

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (3): 422-432.DOI: 10.11983/CBB23141 cstr: 32102.14.CBB23141
• EXPERIMENTAL COMMUNICATIONS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Miaomiao Sun1, Wei Zhang1,2, Linxia Zhang1, Juntao Huo1,2, Zhineng Li2,*( ), Guofeng Liu1,*(
), Guofeng Liu1,*( )
)
Received:2023-10-16
Accepted:2024-03-18
Online:2024-05-10
Published:2024-05-10
Contact:
E-mail: Miaomiao Sun, Wei Zhang, Linxia Zhang, Juntao Huo, Zhineng Li, Guofeng Liu. Inheritance Analysis of Flower Size and Expression of Related Genes in Petunia hybrida[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(3): 422-432.
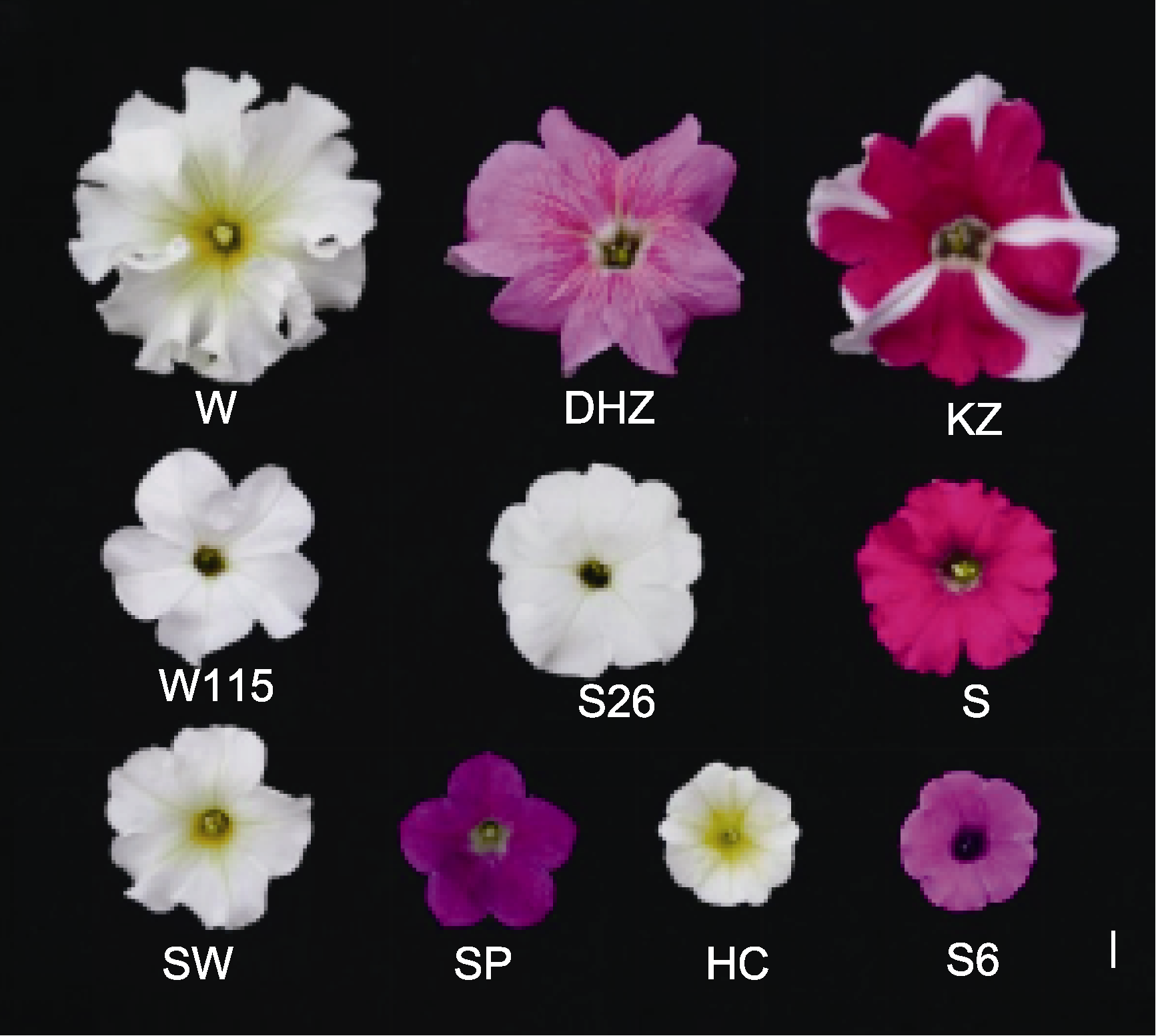

Figure 1 The tested materials of petunia with different flower sizes W, DHZ, KZ, W115, S, SW, HC, and SP: The inbred lines of Petunia hybrida; S26: P. axillaris; S6: P. inflata. Bar=1 cm
| Gene name | Primer name | Primer sequence (5'−3') |
|---|---|---|
| PhARR496 | qPhARR496-F | GCAACAACAAAGAAGCAGAGCAGTT |
| qPhARR496-R | GGTGATGATGGTAATGGCTGTGTCA | |
| PhARR828 | qPhARR828-F | CATCTTCCTCGCTCTCGCTCTC |
| qPhARR828-R | TGAGTCGTCGTGTTGGTGAATGT | |
| PhARR970 | qPhARR970-F | ACTCCTCTTCCTCATCAGTCATCATCA |
| qPhARR970-R | GCTGCTGCCATTCCCATTGTTG | |
| PhARR1029 | qPhARR1029-F | GCAAGAGCATGAACAGAACAAGTCA |
| qPhARR1029-R | CCAGGCATACAGTAGTCCGTGATAA | |
| PhARGOS057 | qPhARGOS057-F | TCTCTTCCATCATACGCTTTGGTCAA |
| qPhARGOS057-R | AGGCAAGAACCATAGGAGATTGTTGA | |
| PhARGOS459 | qPhARGOS459-F | GCACATGGAATCATCAGCAGAAGC |
| qPhARGOS459-R | GGTGGCAATGGTGGAAGGATCAA | |
| PhHK | qPhHK-F | CCAAGTTCTTTGAATCCAAGCCTCAC |
| qPhHK-R | AATAAGAATGCAGCACCAGCAGAATG | |
| PhTCP3b | qPhTCP3b-F | CCTCTCTGCTCACACAGCCATTC |
| qPTCP3b-R | GCCCAGCAATACTGTCAACTAAACT | |
| PhTCP4a | qPhTCP4a-F | TGACCAAGCAGCCCTTTTCTCT |
| qPhTCP4a-R | TGGAACTCTGTGGTGAAATGTCTGT |
Table 1 Primers used for quantitative real-time PCR
| Gene name | Primer name | Primer sequence (5'−3') |
|---|---|---|
| PhARR496 | qPhARR496-F | GCAACAACAAAGAAGCAGAGCAGTT |
| qPhARR496-R | GGTGATGATGGTAATGGCTGTGTCA | |
| PhARR828 | qPhARR828-F | CATCTTCCTCGCTCTCGCTCTC |
| qPhARR828-R | TGAGTCGTCGTGTTGGTGAATGT | |
| PhARR970 | qPhARR970-F | ACTCCTCTTCCTCATCAGTCATCATCA |
| qPhARR970-R | GCTGCTGCCATTCCCATTGTTG | |
| PhARR1029 | qPhARR1029-F | GCAAGAGCATGAACAGAACAAGTCA |
| qPhARR1029-R | CCAGGCATACAGTAGTCCGTGATAA | |
| PhARGOS057 | qPhARGOS057-F | TCTCTTCCATCATACGCTTTGGTCAA |
| qPhARGOS057-R | AGGCAAGAACCATAGGAGATTGTTGA | |
| PhARGOS459 | qPhARGOS459-F | GCACATGGAATCATCAGCAGAAGC |
| qPhARGOS459-R | GGTGGCAATGGTGGAAGGATCAA | |
| PhHK | qPhHK-F | CCAAGTTCTTTGAATCCAAGCCTCAC |
| qPhHK-R | AATAAGAATGCAGCACCAGCAGAATG | |
| PhTCP3b | qPhTCP3b-F | CCTCTCTGCTCACACAGCCATTC |
| qPTCP3b-R | GCCCAGCAATACTGTCAACTAAACT | |
| PhTCP4a | qPhTCP4a-F | TGACCAAGCAGCCCTTTTCTCT |
| qPhTCP4a-R | TGGAACTCTGTGGTGAAATGTCTGT |
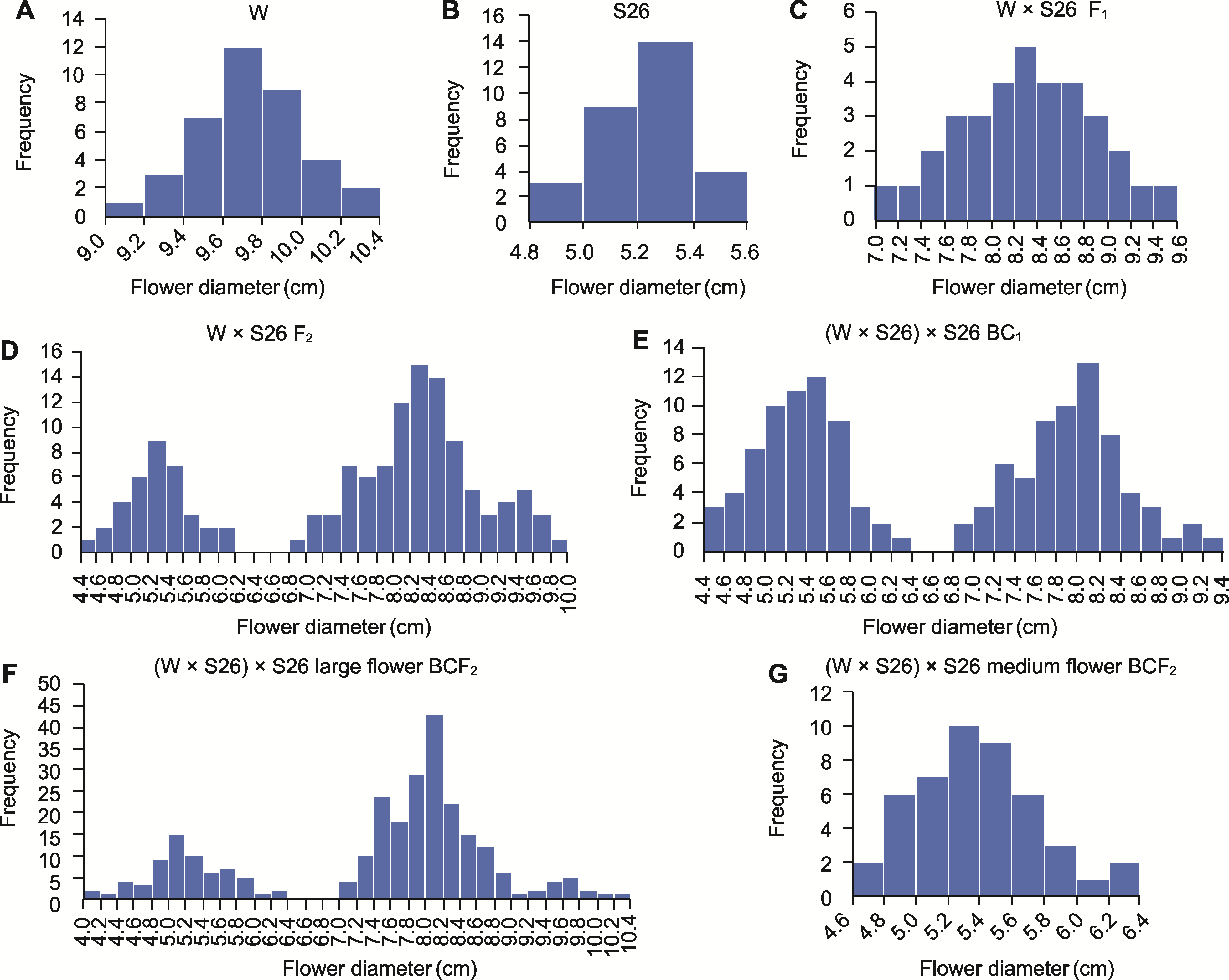
Figure 2 Frequency distribution histogram of flower diameter for parents and filial generations of W × S26 (A) Female parent W; (B) Male parent S26; (C) F1 generation; (D) F2 generation; (E) BC1 generation; (F) BCF2 generation from large flower; (G) BCF2 generation from medium flower
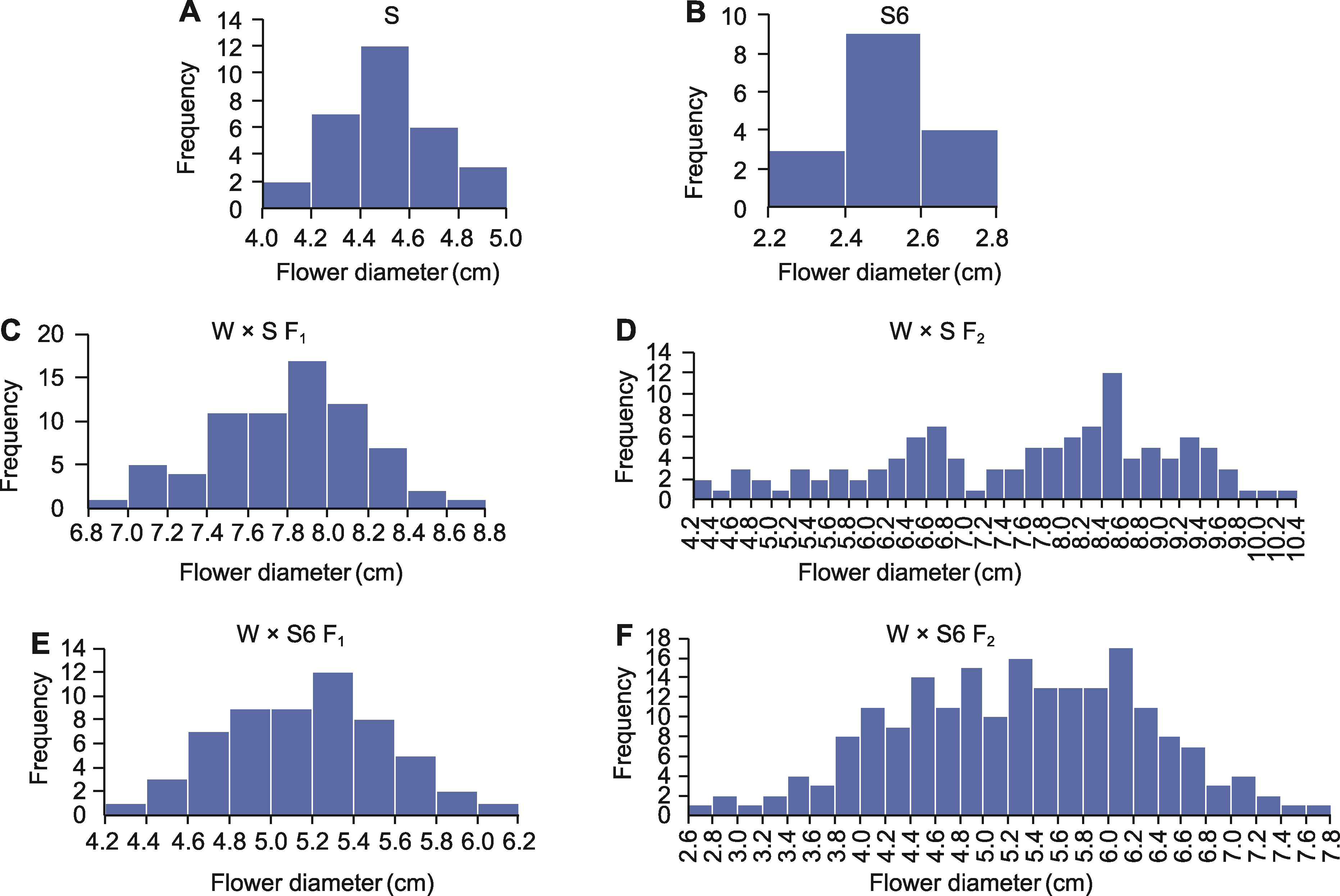
Figure 3 Frequency distribution histogram of flower diameter for parent, F1, and F2 generations of W × S and W × S6 (A) Parent S; (B) Parent S6; (C) F1 generation of W × S; (D) F2 generation of W × S; (E) F1 generation of W × S6; (F) F2 generation of W × S6
| Cross combination | Genetic model | Maximum likelihood value | AIC | Number of significant levels (P<0.05) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U12 | U22 | U32 | nW2 | Dn | ||||
| W × S26 | 1MG-AD | -599.9208 | 1207.8420 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2MG-ADI | -596.0287 | 1212.0570 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| MX1-AD-AD | -596.8717 | 1211.7440 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| W × S | 2MG-EAD | -242.0814 | 492.1628 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MX2-EAD-AD | -245.5385 | 495.0770 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 2MG-EA | -244.9837 | 497.9675 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
Table 2 Maximum likelihood value (MLV), Akaike information criterion (AIC) value, and the number of reaching significant levels for each genetic model
| Cross combination | Genetic model | Maximum likelihood value | AIC | Number of significant levels (P<0.05) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U12 | U22 | U32 | nW2 | Dn | ||||
| W × S26 | 1MG-AD | -599.9208 | 1207.8420 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2MG-ADI | -596.0287 | 1212.0570 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| MX1-AD-AD | -596.8717 | 1211.7440 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| W × S | 2MG-EAD | -242.0814 | 492.1628 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MX2-EAD-AD | -245.5385 | 495.0770 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 2MG-EA | -244.9837 | 497.9675 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Cross combination (female × male) | Population types | Plant numbers | Large flower | Medium flower | Small flower | Theoretical ratio | Actual ratio | (χc²) Chi-square test | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W × S26 | F1 | 32 | 32 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| F2 | 134 | 98 | 36 | 0 | 3:1 | 3:1 | 0.249 | 0.618 | |
| BC1 | 129 | 67 | 62 | 0 | 1:1 | 1:1 | 0.194 | 0.660 | |
| Large flower BCF2 | 259 | 194 | 65 | 0 | 3:1 | 3:1 | 0.001 | 0.971 | |
| Medium flower BCF2 | 44 | 0 | 44 | 0 | - | - | - | - | |
| W × S | F1 | 72 | 72 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| F2 | 115 | 76 | 39 | 0 | - | - | - | - | |
| W × S6 | F1 | 57 | 0 | 57 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| F2 | 200 | 11 | 168 | 21 | - | - | - | - |
Table 3 Chi square test for flower size segregation in the hybrid offsprings of petunia
| Cross combination (female × male) | Population types | Plant numbers | Large flower | Medium flower | Small flower | Theoretical ratio | Actual ratio | (χc²) Chi-square test | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W × S26 | F1 | 32 | 32 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| F2 | 134 | 98 | 36 | 0 | 3:1 | 3:1 | 0.249 | 0.618 | |
| BC1 | 129 | 67 | 62 | 0 | 1:1 | 1:1 | 0.194 | 0.660 | |
| Large flower BCF2 | 259 | 194 | 65 | 0 | 3:1 | 3:1 | 0.001 | 0.971 | |
| Medium flower BCF2 | 44 | 0 | 44 | 0 | - | - | - | - | |
| W × S | F1 | 72 | 72 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| F2 | 115 | 76 | 39 | 0 | - | - | - | - | |
| W × S6 | F1 | 57 | 0 | 57 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| F2 | 200 | 11 | 168 | 21 | - | - | - | - |
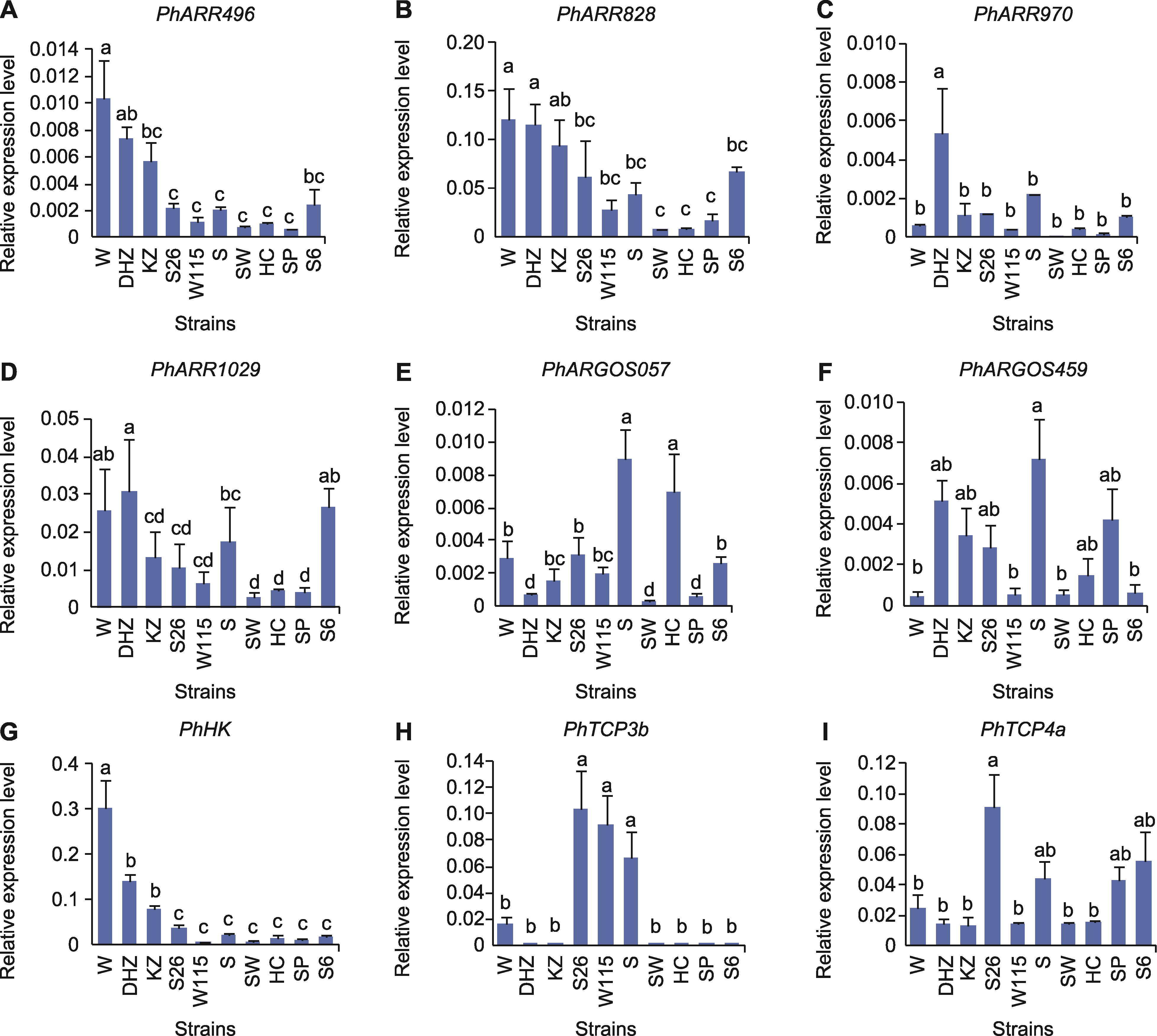
Figure 5 Expression levels of flower size regulating related genes in different strains of petunia Vertical bars represent SE of three biological replicates. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among strains.
| [1] |
Bartrina I, Jensen H, Novák O, Strna M, Werner T, Schmülling T (2017). Gain-of-function mutants of the cytokinin receptors AHK2 and AHK3 regulate plant organ size, flowering time and plant longevity. Plant Physiol 173, 1783-1797.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | Bombarely A, Moser M, Amrad A, Bao MZ, Bapaume L, Barry CS, Bliek M, Boersma MR, Borghi L, Bruggmann R, Bucher M, D'Agostino N, Davies K, Druege U, Dudareva N, Egea-Cortines M, Delledonne M, Fernandez-Pozo N, Franken P, Grandont L, Heslop-Harrison JS, Hintzsche J, Johns M, Koes R, Lv XD, Lyons E, Malla D, Martinoia E, Mattson NS, Morel P, Mueller LA, Muhlemann J, Nouri E, Passeri V, Pezzotti M, Qi QZ, Reinhardt D, Rich M, Richert-Pöggeler KR, Robbins TP, Schatz MC, Schranz ME, Schuurink RC, Sch- warzacher T, Spelt K, Tang HB, Urbanus SL, Vandenbussche M, Vijverberg K, Villarino GH, Warner RM, Weiss J, Yue Z, Zethof J, Quattrocchio F, Sims TL, Kuhlemeier C (2016). Insight into the evolution of the Solanaceae from the parental genomes of Petunia hybrida. Nat Plants 2, 16074. |
| [3] | Cao Z, Guo YF, Yang Q, He YH, Fetouh MI, Warner RM, Deng ZA (2018). Genome-wide search for quantitative trait loci controlling important plant and flower traits in Petunia using an interspecific recombinant inbred population of Petunia axillaris and Petunia exserta. G3 8, 2309-2317. |
| [4] | Cao Z, Guo YF, Yang Q, He YH, Fetouh MI, Warner RM, Deng ZA (2019). Genome-wide identification of quantitative trait loci for important plant and flower traits in Petunia using a high-density linkage map and an interspecific recombinant inbred population derived from Petunia integrifolia and P. axillaris. Horti Res 6, 27. |
| [5] |
Crawford BCW, Nath U, Carpenter R, Coen ES (2004). CINCINNATA controls both cell differentiation and growth in petal lobes and leaves of Antirrhinum. Plant Physiol 135, 244-253.
PMID |
| [6] | Dai SP, Bao MZ (2004). Advances in genetics and breeding of Petunia hybrida Vilm. Chin Bull Bot 21, 385-391. (in Chinese) |
| 代色平, 包满珠 (2004). 矮牵牛育种研究进展. 植物学通报 21, 385-391. | |
| [7] | Ewart L (1984). Plant breeding. In: Sink KC, ed. Petunia. Berlin: Springer. pp. 180-202. |
| [8] | Fenster CB, Armbruster WS, Wilson P, Dudash MR, Thomson JD (2004). Pollination syndromes and floral specialization. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 35, 375-403. |
| [9] |
Galliot C, Hoballah ME, Kuhlemeier C, Stuurman J (2006). Genetics of flower size and nectar volume in Petunia pollination syndromes. Planta 225, 203-212.
PMID |
| [10] | Hu YX, Poh HM, Chua NH (2006). The Arabidopsis ARGOS-LIKE gene regulates cell expansion during organ growth. Plant J 47, 1-9. |
| [11] | Hu YX, Xie Q, Chua NH (2003). The Arabidopsis auxin- inducible gene ARGOS controls lateral organ size. Plant Cell 15, 1951-1961. |
| [12] |
Huang TB, Irish VF (2016). Gene networks controlling petal organogenesis. J Exp Bot 67, 61-68.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | Kieber JJ, Schaller GE (2018). Cytokinin signaling in plant development. Development 145, dev149344. |
| [14] |
Krizek BA, Anderson JT (2013). Control of flower size. J Exp Bot 64, 1427-1437.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 25, 402-408.
DOI PMID |
| [16] | Nag A, King S, Jack T (2009). miR319a targeting of TCP4 is critical for petal growth and development in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106, 22534-22539. |
| [17] |
Nath U, Crawford BCW, Carpenter R, Coen E (2003). Genetic control of surface curvature. Science 299, 1404-1407.
DOI PMID |
| [18] | Nishijima T, Miyaki H, Sasaki K, Okazawa T (2006). Cultivar and anatomical analysis of corolla enlargement of petunia (Petunia hybrida Vilm.) by cytokinin application. Sci Hortic 111, 49-55. |
| [19] | Nishijima T, Niki T, Niki T (2011). The large-flowered petunia (Petunia hybrida Vilm.) genotype promotes expressions of type-A response regulator and cytokinin receptor genes like cytokinin response. J Japan Soc Hort Sci 80, 343-350. |
| [20] |
Santner A, Calderon-Villalobos LIA, Estelle M (2009). Plant hormones are versatile chemical regulators of plant growth. Nat Chem Biol 5, 301-307.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | Tan YQ, Yu HQ, Chen QS, Liu Y (2010). Application of excel in establishment of Chi-square test analysis module in agricultural statistic. Hubei Agricul Sci 49, 3192-3195. (in Chinese) |
| 谭永强, 余华强, 陈桥生, 刘莹 (2010). 利用Excel软件建立卡方检验分析模板在农业统计中的应用. 湖北农业科学 49, 3192-3195. | |
| [22] | To JPC, Deruère J, Maxwell BB, Morris VF, Hutchison CE, Ferreira FJ, Schaller GE, Kieber JJ (2007). Cytokinin regulates type-A Arabidopsis response regulator activity and protein stability via two-component phosphorelay. Plant Cell 19, 3901-3914. |
| [23] | To JPC, Haberer G, Ferreira FJ, Deruère J, Mason MG, Schaller GE, Alonso JM, Ecker JR, Kieber JJ (2004). Type-A Arabidopsis response regulators are partially redundant negative regulators of cytokinin signaling. Plant Cell 16, 658-671. |
| [24] |
Vandenbussche M, Chambrier P, Bento SR, Morel P (2016). Petunia, your next supermodel? Front Plant Sci 7, 72.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Venail J, Dell'olivo A, Kuhlemeier C (2010). Speciation genes in the genus Petunia. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 365, 461-468. |
| [26] | Verdonk JC, Shibuya K, Loucas HM, Colquhoun TA, Underwood BA, Clark DG (2008). Flower-specific expression of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens isopentenyl- transferase gene results in radial expansion of floral organs in Petunia hybrida. Plant Biotech J 6, 694-701. |
| [27] | Wang JT, Zhang YW, Du YW, Ren WL, Li HF, Sun WX, Ge C, Zhang YM (2022). SEA v2.0: an R software package for mixed major genes plus polygenes inheritance analysis of quantitative traits. Acta Agron Sin 48, 1416-1424. (in Chinese) |
|
王靖天, 张亚雯, 杜应雯, 任文龙, 李宏福, 孙文献, 葛超, 章元明 (2022). 数量性状主基因+多基因混合遗传分析R软件包SEA v2.0. 作物学报 48, 1416-1424.
DOI |
|
| [28] | Zhang ST, Zhou Q, Chen F, Wu L, Liu BJ, Li F, Zhang JQ, Bao MZ, Liu GF (2020). Genome-wide identification, characterization and expression analysis of TCP transcription factors in Petunia. Int J Mol Sci 21, 6594. |
| [1] | Ningna Lu, Zhenheng Liu, Yan Ma, Guangmei Lu, Xiuxiang Meng. Phenotypic selection analysis of flower traits in Delphinium kamaonense var. glabrescens (Ranunculaceae) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(7): 772-777. |
| [2] | Yuliang Jiang, Kundong Bai, Yili Guo, Bin Wang, Dongxing Li, Xiankun Li, Zhishang Liu. Floral traits of woody plants and their habitat differentiations in a northern tropical karst forest [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(2): 148-156. |
| [3] | ZHANG Qian,ZHAO Cheng-Zhang,DONG Xiao-Gang,MA Xiao-Li,HOU Zhao-Jiang,LI Yu. Trade-off between the biomass and number of flowers in Stellera chamaejasme along an elevation gradient in a degraded alpine grassland [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2014, 38(5): 452-459. |
| [4] | DAI Se-Ping BAO Man-Zhu①. Advances in Genetics and Breeding of Petunia hybrida Vilm. [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2004, 21(04): 385-391. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||