

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (4): 586-596.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24148 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24148
• TECHNIQUES AND METHODS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Can Ye, Linbo Yao, Ying Jin, Rong Gao, Qi Tan, Xuying Li, Yanjun Zhang, Xifeng Chen, Bojun Ma, Wei Zhang*( ), Kewei Zhang*(
), Kewei Zhang*( )
)
Received:2024-09-25
Accepted:2024-12-14
Online:2025-07-10
Published:1900-01-01
Contact:
*E-mail: wzhang@zjnu.edu.cn;kwzhang@zjnu.edu.cn
Can Ye, Linbo Yao, Ying Jin, Rong Gao, Qi Tan, Xuying Li, Yanjun Zhang, Xifeng Chen, Bojun Ma, Wei Zhang, Kewei Zhang. Establishment and Application of a High-throughput Screening Method for Salicylic Acid Metabolic Mutants in Rice[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(4): 586-596.
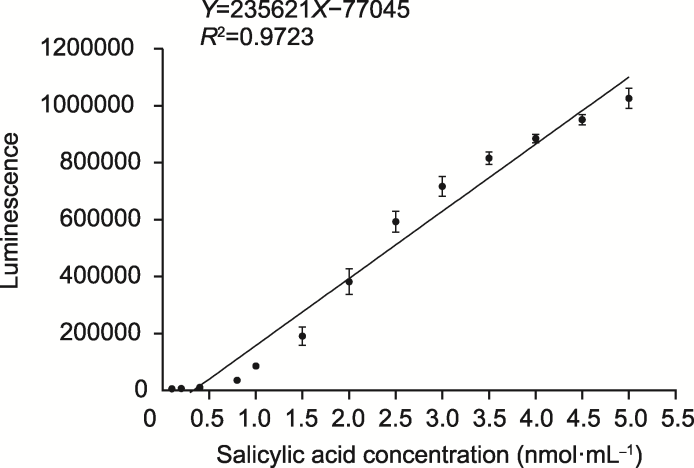
Figure 1 Standard curve of luminescence of Acinetobacter sp. ADPWH_lux strain Equation: Y=235621X-77045, Coefficient of determination: R2=0.9723. Data are means ± SD (n=3).
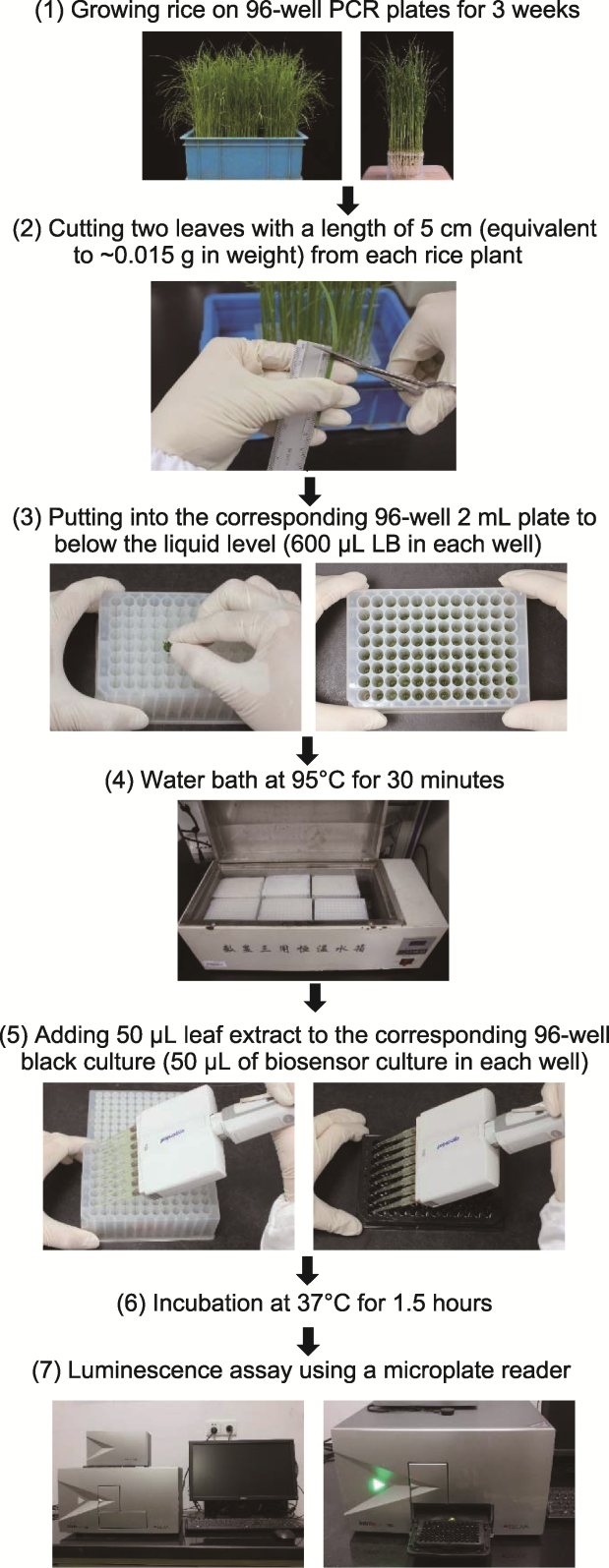
Figure 2 Modified manipulating process for high-throughput determination of salicylic acid (SA) content using SA biosensor Acinetobacter sp. ADPWH_lux strain in rice (adapted from Marek et al., 2010) (1) Rice was hydroponic for about 3 weeks in 96-well PCR plates (The bottom of tube was cut) (As controls, 3 wild type,1 oss5hDM/NIP and S5H1-OE plants were added to each plate); (2) Took two leaves of 5 cm (about 0.015 g) from each rice seedling; (3) Kneaded the leaf into a 2 mL 96-well plate with 600 μL LB, and the positions of the 96-well PCR plate and the 96-well 2 mL plate were one-to-one corresponding; (4) The 2 mL 96-well plate was bathed in water at 95°C for 30 minutes (the lid of the 96-well plate should be re-closed every 5 minutes, because high temperature would make the lid open); (5) After the leaf extract liquid from the 2 mL 96-well plate was cooled to room temperature, 50 μL of the extract liquid was pipetted into the black enzyme-labeled plate that had been added with 50 μL biosensor in advance, and the position of the enzyme-labeled plate was one-to-one corresponding to the 96-well 2 mL plate (two plates were repeated for each rice seedling in each experiment); (6) Incubation at 37°C in a incubator for 1.5 hours in the dark; (7) The relative luminescence value was measured with an enzyme-linked immunodetector (each enzyme plate needs to be measured twice).
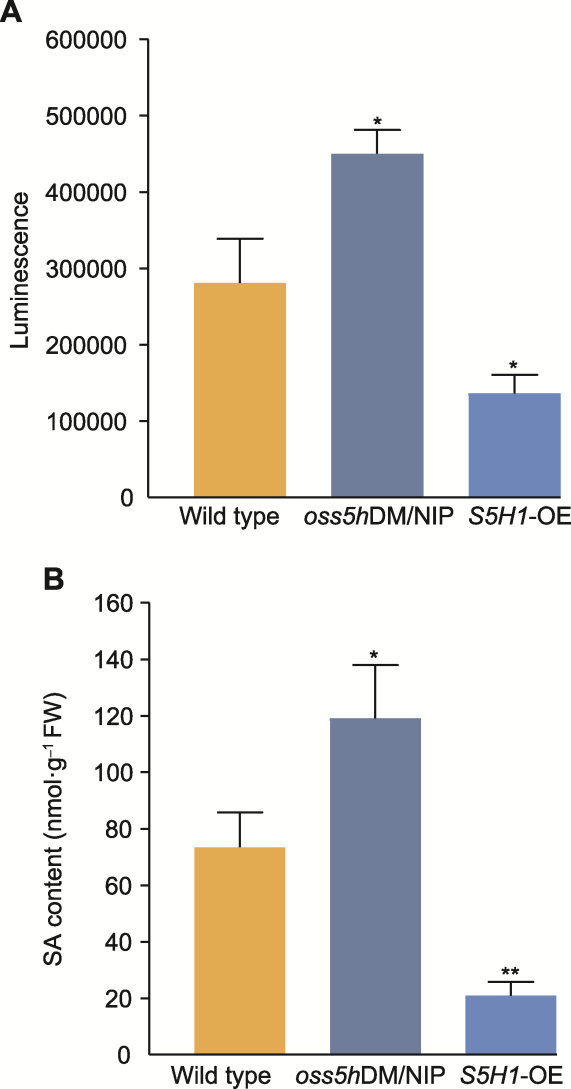
Figure 3 The salicylic acid (SA) luminescence (A) and SA content (B) of wild type (NIP), oss5hDM/NIP and S5H1-OE Rice plants were cultured in greenhouse, and the culture conditions were the same. Data are means ± SD (n=3). The statistical significances were calculated by t-test, * P<0.05; **P<0.01
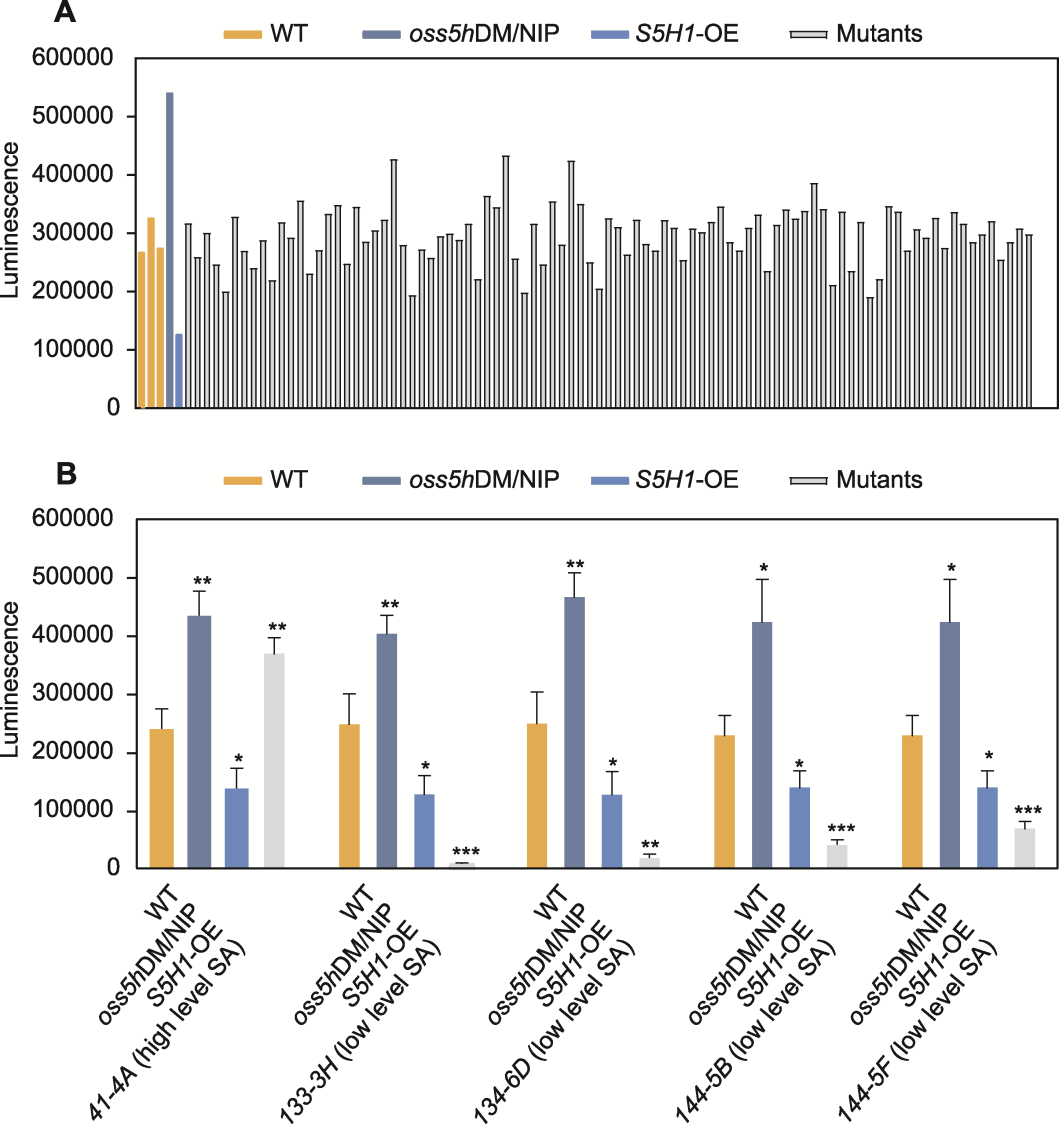
Figure 4 The salicylic acid (SA) luminescence of all rice on the 96-well PCR plate (A) and SA luminescence in the selected candidate mutants (B) Data are means ± SD (n=3). Statistical significance was calculated by t-test, * P<0.05; ** P<0.01; *** P<0.001
| No. | Sample name | Luminescence | SA concentration in extracting solution (nmol·mL-1) | Estimated SA content in rice leaves (nmol·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NIP | 240906.67±33164.52 | 1.35±0.14 | 53.98±5.63 |
| 41-4A | 373098.67±23587.55** | 1.91±0.10* | 76.42±4.00* | |
| 2 | NIP | 251577.33±48090.31 | 1.39±0.20 | 55.79±8.16 |
| 133-3H | 7778.33±1563.11*** | 0.36±0.01*** | 13.21±0.27*** | |
| 3 | NIP | 253330.67±50076.11 | 1.40±0.21 | 56.09±8.50 |
| 134-6D | 21748.67±2827.30** | 0.42±0.01** | 16.77±0.48** | |
| 4 | NIP | 232799.67±29917.16 | 1.32±0.13 | 52.60±5.08 |
| 144-5B | 44528±4907.68*** | 0.52±0.02*** | 20.64±0.83*** | |
| 5 | NIP | 232799.67±29917.16 | 1.32±0.13 | 52.60±5.08 |
| 144-5F | 72798.67±7982.44*** | 0.64±0.03*** | 25.44±1.36*** |
Table 1 The salicylic acid (SA) concentration corresponding to the SA luminescence of mutant in the standard curve and estimated SA content in rice leaves
| No. | Sample name | Luminescence | SA concentration in extracting solution (nmol·mL-1) | Estimated SA content in rice leaves (nmol·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NIP | 240906.67±33164.52 | 1.35±0.14 | 53.98±5.63 |
| 41-4A | 373098.67±23587.55** | 1.91±0.10* | 76.42±4.00* | |
| 2 | NIP | 251577.33±48090.31 | 1.39±0.20 | 55.79±8.16 |
| 133-3H | 7778.33±1563.11*** | 0.36±0.01*** | 13.21±0.27*** | |
| 3 | NIP | 253330.67±50076.11 | 1.40±0.21 | 56.09±8.50 |
| 134-6D | 21748.67±2827.30** | 0.42±0.01** | 16.77±0.48** | |
| 4 | NIP | 232799.67±29917.16 | 1.32±0.13 | 52.60±5.08 |
| 144-5B | 44528±4907.68*** | 0.52±0.02*** | 20.64±0.83*** | |
| 5 | NIP | 232799.67±29917.16 | 1.32±0.13 | 52.60±5.08 |
| 144-5F | 72798.67±7982.44*** | 0.64±0.03*** | 25.44±1.36*** |
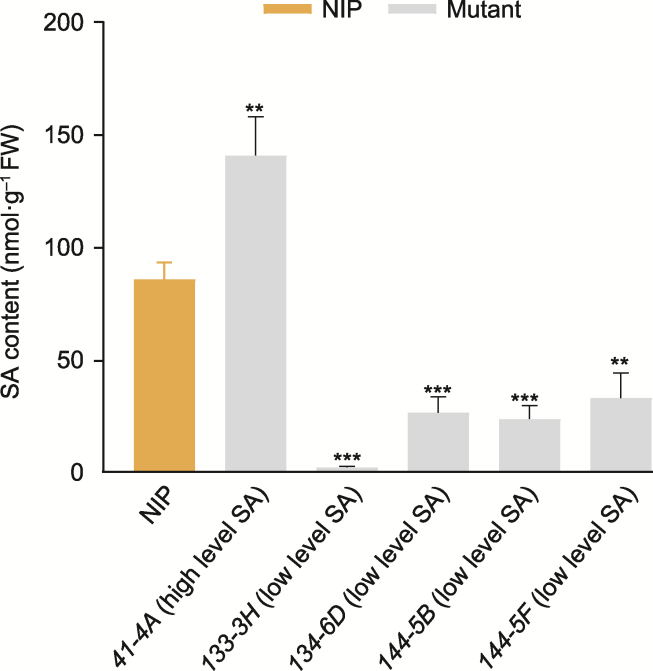
Figure 5 Histogram of salicylic acid (SA) content in wild type (NIP) and 5 SA rice mutant plants FW: Fresh weight. Data are means ± SD (n=3). The statistical significance was calculated by t-test, **P<0.01; ***P<0.001
| [1] | Aboul-Soud MAM, Cook K, Loake GJ (2004). Measurement of salicylic acid by a high-performance liquid chromatography procedure based on ion-exchange. Chromatographia 59, 129-133. |
| [2] | Ahmad P, Prasad MNV (2012). Abiotic Stress Responses in Plants:Metabolism, Productivity and Sustainability. New York: Springer Press. pp. 312-466. |
| [3] | Cao DD, Chen SY, Qin YB, Wu HP, Ruan GH, Huang YT (2020). Regulatory mechanism of salicylic acid on seed germination under salt stress in kale. Chin Bull Bot 55, 49-61. (in Chinese) |
|
曹栋栋, 陈珊宇, 秦叶波, 吴华平, 阮关海, 黄玉韬 (2020). 水杨酸调控盐胁迫下羽衣甘蓝种子萌发的机理. 植物学报 55, 49-61.
DOI |
|
| [4] | Dempsey DA, Vlot AC, Wildermuth MC, Klessig DF (2011). Salicylic acid biosynthesis and metabolism. Arabidopsis Book 9, e0156. |
| [5] |
Ding PT, Ding YL (2020). Stories of salicylic acid: a plant defense hormone. Trends Plant Sci 25, 549-565.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | Ding XY, Zhang J, Su BL, Xu HF (2001). Role of salicylic acid in plant disease resistance. Chin Bull Bot 18, 163-168. (in Chinese) |
| 丁秀英, 张军, 苏宝林, 徐惠风 (2001). 水杨酸在植物抗病中的作用. 植物学通报 18, 163-168. | |
| [7] |
Gaffney T, Friedrich L, Vernooij B, Negrotto D, Nye G, Uknes S, Ward E, Kessmann H, Ryals J (1993). Requirement of salicylic acid for the induction of systemic acquired resistance. Science 261, 754-756.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
Huang WE, Huang LF, Preston GM, Naylor M, Carr JP, Li YH, Singer AC, Whiteley AS, Wang H (2006). Quantitative in situ assay of salicylic acid in tobacco leaves using a genetically modified biosensor strain of Acinetobacter sp. ADP1. Plant J 46, 1073-1083.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Huang WE, Wang H, Zheng HJ, Huang LF, Singer AC, Thompson I, Whiteley AS (2005). Chromosomally located gene fusions constructed in Acinetobacter sp. ADP1 for the detection of salicylate. Environ Microbiol 7, 1339-1348.
PMID |
| [10] |
Koo YM, Heo AY, Choi HW (2020). Salicylic acid as a safe plant protector and growth regulator. Plant Pathol J 36, 1-10.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | Li C, Zhou L, Zhang YJ, Song FP, Zhang J (2009). Influence of ions conditions on salR gene in Acinetobacter sp. ADP1. Biotechnol Bull (9), 57-63. (in Chinese) |
| 李超, 周琳, 张永军, 宋福平, 张杰 (2009). 离子环境对Acinetobacter sp. ADP1的salR基因活性的影响. 生物技术通报 (9), 57-63. | |
| [12] |
Liu SJ, Wu YN, Fang CG, Cui Y, Jiang N, Wang H (2017). Simultaneous determination of 19 plant growth regulator residues in plant-originated foods by QuEChERS and stable isotope dilution-ultra performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal Sci 33, 1047-1052.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Malamy J, Carr JP, Klessig DF, Raskin I (1990). Salicylic acid: a likely endogenous signal in the resistance response of tobacco to viral infection. Science 250, 1002-1004.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
Marek G, Carver R, Ding YZ, Sathyanarayan D, Zhang XD, Mou ZL (2010). A high-throughput method for isolation of salicylic acid metabolic mutants. Plant Methods 6, 21.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
Meighen EA (1993). Bacterial bioluminescence: organization, regulation, and application of the lux genes. FASEB J 7, 1016-1022.
PMID |
| [16] |
Métraux JP, Signer H, Ryals J, Ward E, Wyss-Benz M, Gaudin J, Raschdorf K, Schmid E, Blum W, Inverardi B (1990). Increase in salicylic acid at the onset of systemic acquired resistance in cucumber. Science 250, 1004-1006.
PMID |
| [17] |
Peng YJ, Yang JF, Li X, Zhang YL (2021). Salicylic acid: biosynthesis and signaling. Annu Rev Plant Biol 72, 761-791.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Rasmussen JB, Hammerschmidt R, Zook MN (1991). Systemic induction of salicylic acid accumulation in cucumber after inoculation with Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae. Plant Physiol 97, 1342-1347.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
Rekhter D, Lüdke D, Ding YL, Feussner K, Zienkiewicz K, Lipka V, Wiermer M, Zhang YL, Feussner I (2019). Isochorismate-derived biosynthesis of the plant stress hormone salicylic acid. Science 365, 498-502.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Rivas-San Vicente M, Plasencia J (2011). Salicylic acid beyond defence: its role in plant growth and development. J Exp Bot 62, 3321-3338.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | Saleem M, Fariduddin Q, Castroverde CDM (2021). Salicylic acid: a key regulator of redox signaling and plant immunity. Plant Physiol Biochem 168, 381-397. |
| [22] |
Sanders IO, Smith AR, Hall MA (1989). The measurement of ethylene binding and metabolism in plant tissue. Planta 179, 97-103.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | Shields A, Shivnauth V, Castroverde CDM (2022). Salicylic acid and N-hydroxypipecolic acid at the fulcrum of the plant immunity-growth equilibrium. Front Plant Sci 13, 841688. |
| [24] |
van Butselaar T, Van den Ackerveken G (2020). Salicylic acid steers the growth-immunity tradeoff. Trends Plant Sci 25, 566-576.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Verberne MC, Brouwer N, Delbianco F, Linthorst HJM, Bol JF, Verpoorte R (2002). Method for the extraction of the volatile compound salicylic acid from tobacco leaf material. Phytochem Anal 13, 45-50. |
| [26] | Waadt R, Seller CA, Hsu PK, Takahashi Y, Munemasa S, Schroeder JI (2022). Plant hormone regulation of abiotic stress responses. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 23, 680-694. |
| [27] | Wang YK, Jin GC, Song SY, Jin YJ, Wang XW, Yang SQ, Shen XX, Gan YB, Wang YX, Li R, Liu JX, Hu JP, Pan RH (2024). A peroxisomal cinnamate: CoA ligase-dependent phytohormone metabolic cascade in submerged rice germination. Dev Cell 59, 1363-1378. |
| [28] |
White RF (1979). Acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) induces resistance to tobacco mosaic virus in tobacco. Virology 99, 410-412.
PMID |
| [29] | Xu L, Zhao HY, Wang JB, Wang XM, Jia XQ, Wang L, Xu Z, Li RL, Jiang K, Chen ZX, Luo J, Xie XD, Yi KK (2023). AIM1-dependent high basal salicylic acid accumulation modulates stomatal aperture in rice. New Phytol 238, 1420-1430. |
| [30] | Yang CK, Shen SQ, Zhou S, Li YF, Mao YY, Zhou JJ, Shi YH, An LX, Zhou QQ, Peng WJ, Lyu Y, Liu XM, Chen W, Wang SC, Qu LH, Liu XQ, Fernie AR, Luo J (2022). Rice metabolic regulatory network spanning the entire life cycle. Mol Plant 15, 258-275. |
| [31] | Zhang YJ, Yu QL, Gao SL, Yu NN, Zhao L, Wang JB, Zhao JZ, Huang P, Yao LB, Wang M, Zhang KW (2022). Disruption of the primary salicylic acid hydroxylases in rice enhances broad-spectrum resistance against pathogens. Plant Cell Environ 45, 2211-2225. |
| [32] |
Zhang YL, Li X (2019). Salicylic acid: biosynthesis, perception, and contributions to plant immunity. Curr Opin Plant Biol 50, 29-36.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
Zhao JZ, Yu NN, Ju M, Fan B, Zhang YJ, Zhu EG, Zhang MY, Zhang KW (2019). ABC transporter OsABCG18 controls the shootward transport of cytokinins and grain yield in rice. J Exp Bot 70, 6277-6291.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | Yanan Jiang, Yuqing Xu, Yiting Wei, Jun Chen, Rongwan Zhang, Beibei Zhao, Yuxiang Lin, Yuchun Rao. Research Progress on the Regulatory Mechanism of Rice Disease Resistance [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(5): 1-0. |
| [2] | Juan Cui, Xiaoyu Yu, Yuejiao Yu, Chengwei Liang, Jian Sun, Wenfu Chen. Analysis of the Texture Factors and Genetic Basis Influencing the Differences in Eating Quality between Northeast China and Japanese Japonica Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(4): 533-550. |
| [3] | Zhao Ling, Guan Ju, Liang Wenhua, Zhang Yong, Lu Kai, Zhao Chunfang, Li Yusheng, Zhang Yadong. Mapping of QTLs for Heat Tolerance at the Seedling Stage in Rice Based on a High-density Bin Map [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(3): 342-353. |
| [4] | Jiayi Lü, Legong Li, Congcong Hou. FRET-based Biosensors: Application of Small Molecule Fluorescence Probes in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(2): 283-293. |
| [5] | Xinyu Li, Yue Gu, Feifei Xu, Jinsong Bao. Research Progress on Post-translational Modifications of Starch Biosynthesis-related Proteins in Rice Endosperm [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(2): 256-270. |
| [6] | Jianguo Li, Yi Zhang, Wenjun Zhang. Iron Plaque Formation and Its Effects on Phosphorus Absorption in Rice Roots [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(1): 132-143. |
| [7] | Ruifeng Yao, Daoxin Xie. Activation and Termination of Strigolactone Signal Perception in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(6): 873-877. |
| [8] | Jinjin Lian, Luyao Tang, Yinuo Zhang, Jiaxing Zheng, Chaoyu Zhu, Yuhan Ye, Yuexing Wang, Wennan Shang, Zhenghao Fu, Xinxuan Xu, Richeng Wu, Mei Lu, Changchun Wang, Yuchun Rao. Genetic Locus Mining and Candidate Gene Analysis of Antioxidant Traits in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(5): 738-751. |
| [9] | Jiahui Huang, Huimin Yang, Xinyu Chen, Chaoyu Zhu, Yanan Jiang, Chengxiang Hu, Jinjin Lian, Tao Lu, Mei Lu, Weilin Zhang, Yuchun Rao. Response Mechanism of Rice Mutant pe-1 to Low Light Stress [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(4): 574-584. |
| [10] | Jianmin Zhou. A Combat Vehicle with a Smart Brake [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(3): 343-346. |
| [11] | Chaoyu Zhu, Chengxiang Hu, Zhenan Zhu, Zhining Zhang, Lihai Wang, Jun Chen, Sanfeng Li, Jinjin Lian, Luyao Tang, Qianqian Zhong, Wenjing Yin, Yuexing Wang, Yuchun Rao. Mapping of QTLs Associated with Rice Panicle Traits and Candidate Gene Analysis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(2): 217-230. |
| [12] | Bao Zhu, Jiangzhe Zhao, Kewei Zhang, Peng Huang. OsCKX9 is Involved in Regulating the Rice Lamina Joint Development and Leaf Angle [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(1): 10-21. |
| [13] | Yanli Fang, Chuanyu Tian, Ruyi Su, Yapei Liu, Chunlian Wang, Xifeng Chen, Wei Guo, Zhiyuan Ji. Mining and Preliminary Mapping of Rice Resistance Genes Against Bacterial Leaf Streak [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(1): 1-9. |
| [14] | Tian Chuanyu, Fang Yanli, Shen Qing, Wang Hongjie, Chen Xifeng, Guo Wei, Zhao Kaijun, Wang Chunlian, Ji Zhiyuan. Genotypic Diversity and Pathogenisity of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae Isolated from Southern China in 2019-2021 [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(5): 743-749. |
| [15] | Dai Ruohui, Qian Xinyu, Sun Jinglei, Lu Tao, Jia Qiwei, Lu Tianqi, Lu Mei, Rao Yuchun. Research Progress on the Mechanisms of Leaf Color Regulation and Related Genes in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(5): 799-812. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||