

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (5): 834-846.DOI: 10.11983/CBB23133 cstr: 32102.14.CBB23133
• SPECIAL TOPICS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xuelan Fan1,2,†, Yanjiao Luo1,3,†, Chaoqun Xu1,*( ), Baolin Guo1,*(
), Baolin Guo1,*( )
)
Received:2023-09-22
Accepted:2024-03-18
Online:2024-09-10
Published:2024-08-19
Contact:
Chaoqun Xu, Baolin Guo
About author:First author contact: These authors contributed equally to this paper
Xuelan Fan, Yanjiao Luo, Chaoqun Xu, Baolin Guo. Research Progress on Genes Related to Flavonoids Biosynthesis in Herba Epimedii[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(5): 834-846.
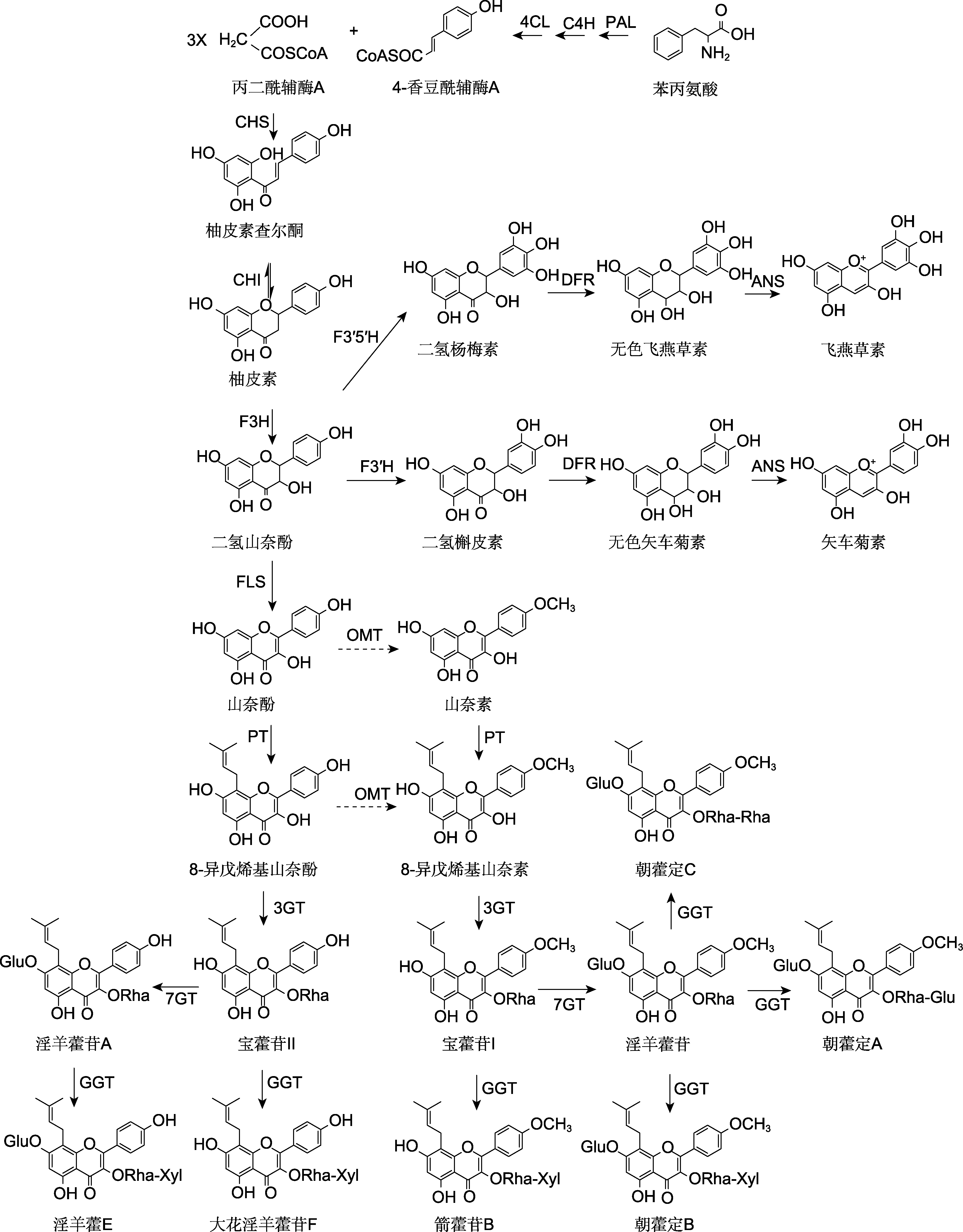
Figure 2 Flavonoid biosynthesis pathway in Epimedium plants 4CL: 4-coumarate:CoA ligase; C4H: Cinnamic acid 4-hydroxylase; PAL: Phenylalanine ammonia lyase; CHS: Chalcone synthase; CHI: Chalcone isomerase; DFR: Dihydro flavonol-4-reductase; ANS: Anthocyanidin synthase; F3H: Flavanone-3-hydroxylase; F3'H: Flavanone-3′-hydroxylase; F3'5'H: Flavanone-3′,5′-hydroxylase; FLS: Flavonol synthase; PT: Prenyltransferase; 3GT: 3-O-glycosyltransferase; GGT: 2"-O-glycosyltransferase; 7GT: 7-O-glycosyltransferase; OMT: O-methyltransferase
| 基因名 | 物种 | 功能 | 验证 方法 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EsPAL1 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 随着叶片的成熟, 表达量增高, 推测其可能参与木质素生物合成 | a | Zeng et al., |
| EsPAL2 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 在各发育阶段及组织中均表达, 推测其可能参与木质素、类黄酮和花青素的生物合成 | a | Zeng et al., |
| EsPAL3 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 主要在叶、花和蒴果中表达, 推测其主要参与花青素和4种主要活性成分的生物合成 | a | Zeng et al., |
| EwPAL | 巫山淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 催化L-苯丙氨酸和L-酪氨酸分别转化为肉桂酸和4-香豆酸 | b | Liu et al., |
| EpPAL2、EpC4H、Ep4CL3、Ep4CL2、EpCHS2、EpCHI1、EpCHI2、EpCHIL和EpF3H | 柔毛淫羊藿 | 表达模式与4种主要活性成分的积累模式呈正相关 | a | Zeng et al., |
| EsC4H和EsCHS1 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 表达模式与4种主要活性成分的积累模式无显著相关性 | a | Zeng et al., |
| Es4CL1、Es4CL2、EsCHS3和EsCHI2 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 表达模式与4种主要活性成分的积累模式呈负相关 | a | Zeng et al., |
| Ew4CL1 | 巫山淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 催化4-香豆酸和肉桂酸乙酰化, 分别转化为4-香豆素基-CoA和肉桂酰基-CoA | b | Liu et al., |
| Ew4CL2 | 巫山淫羊藿 | 与其它物种参与木质素生物合成的4CL基因聚成一簇, 推测其参与木质素的生物合成 | c | Liu et al., |
| EwCHS1 | 巫山淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 催化4-香豆素酰-CoA转化为柚皮素查尔酮和对香豆酰三乙酸内酯; 催化肉桂酰-CoA转化为松属素查尔酮和肉桂酰基三乙酸内酯 | b | Liu et al., |
| eppsCHS1 | 拟巫山淫羊藿 | 表达模式与4种主要活性成分的积累模式相关 | a | Pan et al., |
| EwCHI1 | 巫山淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 催化柚皮素查尔酮和松属素查尔酮环化形成(2S)-柚皮素和(2S)-松属素 | b | Liu et al., |
| EwCHIL3 | 巫山淫羊藿 | 与EwCHS1相互作用, 抑制对香豆酰三乙酸内酯和肉桂酰基三乙酸内酯产物的生成, 增加柚皮素和松属素的产生 | b | Liu et al., |
Table 1 Upstream genes of flavonoid metabolic pathway in Epimedium plants
| 基因名 | 物种 | 功能 | 验证 方法 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EsPAL1 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 随着叶片的成熟, 表达量增高, 推测其可能参与木质素生物合成 | a | Zeng et al., |
| EsPAL2 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 在各发育阶段及组织中均表达, 推测其可能参与木质素、类黄酮和花青素的生物合成 | a | Zeng et al., |
| EsPAL3 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 主要在叶、花和蒴果中表达, 推测其主要参与花青素和4种主要活性成分的生物合成 | a | Zeng et al., |
| EwPAL | 巫山淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 催化L-苯丙氨酸和L-酪氨酸分别转化为肉桂酸和4-香豆酸 | b | Liu et al., |
| EpPAL2、EpC4H、Ep4CL3、Ep4CL2、EpCHS2、EpCHI1、EpCHI2、EpCHIL和EpF3H | 柔毛淫羊藿 | 表达模式与4种主要活性成分的积累模式呈正相关 | a | Zeng et al., |
| EsC4H和EsCHS1 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 表达模式与4种主要活性成分的积累模式无显著相关性 | a | Zeng et al., |
| Es4CL1、Es4CL2、EsCHS3和EsCHI2 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 表达模式与4种主要活性成分的积累模式呈负相关 | a | Zeng et al., |
| Ew4CL1 | 巫山淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 催化4-香豆酸和肉桂酸乙酰化, 分别转化为4-香豆素基-CoA和肉桂酰基-CoA | b | Liu et al., |
| Ew4CL2 | 巫山淫羊藿 | 与其它物种参与木质素生物合成的4CL基因聚成一簇, 推测其参与木质素的生物合成 | c | Liu et al., |
| EwCHS1 | 巫山淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 催化4-香豆素酰-CoA转化为柚皮素查尔酮和对香豆酰三乙酸内酯; 催化肉桂酰-CoA转化为松属素查尔酮和肉桂酰基三乙酸内酯 | b | Liu et al., |
| eppsCHS1 | 拟巫山淫羊藿 | 表达模式与4种主要活性成分的积累模式相关 | a | Pan et al., |
| EwCHI1 | 巫山淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 催化柚皮素查尔酮和松属素查尔酮环化形成(2S)-柚皮素和(2S)-松属素 | b | Liu et al., |
| EwCHIL3 | 巫山淫羊藿 | 与EwCHS1相互作用, 抑制对香豆酰三乙酸内酯和肉桂酰基三乙酸内酯产物的生成, 增加柚皮素和松属素的产生 | b | Liu et al., |
| 基因名 | 物种 | 功能 | 验证 方法 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EsFLS | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 在烟草中过表达导致花中黄酮醇含量增加, 花青素含量降低 | a | Zeng et al., |
| eppsFLS1 | 拟巫山淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 分别催化二氢山奈酚和二氢槲皮素生成山奈酚和槲皮素 | b | Pan et al., |
| EpFLS3和EsUF3GT | 柔毛淫羊藿 箭叶淫羊藿 | 表达模式与4种主要活性成分的积累模式呈正相关 | a | Huang et al., |
| EsPT2 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 分别催化山奈酚、山奈素和柚皮素生成8-异戊烯基山奈酚、淫羊藿素(8-异戊烯基山奈素)和8-异戊烯基柚皮素 | b | Wang et al., |
| EpPT8 | 柔毛淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 分别催化山奈酚、槲皮素和芹菜素生成8-异戊烯基山奈酚、8-异戊烯基槲皮素和8-异戊烯基芹菜素 | b | Shen et al., |
| EkF8DT3 | 朝鲜淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 催化山奈酚生成8-异戊烯基山奈酚 | b | 周景文等, |
| EkF4′OMT1 | 朝鲜淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 催化8-异戊烯基山奈酚C4′-OH甲基化, 生成淫羊藿素 | b | 周景文等, |
| EsUF7GT | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 表达模式与4种主要活性成分的积累模式呈负相关 | a | Huang et al., |
| EkF3UGal | 朝鲜淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 分别催化淫羊藿素和多种不带异戊烯基类黄酮的C3-OH半乳糖基化, 生成8-异戊烯基山奈素-3-O-半乳糖和类黄酮- 3-O-半乳糖苷 | b | Lyu et al., |
| EkF3UGluT | 朝鲜淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 分别催化淫羊藿素和多种不带异戊烯基类黄酮的C3-OH葡萄糖基化, 生成8-异戊烯基山奈素-3-O-葡萄糖和类黄酮- 3-O-葡萄糖苷 | b | Lyu et al., |
| EkF3URhaT | 朝鲜淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 分别催化淫羊藿素和多种不带异戊烯基黄酮醇的C3-OH鼠李糖基化, 生成宝藿苷I和不含异戊烯基的黄酮醇-3-O-鼠李糖苷 | b | Lyu et al., |
| EpGT60 | 柔毛淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 分别催化8-异戊烯基山奈酚和淫羊藿素的C3-OH鼠李糖基化, 生成宝藿苷II和宝藿苷I | b | Yao et al., |
| EpPF3RT | 拟巫山淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 分别催化淫羊藿素、8-异戊烯基山奈酚、山奈酚和山奈素的C3-OH鼠李糖基化, 生成宝藿苷I、宝藿苷II、山奈酚- 3-O-鼠李糖苷和山奈素-3-O-鼠李糖苷 | b | Feng et al., |
| Ep7GT (EpGT8) | 拟巫山淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 分别催化宝藿苷I、宝藿苷II和山奈酚的C7-OH葡萄糖基化, 生成淫羊藿苷、朝藿定A和山奈酚-7-O-葡萄糖苷 | b | Feng et al., |
| EsGT1 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 分别催化宝藿苷I和山奈酚的C7-OH葡萄糖基化, 生成淫羊藿苷和山奈酚-7-O-葡萄糖苷 | b | Yang et al., |
| EwGGTa | 巫山淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 催化鼠李糖2′′-OH位加1分子葡萄糖, 使淫羊藿苷生成朝藿定A | b | 虞沂等, |
| EwGGTb | 巫山淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 催化鼠李糖2′′-OH位加1分子木糖, 使淫羊藿苷生成朝藿定B | b | 虞沂等, |
| EpF3R2"XylT | 柔毛淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 催化鼠李糖2′′-OH位加1分子木糖, 分别使淫羊藿苷、宝藿苷I、宝藿苷II和朝藿定A生成朝藿定B、箭藿苷B、大花淫羊藿苷F和淫羊藿苷E | b | Yao et al., |
Table 2 Genes in the flavonol glycosides biosynthesis pathways in Epimedium plants
| 基因名 | 物种 | 功能 | 验证 方法 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EsFLS | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 在烟草中过表达导致花中黄酮醇含量增加, 花青素含量降低 | a | Zeng et al., |
| eppsFLS1 | 拟巫山淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 分别催化二氢山奈酚和二氢槲皮素生成山奈酚和槲皮素 | b | Pan et al., |
| EpFLS3和EsUF3GT | 柔毛淫羊藿 箭叶淫羊藿 | 表达模式与4种主要活性成分的积累模式呈正相关 | a | Huang et al., |
| EsPT2 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 分别催化山奈酚、山奈素和柚皮素生成8-异戊烯基山奈酚、淫羊藿素(8-异戊烯基山奈素)和8-异戊烯基柚皮素 | b | Wang et al., |
| EpPT8 | 柔毛淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 分别催化山奈酚、槲皮素和芹菜素生成8-异戊烯基山奈酚、8-异戊烯基槲皮素和8-异戊烯基芹菜素 | b | Shen et al., |
| EkF8DT3 | 朝鲜淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 催化山奈酚生成8-异戊烯基山奈酚 | b | 周景文等, |
| EkF4′OMT1 | 朝鲜淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 催化8-异戊烯基山奈酚C4′-OH甲基化, 生成淫羊藿素 | b | 周景文等, |
| EsUF7GT | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 表达模式与4种主要活性成分的积累模式呈负相关 | a | Huang et al., |
| EkF3UGal | 朝鲜淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 分别催化淫羊藿素和多种不带异戊烯基类黄酮的C3-OH半乳糖基化, 生成8-异戊烯基山奈素-3-O-半乳糖和类黄酮- 3-O-半乳糖苷 | b | Lyu et al., |
| EkF3UGluT | 朝鲜淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 分别催化淫羊藿素和多种不带异戊烯基类黄酮的C3-OH葡萄糖基化, 生成8-异戊烯基山奈素-3-O-葡萄糖和类黄酮- 3-O-葡萄糖苷 | b | Lyu et al., |
| EkF3URhaT | 朝鲜淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 分别催化淫羊藿素和多种不带异戊烯基黄酮醇的C3-OH鼠李糖基化, 生成宝藿苷I和不含异戊烯基的黄酮醇-3-O-鼠李糖苷 | b | Lyu et al., |
| EpGT60 | 柔毛淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 分别催化8-异戊烯基山奈酚和淫羊藿素的C3-OH鼠李糖基化, 生成宝藿苷II和宝藿苷I | b | Yao et al., |
| EpPF3RT | 拟巫山淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 分别催化淫羊藿素、8-异戊烯基山奈酚、山奈酚和山奈素的C3-OH鼠李糖基化, 生成宝藿苷I、宝藿苷II、山奈酚- 3-O-鼠李糖苷和山奈素-3-O-鼠李糖苷 | b | Feng et al., |
| Ep7GT (EpGT8) | 拟巫山淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 分别催化宝藿苷I、宝藿苷II和山奈酚的C7-OH葡萄糖基化, 生成淫羊藿苷、朝藿定A和山奈酚-7-O-葡萄糖苷 | b | Feng et al., |
| EsGT1 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 分别催化宝藿苷I和山奈酚的C7-OH葡萄糖基化, 生成淫羊藿苷和山奈酚-7-O-葡萄糖苷 | b | Yang et al., |
| EwGGTa | 巫山淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 催化鼠李糖2′′-OH位加1分子葡萄糖, 使淫羊藿苷生成朝藿定A | b | 虞沂等, |
| EwGGTb | 巫山淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 催化鼠李糖2′′-OH位加1分子木糖, 使淫羊藿苷生成朝藿定B | b | 虞沂等, |
| EpF3R2"XylT | 柔毛淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 催化鼠李糖2′′-OH位加1分子木糖, 分别使淫羊藿苷、宝藿苷I、宝藿苷II和朝藿定A生成朝藿定B、箭藿苷B、大花淫羊藿苷F和淫羊藿苷E | b | Yao et al., |
| 基因名 | 物种 | 功能 | 验证方法 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EsF3′H、EsF3′5′H和EsANS | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 表达模式与叶片花青素的积累模式呈正相关 | a | Huang et al., |
| EsDFR1 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 表达模式与4种主要活性成分的积累模式无显著相关性 | a | Zeng et al., |
| EsDFR2 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 表达模式与4种主要活性成分的积累模式呈负相关 | a | Huang et al., |
| EpGT43 | 柔毛淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 以UDP-葡萄糖为供体, 催化矢车菊素3-O-鼠李糖苷。推测其酶活产物可能为矢车菊素3-O-(2- O-(-葡萄糖基))-鼠李糖苷 | b, c | 姚宇, |
Table 3 Genes in the anthocyanin pathways in Epimedium plants
| 基因名 | 物种 | 功能 | 验证方法 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EsF3′H、EsF3′5′H和EsANS | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 表达模式与叶片花青素的积累模式呈正相关 | a | Huang et al., |
| EsDFR1 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 表达模式与4种主要活性成分的积累模式无显著相关性 | a | Zeng et al., |
| EsDFR2 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 表达模式与4种主要活性成分的积累模式呈负相关 | a | Huang et al., |
| EpGT43 | 柔毛淫羊藿 | 体外功能验证: 以UDP-葡萄糖为供体, 催化矢车菊素3-O-鼠李糖苷。推测其酶活产物可能为矢车菊素3-O-(2- O-(-葡萄糖基))-鼠李糖苷 | b, c | 姚宇, |
| 基因名 | 物种 | 功能 | 验证 方法 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EsMYB1 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 与拟南芥中负调控肉桂酸-4-羟化酶的AtMYB4基因高度同源, 推测其为类黄酮生物合成转录抑制因子 | b | Huang et al., |
| EsMYB5和EsMYB11 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 与葡萄中调控原花青素生物合成的VvMYBPA2具有约50%的相似性, 推测其参与原花青素积累 | b | Huang et al., |
| EsMYB7和EsMYB10 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 与拟南芥中调控原花青素生物合成的AtTT2 (At- MYB123)高度同源, 推测其参与调节种皮中原花青素的积累 | b | Huang et al., |
| EsMYB9 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 单独作用时轻微激活EsCHS的启动子或与bHLH (EsTT8)相互作用强烈激活EsCHS、EsF3H、EsDFR1、EsDFR2和EsANS的启动子, 正调控花青素和黄酮醇的生物合成 | a, c | Huang et al., |
| EsMYB12 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 表达模式与4种主要活性成分的积累模式呈负相关 | a, b | Huang et al., |
| EsMYBA1 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 单独作用或者与bHLH (EsTT8)相互作用激活EsDFR和EsANS的启动子, 正调控花青素的生物合成 | a, c | Huang et al., |
| EsMYBF1 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 强烈激活EsF3H和EsFLS的启动子, 正调控叶片4种主要活性成分的生物合成 | a, c | Huang et al., |
| EsAN2 (MYB) | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 单独作用或与bHLH (EsTT8)相互作用激活早期和晚期花青素途径基因, 正调控花青素的生物合成 | a, c | Huang et al., |
| Ebr05G057070、Ebr05G003750、Ebr05G010200、Ebr05G056880、Ebr01G039680、Ebr01G039880 (MYB)、EsGL3 (bHLH)、EsTTG1 (WD40)、Ebr05G038380 (bZIP) 和Ebr03G071730 (WRKY) | 柔毛淫羊藿和箭叶淫羊藿 | 表达模式与4种主要活性成分的积累模式呈正相关 | a | Huang et al., |
| EsTT8 (bHLH) | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 表达模式与4种主要活性成分的积累模式呈负相关 | a | Huang et al., |
Table 4 Transcription factor genes in Epimedium plants
| 基因名 | 物种 | 功能 | 验证 方法 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EsMYB1 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 与拟南芥中负调控肉桂酸-4-羟化酶的AtMYB4基因高度同源, 推测其为类黄酮生物合成转录抑制因子 | b | Huang et al., |
| EsMYB5和EsMYB11 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 与葡萄中调控原花青素生物合成的VvMYBPA2具有约50%的相似性, 推测其参与原花青素积累 | b | Huang et al., |
| EsMYB7和EsMYB10 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 与拟南芥中调控原花青素生物合成的AtTT2 (At- MYB123)高度同源, 推测其参与调节种皮中原花青素的积累 | b | Huang et al., |
| EsMYB9 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 单独作用时轻微激活EsCHS的启动子或与bHLH (EsTT8)相互作用强烈激活EsCHS、EsF3H、EsDFR1、EsDFR2和EsANS的启动子, 正调控花青素和黄酮醇的生物合成 | a, c | Huang et al., |
| EsMYB12 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 表达模式与4种主要活性成分的积累模式呈负相关 | a, b | Huang et al., |
| EsMYBA1 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 单独作用或者与bHLH (EsTT8)相互作用激活EsDFR和EsANS的启动子, 正调控花青素的生物合成 | a, c | Huang et al., |
| EsMYBF1 | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 强烈激活EsF3H和EsFLS的启动子, 正调控叶片4种主要活性成分的生物合成 | a, c | Huang et al., |
| EsAN2 (MYB) | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 单独作用或与bHLH (EsTT8)相互作用激活早期和晚期花青素途径基因, 正调控花青素的生物合成 | a, c | Huang et al., |
| Ebr05G057070、Ebr05G003750、Ebr05G010200、Ebr05G056880、Ebr01G039680、Ebr01G039880 (MYB)、EsGL3 (bHLH)、EsTTG1 (WD40)、Ebr05G038380 (bZIP) 和Ebr03G071730 (WRKY) | 柔毛淫羊藿和箭叶淫羊藿 | 表达模式与4种主要活性成分的积累模式呈正相关 | a | Huang et al., |
| EsTT8 (bHLH) | 箭叶淫羊藿 | 表达模式与4种主要活性成分的积累模式呈负相关 | a | Huang et al., |
| [1] | Chen S, Wang XJ, Cheng Y, Gao HS, Chen XH (2023). A review of classification, biosynthesis, biological activities and potential applications of flavonoids. Molecules 28, 4982. |
| [2] | Levisson M, Beekwilder J, Vincken JP (2020). Plant aromatic prenyltransferases: tools for microbial cell factories. Trends Biotechnol 38, 917-934. |
| [3] | Dong XW, Fan YJ, Yu LJ, Hu YZ (2007). Synthesis of four natural prenylflavonoids and their estrogen-like activities. Arch Pharm 340, 372-376. |
| [4] | Feng KP, Chen RD, Xie KB, Chen DW, Guo BL, Liu X, Liu JM, Zhang M, Dai JG (2018). A regiospecific rhamnosyltransferase from Epimedium pseudowushanense catalyzes the 3-O-rhamnosylation of prenylflavonols. Org Biomol Chem 16, 452-458. |
| [5] | Feng KP, Chen RD, Xie KB, Chen DW, Liu JM, Du WY, Yang L, Dai JG (2019). Ep7GT, a glycosyltransferase with sugar donor flexibility from Epimedium pseudowushanense, catalyzes the 7-O-glycosylation of baohuoside. Org Biomol Chem 17, 8106-8114. |
| [6] | Gani I, Jameel S, Bhat SA, Amin H, Bhat KA (2023). Prenylated flavonoids of genus Epimedium: phytochemistry, estimation and synthesis. Chemistry Select 8, e202204263. |
| [7] | Hu DG, Sun CH, Zhang QY, An JP, You CX, Hao YJ (2016). Glucose sensor MdHXK1 phosphorylates and stabilizes MdbHLH3 to promote anthocyanin biosynthesis in apple. PLoS Genet 12, e1006273. |
| [8] | Huang WJ, Khaldun ABM, Chen JJ, Zhang CJ, Lv HY, Yuan L, Wang Y (2016a). A R2R3-MYB transcription factor regulates the flavonol biosynthetic pathway in a traditional Chinese medicinal plant, Epimedium sagittatum. Front Plant Sci 7, 1089. |
| [9] | Huang WJ, Khaldun ABM, Lv HY, Du LW, Zhang CJ, Wang Y (2016b). Isolation and functional characterization of a R2R3-MYB regulator of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway from Epimedium sagittatum. Plant Cell Rep 35, 883-894. |
| [10] | Huang WJ, Lv HY, Wang Y (2017). Functional characterization of a novel R2R3-MYB transcription factor modulating the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway from Epimedium sagittatum. Front Plant Sci 8, 1274. |
| [11] | Huang WJ, Sun W, Lv HY, Luo M, Zeng SH, Pattanaik S, Yuan L, Wang Y (2013a). A R2R3-MYB transcription factor from Epimedium sagittatum regulates the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway. PLoS One 8, e70778. |
| [12] | Huang WJ, Sun W, Lv HY, Xiao G, Zeng SH, Wang Y (2013b). Isolation and molecular characterization of thirteen R2R3-MYB transcription factors from Epimedium sagittatum. Int J Mol Sci 14, 594-610. |
| [13] | Huang WJ, Sun W, Wang Y (2012). Isolation and molecular characterisation of flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase and flavonoid 3′,5′-hydroxylase genes from a traditional Chinese medicinal plant, Epimedium sagittatum. Gene 497, 125-130. |
| [14] | Huang WJ, Zeng SH, Xiao G, Wei GY, Liao SH, Chen JJ, Sun W, Lv HY, Wang Y (2015). Elucidating the biosynthetic and regulatory mechanisms of flavonoid-derived bioactive components in Epimedium sagittatum. Front Plant Sci 6, 689. |
| [15] | Jiang J, Song J, Jia XB (2015). Phytochemistry and ethnopharmacology of Epimedium L. species. Chin Herb Med 7, 204-222. |
| [16] | Jiang YH, Liu CH, Yan D, Wen XH, Liu YL, Wang HJ, Dai JY, Zhang YJ, Liu YF, Zhou B, Ren XL (2017). MdHB1 down-regulation activates anthocyanin biosynthesis in the white-fleshed apple cultivar ‘Granny Smith’. J Exp Bot 68, 1055-1069. |
| [17] | Kawai Y, Ono E, Mizutani M (2014). Evolution and diversity of the 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase superfamily in plants. Plant J 78, 328-343. |
| [18] | Kawamura T, Hayashi M, Mukai R, Terao J, Nemoto H (2012). An efficient method for C8-prenylation of flavonols and flavanones. Synthesis 44, 1308-1314. |
| [19] | Kim DH, Jung HA, Sohn HS, Kim JW, Choi JS (2017). Potential of icariin metabolites from Epimedium koreanum Nakai as antidiabetic therapeutic agents. Molecules 22, 986. |
| [20] | Li C, Wu J, Hu KD, Wei SW, Sun HY, Hu LY, Han Z, Yao GF, Zhang H (2020). PyWRKY26 and PybHLH3 cotargeted the PyMYB114 promoter to regulate anthocyanin biosynthesis and transport in red-skinned pears. Hortic Res 7, 37. |
| [21] | Lin CC, Chen DW, Dai JG (2022). Advances of synthetic biology of flavonoids. Acta Pharm Sin 57, 1322-1335. (in Chinese) |
| 林春草, 陈大伟, 戴均贵 (2022). 黄酮类化合物合成生物学研究进展. 药学学报 57, 1322-1335. | |
| [22] | Liu JY, Osbourn A, Ma PD (2015). MYB transcription factors as regulators of phenylpropanoid metabolism in plants. Mol Plant 8, 689-708. |
| [23] | Liu SA, Wang L, Cao M, Pang SY, Li WX, Kato-Noguchi H, Jin B, Wang L (2020). Identification and characterization of long non-coding RNAs regulating flavonoid biosynthesis in Ginkgo biloba leaves. Ind Crops Prod 158, 112980. |
| [24] | Liu WX, Feng Y, Yu SH, Fan ZQ, Li XL, Li JY, Yin HF (2021a). The flavonoid biosynthesis network in plants. Int J Mol Sci 22, 12824. |
| [25] | Liu YT, Wu LR, Deng ZX, Yu Y (2021b). Two putative parallel pathways for naringenin biosynthesis in Epimedium wushanense. RSC Adv 11, 13919-13927. |
| [26] | Lu SW, Zhuge YX, Hao TY, Liu ZJ, Zhang MW, Fang JG (2022). Systematic analysis reveals O-methyltransferase gene family members involved in flavonoid biosynthesis in grape. Plant Physiol Biochem 173, 33-45. |
| [27] | Lyu YB, Liu SK, Gao S, Zhou JW (2020). Identification and characterization of three flavonoid 3-O-glycosyltransferases from Epimedium koreanum Nakai. Biochem Eng J 163, 107759. |
| [28] | Ma HP, He XR, Yang Y, Li MX, Hao DJ, Jia ZP (2011). The genus Epimedium: an ethnopharmacological and phytochemical review. J Ethnopharmacol 134, 519-541. |
| [29] | Mi YL, He RK, Wan HH, Meng XX, Liu D, Huang WJ, Zhang YJ, Yousaf Z, Huang HW, Chen SL, Wang Y, Sun W (2023). Genetic and molecular analysis of the anthocyanin pigmentation pathway in Epimedium. Front Plant Sci 14, 1133616. |
| [30] | Moummou H, Kallberg Y, Tonfack LB, Persson B, van der Rest B (2012). The plant short-chain dehydrogenase (SDR) superfamily: genome-wide inventory and diversification patterns. BMC Plant Biol 12, 219. |
| [31] | Pan JQ (2017). The Effects and Molecular Mechanism of Light on the Physiological Characteristics and Flavonoid Synthesis in Epimedium pseudowushanense B. L.Guo. PhD dissertation. Beijing: Peking Union Medical College. pp. 1-164. (in Chinese) |
| 潘俊倩 (2017). 光影响拟巫山淫羊藿生理特性以及黄酮类化合物合成的分子机制初步研究. 博士论文. 北京: 北京协和医学院. pp. 1-164. | |
| [32] | Pan JQ, Chen HM, Guo BL, Liu C (2017). Understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying the effects of light intensity on flavonoid production by RNA-seq analysis in Epimedium pseudowushanense B.L.Guo. PLoS One 12, e0182348. |
| [33] | Qin WH, Yang Y, Wang YH, Zhang XM, Liu X (2022). Transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis reveals the difference between large and small flower taxa of Herba Epimedii during flavonoid accumulation. Sci Rep 12, 2762. |
| [34] | Ren L, Dai SL, Wang Y (2008). The germplasm resources of Epimedium in China and its application in landscape architecture. J Wuhan Bot Res 26, 644-649. (in Chinese) |
| 任璘, 戴思兰, 王瑛 (2008). 淫羊藿属植物种质资源及其园林应用. 武汉植物学研究 26, 644-649. | |
| [35] | Schijlen EGWM, de Vos CHR, Martens S, Jonker HH, Rosin FM, Molthoff JW, Tikunov YM, Angenent GC, van Tunen AJ, Bovy AG (2007). RNA interference silencing of chalcone synthase, the first step in the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway, leads to parthenocarpic tomato fruits. Plant Physiol 144, 1520-1530. |
| [36] | Shen GA, Luo YJ, Yao Y, Meng GQ, Zhang YX, Wang YY, Xu CQ, Liu X, Zhang C, Ding G, Pang YZ, Zhang H, Guo BL (2022a). The discovery of a key prenyltransferase gene assisted by a chromosome-level Epimedium pubescens genome. Front Plant Sci 13, 1034943. |
| [37] | Shen N, Wang TF, Gan Q, Liu SA, Wang L, Jin B (2022b). Plant flavonoids: classification, distribution, biosynthesis, and antioxidant activity. Food Chem 383, 132531. |
| [38] | Stracke R, Favory JJ, Gruber H, Bartelniewoehner L, Bartels S, Binkert M, Funk M, Weisshaar B, Ulm R (2010). The Arabidopsis bZIP transcription factor HY5 regulates expression of the PFG1/MYB12 gene in response to light and ultraviolet-B radiation. Plant Cell Environ 33, 88-103. |
| [39] | Turnbull JJ, Sobey WJ, Aplin RT, Hassan A, Firmin JL, Schofield CJ, Prescott AG (2000). Are anthocyanidins the immediate products of anthocyanidin synthase? Chem Commun (24), 2473-2474. |
| [40] | Vogt T, Jones P (2000). Glycosyltransferases in plant natural product synthesis: characterization of a supergene family. Trends Plant Sci 5, 380-386. |
| [41] | Wang J, Chu SS, Zhu Y, Cheng H, Yu DY (2015). Positive selection drives neofunctionalization of the UbiA prenyltransferase gene family. Plant Mol Biol 87, 383-394. |
| [42] | Wang PP, Li CJ, Li XD, Huang WJ, Wang Y, Wang JL, Zhang YJ, Yang XM, Yan X, Wang Y, Zhou ZH (2021). Complete biosynthesis of the potential medicine icaritin by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Escherichia coli. Sci Bull 66, 1906-1916. |
| [43] | Wilson AE, Tian L (2019). Phylogenomic analysis of UDP-dependent glycosyltransferases provides insights into the evolutionary landscape of glycosylation in plant metabolism. Plant J 100, 1273-1288. |
| [44] | Xu CQ, Liu X, Shen GA, Fan XL, Zhang Y, Sun C, Suo FM, Guo BL (2023). Time-series transcriptome provides insights into the gene regulation network involved in the icariin-flavonoid metabolism during the leaf development of Epimedium pubescens. Front Plant Sci 14, 1183481. |
| [45] | Xu WJ, Dubos C, Lepiniec L (2015). Transcriptional control of flavonoid biosynthesis by MYB-bHLH-WDR complexes. Trends Plant Sci 20, 176-185. |
| [46] | Yang XM, Chen JJ, Huang WJ, Zhang YJ, Yan X, Zhou ZH, Wang Y (2020). Synthesis of icariin in tobacco leaf by overexpression of a glucosyltransferase gene from Epimedium sagittatum. Ind Crops Prod 156, 112841. |
| [47] | Yao Y (2023). Cloning and Characterization of UDP-glycosyltransferases UGT 79 Family of Epimedium pubescens. PhD dissertation. Beijing: Peking Union Medical Col- lege. pp. 1-126. (in Chinese) |
| 姚宇 (2023). 柔毛淫羊藿糖基转移酶UGT79家族基因的克隆及功能研究. 博士论文. 北京: 北京协和医学院. pp. 1- 126. | |
| [48] | Yao Y, Gu JJ, Luo YJ, Wang YY, Pang YZ, Shen GA, Guo BL (2022a). Genome-wide analysis of UGT gene family identified key gene for the biosynthesis of bioactive flavonol glycosides in Epimedium pubescens Maxim. Synth Syst Biotechnol 7, 1095-1107. |
| [49] | Yao Y, Gu JJ, Luo YJ, Zhang YX, Wang YY, Pang YZ, Jia SG, Xu CQ, Li DD, Suo FM, Shen GA, Guo BL (2022b). A novel 3-O-rhamnoside: 2′′-O-xylosyltransferase responsible for terminal modification of prenylflavonol glycosides in Epimedium pubescens Maxim. Int J Mol Sci 23, 16050. |
| [50] | Yoshitama K (1984). Anthocyanins and their distribution in the genus Epimedium. Bot Mag Tokyo 97, 429-435. |
| [51] | Yu Y, Cao YL, Liu YT (2022). Glycosyltransferase and its coding gene for the synthesis of Epimedin and its applications. Chinese patent, ZL202111673688.6. 2021-12-31. (in Chinese) |
| 虞沂, 曹应龙, 刘亚婷 (2022). 朝藿定合成用糖苷糖基转移酶及其编码基因和应用. 中国专利, ZL202111673688.6. 2021-12-31. | |
| [52] | Zeng SH, Liu YL, Hu WM, Liu YL, Shen XF, Wang Y (2013a). Integrated transcriptional and phytochemical analyses of the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway in Epimedium. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 115, 355-365. |
| [53] | Zeng SH, Liu YL, Zou CY, Huang WJ, Wang Y (2013b). Cloning and characterization of phenylalanine ammonia- lyase in medicinal Epimedium species. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 113, 257-267. |
| [54] | Zhang DW, Cheng Y, Wang NL, Zhang JC, Yang MS, Yao XS (2008). Effects of total flavonoids and flavonol glycosides from Epimedium koreanum Nakai on the proliferation and differentiation of primary osteoblasts. Phytome- dicine 15, 55-61. |
| [55] | Zhang HR, Du C, Wang Y, Wang J, Zheng LL, Wang YC (2016). The Reaumuria trigyna leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase (RtLDOX) gene complements anthocyanidin synthesis and increases the salt tolerance potential of a transgenic Arabidopsis LDOX mutant. Plant Physiol Biochem 106, 278-287. |
| [56] | Zhang YX, Zhang C, Li ZH, Zeng C, Xue Z, Li EW, Li G, Li J, Shen GA, Xu CQ, Wang YY, Ma BP, Zhang H, Guo BL (2022). New 8-prenylated quercetin glycosides from the flowers of Epimedium acuminatum and their testosterone production-promoting activities. Front Chem 10, 1014110. |
| [57] | Zhao H, Guo YM, Li S, Han RQ, Ying JM, Zhu H, Wang YY, Yin L, Han YQ, Sun LZ, Wang ZY, Lin QC, Bi XY, Jiao YC, Jia HY, Zhao JJ, Huang Z, Li ZY, Zhou JG, Song W, Meng K, Cai JQ (2015). A novel anti-cancer agent Icaritin suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma initiation and malignant growth through the IL-6/Jak2/Stat3 pathway. Oncotarget 6, 31927-31943. |
| [58] | Zhao JY, Ohba S, Shinkai M, Chung UI, Nagamune T (2008). Icariin induces osteogenic differentiation in vitro in a BMP- and Runx2-dependent manner. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 369, 444-448. |
| [59] | Zhou JW, Gao S, Chen J, Zeng WZ, Yu SQ (2023a). A flavonoid 4′-O-methyltransferase derived from Epimedium koreanum and its application. Chinese patent, CN202111098372.9. 2021-09-18. (in Chinese) |
| 周景文, 高松, 陈坚, 曾伟主, 余世琴 (2023a). 一种来源于朝鲜淫羊藿的黄酮4′-O-甲基转移酶及其应用. 中国专利, CN202111098372.9. 2021-09-18. | |
| [60] | Zhou JW, Yu SQ, Chen J, Zeng WZ, Gao S (2023b). A flavonoid 8-isoprenyl transferase derived from Epimedium koreanum Nakai and its application. Chinese patent, CN2021- 11098375. 2. 2021-09-18. (in Chinese) |
| 周景文, 余世琴, 陈坚, 曾伟主, 高松 (2023b). 一种朝鲜淫羊藿来源的黄酮8-异戊烯基转移酶及其应用. 中国专利, CN202111098375.2. 2021-09-18. | |
| [61] | Zhu JF, Li ZJ, Zhang GS, Meng K, Kuang WY, Li J, Zhou XF, Li RJ, Peng HL, Dai CW, Shen JK, Gong FJ, Xu YX, Liu SF (2011). Icaritin shows potent anti-leukemia activity on chronic myeloid leukemia in vitro and in vivo by regulating MAPK/ERK/JNK and JAK2/STAT3/AKT signalings. PLoS One 6, e23720. |
| [1] | Zhou Jing, Gao Fei. Advances in Iron Deficiency-induced Coumarin Biosynthesis and Their Functions in Iron Absorption in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(3): 460-471. |
| [2] | Xinyu Li, Yue Gu, Feifei Xu, Jinsong Bao. Research Progress on Post-translational Modifications of Starch Biosynthesis-related Proteins in Rice Endosperm [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(2): 256-270. |
| [3] | Haitao Hu, Yue Wu, Ling Yang. Research Progress on the NAD(P)+ Biosynthesis and Function in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(1): 114-131. |
| [4] | Jing Xia, Yuchun Rao, Danyun Cao, Yi Wang, Linxin Liu, Yating Xu, Wangshu Mou, Dawei Xue. Research Progress on the Regulatory Mechanisms of OsACS and OsACO in Rice Ethylene Biosynthesis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(2): 291-301. |
| [5] | Xiaoxiao Liu, Di Gong, Tianpeng Gao, Lina Yin, Shiwen Wang. The Major Membrane Lipids in Plant Thylakoids and Their Biosynthesis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(1): 144-155. |
| [6] | Haitao Hu, Longbiao Guo. Progress in the Research on Riboflavin Biosynthesis and Function in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(4): 638-655. |
| [7] | Yanjun Guo, Feng Chen, Jingwen Luo, Wei Zeng, Wenliang Xu. The Biosynthesis of Plant Cell Wall Xylan and Its Application [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(2): 316-334. |
| [8] | Yu Miao, Ruan Chengjiang, Ding Jian, Li Jingbin, Lu Shunguang, Wen Xiufeng. Hrh-miRn458 Regulates Oil Biosynthesis of Sea Buckthorn via Targeting Transcription Factor WRI1 [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(5): 635-648. |
| [9] | Deshuai Liu, Lei Yao, Weirong Xu, Mei Feng, Wenkong Yao. Research Progress of Melatonin in Plant Stress Resistance [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(1): 111-126. |
| [10] | Peipei Liu, Geng Zhang, Xiaojuan Li. Biosynthesis and Function of Plant Pectin [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(2): 191-200. |
| [11] | Yu Zhang, Mingjie Zhao, Wei Zhang. Transcriptional Regulatory Network of Secondary Cell Wall Biosynthesis in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(3): 351-368. |
| [12] | Yanmei Dong, Wenying Zhang, Zhengyi Ling, Jingrui Li, Hongtong Bai, Hui Li, Lei Shi. Advances in Transcription Factors Regulating Plant Terpenoids Biosynthesis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(3): 340-350. |
| [13] | Wei Chen,Xiaoxian Zeng,Chuping Xie,Chang’en Tian,Yuping Zhou. The Dynamic Regulation Mechanism of the Endo-genous ABA in Plant [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(6): 677-687. |
| [14] | Ruijun Duan, Aidong Wang, Guoxiong Chen. Advances in Study of Plant Cuticle Genes [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2017, 52(5): 637-651. |
| [15] | Xueyuan Han, Linchun Mao. Research Progress on Constituents, Histochemical Characteristics and Biosynthesis of Suberin [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2017, 52(3): 358-374. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||