

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (2): 256-270.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24067 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24067
• SPECIAL TOPICS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xinyu Li1, Yue Gu1, Feifei Xu1, Jinsong Bao1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-05-05
Accepted:2024-10-14
Online:2025-03-10
Published:2024-10-21
Contact:
Jinsong Bao
Xinyu Li, Yue Gu, Feifei Xu, Jinsong Bao. Research Progress on Post-translational Modifications of Starch Biosynthesis-related Proteins in Rice Endosperm[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(2): 256-270.
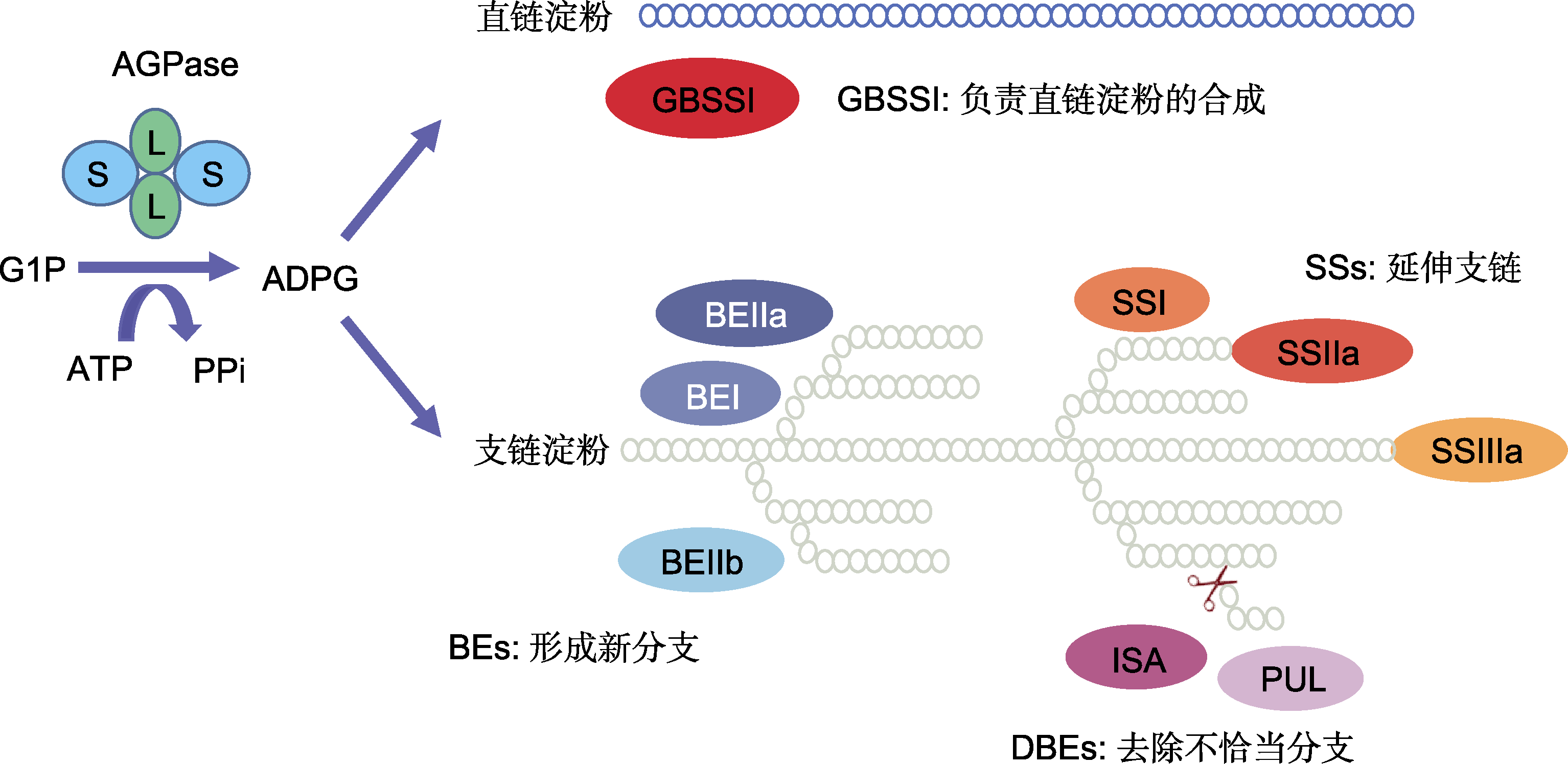
Figure 1 The enzyme functions involved in starch biosynthesis in rice endosperm G1P: Glucose-1-phosphate; ADPG: Adenosine diphosphate glucose; AGPase: ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase; GBSSI: Granule-bound starch synthase I; SSs: Soluble starch synthases; BEs: Branching enzymes; DBEs: Debranching enzymes; ISA: Isoamylase; PUL: Pullulanase
| 修饰类型 | 蛋白数量 | 位点数量 |
|---|---|---|
| 磷酸化 | 7796 | 23513 |
| 赖氨酸2-羟基异丁酰化 | 4719 | 19831 |
| 赖氨酸乙酰化 | 2607 | 4798 |
| 赖氨酸琥珀酰化 | 859 | 2381 |
| 赖氨酸丙二酰化 | 483 | 898 |
| 赖氨酸类泛素化 | 403 | 978 |
| N-糖基化 | 202 | 248 |
| 羰基化 | 181 | 414 |
Table 1 The number of proteins and sites associated with post-translational modifications (PTMs) of rice
| 修饰类型 | 蛋白数量 | 位点数量 |
|---|---|---|
| 磷酸化 | 7796 | 23513 |
| 赖氨酸2-羟基异丁酰化 | 4719 | 19831 |
| 赖氨酸乙酰化 | 2607 | 4798 |
| 赖氨酸琥珀酰化 | 859 | 2381 |
| 赖氨酸丙二酰化 | 483 | 898 |
| 赖氨酸类泛素化 | 403 | 978 |
| N-糖基化 | 202 | 248 |
| 羰基化 | 181 | 414 |
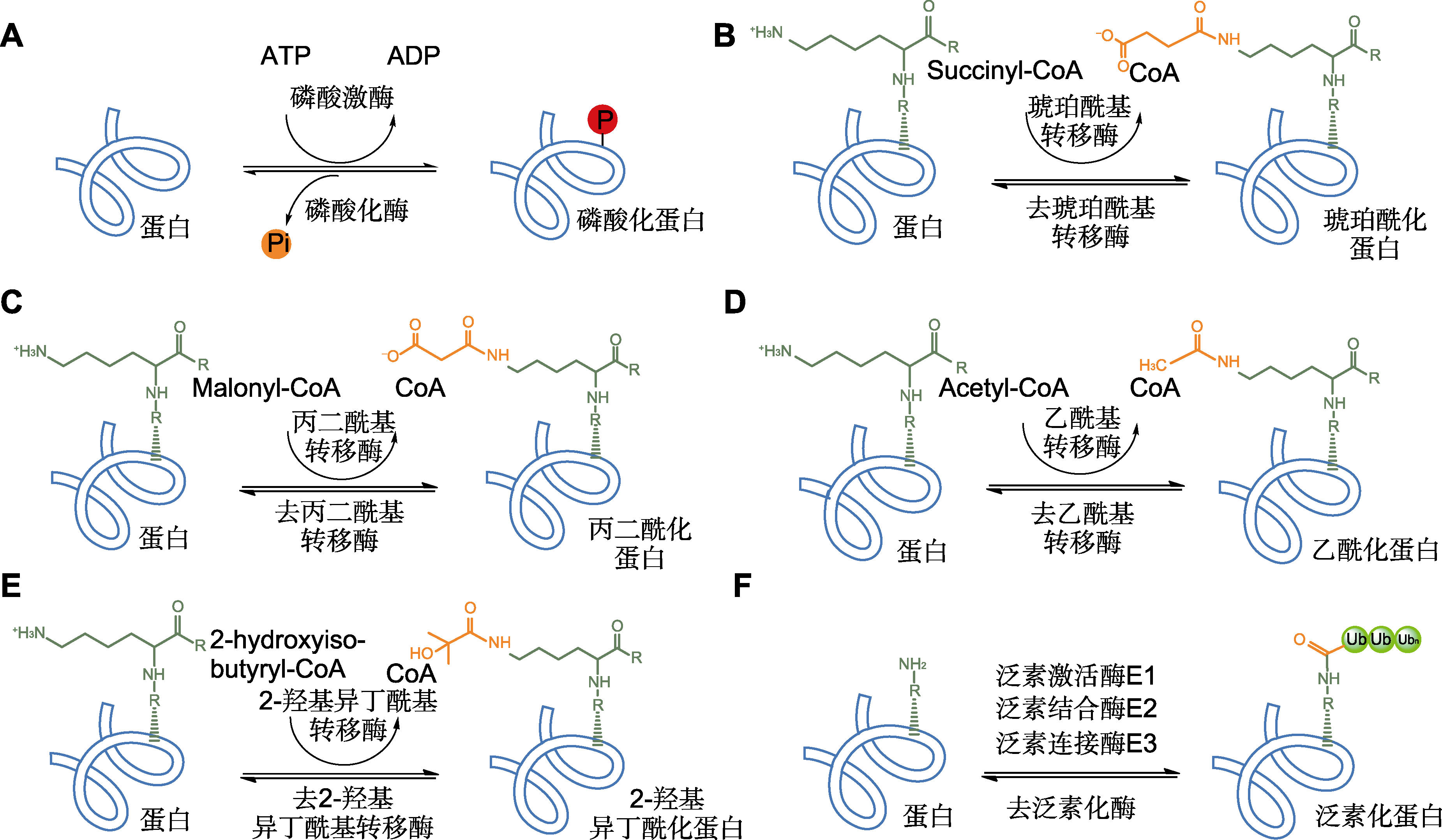
Figure 2 Six common types of post-translational modifications (PTMs) identified from rice seeds (A) Phosphorylation; (B) Succinylation; (C) Malonylation; (D) Acetylation; (E) 2-hydroxyisobutyrylation; (F) Ubiquitination
| 蛋白质磷酸化类型 | 蛋白质磷酸化位点 | 化学键 |
|---|---|---|
| O-磷酸化 | 苏氨酸(Thr) | P-O |
| 丝氨酸(Ser) | ||
| 酪氨酸(Tyr) | ||
| N-磷酸化 | 组氨酸(His) | P-N |
| 精氨酸(Arg) | ||
| 赖氨酸(Lys) | ||
| S-磷酸化 | 谷氨酸(Glu) | P-O |
| 天冬氨酸(Asp) | ||
| 酰基磷酸化 | 半胱氨酸(Cys) | P-S |
Table 2 Types and sites of protein phosphorylation
| 蛋白质磷酸化类型 | 蛋白质磷酸化位点 | 化学键 |
|---|---|---|
| O-磷酸化 | 苏氨酸(Thr) | P-O |
| 丝氨酸(Ser) | ||
| 酪氨酸(Tyr) | ||
| N-磷酸化 | 组氨酸(His) | P-N |
| 精氨酸(Arg) | ||
| 赖氨酸(Lys) | ||
| S-磷酸化 | 谷氨酸(Glu) | P-O |
| 天冬氨酸(Asp) | ||
| 酰基磷酸化 | 半胱氨酸(Cys) | P-S |
| 蛋白 | 登记号 | 修饰位点 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| AGPS2 | BGIOSGA027135 | S13 (i&j)、S17 (i)、S22 (i)、S35 (i)和S36 (i) | Qiu et al., |
| AGPL2 | BGIOSGA004052 | S62 (i)、S381 (i)和T68 (i&j) | Akihiro et al., |
| GBSSI | BGIOSGA022241 | T57 (j)、Y183 (j)、S283 (j)、T298 (j)、T349 (j)、 S358 (j)、P/S415 (j)、S526 (j)和S569 (j) | Zhang et al., |
| SSIIa | BGIOSGA022586 | S126 (i) | Pang et al., |
| SSIIIa | BGIOSGA028122 | S96 (i&j) | Akihiro et al., |
| BEI | BGIOSGA020506 | S562 (i)、S620 (i)、S814 (i)和S815 (i) | Pang et al., |
| BEIIb | BGIOSGA006344 | S685 (i)和S715 (i) | Pang et al., |
| PUL | BGIOSGA015875 | S154 (i)、S155 (i)和S869 (i) | Pang et al., |
| Pho1 | BGIOSGA009780 | S494 (i)、S645 (i)和S124 (j) | Qiu et al., |
Table 3 Identified phosphoproteins involving in starch biosynthesis in rice endosperm based on phosphoproteomics
| 蛋白 | 登记号 | 修饰位点 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| AGPS2 | BGIOSGA027135 | S13 (i&j)、S17 (i)、S22 (i)、S35 (i)和S36 (i) | Qiu et al., |
| AGPL2 | BGIOSGA004052 | S62 (i)、S381 (i)和T68 (i&j) | Akihiro et al., |
| GBSSI | BGIOSGA022241 | T57 (j)、Y183 (j)、S283 (j)、T298 (j)、T349 (j)、 S358 (j)、P/S415 (j)、S526 (j)和S569 (j) | Zhang et al., |
| SSIIa | BGIOSGA022586 | S126 (i) | Pang et al., |
| SSIIIa | BGIOSGA028122 | S96 (i&j) | Akihiro et al., |
| BEI | BGIOSGA020506 | S562 (i)、S620 (i)、S814 (i)和S815 (i) | Pang et al., |
| BEIIb | BGIOSGA006344 | S685 (i)和S715 (i) | Pang et al., |
| PUL | BGIOSGA015875 | S154 (i)、S155 (i)和S869 (i) | Pang et al., |
| Pho1 | BGIOSGA009780 | S494 (i)、S645 (i)和S124 (j) | Qiu et al., |
| 蛋白 | Uniprot 数据库登录号 | 酶编号 | 修饰 位点 | 修饰肽 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGPase S1 | Q69T99 | [EC:2.7.7.27] | 203 | MDYQK(ac)FIQAHR | Wang et al., |
| AGPase S2 | P15280 | [EC:2.7.7.27] | 261 | IVEFAEK(ac)PK | Wang et al., |
| 217 | MDYEK(ac)FIQAHR | Wang et al., | |||
| AGPase L2 | Q7G065 | [EC:2.7.7.27] | 250 | ASDYGLVK(ac)FDDSGR | Wang et al., |
| 260 | VIAFSEK(ac)PK | Xing et al., | |||
| 310 | DVLLDILK(ac)SK | Wang et al., | |||
| 312 | SK(ac)YAHLQDFGSEILPR | Wang et al., | |||
| GBSSI | Q0DEV5 | [EC:2.4.1.242] | 444 | KFEK(ac)LLK | Meng et al., |
| 452 | SMEEK(ac)YPGK | Meng et al., | |||
| SSI | Q0DEC8 | [EC:2.4.1.21] | 193 | NFANAFYTEK(ac)HIK | Wang et al., |
| SSIVa | Q5JMA0 | [EC:2.4.1.-] | 589 | AQYYGEHDDFK(ac)R | Meng et al., |
| BEI | Q0D9D0 | [EC:2.4.1.18] | 108 | CLIEK(ac)HEGGLEEFSK | Wang et al., |
| 89 | LEEFK(ac)DHFNYR | Meng et al., | |||
| 103 | YLDQK(ac)CLIEK | Meng et al., | |||
| 118 | HEGGLEEFSK(ac)GYLK | Meng et al., | |||
| 164 | DK(ac)FGIWSIK | Meng et al., | |||
| 236 | YVFK(ac)HPR | Meng et al., | |||
| 372 | GYHK(ac)LWDSR | Meng et al., | |||
| 614 | EGNNWSYDK(ac)CR | Meng et al., | |||
| 662 | QIVSDMNEK(ac)DK | Meng et al., | |||
| 697 | VGCDLPGK(ac)YR | Meng et al., | |||
| 809 | GMK(ac)FVFR | Meng et al., | |||
| BEIIb | Q6H6P8 | [EC:2.4.1.18] | 134 | VVEELAAEQK(ac)PR | Meng et al., |
| 303 | YIFK(ac)HPQPK | Wang et al., | |||
| 587 | WSEK(ac)CVTYAESHDQALVGDK | Wang et al., | |||
| 688 | FIPGNNNSYDK(ac)CR | Wang et al., | |||
| 738 | KHEEDK(ac)MIIFEK | Meng et al., | |||
| 771 | VGCLKPGK(ac)YK | Meng et al., | |||
| ISA3 | Q6K4A4 | [EC:3.2.1.68] | 130 | K(ac)YFGVAEEK | Meng et al., |
| PUL | Q7X834 | [EC:3.2.1.41] | 805 | NEENWHLIK(ac)PR | Meng et al., |
| PhoH | Q8LQ33 | [EC:2.4.1.1] | 747 | FEEAK(ac)QLIR | Meng et al., |
| 169 | YGLFK(ac)QCITK | He et al., | |||
| 409 | HMEIIEEIDK(ac)R | He et al., | |||
| 645 | LVNDVGAVVNNDPDVNK(ac)YLK | He et al., | |||
| 818 | MSILNTAGSGK(ac)FSSDR | He et al., | |||
| PhoL | Q9AUV8 | [EC:2.4.1.1] | 216 | YK(ac)HGLFK | Meng et al., |
| 255 | TDVSYPVK(ac)FYGK | Meng et al., | |||
| 451 | YGTEDTSLLK(ac)K | Meng et al., | |||
| 504 | SLEPSVVVEEK(ac)TVSK | Meng et al., | |||
| 594 | FQNK(ac)TNGVTPR | Meng et al., | |||
| 734 | AFATYVQAK(ac)R | Wang et al., | |||
| 846 | AQGK(ac)FVPDPR | Meng et al., | |||
| 913 | DQK(ac)LWTR | Meng et al., | |||
| 928 | MSILNTASSSK(ac)FNSDR | Meng et al., | |||
| PGM | Q9AUQ4 | [EC:5.4.2.2] | 18 | ATTPFDGQK(ac) PGTSGLR | He et al., |
| 69 | YFSK(ac)DAVQIITK | He et al., | |||
| 206 | LMK(ac)TIFDFESIK | He et al., | |||
| 215 | TIFDFESIK(ac)K | He et al., | |||
| 275 | EDFGGGHPDPNLTYAK(ac)ELVDR | He et al., | |||
| 361 | NLNLK(ac)FFEVPTGWK | He et al., | |||
| 506 | DPVDGSVSK(ac)HQGVR | He et al., | |||
| 543 | VYIEQYEK(ac)DSSK | Meng et al., |
Table 4 Lysine acetylation on starch biosynthesis proteins from rice seeds
| 蛋白 | Uniprot 数据库登录号 | 酶编号 | 修饰 位点 | 修饰肽 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGPase S1 | Q69T99 | [EC:2.7.7.27] | 203 | MDYQK(ac)FIQAHR | Wang et al., |
| AGPase S2 | P15280 | [EC:2.7.7.27] | 261 | IVEFAEK(ac)PK | Wang et al., |
| 217 | MDYEK(ac)FIQAHR | Wang et al., | |||
| AGPase L2 | Q7G065 | [EC:2.7.7.27] | 250 | ASDYGLVK(ac)FDDSGR | Wang et al., |
| 260 | VIAFSEK(ac)PK | Xing et al., | |||
| 310 | DVLLDILK(ac)SK | Wang et al., | |||
| 312 | SK(ac)YAHLQDFGSEILPR | Wang et al., | |||
| GBSSI | Q0DEV5 | [EC:2.4.1.242] | 444 | KFEK(ac)LLK | Meng et al., |
| 452 | SMEEK(ac)YPGK | Meng et al., | |||
| SSI | Q0DEC8 | [EC:2.4.1.21] | 193 | NFANAFYTEK(ac)HIK | Wang et al., |
| SSIVa | Q5JMA0 | [EC:2.4.1.-] | 589 | AQYYGEHDDFK(ac)R | Meng et al., |
| BEI | Q0D9D0 | [EC:2.4.1.18] | 108 | CLIEK(ac)HEGGLEEFSK | Wang et al., |
| 89 | LEEFK(ac)DHFNYR | Meng et al., | |||
| 103 | YLDQK(ac)CLIEK | Meng et al., | |||
| 118 | HEGGLEEFSK(ac)GYLK | Meng et al., | |||
| 164 | DK(ac)FGIWSIK | Meng et al., | |||
| 236 | YVFK(ac)HPR | Meng et al., | |||
| 372 | GYHK(ac)LWDSR | Meng et al., | |||
| 614 | EGNNWSYDK(ac)CR | Meng et al., | |||
| 662 | QIVSDMNEK(ac)DK | Meng et al., | |||
| 697 | VGCDLPGK(ac)YR | Meng et al., | |||
| 809 | GMK(ac)FVFR | Meng et al., | |||
| BEIIb | Q6H6P8 | [EC:2.4.1.18] | 134 | VVEELAAEQK(ac)PR | Meng et al., |
| 303 | YIFK(ac)HPQPK | Wang et al., | |||
| 587 | WSEK(ac)CVTYAESHDQALVGDK | Wang et al., | |||
| 688 | FIPGNNNSYDK(ac)CR | Wang et al., | |||
| 738 | KHEEDK(ac)MIIFEK | Meng et al., | |||
| 771 | VGCLKPGK(ac)YK | Meng et al., | |||
| ISA3 | Q6K4A4 | [EC:3.2.1.68] | 130 | K(ac)YFGVAEEK | Meng et al., |
| PUL | Q7X834 | [EC:3.2.1.41] | 805 | NEENWHLIK(ac)PR | Meng et al., |
| PhoH | Q8LQ33 | [EC:2.4.1.1] | 747 | FEEAK(ac)QLIR | Meng et al., |
| 169 | YGLFK(ac)QCITK | He et al., | |||
| 409 | HMEIIEEIDK(ac)R | He et al., | |||
| 645 | LVNDVGAVVNNDPDVNK(ac)YLK | He et al., | |||
| 818 | MSILNTAGSGK(ac)FSSDR | He et al., | |||
| PhoL | Q9AUV8 | [EC:2.4.1.1] | 216 | YK(ac)HGLFK | Meng et al., |
| 255 | TDVSYPVK(ac)FYGK | Meng et al., | |||
| 451 | YGTEDTSLLK(ac)K | Meng et al., | |||
| 504 | SLEPSVVVEEK(ac)TVSK | Meng et al., | |||
| 594 | FQNK(ac)TNGVTPR | Meng et al., | |||
| 734 | AFATYVQAK(ac)R | Wang et al., | |||
| 846 | AQGK(ac)FVPDPR | Meng et al., | |||
| 913 | DQK(ac)LWTR | Meng et al., | |||
| 928 | MSILNTASSSK(ac)FNSDR | Meng et al., | |||
| PGM | Q9AUQ4 | [EC:5.4.2.2] | 18 | ATTPFDGQK(ac) PGTSGLR | He et al., |
| 69 | YFSK(ac)DAVQIITK | He et al., | |||
| 206 | LMK(ac)TIFDFESIK | He et al., | |||
| 215 | TIFDFESIK(ac)K | He et al., | |||
| 275 | EDFGGGHPDPNLTYAK(ac)ELVDR | He et al., | |||
| 361 | NLNLK(ac)FFEVPTGWK | He et al., | |||
| 506 | DPVDGSVSK(ac)HQGVR | He et al., | |||
| 543 | VYIEQYEK(ac)DSSK | Meng et al., |
| 蛋白 | Uniprot数据库登录号 | 酶编号 | 修饰位点 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGPase S2 | P15280 | [EC:2.7.7.27] | 217、261、263、403、447和476 | Meng et al., |
| AGPase L2 | Q7G065 | [EC:2.7.7.27] | 37、250、312、449、459和504 | Meng et al., |
| BEI | Q0D9D0 | [EC:2.4.1.18] | 89、103、164、324、372、500、524和697 | Meng et al., |
| BEIIb | Q6H6P8 | [EC:2.4.1.18] | 134、191和587 | Meng et al., |
| PUL | Q7X834 | [EC:3.2.1.41] | 732 | Meng et al., |
| PhoH | Q8LQ33 | [EC:2.4.1.1] | 412和439 | He et al., |
| PhoL | Q9AUV8 | [EC:2.4.1.1] | 259、255、657和734 | Meng et al., |
| PGM | Q9AUQ4 | [EC:5.4.2.2] | 8和568 | He et al., |
Table 5 Lysine succinylation on starch biosynthesis proteins from rice seeds
| 蛋白 | Uniprot数据库登录号 | 酶编号 | 修饰位点 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGPase S2 | P15280 | [EC:2.7.7.27] | 217、261、263、403、447和476 | Meng et al., |
| AGPase L2 | Q7G065 | [EC:2.7.7.27] | 37、250、312、449、459和504 | Meng et al., |
| BEI | Q0D9D0 | [EC:2.4.1.18] | 89、103、164、324、372、500、524和697 | Meng et al., |
| BEIIb | Q6H6P8 | [EC:2.4.1.18] | 134、191和587 | Meng et al., |
| PUL | Q7X834 | [EC:3.2.1.41] | 732 | Meng et al., |
| PhoH | Q8LQ33 | [EC:2.4.1.1] | 412和439 | He et al., |
| PhoL | Q9AUV8 | [EC:2.4.1.1] | 259、255、657和734 | Meng et al., |
| PGM | Q9AUQ4 | [EC:5.4.2.2] | 8和568 | He et al., |
| 蛋白 | Uniprot数据库 登录号 | 酶编号 | Khib修饰位点 | Kmal修饰位点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGPase S1 | Q69T99 | [EC:2.7.7.27] | 442、249、462、234和203 | - |
| AGPase S2 | P15280 | [EC:2.7.7.27] | 102、106、132、217、239、248、261、263、268、285、360、385、403、406、441、447、456、467、476和496 | 106、360和403 |
| AGPase L2 | Q7G065 | [EC:2.7.7.27] | 37、74、187、223、250、263、273、286、301、302、310、312、334、364、371、392、425、443、449、459和504 | 250、312、371和449 |
| AGPase L3 | Q688T8 | [EC:2.7.7.27] | 100、194、196、247、299、326、331、369、446、456和470 | - |
| GBSSI | Q0DEV5 | [EC:2.4.1.242] | 181、192、309、381、385、530、538和549 | - |
| SSI | Q0DEC8 | [EC:2.4.1.21] | 193、196、349、357、429、461、467和570 | - |
| SSIIa | Q0DDE3 | [EC:2.4.1.21] | 151、244、346、378和532 | - |
| SSIIIa | Q6Z1D6 | [EC:2.4.1.21] | 228、 649、761、794、808、961、1203和1604 | - |
| BEI | Q0D9D0 | [EC:2.4.1.18] | 62、64、84、89、103、108、118、122、157、164、171、186、215、236、319、324、372、423、500、506、524、540、549、614、662、664、683、689、697、744、775、796和809 | 108、118、506、524、689和809 |
| BEIIb | Q6H6P8 | [EC:2.4.1.18] | 134、146、158、191、231、268、299、328、386、466、558、564、571、587、603、612、636、677、688、719、738和773 | 719 |
| ISA3 | Q6K4A4 | [EC:3.2.1.68] | 266和269 | - |
| PUL | Q7X834 | [EC:3.2.1.41] | 123、140、163、239、263、274、388、392、488、535、549、573、590、669、682、732、777、796、805、817和832 | 274和871 |
| PhoH | Q8LQ33 | [EC:2.4.1.1] | 115、409、425、533、542、595、721和818 | - |
| PhoL | Q9AUV8 | [EC:2.4.1.1] | 134、255、259、277、289、356、381、410、418、429、441、451、471、493、504、590、617、630、636、657、665、681、725、734、738、846、893、904、913、928、940和946 | 259、493和657 |
| PGM | Q9AUQ4 | [EC:5.4.2.2] | - | 54、458和568 |
Table 6 Lysine 2-hydroxyisobutyrylation (Khib) and malonylation (Kmal) on starch biosynthesis proteins from rice seeds (Meng et al., 2017; Mujahid et al., 2018)
| 蛋白 | Uniprot数据库 登录号 | 酶编号 | Khib修饰位点 | Kmal修饰位点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGPase S1 | Q69T99 | [EC:2.7.7.27] | 442、249、462、234和203 | - |
| AGPase S2 | P15280 | [EC:2.7.7.27] | 102、106、132、217、239、248、261、263、268、285、360、385、403、406、441、447、456、467、476和496 | 106、360和403 |
| AGPase L2 | Q7G065 | [EC:2.7.7.27] | 37、74、187、223、250、263、273、286、301、302、310、312、334、364、371、392、425、443、449、459和504 | 250、312、371和449 |
| AGPase L3 | Q688T8 | [EC:2.7.7.27] | 100、194、196、247、299、326、331、369、446、456和470 | - |
| GBSSI | Q0DEV5 | [EC:2.4.1.242] | 181、192、309、381、385、530、538和549 | - |
| SSI | Q0DEC8 | [EC:2.4.1.21] | 193、196、349、357、429、461、467和570 | - |
| SSIIa | Q0DDE3 | [EC:2.4.1.21] | 151、244、346、378和532 | - |
| SSIIIa | Q6Z1D6 | [EC:2.4.1.21] | 228、 649、761、794、808、961、1203和1604 | - |
| BEI | Q0D9D0 | [EC:2.4.1.18] | 62、64、84、89、103、108、118、122、157、164、171、186、215、236、319、324、372、423、500、506、524、540、549、614、662、664、683、689、697、744、775、796和809 | 108、118、506、524、689和809 |
| BEIIb | Q6H6P8 | [EC:2.4.1.18] | 134、146、158、191、231、268、299、328、386、466、558、564、571、587、603、612、636、677、688、719、738和773 | 719 |
| ISA3 | Q6K4A4 | [EC:3.2.1.68] | 266和269 | - |
| PUL | Q7X834 | [EC:3.2.1.41] | 123、140、163、239、263、274、388、392、488、535、549、573、590、669、682、732、777、796、805、817和832 | 274和871 |
| PhoH | Q8LQ33 | [EC:2.4.1.1] | 115、409、425、533、542、595、721和818 | - |
| PhoL | Q9AUV8 | [EC:2.4.1.1] | 134、255、259、277、289、356、381、410、418、429、441、451、471、493、504、590、617、630、636、657、665、681、725、734、738、846、893、904、913、928、940和946 | 259、493和657 |
| PGM | Q9AUQ4 | [EC:5.4.2.2] | - | 54、458和568 |
| 蛋白 | 登记号 | 修饰位点 |
|---|---|---|
| AGPS1 | BGIOSGA030039 | K94、K464和K484 |
| AGPS2 | BGIOSGA027135 | K106、K132、K385、K403、K406、K476和K496 |
| AGPL2 | BGIOSGA004052 | K41、K78、K134、K191、K227、K254、K316、K338、K394、K396、K463、K508和K513 |
| AGPL3 | BGIOSGA017490 | K509 |
| GBSSI | BGIOSGA022241 | K130、K173、K177、K181、K192、K258、K371、K381、K385、K399、K462、K517、K530、K549、K571和K575 |
| BEI | BGIOSGA020506 | K103、K108和K122 |
| BEIIb | BGIOSGA006344 | K134 |
| PUL | BGIOSGA015875 | K230、K330、K431、K736和K884 |
| Pho1 | BGIOSGA009780 | K277、K445和K941 |
Table 7 Lysine ubiquitination on starch biosynthesis proteins from rice seeds
| 蛋白 | 登记号 | 修饰位点 |
|---|---|---|
| AGPS1 | BGIOSGA030039 | K94、K464和K484 |
| AGPS2 | BGIOSGA027135 | K106、K132、K385、K403、K406、K476和K496 |
| AGPL2 | BGIOSGA004052 | K41、K78、K134、K191、K227、K254、K316、K338、K394、K396、K463、K508和K513 |
| AGPL3 | BGIOSGA017490 | K509 |
| GBSSI | BGIOSGA022241 | K130、K173、K177、K181、K192、K258、K371、K381、K385、K399、K462、K517、K530、K549、K571和K575 |
| BEI | BGIOSGA020506 | K103、K108和K122 |
| BEIIb | BGIOSGA006344 | K134 |
| PUL | BGIOSGA015875 | K230、K330、K431、K736和K884 |
| Pho1 | BGIOSGA009780 | K277、K445和K941 |
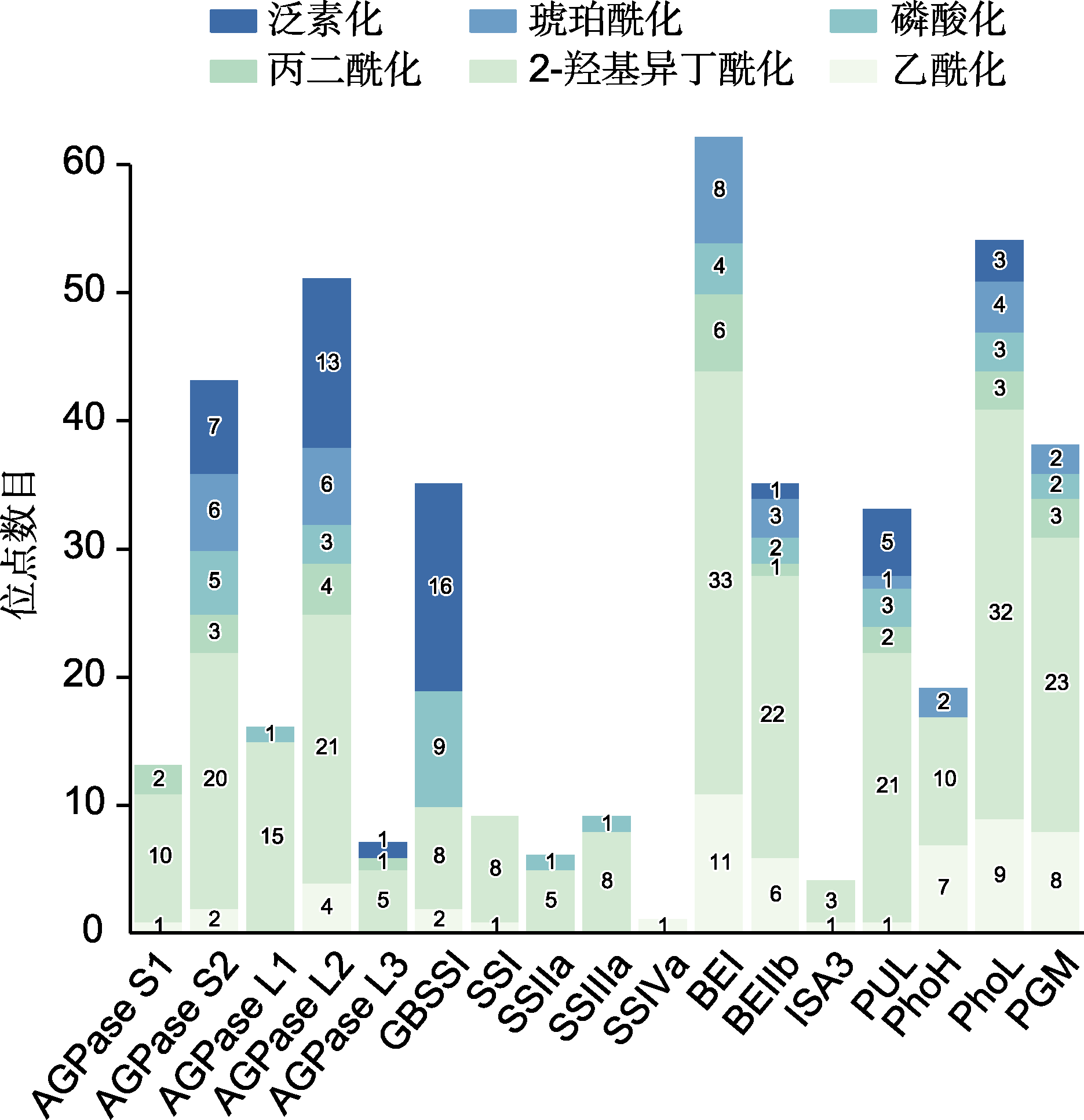
Figure 3 Summary of post-translational modifications (PTMs) targeting starch synthesis related enzymes (SSREs) in rice seeds The number of modification site(s) of PTMs identified for each protein are indicated on the stacked bar.
| [1] |
Ahmed Z, Tetlow IJ, Ahmed R, Morell MK, Emes MJ (2015). Protein-protein interactions among enzymes of starch biosynthesis in high-amylose barley genotypes reveal differential roles of heteromeric enzyme complexes in the synthesis of A and B granules. Plant Sci 233, 95-106.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
Akihiro T, Mizuno K, Fujimura T (2005). Gene expression of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase and starch contents in rice cultured cells are cooperatively regulated by sucrose and ABA. Plant Cell Physiol 46, 937-946.
PMID |
| [3] | Bao JS (2007). Progress in studies on inheritance and improvement of rice starch quality. Mol Plant Breed 5, 1-20. (in Chinese) |
| 包劲松 (2007). 稻米淀粉品质遗传与改良研究进展. 分子植物育种 5, 1-20. | |
| [4] | Bao JS, Deng BW, Zhang L (2023). Molecular and genetic bases of rice cooking and eating quality: an updated review. Cereal Chem 100, 1220-1233. |
| [5] | Bao JS, Kong XL, Xie JK, Xu LJ (2004). Analysis of genotypic and environmental effects on rice starch. 1. Apparent amylose content, pasting viscosity, and gel texture. J Agric Food Chem 52, 6010-6016. |
| [6] | Bao JS, Xia YW (1999). Recent advances on molecular biology of starch biosynthesis in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Chin Bull Bot 16, 352-358. (in Chinese) |
| 包劲松, 夏英武 (1999). 水稻淀粉合成的分子生物学研究进展. 植物学通报 16, 352-358. | |
| [7] | Bao JS, Xu JH (2023). Molecular research for cereal grain quality. Int J Mol Sci 24, 13687. |
| [8] | Bi YD, Wang HX, Lu TC, Li XH, Shen Z, Chen YB, Wang BC (2011). Large-scale analysis of phosphorylated proteins in maize leaf. Planta 233, 383-392. |
| [9] |
Bowman CE, Rodriguez S, Alpergin ESS, Acoba MG, Zhao L, Hartung T, Claypool SM, Watkins PA, Wolfgang MJ (2017). The mammalian malonyl-CoA synthetase ACSF3 is required for mitochondrial protein malonylation and metabolic efficiency. Cell Chem Biol 24, 673-684.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | Cabrera E, Mathews P, Mezhericher E, Beach TG, Deng JJ, Neubert TA, Rostagno A, Ghiso J (2018). Aβ truncated species: implications for brain clearance mechanisms and amyloid plaque deposition. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1864, 208-225. |
| [11] |
Chen C, He BS, Liu XX, Ma XD, Liu YJ, Yao HY, Zhang P, Yin JL, Wei X, Koh HJ, Yang C, Xue HW, Fang ZW, Qiao YL (2020). Pyrophosphate-fructose 6-phosphate 1-phosphotransferase (PFP1) regulates starch biosynthesis and seed development via heterotetramer formation in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Biotechnol J 18, 83-95.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | Chen GX, Zhou JW, Liu YL, Lu XB, Han CX, Zhang WY, Xu YH, Yan YM (2016). Biosynthesis and regulation of wheat amylose and amylopectin from proteomic and phosphoproteomic characterization of granule-binding proteins. Sci Rep 6, 33111. |
| [13] | Ding JJ, Karim H, Li YL, Harwood W, Guzman C, Lin N, Xu Q, Zhang YZ, Tang HP, Jiang YF, Qi PF, Deng M, Ma J, Wang JR, Chen GY, Lan XJ, Wei YM, Zheng YL, Jiang QT (2021). Re-examination of the APETALA2/Ethy- lene-responsive factor gene family in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) indicates a role in the regulation of starch synthesis. Front Plant Sci 12, 791584. |
| [14] |
Finkemeier I, Laxa M, Miguet L, Howden AJM, Sweetlove LJ (2011). Proteins of diverse function and subcellular location are lysine acetylated in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 155, 1779-1790.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
Galván-Peña S, Carroll RG, Newman C, Hinchy EC, Palsson-Mcdermott E, Robinson EK, Covarrubias S, Nadin A, James AM, Haneklaus M, Carpenter S, Kelly VP, Murphy MP, Modis LK, O'Neill LA (2019). Malonylation of GAPDH is an inflammatory signal in macrophages. Nat Commun 10, 338.
DOI PMID |
| [16] | Gao Q, Yan T, Zhang ZJ, Liu SY, Fang XD, Gao DM, Yang YZ, Xu WY, Qiao JH, Cao Q, Ding ZH, Wang Y, Yu JL, Wang XB (2020). Casein kinase 1 regulates cytorhabdovirus replication and transcription by phosphorylating a phosphoprotein serine-rich motif. Plant Cell 32, 2878-2897. |
| [17] | Guo HY, Dong X, An MN, Xia ZH, Wu YH (2024). Research progress in the functions of key enzymes of ubiquitination modification in plant stress responses. Biotechnol Bull 40(4), 1-11. (in Chinese) |
|
郭慧妍, 董雪, 安梦楠, 夏子豪, 吴元华 (2024). 泛素化修饰关键酶在植物抗逆反应中的功能研究进展. 生物技术通报 40(4), 1-11.
DOI |
|
| [18] |
Han C, Yang PF, Sakata K, Komatsu S (2014). Quantitative proteomics reveals the role of protein phosphorylation in rice embryos during early stages of germination. J Proteome Res 13, 1766-1782.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
He DL, Wang Q, Li M, Damaris RN, Yi XL, Cheng ZY, Yang PF (2016). Global proteome analyses of lysine acetylation and succinylation reveal the widespread involvement of both modification in metabolism in the embryo of germinating rice seed. J Proteome Res 15, 879-890.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
He ZQ, Huang TT, Ao K, Yan XF, Huang Y (2017). Sumoylation, phosphorylation, and acetylation fine-tune the turnover of plant immunity components mediated by ubiquitination. Front Plant Sci 8, 1682.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Hennen-Bierwagen TA, Lin QH, Grimaud F, Planchot V, Keeling PL, James MG, Myers AM (2009). Proteins from multiple metabolic pathways associate with starch biosynthetic enzymes in high molecular weight complexes: a model for regulation of carbon allocation in maize amyloplasts. Plant Physiol 149, 1541-1559.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
Hirschey MD, Zhao YM (2015). Metabolic regulation by lysine malonylation, succinylation, and glutarylation. Mol Cell Proteomics 14, 2308-2315.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | Hu YQ, Zhang YN, Yu SW, Deng GF, Dai GX, Bao JS (2023). Combined effects of BEIIb and SSIIa alleles on amylose contents, starch fine structures and physicochemical properties of indica rice. Foods 12, 119. |
| [24] |
Kosova G, Scott NM, Niederberger C, Prins GS, Ober C (2012). Genome-wide association study identifies candidate genes for male fertility traits in humans. Am J Hum Genet 90, 950-961.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
Kulkarni RA, Worth AJ, Zengeya TT, Shrimp JH, Garlick JM, Roberts AM, Montgomery DC, Sourbier C, Gibbs BK, Mesaros C, Tsai YC, Das S, Chan KC, Zhou M, Andresson T, Weissman AM, Linehan WM, Blair IA, Snyder NW, Meier JL (2017). Discovering targets of non-enzymatic acylation by thioester reactivity profiling. Cell Chem Biol 24, 231-242.
DOI PMID |
| [26] | Liu DR, Huang WX, Cai XL (2013). Oligomerization of rice granule-bound starch synthase 1 modulates its activity regulation. Plant Sci 210, 141-150. |
| [27] | Liu FS, Ahmed Z, Lee EA, Donner E, Liu Q, Ahmed R, Morell MK, Emes MJ, Tetlow IJ (2012). Allelic variants of the amylose extender mutation of maize demonstrate phenotypic variation in starch structure resulting from modified protein-protein interactions. J Exp Bot 63, 1167-1183. |
| [28] | Liu FS, Makhmoudova A, Lee EA, Wait R, Emes MJ, Tetlow IJ (2009). The amylose extender mutant of maize conditions novel protein-protein interactions between star- ch biosynthetic enzymes in amyloplasts. J Exp Bot 60, 4423-4440. |
| [29] |
Luo M, Cheng K, Xu YC, Yang SG, Wu KQ (2017). Plant responses to abiotic stress regulated by histone deacetylases. Front Plant Sci 8, 2147.
DOI PMID |
| [30] | Lv DW, Li X, Zhang M, Gu AQ, Zhen SM, Wang C, Li XH, Yan YM (2014). Large-scale phosphoproteome analysis in seedling leaves of Brachypodium distachyon L. BMC Genomics 15, 375. |
| [31] | Mehrpouyan S, Menon U, Tetlow IJ, Emes MJ (2021). Protein phosphorylation regulates maize endosperm starch synthase IIa activity and protein-protein interactions. Plant J 105, 1098-1112. |
| [32] | Meng XX, Lv YD, Mujahid H, Edelmann MJ, Zhao H, Peng XJ, Peng ZH (2018). Proteome-wide lysine acetylation identification in developing rice (Oryza sativa) seeds and protein co-modification by acetylation, succinylation, ubiquitination, and phosphorylation. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom 1866, 451-463. |
| [33] |
Meng XX, Mujahid H, Zhang YD, Peng XJ, Redoña ED, Wang CL, Peng ZH (2019). Comprehensive analysis of the lysine succinylome and protein co-modifications in developing rice seeds. Mol Cell Proteomics 18, 2359-2372.
DOI PMID |
| [34] |
Meng XX, Xing SH, Perez LM, Peng XJ, Zhao QY, Redoña ED, Wang CL, Peng ZH (2017). Proteome-wide analysis of lysine 2-hydroxyisobutyrylation in developing rice (Oryza sativa) seeds. Sci Rep 7, 17486.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
Millar AH, Heazlewood JL, Giglione C, Holdsworth MJ, Bachmair A, Schulze WX (2019). The scope, functions, and dynamics of posttranslational protein modifications. Annu Rev Plant Biol 70, 119-151.
DOI PMID |
| [36] |
Mujahid H, Meng XX, Xing SH, Peng XJ, Wang CL, Peng ZH (2018). Malonylome analysis in developing rice (Oryza sativa) seeds suggesting that protein lysine malonylation is well-conserved and overlaps with acetylation and succinylation substantially. J Proteomics 170, 88-98.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
Nie LT, Shuai L, Zhu MR, Liu P, Xie ZF, Jiang SW, Jiang HW, Li J, Zhao YM, Li JY, Tan MJ (2017). The landscape of histone modifications in a high-fat diet-induced obese (DIO) mouse model. Mol Cell Proteomics 16, 1324-1334.
DOI PMID |
| [38] |
Ohdan T, Francisco PB Jr, Sawada T, Hirose T, Terao T, Satoh H, Nakamura Y (2005). Expression profiling of genes involved in starch synthesis in sink and source organs of rice. J Exp Bot 56, 3229-3244.
DOI PMID |
| [39] | Pan YH, Chen L, Zhu XY, Li JC, Rashid MAR, Chen C, Qing DJ, Zhou WY, Yang XH, Gao LJ, Zhao Y, Deng GF (2023). Utilization of natural alleles for heat adaptability QTLs at the flowering stage in rice. BMC Plant Biol 23, 256. |
| [40] | Pang YH, Hu YQ, Bao JS (2021). Comparative phosphoproteomic analysis reveals the response of starch metabolism to high-temperature stress in rice endosperm. Int J Mol Sci 22, 10546. |
| [41] | Pang YH, Ying YN, Xu FF, Bao JS (2024). Integrated analysis of phosphoproteome and ubiquitinated proteome in rice endosperm under high temperature stress. J Zhejiang Univ Agric Life Sci 50, 382-392. (in Chinese) |
| 庞悦涵, 应逸宁, 徐非非, 包劲松 (2024). 高温胁迫下水稻胚乳磷酸化与泛素化蛋白质组学联合分析. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版) 50, 382-392. | |
| [42] | Pang YH, Zhou X, Chen YL, Bao JS (2018). Comparative phosphoproteomic analysis of the developing seeds in two indica rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars with different starch quality. J Agric Food Chem 66, 3030-3037. |
| [43] | Qiu JH, Hou YX, Tong XH, Wang YF, Lin HY, Liu Q, Zhang W, Li ZY, Nallamilli BR, Zhang J (2016). Quantitative phosphoproteomic analysis of early seed development in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Mol Biol 90, 249-265. |
| [44] |
Smith-Hammond CL, Swatek KN, Johnston ML, Thelen JJ, Miernyk JA (2014). Initial description of the developing soybean seed protein Lys-Nε-acetylome. J Proteomics 96, 56-66.
DOI PMID |
| [45] |
Svensson K, Labarge SA, Sathe A, Martins VF, Tahvilian S, Cunliffe JM, Sasik R, Mahata SK, Meyer GA, Philp A, David LL, Ward SR, Mccurdy CE, Aslan JE, Schenk S (2020). P300 and cAMP response element-binding protein-binding protein in skeletal muscle homeostasis, contractile function, and survival. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 11, 464-477.
DOI PMID |
| [46] | Tan MJ, Peng C, Anderson KA, Chhoy P, Xie ZY, Dai LZ, Park J, Chen Y, Huang H, Zhang Y, Ro J, Wagner GR, Green MF, Madsen AS, Schmiesing J, Peterson BS, Xu GF, Ilkayeva OR, Muehlbauer MJ, Braulke T, Muhlhausen C, Backos DS, Olsen CA, Mcguire PJ, Pletcher SD, Lombard DB, Hirschey MD, Zhao YM (2014). Lysine glutarylation is a protein post-translational modification regulated by SIRT5. Cell Metab 19, 605-617. |
| [47] | Tang ZW, Zhang DP (2023). Research progress on the molecular mechanism of starch accumulation in rice endosperm. Chin Bull Bot 58, 612-621. (in Chinese) |
|
唐子雯, 张冬平 (2023). 水稻胚乳淀粉积累过程的分子机理研究进展. 植物学报 58, 612-621.
DOI |
|
| [48] | Teng B, Zeng RZ, Wang YC, Liu ZQ, Zhang ZM, Zhu HT, Ding XH, Li WT, Zhang GQ (2012). Detection of allelic variation at the Wx locus with single-segment substitution lines in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Breed 30, 583-595. |
| [49] |
Tetlow IJ, Beisel KG, Cameron S, Makhmoudova A, Liu FS, Bresolin NS, Wait R, Morell MK, Emes MJ (2008). Analysis of protein complexes in wheat amyloplasts reveals functional interactions among starch biosynthetic enzymes. Plant Physiol 146, 1878-1891.
DOI PMID |
| [50] |
Tetlow IJ, Wait R, Lu ZX, Akkasaeng R, Bowsher CG, Esposito S, Kosar-Hashemi B, Morell MK, Emes MJ (2004). Protein phosphorylation in amyloplasts regulates starch branching enzyme activity and protein-protein interactions. Plant Cell 16, 694-708.
DOI PMID |
| [51] | Wang YF, Hou YX, Qiu JH, Li ZY, Zhao J, Tong XH, Zhang J (2017). A quantitative acetylomic analysis of early seed development in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Int J Mol Sci 18, 1376. |
| [52] |
Wang ZA, Cole PA (2020). The chemical biology of reversible lysine post-translational modifications. Cell Chem Biol 27, 953-969.
DOI PMID |
| [53] | Wu LP, Meng XX, Huang HZ, Liu YY, Jiang WM, Su XL, Wang ZJ, Meng F, Wang LH, Peng DY, Xing SH (2022). Comparative proteome and phosphoproteome analyses reveal different molecular mechanism between stone plan- ting under the forest and greenhouse planting of Dendrobium huoshanense. Front Plant Sci 13, 937392. |
| [54] | Wu X, Oh MH, Schwarz EM, Larue CT, Sivaguru M, Imai BS, Yau PM, Ort DR, Huber SC (2011). Lysine acetylation is a widespread protein modification for diverse proteins in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 155, 1769-1778. |
| [55] |
Xie X, Kang HX, Liu WD, Wang GL (2015). Comprehensive profiling of the rice ubiquitome reveals the significance of lysine ubiquitination in young leaves. J Proteome Res 14, 2017-2025.
DOI PMID |
| [56] | Xing SH, Meng XX, Zhou LH, Mujahid H, Zhao CF, Zhang YD, Wang CL, Peng ZH (2016). Proteome profile of starch granules purified from rice (Oryza sativa) endosperm. PLoS One 11, e0168467. |
| [57] | Xiong YH, Peng XJ, Cheng ZY, Liu WD, Wang GL (2016). A comprehensive catalog of the lysine-acetylation targets in rice (Oryza sativa) based on proteomic analyses. J Pro- teomics 138, 20-29. |
| [58] | Xu M, Tian XM, Ku TT, Wang GY, Zhang EY (2021). Global identification and systematic analysis of lysine malonylation in maize (Zea mays L.). Front Plant Sci 12, 728338. |
| [59] | Xu Y, Li XX, Liang WX, Liu MJ (2020). Proteome-wide analysis of lysine 2-hydroxyisobutyrylation in the phytopathogenic fungus Botrytis cinerea. Front Microbiol 11, 585614. |
| [60] | Xue C, Liu S, Chen C, Zhu J, Yang XB, Zhou Y, Guo R, Liu XY, Gong ZY (2018). Global proteome analysis links lysine acetylation to diverse functions in Oryza sativa. Pro- teomics 18, 1700036. |
| [61] | Xue C, Qiao ZY, Chen X, Cao PH, Liu K, Liu S, Ye L, Gong ZY (2020). Proteome-wide analyses reveal the diverse functions of lysine 2-hydroxyisobutyrylation in Oryza sativa. Rice 13, 34. |
| [62] | Xue H, Zhang QF, Wang PQ, Cao BJ, Jia CC, Cheng B, Shi YH, Guo WF, Wang ZL, Liu ZX, Cheng H (2022). QPTMplants: an integrative database of quantitative post- translational modifications in plants. Nucleic Acids Res 50, D1491-D1499. |
| [63] | Yang WQ, Zhang W, Wang XX (2017). Post-translational control of ABA signaling: the roles of protein phosphorylation and ubiquitination. Plant Biotechnol J 15, 4-14. |
| [64] | Yin XJ, Wang X, Komatsu S (2018). Phosphoproteomics: protein phosphorylation in regulation of seed germination and plant growth. Curr Protein Pept Sci 19, 401-412. |
| [65] | Ying YN, Hu YQ, Zhang YN, Tappiban P, Zhang ZW, Dai GX, Deng GF, Bao JS, Xu FF (2023a). Identification of a new allele of soluble starch synthase IIIa involved in the elongation of amylopectin long chains in a chalky rice mu- tant. Plant Sci 328, 111567. |
| [66] | Ying YN, Pang YH, Bao JS (2023b). Comparative ubiquitome analysis reveals diverse functions of ubiquitination in rice seed development under high-temperature stress. Seed Biol 2, 23. |
| [67] | Ying YN, Xu FF, Zhang ZW, Tappiban P, Bao JS (2022). Dynamic change in starch biosynthetic enzymes complexes during grain-filling stages in BEIIb active and deficient rice. Int J Mol Sci 23, 10714. |
| [68] | Yu GW, Gaoyang YZ, Liu L, Shoaib N, Deng YW, Zhang N, Li YP, Huang YB (2022). The structure, function, and regulation of starch synthesis enzymes SSIII with emphasis on maize. Agronomy 12, 1359. |
| [69] | Yu GW, Lv YA, Shen LY, Wang YB, Qing Y, Wu N, Li YP, Huang HH, Zhang N, Liu YH, Hu YF, Liu HM, Zhang JJ, Huang YB (2019). The proteomic analysis of maize endosperm protein enriched by phos-tagtm reveals the phosphorylation of Brittle-2 subunit of ADP-Glc pyrophosphorylase in starch biosynthesis process. Int J Mol Sci 20, 986. |
| [70] |
Yu HT, Wang T (2016). Proteomic dissection of endosperm starch granule associated proteins reveals a network coordinating starch biosynthesis and amino acid metabolism and glycolysis in rice endosperms. Front Plant Sci 7, 707.
DOI PMID |
| [71] | Zhang CQ, Zhu JH, Chen SJ, Fan XL, Li QF, Lu Y, Wang M, Yu HX, Yi CD, Tang SZ, Gu MH, Liu QQ (2019a). Wxlv, the ancestral allele of rice Waxy gene. Mol Plant 12, 1157-1166. |
| [72] | Zhang K, Xiong YH, Sun WX, Wang GL, Liu WD (2019b). Global proteomic analysis reveals widespread lysine succinylation in rice seedlings. Int J Mol Sci 20, 5911. |
| [73] | Zhang M, Lv DW, Ge P, Bian YW, Chen GX, Zhu GR, Li XH, Yan YM (2014a). Phosphoproteome analysis reveals new drought response and defense mechanisms of seedling leaves in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Proteomics 109, 290-308. |
| [74] | Zhang M, Ma CY, Lv DW, Zhen SM, Li XH, Yan YM (2014b). Comparative phosphoproteome analysis of the developing grains in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under well-watered and water-deficit conditions. J Proteome Res 13, 4281-4297. |
| [75] |
Zhang YM, Song LM, Liang WX, Mu P, Wang S, Lin Q (2016). Comprehensive profiling of lysine acetylproteome analysis reveals diverse functions of lysine acetylation in common wheat. Sci Rep 6, 21069.
DOI PMID |
| [76] |
Zhang ZH, Tan MJ, Xie ZY, Dai LZ, Chen Y, Zhao YM (2011). Identification of lysine succinylation as a new post-translational modification. Nat Chem Biol 7, 58-63.
DOI PMID |
| [77] | Zhang ZW, Ying YN, Zhang L, Dai GX, Deng GF, Bao JS, Xu FF (2023). Starch structural reasons for the effects of SSIIIa deficiency on the textural and digestive properties of cooked rice. J Cereal Sci 111, 103671. |
| [78] | Zhang ZX, Zhao H, Tang J, Li Z, Li Z, Chen DM, Lin WX (2014c). A proteomic study on molecular mechanism of poor grain-filling of rice (Oryza sativa L.) inferior spikelets. PLoS One 9, e89140. |
| [79] | Zhou X (2020). Genetic and Molecular Structural Basis for Resistant Starch and Other Functional Properties in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). PhD dissertation. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University. pp. 1-134. (in Chinese) |
| 周鑫 (2020). 稻米淀粉消化特性等功能性状的遗传与结构基础研究. 博士论文. 杭州: 浙江大学. pp. 1-134. | |
| [80] |
Zhu LY, Cheng H, Peng GQ, Wang SS, Zhang ZG, Ni ED, Fu XD, Zhuang CX, Liu ZX, Zhou H (2020). Ubiquitinome profiling reveals the landscape of ubiquitination regulation in rice young panicles. Genom Proteom Bioinf 18, 305-320.
DOI PMID |
| [1] |
Juan Cui, Xiaoyu Yu, Yuejiao Yu, Chengwei Liang, Jian Sun, Wenfu Chen.
Analysis of Texture Factors and Genetic Basis Influencing the Differences in Eating Quality between Northeast China and Japanese Japonica Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | Zhao Ling, Guan Ju, Liang Wenhua, Zhang Yong, Lu Kai, Zhao Chunfang, Li Yusheng, Zhang Yadong. Mapping of QTLs for Heat Tolerance at the Seedling Stage in Rice Based on a High-density Bin Map [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(3): 342-353. |
| [3] | Zhou Jing, Gao Fei. Advances in Iron Deficiency-induced Coumarin Biosynthesis and Their Functions in Iron Absorption in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(3): 460-471. |
| [4] | Haitao Hu, Yue Wu, Ling Yang. Research Progress on the NAD(P)+ Biosynthesis and Function in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(1): 114-131. |
| [5] | Xiuping Xu, Xiaoyu Yang, Min Feng. A New Cereal Seed Treatment Method for Displaying Endosperm Cell Structures Under Micro CT Scanning [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(1): 81-89. |
| [6] | Jianguo Li, Yi Zhang, Wenjun Zhang. Iron Plaque Formation and Its Effects on Phosphorus Absorption in Rice Roots [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(1): 132-143. |
| [7] | CAI Hui-Ying, LI Lan-Hui, LIN Yang, LIANG Ya-Tao, YANG Guang, SUN Long. Responses of non-structural carbohydrates in Betula platyphylla leaves and fine roots to time since fire [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2024, 48(6): 780-793. |
| [8] | Ruifeng Yao, Daoxin Xie. Activation and Termination of Strigolactone Signal Perception in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(6): 873-877. |
| [9] | Xuelan Fan, Yanjiao Luo, Chaoqun Xu, Baolin Guo. Research Progress on Genes Related to Flavonoids Biosynthesis in Herba Epimedii [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(5): 834-846. |
| [10] | Jinjin Lian, Luyao Tang, Yinuo Zhang, Jiaxing Zheng, Chaoyu Zhu, Yuhan Ye, Yuexing Wang, Wennan Shang, Zhenghao Fu, Xinxuan Xu, Richeng Wu, Mei Lu, Changchun Wang, Yuchun Rao. Genetic Locus Mining and Candidate Gene Analysis of Antioxidant Traits in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(5): 738-751. |
| [11] | Jiahui Huang, Huimin Yang, Xinyu Chen, Chaoyu Zhu, Yanan Jiang, Chengxiang Hu, Jinjin Lian, Tao Lu, Mei Lu, Weilin Zhang, Yuchun Rao. Response Mechanism of Rice Mutant pe-1 to Low Light Stress [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(4): 574-584. |
| [12] | Jianmin Zhou. A Combat Vehicle with a Smart Brake [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(3): 343-346. |
| [13] | Jing Xia, Yuchun Rao, Danyun Cao, Yi Wang, Linxin Liu, Yating Xu, Wangshu Mou, Dawei Xue. Research Progress on the Regulatory Mechanisms of OsACS and OsACO in Rice Ethylene Biosynthesis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(2): 291-301. |
| [14] | Chaoyu Zhu, Chengxiang Hu, Zhenan Zhu, Zhining Zhang, Lihai Wang, Jun Chen, Sanfeng Li, Jinjin Lian, Luyao Tang, Qianqian Zhong, Wenjing Yin, Yuexing Wang, Yuchun Rao. Mapping of QTLs Associated with Rice Panicle Traits and Candidate Gene Analysis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(2): 217-230. |
| [15] | Bao Zhu, Jiangzhe Zhao, Kewei Zhang, Peng Huang. OsCKX9 is Involved in Regulating the Rice Lamina Joint Development and Leaf Angle [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(1): 10-21. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||