

植物学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (3): 383-396.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24013 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24013
杜锦瑜1,2,3,4, 孙震2,3,4, 苏彦龙2,3,4, 王贺萍2,3,4, 刘亚玲5, 吴振映2,3,4, 何峰2,3,4,*( ), 赵彦1,*(
), 赵彦1,*( ), 付春祥2,3,4,*(
), 付春祥2,3,4,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-01-24
接受日期:2024-03-20
出版日期:2024-05-10
发布日期:2024-05-10
通讯作者:
E-mail: 基金资助:
Jinyu Du1,2,3,4, Zhen Sun2,3,4, Yanlong Su2,3,4, Heping Wang2,3,4, Yaling Liu5, Zhenying Wu2,3,4, Feng He2,3,4,*( ), Yan Zhao1,*(
), Yan Zhao1,*( ), Chunxiang Fu2,3,4,*(
), Chunxiang Fu2,3,4,*( )
)
Received:2024-01-24
Accepted:2024-03-20
Online:2024-05-10
Published:2024-05-10
Contact:
E-mail: 摘要: 蒙古冰草(即沙芦草(Agropyron mongolicum))是我国北方代表性的多年生牧草之一, 具有较强的耐寒和耐旱能力。在植物中, 咖啡酸氧甲基转移酶基因(COMT)是参与木质素和褪黑素生物合成的关键基因, 在调节植物生长、品质和抗逆性中发挥重要作用。通过分析蒙古冰草全长转录组数据, 从蒙古冰草中克隆了COMT候选基因AmCOMT1。该基因在茎秆和根等木质素含量高的组织中高表达, 且其表达受多种非生物胁迫诱导。在拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)野生型(Col-0)和突变体(omt1-2)中过表达AmCOMT1, 显著促进了转基因拟南芥的木质素合成, 使突变体的木质素单体和组分恢复至野生型水平, 同时Col-0/35S:AmCOMT1中木质素总量提高11%。此外, AmCOMT1过表达显著提高了Col-0/35S:AmCOMT1转基因拟南芥的褪黑素含量。在盐胁迫条件下, 该株系平均根长相比野生型拟南芥提高20.3%, 表现出更强的抗逆性。综上,蒙古冰草AmCOMT1基因在木质素和褪黑素合成中发挥关键作用, 可提高转基因拟南芥的抗逆性, 在蒙古冰草等单子叶牧草遗传改良方面具有重要应用潜力。
杜锦瑜, 孙震, 苏彦龙, 王贺萍, 刘亚玲, 吴振映, 何峰, 赵彦, 付春祥. 蒙古冰草咖啡酸氧甲基转移酶基因AmCOMT1的鉴定及功能分析. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 383-396.
Jinyu Du, Zhen Sun, Yanlong Su, Heping Wang, Yaling Liu, Zhenying Wu, Feng He, Yan Zhao, Chunxiang Fu. Identification and Functional Analysis of an Agropyron mongolicum Caffeic Acid 3-O-methyltransferase Gene AmCOMT1. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(3): 383-396.
| Purpose | Primer name | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Gene clone | AmCOMT1-CDS-F | ATGGGCTCCATCGCCGCCGG |
| AmCOMT1-CDS-R | CTACTTAGTGAACTCGATGGCCC | |
| AmCOMT1-pMDC32-F | CTAGAGGATCCCCGGATGGGCTCCATCGCCG | |
| AmCOMT1-pMDC32-R | GATCGGGGAAATTCGCTACTTAGTGAACTCGATGGCC | |
| AmCOMT1-pGWC-F | AGCAGGCTTTGACTTTATGGGCTCCATCGCCGCCGG | |
| AmCOMT1-pGWC-R | TGGGTCTAGAGACTTCTACTTAGTGAACTCGATGGCCC | |
| Positive detection | M13F | ACTGGCCGTCGTTTTAC |
| M13R | GTCATAGCTGTTTCCTG | |
| pMDC32-JC-F | CACTATCCTTCGCAAGACCCTTC | |
| pMDC32-JC-R | TTGAACGATCGGGGAAATTCGAG | |
| PGWC-JC-F | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGG | |
| PGWC-JC-R | ATTTAGGTGACACTATAG | |
| qRT-PCR | AmCOMT1-qRT-F | GACGCTGCTCAAGAACTGCT |
| AmCOMT1-qRT-R | CCATGCGTTGGCGTAGATGT | |
| 18s-qRT-F | CAATGGGAAGCAAGGCTGTAA | |
| 18s-qRT-R | AACAATCCGAACTGAGGCAATC | |
| AtACTIN-F | CATCAGGAAGGACTTGTACGG | |
| AtACTIN-R | GATGGACCTGACTCGTCATAC | |
| Identification of Arabidopsis mutant | LP | TCCGGTTTGCAAGTATTTGAC |
| BP | ATTTTGCCGATTTCGGAAC | |
| RP | CTAGGGTCAGTCCCGTGGTAC |
表1 本研究使用的引物
Table 1 Primers used in this study
| Purpose | Primer name | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Gene clone | AmCOMT1-CDS-F | ATGGGCTCCATCGCCGCCGG |
| AmCOMT1-CDS-R | CTACTTAGTGAACTCGATGGCCC | |
| AmCOMT1-pMDC32-F | CTAGAGGATCCCCGGATGGGCTCCATCGCCG | |
| AmCOMT1-pMDC32-R | GATCGGGGAAATTCGCTACTTAGTGAACTCGATGGCC | |
| AmCOMT1-pGWC-F | AGCAGGCTTTGACTTTATGGGCTCCATCGCCGCCGG | |
| AmCOMT1-pGWC-R | TGGGTCTAGAGACTTCTACTTAGTGAACTCGATGGCCC | |
| Positive detection | M13F | ACTGGCCGTCGTTTTAC |
| M13R | GTCATAGCTGTTTCCTG | |
| pMDC32-JC-F | CACTATCCTTCGCAAGACCCTTC | |
| pMDC32-JC-R | TTGAACGATCGGGGAAATTCGAG | |
| PGWC-JC-F | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGG | |
| PGWC-JC-R | ATTTAGGTGACACTATAG | |
| qRT-PCR | AmCOMT1-qRT-F | GACGCTGCTCAAGAACTGCT |
| AmCOMT1-qRT-R | CCATGCGTTGGCGTAGATGT | |
| 18s-qRT-F | CAATGGGAAGCAAGGCTGTAA | |
| 18s-qRT-R | AACAATCCGAACTGAGGCAATC | |
| AtACTIN-F | CATCAGGAAGGACTTGTACGG | |
| AtACTIN-R | GATGGACCTGACTCGTCATAC | |
| Identification of Arabidopsis mutant | LP | TCCGGTTTGCAAGTATTTGAC |
| BP | ATTTTGCCGATTTCGGAAC | |
| RP | CTAGGGTCAGTCCCGTGGTAC |
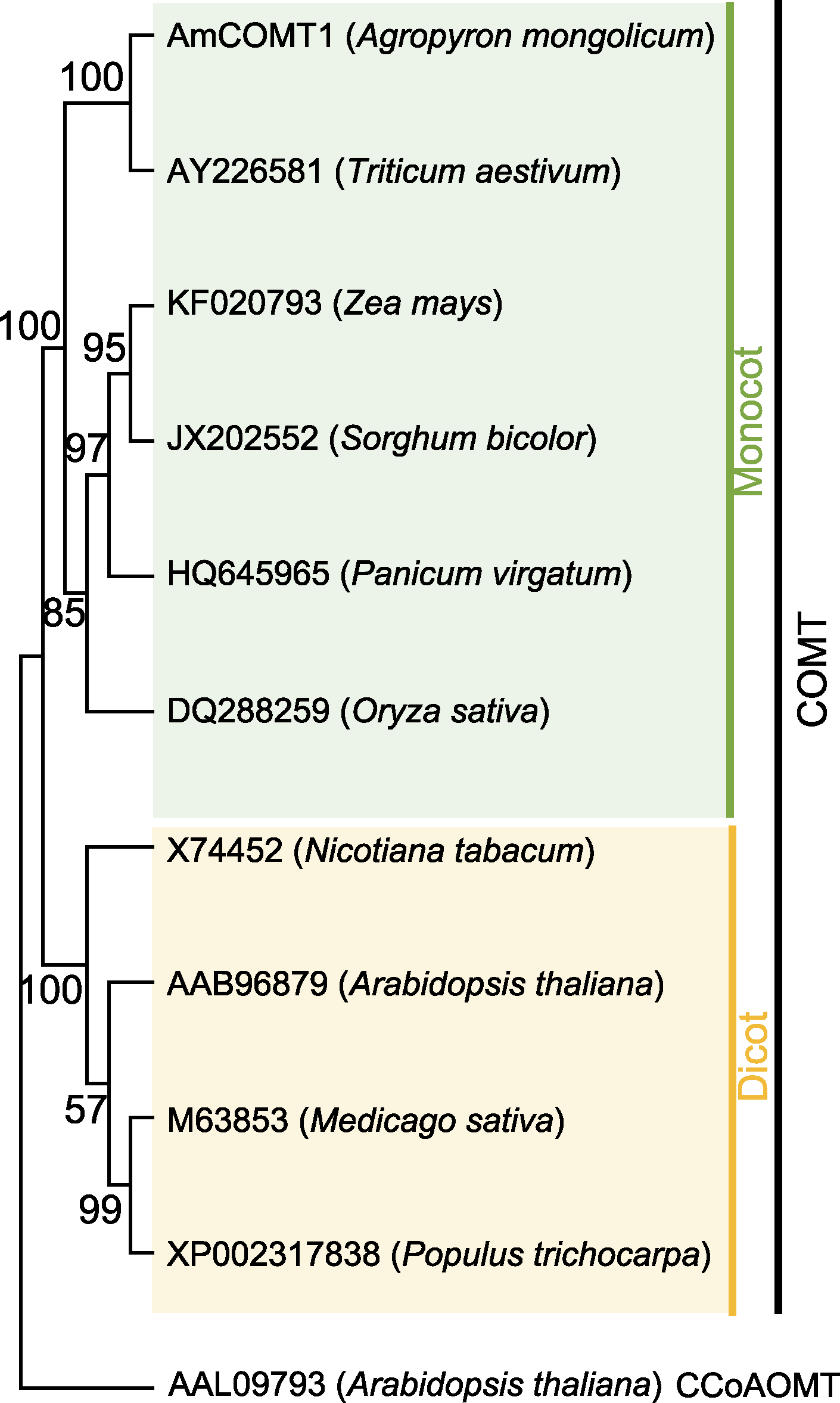
图1 不同物种中COMT蛋白的系统进化树分析 通过NCBI数据库获得不同物种来源的COMT蛋白和拟南芥CCoAOMT序列, 与本实验克隆到的AmCOMT1序列经MEGA软件进行比对后通过邻接法(Neighbor-Joining, NJ)构建系统进化树(Bootstrap=1 000)
Figure 1 Phylogenetic tree of COMT proteins in different species COMT protein sequences from different species and CCoAOMT sequence from Arabidopsis were obtained from NCBI database, and the phylogenetic tree (Bootstrap=1 000) was constructed by Neighbor-Joining (NJ) method with MEGA with AmCOMT1.
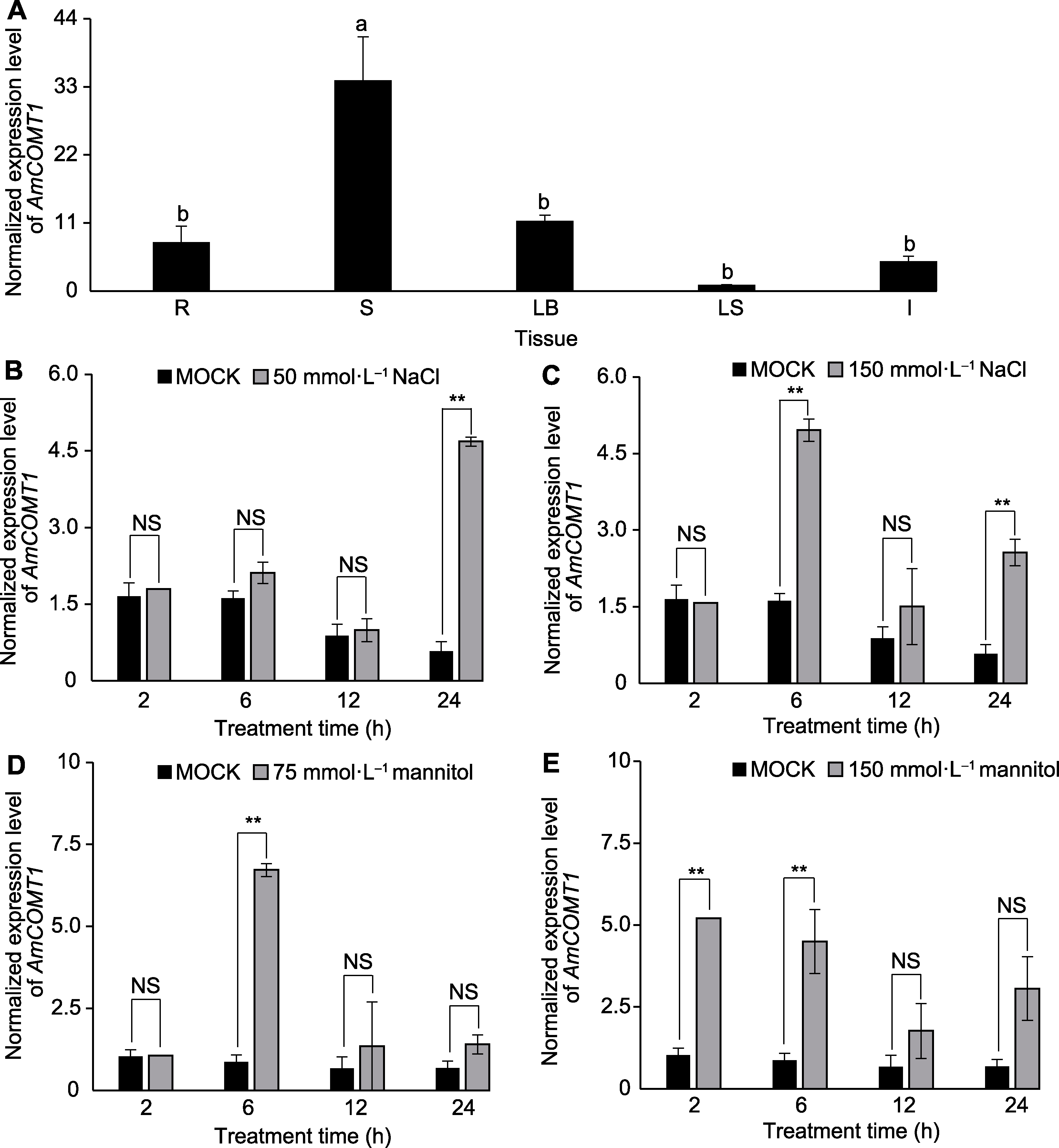
图3 AmCOMT1在蒙古冰草不同组织及不同胁迫诱导下的表达情况 (A) 蒙古冰草不同组织中AmCOMT1的表达(R: 根; S: 茎; LB: 叶片; LS: 叶鞘; I: 幼穗); (B), (C) 50和150 mmol·L-1 NaCl处理下AmCOMT1的表达; (D), (E) 75和150 mmol·L-1甘露醇处理下AmCOMT1的表达。柱状图中的不同小写字母表示根据ANOVA分析结果(n=3)数据间存在显著性差异(P<0.05), NS表示差异不显著, ** P<0.01。
Figure 3 Expression of AmCOMT1 in different tissue of Agropyron mongolicum and under different treatments (A) The expression of AmCOMT1 in different tissues of A. mongolicum (R: Root; S: Stem; LB: Leaf blade; LS: Leaf sheath; I: Inflorescence); (B), (C) The expression of AmCOMT1 under 50 and 150 mmol·L-1 NaCl treatments; (D), (E) The expression of AmCOMT1 under 75 and 150 mmol·L-1 mannitol treatments. Different lowercase letters in the bar chart indicate significant differences (P<0.05) among the data according to the results of ANOVA analysis (n=3), NS indicate not significant, ** P<0.01.
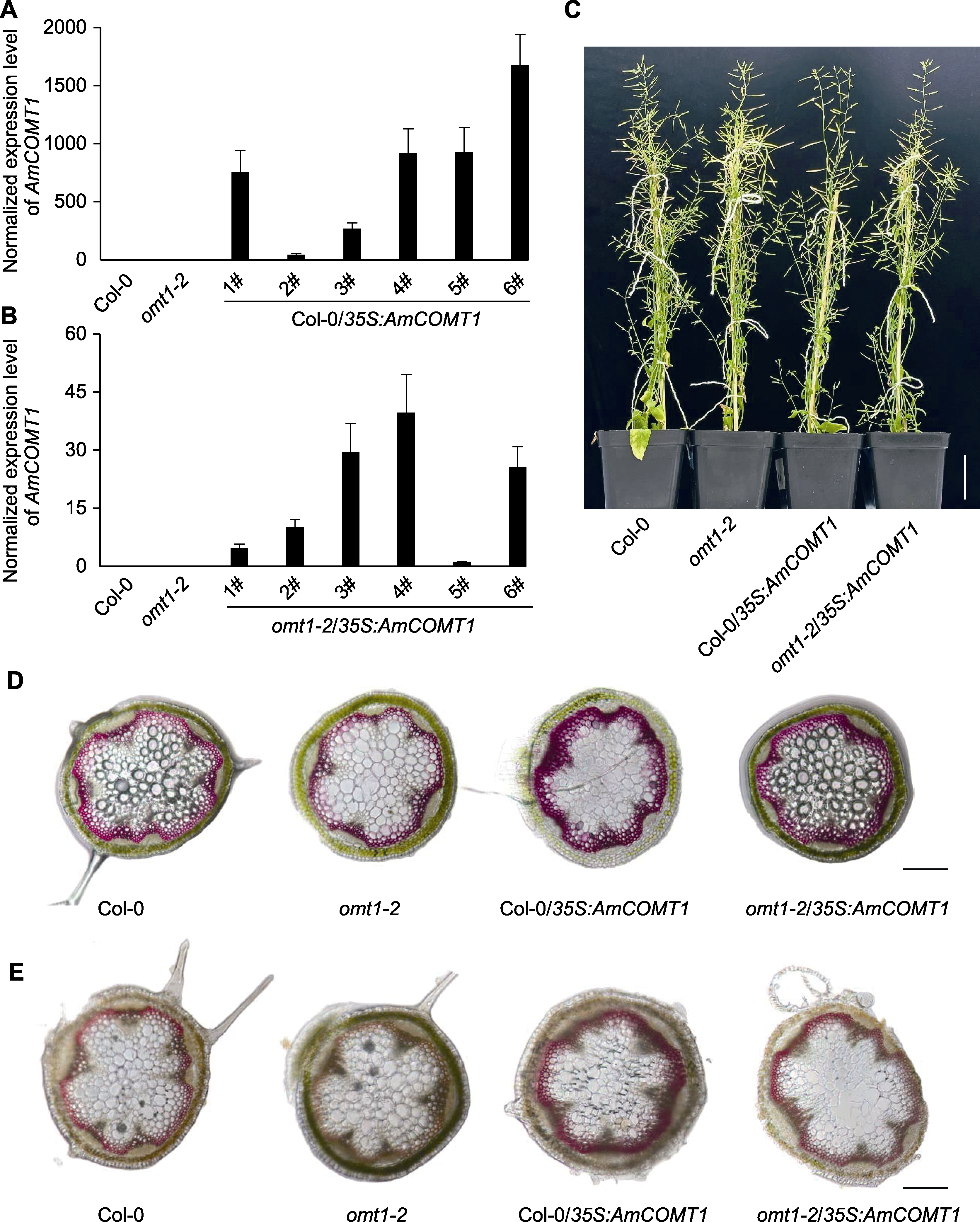
图4 转基因拟南芥的表型和木质素染色分析 (A), (B) 转基因拟南芥中AmCOMT1的表达水平; (C) 转基因拟南芥在培养箱中生长8周后与Col-0及omt1-2的生长状态比较(bar=3.5 cm); (D), (E) 转基因拟南芥茎切片的间苯三酚染色(D)和Mäule染色结果(E) (bars=100 μm)。
Figure 4 Phenotypic and lignin staining analysis of transgenic Arabidopsis (A), (B) Expression level of AmCOMT1 in transgenic Arabidopsis; (C) 8-week-old transgenic Arabidopsis plants comparing with Col-0 and omt1-2; (D), (E) Lignin staining of stem cross section of different Arabidopsis lines with phloroglucinol staining method (D) and Mäule staining method (E) (bars=100 μm).
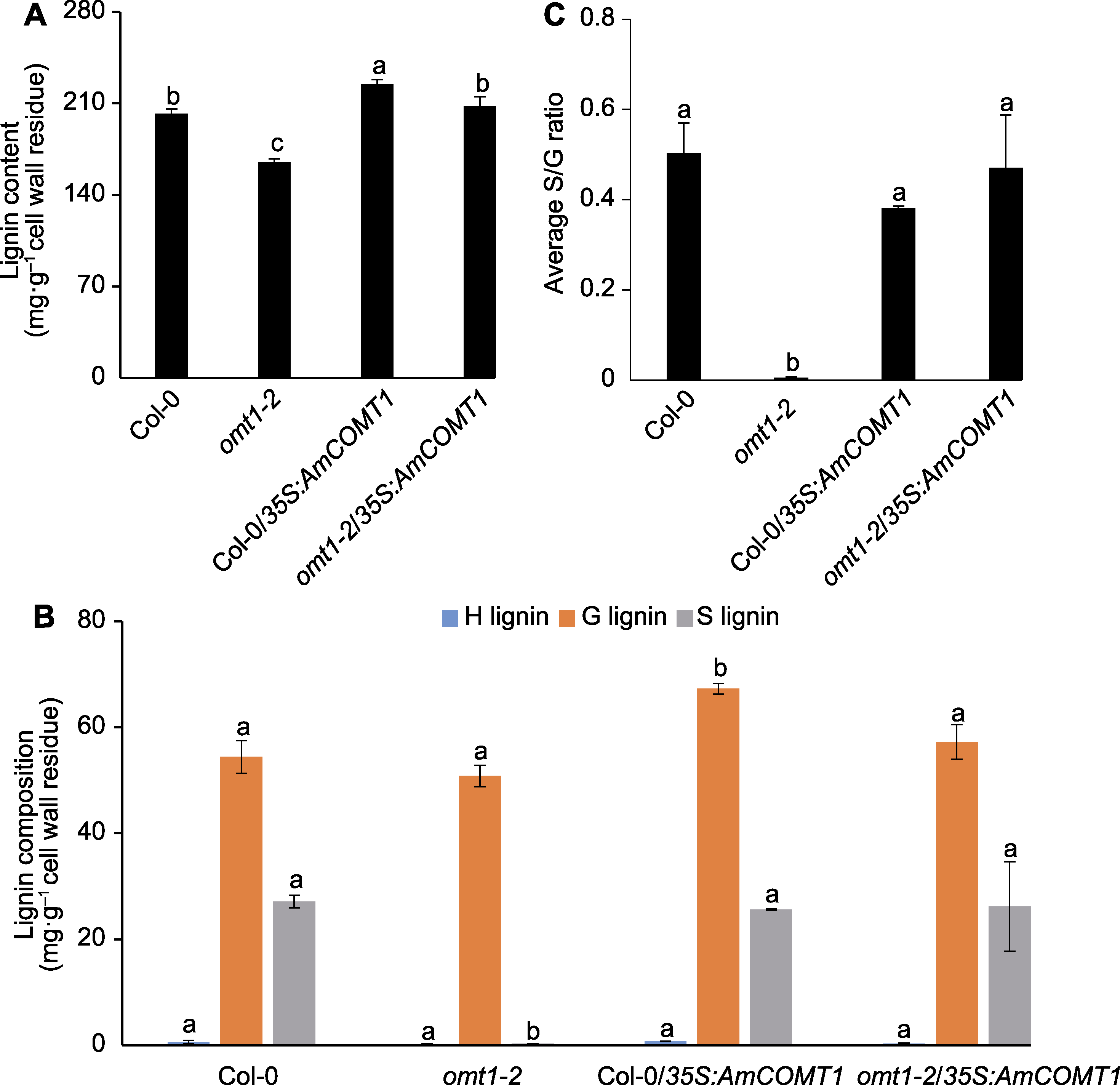
图5 过表达AmCOMT1对拟南芥Col-0和omt1-2突变体木质素含量(A)、组分(B)和S/G比例(C)的影响 柱状图中的不同小写字母表示根据ANOVA分析结果(n=3)数据间存在显著性差异(P<0.05)。
Figure 5 Effects of AmCOMT1 overexpression on lignin content (A), composition (B), and S/G ratio (C) of Arabidopsis Col-0 and omt1-2 Different lowercase letters in the bar chart indicate significant differences (P<0.05) among the data according to the results of ANOVA analysis (n=3).
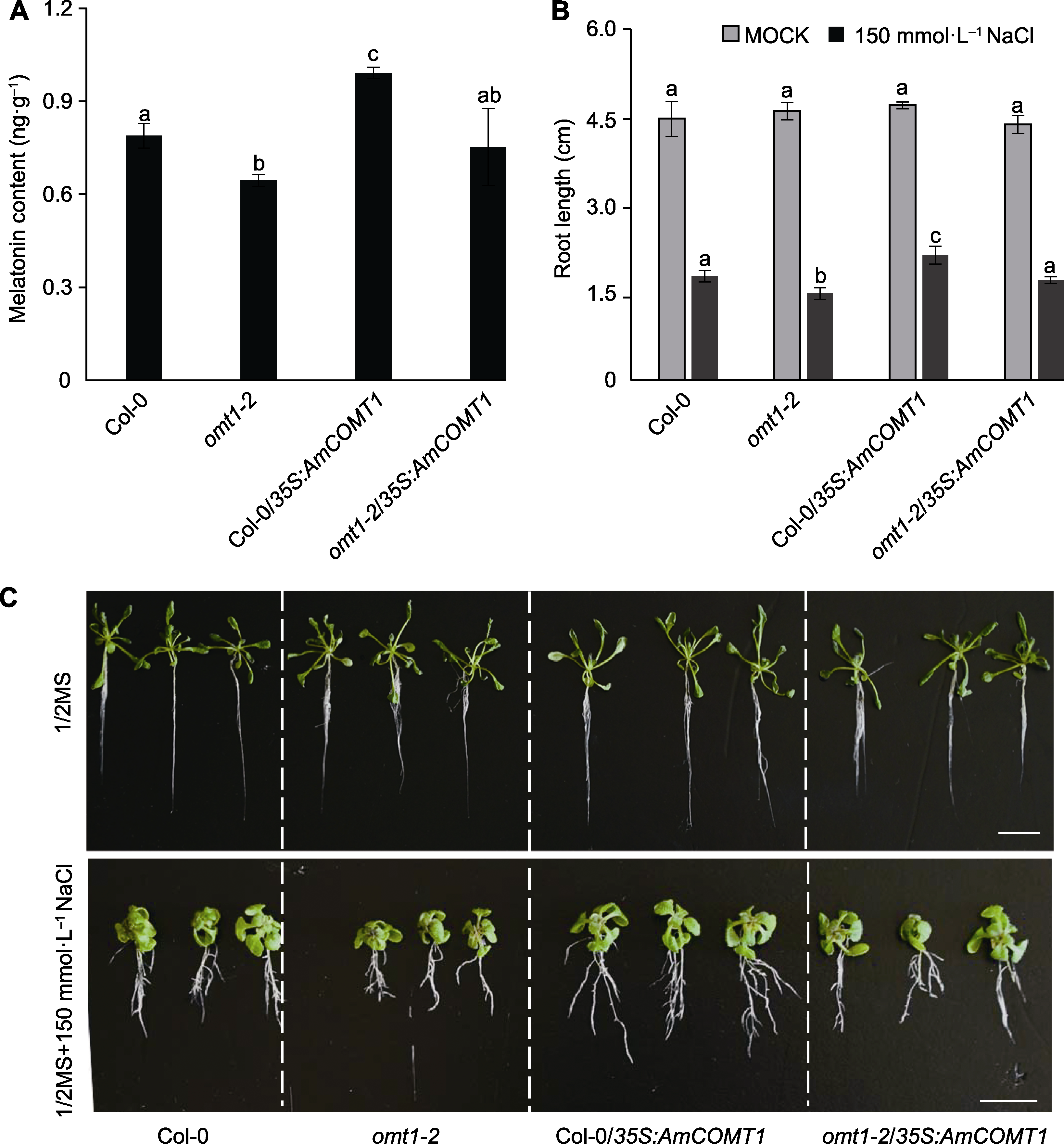
图6 过表达AmCOMT1对转基因拟南芥褪黑素合成和耐盐性的影响 (A) 拟南芥不同株系中的褪黑素含量; (B), (C) 盐胁迫处理后拟南芥不同株系的根长统计和生长表型(bars=1 cm)。柱状图中的不同小写字母表示根据ANOVA分析结果(n=3)数据间存在显著性差异(P<0.05)。
Figure 6 Overexpression of AmCOMT1 improved melatonin synthesis and salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis (A) Melatonin content in different Arabidopsis lines; (B), (C) Root length and growth phenotype of different Arabidopsis lines growing on plates after NaCl treatment (bars=1 cm). Different lowercase letters in the bar chart indicate significant differences (P<0.05) among the data according to the results of ANOVA analysis (n=3).
| [1] | Byeon Y, Lee HY, Lee K, Back K (2014). Caffeic acid O-methyltransferase is involved in the synthesis of melatonin by methylating N-acetylserotonin in Arabidopsis. J Pineal Res 57, 219-227. |
| [2] | Cao YR, Yan XY, Ran SY, Ralph J, Smith RA, Chen XP, Qu CM, Li JN, Liu LZ (2022). Knockout of the lignin pathway gene BnF5H decreases the S/G lignin compositional ratio and improves Sclerotinia sclerotiorum resistance in Brassica napus. Plant Cell Environ 45, 248-261. |
| [3] | Cen HF, Wang TT, Liu HY, Wang H, Tian DY, Li X, Cui X, Guan C, Zang H, Li MQ, Zhang YW (2020). Overexpression of MsASMT1 promotes plant growth and decreases flavonoids biosynthesis in transgenic alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Front Plant Sci 11, 489. |
| [4] | Chang JJ (2021). Identification of Melatonin Synthesis Gene and the Signal Transduction Mechanism of Melatonin-regulating Cold Tolerance in Watermelon. Doctoral dissertation. Yangling: Northwest A&F University. pp. 1-104. (in Chinese) |
| 常静静 (2021). 西瓜褪黑素合成基因鉴定及褪黑素调控抗冷性的信号传导机制. 博士论文. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学. pp. 1-104. | |
| [5] | Chang JJ, Guo YL, Yan JY, Zhang ZX, Yuan L, Wei CH, Zhang Y, Ma JX, Yang JQ, Zhang X, Li H (2021). The role of watermelon caffeic acid O-methyltransferase (ClCOMT1) in melatonin biosynthesis and abiotic stress tolerance. Hortic Res 8, 210. |
| [6] |
Chen F, Zhuo CL, Xiao XR, Pendergast TH, Devos KM (2021). A rapid thioacidolysis method for biomass lignin composition and tricin analysis. Biotechnol Biofuels 14, 18.
DOI PMID |
| [7] | Do CT, Pollet B, Thévenin J, Sibout R, Denoue D, Barrière Y, Lapierre C, Jouanin L (2007). Both caffeoyl coenzyme A 3-O-methyltransferase 1 and caffeic acid O-methyltransferase 1 are involved in redundant functions for lignin, flavonoids and sinapoyl malate biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Planta 226, 1117-1129. |
| [8] |
Fu CX, Mielenz JR, Xiao XR, Ge YX, Hamilton CY, Rodriguez M Jr, Chen F, Foston M, Ragauskas A, Bouton J, Dixon RA, Wang ZY (2011). Genetic manipulation of lignin reduces recalcitrance and improves ethanol production from switchgrass. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108, 3803-3808.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | Fu LP (2016). Cloning of TaCOMT Genes Associated with Stem Lignin Content in Wheat, Development of Functional Markers and Association Analysis. Master’s thesis. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences. pp. 1-59. (in Chinese) |
| 付路平 (2016). 小麦茎秆木质素含量相关基因TaCOMT克隆、功能标记开发和关联分析. 硕士论文. 北京: 中国农业科学院. pp. 1-59. | |
| [10] | Guo Z, Zhao YL, Liu JL, Xue YC (2006). The genetic control and development of caffeic acid O-methyltransferase (COMT). Mol Plant Breed 4(S2), 122-126. (in Chinese) |
| 郭昭, 赵一玲, 刘景利, 薛永常 (2006). 木质素合成酶咖啡酸3-O-甲基转移酶(COMT)的遗传调控研究. 分子植物育种 4(S2), 122-126. | |
| [11] | He F, Machemer-Noonan K, Golfier P, Unda F, Dechert J, Zhang W, Hoffmann N, Samuels L, Mansfield SD, Rausch T, Wolf S (2019). The in vivo impact of MsLAC1, a Miscanthus laccase isoform, on lignification and lignin composition contrasts with its in vitro substrate preference. BMC Plant Biol 19, 552. |
| [12] | Huang WH (2014). Selection of Control Gene in Quantitative PCR and Analysis of Differential Expression of P5CS Gene in Agropyron mongolicum Keng under Drought Stress. Master's thesis. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University. pp. 1-33. (in Chinese) |
| 黄文华 (2014). 蒙古冰草干旱胁迫下内参基因的筛选及P5CS基因定量表达分析. 硕士论文. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学. pp. 1-33. | |
| [13] |
Huang YH, Liu SJ, Yuan S, Guan C, Tian DY, Cui X, Zhang YW, Yang FY (2017). Overexpression of ovine AANAT and HIOMT genes in switchgrass leads to improved growth performance and salt-tolerance. Sci Rep 7, 12212.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | Jung JH, Altpeter F (2016). TALEN mediated targeted mutagenesis of the caffeic acid O-methyltransferase in highly polyploid sugarcane improves cell wall composition for production of bioethanol. Plant Mol Biol 92, 131-142. |
| [15] | Lam KC, Ibrahim RK, Behdad B, Dayanandan S (2007). Structure, function, and evolution of plant O-methyltransferases. Genome 50, 1001-1013. |
| [16] | Li C, He QL, Zhang F, Yu JW, Li C, Zhao TL, Zhang Y, Xie QW, Su BR, Mei L, Zhu SJ, Chen JH (2019a). Melatonin enhances cotton immunity to Verticillium wilt via manipulating lignin and gossypol biosynthesis. Plant J 100, 784-800. |
| [17] | Li SG, Xu YH, Bi Y, Zhang B, Shen SL, Jiang TJ, Zheng XL (2019b). Melatonin treatment inhibits gray mold and induces disease resistance in cherry tomato fruit during postharvest. Postharvest Biol Technol 157, 110962. |
| [18] | Li Z, Wang HZ, Li RF, Wei JH (2009). Lignin biosynthesis and manipulation in plants and utilization of biomass energy. Chin Bull Bot 44, 262-272. (in Chinese) |
|
李桢, 王宏芝, 李瑞芬, 魏建华 (2009). 植物木质素合成调控与生物质能源利用. 植物学报 44, 262-272.
DOI |
|
| [19] | Lü XP (2022). Response of Lignin Synthesis in Haloxylon ammodendron to Salt and Osmotic Stress and Functional Identification of HaLAC15 and HaCOMT. Doctoral dissertation. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University. pp. 1-193. (in Chinese) |
| 吕昕培 (2022). 梭梭木质素合成对盐和渗透胁迫的响应及HaLAC15和HaCOMT的功能鉴定. 博士论文. 兰州: 兰州大学. pp. 1-193. | |
| [20] | Ma C, Pei ZQ, Bai X, Zhang TG (2023). Advances in functions and action mechanisms of phytomelatonin. J Cold- Arid Agric Sci 2, 883-888. (in Chinese) |
| 马成, 裴子琦, 白雪, 张腾国 (2023). 植物褪黑素功能及其作用机制的研究进展. 寒旱农业科学 2, 883-888. | |
| [21] | Ma QH, Xu Y (2008). Characterization of a caffeic acid 3-O-methyltransferase from wheat and its function in lignin biosynthesis. Biochimie 90, 515-524. |
| [22] | Peng DL, Chen XG, Yin YP, Lu KL, Yang WB, Tang YH, Wang ZL (2014). Lodging resistance of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.): lignin accumulation and its related enzymes activities due to the application of paclobutrazol or gibberellin acid. Field Crops Res 157, 1-7. |
| [23] | Ralph J, Lapierre C, Boerjan W (2019). Lignin structure and its engineering. Curr Opin Biotechnol 56, 240-249. |
| [24] | Rashid S, Raza AA, Muhammad T (2017). Expression profiling of Hspb1 and Tp53 genes through RT-qPCR in different cancer types of Canis familiaris. Iranian J Biotechnol 15, 186-193. |
| [25] | Sa CN (2023). Study on growth and physiological adaptation strategy of Agropyron mongolicum under drought stress. Master’s thesis. Yinchuan: Ningxia University. pp. 1-44. (in Chinese) |
| 撒春宁 (2023). 干旱胁迫条件下蒙古冰草生长及生理适应策略研究. 硕士论文. 银川: 宁夏大学. pp. 1-44. | |
| [26] | Shan CR, Chen XH, Ding YF, Zhao W, Lu H, Gao SZ, Qi FH, Zhan YG, Zeng FS (2023). Functional analysis of FmCCoAOMT gene in Fraxinus mandshurica during lignin synthesis and abiotic stress. Bull Bot Res 43, 768-778. (in Chinese) |
|
单超然, 陈晓慧, 丁云飞, 赵威, 卢晗, 高尚珠, 齐凤慧, 詹亚光, 曾凡锁 (2023). 水曲柳FmCCoAOMT基因在木质素合成及非生物胁迫中的功能分析. 植物研究 43, 768-778.
DOI |
|
| [27] | Shi JX, Yan YJ, Dong R, Tao X, Sun XL, Huang CC (2023). The Arabidopsis HSP1 mediates chitin-induced defense response by regulating CERK1 protein level. Chin Bull Bot 58, 712-719. (in Chinese) |
|
史君星, 闫一嘉, 董汝, 陶轩, 孙晓龙, 黄聪聪 (2023). 拟南芥HSP1调节CERK1蛋白水平影响几丁质激发的防御反应. 植物学报 58, 712-719.
DOI |
|
| [28] | Song Y, Wang DH, Wu JB, Zhou L, Wang GD, Wang ZZ (2012). Cloning and analysis of caffeic acid O-methyl- transferase gene (SmCOMT1) from Salvia miltiorrhiza Bge. Bull Bot Res 32, 437-443. (in Chinese) |
|
宋银, 王东浩, 吴锦斌, 周露, 王国栋, 王喆之 (2012). 丹参咖啡酸-O-甲基转移酶基因(SmCOMT1)的克隆及其分析. 植物研究 32, 437-443.
DOI |
|
| [29] | Sun SS, Han YP, Yan YY, Gong B, Shi QH (2019). Overexpression of caffeic acid-O-methyltransferase gene (CO- MT1) regulates physiological response of tomato seedlings to drought stress. Plant Physiol J 55, 1109-1122. (in Chinese) |
| 孙莎莎, 韩亚萍, 闫燕燕, 巩彪, 史庆华 (2019). 过表达咖啡酸-O-甲基转移酶基因(COMT1)调控番茄幼苗对干旱胁迫生理响应. 植物生理学报 55, 1109-1122. | |
| [30] | Tan DX, Manchester LC, Reiter RJ, Qi WB, Karbownik M, Calvo JR (2000). Significance of melatonin in antioxidative defense system: reactions and products. Biol Signals Recept 9, 137-159. |
| [31] | Wang HM, Yu YC, Fu CX, Zhou GK, Gao HH (2014). Progress of a key enzyme caffeoyl-CoA 3-O-methyltransferase in lignin biosynthesis. Genom Appl Biol 33, 458-466. (in Chinese) |
| 王华美, 于延冲, 付春祥, 周功克, 高欢欢 (2014). 木质素合成关键酶咖啡酰辅酶A氧甲基转移酶的研究进展. 基因组学与应用生物学 33, 458-466. | |
| [32] | Wang MX, Zhu XL, Wang K, Lu CG, Luo MY, Shan TL, Zhang ZY (2018). A wheat caffeic acid 3-O-methyltrans- ferase TaCOMT-3D positively contributes to both resistance to sharp eyespot disease and stem mechanical strength. Sci Rep 8, 6543. |
| [33] | Wang RH, Shi L, Tang GG, Liang YC, Zhang CY (2003). Effect of osmotic stress on activities of protective enzymes system in Agropyron mongolicum seedling. Chin Bull Bot 20, 330-335. (in Chinese) |
| 王荣华, 石雷, 汤庚国, 梁寅初, 张称意 (2003). 渗透胁迫对蒙古冰草幼苗保护酶系统的影响. 植物学通报 20, 330-335. | |
| [34] | Wang RH, Shi L, Tang GG, Liang YC, Zhang CY (2004). Effect of NaCl stress on growth and content of severalions of wheatgrass. Bull Bot Res 24, 326-330. (in Chinese) |
| 王荣华, 石雷, 汤庚国, 梁寅初, 张称意 (2004). 盐胁迫下蒙古冰草幼苗生长和离子含量的变化. 植物研究 24, 326-330. | |
| [35] | Wei JH, Zhao HY, Lu SF, Wang T, Ma QH, Song YR (2001). Cloning of cDNA encoding COMT from Chinese white poplar (Populus tomentosa), sequence analysis and specific expression. Acta Bot Sin 43, 326-328. (in Chinese) |
| 魏建华, 赵华燕, 卢善发, 王台, 马庆虎, 宋艳茹 (2001). 毛白杨COMT基因cDNA的克隆、序列与特异性表达分析. 植物学报 43, 326-328. | |
| [36] | Weng JK, Mo HP, Chapple C (2010). Over-expression of F5H in COMT-deficient Arabidopsis leads to enrichment of an unusual lignin and disruption of pollen wall formation. Plant J 64, 898-911. |
| [37] | Wu ZY, Wang NF, Hisano H, Cao YP, Wu FY, Liu WW, Bao Y, Wang ZY, Fu CX (2019). Simultaneous regulation of F5H in COMT-RNAi transgenic switchgrass alters effects of COMT suppression on syringyl lignin biosynthesis. Plant Biotechnol J 17, 836-845. |
| [38] | Yang WJ (2019). Cloning and Functional Analysis of Melatonin Synthesis Related Gene TaCOMT in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Master's thesis. Yangling: Northwest A&F University. pp. 1-57. (in Chinese) |
| 杨雯晶 (2019). 小麦褪黑素合成相关基因TaCOMT的克隆及功能分析. 硕士论文. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学. pp. 1-57. | |
| [39] | Yang WJ, Du YT, Zhou YB, Chen J, Xu ZS, Ma YZ, Chen M, Min DH (2019). Overexpression of TaCOMT improves melatonin production and enhances drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Int J Mol Sci 20, 652. |
| [40] | Yao LM, Hu XQ, Zhou F, Zheng YQ, Wang GD, Liu XM (2019). Antisense CCoAOMT gene regulates lignin biosynthesis in Betula platyphylla. Bull Bot Res 39, 123-130. (in Chinese) |
| 姚连梅, 胡晓晴, 周菲, 郑要强, 王国东, 刘雪梅 (2019). 白桦反义CCoAOMT基因调控木质素生物合成. 植物研究 39, 123-130. | |
| [41] | Yue LR, Liu YJ, Liu CX, Zhou YW (2022). Cloning and functional analysis of miR398a from Chrysanthemum × grandiflora in response to salt stress. Bull Bot Res 42, 986-996. (in Chinese) |
|
岳莉然, 刘颖婕, 刘晨旭, 周蕴薇 (2022). 响应盐胁迫调控的露地菊miR398a的克隆及功能研究. 植物研究 42, 986-996.
DOI |
|
| [42] | Zhao DK, Yao ZP, Zhang JM, Zhang RJ, Mou ZM, Zhang X, Li ZH, Feng XL, Chen SY, Reiter RJ (2021). Melatonin synthesis genes N-acetylserotonin methyltransferases evolved into caffeic acid O-methyltransferases and both assisted in plant terrestrialization. J Pineal Res 71, e12737. |
| [43] | Zhao DQ, Luan YT, Shi WB, Tang YH, Huang XQ, Tao J (2022). Melatonin enhances stem strength by increasing lignin content and secondary cell wall thickness in herbaceous peony. J Exp Bot 73, 5974-5991. |
| [44] | Zhao Y, Chen XY, Shi FM, Yun JF, Wang JJ (2015). Cloning and expression analysis of MwDREB3 from Mongolian wheatgrass. Acta Agrest Sin 23, 377-382. (in Chinese) |
|
赵彦, 陈雪英, 石凤敏, 云锦凤, 王俊杰 (2015). 蒙古冰草MwDREB3基因的克隆及表达分析. 草地学报 23, 377-382.
DOI |
|
| [45] | Zhao Y, Gao X, Wang D, Gao CP, Yun JF (2017). Cloning and expression analysis of LHcb1 from Agropyron mongolicum Keng under drought stress. Acta Bot Boreal-Occident Sin 37, 211-216. (in Chinese) |
| 赵彦, 高鑫, 王丹, 高翠萍, 云锦凤 (2017). 蒙古冰草LHcb1基因克隆及干旱胁迫下的表达分析. 西北植物学报 37, 211-216. | |
| [46] | Zhao Y, Han HJ, Zhang R, Tong XM, Gao CP (2020). Functional identification of MwMYB4 gene from Agropyron mongolicum Keng. Acta Bot Boreal-Occident Sin 40, 565-571. (in Chinese) |
| 赵彦, 韩慧杰, 张锐, 童新梅, 高翠萍 (2020). 蒙古冰草MwMYB4基因功能鉴定. 西北植物学报 40, 565-571. |
| [1] | 徐田甜, 杨培建, 周晓茜, 曹怡, 陈艳红, 刘国元, 张健, 魏辉. 紫薇GolS家族基因的理化特性与表达特征[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 393-406. |
| [2] | 杜淑辉, 褚建民, 段俊光, 薛建国, 徐磊, 徐晓庆, 王其兵, 黄建辉, 张倩. 木质素酚类物质对内蒙古退化草地土壤有机碳的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(1): 30-41. |
| [3] | 李宇琛, 赵海霞, 姜希萍, 黄馨田, 刘亚玲, 吴振映, 赵彦, 付春祥. 根癌农杆菌介导的蒙古冰草稳定遗传转化体系建立[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 600-612. |
| [4] | 王贺萍, 孙震, 刘雨辰, 苏彦龙, 杜锦瑜, 赵彦, 赵竑博, 王召明, 苑峰, 刘亚玲, 吴振映, 何峰, 付春祥. 蒙古冰草肉桂醇脱氢酶基因序列鉴定及功能分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 204-216. |
| [5] | 蔡淑钰, 刘建新, 王国夫, 吴丽元, 宋江平. 褪黑素促进镉胁迫下番茄种子萌发的调控机理[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 720-732. |
| [6] | 邱锐, 何峰, 李瑞, 王亚梅, 邢思年, 曹英萍, 刘叶飞, 周昕越, 赵彦, 付春祥. 柳枝稷木质素基因F5H的高效编辑[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(2): 298-307. |
| [7] | 王菲菲, 周振祥, 洪益, 谷洋洋, 吕超, 郭宝健, 朱娟, 许如根. 大麦NF-YC基因鉴定及在盐胁迫下的表达分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 140-149. |
| [8] | 张琦, 张文静, 袁宪凯, 李明, 赵强, 杜艳丽, 杜吉到. 褪黑素对盐胁迫下普通菜豆芽期核酸修复的调控机制[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 108-121. |
| [9] | 艾金祥, 宋嘉怡, 严浙楠, 王志超, 陈文倩, 吴玉环, 王燕燕, 潘蕾蕾, 许俞韬, 刘鹏. 褪黑素对铅胁迫下虎舌红和朱砂根生理响应及DNA损伤的调控效应[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(2): 171-181. |
| [10] | 刘德帅, 姚磊, 徐伟荣, 冯美, 姚文孔. 褪黑素参与植物抗逆功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 111-126. |
| [11] | 张楠,刘自广,孙世臣,刘圣怡,林建辉,彭疑芳,张晓旭,杨贺,岑曦,吴娟. 拟南芥AtR8 lncRNA对盐胁迫响应及其对种子萌发的调节作用[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(4): 421-429. |
| [12] | 曹栋栋,陈珊宇,秦叶波,吴华平,阮关海,黄玉韬. 水杨酸调控盐胁迫下羽衣甘蓝种子萌发的机理[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(1): 49-61. |
| [13] | 李伟滔, 贺闽, 陈学伟. ZmFBL41 Chang7-2: 玉米抗纹枯病的关键利器[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(5): 547-549. |
| [14] | 栗露露,殷文超,牛梅,孟文静,张晓星,童红宁. 油菜素甾醇调控水稻盐胁迫应答的作用研究[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(2): 185-193. |
| [15] | 曾引伟, 曹玉曼, 沙煦旸, 李淑霞, 杨培志, 呼天明, 刘金隆. 一种简单有效的非损伤观测根瘤和根系形态的方法[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(5): 661-670. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||