

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (1): 10-21.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22226 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22226
• EXPERIMENTAL COMMUNICATIONS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Bao Zhu, Jiangzhe Zhao, Kewei Zhang, Peng Huang*( )
)
Received:2022-09-28
Accepted:2022-12-13
Online:2024-01-10
Published:2024-01-10
Contact:
*E-mail: Bao Zhu, Jiangzhe Zhao, Kewei Zhang, Peng Huang. OsCKX9 is Involved in Regulating the Rice Lamina Joint Development and Leaf Angle[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(1): 10-21.
| Primer name | Primer sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| OsCKX9 F | CTATCCTCAGCACTTGGCCC |
| OsCKX9 R | AAATGGGACTGCCACTCCTG |
| OsUBQ5 F | GCACAAGCACAAGAAGGTGA |
| OsUBQ5 R | CCAAAGAACAGGAGCCTACG |
| OsCYC U4;1 F | CGACGACATATGCTACAACAATGC |
| OsCYC U4;1 R | CCAAAGAGGAAGTCCACCTCAAG |
Table 1 The primers used in this study
| Primer name | Primer sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| OsCKX9 F | CTATCCTCAGCACTTGGCCC |
| OsCKX9 R | AAATGGGACTGCCACTCCTG |
| OsUBQ5 F | GCACAAGCACAAGAAGGTGA |
| OsUBQ5 R | CCAAAGAACAGGAGCCTACG |
| OsCYC U4;1 F | CGACGACATATGCTACAACAATGC |
| OsCYC U4;1 R | CCAAAGAGGAAGTCCACCTCAAG |
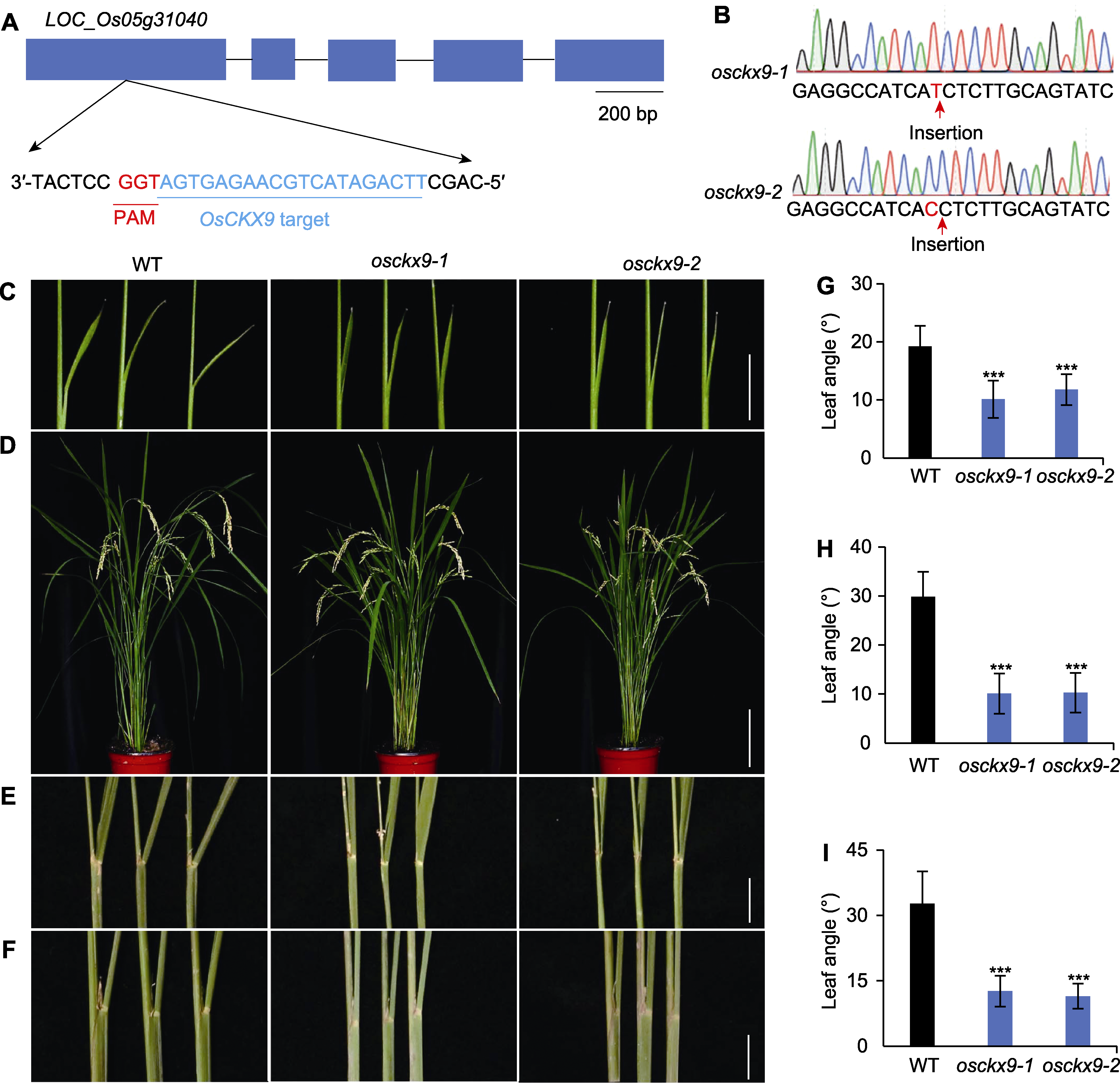
Figure 1 osckx9 mutants show smaller leaf angle (A) OsCKX9 was knocked out using CRISPR/Cas9 technique, “target” means knockout target positions (blue boxes represent exons, black horizontal lines represent untranslated regions; PAM: Primitive interval sequence adjacent to the motif); (B) Sequencing verification of gene knockout strains; (C) Morphological phenotypes of the 7-DAG (days after germination) seedlings of wild type (WT), osckx9-1 and osckx9-2 (bar=1 cm); (D) Morphological phenotypes of the adult plants of WT, osckx9-1 and osckx9-2 at 110-DAG (bar=15 cm); (E) Flag leaf phenotype of 110-DAG of WT, osckx9-1 and osckx9-2 (bar=1 cm); (F) The second leaf phenotype of 110-DAG of WT, osckx9-1 and osckx9-2 (bar=1 cm); (G) Quantification of the leaf angle of the plants shown in (C) (means±SD, n=24); (H), (I) Quantification of the flag leaf angle (H) and the second leaf angle (I) of the 110-DAG plants shown in (E), (F) (means±SD, n=16). Statistical analyses were performed by Student’s t-test. *** P<0.001
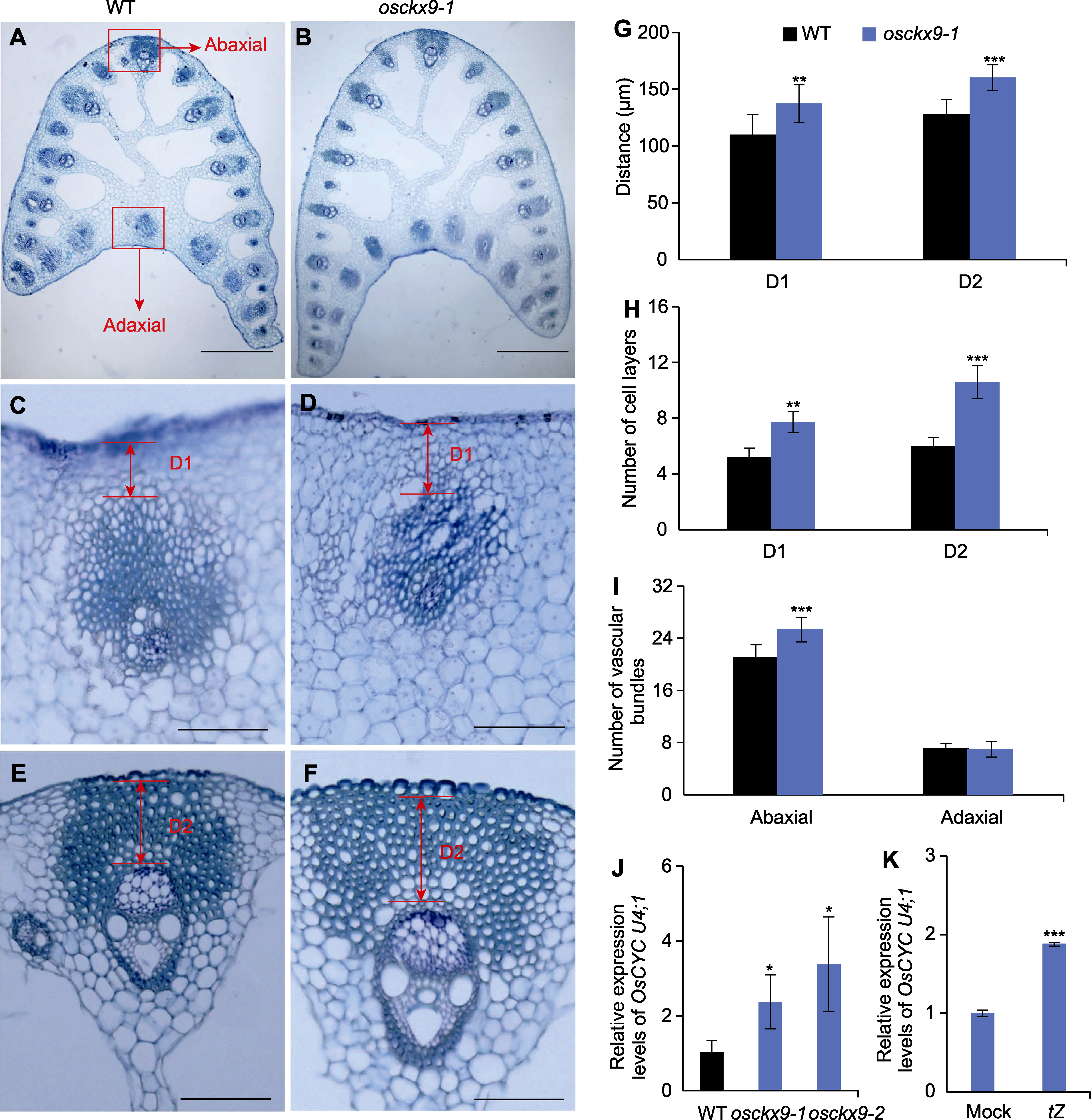
Figure 2 OsCKX9 affects the cell proliferation and vascular number in the abaxial of lamina joint (A)-(B) Transverse section of the lamina joints of wild type (WT) and osckx9-1 (red box represent the adaxial and the abaxial side of the lamina joint) (bars=250 μm); (C)-(D) High magnification images of the adaxial side of the lamina joints of WT and osckx9-1 (bars=100 μm); (E)-(F) High magnification images of the abaxial side of the lamina joints of WT and osckx9-1 (bars=250 μm); (G) Lengths of the D1 and D2 of the lamina joints shown in (C) to (F) (means±SD, n=15); (H) Quantification of the parenchyma cell layers in D1 and sclerenchyma cell layers in D2 shown in (D) to (F) (means±SD, n=15); (I) Quantification of vascular bundles on the abaxial and adaxial sides (means±SD, n=15). (J) Expression analysis of OsCYC U4;1 in WT, osckx9-1 and osckx9-2 by qRT-PCR (means±SD, n=3); (K) Expression analysis of OsCYC U4;1 in Mock and tZ treatment by qRT-PCR (means±SD, n=3). D1: The region between the adaxial epidermis and the adaxial central vascular bundle; D2: The region between the abaxial epidermis and the sclerenchyma; tZ: Trans-zeatin. Statistical analyses were performed by Student’s t-test. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001
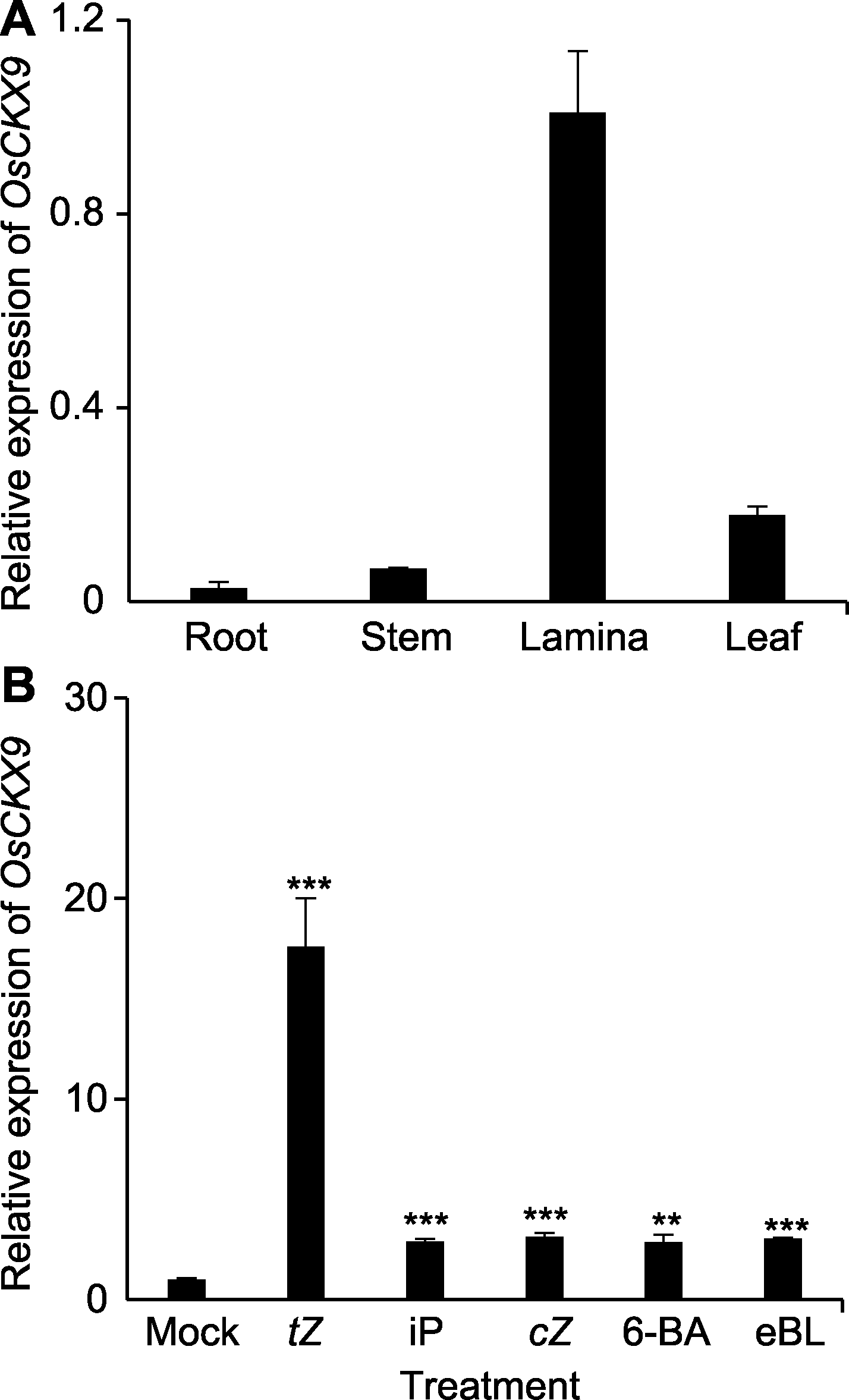
Figure 3 The expression pattern of OsCKX9 (A) Expression analysis of OsCKX9 in various rice tissues (root, stem, lamina, and leaf) in the heading stage at the wild type (WT) by qRT-PCR; (B) Relative expression levels of OsCKX9 in 7-DAG seedlings treated by tZ (trans-zeatin), iP (isopentenyladenine), cZ (cis-zeatin), 6-BA and eBL (epibrassinolide) for 3 h. OsUBQ5 was used as an internal control. Values are means±SD, n=3; statistical analyses were performed by Student’s t-test. ** P<0.01; *** P<0.001
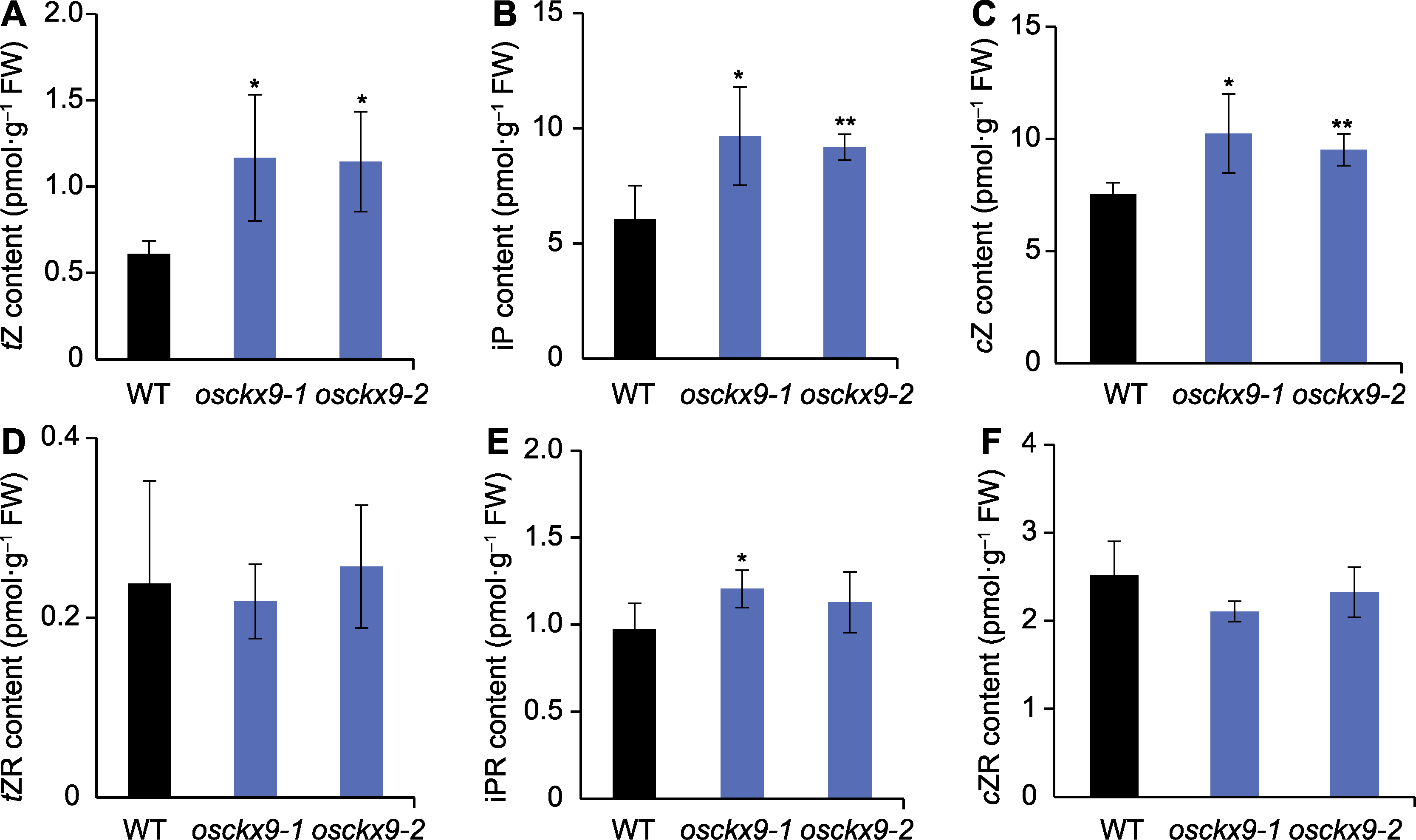
Figure 4 Quantification of cytokinin (CTK) content in osckx9 lamina joint (A)-(F) Quantification of endogenous CTK contents in the lamina joint of wild type (WT), osckx9-1 and osckx9-2. tZR: Trans-zea tin riboside; iPR: Isopentenyladenine riboside; cZR: Cis-zeatin riboside; tZ, iP, and cZ are the same as shown in Figure 3. Values are means±SD, n=3; statistical analyses were performed by Student’s t-test. * P<0.05; ** P<0.01
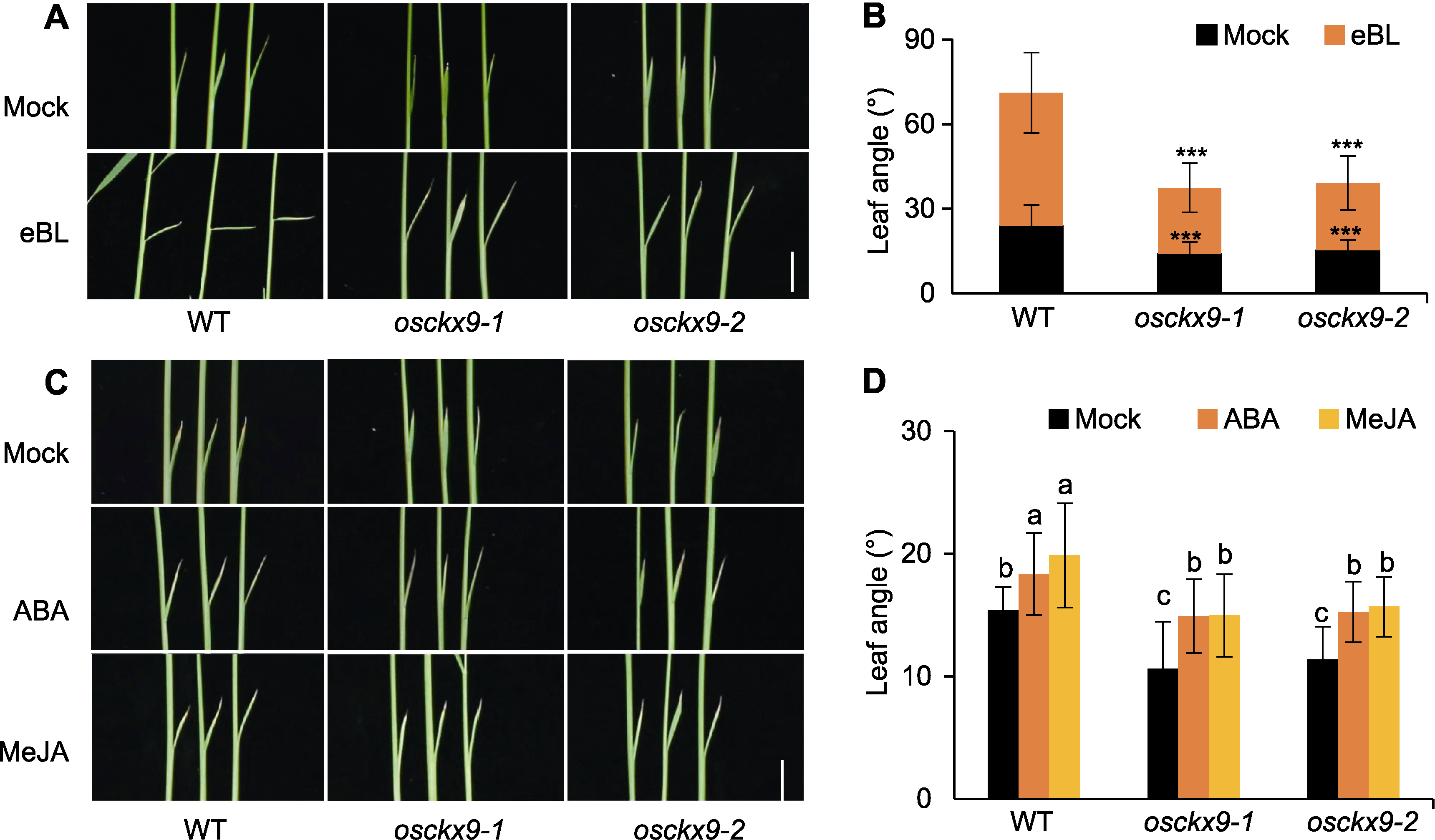
Figure 5 osckx9 shows insensitivity to BR (A) Wild type (WT), osckx9-1 and osckx9-2 plants responded with 7-DAG seedling leaf angles using Mock and eBL (epibrassinolide) treatment (bar=1 cm); (B) Measurement of leaf angles treated with Mock or eBL (black is the angle of the Mock leaf, orange is the angle added after eBL treatment (values are means±SD, n=20; statistical analyses were performed by Student’s t-test. *** P<0.001); (C) WT, osckx9-1 and osckx9-2 plants responded with 7-DAG seedling leaf angles using Mock, ABA and MeJA (jasmonates) treatments (bar=1 cm); (D) Mock-, ABA- and MeJA-treated measurement of leaf angles (values are means±SD, n=20; data were analyzed statistically using the One-way ANOVAL of the LSD test, and the different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in the Mock group and the treatment group at P<0.05 level).
| [1] | 宋松泉, 刘军, 杨华, 张文虎, 张琪, 高家东 (2021). 细胞分裂素调控种子发育、休眠与萌发的研究进展. 植物学报 56, 218-231. |
| [2] | 俞启璐, 赵江哲, 朱晓仙, 张可伟 (2021). 水稻根分泌激素调节生长速度. 植物学报 56, 175-182. |
| [3] | 张芬, 郭得平, 林明丽, 闫淼淼 (2008). 细胞分裂素氧化酶/脱氢酶的生理生化和分子特性. 植物生理学通讯 44, 797-803. |
| [4] |
Allen M, Qin WS, Moreau F, Moffatt B (2002). Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase isoforms of Arabidopsis and their potential contributions to adenine and cytokinin metabolism. Physiol Plant 115, 56-68.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Ashikari M, Sakakibara H, Lin SY, Yamamoto T, Takashi T, Nishimura A, Angeles ER, Qian Q, Kitano H, Matsuoka M (2005). Cytokinin oxidase regulates rice grain pro- duction. Science 309, 741-745.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Bai MY, Zhang LY, GampalaSS, Zhu SW, Song WY, Chong K, Wang ZY (2007). Functions of OsBZR1 and 14-3-3 proteins in brassinosteroid signaling in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104, 13839-13844.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Cao HP, Chen SK (1995). Brassinosteroid-induced rice lamina joint inclination and its relation to indole-3-acetic acid and ethylene. Plant Growth Regul 16, 189-196.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Cao YY, Zhong ZJ, Wang HY, Shen RX (2022). Leaf angle: a target of genetic improvement in cereal crops tailored for high-density planting. Plant Biotechnol J 20, 426-436.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Duan JB, Yu H, Yuan K, Liao ZG, Meng XB, Jing YH, Liu GF, Chu JF, Li JY (2019). Strigolactone promotes cytokinin degradation through transcriptional activation of CYTO- KININ OXIDASE/DEHYDROGENASE 9in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116, 14319-14324.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Frébort I, Kowalska M, Hluska T, Frébortová J, Galuszka P (2011). Evolution of cytokinin biosynthesis and degradation. J Exp Bot 62, 2431-2452.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
Gan LJ, Wu H, Wu DP, Zhang ZF, Guo ZF, Yang N, Xia K, Zhou X, Oh K, Matsuoka M, Ng D, Zhu CH (2015). Methyl jasmonate inhibits lamina joint inclination by repressing brassinosteroid biosynthesis and signaling in rice. Plant Sci 241, 238-245.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Gao SP, Fang J, Xu F, Wang W, Sun XH, Chu JF, Cai BD, Feng YQ, Chu CC (2014). CYTOKININ OXIDASE/DEHYDROGENASE4integrates cytokinin and auxin signaling to control rice crown root formation. Plant Physiol 165, 1035-1046.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Golovko A, Sitbon F, Tillberg E, Nicander B (2002). Identification of a tRNA isopentenyltransferase gene from Ara- bidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 49, 161-169.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
Guo JF, Li W, Shang LG, Wang YG, Yan P, Bai YH, Da XW, Wang K, Guo QQ, Jiang RR, Mao CZ, Mo XR (2021). OsbHLH98 regulates leaf angle in rice through transcriptional repression of OsBUL1. New Phytol 230, 1953-1966.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Hothorn M, Dabi T, Chory J (2011). Structural basis for cytokinin recognition by Arabidopsis thaliana histidine kinase 4. Nat Chem Biol 7, 766-768.
DOI |
| [16] |
Huang GQ, Hu H, van de Meene A, Zhang J, Dong L, Zheng S, Zhang FL, Betts NS, Liang WQ, Bennett MJ, Persson S, Zhang DB (2021). AUXIN RESPONSE FACTORS 6and 17 control the flag leaf angle in rice by regulating secondary cell wall biosynthesis of lamina joints. Plant Cell 33, 3120-3133.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Huang P, Zhao JZ, Hong JL, Zhu B, Xia S, Zhu EG, Han PF, Zhang KW (2023). Cytokinins regulate rice lamina joint development and leaf angle. Plant Physiol 191, 56-69.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Hwang I, Sheen J, Müller B (2012). Cytokinin signaling networks. Annu Rev Plant Biol 63, 353-380.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
Kiba T, Takei K, Kojima M, Sakakibara H (2013). Side- chain modification of cytokinins controls shoot growth in Arabidopsis. Dev Cell 27, 452-461.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Kuroha T, Tokunaga H, Kojima M, Ueda N, Ishida T, Nagawa S, Fukuda H, Sugimoto K, Sakakibara H (2009). Functional analyses of LONELY GUY cytokinin-activating enzymes reveal the importance of the direct activation pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21, 3152-3169.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Lee J, Park JJ, Kim SL, Yim J, An G (2007). Mutations in the rice liguleless gene result in a complete loss of the auricle, ligule, and laminar joint. Plant Mol Biol 65, 487-499.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
Li QQ, Xu F, Chen Z, Teng ZF, Sun K, Li XC, Yu JY, Zhang GX, Liang Y, Huang XH, Du L, Qian YW, Wang YC, Chu CC, Tang JY (2021). Synergistic interplay of ABA and BR signal in regulating plant growth and adaptation. Nat Plants 7, 1108-1118.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
Li XM, Sun SY, Li CX, Qiao SL, Wang T, Leng LN, Shen HY, Wang XL (2014). The strigolactone-related mutants have enhanced lamina joint inclination phenotype at the seedling stage. J Genet Genomics 41, 605-608.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
Sakakibara H (2006). Cytokinins: activity, biosynthesis, and translocation. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57, 431-449.
PMID |
| [25] |
Sakamoto T, Morinaka Y, Ohnishi T, Sunohara H, Fujioka S, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Mizutani M, Sakata K, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Tanaka H, Kitano H, Matsuoka M (2006). Erect leaves caused by brassinosteroid deficiency increase biomass production and grain yield in rice. Nat Biotechnol 24, 105-109.
DOI PMID |
| [26] |
Schmülling T, Werner T, Riefler M, Krupková E, Bartrinay Manns I (2003). Structure and function of cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase genes of maize, rice, Arabidopsis and other species. J Plant Res 116, 241-252.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
Šimášková M, O'Brien JA, Khan M, Van Noorden G, Ötvös K, Vieten A, De Clercq I, Van Haperen JMA, Cuesta C, Hoyerová K, Vanneste S, Marhavý P, Wabnik K, Van Breusegem F, Nowack M, Murphy A, Friml J, Weijers D, Beeckman T, Benková E (2015). Cytokinin response factors regulate PIN-FORMED auxin transporters. Nat Commun 6, 8717.
DOI PMID |
| [28] | Sun SY, Chen DH, Li XM, Qiao SL, Shi CN, Li CX, Shen HY, Wang XL (2015). Brassinosteroid signaling regulates leaf erectness in Oryza sativa via the control of a specific U-type cyclin and cell proliferation. Dev Cell 34, 220-228. |
| [29] |
Tong HN, Chu CC (2018). Functional specificities of brassinosteroid and potential utilization for crop improvement. Trends Plant Sci 23, 1016-1028.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
Wang B, Smith SM, Li JY (2018). Genetic regulation of shoot architecture. Annu Rev Plant Biol 69, 437-468.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
Yang WB, Cortijo S, Korsbo N, Roszak P, Schiessl K, Gurzadyan A, Wightman R, Jönsson H, Meyerowitz E (2021). Molecular mechanism of cytokinin-activated cell division in Arabidopsis. Science 371, 1350-1355.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Zhang SN, Wang SK, Xu YX, Yu CL, Shen CJ, Qian Q, Geisler M, Jiang DA, Qi YH (2015). The auxin response factor, OsARF19, controls rice leaf angles through positively regulating OsGH3-5 and OsBRI1. Plant Cell Environ 38, 638-654.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Zhang W, Peng KX, Cui FB, Wang DL, Zhao JZ, Zhang YJ, Yu NN, Wang YY, Zeng DL, Wang YH, Cheng ZK, Zhang KW (2021). Cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase OsCKX11 coordinates source and sink relationship in rice by simultaneous regulation of leaf senescence and grain number. Plant Biotechnol J 19, 335-350.
DOI PMID |
| [34] |
Zhang XY, Chen YT, Lin X, Hong XY, Zhu Y, Li WY, He WR, An FY, Guo HW (2013). Adenine phosphoribosyl transferase 1 is a key enzyme catalyzing cytokinin conversion from nucleobases to nucleotides in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 6, 1661-1672.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Zhao JZ, Yu NN, Ju M, Fan B, Zhang YJ, Zhu EG, Zhang MY, Zhang KW (2019). ABC transporter OsABCG18 controls the shootward transport of cytokinins and grain yield in rice. J Exp Bot 70, 6277-6291.
DOI PMID |
| [1] |
Juan Cui, Xiaoyu Yu, Yuejiao Yu, Chengwei Liang, Jian Sun, Wenfu Chen.
Analysis of Texture Factors and Genetic Basis Influencing the Differences in Eating Quality between Northeast China and Japanese Japonica Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | Zhao Ling, Guan Ju, Liang Wenhua, Zhang Yong, Lu Kai, Zhao Chunfang, Li Yusheng, Zhang Yadong. Mapping of QTLs for Heat Tolerance at the Seedling Stage in Rice Based on a High-density Bin Map [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(3): 342-353. |
| [3] | Xinyu Li, Yue Gu, Feifei Xu, Jinsong Bao. Research Progress on Post-translational Modifications of Starch Biosynthesis-related Proteins in Rice Endosperm [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(2): 256-270. |
| [4] | Jianguo Li, Yi Zhang, Wenjun Zhang. Iron Plaque Formation and Its Effects on Phosphorus Absorption in Rice Roots [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(1): 132-143. |
| [5] | Ruifeng Yao, Daoxin Xie. Activation and Termination of Strigolactone Signal Perception in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(6): 873-877. |
| [6] | Jinjin Lian, Luyao Tang, Yinuo Zhang, Jiaxing Zheng, Chaoyu Zhu, Yuhan Ye, Yuexing Wang, Wennan Shang, Zhenghao Fu, Xinxuan Xu, Richeng Wu, Mei Lu, Changchun Wang, Yuchun Rao. Genetic Locus Mining and Candidate Gene Analysis of Antioxidant Traits in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(5): 738-751. |
| [7] | Jiahui Huang, Huimin Yang, Xinyu Chen, Chaoyu Zhu, Yanan Jiang, Chengxiang Hu, Jinjin Lian, Tao Lu, Mei Lu, Weilin Zhang, Yuchun Rao. Response Mechanism of Rice Mutant pe-1 to Low Light Stress [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(4): 574-584. |
| [8] | Jianmin Zhou. A Combat Vehicle with a Smart Brake [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(3): 343-346. |
| [9] | Miaomiao Sun, Wei Zhang, Linxia Zhang, Juntao Huo, Zhineng Li, Guofeng Liu. Inheritance Analysis of Flower Size and Expression of Related Genes in Petunia hybrida [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(3): 422-432. |
| [10] | Chaoyu Zhu, Chengxiang Hu, Zhenan Zhu, Zhining Zhang, Lihai Wang, Jun Chen, Sanfeng Li, Jinjin Lian, Luyao Tang, Qianqian Zhong, Wenjing Yin, Yuexing Wang, Yuchun Rao. Mapping of QTLs Associated with Rice Panicle Traits and Candidate Gene Analysis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(2): 217-230. |
| [11] | Yanli Fang, Chuanyu Tian, Ruyi Su, Yapei Liu, Chunlian Wang, Xifeng Chen, Wei Guo, Zhiyuan Ji. Mining and Preliminary Mapping of Rice Resistance Genes Against Bacterial Leaf Streak [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(1): 1-9. |
| [12] | Tian Chuanyu, Fang Yanli, Shen Qing, Wang Hongjie, Chen Xifeng, Guo Wei, Zhao Kaijun, Wang Chunlian, Ji Zhiyuan. Genotypic Diversity and Pathogenisity of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae Isolated from Southern China in 2019-2021 [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(5): 743-749. |
| [13] | Dai Ruohui, Qian Xinyu, Sun Jinglei, Lu Tao, Jia Qiwei, Lu Tianqi, Lu Mei, Rao Yuchun. Research Progress on the Mechanisms of Leaf Color Regulation and Related Genes in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(5): 799-812. |
| [14] | Shang Sun, Yingying Hu, Yangshuo Han, Chao Xue, Zhiyun Gong. Double-stranded Labelled Oligo-FISH in Rice Chromosomes [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(3): 433-439. |
| [15] | Jiayi Jin, Yiting Luo, Huimin Yang, Tao Lu, Hanfei Ye, Jiyi Xie, Kexin Wang, Qianyu Chen, Yuan Fang, Yuexing Wang, Yuchun Rao. QTL Mapping and Expression Analysis on Candidate Genes Related to Chlorophyll Content in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(3): 394-403. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||