

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (5): 722-733.DOI: 10.11983/CBB25088 cstr: 32102.14.CBB25088
• INVITED REVIEWS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Su Silin1,2, Tang Xianyu1,2, Chen Yi1,2, Wang Ting1,2, Xia Shitou1,2,*( )
)
Received:2025-05-19
Accepted:2025-07-08
Online:2025-09-10
Published:2025-07-08
Contact:
Xia Shitou
Su Silin, Tang Xianyu, Chen Yi, Wang Ting, Xia Shitou. Transcriptional Regulation of Systemic Acquired Resistance in Plants[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(5): 722-733.
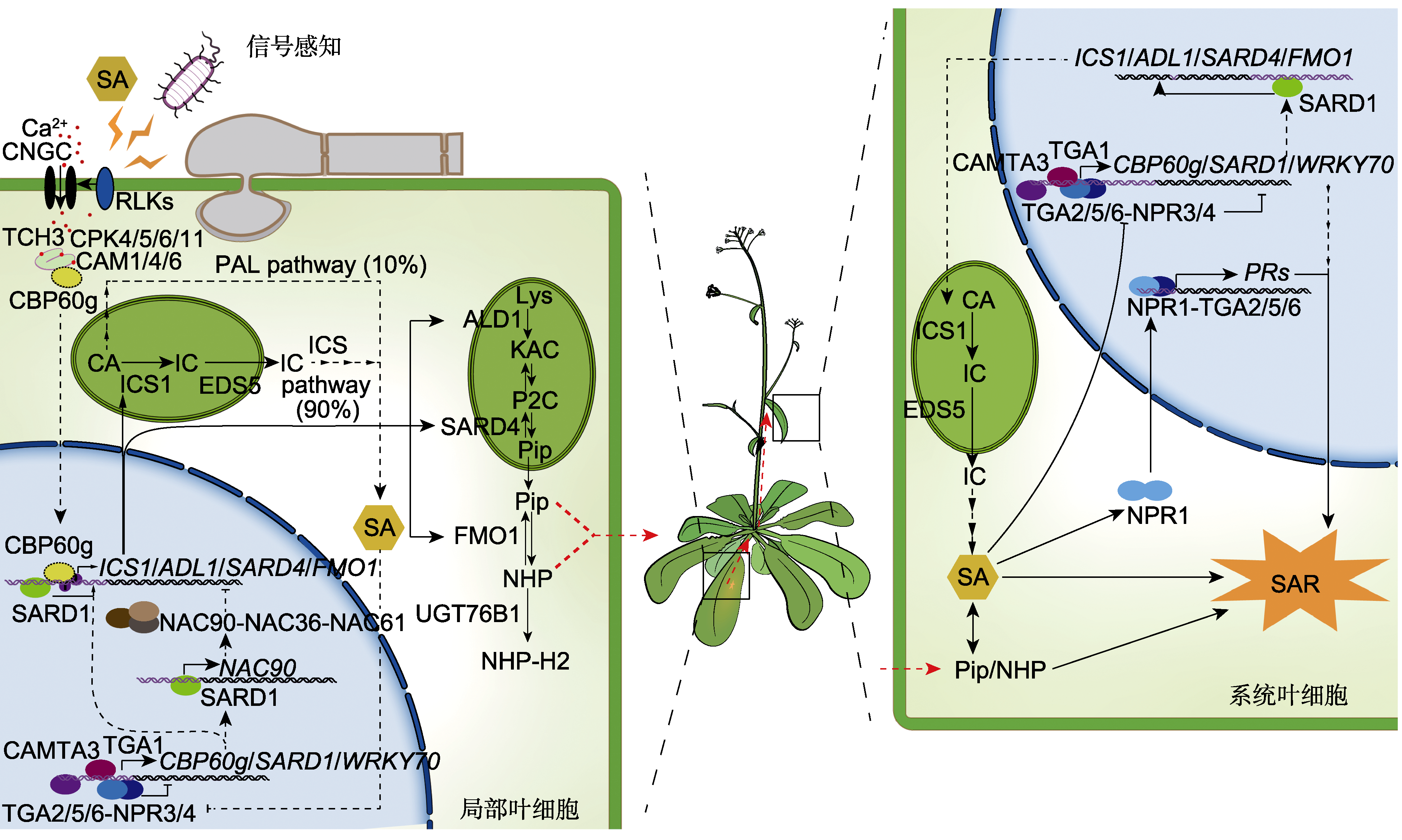
Figure 1 Transcriptional regulation of systemic acquired resistance (SAR) in plants When local leaf cells of plants are infected by pathogens (bacteria or fungi) or salicylic acid (SA), is applied receptor like kinases (RLKs) are activated after local signal perception, leading to the influx of calcium ions. The calmodulin CAM1/4/6 then combines with calcium ions and interacts with CBP60g, triggeringa local resistance response through the phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) and isochorismate synthase 1 (ICS1) pathways to increase SA synthesis. Lysine, whereas, is catalyzed by ALD1 and SARD4 to form piperidine-2-carboxylic acid (Pip), which is then hydroxylated to N-hydroxy-piperidine-2-carboxylic acid (NHP) by FMO1. Pip/NHP can be transported to distal leaves through phloem transportation. After the levels of SA and Pip/NHP increase in systemic leaf cells, SA binds to the receptor NPR1, and triggers the conformational changes in NPR1, which enter into the nucleus, where NPR1 forms a complex with TGA2/5/6, and activates the expression of PRs genes and SAR. Moreover, SA can also directly bind NPR3/NPR4 to inhibit their transcriptional inhibitory activity, thereby relieving the inhibition of genes such as SARD1 and WRKY70, achieving the goal of fine tuning the SAR. The solid arrows indicate direct regulation; the dashed arrows indicate indirect regulation; the T-shaped line indicates inhibition.
| [1] |
Arndt LC, Heine S, Wendt L, Wegele E, Schomerus JT, Schulze J, Hehl R (2022). Genomic distribution and context dependent functionality of novel WRKY transcription factor binding sites. BMC Genomics 23, 673.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | Bauer S, Mekonnen DW, Hartmann M, Yildiz I, Janowski R, Lange B, Geist B, Zeier J, Schäffner AR (2021). UGT76B1, a promiscuous hub of small molecule-based immune signaling, glucosylates N-hydroxypipecolic acid, and balances plant immunity. Plant Cell 33, 714-734. |
| [3] |
Boatwright JL, Pajerowska-Mukhtar K (2013). Salicylic acid: an old hormone up to new tricks. Mol Plant Pathol 14, 623-634.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | Cai JH, Jozwiak A, Holoidovsky L, Meijler MM, Meir S, Rogachev I, Aharoni A (2021). Glycosylation of N-hydroxy-pipecolic acid equilibrates between systemic acquired resistance response and plant growth. Mol Plant 14, 440-455. |
| [5] | Cai JH, Panda S, Kazachkova Y, Amzallag E, Li ZG, Meir S, Rogachev I, Aharoni A (2024). A NAC triad modulates plant immunity by negatively regulating N-hydroxy pipecolic acid biosynthesis. Nat Commun 15, 7212. |
| [6] | Cao H, Bowling SA, Gordon AS, Dong X (1994). Characterization of an Arabidopsis mutant that is nonresponsive to inducers of systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 6, 1583-1592. |
| [7] | Cao LJ, Karapetyan S, Yoo H, Chen TY, Mwimba M, Zhang X, Dong XN (2024). H2O2 sulfenylates CHE, linking local infection to the establishment of systemic acquired resistance. Science 385, 1211-1217. |
| [8] | Chen Y, Han Y, Huang WJ, Zhang YJ, Chen XL, Li DY, Hong Y, Gao HH, Zhang KW, Zhang YL, Sun TJ (2024). LAZARUS 1 functions as a positive regulator of plant immunity and systemic acquired resistance. Front Plant Sci 15, 1490466. |
| [9] | Chen YE, Xia PG (2025). NAC transcription factors as biological macromolecules responded to abiotic stress: a comprehensive review. Int J Biol Macromol 308, 142400. |
| [10] | Choudhary A, Senthil-Kumar M (2022). Drought attenuates plant defence against bacterial pathogens by suppressing the expression of CBP60g/SARD1 during combined stress. Plant Cell Environ 45, 1127-1145. |
| [11] |
Ding PT, Ding YL (2020). Stories of salicylic acid: a plant defense hormone. Trends Plant Sci 25, 549-565.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | Ding PT, Rekhter D, Ding YL, Feussner K, Busta L, Haroth S, Xu SH, Li X, Jetter R, Feussner I, Zhang YL (2016). Characterization of a pipecolic acid biosynthesis pathway required for systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 28, 2603-2615. |
| [13] |
Ding YL, Sun TJ, Ao K, Peng YJ, Zhang YX, Li X, Zhang YL (2018). Opposite roles of salicylic acid receptors NPR1 and NPR3/NPR4 in transcriptional regulation of plant immunity. Cell 173, 1454-1467.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
Dong XN (2004). NPR1, all things considered. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7, 547-552.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
Dubois M, van den Broeck L, Inzé D (2018). The pivotal role of ethylene in plant growth. Trends Plant Sci 23, 311-323.
DOI PMID |
| [16] | Foret J, Kim JG, Sattely ES, Mudgett MB (2024). Transcriptome analysis reveals role of transcription factor WRKY70 in early N-hydroxy-pipecolic acid signaling. Plant Physiol 197, kiae544. |
| [17] |
Fu ZQ, Dong XN (2013). Systemic acquired resistance: turning local infection into global defense. Annu Rev Plant Biol 64, 839-863.
DOI PMID |
| [18] | Fu ZQ, Yan SP, Saleh A, Wang W, Ruble J, Oka N, Mohan R, Spoel SH, Tada Y, Zheng N, Dong XN (2012). NPR3 and NPR4 are receptors for the immune signal salicylic acid in plants. Nature 486, 228-232. |
| [19] | Fuertes-Aguilar J, Matilla AJ (2024). Transcriptional control of seed life: new insights into the role of the NAC family. Int J Mol Sci 25, 5369. |
| [20] | Goyal P, Devi R, Verma B, Hussain S, Arora P, Tabassum R, Gupta S (2023). WRKY transcription factors: evolution, regulation, and functional diversity in plants. Protoplasma 260, 331-348. |
| [21] | Han Q, Tan WR, Zhao YQ, Yang F, Yao XH, Lin HH, Zhang DW (2022). Salicylic acid-activated BIN2 phosphorylation of TGA3 promotes Arabidopsis PR gene expression and disease resistance. EMBO J 41, e110682. |
| [22] |
Hartmann M, Kim D, Bernsdorff F, Ajami-Rashidi Z, Scholten N, Schreiber S, Zeier T, Schuck S, Reichel- Deland V, Zeier J (2017). Biochemical principles and functional aspects of pipecolic acid biosynthesis in plant immunity. Plant Physiol 174, 124-153.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | Hartmann M, Zeier J (2018). L-lysine metabolism to N-hydroxypipecolic acid: an integral immune-activating pathway in plants. Plant J 96, 5-21. |
| [24] |
Hartmann M, Zeier T, Bernsdorff F, Reichel-Deland V, Kim D, Hohmann M, Scholten N, Schuck S, Bräutigam A, Hölzel T, Ganter C, Zeier J (2018). Flavin monooxygenase-generated N-hydroxypipecolic acid is a critical element of plant systemic immunity. Cell 173, 456-469.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Holmes EC, Chen YC, Mudgett MB, Sattely ES (2021). Arabidopsis UGT76B1 glycosylates N-hydroxy-pipecolic acid and inactivates systemic acquired resistance in tomato. Plant Cell 33, 750-765. |
| [26] | Hsin KT, Hsieh MC, Lee YH, Lin KC, Cheng YS (2022). Insight into the phylogeny and binding ability of WRKY transcription factors. Int J Mol Sci 23, 2895. |
| [27] |
Huang SJ, Jia AL, Ma SC, Sun Y, Chang XY, Han ZF, Chai JJ (2023). NLR signaling in plants: from resistosomes to second messengers. Trends Biochem Sci 48, 776-787.
DOI PMID |
| [28] | Huang WJ, Wang YR, Li X, Zhang YL (2020). Biosynthesis and regulation of salicylic acid and N-hydroxypipecolic acid in plant immunity. Mol Plant 13, 31-41. |
| [29] | Huang WJ, Wu ZS, Tian HN, Li X, Zhang YL (2021). Arabidopsis CALMODULIN-BINDING PROTEIN 60b plays dual roles in plant immunity. Plant Commun 2, 100213. |
| [30] |
Hussain RMF, Sheikh AH, Haider I, Quareshy M, Linthorst HJM (2018). Arabidopsis WRKY50 and TGA transcription factors synergistically activate expression of PR1. Front Plant Sci 9, 930.
DOI PMID |
| [31] | Javed T, Gao SJ (2023). WRKY transcription factors in plant defense. Trends Genet 39, 787-801. |
| [32] |
Jiang X, Yang YS, Li Y, Wang YZ, Rodamilans B, Ji WQ, Wu XX, García JA, Wu XY, Cheng XF (2025). Plant viruses convergently target NPR1 with various strategies to suppress salicylic acid-mediated antiviral immunity. J Integr Plant Biol 67, 1395-1412.
DOI |
| [33] | Jones JDG, Dangl JL (2006). The plant immune system. Nature 444, 323-329. |
| [34] |
Kazan K, Manners JM (2008). Jasmonate signaling: toward an integrated view. Plant Physiol 146, 1459-1468.
DOI PMID |
| [35] | Khan MSS, Islam F, Chen H, Chang M, Wang DW, Liu FQ, Fu ZQ, Chen J (2022). Transcriptional coactivators: driving force of plant immunity. Front Plant Sci 13, 823937. |
| [36] | Kim Y, Gilmour SJ, Chao LM, Park S, Thomashow MF (2020). Arabidopsis CAMTA transcription factors regulate pipecolic acid biosynthesis and priming of immunity genes. Mol Plant 13, 157-168. |
| [37] | Kim YW, Youn JH, Roh J, Kim JM, Kim SK, Kim TW (2022). Brassinosteroids enhance salicylic acid-mediated immune responses by inhibiting BIN2 phosphorylation of clade I TGA transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 15, 991-1007. |
| [38] | Kumar S, Zavaliev R, Wu QL, Zhou Y, Cheng J, Dillard L, Powers J, Withers J, Zhao JS, Guan ZQ, Borgnia MJ, Bartesaghi A, Dong XN, Zhou P (2022). Structural basis of NPR1 in activating plant immunity. Nature 605, 561-566. |
| [39] | Kumari M, Sharma P, Singh A (2025). Pipecolic acid: a positive regulator of systemic acquired resistance and plant immunity. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj 1869, 130808. |
| [40] |
Lefevere H, Bauters L, Gheysen G (2020). Salicylic acid biosynthesis in plants. Front Plant Sci 11, 338.
DOI PMID |
| [41] | Li LS, Yang YY, Chen YX, Yu F, Hao GJ, Yin GM, Dou Y, Zhi JY, Ma L, Wang JF, Feng QN, Zhang Y, Li S (2024). CBP60b clade proteins are prototypical transcription factors mediating immunity. Plant Physiol 196, 1489-1501. |
| [42] | Li LS, Ying J, Li E, Ma T, Li M, Gong LM, Wei G, Zhang Y, Li S (2021). Arabidopsis CBP60b is a central transcriptional activator of immunity. Plant Physiol 186, 1645-1659. |
| [43] | Liu YN, Sun TJ, Sun YL, Zhang YJ, Radojičić A, Ding YL, Tian HN, Huang XC, Lan JM, Chen SY, Orduna AR, Zhang KW, Jetter R, Li X, Zhang YL (2020). Diverse roles of the salicylic acid receptors NPR1 and NPR3/ NPR4 in plant immunity. Plant Cell 32, 4002-4016. |
| [44] | Lu CF, Liu XY, Tang YQ, Fu YQ, Zhang JM, Yang LT, Li PH, Zhu ZL, Dong P (2024). A comprehensive review of TGA transcription factors in plant growth, stress responses, and beyond. Int J Biol Macromol 258, 128880. |
| [45] |
Ma N, Sun P, Li ZY, Zhang FJ, Wang XF, You CX, Zhang CL, Zhang ZL (2024). Plant disease resistance outputs regulated by AP2/ERF transcription factor family. Stress Biol 4, 2.
DOI PMID |
| [46] | Mishra S, Roychowdhury R, Ray S, Hada A, Kumar A, Sarker U, Aftab T, Das R (2024). Salicylic acid (SA)- mediated plant immunity against biotic stresses: an insight on molecular components and signaling mechanism. Plant Stress 11, 100427. |
| [47] | Mohnike L, Huang WJ, Worbs B, Feussner K, Zhang YL, Feussner I (2023). N-hydroxy pipecolic acid methyl ester is involved in Arabidopsis immunity. J Exp Bot 74, 458-471. |
| [48] | Mohnike L, Rekhter D, Huang WJ, Feussner K, Tian HN, Herrfurth C, Zhang YL, Feussner I (2021). The glycosyltransferase UGT76B1 modulates N-hydroxy-pipecolic acid homeostasis and plant immunity. Plant Cell 33, 735-749. |
| [49] |
Nair A, Goyal I, Voß E, Mrozek P, Prajapati S, Thurow C, Tietze L, Tittmann K, Gatz C (2021). N-hydroxypipecolic acid-induced transcription requires the salicylic acid signaling pathway at basal SA levels. Plant Physiol 187, 2803-2819.
DOI PMID |
| [50] | Návarová H, Bernsdorff F, Döring AC, Zeier J (2012). Pipecolic acid, an endogenous mediator of defense amplification and priming, is a critical regulator of inducible plant immunity. Plant Cell 24, 5123-5141. |
| [51] | Nomoto M, Skelly MJ, Itaya T, Mori T, Suzuki T, Matsushita T, Tokizawa M, Kuwata K, Mori H, Yamamoto YY, Higashiyama T, Tsukagoshi H, Spoel SH, Tada Y (2021). Suppression of MYC transcription activators by the immune cofactor NPR1 fine-tunes plant immune responses. Cell Rep 37, 110125. |
| [52] | Patil V, Nandi AK (2022). POWERDRESS positively regulates systemic acquired resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep 41, 2351-2362. |
| [53] |
Peng YJ, Yang JF, Li X, Zhang YL (2021). Salicylic acid: biosynthesis and signaling. Annu Rev Plant Biol 72, 761-791.
DOI PMID |
| [54] |
Pieterse CMJ, van Loon LC (2004). NPR1: the spider in the web of induced resistance signaling pathways. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7, 456-464.
DOI PMID |
| [55] |
Powers J, Zhang X, Reyes AV, Zavaliev R, Ochakovski R, Xu SL, Dong XN (2024). Next-generation mapping of the salicylic acid signaling hub and transcriptional cascade. Mol Plant 17, 1558-1572.
DOI PMID |
| [56] | Ryals JA, Neuenschwander UH, Willits MG, Molina A, Steiner HY, Hunt MD (1996). Systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 8, 1809-1819. |
| [57] |
Shine MB, Yang JW, El-Habbak M, Nagyabhyru P, Fu DQ, Navarre D, Ghabrial S, Kachroo P, Kachroo A (2016). Cooperative functioning between phenylalanine ammonia lyase and isochorismate synthase activities contributes to salicylic acid biosynthesis in soybean. New Phytol 212, 627-636.
DOI PMID |
| [58] | Su ZH, Niu CQ, Zhou SC, Xu G, Zhu PC, Fu Q, Zhang YL, Ming ZH (2024). Structural basis of chorismate isomerization by Arabidopsis ISOCHORISMATE SYNTHASE1. Plant Physiol 196, 773-787. |
| [59] | Sun LF, Qin J, Wu XY, Zhang JH, Zhang J (2022). TOUCH 3 and CALMODULIN 1/4/6 cooperate with calcium-dependent protein kinases to trigger calcium-dependent activation of CAM-BINDING PROTEIN 60-LIKE G and regulate fungal resistance in plants. Plant Cell 34, 4088-4104. |
| [60] | Sun TJ, Busta L, Zhang Q, Ding PT, Jetter R, Zhang YL (2018a). TGACG-BINDING FACTOR 1 (TGA1) and TGA4 regulate salicylic acid and pipecolic acid biosynthesis by modulating the expression of SYSTEMIC ACQUIRED RESISTANCE DEFICIENT 1 (SARD1) and CALMODULIN- BINDING PROTEIN 60g (CBP60g). New Phytol 217, 344-354. |
| [61] | Sun TJ, Huang JH, Xu Y, Verma V, Jing BB, Sun YL, Ruiz Orduna A, Tian HN, Huang XC, Xia ST, Schafer L, Jetter R, Zhang YL, Li X (2020). Redundant CAMTA transcription factors negatively regulate the biosynthesis of salicylic acid and N-hydroxypipecolic acid by modulating the expression of SARD1 and CBP60g. Mol Plant 13, 144-156. |
| [62] | Sun TJ, Liang WW, Zhang YL, Li X (2018b). Negative regulation of resistance protein-mediated immunity by master transcription factors SARD1 and CBP60g. J Integr Plant Biol 60, 1023-1027. |
| [63] |
Sun TJ, Zhang YX, Li Y, Zhang Q, Ding YL, Zhang YL (2015). ChIP-seq reveals broad roles of SARD1 and CBP60g in regulating plant immunity. Nat Commun 6, 10159.
DOI PMID |
| [64] | Tada Y, Spoel SH, Pajerowska-Mukhtar K, Mou ZL, Song JQ, Wang C, Zuo JR, Dong XN (2008). Plant immunity requires conformational charges of NPR1 via S-nitrosylation and thioredoxins. Science 321, 952-956. |
| [65] |
Tian HN, Xu L, Li X, Zhang YL (2025). Salicylic acid: the roles in plant immunity and crosstalk with other hormones. J Integr Plant Biol 67, 773-785.
DOI |
| [66] |
Tian HN, Zhang YL (2019). The emergence of a mobile signal for systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 31, 1414-1415.
DOI |
| [67] | Tomaž Š, Gruden K, Coll A (2022). TGA transcription factors—structural characteristics as basis for functional variability. Front Plant Sci 13, 935819. |
| [68] | Ueno Y, Yoshida R, Kishi-Kaboshi M, Matsushita A, Jiang CJ, Goto S, Takahashi A, Hirochika H, Takatsuji H (2013). MAP kinases phosphorylate rice WRKY45. Plant Signal Behav 8, e24510. |
| [69] | Wang H, Tariq L, Yan YQ, Bi Y, Song FM (2025a). NAC transcription factors transcriptionally fine-tune signal homeostasis in plant systemic acquired resistance. Physiol Plant 177, e70123. |
| [70] | Wang L, Tsuda K, Sato M, Cohen JD, Katagiri F, Glazebrook J (2009). Arabidopsis CaM binding protein CBP60g contributes to MAMP-induced SA accumulation and is involved in disease resistance against Pseudomonas syringae. PLoS Pathog 5, e1000301. |
| [71] | Wang L, Tsuda K, Truman W, Sato M, Nguyen LV, Katagiri F, Glazebrook J (2011). CBP60g and SARD1 play partially redundant critical roles in salicylic acid signaling. Plant J 67, 1029-1041. |
| [72] | Wang W, Withers J, Li H, Zwack PJ, Rusnac DV, Shi H, Liu LJ, Yan SP, Hinds TR, Guttman M, Dong XN, Zheng N (2020). Structural basis of salicylic acid perception by Arabidopsis NPR proteins. Nature 586, 311-316. |
| [73] | Wang XY, Wen HY, Suprun A, Zhu HL (2025b). Ethylene signaling in regulating plant growth, development, and stress responses. Plants 14, 309. |
| [74] | Wang YM, Schuck S, Wu JN, Yang P, Döring AC, Zeier J, Tsuda K (2018). A MPK3/6-WRKY33-ALD1-pipecolic acid regulatory loop contributes to systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 30, 2480-2494. |
| [75] | Wang YR, Huang WJ, Li X, Zhang YL (2025c). The deubiquitinating enzyme AMSH1 contributes to plant immunity through regulating the stability of BDA1. Plants 14, 429. |
| [76] | Wu J, Zhu WT, Zhao Q (2023). Salicylic acid biosynthesis is not from phenylalanine in Arabidopsis. J Integr Plant Biol 65, 881-887. |
| [77] | Wu N, Qin L, Peng ZH, Xia ST (2022). Research progress of mobile signal Pip/NHP in systemic acquired resistance. Chin Bull Bot 57, 412-421. (in Chinese) |
|
吴楠, 覃磊, 彭志红, 夏石头 (2022). 系统获得性抗性移动信号Pip/NHP研究进展. 植物学报 57, 412-421.
DOI |
|
| [78] | Yang XH, Tannous J, Rush TA, Del Valle I, Xiao SY, Maharjan B, Liu Y, Weston DJ, De K, Tschaplinski TJ, Lee JH, Morgan M, Jacobson D, Islam MT, Chen F, Abraham PE, Tuskan GA, Doktycz MJ, Chen JG (2025). Utilizing plant synthetic biology to accelerate plant-microbe interactions research. BioDesign Res 7, 100007. |
| [79] | Yildiz I, Gross M, Moser D, Petzsch P, Köhrer K, Zeier J (2023). N-hydroxypipecolic acid induces systemic acquired resistance and transcriptional reprogramming via TGA transcription factors. Plant Cell Environ 46, 1900-1920. |
| [80] |
Yildiz I, Mantz M, Hartmann M, Zeier T, Kessel J, Thurow C, Gatz C, Petzsch P, Köhrer K, Zeier J (2021). The mobile SAR signal N-hydroxypipecolic acid induces NPR1-dependent transcriptional reprogramming and immune priming. Plant Physiol 186, 1679-1705.
DOI PMID |
| [81] |
Zavaliev R, Dong XN (2024). NPR1, a key immune regulator for plant survival under biotic and abiotic stresses. Mol Cell 84, 131-141.
DOI PMID |
| [82] | Zeier J (2021). Metabolic regulation of systemic acquired resistance. Curr Opin Plant Biol 62, 102050. |
| [83] | Zhang YL, Tessaro MJ, Lassner M, Li X (2003). Knockout analysis of Arabidopsis transcription factors TGA2, TGA5, and TGA6 reveals their redundant and essential roles in systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 15, 2647-2653. |
| [84] | Zhao SQ, Li MY, Ren XP, Wang CY, Sun XB, Sun ML, Yu XM, Wang XD (2024). Enhancement of broad-spectrum disease resistance in wheat through key genes involved in systemic acquired resistance. Front Plant Sci 15, 1355178. |
| [85] | Zhou P, Zavaliev R, Xiang YZ, Dong XN (2023). Seeing is believing: understanding functions of NPR1 and its paralogs in plant immunity through cellular and structural analyses. Curr Opin Plant Biol 73, 102352. |
| [86] | Zhou QF, Meng Q, Tan XM, Ding W, Ma K, Xu ZQ, Huang X, Gao H (2021). Protein phosphorylation changes during systemic acquired resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front Plant Sci 12, 748287. |
| [1] | Zhu Xiaobo, Wang Liyin, Chen Xuewei. Salicylic Acid-mediated Plant Immune Responses: From Metabolism and Perception to Immune Activation [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(5): 679-692. |
| [2] | Shi Shixi, Yan Shunping. Optimization of an High-performance Liquid Chromatography Method for the Determination of Salicylic Acid [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(5): 846-853. |
| [3] | Can Ye, Linbo Yao, Ying Jin, Rong Gao, Qi Tan, Xuying Li, Yanjun Zhang, Xifeng Chen, Bojun Ma, Wei Zhang, Kewei Zhang. Establishment and Application of a High-throughput Screening Method for Salicylic Acid Metabolic Mutants in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(4): 586-596. |
| [4] | Yang Li, Qu Xitong, Chen Zihang, Zou Tingting, Wang Quanhua, Wang Xiaoli. Identification of the Spinach AT-hook Gene Family and Analysis of Expression Profiles [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(3): 377-392. |
| [5] | Yuan Yuan, Enhebayaer, Qi Yanhua. Research Advances in Biological Functions of GH3 Gene Family in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(5): 770-782. |
| [6] | Wu Nan, Qin Lei, Peng Zhihong, Xia Shitou. Research Progress of Mobile Signal Pip/NHP in Systemic Acquired Resistance [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(4): 412-421. |
| [7] | Yi Qin, Yanshuang Liu, Liuliu Qiu, Min Zhou, Xiaoshan Du, Shaojun Dai, Meihong Sun. Advance in Molecular Mechanism of MBF1 Regulating Plant Heat Response and Development [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(1): 56-68. |
| [8] | Xibao Li, Minyi Lai, Shan Liang, Xiaojing Wang, Caiji Gao, Chao Yang. Function and Transcriptional Regulation of Autophagy-related Genes in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(2): 201-217. |
| [9] | Yanmei Dong, Wenying Zhang, Zhengyi Ling, Jingrui Li, Hongtong Bai, Hui Li, Lei Shi. Advances in Transcription Factors Regulating Plant Terpenoids Biosynthesis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(3): 340-350. |
| [10] | Dongdong Cao,Shanyu Chen,Yebo Qin,Huaping Wu,Guanhai Ruan,Yutao Huang. Regulatory Mechanism of Salicylic Acid on Seed Germination Under Salt Stress in Kale [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(1): 49-61. |
| [11] | Yujia Dai,Xiaofeng Luo,Wenguan Zhou,Feng Chen,Haiwei Shuai,Wenyu Yang,Kai Shu. Plant Systemic Signaling Under Biotic and Abiotic Stresses Conditions [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(2): 255-264. |
| [12] | Xuewei Song,Jiebing Wei,Shaokang Di,Yongzhen Pang. Recent Advances in the Regulation Mechanism of Transcription Factors and Metabolic Engineering of Anthocyanins [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(1): 133-156. |
| [13] | Dongmei Li, Luya Wang, Lanyue Zhang, Ziyang Tie, Huiping Mao. Mechanism of Arabidopsis Short Peptide Hormones PROPEP Gene Family in the Root Growth [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2016, 51(2): 202-209. |
| [14] | Zhenzhen Lei, Jinglong Ye, Haili Cheng, Yun Chen, Huixing Wang, Kejing Xu, Chaoyin Yue. Characterization of Soft-rot-resistant Amorphophallus konjac and Preliminary Analysis of the Resistance Mechanism [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2013, 48(3): 295-302. |
| [15] | Hongtao Liu;Haoru Yang;Weidong Huang*;Zhixia Hou;Ke Tang. Salicylic Acid 2-O-β-D-glucose: A Possible Signal Substance Involved Thermotolerance Induced by Heat Acclimation [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2009, 44(02): 211-215. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||