

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (2): 291-301.DOI: 10.11983/CBB23143 cstr: 32102.14.CBB23143
• SPECIAL TOPICS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jing Xia1,†, Yuchun Rao2,†, Danyun Cao1, Yi Wang1, Linxin Liu1, Yating Xu1, Wangshu Mou1,*( ), Dawei Xue1,*(
), Dawei Xue1,*( )
)
Received:2023-10-29
Accepted:2024-01-30
Online:2024-03-10
Published:2024-03-10
Contact:
* E-mail: About author:† These authors contributed equally to this paper
Jing Xia, Yuchun Rao, Danyun Cao, Yi Wang, Linxin Liu, Yating Xu, Wangshu Mou, Dawei Xue. Research Progress on the Regulatory Mechanisms of OsACS and OsACO in Rice Ethylene Biosynthesis[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(2): 291-301.

Figure 2 Phylogenetic tree of the ACC synthase (ACS) protein sequences of Oryza sativa (Os), Hordeum vulgare (Hv), Arabidopsis thaliana (At) and Solanum lycopersicum (Sl)
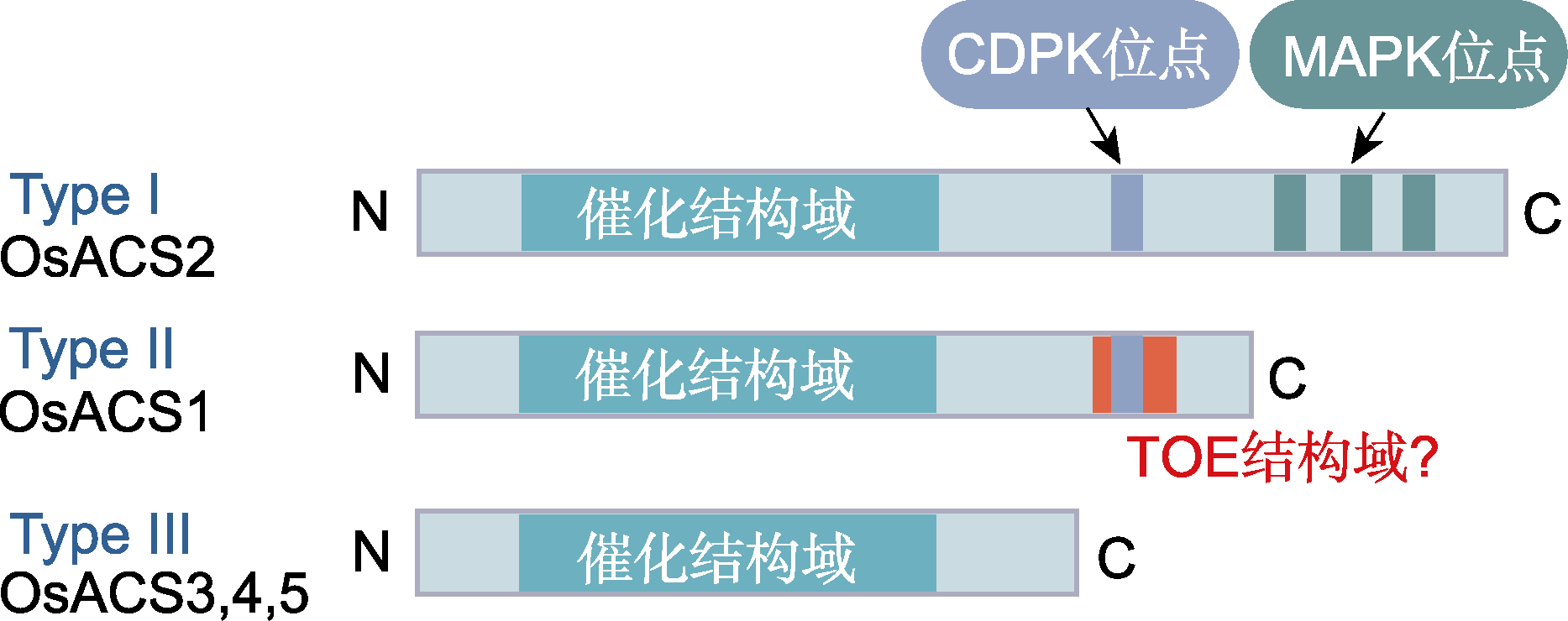
Figure 3 The structure of three types of ACS proteins in rice (refer to Lee and Yoon, 2018) CDPK: Calcium-dependent protein kinase; MAPK: Mitogen- activated protein kinase. ACS is the same as shown in Figure 2.

Figure 4 Sequence alignment of C-terminal amino acids of Type II ACSs from Oryza sativa (Os), Arabidopsis thaliana (At) and Solanum lycopersicum (Sl) The near invariant TOE motif sequence WVFRLSF/W are shown in red, while the possible conserved TOE motif in OsACS1 is marked with red box. ACS is the same as shown in Figure 2.
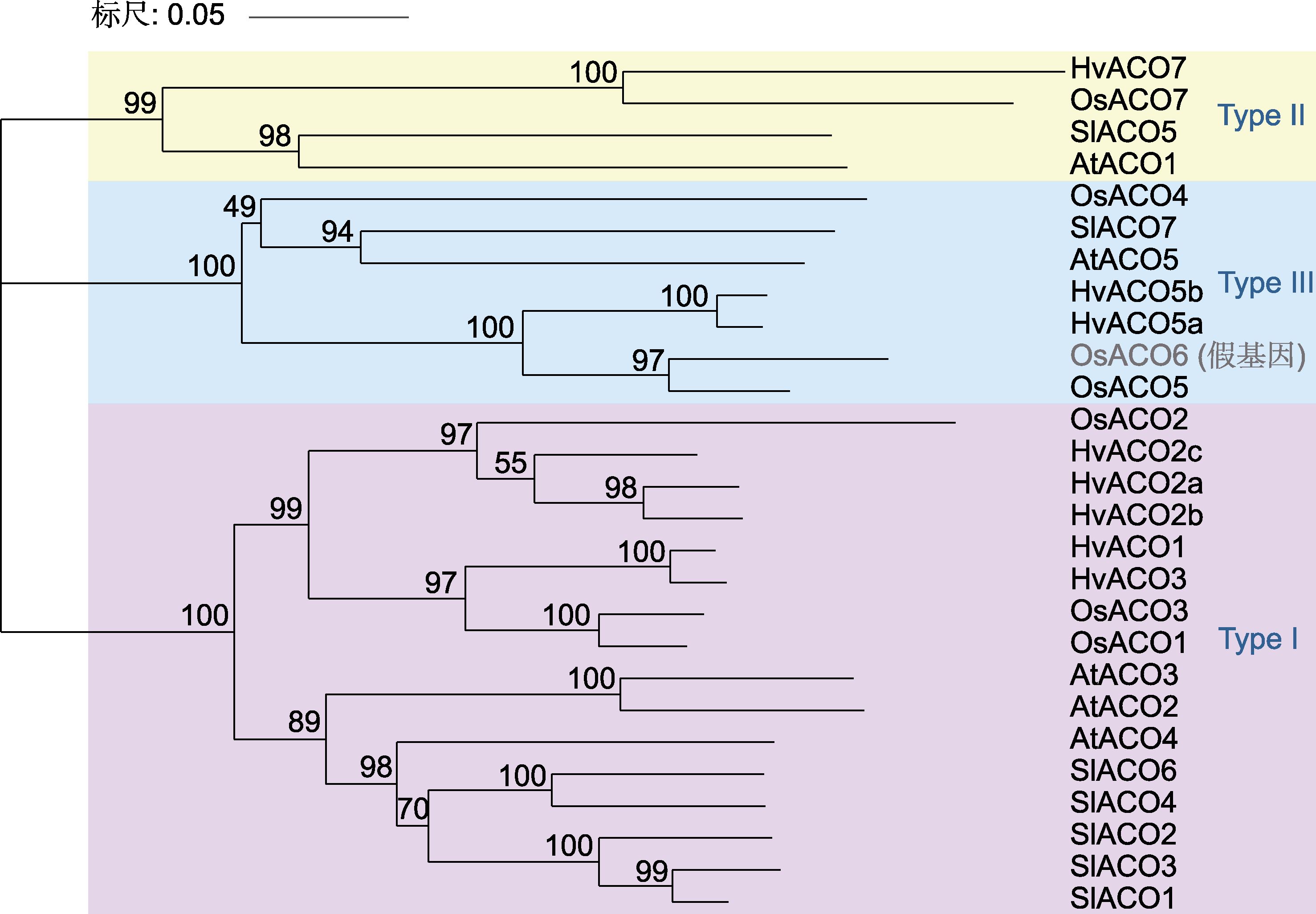
Figure 5 Phylogenetic tree for ACC oxidase (ACO) protein sequences of Oryza sativa (Os), Hordeum vulgare (Hv), Arabidopsis thaliana (At) and Solanum lycopersicum (Sl)
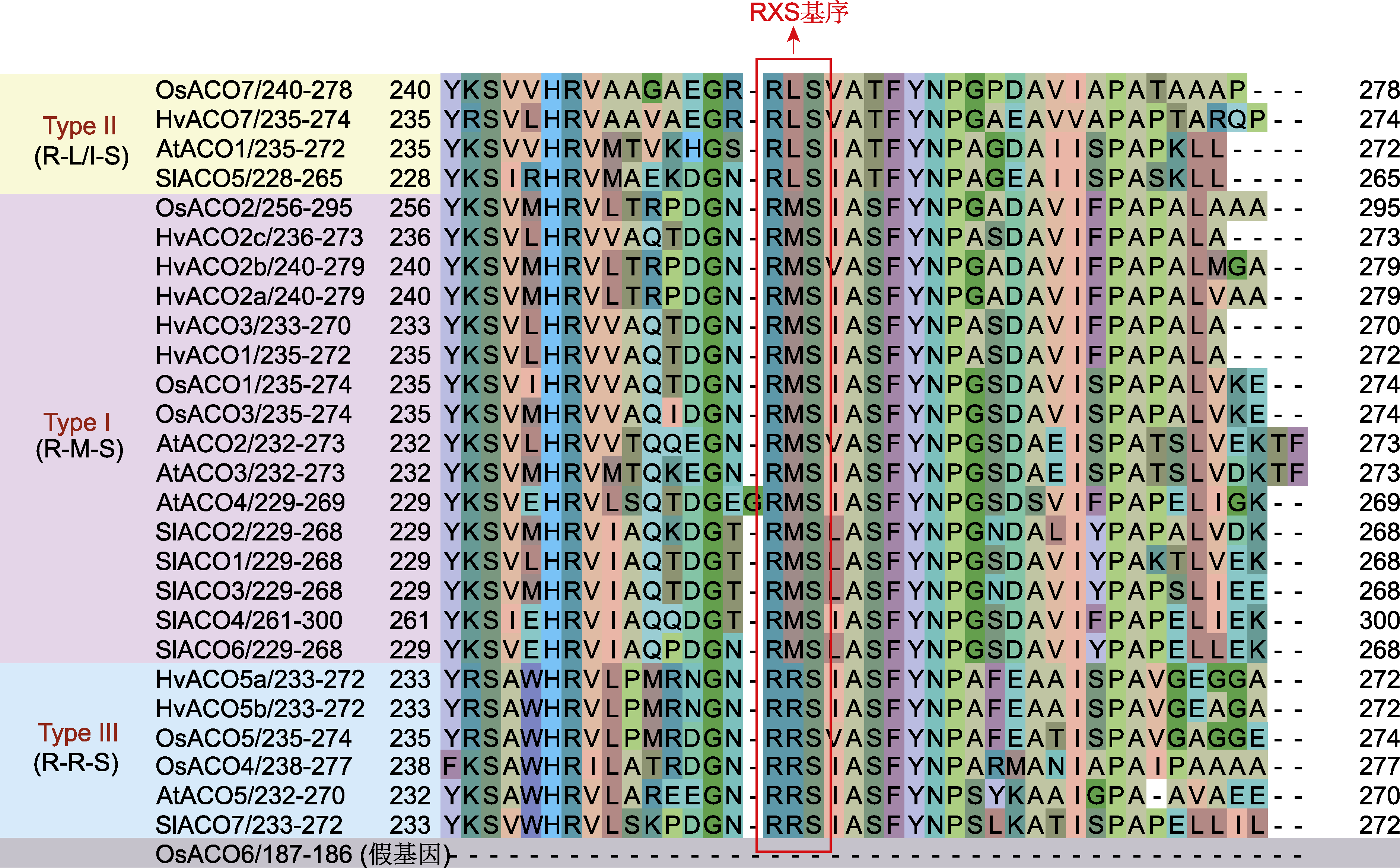
Figure 6 ACO protein sequence alignment of Oryza sativa (Os), Hordeum vulgare (Hv), Arabidopsis thaliana (At) and Solanum lycopersicum (Sl) ACO is the same as shown in Figure 5.
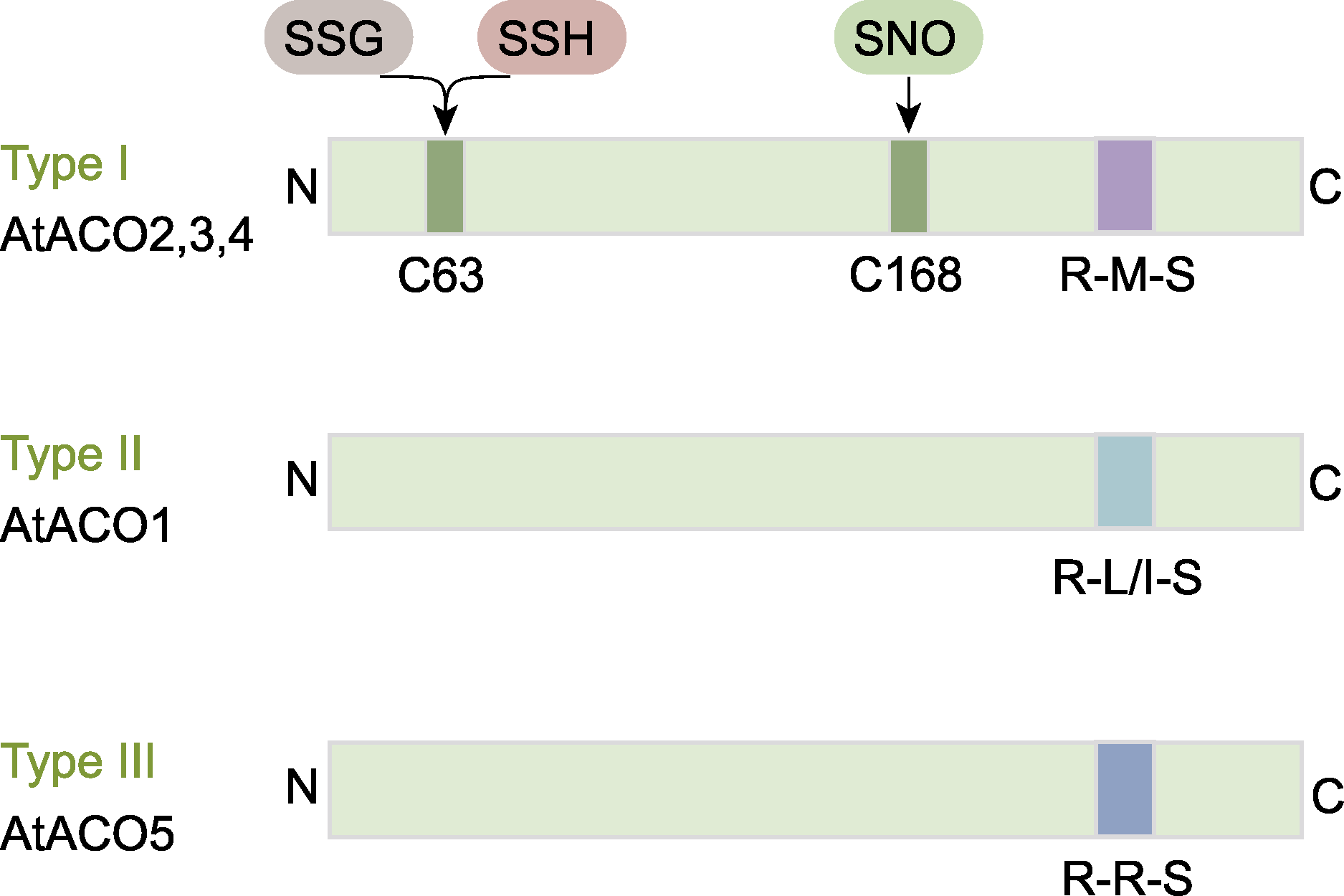
Figure 7 The structure of three types of ACO proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana (refer to Pattyn et al., 2021) Post-translational modifications at C63 include S-glutathionylation (SSG) and S-sulfhydration (SSH), while modifications at C168 involve S-nitrosylation (SNO). ACO is the same as shown in Figure 5.

Figure 8 AtACO2 and OsACOs protein sequence alignment The blue stars represent the two conserved cysteine residue sites (C63 and C168) in AtACO2, and red box indicates the conserved cysteine residues (C168) of the OsACOs.
| [1] | Ahmadizadeh M, Chen JT, Hasanzadeh S, Ahmar S, Heidari P (2020). Insights into the genes involved in the ethylene biosynthesis pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana and Oryza sativa. J Genet Engin Biotechnol 18, 62. |
| [2] |
Althiab-Almasaud R, Sallanon H, Chang CR, Chervin C (2021). 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid stimulates tomato pollen tube growth independently of ethylene receptors. Physiol Plant 173, 2291-2297.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
Argueso CT, Hansen M, Kieber JJ (2007). Regulation of ethylene biosynthesis. J Plant Growth Regul 26, 92-105.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Aroca A, Benito JM, Gotor C, Romero LC (2017). Persulfidation proteome reveals the regulation of protein function by hydrogen sulfide in diverse biological processes in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 68, 4915-4927.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | Booker MA, DeLong A (2015). Producing the ethylene signal: regulation and diversification of ethylene biosynthetic enzymes. Plant Physiol 169, 42-50. |
| [6] |
Chae HS, Faure F, Kieber JJ (2003). The eto1, eto2, and eto3 mutations and cytokinin treatment increase ethylene biosynthesis in Arabidopsis by increasing the stability of ACS protein. Plant Cell 15, 545-559.
PMID |
| [7] |
Chen J, Wang X, Zhang WW, Zhang SQ, Zhao FJ (2020). Protein phosphatase 2A alleviates cadmium toxicity by modulating ethylene production in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Environ 43, 1008-1022.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Christians MJ, Gingerich DJ, Hansen M, Binder BM, Kieber JJ, Vierstra RD (2009). The BTB ubiquitin ligases ETO1, EOL1 and EOL2 act collectively to regulate ethylene biosynthesis in Arabidopsis by controlling type-2 ACC synthase levels. Plant J 57, 332-345.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Datta R, Kumar D, Sultana A, Hazra S, Bhattacharyya D, Chattopadhyay S (2015). Glutathione regulates 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase transcription via WRKY33 and 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate oxidase by modulating messenger RNA stability to induce ethylene synthesis during stress. Plant Physiol 169, 2963-2981.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | Dilley DR, Wang ZY, Kadirjan-Kalbach DK, Ververidis F, Beaudry R, Padmanabhan K (2013). 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid oxidase reaction mechanism and putative post-translational activities of the ACCO protein. AoB Plants 5, plt031. |
| [11] |
Du H, Wu N, Cui F, You L, Li XH, Xiong LZ (2014). A homolog of ETHYLENE OVERPRODUCER, OsETOL1, differentially modulates drought and submergence tolerance in rice. Plant J 78, 834-849.
DOI URL |
| [12] | Freeman AK, Morrison DK (2011). 14-3-3 proteins: diverse functions in cell proliferation and cancer progression. Semi Cell Devel Biol 22, 681-687. |
| [13] | Han L, Li GJ, Yang KY, Mao GH, Wang RG, Liu YD, Zhang SQ (2010). Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 and 6 regulate Botrytis cinerea-induced ethylene production in Arabidopsis. Plant J 64, 114-127. |
| [14] | Houben M, Van de Poel B(2019). 1-aminocyclopropane- 1-carboxylic acid oxidase (ACO): the enzyme that makes the plant hormone ethylene. Front Plant Sci 10, 695. |
| [15] | Hu JL, Huang XH, Chen LC, Sun XW, Lu CM, Zhang LX, Wang YC, Zuo JR (2015). Site-specific nitrosoproteomic identification of endogenously S-nitrosylated proteins in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 167, 1731-1746. |
| [16] | Iwai T, Miyasaka A, Seo S, Ohashi Y (2006). Contribution of ethylene biosynthesis for resistance to blast fungus infection in young rice plants. Plant Physiol 142, 1202-1215. |
| [17] |
Iwamoto M, Takano M (2011). Phytochrome-regulated EBL1 contributes to ACO1 upregulation in rice. Biotechnol Lett 33, 173-178.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Jia HL, Chen SS, Liu D, Liesche J, Shi C, Wang J, Ren MJ, Wang XF, Yang J, Shi W, Li JS (2018). Ethylene-induced hydrogen sulfide negatively regulates ethylene biosynthesis by persulfidation of ACO in tomato under osmotic stress. Front Plant Sci 9, 1517.
DOI PMID |
| [19] | Joo S, Liu YD, Lueth A, Zhang SQ (2008). MAPK phosphorylation-induced stabilization of ACS6 protein is mediated by the non-catalytic C-terminal domain, which also contains the cis-determinant for rapid degradation by the 26S proteasome pathway. Plant J 54, 129-140. |
| [20] |
Kawai Y, Ono E, Mizutani M (2014). Evolution and diversity of the 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase superfamily in plants. Plant J 78, 328-343.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Lee HY, Chen YC, Kieber JJ, Yoon GM (2017). Regulation of the turnover of ACC synthases by phytohormones and heterodimerization in Arabidopsis. Plant J 91, 491-504.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Lee HY, Park HL, Park C, Chen YC, Yoon GM (2021). Reciprocal antagonistic regulation of E3 ligases controls ACC synthase stability and responses to stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 34, e2011900118. |
| [23] | Lee HY, Yoon GM (2018). Regulation of ethylene biosynthesis by phytohormones in etiolated rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Mol Cells 41, 311-319. |
| [24] | Li CH, Wang G, Zhao JL, Zhang LQ, Ai LF, Han YF, Sun DY, Zhang SW, Sun Y (2014). The receptor-like kinase SIT1 mediates salt sensitivity by activating MAPK3/6 and regulating ethylene homeostasis in rice. Plant Cell 26, 2538-2553. |
| [25] | Li DD, Flores-Sandoval E, Ahtesham U, Coleman A, Clay JM, Bowman JL, Chang CR (2020). Ethylene-independent functions of the ethylene precursor ACC in Marchantia polymorpha. Nat Plants 6, 1335-1344. |
| [26] |
Liu H, Dong SY, Gu FW, Liu W, Yang GL, Huang M, Xiao WM, Liu YZ, Guo T, Wang H, Chen ZQ, Wang JF (2017). NBS-LRR protein Pik-H4 interacts with OsBIHD1 to balance rice blast resistance and growth by coordinating ethylene-brassinosteroid pathway. Front Plant Sci 8, 127.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | Liu HQ, Zou YJ, Li XF, Wu L, Guo GQ (2021). Stablization of ACOs by NatB mediated N-terminal acetylation is required for ethylene homeostasis. BMC Plant Biol 21, 320. |
| [28] |
Liu MH, Wei JW, Liu W, Gong B (2023). S-nitrosylation of ACO homolog 4 improves ethylene synthesis and salt tolerance in tomato. New Phytol 239, 159-173.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Ludwików A, Cieśla A, Kasprowicz-Maluśki A, Mituła F, Tajdel M, Gałgański L, Ziółkowski PA, Kubiak P, Małecka A, Piechalak A, Szabat M, Górska A, Dąbrowski M, Ibragimow I, Sadowski J (2014). Arabidopsis protein phosphatase 2C ABI1 interacts with Type I ACC synthases and is involved in the regulation of ozone-induced ethylene biosynthesis. Mol Plant 7, 960-976.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
Lyzenga WJ, Booth JK, Stone SL (2012). The Arabidopsis RING-type E3 ligase XBAT32 mediates the proteasomal degradation of the ethylene biosynthetic enzyme, 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase 7. Plant J 71, 23-34.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Matsushima R, Maekawa M, Kusano M, Tomita K, Kondo H, Nishimura H, Crofts N, Fujita N, Sakamoto W (2016). Amyloplast membrane protein SUBSTANDARD STARCH GRAIN6 controls starch grain size in rice endosperm. Plant Physiol 170, 1445-1459.
DOI PMID |
| [32] | Mou WS, Kao YT, Michard E, Simon AA, Li DD, Wudick MM, Lizzio MA, Feijó JA, Chang CR (2020). Ethylene-independent signaling by the ethylene precursor ACC in Arabidopsis ovular pollen tube attraction. Nat Commun 11, 4082. |
| [33] | Ouyang S, Zhu W, Hamilton J, Lin HN, Campbell M, Childs K, Thibaud-Nissen F, Malek RL, Lee Y, Zheng L, Orvis J, Haas B, Wortman J, Buell CR (2007). The TIGR rice genome annotation resource: improvements and new features. Nucleic Acids Res 35, D883-D887. |
| [34] | Park C, Lee HY, Yoon GM (2021). The regulation of ACC synthase protein turnover: a rapid route for modulating plant development and stress responses. Curr Opin Plant Biol 63, 102046. |
| [35] | Pattyn J, Vaughan-Hirsch J, Van de Poel B (2021). The regulation of ethylene biosynthesis: a complex multilevel control circuitry. New Phytol 229, 770-782. |
| [36] |
Qin H, Wang J, Chen XB, Wang FF, Peng P, Zhou Y, Miao YC, Zhang YQ, Gao YD, Qi YD, Zhou JH, Huang RF (2019). Rice OsDOF15 contributes to ethylene-inhibited primary root elongation under salt stress. New Phytol 223, 798-813.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
Rauf M, Arif M, Fisahn J, Xue GP, Balazadeh S, Mueller-Roeber B (2013). NAC transcription factor SPEEDY HYPONASTIC GROWTH regulates flooding-induced leaf movement in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25, 4941-4955.
DOI URL |
| [38] | Stange LMC, Osborne DJ (1989). Contrary effects of ethylene and ACC on cell growth in the liverwort Riella helicophylla. In: Clijsters H, Proft M, Marcelle R, Poucke M, eds. Biochemical and Physiological Aspects of Ethylene Production in Lower and Higher Plants. Dordrecht: Springer. pp. 341-348. |
| [39] |
Tan ST, Xue HW (2014). Casein kinase 1 regulates ethylene synthesis by phosphorylating and promoting the turnover of ACS5. Cell Rep 9, 1692-1702.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Tsolakidou MD, Pantelides LS, Tzima AK, Kang S, Paplomatas EJ, Tsaltas D (2019). Disruption and overexpression of the gene encoding ACC (1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid) deaminase in soil-borne fungal pathogen Verticillium dahliae revealed the role of ACC as a potential regulator of virulence and plant defense. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 32, 639-653.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Tsuchisaka A, Theologis A (2004). Unique and overlapping expression patterns among the Arabidopsis 1-amino- cyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase gene family members. Plant Physiol 136, 2982-3000.
DOI PMID |
| [42] |
Uji T, Endo H, Mizuta H (2020). Sexual reproduction via a 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid-dependent pathway through redox modulation in the marine red alga Pyropia yezoensis (Rhodophyta). Front Plant Sci 11, 60.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Van de Poel B, Bulens I, Hertog MLATM, Nicolai BM, Geeraerd AH (2014a). A transcriptomics-based kinetic model for ethylene biosynthesis in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) fruit: development, validation and exploration of novel regulatory mechanisms. New Phytol 202, 952-963.
DOI URL |
| [44] | Van de Poel B, Bulens I, Markoula A, Hertog MLATM, Dreesen R, Wirtz M, Vandoninck S, Oppermann Y, Keulemans J, Hell R, Waelkens E, De Proft MP, Sauter M, Nicolai BM, Geeraerd AH (2012). Targeted systems biology profiling of tomato fruit reveals coordination of the Yang cycle and a distinct regulation of ethylene biosynthesis during postclimacteric ripening. Plant Physiol 160, 1498-1514. |
| [45] |
Van de Poel B, Vandenzavel N, Smet C, Nicolay T, Bulens I, Mellidou I, Vandoninck S, Hertog MLATM, Derua R, Spaepen S, Vanderleyden J, Waelkens E, De Proft MP, Nicolai BM, Geeraerd AH (2014b). Tissue specific analysis reveals a differential organization and regulation of both ethylene biosynthesis and E8 during climacteric ripening of tomato. BMC Plant Biol 14, 11.
DOI |
| [46] | Vanderstraeten L, Depaepe T, Bertrand S, Van Der Straeten D (2019). The ethylene precursor ACC affects early vegetative development independently of ethylene signaling. Front Plant Sci 10, 1591. |
| [47] |
Wang KLC, Yoshida H, Lurin C, Ecker JR (2004). Regulation of ethylene gas biosynthesis by the Arabidopsis ETO1 protein. Nature 428, 945-950.
DOI |
| [48] |
Wang ZQ, Wei XY, Wang YQ, Sun MT, Zhao PY, Wang QN, Yang B, Li J, Jiang YQ (2023). WRKY 29 transcription factor regulates ethylene biosynthesis and response in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol Biochem 194, 134-145.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Xiong L, Xiao D, Xu XX, Guo ZX, Wang NN (2014). The non-catalytic N-terminal domain of ACS7 is involved in the post-translational regulation of this gene in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 65, 4397-4408.
DOI PMID |
| [50] | Xu SL (2008). Two Leucine-rich Receptor Kinases Mediate Signaling Linking Cell Wall Bio-synthesis and ACC Synthase in Arabidopsis and Possible Downstream Elements in the Pathway. Doctoral dissertation. United States-North Carolina: The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. pp. 1-128. |
| [51] |
Yao Y, Du Y, Jiang L, Liu JY (2007). Interaction between ACC synthase 1 and 14-3-3 proteins in rice: a new insight. Biochem (Moscow) 72, 1003-1007.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Yin J, Zhang XQ, Zhang GS, Wen YY, Liang G, Chen XL (2019). Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid is a key regulator of guard mother cell terminal division in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 70, 897-908.
DOI PMID |
| [53] |
Yoon GM (2015). New insights into the protein turnover regulation in ethylene biosynthesis. Mol Cells 38, 597-603.
DOI PMID |
| [54] |
Yoon GM, Kieber JJ (2013a). 14-3-3 regulates 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase protein turnover in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25, 1016-1028.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
Yoon GM, Kieber JJ (2013b). ACC synthase and its cognate E3 ligase are inversely regulated by light. Plant Signal Behav 8, e26478.
DOI URL |
| [56] | Yoon J, Cho LH, Yang WZ, Pasriga R, Wu YF, Hong WJ, Bureau C, Wi SJ, Zhang T, Wang RC, Zhang DB, Jung KH, Park KY, Périn C, Zhao YD, An G (2020). Homeobox transcription factor OsZHD2 promotes root meristem activity in rice by inducing ethylene biosynthesis. J Exp Bot 71, 5348-5364. |
| [57] |
Yoshida H, Nagata M, Saito K, Wang KLC, Ecker JR (2005). Arabidopsis ETO1 specifically interacts with and negatively regulates type 2 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthases. BMC Plant Biol 5, 14.
PMID |
| [58] |
Yoshida H, Wang KLC, Chang CM, Mori K, Uchida E, Ecker JR (2006). The ACC synthase TOE sequence is required for interaction with ETO1 family proteins and destabilization of target proteins. Plant Mol Biol 62, 427-437.
PMID |
| [59] |
Yu JT, Mao CJ, Zhong Q, Yao XF, Li P, Liu CM, Ming F (2021). OsNAC2 is involved in multiple hormonal pathways to mediate germination of rice seeds and establishment of seedling. Front Plant Sci 12, 699303.
DOI URL |
| [60] | Yuan M, Qu LJ, Wang XJ, Qian Q, Yang WC, Wang T, Kong HZ, Jiang GM, Chong K (2014). Research advances on plant science in China in 2013. Chin Bull Bot 49, 347-406. (in Chinese) |
| 袁明, 瞿礼嘉, 王小菁, 钱前, 杨维才, 王台, 孔宏智, 蒋高明, 种康 (2014). 2013年中国植物科学若干领域重要研究进展. 植物学报 49, 347-406. | |
| [61] |
Zhang HW, Zhang JF, Quan RD, Pan XW, Wan LY, Huang RF (2013). EAR motif mutation of rice OsERF3 alters the regulation of ethylene biosynthesis and drought tolerance. Planta 237, 1443-1451.
DOI PMID |
| [62] |
Zhou Y, Xiong Q, Yin CC, Ma B, Chen SY, Zhang JS (2020). Ethylene biosynthesis, signaling, and crosstalk with other hormones in rice. Small Methods 4, 1900278.
DOI URL |
| [1] | Zhou Jing, Gao Fei. Advances in Iron Deficiency-induced Coumarin Biosynthesis and Their Functions in Iron Absorption in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(3): 460-471. |
| [2] | Xiong Lianglin, Liang Guolu, Guo Qigao, Jing Danlong. Advances in the Regulation of Alternative Splicing of Genes in Plants in Response to Abiotic Stress [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(3): 435-448. |
| [3] | Xinyu Li, Yue Gu, Feifei Xu, Jinsong Bao. Research Progress on Post-translational Modifications of Starch Biosynthesis-related Proteins in Rice Endosperm [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(2): 256-270. |
| [4] | Haitao Hu, Yue Wu, Ling Yang. Research Progress on the NAD(P)+ Biosynthesis and Function in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(1): 114-131. |
| [5] | Hongju Li, Weicai Yang. A Micropeptide With a Big Role: New Molecular Mechanism in Seed Desiccation [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(6): 869-872. |
| [6] | Xuelan Fan, Yanjiao Luo, Chaoqun Xu, Baolin Guo. Research Progress on Genes Related to Flavonoids Biosynthesis in Herba Epimedii [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(5): 834-846. |
| [7] | Xiaoxiao Liu, Di Gong, Tianpeng Gao, Lina Yin, Shiwen Wang. The Major Membrane Lipids in Plant Thylakoids and Their Biosynthesis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(1): 144-155. |
| [8] | Qiwei Jia, Qianqian Zhong, Yujia Gu, Tianqi Lu, Wei Li, Shuai Yang, Chaoyu Zhu, Chengxiang Hu, Sanfeng Li, Yuexing Wang, Yuchun Rao. Mapping of QTL for Cell Wall Related Components in Rice Stem and Analysis of Candidate Genes [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(6): 882-892. |
| [9] | Dai Ruohui, Qian Xinyu, Sun Jinglei, Lu Tao, Jia Qiwei, Lu Tianqi, Lu Mei, Rao Yuchun. Research Progress on the Mechanisms of Leaf Color Regulation and Related Genes in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(5): 799-812. |
| [10] | Haitao Hu, Longbiao Guo. Progress in the Research on Riboflavin Biosynthesis and Function in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(4): 638-655. |
| [11] | Jiayi Jin, Yiting Luo, Huimin Yang, Tao Lu, Hanfei Ye, Jiyi Xie, Kexin Wang, Qianyu Chen, Yuan Fang, Yuexing Wang, Yuchun Rao. QTL Mapping and Expression Analysis on Candidate Genes Related to Chlorophyll Content in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(3): 394-403. |
| [12] | Yanjun Guo, Feng Chen, Jingwen Luo, Wei Zeng, Wenliang Xu. The Biosynthesis of Plant Cell Wall Xylan and Its Application [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(2): 316-334. |
| [13] | Li Cong, Qi Lijuan, Gu Xiaofeng, Li Jigang. Research Progress on TZP, a Novel Key Regulator of Light Signal Transduction in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(5): 579-587. |
| [14] | Yu Miao, Ruan Chengjiang, Ding Jian, Li Jingbin, Lu Shunguang, Wen Xiufeng. Hrh-miRn458 Regulates Oil Biosynthesis of Sea Buckthorn via Targeting Transcription Factor WRI1 [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(5): 635-648. |
| [15] | Liu Xiaolong, Ji Ping, Yang Hongtao, Ding Yongdian, Fu Jialing, Liang Jiangxia, Yu Congcong. Priming Effect of Abscisic Acid on High Temperature Stress During Rice Heading-flowering Stage [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(5): 596-610. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||