

植物学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (4): 481-496.DOI: 10.11983/CBB19243 cstr: 32102.14.CBB19243
收稿日期:2019-12-17
接受日期:2020-02-26
出版日期:2020-07-01
发布日期:2020-05-21
通讯作者:
洪林
基金资助:
Lin Hong( ),Lei Yang,Haijian Yang,Wu Wang
),Lei Yang,Haijian Yang,Wu Wang
Received:2019-12-17
Accepted:2020-02-26
Online:2020-07-01
Published:2020-05-21
Contact:
Lin Hong
摘要: 低温、干旱、高盐和缺氧等多种不良环境影响植物的生长发育, 植物通过长期进化形成复杂的调节机制来适应这些不利条件。AP2/ERF是植物特有的转录因子, 在各种胁迫响应过程中发挥关键调控作用。近年来, 越来越多的研究表明, 植物激素介导的信号级联通路与逆境胁迫响应关系密切, AP2/ERF转录因子可与激素信号转导协同形成交叉调控网络。许多AP2/ERF转录因子通过响应植物激素脱落酸和乙烯, 激活依赖或不依赖于脱落酸和乙烯的胁迫响应基因的表达。此外, AP2/ERF转录因子参与赤霉素、细胞分裂素和油菜素内酯介导的生长发育和胁迫应答。该文简要综述了AP2/ERF转录因子的结构特征、转录调控、翻译后修饰、结合位点、协同互作蛋白及其参与调控依赖或不依赖激素信号转导途径的非生物胁迫响应研究进展, 为解析不同AP2/ERF转录因子在调控激素和胁迫响应网络中的作用提供理论依据。
洪林,杨蕾,杨海健,王武. AP2/ERF转录因子调控植物非生物胁迫响应研究进展. 植物学报, 2020, 55(4): 481-496.
Lin Hong,Lei Yang,Haijian Yang,Wu Wang. Research Advances in AP2/ERF Transcription Factors in Regulating Plant Responses to Abiotic Stress. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(4): 481-496.
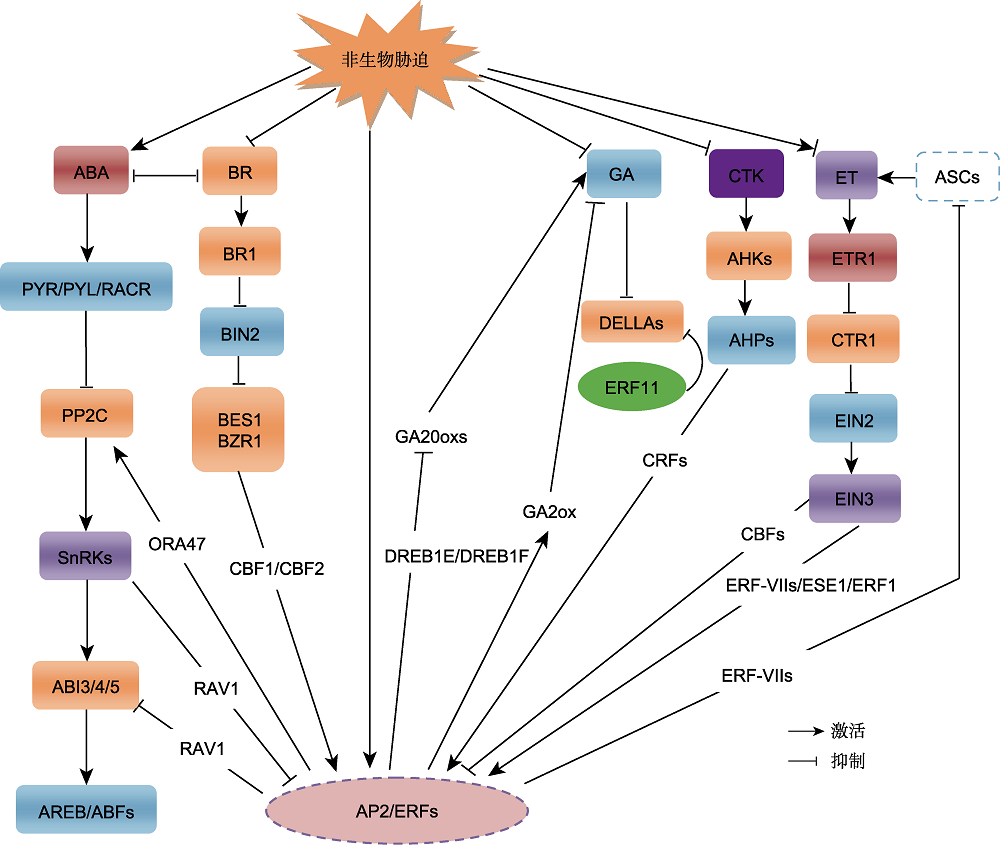
图1 AP2/ERF转录因子参与调控激素介导的非生物胁迫响应网络 ABA:脱落酸; BR:油菜素内酯; GA:赤霉素; CTK:细胞分裂素; ET:乙烯
Figure 1 AP2/ERF transcription factors are involved in regulating hormone-mediated response networks during abiotic stress ABA: Abscisic acid; BR: Brassinolide; GA: Gibberellin; CTK: Cytokinin; ET: Ethylene
| [1] | 郭倩倩, 周文彬 (2019). 植物响应联合胁迫机制的研究进展. 植物学报 54, 662-672. |
| [2] | 刘静妍, 施怡婷, 杨淑华 (2017). CBF: 平衡植物低温应答与生长发育的关键. 植物学报 52, 689-698. |
| [3] |
Abbas M, Berckhan S, Rooney DJ, Gibbs DJ, Conde VJ, Correia CS, Basse GW, de la Rosa MN, Leon J, Alabadí D, Blázquez MA, Holdsworth MJ (2015). Oxygen sensing coordinates photomorphogenesis to facilitate seedling survival. Curr Biol 25, 1483-1488.
URL PMID |
| [4] | Abiri R, Shaharuddin NA, Maziah M, Yusof BZN, Atabaki N, Sahebi M, Valdiani A, Kalhori N, Azizi P, Hanafi MM (2017). Role of ethylene and the APETALA 2/ethylene response factor superfamily in rice under various abiotic and biotic stress conditions. Environ Exp Bot 134, 33-44. |
| [5] |
Achard P, Gong F, Cheminant S, Alioua M, Hedden P, Genschik P (2008). The cold-inducible CBF1 factor-de-pendent signaling pathway modulates the accumulation of the growth-repressing DELLA proteins via its effect on gibberellin metabolism. Plant Cell 20, 2117-2129.
DOI URL PMID |
| [6] |
Agarwal M, Hao YJ, Kapoor A, Dong CH, Fujii H, Zheng XW, Zhu JK (2006). A R2R3 type MYB transcription factor is involved in the cold regulation of CBF genes and in acquired freezing tolerance. J Biol Chem 281, 37636-37645.
URL PMID |
| [7] | Asensi-Fabado MA, Amtmann A, Perrella G (2017). Plant responses to abiotic stress: the chromatin context of transcriptional regulation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1860, 106-122. |
| [8] |
Ayano M, Kani T, Kojima M, Sakakibara H, Kitaoka T, Kuroha T, Angeles-Shim RB, Kitano H, Nagai K, Ashikari M (2014). Gibberellin biosynthesis and signal transduction is essential for internode elongation in deepwater rice. Plant Cell Environ 37, 2313-2324.
DOI URL PMID |
| [9] |
Bossi F, Cordoba E, Dupré P, Mendoza MS, Román CS, León P (2009). The Arabidopsis ABA-INSENSITIVE (ABI) 4 factor acts as a central transcription activator of the expression of its own gene, and for the induction of ABI5 and SBE2.2 genes during sugar signaling. Plant J 59, 359-374.
DOI URL PMID |
| [10] |
Bui LT, Giuntoli B, Kosmacz M, Parlanti S, Licausi F (2015). Constitutively expressed ERF-VII transcription factors redundantly activate the core anaerobic response in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Sci 236, 37-43.
DOI URL PMID |
| [11] |
Causier B, Ashworth M, Guo WJ, Davies B (2012). The TOPLESS interactome: a framework for gene repression in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 158, 423-438.
DOI URL PMID |
| [12] |
Chandler JW (2018). Class VIIIb APETALA2 ethylene response factors in plant development. Trends Plant Sci 23, 151-162.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] |
Chen H, Je J, Song C, Hwang JE, Lim CO (2012). A proximal promoter region of Arabidopsis DREB2C confers tissue-specific expression under heat stress. J Integr Plant Biol 54, 640-651.
URL PMID |
| [14] |
Chen HY, Hsieh EJ, Cheng MC, Chen YC, Hwang YS, Lin TP (2016). ORA47 (octadecanoid-responsive AP2/ERF- domain transcription factor 47) regulates jasmonic acid and abscisic acid biosynthesis and signaling through binding to a novel cis-element. New Phytol 211, 599-613.
URL PMID |
| [15] |
Cheng MC, Hsieh EJ, Chen JH, Chen HY, Lin TP (2012). Arabidopsis RGLG2, functioning as a RING E3 ligase, interacts with AtERF53 and negatively regulates the plant drought stress response. Plant Physiol 158, 363-375.
DOI URL PMID |
| [16] |
Chinnusamy V, Zhu JH, Zhu JK (2007). Cold stress regulation of gene expression in plants. Trends Plant Sci 12, 444-451.
URL PMID |
| [17] |
Claeys H, Skirycz A, Maleux K, Inzé D (2012). DELLA signaling mediates stress-induced cell differentiation in Arabidopsis leaves through modulation of anaphasepromoting complex/cyclosome activity. Plant Physiol 159, 739-747.
DOI URL PMID |
| [18] |
Colebrook EH, Thomas SG, Phillips AL, Hedden P (2014). The role of gibberellin signaling in plant responses to abiotic stress. J Exp Biol 217, 67-75.
DOI URL PMID |
| [19] |
Deepika L, Ashutosh P, Yogeshwar VD, Sumit KB, Prabodh KT, Mehar HA (2016). Genome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF family in Musa species reveals divergence and neofunctionalisation during evolution. Sci Rep 6, 18878.
URL PMID |
| [20] |
Dong CJ, Liu JY (2010). The Arabidopsis EAR-motif-containing protein RAP2.1 functions as an active transcriptional repressor to keep stress responses under tight control. BMC Plant Biol 10, 47.
DOI URL PMID |
| [21] |
Dou HO, Xv KP, Meng QW, Li G, Yang XH (2015). Potato plants ectopically expressing Arabidopsis thaliana CBF3 exhibit enhanced tolerance to high-temperature stress. Plant Cell Environ 38, 61-72.
DOI URL PMID |
| [22] |
Dubois M, Skirycz A, Claeys H, Maleux K, Dhondt S, De Bodt S, Bossche RV, De Milde L, Yoshizumi T, Matsui M, Inzé D (2013). Ethylene Response Factor 6 acts as a central regulator of leaf growth under water-limiting conditions in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 162, 319-332.
DOI URL PMID |
| [23] |
Dubois M, Van den Broeck L, Claeys H, Van Vlierberghe K, Matsui M, Inzé D (2015). The ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTORs ERF6 and ERF11 antagonistically regulate mannitol-induced growth inhibition in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 169, 166-179.
DOI URL PMID |
| [24] |
Feng CZ, Chen Y, Wang C, Kong YH, Wu WH, Chen YF (2014). Arabidopsis RAV1 transcription factor, phosphorylated by SnRK2 kinases, regulates the expression of ABI3, ABI4, and ABI5 during seed germination and early seedling development. Plant J 80, 654-668.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Finkelstein R (2013). Abscisic acid synthesis and response. Arabidopsis Book 11, e0166.
URL PMID |
| [26] |
Fowler S, Thomashow MF (2002). Arabidopsis transcriptome profiling indicates that multiple regulatory pathways are activated during cold acclimation in addition to the CBF cold response pathway. Plant Cell 14, 1675-1690.
URL PMID |
| [27] |
Franco-Zorrilla JM, López-Vidriero I, Carrasco JL, Godoy M, Vera P, Solano R (2014). DNA-binding specificities of plant transcription factors and their potential to define target genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, 2367-2372.
DOI URL PMID |
| [28] |
Fu MJ, Kang HK, Son SH, Kim SK, Nam KH (2014). A subset of Arabidopsis RAV transcription factors modulates drought and salt stress responses independent of ABA. Plant Cell Physiol 55, 1892-1904.
DOI URL PMID |
| [29] |
Fukao T, Bailey-Serres J (2008). Submergence tolerance conferred by Sub1A is mediated by SLR1 and SLRL1 restriction of gibberellin responses in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105, 16814-16819.
DOI URL PMID |
| [30] |
Fursova OV, Pogorelko GV, Tarasov VA (2009). Identification of ICE2, a gene involved in cold acclimation which determines freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Gene 429, 98-103.
URL PMID |
| [31] |
Gasch P, Fundinger M, Müller JT, Lee T, Bailey-Serres J, Mustroph A (2016). Redundant ERF-VII transcription factors bind to an evolutionarily conserved cis-motif to regulate hypoxia-responsive gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 28, 160-180.
URL PMID |
| [32] |
Gibbs DJ, Conde JV, Berckhan S, Prasad G, Mendiondo GM, Holdsworth MJ (2015). Group VII ethylene response factors coordinate oxygen and nitric oxide signal transduction and stress responses in plants. Plant Physiol 169, 23-31.
URL PMID |
| [33] |
Guo HQ, Li L, Aluru M, Aluru S, Yin YH (2013). Mechanisms and networks for brassinosteroid regulated gene expression. Curr Opin Plant Biol 16, 545-553.
URL PMID |
| [34] |
Hattori Y, Nagai K, Furukawa S, Song XJ, Kawano R, Sakakibara H, Wu JZ, Matsumoto T, Yoshimura A, Kitano H, Matsuoka M, Mori H, Ashikari M (2009). The ethylene response factors SNORKEL1 and SNORKEL2 allow rice to adapt to deep water. Nature 460, 1026-1030.
URL PMID |
| [35] |
Hinz M, Wilson IW, Yang J, Buerstenbinder K, Llewellyn D, Dennis ES, Sauter M, Dolferus R (2010). Arabidopsis RAP2.2: an ethylene response transcription factor that is important for hypoxia survival. Plant Physiol 153, 757-772.
DOI URL PMID |
| [36] |
Horstman A, Willemsen V, Boutilier K, Heidstra R (2014). AINTEGUMENTA-LIKE proteins: hubs in a plethora of networks. Trends Plant Sci 19, 146-157.
DOI URL PMID |
| [37] |
Hsieh EJ, Cheng MC, Lin TP (2013). Functional characterization of an abiotic stress-inducible transcription factor AtERF53 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 82, 223-237.
DOI URL PMID |
| [38] |
Ikeda M, Ohme-Takagi M (2009). A novel group of transcriptional repressors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 50, 970-975.
DOI URL PMID |
| [39] |
Jeon J, Cho C, Lee MR, van Binh N, Kim J (2016). CYTOKININ RESPONSE FACTOR 2 (CRF2) and CRF3 regulate lateral root development in response to cold stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 28, 1828-1843.
URL PMID |
| [40] |
Jia YX, Ding YL, Shi YT, Zhang XY, Gong ZZ, Yang SH (2016). The cbfs triple mutants reveal the essential functions of CBFs in cold acclimation and allow the definition of CBF regulons in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 212, 345-353.
URL PMID |
| [41] |
Kagale S, Rozwadowski K (2011). EAR motif-mediated transcriptional repression in plants: an underlying mechanism for epigenetic regulation of gene expression. Epigenetics 6, 141-146.
DOI URL PMID |
| [42] |
Karaba A, Dixit S, Greco R, Aharoni A, Trijatmiko KR, Marsch-Martinez N, Krishnan A, Nataraja KN, Udayakumar M, Pereira A (2007). Improvement of water use efficiency in rice by expression of HARDY, an Arabidopsis drought and salt tolerance gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104, 15270-15275.
DOI URL PMID |
| [43] |
Kavas M, Kizildogan A, Gökdemir G, Baloglu MC (2015). Genome-wide investigation and expression analysis of AP2-ERF gene family in salt tolerant common bean. EXCLI J 14, 1187-1206.
URL PMID |
| [44] |
Kazan K (2015). Diverse roles of jasmonates and ethylene in abiotic stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 20, 219-229.
DOI URL PMID |
| [45] |
Kim J (2016). CYTOKININ RESPONSE FACTORs gating environmental signals and hormones. Trends Plant Sci 21, 993-996.
DOI URL PMID |
| [46] |
Kim JS, Mizoi J, Yoshida T, Fujita Y, Nakajima J, Ohori T, Todaka D, Nakashima K, Hirayama T, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2011). An ABRE promoter sequence is involved in osmotic stress-responsive expression of the DREB2A gene, which encodes a transcription factor regulating drought-inducible genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 52, 2136-2146.
DOI URL PMID |
| [47] |
Kim NY, Jang YJ, Park OK (2018). AP2/ERF family transcription factors ORA59 and RAP2.3 interact in the nucleus and function together in ethylene responses. Front Plant Sci 9, 1675.
URL PMID |
| [48] |
Lee DK, Yoon S, Kim YS, Kim JK (2017). Rice OsERF71-mediated root modification affects shoot drought tolerance. Plant Signal Behav 12, e1268311.
URL PMID |
| [49] |
Lee SY, Boon NJ, Webb AAR, Tanaka RJ (2016). Synergistic activation of RD29A via integration of salinity stress and abscisic acid in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol 57, 2147-2160.
DOI URL PMID |
| [50] |
Lee SY, Hwang EY, Seok HY, Tarte VN, Jeong MS, Jang SB, Moon YH (2015). Arabidopsis AtERF71/HRE2 functions as transcriptional activator via cis-acting GCC box or DRE/CRT element and is involved in root development through regulation of root cell expansion. Plant Cell Rep 34, 223-231.
DOI URL PMID |
| [51] |
Li H, Ye KY, Shi YT, Cheng JK, Zhang XY, Yang SH (2017). BZR1 positively regulates freezing tolerance via CBF-dependent and CBF-independent pathways in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 10, 545-559.
DOI URL PMID |
| [52] |
Li JJ, Guo X, Zhang MH, Wang X, Zhao Y, Yin ZG, Zhang ZY, Wang YM, Xiong HY, Zhang HL, Todorovska E, Li ZC (2018). OsERF71 confers drought tolerance via modulating ABA signaling and proline biosynthesis. Plant Sci 270, 131-139.
URL PMID |
| [53] |
Li PC, Huang JG, Yu SW, Li YY, Sun P, Wu CA, Zheng CC (2016). Arabidopsis YL1/BPG2 is involved in seedling shoot response to salt stress through ABI4. Sci Rep 6, 30163.
DOI URL PMID |
| [54] |
Licausi F, Ohme-Takagi M, Perata P (2013). APETALA2/ Ethylene Responsive Factor (AP2/ERF) transcription factors: mediators of stress responses and developmental programs. New Phytol 199, 639-649.
URL PMID |
| [55] |
Lin RC, Park HJ, Wang HY (2008). Role of Arabidopsis RAP2.4 in regulating light and ethylene-mediated developmental processes and drought stress tolerance. Mol Plant 1, 42-57.
DOI URL PMID |
| [56] |
Liu HC, Liao HT, Charng YY (2011). The role of class A1 heat shock factors (HSFA1s) in response to heat and other stresses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ 34, 738-751.
DOI URL PMID |
| [57] |
Liu JY, Shi YT, Yang SH (2018a). Insights into the regulation of C-repeat binding factors in plant cold signaling. J Integr Plant Biol 60, 780-795.
URL PMID |
| [58] |
Liu K, Li YH, Chen XN, Li LJ, Liu K, Zhao HP, Wang YD, Han SC (2018b). ERF72 interacts with ARF6 and BZR1 to regulate hypocotyl elongation in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 69, 3933-3947.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
Liu PQ, Sun F, Gao R, Dong HS (2012). RAP2.6L overexpression delays waterlogging induced premature senescence by increasing stomatal closure more than antioxidant enzyme activity. Plant Mol Biol 79, 609-622.
DOI URL PMID |
| [60] |
Locke AM, Barding GA Jr, Sathnur S, Larive CK, Bailey-Serres J (2018). Rice SUB1A constrains remodelling of the transcriptome and metabolome during submergence to facilitate post-submergence recovery. Plant Cell Environ 41, 721-736.
DOI URL PMID |
| [61] |
Magome H, Yamaguchi S, Hanada A, Kamiya YJ, Oda KJ (2004). Dwarf and delayed-flowering 1, a novel Arabidopsis mutant deficient in gibberellin biosynthesis because of overexpression of a putative AP2 transcription factor. Plant J 37, 720-729.
URL PMID |
| [62] |
Mähönen AP, Higuchi M, Törmäkangas K, Miyawaki K, Pischke MS, Sussman MR, Helariutta Y, Kakimoto T (2006). Cytokinins regulate a bidirectional phosphorelay network in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol 16, 1116-1122.
DOI URL PMID |
| [63] |
Maruyama K, Takeda M, Kidokoro S, Yamada K, Sakuma Y, Urano K, Fujita M, Yoshiwara K, Matsukura S, Morishita Y, Sasaki R, Suzuki H, Saito K, Shibata D, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2009). Metabolic pathways involved in cold acclimation identified by integrated analysis of metabolites and transcripts regulated by DREB1A and DREB2A. Plant Physiol 150, 1972-1980.
DOI URL PMID |
| [64] |
Matsukura S, Mizoi J, Yoshida T, Todaka D, Ito Y, Maruyama K, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2010). Comprehensive analysis of rice DREB2-type genes that encode transcription factors involved in the expression of abiotic stress-responsive genes. Mol Genet Genomics 283, 185-196.
URL PMID |
| [65] |
Meng LS, Wang YB, Yao SQ, Liu AZ (2015a) Arabidopsis AINTEGUMENTA mediates salt tolerance by trans-re-pressing SCABP8. J Cell Sci 128, 2919-2927.
URL PMID |
| [66] | Meng LS, Wang ZB, Yao SQ, Liu AZ (b). 2015 The ARF2- ANT-COR15A gene cascade regulates ABA-signaling- mediated resistance of large seeds to drought in Arabidopsis. J Cell Sci 128, 3922-3932. |
| [67] | Meng XZ, Xu J, He YX, Yang KY, Mordorski B, Liu YD, Zhang SQ (2013). Phosphorylation of an ERF transcription factor by Arabidopsis MPK3/MPK6 regulates plant defense gene induction and fungal resistance. Plant Cell 25, 1126-1142. |
| [68] | Mizoi J, Kanazawa N, Kidokoro S, Takahashi F, Qin F, Morimoto K, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2019). Heat-induced inhibition of phosphorylation of the stress-protective transcription factor DREB2A promotes thermotolerance of Arabidopsis thaliana. J Biol Chem 294, 902-917. |
| [69] | Mizoi J, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2012). AP2/ERF family transcription factors in plant abiotic stress responses. Biochim Biophys Acta 1819, 86-96. |
| [70] | Morimoto K, Ohama N, Kidokoro S, Mizoi J, Takahashi F, Todaka D, Mogami J, Sato H, Qin F, Kim JS, Fukao Y, Fujiwara M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2017). BPM-CUL3 E3 ligase modulates thermotolerance by facilitating negative regulatory domain-mediated degradation of DREB2A in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114, E8528-E8536. |
| [71] | Müller M, Munné-Bosch S (2015). Ethylene response factors: a key regulatory hub in hormone and stress signaling. Plant Physiol 169, 32-41. |
| [72] | Nakano T, Suzuki K, Fujimura T, Shinshi H (2006). Genome-wide analysis of the ERF gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol 140, 411-432. |
| [73] | Nolan TM, Brennan B, Yang MR, Chen JN, Zhang MC, Li ZH, Wang XL, Bassham DC, Walley J, Yin YH (2017). Selective autophagy of BES1 mediated by DSK2 balances plant growth and survival. Dev Cell 41, 33-46. |
| [74] | Novillo F, Medina J, Salinas J (2007). Arabidopsis CBF1 and CBF3 have a different function than CBF2 in cold acclimation and define different gene classes in the CBF regulon. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104, 21002-21007. |
| [75] | Oh E, Zhu JY, Wang ZY (2012). Interaction between BZR1 and PIF4 integrates brassinosteroid and environmental responses. Nat Cell Biol 14, 802-809. |
| [76] | Osnato M, Castillejo C, Matías-Hernández L, Pelaz S (2012). TEMPRANILLO genes link photoperiod and gibberellin pathways to control flowering in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun 3, 808. |
| [77] | Owji H, Hajiebrahimi A, Seradj H, Hemmati S (2017). Identification and functional prediction of stress responsive AP2/ERF transcription factors in Brassica napus by genome-wide analysis. Comput Biol Chem 71, 32-56. |
| [78] | Papdi C, Pérez-Salamó I, Joseph MP, Giuntoli B, Bögre L, Koncz C, Szabados L (2015). The low oxygen, oxidative and osmotic stress responses synergistically act through the ethylene response factor VII genes RAP2.12, RAP2.2 and RAP2.3. Plant J 82, 772-784. |
| [79] | Park CS, Go YS, Suh MC (2016). Cuticular wax biosynthesis is positively regulated by WRINKLED 4, an AP2/ERF- type transcription factor, in Arabidopsis stems. Plant J 88, 257-270. |
| [80] | Park SC, Lee CM, Doherty CJ, Gilmour SJ, Kim Y, Thomashow MF (2015). Regulation of the Arabidopsis CBF regulon by a complex low-temperature regulatory network. Plant J 82, 193-207. |
| [81] | Perata P (2018). The rice SUB1A gene: making adaptation to submergence and post-submergence possible. Plant Cell Environ 41, 717-720. |
| [82] | Pfluger J, Wagner D (2007). Histone modifications and dynamic regulation of genome accessibility in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10, 645-652. |
| [83] | Qi JS, Song CP, Wang BS, Zhou JM, Kangasjärvi J, Zhu JK, Gong ZZ (2018). Reactive oxygen species signaling and stomatal movement in plant responses to drought stress and pathogen attack. J Integr Plant Biol 60, 805-826. |
| [84] | Qiao H, Shen ZX, Huang SSC, Schmitz RJ, Urich MA, Briggs SP, Ecker JR (2012). Processing and subcellular trafficking of ER-tethered EIN2 control response to ethylene gas. Science 338, 390-393. |
| [85] | Qin F, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2011). Achievements and challenges in understanding plant abiotic stress responses and tolerance. Plant Cell Physiol 52, 1569-1582. |
| [86] | Rashotte AM, Mason MG, Hutchison CE, Ferreira FJ, Schaller EG, Kieber JJ (2006). A subset of Arabidopsis AP2 transcription factors mediates cytokinin responses in concert with a two-component pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103, 11081-11085. |
| [87] | Rieu I, Eriksson S, Powers SJ, Gong F, Griffiths J, Woolley L, Benlloch R, Nilsson O, Thomas SG, Hedden P, Phillips AL (2008). Genetic analysis reveals that C19-GA 2-oxidation is a major gibberellin inactivation pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 20, 2420-2436. |
| [88] | Rudnik R, Bulcha JT, Reifschneider E, Ellersiek U, Baier M (2017). Specificity versus redundancy in the RAP2.4 transcription factor family of Arabidopsis thaliana: transcriptional regulation of genes for chloroplast peroxidases. BMC Plant Biol 17, 144. |
| [89] | Sah SK, Reddy KR, Li JX (2016). Abscisic acid and abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Front Plant Sci 7, 571. |
| [90] | Saito S, Hirai N, Matsumoto C, Ohigashi H, Ohta D, Sakata K, Mizutani M (2004). Arabidopsis CYP707As encode(+)-abscisic acid 8°-hydroxylase, a key enzyme in the oxidative catabolism of abscisic acid. Plant Physiol 134, 1439-1449. |
| [91] | Sakuma Y, Liu Q, Dubouzet JG, Abe H, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozakia K (2002). DNA-binding specificity of the ERF/AP2 domain of Arabidopsis DREBs, transcription factors involved in dehydration- and cold-inducible gene expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 290, 998-1009. |
| [92] | Sazegari S, Niazi A, Ahmadi FS (2015). A study on the regulatory network with promoter analysis for Arabidopsis DREB-genes. Bioinformation 11, 101-106. |
| [93] | Schmitz AJ, Folsom JJ, Jikamaru Y, Ronald P, Walia H (2013). SUB1A-mediated submergence tolerance response in rice involves differential regulation of the brassinosteroid pathway. New Phytol 198, 1060-1070. |
| [94] | Shi YT, Ding YL, Yang SH (2018). Molecular regulation of CBF signaling in cold acclimation. Trends Plant Sci 23, 623-637. |
| [95] | Shi YT, Tian SW, Hou LY, Huang XZ, Zhang XY, Guo HW, Yang SH (2012). Ethylene signaling negatively regulates freezing tolerance by repressing expression of CBF and type-A ARR genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24, 2578-2595. |
| [96] | Song CP, Agarwal M, Ohta M, Guo Y, Halfter U, Wang PC, Zhu JK (2005). Role of an Arabidopsis AP2/EREBP- type transcriptional repressor in abscisic acid and drought stress responses. Plant Cell 17, 2384-2396. |
| [97] | Song CP, Galbraith DW (2006). AtSAP18, an orthologue of human SAP18, is involved in the regulation of salt stress and mediates transcriptional repression in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 60, 241-257. |
| [98] | Sun Y, Fan XY, Cao DM, Tang WQ, He K, Zhu JY, He JX, Bai MY, Zhu SW, Oh E, Patil S, Kim TW, Ji HK, Wong WH, Rhee SY, Wang ZY (2010). Integration of brassinosteroid signal transduction with the transcription network for plant growth regulation in Arabidopsis. Dev Cell 19, 765-777. |
| [99] | Sun ZM, Zhou ML, Wang D, Tang YX, Lin M, Wu YM (2016). Overexpression of the lotus corniculatus soloist gene LcAP2/ERF107 enhances tolerance to salt stress. Protein Peptide Lett 23, 442-449. |
| [100] | Tao JJ, Chen HW, Ma B, Zhang WK, Chen SY, Zhang JS (2015). The role of ethylene in plants under salinity stress. Front Plant Sci 6, 1059. |
| [101] | Tiwari SB, Belachew A, Ma SF, Young M, Ade J, Shen Y, Marion MC, Holtan HE, Bailey A, Stone JK, Edwards L, Wallace AD, Canales RD, Adam L, Ratcliffe OJ, Repetti PP (2012). The EDLL motif: a potent plant transcriptional activation domain from AP2/ERF transcription factors. Plant J 70, 855-865. |
| [102] | Tsutsui T, Kato W, Asada Y, Sako K, Sato T, Sonoda Y, Kidokoro S, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Tamaoki M, Arakawa K, Ichikawa T, Nakazawa M, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Matsui M, Ikeda A, Yamaguchi J (2009). DEAR1, a transcriptional repressor of DREB protein that mediates plant defense and freezing stress responses in Arabidopsis. J Plant Res 122, 633-643. |
| [103] | Van den Broeck L, Dubois M, Vermeersch M, Storme V, Matsui M, Inzé D (2017). From network to phenotype: the dynamic wiring of an Arabidopsis transcriptional network induced by osmotic stress. Mol Syst Biol 13, 961. |
| [104] | Verma V, Ravindran P, Kumar PP (2016). Plant hormone- mediated regulation of stress responses. BMC Plant Biol 16, 86. |
| [105] | Wang HJ, Yang CJ, Zhang C, Wang NY, Lu DH, Wang J, Zhang SS, Wang ZX, Ma H, Wang XL (2011). Dual role of BKI1 and 14-3-3s in brassinosteroid signaling to link receptor with transcription factors. Dev Cell 21, 825-834. |
| [106] | Xiao HG, Siddiqua M, Braybrook S, Nassuth A (2006). Three grape CBF/DREB1 genes respond to low temperature, drought and abscisic acid. Plant Cell Environ 29, 1410-1421. |
| [107] | Xiong HY, Yu JP, Miao JL, Li JJ, Zhang HL, Wang X, Liu PL, Zhao Y, Jiang CH, Yin ZG, Li Y, Guo Y, Fu BY, Wang WS, Li ZK, Ali J, Li ZC (2018). Natural variation in OsLG3 increases drought tolerance in rice by inducing ROS scavenging. Plant Physiol 178, 451-467. |
| [108] | Xu J, Chua NH (2011). Processing bodies and plant development. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14, 88-93. |
| [109] | Xu KN, Xu X, Fukao T, Canlas P, Maghirang-Rodriguez R, Heuer S, Ismail AM, Bailey-Serres J, Ronald PC, Mackill DJ (2006). Sub1A is an ethylene-response-factor- like gene that confers submergence tolerance to rice. Nature 442, 705-708. |
| [110] | Yamasaki YJ, Randall SK (2016). Functionality of soybean CBF/DREB1 transcription factors. Plant Sci 246, 80-90. |
| [111] | Yang CY, Hsu FC, Li JP, Wang NN, Shih MC (2011). The AP2/ERF transcription factor AtERF73/HRE1 modulates ethylene responses during hypoxia in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 156, 202-212. |
| [112] | Yao Y, He RJ, Xie QL, Zhao XH, Deng XM, He JB, Song LL, He J, Marchant A, Chen XY, Wu AM (2017). ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR 74 (ERF74) plays an essential role in controlling a respiratory burst oxidase homolog D (RbohD)-dependent mechanism in response to different stresses in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 213, 1667-1681. |
| [113] | Ye HX, Liu SZ, Tang BY, Chen JN, Xie ZL, Nolan TM, Jiang H, Guo HQ, Lin HY, Li L, Wang YQ, Tong HN, Zhang MC, Chu CC, Li ZH, Aluru M, Aluru S, Schnable PS, Yin YH (2017). RD26 mediates crosstalk between drought and brassinosteroid signaling pathways. Nat Commun 8, 14573. |
| [114] | Yi J, Zhao DM, Chu JF, Yan JJ, Liu JS, Wu MJ, Cheng JF, Jiang HY, Zeng YJ, Liu D (2019). AtDPG1 is involved in the salt stress response of Arabidopsis seedling through ABI4. Plant Sci 287, 110180. |
| [115] | Yoshida T, Fujita Y, Sayama H, Kidokoro S, Maruyama K, Mizoi J, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2010). AREB1, AREB2, and ABF3 are master transcription factors that cooperatively regulate ABRE-dependent ABA signaling involved in drought stress tolerance and require ABA for full activation. Plant J 61, 672-685. |
| [116] | Yu XF, Li L, Zola J, Aluru M, Ye HX, Foudree A, Guo HQ, Anderson S, Aluru S, Liu P, Rodermel S, Yin YH (2011). A brassinosteroid transcriptional network revealed by genome-wide identification of BESI target genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 65, 634-646. |
| [117] | Zhang F, Wang LK, Ko EE, Shao K, Qiao H (2018). Histone deacetylases SRT1 and SRT2 interact with ENAP1 to mediate ethylene-induced transcriptional repression. Plant Cell 30, 153-166. |
| [118] | Zhang GY, Chen M, Li LC, Xu ZS, Chen XP, Guo JM, Ma YZ (2009). Overexpression of the soybean GmERF3 gene, an AP2/ERF type transcription factor for increased tolerances to salt, drought, and diseases in transgenic tobacco. J Exp Bot 60, 3781-3796. |
| [119] | Zhang LX, Li ZF, Quan RD, Li GJ, Wang RG, Huang RF (2011). An AP2 domain-containing gene,ESE1, targeted by the ethylene signaling component EIN3 is important for the salt response in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 157, 854-865. |
| [120] | Zhang ZW, Feng LY, Cheng J, Tang H, Xu F, Zhu F, Zhao ZY, Yuan M, Chen YE, Wang JH, Yuan S, Lin HH (2013). The roles of two transcription factors, ABI4 and CBFA, in ABA and plastid signaling and stress responses. Plant Mol Biol 83, 445-458. |
| [121] | Zhao CZ, Zhang ZJ, Xie SJ, Si T, Li YY, Zhu JK (2016). Mutational evidence for the critical role of CBF transcription factors in cold acclimation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 171, 2744-2759. |
| [122] | Zhao CZ, Zhu JK (2016). The broad roles of CBF genes: from development to abiotic stress. Plant Signal Behav 11, e1215794. |
| [123] | Zhou MQ, Shen C, Wu LH, Tang KX, Lin J (2011). CBF-dependent signaling pathway: a key responder to low temperature stress in plants. Crit Rev Biotechnol 31, 186-192. |
| [124] | Zhou X, Zhang ZL, Park J, Tyler L, Yusuke J, Qiu K, Nam EA, Lumba S, Desveaux D, McCourt P, Kamiya YJ, Sun TP (2016). The ERF11 transcription factor promotes internode elongation by activating gibberellin biosynthesis and signaling. Plant Physiol 171, 2760-2770. |
| [125] | Zhu DL, Wu Z, Cao GY, Li JG, Wei J, Tsuge T, Gu HY, Aoyama T, Qu LJ (2014). TRANSLUCENT GREEN, an ERF family transcription factor, controls water balance in Arabidopsis by activating the expression of aquaporin genes. Mol Plant 7, 601-615. |
| [126] | Zhu Q, Zhang JT, Gao XS, Tong JH, Xiao LT, Li WB, Zhang HX (2010). The Arabidopsis AP2/ERF transcription factor RAP2.6 participates in ABA, salt and osmotic stress responses. Gene 457, 1-12. |
| [127] | Zwack PJ, Compton MA, Adams CI, Rashotte AM (2016a). Cytokinin response factor 4 (CRF4) is induced by cold and involved in freezing tolerance. Plant Cell Rep 35, 573-584. |
| [128] | Zwack PJ, De Clercq I, Howton TC, Hallmark HT, Hurny A, Keshishian EA, Parish AM, Benkova E, Mukhtar MS, van Breusegem F, Rashotte AM (2016b). Cytokinin response factor 6 represses cytokinin-associated genes during oxidative stress. Plant Physiol 172, 1249-1258. |
| [129] | Zwack PJ, Rashotte AM (2015). Interactions between cytokinin signaling and abiotic stress responses. J Exp Bot 66, 4863-4871. |
| [130] | Zwack PJ, Robinson BR, Risley MG, Rashotte AM (2013). Cytokinin response factor 6 negatively regulates leaf senescence and is induced in response to cytokinin and numerous abiotic stresses. Plant Cell Physiol 54, 971-981. |
| [1] | 王子韵, 吕燕文, 肖钰, 吴超, 胡新生. 植物基因表达调控与进化机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | 王鸿梅, 袁蔚, 薛芳, 张召聪, 刘坤, 陈四龙. 植物SWEET基因参与逆境胁迫响应及其调控机制[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [3] | 刘旭鹏, 王敏, 韩守安, 朱学慧, 王艳蒙, 潘明启, 张雯. 植物器官脱落调控因素及分子机理研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 472-482. |
| [4] | 熊良林, 梁国鲁, 郭启高, 景丹龙. 基因可变剪接调控植物响应非生物胁迫研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 435-448. |
| [5] | 周婧, 高飞. 植物缺铁诱导型香豆素合成及其在铁吸收中的功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 460-471. |
| [6] | 刘志祥, 谢华, 张慧, 黄晓磊. 表皮碳氢化合物在社会性昆虫中的功能多样性及其调控[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24302-. |
| [7] | 杜庆国, 李文学. lncRNA调控玉米生长发育和非生物胁迫研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 950-962. |
| [8] | 李巧峡, 李有龙, 李纪纲, 陈晨龙, 孙坤. 光周期调控维西堇菜与裂叶堇菜开放花和闭锁花的发育[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 23484-. |
| [9] | 周文杰, 张文瀚, 贾玮, 许自成, 黄五星. 植物miRNA响应非生物胁迫研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 810-833. |
| [10] | 陈婷欣, 符敏, 李娜, 杨蕾蕾, 李凌飞, 钟春梅. 铁甲秋海棠DNA甲基转移酶全基因组鉴定及表达分析(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 726-737. |
| [11] | 范雪兰, 落艳娇, 徐超群, 郭宝林. 淫羊藿类黄酮生物合成相关基因研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 834-846. |
| [12] | 夏婧, 饶玉春, 曹丹芸, 王逸, 柳林昕, 徐雅婷, 牟望舒, 薛大伟. 水稻中乙烯生物合成关键酶OsACS和OsACO调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 291-301. |
| [13] | 陈雯, 周颖盈, 罗平, 崔永一. 被子植物花朵重瓣化分子调控机制[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 257-277. |
| [14] | 仲昭暄, 张冬瑞, 李璐, 苏颖, 王黛宁, 王泽冉, 刘洋, 常缨. 香鳞毛蕨dfr-miR160a和靶基因DfARF10的生物信息学及表达模式分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 22-33. |
| [15] | 朱璐, 袁冲, 刘义飞. 植物次生代谢产物生物合成基因簇研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 134-143. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||