

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2022, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (1): 30-41.DOI: 10.11983/CBB21168 cstr: 32102.14.CBB21168
• INVITED REVIEWS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2021-09-24
Accepted:2021-12-28
Online:2022-01-01
Published:2022-01-17
Contact:
Yanhua Qi
Yanyan Li, Yanhua Qi. Advances in Biological Functions of Aux/IAA Gene Family in Plants[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(1): 30-41.
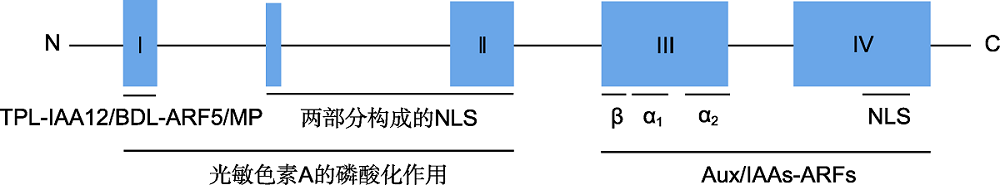
Figure 1 Structure and functional domains of Aux/IAA protein (Colón-Carmona et al., 2000; Szemenyei et al., 2008) TPL-IAA12/BDL-ARF5/MP: Transcription co-inhibitor TOPLESS (TPL) interacts with ARF5/MONOPTEROS (ARF5/MP) regulated by IAA12/BODENLOS (IAA12/BDL); NLS: Nuclear localization sequence; Aux/IAAs-ARFs: Aux/IAA protein interacts with ARF protein
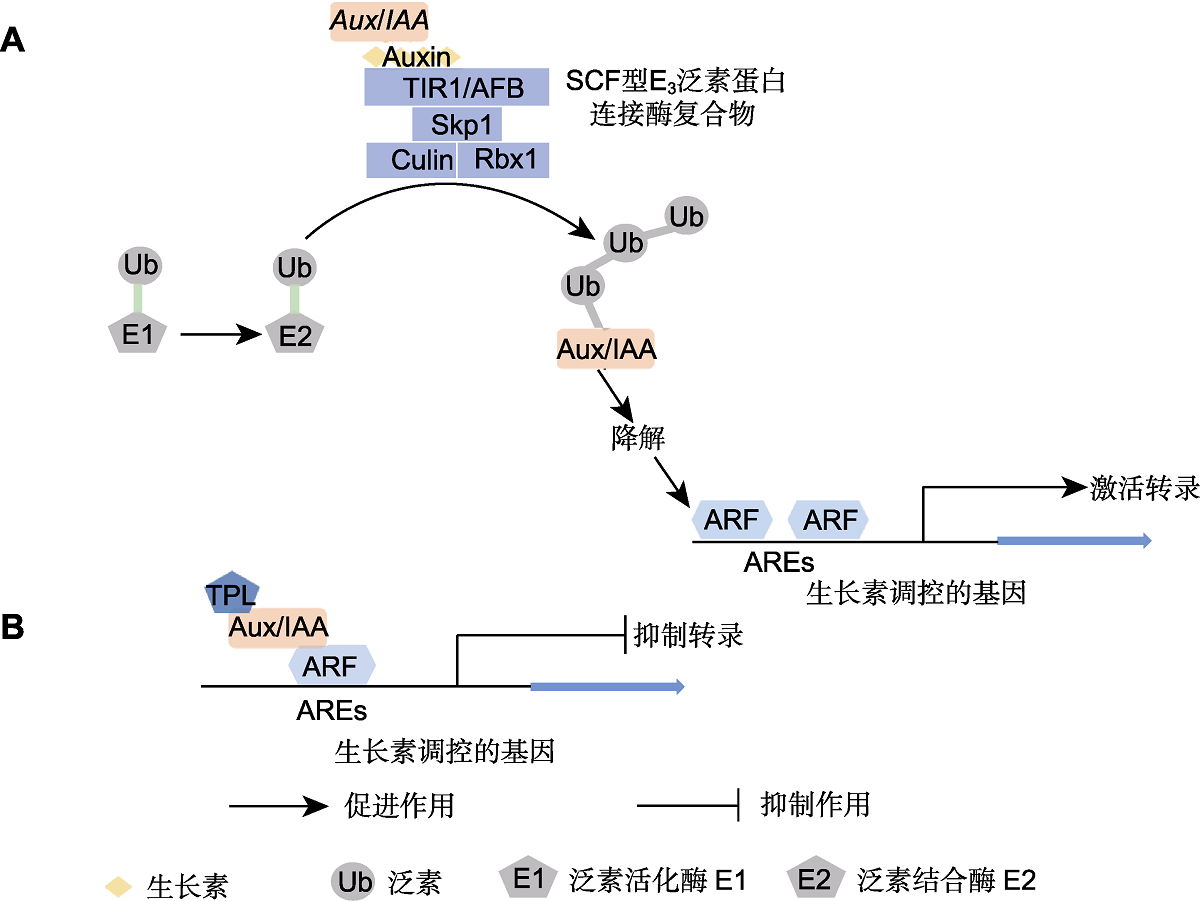
Figure 2 Canonical auxin signaling pathway (Woodward and Bartel, 2005; Leyser, 2018) (A) TIR1-mediated signaling pathway under high auxin concentration; (B) TIR1-mediated signaling pathway under low auxin concentration. TIR1/AFB: Transport inhibitor response 1/Auxin signaling F-box; Skp1, Culin and Rbx1: SCF-type ubiquitin protein ligase E3; Ub: Ubiquitin; E1: Ubiquitin activating enzyme; E2: Ubiquitin conjugating enzyme; Aux/IAA: Auxin/indole acetic acid repressors; ARF: Auxin response factor; AREs: Auxin response element; TPL: TOPLESS
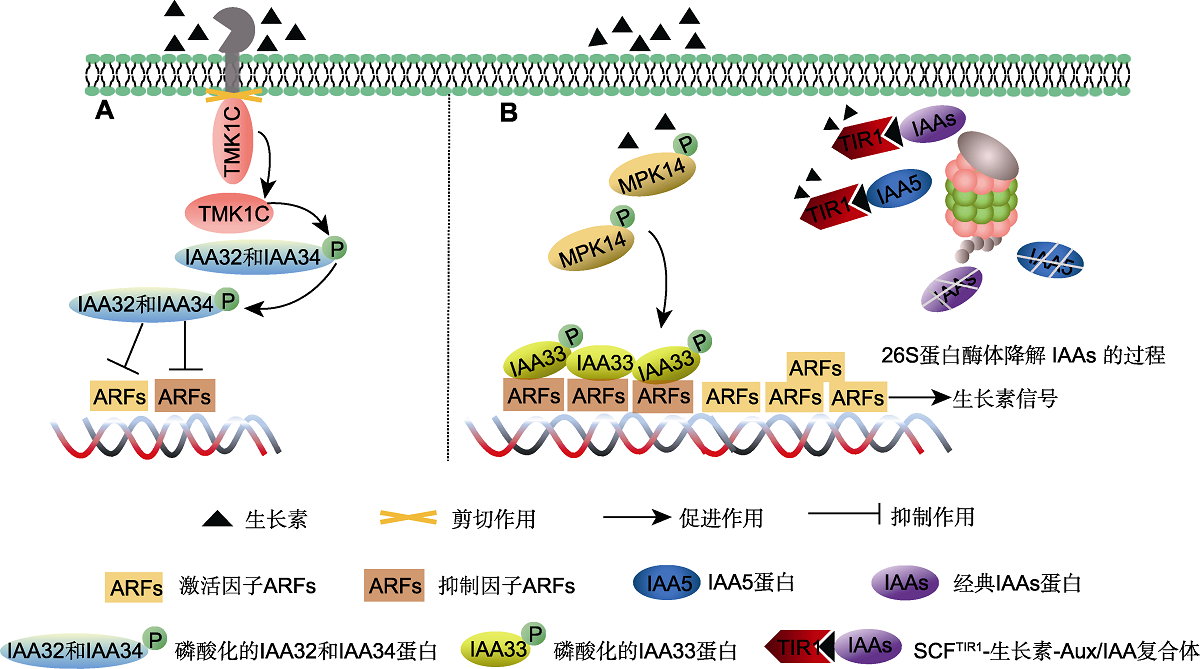
Figure 3 Non-canonical auxin signaling pathway (Cao et al., 2019; Lv et al., 2020) (A) Auxin mediates the TMK1-IAA32/34-ARFs signaling pathway; (B) Auxin mediates the MPK14-IAA33-ARFs signaling pathway. TMK1C: C-terminal of transmembrane kinase 1; MPK14: MITOGEN-ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE 14
| 基因名称 | 功能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| AtIAA3 | 调控侧根数目与长度, 及下胚轴长度和子叶大小 | Tian and Reed, |
| AtIAA5/AtIAA6/AtIAA19 | 调控拟南芥的耐旱性 | Salehin et al., |
| AtIAA7 | 参与植物的向地性生长 | Wilson et al., |
| AtIAA8 | 调节花器官发育 | 王婧, |
| AtIAA14 | 调控植物侧根和根毛的数量 | López-Bucio et al., |
| AtIAA17 | 调控植物下胚轴长度、根毛数量及叶形态 | Rouse et al., |
| AtIAA18 | 调控侧根的形成 | Uehara et al., |
| AtIAA19 | 调控下胚轴和侧根的形成 | Harper et al., |
| AtIAA28 | 参与侧根的形成 | Rogg et al., |
| AtIAA32/34 | 调控顶端弯钩发育 | Cao et al., |
| AtIAA33 | 维持根尖干细胞活性 | Lv et al., |
Table 1 Biofunctions of Aux/IAA genes in Arabidopsis thaliana
| 基因名称 | 功能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| AtIAA3 | 调控侧根数目与长度, 及下胚轴长度和子叶大小 | Tian and Reed, |
| AtIAA5/AtIAA6/AtIAA19 | 调控拟南芥的耐旱性 | Salehin et al., |
| AtIAA7 | 参与植物的向地性生长 | Wilson et al., |
| AtIAA8 | 调节花器官发育 | 王婧, |
| AtIAA14 | 调控植物侧根和根毛的数量 | López-Bucio et al., |
| AtIAA17 | 调控植物下胚轴长度、根毛数量及叶形态 | Rouse et al., |
| AtIAA18 | 调控侧根的形成 | Uehara et al., |
| AtIAA19 | 调控下胚轴和侧根的形成 | Harper et al., |
| AtIAA28 | 参与侧根的形成 | Rogg et al., |
| AtIAA32/34 | 调控顶端弯钩发育 | Cao et al., |
| AtIAA33 | 维持根尖干细胞活性 | Lv et al., |
| 基因名称 | 功能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| OsIAA1 | 调控株高和叶夹角 | Song et al., |
| OsIAA3/OsIAA17 | 参与调控籽粒长度和叶夹角 | 张战营, |
| OslAA4 | 调控株高、叶夹角、分蘖角和向重力性 | Song and Xu, |
| OsIAA6 | 调控分蘖数和参与干旱胁迫响应 | Jung et al., |
| OsIAA11 | 参与侧根的形成 | Zhu et al., |
| OsIAA12 | 调控叶夹角 | Chen et al., |
| OsIAA13 | 调控侧根数目 | Kitomi et al., |
| OsIAA16 | 调控独脚金内酯水平从而影响水稻分蘖 | 王闵霞, |
| OsIAA20 | 参与干旱和盐胁迫响应 | Zhang et al., |
| OslAA23 | 调控根冠生长状态, 使根终止生长 | Ni et al., |
| OsIAA31 | 调控叶和根冠生长 | Nakamura et al., |
Table 2 Biofunctions of Aux/IAA genes in rice
| 基因名称 | 功能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| OsIAA1 | 调控株高和叶夹角 | Song et al., |
| OsIAA3/OsIAA17 | 参与调控籽粒长度和叶夹角 | 张战营, |
| OslAA4 | 调控株高、叶夹角、分蘖角和向重力性 | Song and Xu, |
| OsIAA6 | 调控分蘖数和参与干旱胁迫响应 | Jung et al., |
| OsIAA11 | 参与侧根的形成 | Zhu et al., |
| OsIAA12 | 调控叶夹角 | Chen et al., |
| OsIAA13 | 调控侧根数目 | Kitomi et al., |
| OsIAA16 | 调控独脚金内酯水平从而影响水稻分蘖 | 王闵霞, |
| OsIAA20 | 参与干旱和盐胁迫响应 | Zhang et al., |
| OslAA23 | 调控根冠生长状态, 使根终止生长 | Ni et al., |
| OsIAA31 | 调控叶和根冠生长 | Nakamura et al., |
| 物种 | 基因名称 | 功能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 小麦(Triticum aestivum) | TaIAA1 | 参与调控光敏性 | Singla et al., |
| TaIAA7 | 参与调控根系生长 | Chen et al., | |
| TaIAA8 | 调控侧根数目 | 刘艳娜, | |
| TaIAA21 | 调控小麦籽粒大小和粒重 | Jia et al., | |
| 番茄(Lycopersicon esculentum) | SlIAA3 | 主要参与番茄的生长发育 | Chaaboun et al., |
| SlIAA9 | 参与果实发育和叶形态建成 | Zhang et al., | |
| SlIAA15 | 参与叶和侧根的发育 | Deng et al., | |
| SlIAA17 | 调控番茄肉质果实的大小 | Su et al., | |
| SlIAA27 | 参与番茄根、叶、花和器官的生长发育 | Bassa et al., | |
| 陆地棉(Gossypium hirsutum) | GhIAA4/GhIAA5 | 参与棉纤维的起始 | Han et al., |
| GhIAA8 | 参与早期纤维的伸长, 与次生壁合成有关 | Han et al., | |
| 马铃薯(Solanum tuberosum) | StIAA2 | 调控株高、叶柄和茎的生长发育 | Kloosterman et al., |
| StIAA9 | 参与马铃薯块茎的形成和发育 | Gao et al., |
Table 3 Biofunctions of Aux/IAA genes in other plants
| 物种 | 基因名称 | 功能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 小麦(Triticum aestivum) | TaIAA1 | 参与调控光敏性 | Singla et al., |
| TaIAA7 | 参与调控根系生长 | Chen et al., | |
| TaIAA8 | 调控侧根数目 | 刘艳娜, | |
| TaIAA21 | 调控小麦籽粒大小和粒重 | Jia et al., | |
| 番茄(Lycopersicon esculentum) | SlIAA3 | 主要参与番茄的生长发育 | Chaaboun et al., |
| SlIAA9 | 参与果实发育和叶形态建成 | Zhang et al., | |
| SlIAA15 | 参与叶和侧根的发育 | Deng et al., | |
| SlIAA17 | 调控番茄肉质果实的大小 | Su et al., | |
| SlIAA27 | 参与番茄根、叶、花和器官的生长发育 | Bassa et al., | |
| 陆地棉(Gossypium hirsutum) | GhIAA4/GhIAA5 | 参与棉纤维的起始 | Han et al., |
| GhIAA8 | 参与早期纤维的伸长, 与次生壁合成有关 | Han et al., | |
| 马铃薯(Solanum tuberosum) | StIAA2 | 调控株高、叶柄和茎的生长发育 | Kloosterman et al., |
| StIAA9 | 参与马铃薯块茎的形成和发育 | Gao et al., |
| [1] | 韩悌倩 (2020). 干旱胁迫下马铃薯根系Aux/IAA转录因子的挖掘. 硕士论文. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学. pp. 3-4. |
| [2] |
胡晓, 侯旭, 袁雪, 管丹, 刘悦萍 (2017). ARF和Aux/IAA调控果实发育成熟机制研究进展. 生物技术通报 33(12), 37-44.
DOI |
| [3] | 林雨晴, 齐艳华 (2021). 生长素输出载体PIN家族研究进展. 植物学报 56, 151-165. |
| [4] | 刘艳娜 (2020). 小麦TaIAA8-1B基因的克隆与功能分析. 硕士论文. 青岛: 青岛大学. pp. 12-19. |
| [5] |
马军, 徐通达 (2020). 植物非经典生长素信号转导通路解析. 生物技术通报 36(7), 15-22.
DOI |
| [6] | 王婧 (2012). 拟南芥Aux/IAA家族基因IAA8参与花器官发育的研究. 博士论文. 武汉: 武汉大学. pp. 102-118. |
| [7] | 王闵霞 (2016). 水稻分蘖调控基因OsIAA16的功能研究和d14突变体遗传修饰因子的创制. 博士论文. 北京: 中国农业科学院. pp. 115-121. |
| [8] | 王曦烨 (2016). 棉花Aux/IAA家族基因功能的初步探究. 硕士论文. 河南: 河南师范大学. pp. 15-17. |
| [9] | 张战营 (2015). 水稻产量基因Gnp4的克隆与功能机理分析. 博士论文. 北京: 中国农业大学. pp. 97-109. |
| [10] |
Abel S, Oeller PW, Theologis A (1994). Early auxin-indu-ced genes encode short-lived nuclear proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91, 326-330.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Abel S, Theologis A (1995). A polymorphic bipartite motif signals nuclear targeting of early auxin-inducible proteins related to PS-IAA4 from pea (Pisum sativum). Plant J 8, 87-96.
PMID |
| [12] |
Audran-Delalande C, Bassa C, Mila I, Regad F, Zouine M, Bouzayen M (2012). Genome-wide identification, functio-nal analysis and expression profiling of the Aux/IAA gene family in tomato. Plant Cell Physiol 53, 659-672.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Bassa C, Mila I, Bouzayen M, Audran-Delalande C (2012). Phenotypes associated with down-regulation of Sl-IAA27support functional diversity among Aux/IAA family members in tomato. Plant Cell Physiol 53, 1583-1595.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Belin C, Megies C, Hauserová E, Lopez-Molina L (2009). Abscisic acid represses growth of the Arabidopsis embryonic axis after germination by enhancing auxin signaling. Plant Cell 21, 2253-2268.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Cao M, Chen R, Li P, Yu YQ, Zheng R, Ge DF, Zheng W, Wang XH, Gu YT, Gelová Z, Friml J, Zhang H, Liu RY, He J, Xu TD (2019). TMK1-mediated auxin signaling regulates differential growth of the apical hook. Nature 568, 240-243.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Chaaboun IS, Jones B, Delalande C, Wang H, Li ZG, Mila I, Frasse P, Latché A, Pech JC, Bouzayen M (2009). Sl- IAA3, a tomato Aux/IAA at the crossroads of auxin and ethylene signaling involved in differential growth. J Exp Bot 60, 1349-1362.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Chen DD, Richardson T Chai SC, McIntyre CL, Rae AL, Xue GP (2016). Drought-up-regulated TaNAC69-1 is a transcriptional repressor of TaSHY2 and TaIAA7, and enhances root length and biomass in wheat. Plant Cell Physiol 57, 2076-2090.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Chen SH, Zhou LJ, Xu P, Xue HW (2018). SPOC domain- containing protein Leaf inclination3 interacts with LIP1 to regulate rice leaf inclination through auxin signaling. PLoS Genet 14, e1007829.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Colón-Carmona A, Chen DL, Yeh KC, Abel S (2000). Aux/ IAA proteins are phosphorylated by phytochrome in vitro. Plant Physiol 124, 1728-1738.
PMID |
| [20] |
Deng W, Yan F, Liu MC, Wang XY, Li ZG (2012). Down-regulation of SlIAA15 in tomato altered stem xylem development and production of volatile compounds in leaf exudates. Plant Signal Behav 7, 911-913.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Dharmasiri N, Dharmasiri S, Jones AM, Estelle M (2003). Auxin action in a cell-free system. Curr Biol 13, 1418-1422.
PMID |
| [22] |
Friml J (2003). Auxin transport-shaping the plant. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6, 7-12.
PMID |
| [23] |
Galli M, Liu QJ, Moss BL, Malcomber S, Li W, Gaines C, Federici S, Roshkovan J, Meeley R, Nemhauser JL, Gallavotti A (2015). Auxin signaling modules regulate maize inflorescence architecture. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112, 13372-13377.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Gao JP, Cao XL, Shi SD, Ma YL, Wang K, Liu SJ, Chen D, Chen Q, Ma HL (2016). Genome-wide survey of Aux/IAA gene family members in potato (Solanum tuberosum): identification, expression analysis, and evaluation of their roles in tuber development. Biochem Biophys Res Com-mun 471, 320-327.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Goh T, Kasahara H, Mimura T, Kamiya Y, Fukaki H (2012). Multiple AUX/IAA-ARF modules regulate lateral root formation: the role of Arabidopsis SHY2/IAA3-media-ted auxin signaling. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 367, 1461-1468.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Guilfoyle TJ (2015). The PB1 domain in auxin response factor and Aux/IAA proteins: a versatile protein interaction module in the auxin response. Plant Cell 27, 33-43.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Guilfoyle TJ, Hagen G (2007). Auxin response factors. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10, 453-460.
PMID |
| [28] |
Hagen G, Guilfoyle T (2002). Auxin-responsive gene exp-ression: genes, promoters and regulatory factors. Plant Mol Biol 49, 373-385.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Han XY, Xu XY, Fang DD, Zhang TZ, Guo WZ (2012). Cloning and expression analysis of novel Aux/IAA family genes in Gossypium hirsutum. Gene 503, 83-91.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Harper RM, Stowe-Evans EL, Luesse DR, Muto H, Tatematsu K, Watahiki MK, Yamamoto K, Liscum E (2000). The NPH4 locus encodes the auxin response factor ARF7, a conditional regulator of differential growth in aerial Arabidopsis tissue. Plant Cell 12, 757-770.
PMID |
| [31] |
Ishiguro S, Kawai-Oda A, Ueda J, Nishida I, Okada K (2001). The DEFECTIVE IN ANTHER DEHISCENCE1 gene encodes a novel phospholipase A1 catalyzing the initial step of jasmonic acid biosynthesis, which synchroni-a)zes pollen maturation, anther dehiscence, and flower ope-ning in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 13, 2191-2209.
PMID |
| [32] |
Jain M, Kaur N, Garg R, Thakur JK, Tyagi AK, Khurana JP (2006). Structure and expression analysis of early auxin-responsive Aux/IAA gene family in rice (Oryza sati-va). Funct Integr Genomics 6, 47-59.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Jain M, Khurana JP (2009). Transcript profiling reveals diverse roles of auxin-responsive genes during reproduc-tive development and abiotic stress in rice. FEBS J 276, 3148-3162.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Jia ML, Li YN, Wang ZY, Tao S, Sun GL, Kong XC, Wang K, Ye XG, Liu SS, Geng SF, Mao L, Li AL (2021). TaIAA21 represses TaARF25-mediated expression of TaERFs required for grain size and weight development in wheat. Plant J 108, 1754-1767.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Jiang L, Li ZN, Yu XM, Liu CB (2021). Bioinformatics analysis of Aux/IAA gene family in maize. Agron J 113, 932-942.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
John ME, Keller G (1996). Metabolic pathway engineering in cotton: biosynthesis of polyhydroxybutyrate in fiber cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93, 12768-12773.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Jung H, Lee DK, Choi YD, Kim JK (2015). OsIAA6, a member of the rice Aux/IAA gene family, is involved in drought tolerance and tiller outgrowth. Plant Sci 236, 304-312.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Kitomi Y, Inahashi H, Takehisa H, Sato Y, Inukai Y (2012). OsIAA13-mediated auxin signaling is involved in lateral root initiation in rice. Plant Sci 190, 116-122.
DOI PMID |
| [39] |
Kloosterman B, Visser RGF, Bachem CWB (2006). Iso-lation and characterization of a novel potato Auxin/Indole-3- Acetic Acid family member (StIAA2) that is involved in petiole hyponasty and shoot morphogenesis. Plant Physiol Biochem 44, 766-775.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Leyser O (2018). Auxin signaling. Plant Physiol 176, 465-479.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Liscum E, Reed JW (2002). Genetics of Aux/IAA and ARF action in plant growth and development. Plant Mol Biol 49, 387-400.
PMID |
| [42] |
Liu JY, Shi MJ, Wang J, Zhang B, Li YS, Wang J, El- Sappah AH, Liang Y (2020). Comparative transcriptomic analysis of the development of sepal morphology in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Int J Mol Sci 21, 5914.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
López-Bucio J, Ortiz-Castro R, Ruíz-Herrera LF, Juárez CV, Hernández-Madrigal F, Carreón-Abud Y, Martínez- Trujillo M (2015). Chromate induces adventitious root formation via auxin signaling and SOLITARY-ROOT/IAA-14 gene function in Arabidopsis thaliana. BioMetals 28, 353-365.
DOI PMID |
| [44] | Lv BS, Yu QQ, Liu JJ, Wen XJ, Yan ZW, Hu KQ, Li HB, Kong XP, Li CL, Tian HY, De Smet I, Zhang XS, Ding ZJ (2020). Non-canonical AUX/IAA protein IAA33 compe-tes with canonical AUX/IAA repressor IAA5 to negatively regulate auxin signaling. EMBO J 39, e101515. |
| [45] |
Mockaitis K, Estelle M (2008). Auxin receptors and plant development: a new signaling paradigm. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 24, 55-80.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Morgan KE, Zarembinski TI, Theologis A, Abel S (1999). Biochemical characterization of recombinant polypeptides corresponding to the predicted βααfold in Aux/IAA protein-s. FEBS Lett 454, 283-287.
PMID |
| [47] |
Nagpal P, Ellis CM, Weber H, Ploense SE, Barkawi LS, Guilfoyle TJ, Hagen G, Alonso JM, Cohen JD, Farmer EE, Ecker JR, Reed JW (2005). Auxin response factors ARF6 and ARF8 promote jasmonic acid production and flower maturation. Development 132, 4107-4118.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
Nakamura A, Umemura I, Gomi K, Hasegawa Y, Kitano H, Sazuka T, Matsuoka M (2006). Production and characte-rization of auxin-insensitive rice by overexpression of a mutagenized rice IAA protein. Plant J 46, 297-306.
PMID |
| [49] |
Ni J, Wang GH, Zhu ZX, Zhang HH, Wu YR, Wu P (2011). OsIAA23-mediated auxin signaling defines postembryonic maintenance of QC in rice. Plant J 68, 433-442.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Qiao JY, Jiang HZ, Lin YQ, Shang LG, Wang M, Li DM, Fu XD, Geisler M, Qi YH, Gao ZY, Qian Q (2021). A novel miR167a-OsARF6-OsAUX3 module regulates grain length and weight in rice. Mol Plant 14, 1683-1698.
DOI URL |
| [51] | Qiao LY, Zhang XJ, Han X, Zhang L, Li X, Zhan HX, Ma J, Luo PG, Zhang WP, Cui L, Li XY, Chang ZJ (2015). A genome-wide analysis of the auxin/indole-3-acetic acid gene family in hexaploid bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Front Plant Sci 6, 770. |
| [52] |
Reed JW (2001). Roles and activities of Aux/IAA proteins in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci 6, 420-425.
PMID |
| [53] |
Rogg LE, Lasswell J, Bartel B (2001). A gain-of-function mutation in IAA28 suppresses lateral root development. Plant Cell 13, 465-480.
PMID |
| [54] |
Rouse D, Mackay P, Stirnberg P, Estelle M, Leyser O (1998). Changes in auxin response from mutations in an AUX/IAA gene. Science 279, 1371-1373.
PMID |
| [55] |
Sakamoto T, Morinaka Y, Inukai Y, Kitano H, Fujioka S (2013). Auxin signal transcription factor regulates expression of the brassinosteroid receptor gene in rice. Plant J 73, 676-688.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
Salehin M, Li BH, Tang M, Katz E, Song L, Ecker JR, Kliebenstein DJ, Estelle M (2019). Auxin-sensitive Aux/IAA proteins mediate drought tolerance in Arabidopsis by regulating glucosinolate levels. Nat Commun 10, 4021.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
Singla B, Chugh A, Khurana JP, Khurana P (2006). An early auxin-responsive Aux/IAA gene from wheat (Triti-cum aestivum) is induced by epibrassinolide and differen-tially regulated by light and calcium. J Exp Bot 57, 4059-4070.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
Smalle J, Vierstra RD (2004). The ubiquitin 26S proteaso-me proteolytic pathway. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55, 555-590.
PMID |
| [59] |
Song YL, Xu ZF (2013). Ectopic overexpression of an AUXIN/INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID (Aux/IAA) gene OsIAA4 in rice induces morphological changes and reduces res-ponsiveness to auxin. Int J Mol Sci 14, 13645-13656.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
Song YL, You J Xiong LZ (2009). Characterization of OsIAA1 gene, a member of rice Aux/IAA family involved in auxin and brassinosteroid hormone responses and plant morphogenesis. Plant Mol Biol 70, 297-309.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
Su LY, Audran C, Bouzayen M, Roustan JP, Chervin C (2015). The Aux/IAA, Sl-IAA17 regulates quality parame-ters over tomato fruit development. Plant Signal Behav 10, e1071001.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
Su LY, Bassa C, Audran C, Mila I, Cheniclet C, Chevalier C, Bouzayen M, Roustan JP, Chervin C (2014). The auxin Sl-IAA17 transcriptional repressor controls fruit size via the regulation of endoreduplication-related cell expan-sion. Plant Cell Physiol 55, 1969-1976.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
Szemenyei H, Hannon M, Long JA (2008). TOPLESS mediates auxin-dependent transcriptional repression du-ring Arabidopsis embryogenesis. Science 319, 1384-1386.
DOI PMID |
| [64] |
Tan X, Calderon-Villalobos LIA, Sharon M, Zheng CX, Robinson CV, Estelle M, Zheng N (2007). Mechanism of auxin perception by the TIR1 ubiquitin ligase. Nature 446, 640-645.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
Tatematsu K, Kumagai S, Muto H, Sato A, Watahiki MK, Harper RM, Liscum E, Yamamoto KT (2004). MASSU-GU2 encodes Aux/IAA19, an auxin-regulated protein that functions together with the transcriptional activator NPH4/ARF7 to regulate differential growth responses of hypo-cotyl and formation of lateral roots in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 16, 379-393.
PMID |
| [66] |
Tian Q, Reed JW (1999). Control of auxin-regulated root development by the Arabidopsis thaliana SHY2/IAA3 ge-ne. Development 126, 711-721.
PMID |
| [67] |
Timpte C, Wilson AK, Estelle M (1994). The axr2-1mutation of Arabidopsis thaliana is a gain-of-function mutation that disrupts an early step in auxin response. Genetics 138, 1239-1249.
DOI PMID |
| [68] |
Tiwari SB, Hagen G, Guilfoyle TJ (2004). Aux/IAA proteins contain a potent transcriptional repression domain. Plant Cell 16, 533-543.
PMID |
| [69] |
Tiwari SB, Wang XJ, Hagen G, Guilfoyle TJ (2001). AUX/ IAA proteins are active repressors, and their stability and activity are modulated by auxin. Plant Cell 13, 2809-2822.
PMID |
| [70] |
Uehara T, Okushima Y, Mimura T, Tasaka M, Fukaki H (2008). Domain II mutations in CRANE/IAA18 suppress lateral root formation and affect shoot development in Ara- bidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol 49, 1025-1038.
DOI PMID |
| [71] |
Ulmasov T, Murfett J, Hagen G, Guilfoyle TJ (1997). Aux/IAA proteins repress expression of reporter genes containing natural and highly active synthetic auxin response elements. Plant Cell 9, 1963-1971.
PMID |
| [72] |
Von Behrens I, Komatsu M, Zhang YX, Berendzen KW, Niu XM, Sakai H, Taramino G, Hochholdinger F (2011). Rootless with undetectable meristem 1encodes a monocot-specific AUX/IAA protein that controls embryonic se-minal and post-embryonic lateral root initiation in maize. Plant J 66, 341-353.
DOI URL |
| [73] |
Walker JC, Key JL (1982). Isolation of cloned cDNAs to auxin-responsive poly(A)+RNAs of elongating soybean hypocotyl. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79, 7185-7189.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
Wang SK, Bai YH, Shen CJ, Wu YR, Zhang SN, Jiang DA, Guilfoyle TJ, Chen M, Qi YH (2010a). Auxin-related gene families in abiotic stress response in Sorghum bico-lor. Funct Integr Genomics 10, 533-546.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
Wang YJ, Deng DX, Bian YL, Lv YP, Xie Q (2010b). Genome-wide analysis of primary auxin-responsive Aux/IAA gene family in maize (Zea mays L.). Mol Biol Rep 37, 3991-4001.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
Weijers D, Wagner D (2016). Transcriptional responses to the auxin hormone. Annu Rev Plant Biol 67, 539-574.
DOI PMID |
| [77] |
Wilson AK, Pickett FB, Turner JC, Estelle M (1990). A dominant mutation in Arabidopsis confers resistance to auxin, ethylene and abscisic acid. Mol Gen Genet 222, 377-383.
DOI URL |
| [78] |
Woodward AW, Bartel B (2005). Auxin: regulation, action, and interaction. Ann Bot 95, 707-735.
DOI URL |
| [79] |
Worley CK, Zenser N, Ramos J, Rouse D, Leyser O, Theo- logis A, Callis J (2000). Degradation of Aux/IAA proteins is essential for normal auxin signaling. Plant J 21, 553-562.
PMID |
| [80] |
Yang XQ, Lee S, So JH, Dharmasiri S, Dharmasiri N, Ge L, Jensen C, Hangarter R, Hobbie L, Estelle M (2004). The IAA1 protein is encoded by AXR5 and is a substrate of SCFTIR1. Plant J 40, 772-782.
DOI URL |
| [81] |
Zhang AY, Yang X, Lu J, Song FY, Sun JH, Wang C, Lian J, Zhao LL, Zhao BC (2021). OsIAA20, an Aux/IAA protein, mediates abiotic stress tolerance in rice through an ABA pathway. Plant Sci 308, 110903.
DOI URL |
| [82] |
Zhang JH, Chen RG, Xiao JH, Qian CJ, Wang TT, Li HX, Ouyang B Ye ZB (2007). A single-base deletion mutation in SlIAA9 gene causes tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) entire mutant. J Plant Res 120, 671-678.
DOI URL |
| [83] |
Zhang SN, Wang SK, Xu YX, Yu CL, Shen CJ, Qian Q, Geisler M, Jiang DA, Qi YH (2015). The auxin response factor, OsARF19, controls rice leaf angles through positi-vely regulating OsGH3-5 and OsBRI1. Plant Cell Environ 38, 638-654.
DOI URL |
| [84] |
Zhao Z, Andersen SU, Ljung K, Dolezal K, Miotk A, Schultheiss SJ, Lohmann JU (2010). Hormonal control of the shoot stem-cell niche. Nature 465, 1089-1092.
DOI URL |
| [85] |
Zhu ZX, Liu Y, Liu SJ, Mao CZ, Wu YR, Wu P (2012). A gain-of-function mutation in OsIAA11affects lateral root development in rice. Mol Plant 5, 154-161.
DOI URL |
| [1] | Yuying Zhou, Hui Chen, Simu Liu. Research Progress on Auxin Responsive Non-canonical Aux/IAA Proteins in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(4): 651-658. |
| [2] | Yanxiao Chen, Yaping Li, Jinjun Zhou, Lixia Xie, Yongbin Peng, Wei Sun, Yanan He, onghui Jiang, Zenglan Wang, Chongke Zheng, Xianzhi Xie. Effect of Amino Acid Point Mutations on the Structure and Function of Phytochrome B in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(3): 481-494. |
| [3] | Jixuan Yang, Xuefei Wang, Hongya Gu. Genetic Basis of Flowering Time Variations in Tibetan Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(3): 373-382. |
| [4] | Xiangpei Kong, Mengyue Zhang, Zhaojun Ding. There Is a Way Out-new Breakthroughs in Extracellular Auxin Sensing [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(6): 861-865. |
| [5] | Yuan Yuan, Enhebayaer, Qi Yanhua. Research Advances in Biological Functions of GH3 Gene Family in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(5): 770-782. |
| [6] | Gang Wang, Ertao Wang. The Broad-spectrum Innate Resistance Against Clubroot Disease Conferred by WeiTsing is Mechanistically Revealed [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(3): 356-358. |
| [7] | Shuyao Zhou, Jianming Li, Juan Mao. AtGH3.17-mediated Regulation of Auxin and Brassinosteroid Response in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(3): 373-384. |
| [8] | Ye Qing, Yan Xiaoyan, Chen Huize, Feng Jinlin, Han Rong. Effect of Nitrogen-doped Graphene Quantum Dots on Growth Direction of Primary Root in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(5): 623-634. |
| [9] | Yang Yongqing, Guo Yan. Analysis of the pH Sensing Mechanism of Plant Apoplasts [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(4): 409-411. |
| [10] | Lixia Jia, Yanhua Qi. Advances in the Regulation of Rice (Oryza sativa) Grain Shape by Auxin Metabolism, Transport and Signal Transduction [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(3): 263-275. |
| [11] | Tiantian Zhi, Zhou Zhou, Chengyun Han, Chunmei Ren. PAD4 Mutation Accelerating Programmed Cell Death in Arabidopsis thaliana Tyrosine Degradation Deficient Mutant sscd1 [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(3): 288-298. |
| [12] | Binqi Li, Jiahui Yan, Hao Li, Wei Xin, Yunhe Tian, Zhenbiao Yang, Wenxin Tang. Changes of Small GTPases Activity During Cucumber Tendril Winding [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(3): 299-307. |
| [13] | Jingwen Wang, Xingjun Wang, Changle Ma, Pengcheng Li. A Review on the Mechanism of Ribosome Stress Response in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(1): 80-89. |
| [14] | Yongmei Che, Yanjun Sun, Songchong Lu, Lixia Hou, Xinxin Fan, Xin Liu. AtMYB77 Involves in Lateral Root Development via Regulating Nitric Oxide Biosynthesis under Drought Stress in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(4): 404-413. |
| [15] | Ting Wang, Huanhuan Yang, Hongwei Zhao, Josef Voglmeir, Li Liu. Changes of Protein N-glycosylation in the Growth of Arabidopsis thaliana and Effects of Enzymatic Deglycosylation on Root Development [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(3): 262-274. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
