

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (3): 460-471.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24106 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24106
• SPECIAL TOPICS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2024-07-17
Accepted:2024-12-14
Online:2025-05-10
Published:2024-12-27
Contact:
*E-mail: gaofei@hunau.edu.cn
Zhou Jing, Gao Fei. Advances in Iron Deficiency-induced Coumarin Biosynthesis and Their Functions in Iron Absorption in Plants[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(3): 460-471.
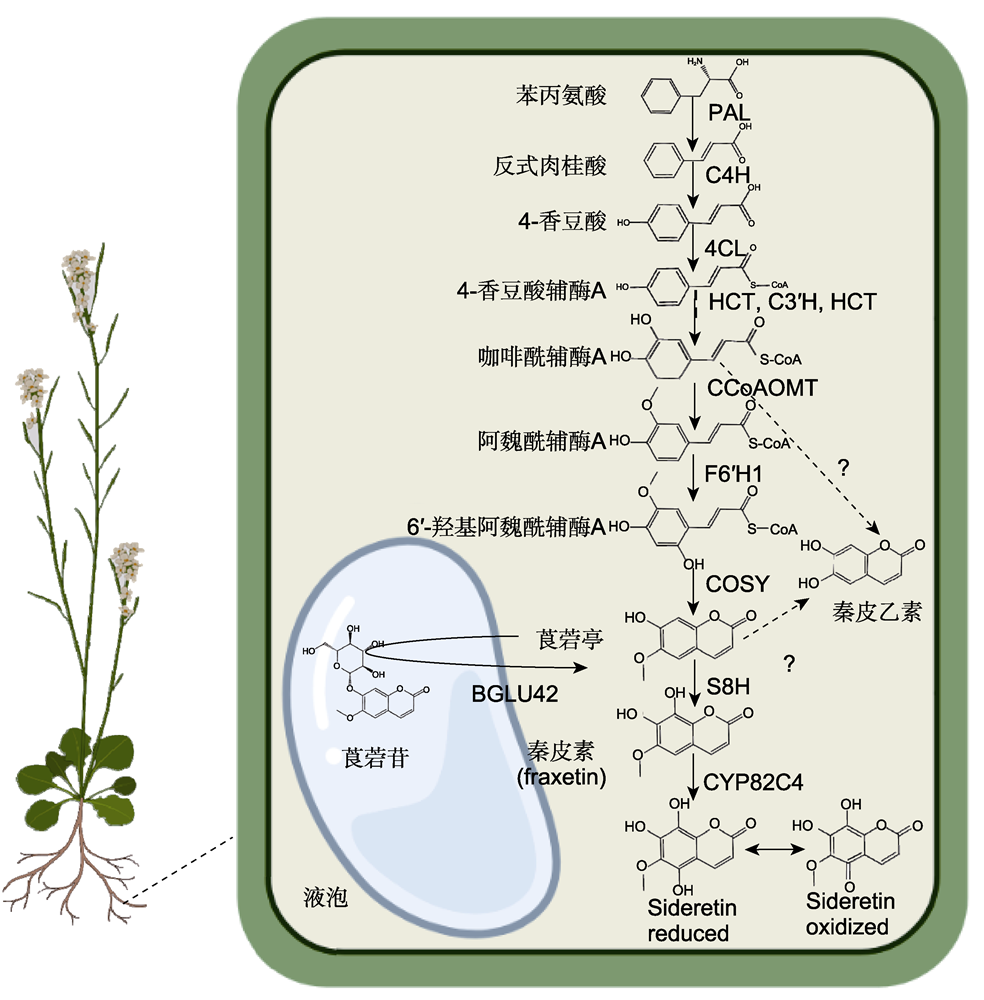
Figure 1 Biosynthesis pathways of iron deficiency-induced coumarins in Arabidopsis PAL: Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase; C4H: Cinnamate-4-hydroxylase; 4CL: 4-coumarate:CoA ligases; HCT: Hydroxycinnamoyl-CoA shikimate/quinate hydroxycinnamoyl transferase; C3′H: 4-coumaroyl shikimate/quinate 3′-hydroxylase; CCoAOMT: Caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase; F6′H1: Feruloyl-CoA 6′-hydroxylase; COSY: Coumarin synthase; S8H: Scopoletin 8-hydroxylase; CYP82C4: Cytochrome P450 family enzymes
| 功能分类 | 基因 | 功能 | 缺铁应答 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 香豆素前体合成 | PAL | 反式肉桂酸合成 | 诱导型 | Rodríguez-Celma et al., |
| C4H | 4-香豆酸合成 | 诱导型 | Rodríguez-Celma et al., | |
| 4CL1/2 | 香豆酰辅酶A合成 | 诱导型 | Rodríguez-Celma et al., | |
| HCT | 咖啡酰辅酶A合成 | 诱导型 | Rodríguez-Celma et al., | |
| CCoAOMT1 | 阿魏酰辅酶A合成 | 诱导型 | Rodríguez-Celma et al., | |
| 香豆素合成 | F6H'1 | 6'-羟基阿魏酰辅酶A合成 | 诱导型 | Kai et al., |
| COSY | 莨菪亭合成 | 诱导型 | Vanholme et al., | |
| S8H | 秦皮素合成 | 诱导型 | Siwinska et al., | |
| CYP82C4 | Sideretin合成 | 诱导型 | Murgia et al., | |
| 香豆素分泌 | PDR9 | 香豆素类化合物外排分泌 | 诱导型 | Rodríguez-Celma et al., |
| BGLU42 | 莨菪苷去糖基化 | 诱导型 | Ziegler et al., | |
| 调控 | FIT | 正调控香豆素合成 | 诱导型 | Schmid et al., |
| MYB72 | 正调控香豆素合成 | 诱导型 | Stringlis et al., | |
| MYB63 | 正调控香豆素合成 | ? | DeLoose et al., | |
| bHLH121 | 正调控香豆素合成 | 组成型 | Gao et al., | |
| MYB15 | 正调控香豆素合成 | ? | Schwarz and Bauer, | |
| KFB1 | 正调控香豆素合成 | 诱导型 | Zhang et al., | |
| KFB20 | 正调控香豆素合成 | 诱导型 | Zhang et al., | |
| KFB50 | 正调控香豆素合成 | 诱导型 | Zhang et al., |
Table 1 Genes responsible for the biosynthesis and regulation of iron deficiency-induced coumarins
| 功能分类 | 基因 | 功能 | 缺铁应答 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 香豆素前体合成 | PAL | 反式肉桂酸合成 | 诱导型 | Rodríguez-Celma et al., |
| C4H | 4-香豆酸合成 | 诱导型 | Rodríguez-Celma et al., | |
| 4CL1/2 | 香豆酰辅酶A合成 | 诱导型 | Rodríguez-Celma et al., | |
| HCT | 咖啡酰辅酶A合成 | 诱导型 | Rodríguez-Celma et al., | |
| CCoAOMT1 | 阿魏酰辅酶A合成 | 诱导型 | Rodríguez-Celma et al., | |
| 香豆素合成 | F6H'1 | 6'-羟基阿魏酰辅酶A合成 | 诱导型 | Kai et al., |
| COSY | 莨菪亭合成 | 诱导型 | Vanholme et al., | |
| S8H | 秦皮素合成 | 诱导型 | Siwinska et al., | |
| CYP82C4 | Sideretin合成 | 诱导型 | Murgia et al., | |
| 香豆素分泌 | PDR9 | 香豆素类化合物外排分泌 | 诱导型 | Rodríguez-Celma et al., |
| BGLU42 | 莨菪苷去糖基化 | 诱导型 | Ziegler et al., | |
| 调控 | FIT | 正调控香豆素合成 | 诱导型 | Schmid et al., |
| MYB72 | 正调控香豆素合成 | 诱导型 | Stringlis et al., | |
| MYB63 | 正调控香豆素合成 | ? | DeLoose et al., | |
| bHLH121 | 正调控香豆素合成 | 组成型 | Gao et al., | |
| MYB15 | 正调控香豆素合成 | ? | Schwarz and Bauer, | |
| KFB1 | 正调控香豆素合成 | 诱导型 | Zhang et al., | |
| KFB20 | 正调控香豆素合成 | 诱导型 | Zhang et al., | |
| KFB50 | 正调控香豆素合成 | 诱导型 | Zhang et al., |
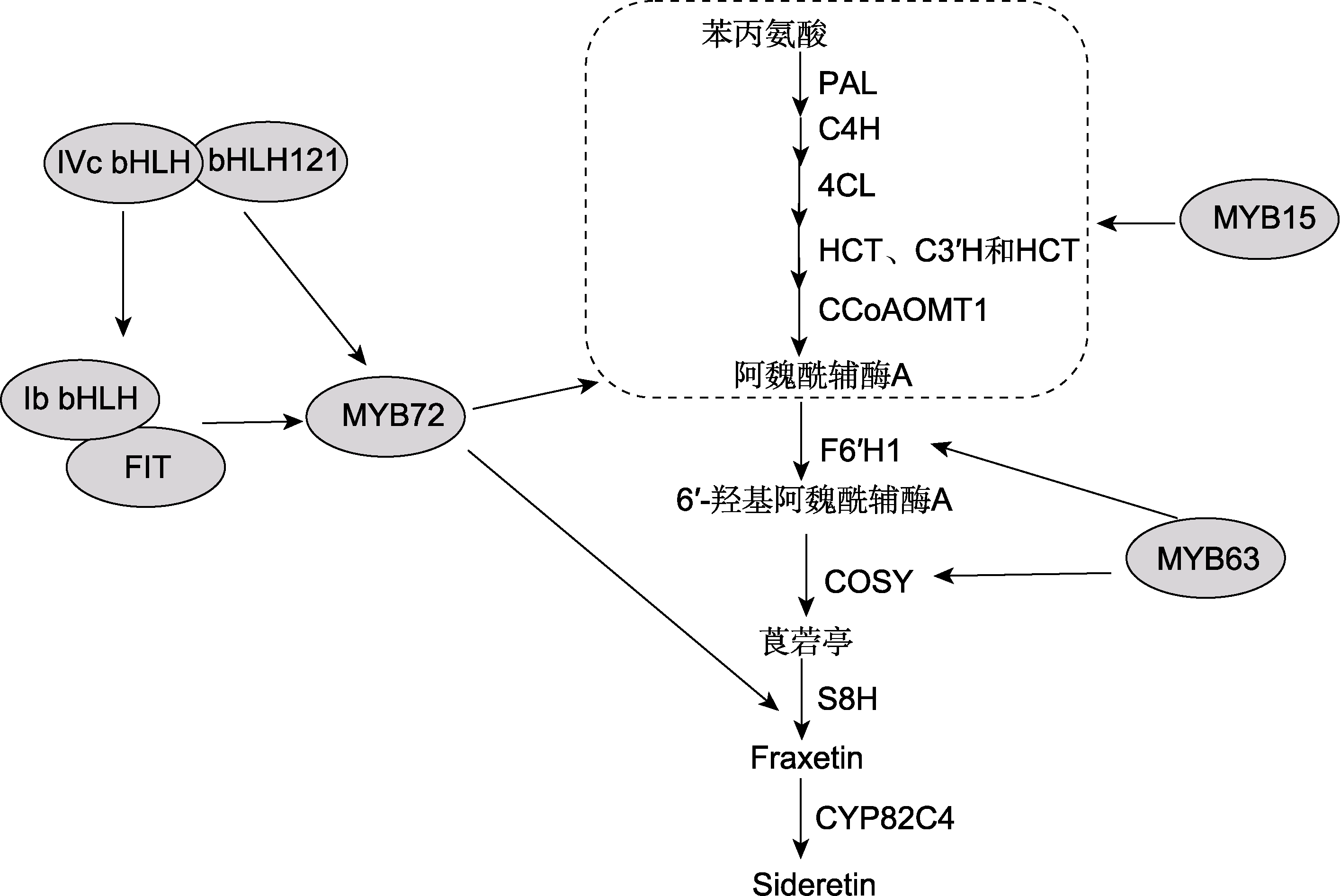
Figure 2 Regulation of iron deficiency-induced coumarin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis The legends of PAL, C4H, 4CL, HCT, C3′H, CCoAOMT1, F6′H1, COSY, S8H, and CYP82C4 are the same as shown in Figure 1. IVc bHLH: Arabidopsis IVc bHLH subfamily transcription factors; Ib bHLH: Arabidopsis Ib bHLH subfamily transcription factors; FIT: Arabidopsis bHLH29 transcription factor
| [1] | Ahn YO, Shimizu BI, Sakata K, Gantulga D, Zhou Z, Bevan DR, Esen A (2010). Scopolin-hydrolyzing β-glucosidases in roots of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 51, 132-143. |
| [2] | Bauer P, Ling HQ, Guerinot ML (2007). FIT, the FER-like iron deficiency induced transcription factor in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol Biochem 45, 260-261. |
| [3] | Briat JF, Dubos C, Gaymard F (2015). Iron nutrition, biomass production, and plant product quality. Trends Plant Sci 20, 33-40. |
| [4] | Brown JC, Ambler JE (1973). “Reductants” released by roots of Fe-deficient soybeans. Agron J 65, 311-314. |
| [5] |
Brumbarova T, Bauer P, Ivanov R (2015). Molecular mechanisms governing Arabidopsis iron uptake. Trends Plant Sci 20, 124-133.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | Carvalhais LC, Dennis PG, Fedoseyenko D, Hajirezaei MR, Borriss R, von Wirén N (2011). Root exudation of sugars, amino acids, and organic acids by maize as affected by nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and iron deficiency. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 174, 3-11. |
| [7] | Chezem WR, Memon A, Li FS, Weng JK, Clay NK (2017). SG2-type R2R3-MYB transcription factor MYB15 controls defense-induced lignification and basal immunity in Arabidop-sis. Plant Cell 29, 1907-1926. |
| [8] |
Chutia R, Abel S, Ziegler J (2019). Iron and phosphate deficiency regulators concertedly control coumarin profiles in Arabidopsis thaliana roots during iron, phosphate, and combined deficiencies. Front Plant Sci 10, 113.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | Colangelo EP, Guerinot ML (2004). The essential basic helix-loop-helix protein FIT1 is required for the iron deficiency response. Plant Cell 16, 3400-3412. |
| [10] |
de Brito Francisco R, Martinoia E (2018). The vacuolar transportome of plant specialized metabolites. Plant Cell Physiol 59, 1326-1336.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | DeLoose M, Cho H, Bouain N, Choi I, Prom-U-Thai C, Shahzad Z, Zheng LQ, Rouached H (2024). PDR9 allelic variation and MYB63 modulate nutrient-dependent coumarin homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant J 117, 1716-1727. |
| [12] | Dong NQ, Lin HX (2021). Contribution of phenylpropanoid metabolism to plant development and plant-environment interactions. J Integr Plant Biol 63, 180-209. |
| [13] | Ducos E, Fraysse ÅS, Boutry M (2005). NtPDR3, an iron-deficiency inducible ABC transporter in Nicotiana taba-cum. FEBS Lett 579, 6791-6795. |
| [14] |
Fourcroy P, Sisó-Terraza P, Sudre D, Savirón M, Reyt G, Gaymard F, Abadía A, Abadia J, Álvarez-Fernández A, Briat JF (2014). Involvement of the ABCG37 transporter in secretion of scopoletin and derivatives by Arabidopsis roots in response to iron deficiency. New Phytol 201, 155-167.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
Fourcroy P, Tissot N, Gaymard F, Briat JF, Dubos C (2016). Facilitated Fe nutrition by phenolic compounds excreted by the Arabidopsis ABCG37/PDR9 transporter requires the IRT1/FRO2 high-affinity root Fe2+ transport system. Mol Plant 9, 485-488.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
Gao F, Dubos C (2021). Transcriptional integration of plant responses to iron availability. J Exp Bot 72, 2056-2070.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | Gao F, Robe K, Bettembourg M, Navarro N, Rofidal V, Santoni V, Gaymard F, Vignols F, Roschzttardtz H, Izquierdo E, Dubos C (2020a). The transcription factor bHLH121 interacts with bHLH105 (ILR3) and its closest homologs to regulate iron homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 32, 508-524. |
| [18] | Gao F, Robe K, Dubos C (2020b). Further insights into the role of bHLH121 in the regulation of iron homeostasis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Signal Behav 15, 1795582. |
| [19] |
Gao F, Robe K, Gaymard F, Izquierdo E, Dubos C (2019). The transcriptional control of iron homeostasis in plants: a tale of bHLH transcription factors? Front Plant Sci 10, 6.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Guerinot ML, Yi Y (1994). Iron: nutritious, noxious, and not readily available. Plant Physiol 104, 815-820.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Hänsch R, Mendel RR (2009). Physiological functions of mineral micronutrients (Cu, Zn, Mn, Fe, Ni, Mo, B, Cl). Curr Opin Plant Biol 12, 259-266.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | Hether NH, Olsen RA, Jackson LL (1984). Chemical identification of iron reductants exuded by plant roots. J Plant Nutr 7, 667-676. |
| [23] |
Jin CW, You GY, He YF, Tang CX, Wu P, Zheng SJ (2007). Iron deficiency-induced secretion of phenolics facilitates the reutilization of root apoplastic iron in red clover. Plant Physiol 144, 278-285.
DOI PMID |
| [24] | Kai K, Mizutani M, Kawamura N, Yamamoto R, Tamai M, Yamaguchi H, Sakata K, Shimizu BI (2008). Scopoletin is biosynthesized via ortho-hydroxylation of feruloyl CoA by a 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 55, 989-999. |
| [25] |
Knoblauch M, Vendrell M, De Leau E, Paterlini A, Knox K, Ross-Elliot T, Reinders A, Brockman SA, Ward J, Oparka K (2015). Multispectral phloem-mobile probes: properties and applications. Plant Physiol 167, 1211-1220.
DOI PMID |
| [26] |
Kobayashi T, Nishizawa NK (2012). Iron uptake, translocation, and regulation in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 63, 131-152.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | Lan P, Li WF, Wen TN, Shiau JY, Wu YC, Lin W, Schmidt W (2011). iTRAQ protein profile analysis of Arabidopsis roots reveals new aspects critical for iron homeostasis. Plant Physiol 155, 821-834. |
| [28] | Lefèvre F, Fourmeau J, Pottier M, Baijot A, Cornet T, Abadía J, Álvarez-Fernández A, Boutry M (2018). The Nicotiana tabacum ABC transporter NtPDR3 secretes O- methylated coumarins in response to iron deficiency. J Exp Bot 69, 4419-4431. |
| [29] |
Leiková A, Giehl RFH, Hartmann A, Fargaiová A, von Wirén N (2017). Heavy metals induce iron deficiency responses at different hierarchic and regulatory levels. Plant Physiol 174, 1648-1668.
DOI PMID |
| [30] | Li LM, Wu LH, Ma GR (2010). The progress on iron-absorbing mechanism and related gene in plant. Chin J Soil Sci 41, 994-999. (in Chinese) |
| 李利敏, 吴良欢, 马国瑞 (2010). 植物吸收铁机理及其相关基因研究进展. 土壤通报 41, 994-999. | |
| [31] | Murgia I, Tarantino D, Soave C, Morandini P (2011). Arabidopsis CYP82C4 expression is dependent on Fe availability and circadian rhythm, and correlates with genes involved in the early Fe deficiency response. J Plant Physiol 168, 894-902. |
| [32] | Paffrath V, Tandron Moya YA, Weber G, von Wirén N, Giehl RFH (2024). A major role of coumarin-dependent ferric iron reduction in strategy I-type iron acquisition in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 36, 642-664. |
| [33] |
Pan IC, Tsai HH, Cheng YT, Wen TN, Buckhout TJ, Schmidt W (2015). Post-transcriptional coordination of the Arabidopsis iron deficiency response is partially dependent on the E3 ligases RING DOMAIN LIGASE1 (RGLG1) and RING DOMAIN LIGASE2 (RGLG2). Mol Cell Proteomics 14, 2733-2752.
DOI PMID |
| [34] |
Rajniak J, Giehl RFH, Chang E, Murgia I, von Wirén N, Sattely ES (2018). Biosynthesis of redox-active metabolites in response to iron deficiency in plants. Nat Chem Biol 14, 442-450.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
Riaz N, Guerinot ML (2021). All together now: regulation of the iron deficiency response. J Exp Bot 72, 2045-2055.
DOI PMID |
| [36] | Robe K, Conejero G, Gao F, Lefebvre-Legendre L, Sylvestre-Gonon E, Rofidal V, Hem S, Rouhier N, Barberon M, Hecker A, Gaymard F, Izquierdo E, Dubos C (2021a). Coumarin accumulation and trafficking in Arabidopsis thaliana: a complex and dynamic process. New Phytol 229, 2062-2079. |
| [37] | Robe K, Izquierdo E, Vignols F, Rouached H, Dubos C (2021b). The coumarins: secondary metabolites playing a primary role in plant nutrition and health. Trends Plant Sci 26, 248-259. |
| [38] | Rodríguez-Celma J, Lin WD, Fu GM, Abadía J, Lopez-Millan AF, Schmidt W (2013). Mutually exclusive alterations in secondary metabolism are critical for the uptake of insoluble iron compounds by Arabidopsis and Medicago truncatula. Plant Physiol 162, 1473-1485. |
| [39] |
Rodríguez-Celma J, Tsai YH, Wen TN, Wu YC, Curie C, Schmidt W (2016). Systems-wide analysis of manganese deficiency-induced changes in gene activity of Arabidopsis roots. Sci Rep 6, 35846.
DOI PMID |
| [40] | Rodríguez-Celma J, Vázquez-Reina S, Orduna J, Abadía A, Abadía J, Álvarez-Fernández A, López-Millán AF (2011). Characterization of flavins in roots of Fe-deficient strategy I plants, with a focus on Medicago truncatula. Plant Cell Physiol 52, 2173-2189. |
| [41] | Römheld V, Marschner H (1981). Iron deficiency stress induced morphological and physiological changes in root tips of sunflower. Physiol Plant 53, 354-360. |
| [42] | Römheld V, Marschner H (1983). Mechanism of iron uptake by peanut plants: I. FeIII reduction, chelate splitting, and release of phenolics. Plant Physiol 71, 949-954. |
| [43] | Römheld V, Marschner H (1986). Evidence for a specific uptake system for iron phytosiderophores in roots of gras- ses. Plant Physiol 80, 175-180. |
| [44] | Schmid NB, Giehl RFH, Döll S, Mock HP, Strehmel N, Scheel D, Kong XL, Hider RC, von Wirén N (2014). Feruloyl-CoA 6′-hydroxylase1-dependent coumarins mediate iron acquisition from alkaline substrates in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 164, 160-172. |
| [45] | Schmidt W (1999). Mechanisms and regulation of reduction-based iron uptake in plants. New Phytol 141, 1-26. |
| [46] |
Schmidt W (2003). Iron solutions: acquisition strategies and signaling pathways in plants. Trends Plant Sci 8, 188-193.
DOI PMID |
| [47] |
Schwarz B, Bauer P (2020). FIT, a regulatory hub for iron deficiency and stress signaling in roots, and FIT-dependent and independent gene signatures. J Exp Bot 71, 1694-1705.
DOI PMID |
| [48] | Shen HY, Xiong HC, Guo XT, Zuo YM (2011). Progress of molecular and physiological mechanism of iron uptake and translocation in plants. Plant Nutr Fert Sci 17, 1522-1530. (in Chinese) |
| 申红芸, 熊宏春, 郭笑彤, 左元梅 (2011). 植物吸收和转运铁的分子生理机制研究进展. 植物营养与肥料学报 17, 1522-1530. | |
| [49] | Siwinska J, Siatkowska K, Olry A, Grosjean J, Hehn A, Bourgaud F, Meharg AA, Carey M, Lojkowska E, Ihnatowicz A (2018). Scopoletin 8-hydroxylase: a novel enzyme involved in coumarin biosynthesis and iron-deficiency responses in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 69, 1735-1748. |
| [50] | Stringlis IA, Yu KE, Feussner K, de Jonge R, Van Bentum S, Van Verk MC, Berendsen RL, Bakker PA, Feussner I, Pieterse CM (2018). MYB72-dependent coumarin exudation shapes root microbiome assembly to promote plant health. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115, E5213- E5222. |
| [51] | Takemoto T, Nomoto K, Fushiya S, Ouchi R, Kusano G, Hikino H, Takagi SI, Matsuura Y, Kakudo M (1978). Structure of mugineic acid, a new amino acid possessing an iron-chelating activity from roots washings of water-cultured Hordeum vulgare L. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B 54, 469-473. |
| [52] | Tsai HH, Rodríguez-Celma J, Lan P, Wu YC, Vélez- Bermúdez IC, Schmidt W (2018). Scopoletin 8-hydroxylase-mediated fraxetin production is crucial for iron mobi- lization. Plant Physiol 177, 194-207. |
| [53] | Tsai HH, Schmidt W (2017). Mobilization of iron by plant- borne coumarins. Trends Plant Sci 22, 538-548. |
| [54] |
Vanholme R, Sundin L, Seetso KC, Kim H, Liu XY, Li J, De Meester B, Hoengenaert L, Goeminne G, Morreel K, Haustraete J, Tsai HH, Schmidt W, Vanholme B, Ralph J, Boerjan W (2019). COSY catalyses trans-cis isomerization and lactonization in the biosynthesis of coumarins. Nat Plants 5, 1066-1075.
DOI PMID |
| [55] |
Vogt T (2010). Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. Mol Plant 3, 2-20.
DOI PMID |
| [56] |
Waters BM, Amundsen K, Graef G (2018). Gene expression profiling of iron deficiency chlorosis sensitive and tolerant soybean indicates key roles for phenylpropanoids under alkalinity stress. Front Plant Sci 9, 10.
DOI PMID |
| [57] | Welkie GW (2000). Taxonomic distribution of dicotyledonous species capable of root excretion of riboflavin under iron deficiency. J Plant Nutr 23, 1819-1831. |
| [58] | Werner C, Matile P (1985). Accumulation of coumarylglucosides in vacuoles of barley mesophyll protoplasts. J Plant Physiol 118, 237-249. |
| [59] | World Health Organization (2003). Diet, Nutrition and the Prevention of Chronic Diseases. Geneva: WHO. pp. 1-149. |
| [60] | Wu HL, Wang N, Ling HQ (2007). Uptake, translocation and regulation of iron in plants. Chin Bull Bot 24, 779-788. (in Chinese) |
| 吴慧兰, 王宁, 凌宏清 (2007). 植物铁吸收、转运和调控的分子机制研究进展. 植物学通报 24, 779-788. | |
| [61] |
Xu WJ, Dubos C, Lepiniec L (2015). Transcriptional control of flavonoid biosynthesis by MYB-bHLH-WDR complexes. Trends Plant Sci 20, 176-185.
DOI PMID |
| [62] | Yang TJW, Lin WD, Schmidt W (2010). Transcriptional profiling of the Arabidopsis iron deficiency response reveals conserved transition metal homeostasis networks. Plant Physiol 152, 2130-2141. |
| [63] |
Zamioudis C, Hanson J, Pieterse CMJ (2014). β-glucosidase BGLU42 is a MYB72-dependent key regulator of rhizobacteria-induced systemic resistance and modulates iron deficiency responses in Arabidopsis roots. New Phytol 204, 368-379.
DOI PMID |
| [64] | Zhang XB, Gou MY, Guo CR, Yang H, Liu CJ (2015). Down-regulation of Kelch domain-containing F-box protein in Arabidopsis enhances the production of (poly) phe- nols and tolerance to ultraviolet radiation. Plant Physiol 167, 337-350. |
| [65] | Zhang XB, Gou MY, Liu CJ (2013). Arabidopsis Kelch repeat F-box proteins regulate phenylpropanoid biosynthesis via controlling the turnover of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase. Plant Cell 25, 4994-5010. |
| [66] | Zhao AN, Luo GM, Luo YJ, Song DD, Xia HD, Ren HM, Zhang P (2021). Mechanism of bHLH transcription factors in the regulatory network of plant iron deficiency. J Agric Biotechnol 29, 2427-2435. (in Chinese) |
| 赵安娜, 罗光明, 罗扬婧, 宋丹丹, 夏鸿东, 任洪曼, 张攀 (2021). bHLH转录因子在植物缺铁调控网络中的作用机制. 农业生物技术学报 29, 2427-2435. | |
| [67] |
Ziegler J, Schmidt S, Chutia R, Müller J, Böttcher C, Strehmel N, Scheel D, Abel S (2016). Non-targeted profiling of semi-polar metabolites in Arabidopsis root exudates uncovers a role for coumarin secretion and lignification during the local response to phosphate limitation. J Exp Bot 67, 1421-1432.
DOI PMID |
| [68] | Ziegler J, Schmidt S, Strehmel N, Scheel D, Abel S (2017). Arabidopsis transporter ABCG37/PDR9 contributes primarily highly oxygenated coumarins to root exudation. Sci Rep 7, 3704. |
| [1] | Yanan Jiang, Yuqing Xu, Yiting Wei, Jun Chen, Rongwan Zhang, Beibei Zhao, Yuxiang Lin, Yuchun Rao. Research Progress on the Regulatory Mechanism of Rice Disease Resistance [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(5): 1-0. |
| [2] | Ting Wang Shitou Xia. Transcriptional regulation of systemic acquired resistance [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(5): 1-0. |
| [3] | Ziyun Wang, Yanwen Lv, Yu Xiao, Chao Wu, Xinsheng Hu. Advances in Regulation and Evolutionary Mechanisms of Plant Gene Expression [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [4] | Xinyu Li, Yue Gu, Feifei Xu, Jinsong Bao. Research Progress on Post-translational Modifications of Starch Biosynthesis-related Proteins in Rice Endosperm [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(2): 256-270. |
| [5] | Haitao Hu, Yue Wu, Ling Yang. Research Progress on the NAD(P)+ Biosynthesis and Function in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(1): 114-131. |
| [6] | Xuelan Fan, Yanjiao Luo, Chaoqun Xu, Baolin Guo. Research Progress on Genes Related to Flavonoids Biosynthesis in Herba Epimedii [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(5): 834-846. |
| [7] | Jing Xia, Yuchun Rao, Danyun Cao, Yi Wang, Linxin Liu, Yating Xu, Wangshu Mou, Dawei Xue. Research Progress on the Regulatory Mechanisms of OsACS and OsACO in Rice Ethylene Biosynthesis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(2): 291-301. |
| [8] | Lu Zhu, Chong Yuan, Yifei Liu. Research Progress on Plant Secondary Metabolite Biosyn-thetic Gene Clusters [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(1): 134-143. |
| [9] | Xiaoxiao Liu, Di Gong, Tianpeng Gao, Lina Yin, Shiwen Wang. The Major Membrane Lipids in Plant Thylakoids and Their Biosynthesis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(1): 144-155. |
| [10] | Xiaoyun Dong, Jiaping Wei, Junmei Cui, Zefeng Wu, Guoqiang Zheng, Hui Li, Ying Wang, Haiyan Tian, Zigang Liu. Research Progress in Plant Antifreeze Protein [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(6): 966-981. |
| [11] | Lufang Su, Ping Wang, Shun Li, Yan Cai, Dandan Guo, Qin Liu, Xiaoyun Liu. Research Progress in Sirtuin Protein Family in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(6): 998-1007. |
| [12] | Haitao Hu, Longbiao Guo. Progress in the Research on Riboflavin Biosynthesis and Function in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(4): 638-655. |
| [13] | Yanjun Guo, Feng Chen, Jingwen Luo, Wei Zeng, Wenliang Xu. The Biosynthesis of Plant Cell Wall Xylan and Its Application [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(2): 316-334. |
| [14] | Yu Miao, Ruan Chengjiang, Ding Jian, Li Jingbin, Lu Shunguang, Wen Xiufeng. Hrh-miRn458 Regulates Oil Biosynthesis of Sea Buckthorn via Targeting Transcription Factor WRI1 [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(5): 635-648. |
| [15] | Zhou Yuping, Yan Jiahao, Tian Chang’en. Research Progress on the Regulatory Mechanisms of ABA Signal Transduction in Guard Cells [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(5): 684-696. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
