and root gravitropic response in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25, 1592-1608.
DOI URL |
| [82] |
Roman G, Lubarsky B, Kieber JJ, Rothenberg M, Ecker JR (1995). Genetic analysis of ethylene signal transduction in Arabidopsis thaliana: five novel mutant loci integrated into a stress response pathway. Genetics 139,1393-1409.
DOI URL |
| [83] |
Rosquete MR, Waidmann S, Kleine-Vehn J,(2018). PIN7 auxin carrier has a preferential role in terminating radial root expansion in Arabidopsis thaliana. Int J Mol Sci 19, 1238.
DOI URL |
| [84] |
Rubery PH, Sheldrake AR (1974). Carrier-mediated auxin transport. Planta 118,101-121.
DOI URL |
| [85] |
Růžička K, Ljung K, Vanneste S, Podhorská R, Beeckman T, Friml J, Benková E (2007). Ethylene regulates root growth through effects on auxin biosynthesis and transport-dependent auxin distribution. Plant Cell 19, 2197- 2212.
DOI URL |
| [86] |
Růžička K, Šimášková M, Duclercq J, Petrášek J, Zažímalová E, Simon S, Friml J, Van Montagu MCE, Benková E (2009). Cytokinin regulates root meristem activity via modulation of the polar auxin transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106,4284-4289.
DOI URL |
| [87] |
Sabatini S, Beis D, Wolkenfelt H, Murfett J, Guilfoyle T, Malamy J, Benfey P, Leyser O, Bechtold N, Weisbeek P, Scheres B (1999). An auxin-dependent distal organi- zer of pattern and polarity in the Arabidopsis root. Cell 99,463-472.
DOI URL |
| [88] |
Sancho-Andrés G, Soriano-Ortega E, Gao CJ, Berna- bé-Orts JM, Narasimhan M, Müller AO, Tejos R, Jiang L, Friml J, Aniento F, Marcote MJ (2016). Sorting motifs involved in the trafficking and localization of the PIN1 auxin efflux carrier. Plant Physiol 171,1965-1982.
DOI URL |
| [89] | Santin F, Bhogale S, Fantino E, Grandellis C, Banerjee AK, Ulloa RM (2017). Solanum tuberosum StCDPK1 is regulated by miR390 at the posttranscriptional level and phosphorylates the auxin efflux carrier StPIN4 in vitro, a potential downstream target in potato development. Phy- siol Plant 159,244-261. |
| [90] |
Shen CJ, Bai YH, Wang SK, Zhang SN, Wu YR, Chen M, Jiang DA, Qi YH (2010). Expression profile of PIN, AUX/LAX and PGP auxin transporter gene families in Sorghum bicolor under phytohormone and abiotic stress. FEBS J 277,2954-2969.
DOI URL |
| [91] |
Sidler M, Hassa P, Hasan S, Ringli C, Dudler R (1998). Involvement of an ABC transporter in a developmental pathway regulating hypocotyl cell elongation in the light. Plant Cell 10,1623-1636.
DOI URL |
| [92] |
Šimášková M, O’Brien JA, Khan M, Van Noorden G, Ötvös K, Vieten A, De Clercq I, Van Haperen JMA, Cuesta C, Hoyerová K, Vanneste S, Marhavý P, Wabnik K, Van Breusegem F, Nowack M, Murphy A, Friml J, Weijers D, Beeckman T, Benková E (2015). Cytokinin response factors regulate PIN-FORMED auxin transpor- ters. Nat Commun 6,8717.
DOI PMID |
| [93] |
Sun HW, Tao JY, Bi Y, Hou MM, Lou JJ, Chen XN, Zhang XH, Luo L, Xie XN, Yoneyama K, Zhao QZ, Xu GH, Zhang YL (2018). OsPIN1b is involved in rice seminal root elongation by regulating root apical meristem activity in response to low nitrogen and phosphate. Sci Rep 8,13014.
DOI URL |
| [94] |
Sun JQ, Chen Q, Qi LL, Jiang HL, Li SY, Xu YX, Liu F, Zhou WK, Pan JW, Li XG, Palme K, Li CY (2011). Jasmonate modulates endocytosis and plasma memb- rane accumulation of the Arabidopsis PIN2 protein. New Phytol 191,360-375.
DOI URL |
| [95] |
Tejos R, Sauer M, Vanneste S, Palacios-Gomez M, Li HJ, Heilmann M, Van Wijk R, Vermeer JEM, Heilmann I, Munnik T, Friml J (2014). Bipolar plasma membrane distribution of phosphoinositides and their requirement for auxin-mediated cell polarity and patterning in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 26, 2114-2128.
DOI URL |
| [96] |
Utsuno K, Shikanai T, Yamada Y, Hashimoto T (1998). AGR, an Agravitropic locus of Arabidopsis thaliana, encodes a novel membrane-protein family member. Plant Cell Physiol 39,1111-1118.
PMID |
| [97] |
Vieten A, Sauer M, Brewer PB, Friml J (2007). Molecular and cellular aspects of auxin-transport-mediated deve- lopment. Trends Plant Sci 12,160-168.
DOI URL |
| [98] | Vieten A, Vanneste S, Wisniewska J, Benková E, Benjamins R, Beeckman T, Luschnig C, Friml J (2005). Functional redundancy of PIN proteins is accompanied by auxin-dependent cross-regulation of PIN expression. De- velopment 132,4521-4531. |
| [99] |
Wang JR, Hu H, Wang GH, Li J, Chen JY, Wu P (2009). Expression of PIN genes in rice ( Oryza sativa L.): tissue specificity and regulation by hormones. Mol Plant 2,823- 831.
DOI URL |
| [100] |
Wang PP, Shen L, Guo JH, Jing W, Qu YN, Li WY, Bi RR, Xuan W, Zhang Q, Zhang WH (2019). Phosphatidic acid directly regulates PINOID-dependent phosphorylation and activation of the PIN-FORMED2 auxin efflux transporter in response to salt stress. Plant Cell 31,250-271.
DOI URL |
| [101] |
Wang SK, Shen CJ, Zhang SN, Xu YX, Jiang DA (2011). Analysis of subcellular localization of auxin carriers PIN, AUX/LAX and PGP in Sorghum bicolor. Plant Signal Behav 6, 2023-2025.
DOI URL |
| [102] |
Wiśniewska J, Xu J, Seifertová D, Brewer PB, Růžička K, Blilou I, Rouquié D, Benková E, Scheres B, Friml J (2006). Polar PIN localization directs auxin flow in plants. Science 312,883.
DOI URL |
| [103] |
Wu HM, Xie DJ, Tang ZS, Shi DQ, Yang WC (2020). PINOID regulates floral organ development by modulating auxin transport and interacts with MADS16 in rice. Plant Biotechnol J 18,1778-1795.
DOI URL |
| [104] |
Xi DD, Chen X, Wang YX, Zhong RL, He JM, Shen JB, Ming F (2019). Arabidopsis ANAC092 regulates auxin- mediated root development by binding to the ARF8 and PIN4 promoters. J Integr Plant Biol 61,1015-1031.
DOI URL |
| [105] |
Xi WY, Gong XM, Yang QY, Yu H, Liou YC (2016). Pin1At regulates PIN1 polar localization and root gravitropism. Nat Commun 7,10430.
DOI URL |
| [106] |
Xu HW, Mo YW, Wang W, Wang H, Wang Z (2014). OsPIN1a gene participates in regulating negative phototropism of rice roots. Rice Sci 21,83-89.
DOI URL |
| [107] |
Xu M, Zhu L, Shou HX, Wu P (2005). A PIN1 family gene, OsPIN1, involved in auxin-dependent adventitious root emergence and tillering in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 46,1674-1681.
DOI URL |
| [108] |
Xu WW, Huang WH (2017). Calcium-dependent protein kinases in phytohormone signaling pathways. Int J Mol Sci 18,2436.
DOI URL |
| [109] |
Yang HB, Murphy AS (2009). Functional expression and characterization of Arabidopsis ABCB, AUX1 and PIN auxin transporters in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Plant J 59,179-191.
DOI URL |
| [110] |
Yang SG, Li CL, Zhao LM, Gao SJ, Lu JX, Zhao ML, Chen CY, Liu XC, Luo M, Cui YH, Yang CW, Wu KQ (2015). The Arabidopsis SWI2/SNF2 chromatin remodeling ATPase BRAHMA targets directly to PINs and is required for root stem cell niche maintenance. Plant Cell 27, 1670- 1680.
DOI URL |
| [111] |
Yue RQ, Tie SG, Sun T, Zhang L, Yang YJ, Qi JS, Yan SF, Han XH, Wang HZ, Shen CJ (2015). Genome-wide identification and expression profiling analysis of ZmPIN, ZmPILS, ZmLAX and ZmABCB auxin transporter gene families in maize (Zea mays L.) under various abiotic stresses. PLoS One 10,e0118751.
DOI URL |
| [112] |
Zeng YF, Wen JY, Zhao WB, Wang Q, Huang WC (2020). Rational improvement of rice yield and cold tolerance by editing the three genes OsPIN5b, GS3, and OsMYB30 with the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Front Plant Sci 10,1663.
DOI URL |
| [113] |
Zhang J, Mazur E, Balla J, Gallei M, Kalousek P, Medveďová Z, Li Y, Wang YP, Prát T, Vasileva M, Reinöhl V, Procházka S, Halouzka R, Tarkowski P, Luschnig C, Brewer PB, Friml J (2020). Strigolactones inhibit auxin feedback on PIN-dependent auxin transport canalization. Nat Commun 11,3508.
DOI PMID |
| [114] |
Zhang Q, Li JJ, Zhang WJ, Yan SN, Wang R, Zhao JF, Li YJ, Qi ZG, Sun ZX, Zhu ZG (2012). The putative auxin efflux carrier OsPIN3t is involved in the drought stress response and drought tolerance. Plant J 72,805-816.
DOI URL |
| [115] |
Zhou JJ, Luo J (2018). The PIN-FORMED auxin efflux carriers in plants. Int J Mol Sci 19,2759.
DOI URL |
| [116] |
Zhu ZX, Liu Y, Liu SJ, Mao CZ, Wu YR, Wu P (2012). A gain-of-function mutation in OsIAA11 affects lateral root development in rice. Mol Plant 5,154-161.
DOI URL |
| [117] |
Zourelidou M, Absmanner B, Weller B, Barbosa IC, Willige BC, Fastner A, Streit V, Port SA, Colcombet J, De La Fuente, Van Bentem S, Hirt H, Kuster B, Schulze WX, Hammes UZ, Schwechheimer C (2014). Auxin efflux by PIN-FORMED proteins is activated by two different protein kinases, D6 PROTEIN KINASE and PINOID. eLife 3,e02860.
DOI URL |
| [1] | Jixuan Yang, Xuefei Wang, Hongya Gu. Genetic Basis of Flowering Time Variations in Tibetan Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(3): 373-382. |
| [2] | Yanxiao Chen, Yaping Li, Jinjun Zhou, Lixia Xie, Yongbin Peng, Wei Sun, Yanan He, onghui Jiang, Zenglan Wang, Chongke Zheng, Xianzhi Xie. Effect of Amino Acid Point Mutations on the Structure and Function of Phytochrome B in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(3): 481-494. |
| [3] | Gang Wang, Ertao Wang. The Broad-spectrum Innate Resistance Against Clubroot Disease Conferred by WeiTsing is Mechanistically Revealed [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(3): 356-358. |
| [4] | Yang Yongqing, Guo Yan. Analysis of the pH Sensing Mechanism of Plant Apoplasts [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(4): 409-411. |
| [5] | Tiantian Zhi, Zhou Zhou, Chengyun Han, Chunmei Ren. PAD4 Mutation Accelerating Programmed Cell Death in Arabidopsis thaliana Tyrosine Degradation Deficient Mutant sscd1 [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(3): 288-298. |
| [6] | Yanyan Li, Yanhua Qi. Advances in Biological Functions of Aux/IAA Gene Family in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(1): 30-41. |
| [7] | Yongmei Che, Yanjun Sun, Songchong Lu, Lixia Hou, Xinxin Fan, Xin Liu. AtMYB77 Involves in Lateral Root Development via Regulating Nitric Oxide Biosynthesis under Drought Stress in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(4): 404-413. |
| [8] | Ting Wang, Huanhuan Yang, Hongwei Zhao, Josef Voglmeir, Li Liu. Changes of Protein N-glycosylation in the Growth of Arabidopsis thaliana and Effects of Enzymatic Deglycosylation on Root Development [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(3): 262-274. |
| [9] | Long Ma, Guilin Li, Shipeng Li, Su Jiang. An Improved Protocol for Whole Mount Clearing of Plant Root Tip [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(5): 596-604. |
| [10] | Fei Qi, Piyi Xing, Yinguang Bao, Honggang Wang, Xingfeng Li. Advances in Genetic Studies of the Awn in Cereal Crops [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(5): 613-622. |
| [11] | Nan Zhang,Ziguang Liu,Shichen Sun,Shengyi Liu,Jianhui Lin,Yifang Peng,Xiaoxu Zhang,He Yang,Xi Cen,Juan Wu. Response of AtR8 lncRNA to Salt Stress and Its Regulation on Seed Germination in Arabidopsis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(4): 421-429. |
| [12] | Fangfang He,Huize Chen,Jinlin Feng,Lin Gao,Jiao Niu,Rong Han. Response of Arabidopsis Cohesin RAD21 to Cell Division after Enhanced UV-B Radiation [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(4): 407-420. |
| [13] | Yuting Yao,Jiaqi Ma,Xiaoli Feng,Jianwei Pan,Chao Wang. A Role of Arabidopsis Phosphoinositide Kinase, FAB1, in Root Hair Growth [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(2): 126-136. |
| [14] | Zeyuan Zuo,Wanlin Liu,Jie Xu. Evolution and Functional Analysis of Gene Clusters in Anther Tapetum Cells of Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(2): 147-162. |
| [15] | Zhenmei He,Dongming Li,Yanhua Qi. Advances in Biofunctions of the ABCB Subfamily in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(6): 688-698. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
