

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2021, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (3): 262-274.DOI: 10.11983/CBB20163 cstr: 32102.14.CBB20163
Previous Articles Next Articles
Ting Wang, Huanhuan Yang, Hongwei Zhao, Josef Voglmeir, Li Liu*( )
)
Received:2020-09-29
Accepted:2020-12-25
Online:2021-05-01
Published:2021-04-30
Contact:
Li Liu
About author:First author contact:† These authors contributed equally to this paper
Ting Wang, Huanhuan Yang, Hongwei Zhao, Josef Voglmeir, Li Liu. Changes of Protein N-glycosylation in the Growth of Arabidopsis thaliana and Effects of Enzymatic Deglycosylation on Root Development[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(3): 262-274.
| Number | Retention time (min) | GU value | The theoretical electron charge-mass ratio (m/z) | Detection value of charge-mass ratio (m/z) | Name | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 17.2 | 4.86 | 1185.43 | 1185.51 | Man3XylGlcNAc2 | MMXF |
| 2 | 17.9 | 5.03 | - | 806.99 | Unknown | - |
| 3 | 19.4 | 5.39 | 1388.51 | - | GlcNAcMan3XylGlcNAc2 | GnMXF |
| 4 | 20.1 | 5.56 | 1331.49 | 1331.39 | Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | MMX |
| 5 | 21.4 | 5.90 | 1591.558 | 1591.74 | GlcNAc2Man3XylGlcNAc2 | GnGnX |
| 6 | 22.3 | 6.10 | 1534.57 | 1534.70 | GlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | GnMX |
| 7 | 23.2 | 6.35 | 1493.53 | 1494.16 | Man4XylFucGlcNAc2 | M4XF |
| 8 | 24.0 | 6.58 | 1737.64 | 1737.93 | GlcNAc2Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | GnGnXF |
| 9 | 24.9 | 6.82 | 1696.62 | 1697.37 | GalGlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | GGnXF |
| 10 | 25.5 | 6.97 | 1539.54 | 1540.16 | Man6GlcNAc2 | M6 |
| 11 | 27.3 | 7.47 | - | 1620.53 | Unknown | - |
| 12 | 28.6 | 7.86 | 1701.89 | 1701.74 | Man7GlcNAc2 | M7 |
| 13 | 31.4 | 8.73 | 1863.65 | 1863.86 | Man8GlcNAc2 | M8 |
| 14 | 33.4 | 9.44 | 2025.70 | 2025.88 | Man9GlcNAc2 | M9 |
Table 1 The summary of N-glycan structures from glycoprotein in Arabidopsis thaliana
| Number | Retention time (min) | GU value | The theoretical electron charge-mass ratio (m/z) | Detection value of charge-mass ratio (m/z) | Name | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 17.2 | 4.86 | 1185.43 | 1185.51 | Man3XylGlcNAc2 | MMXF |
| 2 | 17.9 | 5.03 | - | 806.99 | Unknown | - |
| 3 | 19.4 | 5.39 | 1388.51 | - | GlcNAcMan3XylGlcNAc2 | GnMXF |
| 4 | 20.1 | 5.56 | 1331.49 | 1331.39 | Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | MMX |
| 5 | 21.4 | 5.90 | 1591.558 | 1591.74 | GlcNAc2Man3XylGlcNAc2 | GnGnX |
| 6 | 22.3 | 6.10 | 1534.57 | 1534.70 | GlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | GnMX |
| 7 | 23.2 | 6.35 | 1493.53 | 1494.16 | Man4XylFucGlcNAc2 | M4XF |
| 8 | 24.0 | 6.58 | 1737.64 | 1737.93 | GlcNAc2Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | GnGnXF |
| 9 | 24.9 | 6.82 | 1696.62 | 1697.37 | GalGlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | GGnXF |
| 10 | 25.5 | 6.97 | 1539.54 | 1540.16 | Man6GlcNAc2 | M6 |
| 11 | 27.3 | 7.47 | - | 1620.53 | Unknown | - |
| 12 | 28.6 | 7.86 | 1701.89 | 1701.74 | Man7GlcNAc2 | M7 |
| 13 | 31.4 | 8.73 | 1863.65 | 1863.86 | Man8GlcNAc2 | M8 |
| 14 | 33.4 | 9.44 | 2025.70 | 2025.88 | Man9GlcNAc2 | M9 |
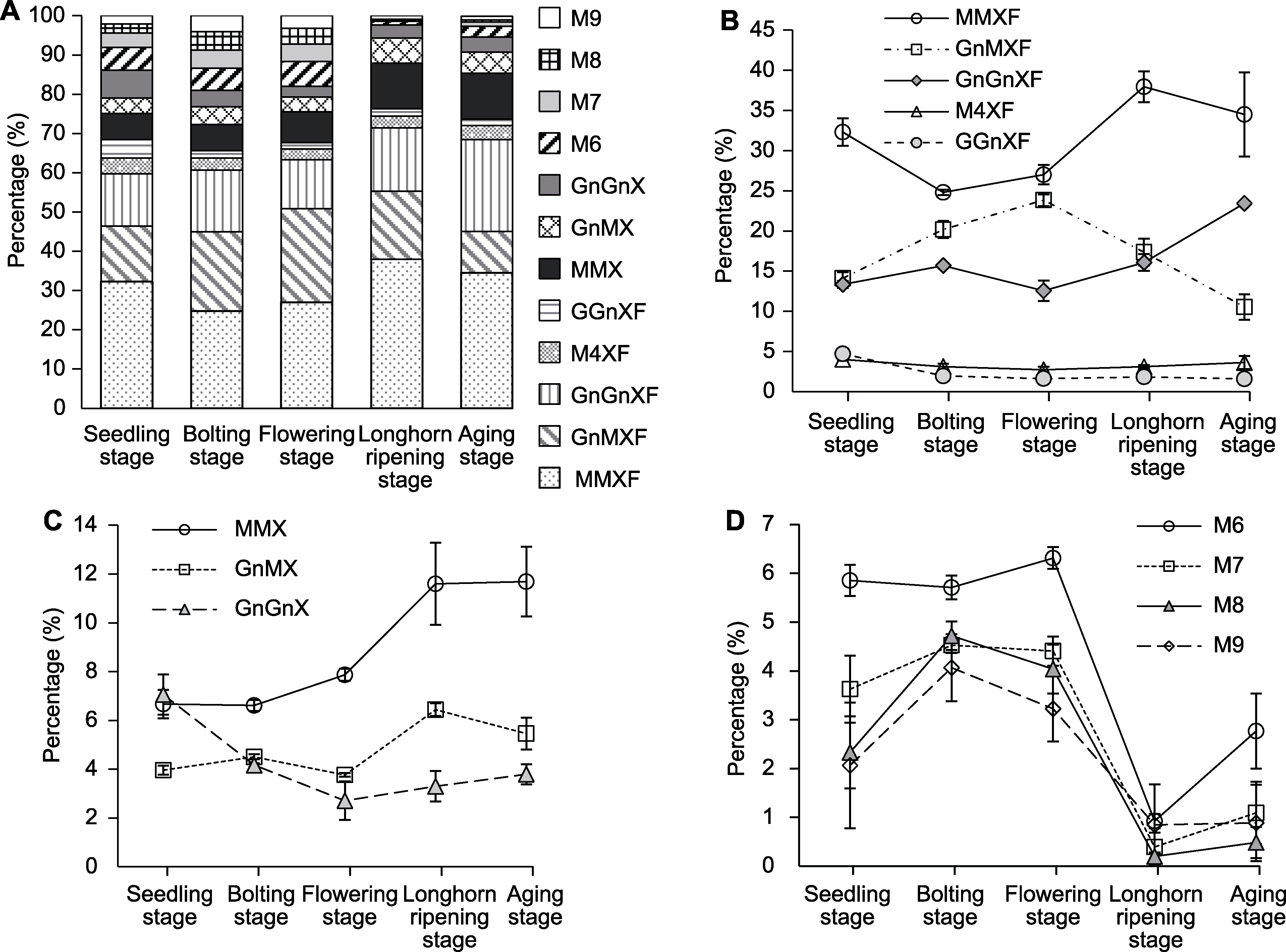
Figure 2 The relative proportion of different N-glycans from Arabidopsis thaliana at different growth stages (A) The changes of the proportions for each N-glycan structure; (B) The changes of the proportions of complex N-glycans with Xyl and Fuc; (C) The changes of the proportions of complex N-glycans only with Xyl; (D) The changes of the proportions of high-mannose N-glycans. The abbreviations of different N-glycans are the same as Table 1.
| N-glycans | Relative content (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seedling stage | Bolting stage | Flowering stage | Longhorn ripening stage | Aging stage | |
| Complex type with Xyl and Fuc | |||||
| Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 (MMXF) | 32.31±1.71 b | 24.79±0.33 c | 27.00±1.21 c | 37.96±1.92 a | 34.51±5.23 ab |
| GlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 (GnMXF) | 14.11±0.75 d | 20.18±1.05 b | 23.83±0.74 a | 17.37±1.67 c | 10.53±1.58 e |
| Man4XylFucGlcNAc2 (M4XF) | 3.99±0.15 a | 3.11±0.36 ab | 2.70±0.40 b | 3.10±0.21 ab | 3.61±0.80 ab |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 (GnGnXF) | 13.33±0.42 b | 15.68±0.15 b | 12.55±1.26 b | 16.06±1.03 b | 23.44±0.12 a |
| GalGlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 (GGnXF) | 4.69±0.36 a | 1.93±0.20 b | 1.61±0.29 b | 1.82±0.09 b | 1.58±0.36 b |
| Sum | 68.44±1.51 b | 65.69±0.98 b | 67.68±2.33 b | 76.31±3.13 a | 73.84±2.79 a |
| Complex type only with Xyl | |||||
| Man3XylGlcNAc2 (MMX) | 6.67±0.58 b | 6.62±0.23 b | 7.87±0.25 b | 11.59±1.68 a | 10.69±1.43 a |
| GlcNAcMan3XylGlcNAc2 (GnMX) | 3.96±0.18 cd | 4.51±0.10 c | 3.77±0.08 d | 6.44±0.26 a | 5.46±0.65 b |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylGlcNAc2 (GnGnX) | 7.06±0.82 a | 4.17±0.08 b | 2.71±0.79 bc | 3.30±0.62 bc | 3.80±0.41 c |
| Sum | 17.69±1.57 b | 15.29±0.41 bc | 14.34±0.70 c | 21.33±2.39 a | 20.94±2.79 a |
| Sum of complex | 86.13±2.95 b | 80.98±0.92 c | 82.02±1.65 c | 97.64±0.78 a | 94.77±0.94 a |
| High-mannose type | |||||
| Man6GlcNAc2 (M6) | 5.85±0.32 a | 5.71±0.24 a | 6.31±0.22 a | 0.92±0.15 c | 2.77±0.77 b |
| Man7GlcNAc2 (M7) | 3.63±0.69 b | 4.53±0.16 a | 4.41±0.30 ab | 0.39±0.30 c | 1.09±0.64 c |
| Man8GlcNAc2 (M8) | 2.33±0.74 b | 4.72±0.29 a | 4.04±0.50 a | 0.20±0.09 c | 0.48±0.32 c |
| Man9GlcNAc2 (M9) | 2.06±1.29 bc | 4.06±0.69 a | 3.23±0.67 ab | 0.84±0.83 c | 0.88±0.78 c |
| Sum of high-mannose | 13.87±2.95 b | 19.02±0.92 a | 17.98±1.65 a | 2.36±0.78 c | 5.23±0.94 c |
Table 2 The relative content of different N-glycans from Arabidopsis thaliana at different growth stages
| N-glycans | Relative content (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seedling stage | Bolting stage | Flowering stage | Longhorn ripening stage | Aging stage | |
| Complex type with Xyl and Fuc | |||||
| Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 (MMXF) | 32.31±1.71 b | 24.79±0.33 c | 27.00±1.21 c | 37.96±1.92 a | 34.51±5.23 ab |
| GlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 (GnMXF) | 14.11±0.75 d | 20.18±1.05 b | 23.83±0.74 a | 17.37±1.67 c | 10.53±1.58 e |
| Man4XylFucGlcNAc2 (M4XF) | 3.99±0.15 a | 3.11±0.36 ab | 2.70±0.40 b | 3.10±0.21 ab | 3.61±0.80 ab |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 (GnGnXF) | 13.33±0.42 b | 15.68±0.15 b | 12.55±1.26 b | 16.06±1.03 b | 23.44±0.12 a |
| GalGlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 (GGnXF) | 4.69±0.36 a | 1.93±0.20 b | 1.61±0.29 b | 1.82±0.09 b | 1.58±0.36 b |
| Sum | 68.44±1.51 b | 65.69±0.98 b | 67.68±2.33 b | 76.31±3.13 a | 73.84±2.79 a |
| Complex type only with Xyl | |||||
| Man3XylGlcNAc2 (MMX) | 6.67±0.58 b | 6.62±0.23 b | 7.87±0.25 b | 11.59±1.68 a | 10.69±1.43 a |
| GlcNAcMan3XylGlcNAc2 (GnMX) | 3.96±0.18 cd | 4.51±0.10 c | 3.77±0.08 d | 6.44±0.26 a | 5.46±0.65 b |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylGlcNAc2 (GnGnX) | 7.06±0.82 a | 4.17±0.08 b | 2.71±0.79 bc | 3.30±0.62 bc | 3.80±0.41 c |
| Sum | 17.69±1.57 b | 15.29±0.41 bc | 14.34±0.70 c | 21.33±2.39 a | 20.94±2.79 a |
| Sum of complex | 86.13±2.95 b | 80.98±0.92 c | 82.02±1.65 c | 97.64±0.78 a | 94.77±0.94 a |
| High-mannose type | |||||
| Man6GlcNAc2 (M6) | 5.85±0.32 a | 5.71±0.24 a | 6.31±0.22 a | 0.92±0.15 c | 2.77±0.77 b |
| Man7GlcNAc2 (M7) | 3.63±0.69 b | 4.53±0.16 a | 4.41±0.30 ab | 0.39±0.30 c | 1.09±0.64 c |
| Man8GlcNAc2 (M8) | 2.33±0.74 b | 4.72±0.29 a | 4.04±0.50 a | 0.20±0.09 c | 0.48±0.32 c |
| Man9GlcNAc2 (M9) | 2.06±1.29 bc | 4.06±0.69 a | 3.23±0.67 ab | 0.84±0.83 c | 0.88±0.78 c |
| Sum of high-mannose | 13.87±2.95 b | 19.02±0.92 a | 17.98±1.65 a | 2.36±0.78 c | 5.23±0.94 c |
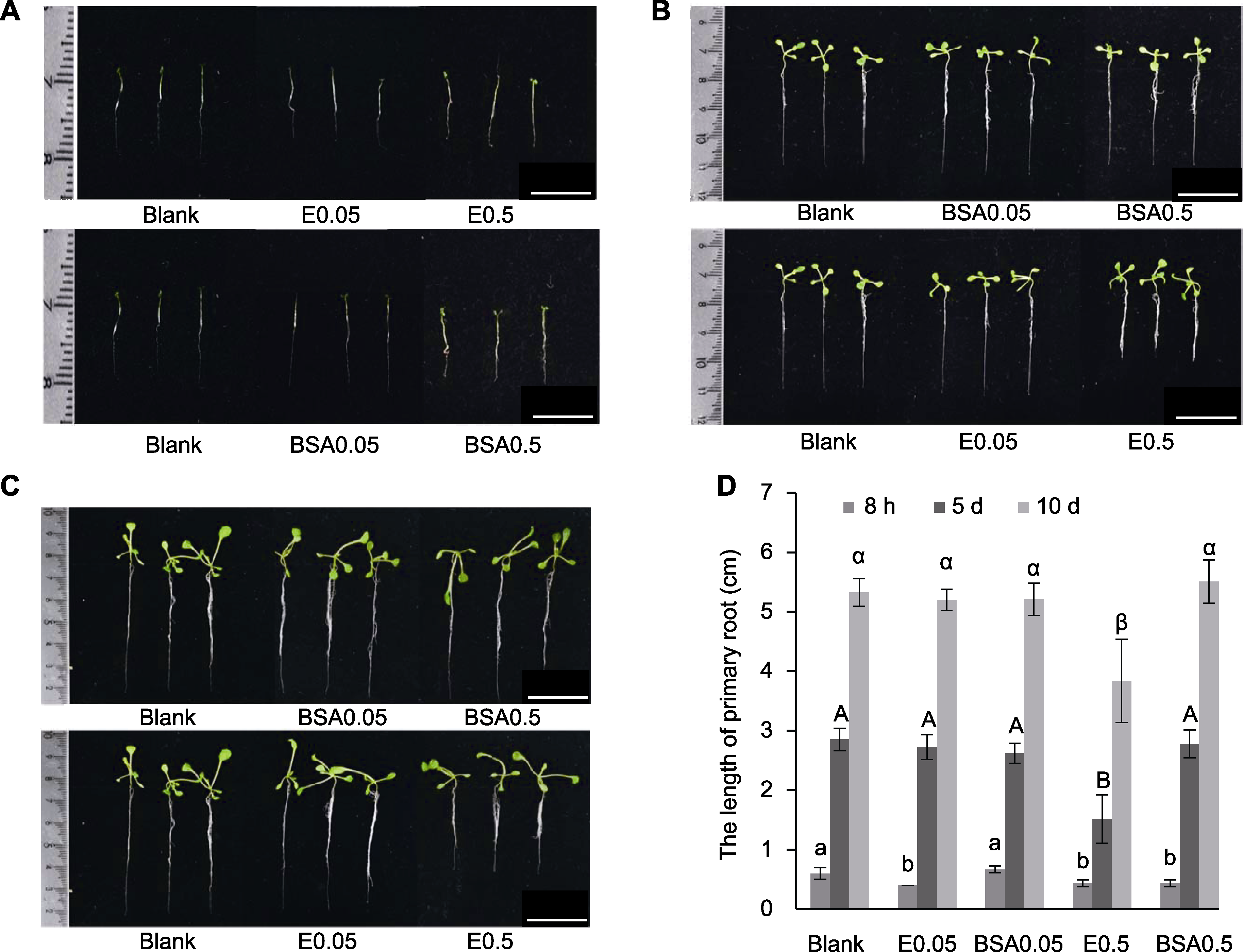
Figure 3 The influence of PNGase Rz with different concentrations on the growth of Arabidopsis primary root (A) Seedlings cultured for 8 hours; (B) Seedlings in the fifth day of growth; (C) Seedlings in the tenth day of growth; (D) Statistical analysis of primary root length of Arabidopsis seedlings treated with different concentrations of PNGase Rz for 8 hours at different time points (different letters indicate significant dfferences). Blank: Sterile deionized water; BSA0.05: 0.05 mg·mL-1 BSA; BSA0.5: 0.5 mg·mL-1 BSA; E0.05: 0.05 mg·mL-1 PNGase Rz; E0.5: 0.5 mg·mL-1 PNGase Rz. Bars=1 cm
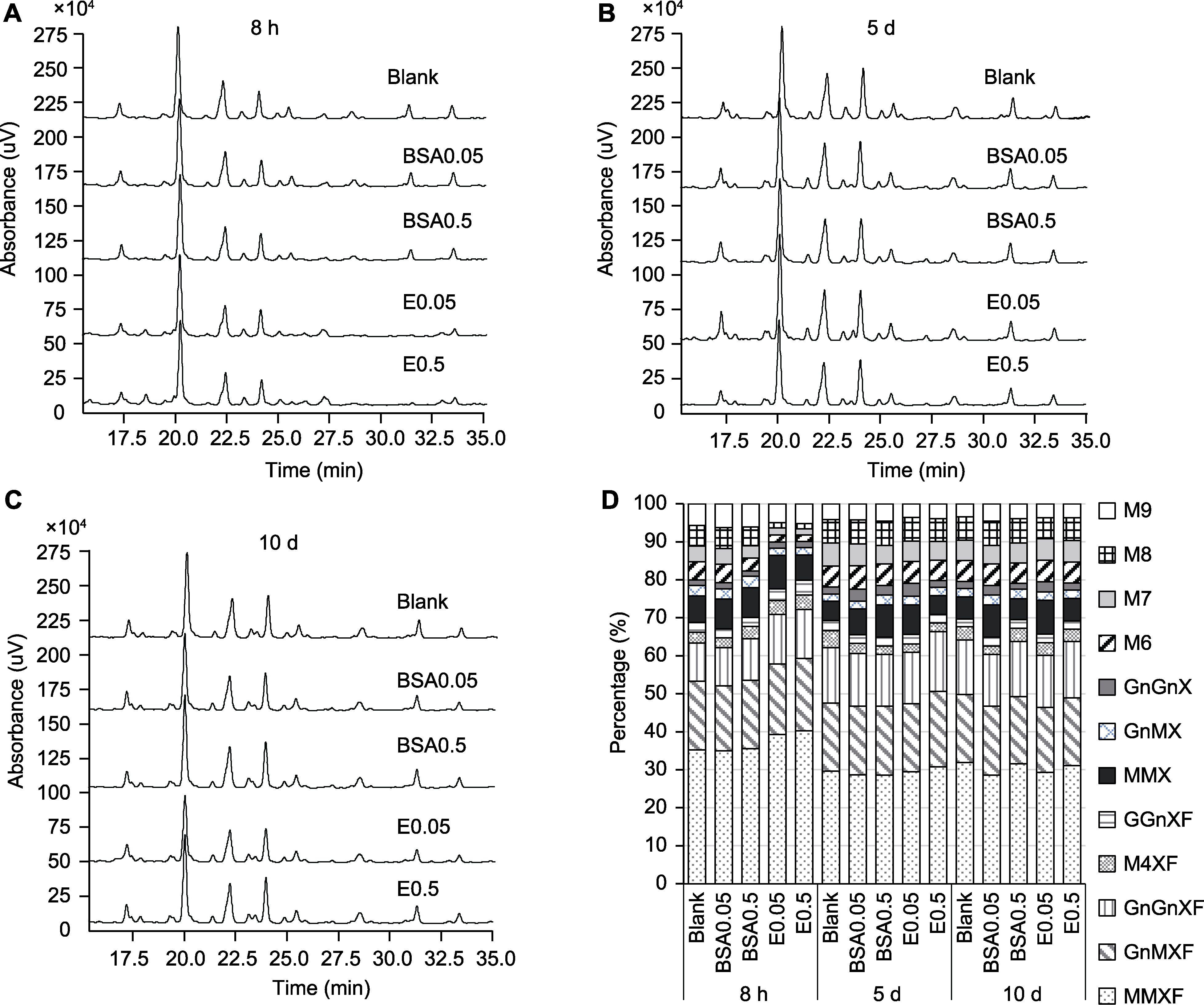
Figure 4 HPLC spectra of N-glycans from different groups at three growth points and the relative content of each N-glycan of Arabidopsis (A) HPLC spectra of N-glycans at 8 h; (B) HPLC spectra of N-glycans at 5 d; (C) HPLC spectra of N-glycans at 10 d; (D) The relative content of different N-glycans. The abbreviations of dfferent N-glycans are the same as Table 1. Blank, BSA0.05, BSA0.5, E0.05, and E0.5 are the same as Figure 3.
| N-glycans | The relative content of each N-glycan (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | BSA0.05 | BSA0.5 | E0.05 | E0.5 | |
| Culture for 8 hours | |||||
| Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 35.22±0.42 b | 35.00±0.07 b | 35.57±0.99 b | 39.29±0.14 a | 40.25±0.62 a |
| GlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 18.12±0.07 bc | 17.10±0.07 b | 18.00±0.55 c | 18.51±0.05 b | 19.03±0.20 a |
| Man4XylFucGlcNAc2 | 2.83±0.20 c | 2.61±0.10 c | 3.24±0.16 b | 3.63±0.14 a | 3.86±0.18 a |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 9.98±0.13 c | 10.02±0.08 c | 10.95±0.79 b | 13.09±0.13 a | 12.89±0.55 a |
| GalGlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 2.63±0.09 c | 2.35±0.11 d | 2.35±0.16 d | 3.06±0.05 b | 3.83±0.12 a |
| Man3XylGlcNAc2 | 6.98±0.16 c | 7.89±0.15 b | 7.86±0.19 b | 8.83±0.15 a | 6.66±0.32 c |
| GlcNAcMan3XylGlcNAc2 | 2.77±0.14 a | 2.60±0.16 a | 2.95±0.22 a | 1.88±0.24 b | 1.94±0.21 b |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylGlcNAc2 | 1.44±0.14 b | 1.69±0.10 a | 1.40±0.13 b | 1.67±0.21 ab | 1.64±0.11 ab |
| Sum of complex | 79.97±0.52 c | 79.26±0.48 d | 82.31±0.22 b | 89.95±0.12 a | 90.10±0.29 a |
| Man6GlcNAc2 | 4.78±0.10 a | 4.81±0.05 a | 3.41±0.27 b | 1.86±0.09 c | 1.70±0.16 c |
| Man7GlcNAc2 | 4.16±0.13 a | 4.16±0.11 a | 3.25±0.11 b | 1.87±0.11 c | 1.58±0.29 c |
| Man8GlcNAc2 | 5.37±0.10 a | 5.52±0.11 a | 4.90±0.20 b | 1.39±0.21 c | 1.44±0.18 c |
| Man9GlcNAc2 | 5.71±0.28 b | 6.25±0.29 a | 6.12±0.13 a | 4.93±0.30 c | 5.18±0.13 c |
| Sum of high-mannose | 20.03±0.52 b | 20.74±0.48 a | 17.69±0.22 c | 10.05±0.12 d | 9.90±0.29 d |
| Culture for 5 days | |||||
| Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 29.60±0.18 b | 28.68±0.15 c | 28.60±0.87 c | 29.51±0.24 b | 30.74±0.36 a |
| GlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 17.97±0.10 b | 18.06±0.12 b | 18.15±0.61 b | 17.84±0.10 b | 19.85±0.28 a |
| Man4XylFucGlcNAc2 | 4.46±0.08 a | 2.71±0.12 b | 2.24±0.15 c | 2.23±0.12 c | 2.34±0.11 c |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 14.58±0.11 b | 13.80±0.15 c | 13.56±0.27 c | 13.54±0.18 c | 15.72±0.14 a |
| GalGlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 2.62±0.13 a | 2.29±0.10 b | 2.29±0.12 b | 2.46±0.11 ab | 2.22±0.18 b |
| Man3XylGlcNAc2 | 5.17±0.07 d | 6.80±0.11 c | 8.56±0.26 a | 7.77±0.30 b | 5.00±0.16 d |
| GlcNAcMan3XylGlcNAc2 | 1.81±0.17 d | 2.02±0.10 cd | 2.58±0.11 a | 2.33±0.11 b | 2.19±0.07 bc |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylGlcNAc2 | 1.89±0.10 c | 3.14±0.05 a | 2.54±0.17 b | 3.36±0.25 a | 1.75±0.21 c |
| Sum of complex | 78.10±0.10 c | 77.51±0.15 d | 78.52±0.26 c | 79.05±0.18 b | 79.80±0.52 a |
| Man6GlcNAc2 | 5.46±0.09 c | 6.16±0.05 a | 5.64±0.15 bc | 5.81±0.30 ab | 5.38±0.32 c |
| Man7GlcNAc2 | 6.09±0.13 a | 5.78±0.15 b | 4.90±0.13 d | 5.33±0.22 c | 4.87±0.11 d |
| Man8GlcNAc2 | 6.22±0.15 b | 6.35±0.04 a | 6.41±0.09 a | 6.27±0.17 ab | 6.04±0.10 b |
| Man9GlcNAc2 | 4.12±0.11 b | 4.20±0.15 ab | 4.53±0.26 a | 3.55±0.25 c | 3.90±0.20 bc |
| Sum of high-mannose | 21.90±0.10 b | 22.49±0.15 a | 21.48±0.26 b | 20.95±0.18 c | 20.20±0.52 d |
| Culture for 10 days | |||||
| Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 31.88±0.19 a | 31.64±0.09 ab | 31.58±0.08 ab | 29.30±0.12 c | 31.11±0.12 b |
| GlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 17.96±0.09 a | 17.66±0.10 a | 17.70±0.37 a | 17.07±0.09 b | 17.77±0.13 a |
| Man4XylFucGlcNAc2 | 3.46±0.57 a | 3.57±0.11 a | 3.43±0.13 a | 3.32±0.12 a | 3.28±0.12 a |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 14.34±0.07 ab | 13.88±0.10 bc | 14.50±0.58 a | 13.73±0.05 c | 14.85±0.16 a |
| GalGlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 2.05±0.09 a | 2.21±0.17 a | 2.30±0.20 a | 2.25±0.09 a | 2.20±0.23 a |
| Man3XylGlcNAc2 | 5.81±0.23 c | 6.62±0.10 b | 5.48±0.38 c | 8.96±0.03 a | 5.86±0.14 c |
| GlcNAcMan3XylGlcNAc2 | 2.20±0.15 a | 2.27±0.12 a | 2.51±0.42 a | 2.20±0.07 a | 2.19±0.11 a |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylGlcNAc2 | 1.87±0.10 c | 2.23±0.13 b | 1.56±0.19 d | 2.64±0.07 a | 1.88±0.05 c |
| Sum of complex | 79.57±0.47 ab | 80.08±0.30 a | 79.06±0.64 b | 79.47±0.07 ab | 79.15±0.15 b |
| Man6GlcNAc2 | 5.47±0.09 a | 5.59±0.08 a | 5.39±0.32 a | 5.68±0.17 a | 5.52±0.10 a |
| Man7GlcNAc2 | 5.36±0.16 b | 5.27±0.09 b | 5.24±0.10 b | 5.69±0.17 a | 5.66±0.17 a |
| Man8GlcNAc2 | 6.20±0.07 a | 5.71±0.13 bc | 6.42±0.40 a | 5.52±0.21 c | 6.04±0.10 ab |
| Man9GlcNAc2 | 3.41±0.22 b | 3.35±0.23 b | 3.89±0.15 a | 3.64±0.22 ab | 3.64±0.11 ab |
| Sum of high-mannose | 20.43±0.47 ab | 19.92±0.30 b | 20.94±0.64 a | 20.53±0.07 a | 20.85±0.15 a |
Table 3 The relative content of each N-glycan of Arabidopsis from different groups at different time points
| N-glycans | The relative content of each N-glycan (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | BSA0.05 | BSA0.5 | E0.05 | E0.5 | |
| Culture for 8 hours | |||||
| Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 35.22±0.42 b | 35.00±0.07 b | 35.57±0.99 b | 39.29±0.14 a | 40.25±0.62 a |
| GlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 18.12±0.07 bc | 17.10±0.07 b | 18.00±0.55 c | 18.51±0.05 b | 19.03±0.20 a |
| Man4XylFucGlcNAc2 | 2.83±0.20 c | 2.61±0.10 c | 3.24±0.16 b | 3.63±0.14 a | 3.86±0.18 a |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 9.98±0.13 c | 10.02±0.08 c | 10.95±0.79 b | 13.09±0.13 a | 12.89±0.55 a |
| GalGlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 2.63±0.09 c | 2.35±0.11 d | 2.35±0.16 d | 3.06±0.05 b | 3.83±0.12 a |
| Man3XylGlcNAc2 | 6.98±0.16 c | 7.89±0.15 b | 7.86±0.19 b | 8.83±0.15 a | 6.66±0.32 c |
| GlcNAcMan3XylGlcNAc2 | 2.77±0.14 a | 2.60±0.16 a | 2.95±0.22 a | 1.88±0.24 b | 1.94±0.21 b |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylGlcNAc2 | 1.44±0.14 b | 1.69±0.10 a | 1.40±0.13 b | 1.67±0.21 ab | 1.64±0.11 ab |
| Sum of complex | 79.97±0.52 c | 79.26±0.48 d | 82.31±0.22 b | 89.95±0.12 a | 90.10±0.29 a |
| Man6GlcNAc2 | 4.78±0.10 a | 4.81±0.05 a | 3.41±0.27 b | 1.86±0.09 c | 1.70±0.16 c |
| Man7GlcNAc2 | 4.16±0.13 a | 4.16±0.11 a | 3.25±0.11 b | 1.87±0.11 c | 1.58±0.29 c |
| Man8GlcNAc2 | 5.37±0.10 a | 5.52±0.11 a | 4.90±0.20 b | 1.39±0.21 c | 1.44±0.18 c |
| Man9GlcNAc2 | 5.71±0.28 b | 6.25±0.29 a | 6.12±0.13 a | 4.93±0.30 c | 5.18±0.13 c |
| Sum of high-mannose | 20.03±0.52 b | 20.74±0.48 a | 17.69±0.22 c | 10.05±0.12 d | 9.90±0.29 d |
| Culture for 5 days | |||||
| Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 29.60±0.18 b | 28.68±0.15 c | 28.60±0.87 c | 29.51±0.24 b | 30.74±0.36 a |
| GlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 17.97±0.10 b | 18.06±0.12 b | 18.15±0.61 b | 17.84±0.10 b | 19.85±0.28 a |
| Man4XylFucGlcNAc2 | 4.46±0.08 a | 2.71±0.12 b | 2.24±0.15 c | 2.23±0.12 c | 2.34±0.11 c |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 14.58±0.11 b | 13.80±0.15 c | 13.56±0.27 c | 13.54±0.18 c | 15.72±0.14 a |
| GalGlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 2.62±0.13 a | 2.29±0.10 b | 2.29±0.12 b | 2.46±0.11 ab | 2.22±0.18 b |
| Man3XylGlcNAc2 | 5.17±0.07 d | 6.80±0.11 c | 8.56±0.26 a | 7.77±0.30 b | 5.00±0.16 d |
| GlcNAcMan3XylGlcNAc2 | 1.81±0.17 d | 2.02±0.10 cd | 2.58±0.11 a | 2.33±0.11 b | 2.19±0.07 bc |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylGlcNAc2 | 1.89±0.10 c | 3.14±0.05 a | 2.54±0.17 b | 3.36±0.25 a | 1.75±0.21 c |
| Sum of complex | 78.10±0.10 c | 77.51±0.15 d | 78.52±0.26 c | 79.05±0.18 b | 79.80±0.52 a |
| Man6GlcNAc2 | 5.46±0.09 c | 6.16±0.05 a | 5.64±0.15 bc | 5.81±0.30 ab | 5.38±0.32 c |
| Man7GlcNAc2 | 6.09±0.13 a | 5.78±0.15 b | 4.90±0.13 d | 5.33±0.22 c | 4.87±0.11 d |
| Man8GlcNAc2 | 6.22±0.15 b | 6.35±0.04 a | 6.41±0.09 a | 6.27±0.17 ab | 6.04±0.10 b |
| Man9GlcNAc2 | 4.12±0.11 b | 4.20±0.15 ab | 4.53±0.26 a | 3.55±0.25 c | 3.90±0.20 bc |
| Sum of high-mannose | 21.90±0.10 b | 22.49±0.15 a | 21.48±0.26 b | 20.95±0.18 c | 20.20±0.52 d |
| Culture for 10 days | |||||
| Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 31.88±0.19 a | 31.64±0.09 ab | 31.58±0.08 ab | 29.30±0.12 c | 31.11±0.12 b |
| GlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 17.96±0.09 a | 17.66±0.10 a | 17.70±0.37 a | 17.07±0.09 b | 17.77±0.13 a |
| Man4XylFucGlcNAc2 | 3.46±0.57 a | 3.57±0.11 a | 3.43±0.13 a | 3.32±0.12 a | 3.28±0.12 a |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 14.34±0.07 ab | 13.88±0.10 bc | 14.50±0.58 a | 13.73±0.05 c | 14.85±0.16 a |
| GalGlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 2.05±0.09 a | 2.21±0.17 a | 2.30±0.20 a | 2.25±0.09 a | 2.20±0.23 a |
| Man3XylGlcNAc2 | 5.81±0.23 c | 6.62±0.10 b | 5.48±0.38 c | 8.96±0.03 a | 5.86±0.14 c |
| GlcNAcMan3XylGlcNAc2 | 2.20±0.15 a | 2.27±0.12 a | 2.51±0.42 a | 2.20±0.07 a | 2.19±0.11 a |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylGlcNAc2 | 1.87±0.10 c | 2.23±0.13 b | 1.56±0.19 d | 2.64±0.07 a | 1.88±0.05 c |
| Sum of complex | 79.57±0.47 ab | 80.08±0.30 a | 79.06±0.64 b | 79.47±0.07 ab | 79.15±0.15 b |
| Man6GlcNAc2 | 5.47±0.09 a | 5.59±0.08 a | 5.39±0.32 a | 5.68±0.17 a | 5.52±0.10 a |
| Man7GlcNAc2 | 5.36±0.16 b | 5.27±0.09 b | 5.24±0.10 b | 5.69±0.17 a | 5.66±0.17 a |
| Man8GlcNAc2 | 6.20±0.07 a | 5.71±0.13 bc | 6.42±0.40 a | 5.52±0.21 c | 6.04±0.10 ab |
| Man9GlcNAc2 | 3.41±0.22 b | 3.35±0.23 b | 3.89±0.15 a | 3.64±0.22 ab | 3.64±0.11 ab |
| Sum of high-mannose | 20.43±0.47 ab | 19.92±0.30 b | 20.94±0.64 a | 20.53±0.07 a | 20.85±0.15 a |
| 1 | 王梦, 危双, 王婷, Voglmeir J, 刘丽 (2017). Solitalea canadensis源β-N-乙酰氨基己糖苷酶的基因克隆、异源表达和酶学特性. 微生物学报 57, 1270-1282. |
| 2 |
Altmann F (2007). The role of protein glycosylation in allergy. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 142, 99-115.
DOI URL |
| 3 |
Bao LG, Ma SW, van Huystee RB (2001). The effects of the site-directed removal of N-glycosylation from cationic peanut peroxidase on its function. Arch Biochem Biophys 386, 17-24.
DOI URL |
| 4 |
Dam S, Thaysen-Andersen M, Stenkjær E, Lorentzen A, Roepstorff P, Packer NH, Stougaard J (2013). Combined N-glycome and N-glycoproteome analysis of the Lotus japonicus seed globulin fraction shows conservation of protein structure and glycosylation in legumes. J Proteome Res 12, 3383-3392.
DOI URL |
| 5 |
Du YM, Xia T, Gu XQ, Wang T, Ma HY, Voglmeir J, Liu L (2015). Rapid sample preparation methodology for plant N-glycan analysis using acid-stable PNGase H+. J Agric Food Chem 63, 10550-10555.
DOI URL |
| 6 |
Ghazarian H, Idoni B, Oppenheimer SB (2011). A glycobiology review: carbohydrates, lectins and implications in cancer therapeutics. Acta Histochem 113, 236-247.
DOI URL |
| 7 |
Horiuchi R, Hirotsu N, Miyanishi N (2015). Comparative analysis of N-glycans in the ungerminated and germinated stages of Oryza sativa. Carbohydr Res 418, 1-8.
DOI URL |
| 8 | Ihara Y, Ikezaki M, Takatani M, Ito Y (2020). Calnexin/calreticulin and assays related to N-glycoprotein folding in vitro. In: Hirabayashi J, ed. Lectin Purification and Analysis: Methods and Protocols. Humana: Springer. pp. 295-308. |
| 9 |
Kajiura H, Koiwa H, Nakazawa Y, Okazawa A, Kobayashi A, Seki T, Fujiyama K (2010). Two Arabidopsis thaliana Golgi, α-mannosidase I enzymes are responsible for plant N-glycan maturation. Glycobiology 20, 235-247.
DOI URL |
| 10 |
Kang JS, Frank J, Kang CH, Kajiura H, Vikram M, Ueda A, Kim S, Bahk JD, Triplett B, Fujiyama K, Lee SY, von Schaewen A, Koiwa H (2008). Salt tolerance of Arabidopsis thaliana requires maturation of N-glycosylated proteins in the Golgi apparatus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105, 5933-5938.
DOI URL |
| 11 |
Kato S, Hayashi M, Kitagawa M, Kajiura H, Maeda M, Kimura Y, Igarashi K, Kasahara M, Ishimizu T (2018). Degradation pathway of plant complex-type N-glycans: identification and characterization of a key α1,3-fucosidase from glycoside hydrolase family 29. Biochem J 475, 305-317.
DOI URL |
| 12 |
Kimura Y, Matsuo S (2000). Changes in N-linked oligosaccharides during seed development of Ginkgo biloba. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 64, 562-568.
DOI URL |
| 13 |
Kimura Y, Takeoka Y, Inoue M, Maeda M, Fujiyama K (2011). Double-knockout of putative endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase (ENGase) genes in Arabidopsis thaliana: loss of ENGase activity induced accumulation of high- mannose type free N-glycans bearing N,N'-acetylchitobiosyl unit. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 75, 1019-1021.
DOI URL |
| 14 |
Koiwa H, Li F, McCully MG, Mendoza I, Koizumi N, Manabe Y, Nakagawa Y, Zhu JH, Rus A, Pardo JM, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM (2003). The STT3a subunit isoform of the Arabidopsis oligosaccharyltransferase controls adaptive responses to salt/osmotic stress. Plant Cell 15, 2273-2284.
DOI URL |
| 15 |
Liebminger E, Hüttner S, Vavra U, Fischl R, Schoberer J, Grass J, Blaukopf C, Seifert GJ, Altmann F, Mach L, Strasser R (2009). Class I α-mannosidases are required for N-glycan processing and root development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 21, 3850-3867.
DOI URL |
| 16 |
Liebminger E, Veit C, Pabst M, Batoux M, Zipfel C, Altmann F, Mach L, Strasser R (2011). β-N-acetylhexosaminidases HEXO1 and HEXO3 are responsible for the formation of paucimannosidic N-glycans in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Biol Chem 286, 10793-10802.
DOI URL |
| 17 |
Lindner H, Kessler SA, Müller LM, Shimosato-Asano H, Boisson-Dernier A, Grossniklaus U (2015). TURAN and EVAN mediate pollen tube reception in Arabidopsis Synergids through protein glycosylation. PLoS Biol 13, e1002139.
DOI URL |
| 18 | Maeda M, Kimura Y (2014). Structural features of free N-glycans occurring in plants and functional features of de-N-glycosylation enzymes, ENGase, and PNGase: the presence of unusual plant complex type N-glycans. Front Plant Sci 5, 429. |
| 19 |
Misaki R, Kimura Y, Fujiyama K, Seki T (2001). Glycoproteins secreted from suspension -cultured tobacco BY2 cells have distinct glycan structures from intracellular glycoproteins. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 65, 2482-2488.
DOI URL |
| 20 |
Nagashima Y, von Schaewen A, Koiwa H (2018). Function of N-glycosylation in plants. Plant Sci 274, 70-79.
DOI URL |
| 21 |
Nakamura K, Inoue M, Yoshiie T, Hosoi K, Kimura Y (2008). Changes in structural features of free N-glycan and endoglycosidase activity during tomato fruit ripening. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 72, 2936-2945.
DOI URL |
| 22 |
Rips S, Bentley N, Jeong IS, Welch JL, von Schaewen A, Koiwa H (2014). Multiple N-glycans cooperate in the subcellular targeting and functioning of Arabidopsis KORRIGAN1. Plant Cell 26, 3792-3808.
DOI URL |
| 23 |
Saijo Y (2010). ER quality control of immune receptors and regulators in plants. Cell Microbiol 12, 716-724.
DOI URL |
| 24 |
Shen JB, Ding Y, Gao CJ, Rojo E, Jiang LW (2014). N-linked glycosylation of AtVSR1 is important for vacuolar protein sorting in Arabidopsis. Plant J 80, 977-992.
DOI URL |
| 25 |
Strasser R, Schoberer J, Jin CS, Glössl J, Mach L, Steinkellner H (2006). Molecular cloning and characterization of Arabidopsis thaliana Golgi α-mannosidase II, a key enzyme in the formation of complex N-glycans in plants. Plant J 45, 789-803.
PMID |
| 26 |
Viëtor R, Loutelier-Bourhis C, Fitchette AC, Margerie P, Gonneau M, Faye L, Lerouge P (2003). Protein N-glycosylation is similar in the moss Physcomitrella patens and in higher plants. Planta 218, 269-275.
PMID |
| 27 |
Wang T, Hu XC, Cai ZP, Voglmeir J, Liu L (2017a). Qualitative and quantitative analysis of carbohydrate modification on glycoproteins from seeds of Ginkgo biloba. J Agric Food Chem 65, 7669-7679.
DOI URL |
| 28 |
Wang T, Voglmeir J (2014). PNGases as valuable tools in glycoprotein analysis. Protein Pept Lett 21, 976-985.
DOI URL |
| 29 |
Wang WL, Wang W, Du YM, Wu H, Yu XB, Ye KP, Li CB, Jung YS, Qian YJ, Voglmeir J, Liu L (2017b). Comparison of anti-pathogenic activities of the human and bovine milk N-glycome: fucosylation is a key factor. Food Chem 235, 167-174.
DOI URL |
| 30 |
Wang ZY, Gehring C, Zhu JH, Li FM, Zhu JK, Xiong LM (2015). The Arabidopsis Vacuolar Sorting Receptor 1 is required for osmotic stress-induced abscisic acid biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 167, 137-152.
DOI URL |
| 31 |
Wei S, Henquet MGL, Mentink RA, van Dijk AJ, Cordewener JHG, Bosch D, America AHP, van der Krol AR (2011). N-glycoproteomics in plants: perspectives and challenges. J Proteomics 74, 1463-1474.
DOI URL |
| 32 |
Wilson IBH, Zeleny R, Kolarich D, Staudacher E, Stroop CJM, Kamerling JP, Altmann F (2001). Analysis of Asn -linked glycans from vegetable foodstuffs: widespread occurrence of Lewis a, core α1,3-linked fucose and xylose substitutions. Glycobiology 11, 261-274.
PMID |
| 33 |
Xu SL, Medzihradszky KF, Wang ZY, Burlingame AL, Chalkley RJ (2016). N-glycopeptide profiling in Arabidopsis inflorescence. Mol Cell Proteomics 15, 2048-2054.
DOI URL |
| 34 |
Zeng W, Ford KL, Bacic A, Heazlewood JL (2018). N- linked glycan micro-heterogeneity in glycoproteins of Arabidopsis. Mol Cell Proteomics 17, 413-421.
DOI URL |
| [1] | Yanxiao Chen, Yaping Li, Jinjun Zhou, Lixia Xie, Yongbin Peng, Wei Sun, Yanan He, onghui Jiang, Zenglan Wang, Chongke Zheng, Xianzhi Xie. Effect of Amino Acid Point Mutations on the Structure and Function of Phytochrome B in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(3): 481-494. |
| [2] | Jixuan Yang, Xuefei Wang, Hongya Gu. Genetic Basis of Flowering Time Variations in Tibetan Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(3): 373-382. |
| [3] | Gang Wang, Ertao Wang. The Broad-spectrum Innate Resistance Against Clubroot Disease Conferred by WeiTsing is Mechanistically Revealed [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(3): 356-358. |
| [4] | Yang Yongqing, Guo Yan. Analysis of the pH Sensing Mechanism of Plant Apoplasts [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(4): 409-411. |
| [5] | Tiantian Zhi, Zhou Zhou, Chengyun Han, Chunmei Ren. PAD4 Mutation Accelerating Programmed Cell Death in Arabidopsis thaliana Tyrosine Degradation Deficient Mutant sscd1 [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(3): 288-298. |
| [6] | Yanyan Li, Yanhua Qi. Advances in Biological Functions of Aux/IAA Gene Family in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(1): 30-41. |
| [7] | Yongmei Che, Yanjun Sun, Songchong Lu, Lixia Hou, Xinxin Fan, Xin Liu. AtMYB77 Involves in Lateral Root Development via Regulating Nitric Oxide Biosynthesis under Drought Stress in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(4): 404-413. |
| [8] | Yuqing Lin, Yanhua Qi. Advances in Auxin Efflux Carrier PIN Proteins [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(2): 151-165. |
| [9] | Long Ma, Guilin Li, Shipeng Li, Su Jiang. An Improved Protocol for Whole Mount Clearing of Plant Root Tip [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(5): 596-604. |
| [10] | Fangfang He,Huize Chen,Jinlin Feng,Lin Gao,Jiao Niu,Rong Han. Response of Arabidopsis Cohesin RAD21 to Cell Division after Enhanced UV-B Radiation [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(4): 407-420. |
| [11] | Nan Zhang,Ziguang Liu,Shichen Sun,Shengyi Liu,Jianhui Lin,Yifang Peng,Xiaoxu Zhang,He Yang,Xi Cen,Juan Wu. Response of AtR8 lncRNA to Salt Stress and Its Regulation on Seed Germination in Arabidopsis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(4): 421-429. |
| [12] | Yuting Yao,Jiaqi Ma,Xiaoli Feng,Jianwei Pan,Chao Wang. A Role of Arabidopsis Phosphoinositide Kinase, FAB1, in Root Hair Growth [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(2): 126-136. |
| [13] | Zeyuan Zuo,Wanlin Liu,Jie Xu. Evolution and Functional Analysis of Gene Clusters in Anther Tapetum Cells of Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(2): 147-162. |
| [14] | Wanyue Xu,Yingxiang Wang. Chromosome Behaviors of Male Meiocytes by Chromosome Spread in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(5): 620-624. |
| [15] | Juqing Kang, Tianshu Sun, Huiting Zhang, Yihao Shi. Quantitative Trait Loci Mapping Platform of Natural Populations of Arabidopsis thaliana along the Yangtze River in China [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2016, 51(5): 659-666. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||