

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (1): 34-50.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22171 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22171
Special Issue: 杂粮生物学专辑 (2023年58卷1期)
• EXPERIMENTAL COMMUNICATIONS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Hui Zhang, Hongkai Liang, Hui Zhi, Linlin Zhang, Xianmin Diao*( ), Guanqing Jia*(
), Guanqing Jia*( )
)
Received:2022-07-28
Accepted:2022-12-01
Online:2023-01-01
Published:2023-01-05
Contact:
*E-mail: diaoxianmin@caas.cn;jiaguanqing@caas.cn
Hui Zhang, Hongkai Liang, Hui Zhi, Linlin Zhang, Xianmin Diao, Guanqing Jia. Analyses on the Transcription and Structure Variation of β-carotene Isomerase Gene Family in Foxtail Millet[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(1): 34-50.
| Primer name | Primer sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| D27-8G-N-F | GCTGTACAAGACTAGTATGGAGGTC- GCGGCCACTTC |
| D27-8G-N-R | GGGGAAATTCGAGCTCTCAAATCAC- TTGACGATTCT |
| D27family-6G-N-F | GCTGTACAAGACTAGTATGGCAGCA- GCCCTGCCCAT |
| D27family-6G-N-R | GGGGAAATTCGAGCTCCTATGTCTG-AAGTTTGGGGC |
| D27family-3G-N-F | GCTGTACAAGACTAGTATGGCGACG- CCGCTCGCGAC |
| D27family-3G-N-R | GGGGAAATTCGAGCTCTCAAACTTG-GGGGCAACCGA |
| QRT-8G-F | ATGAAACGAAGCTACTACACGA |
| QRT-8G-R | CAGATTGTCGAACCAGTTGTC |
| QRT-6G-F | GATGGGGGAGAAGACGGAGTA |
| QRT-6G-R | TTCTTCTTCTTCTCCAACTCCG |
| QRT-3G-F | CGCCTCTATTGCTTGTCCTATA |
| QRT-3G-R | AACTGAACATGTGCCCATTAAC |
| Culin-F | TATGGGTCATCAACAGCTTGTC |
| Culin-R | GTAGTCCCTCGTGATGAGATCC |
Table 1 List of primers
| Primer name | Primer sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| D27-8G-N-F | GCTGTACAAGACTAGTATGGAGGTC- GCGGCCACTTC |
| D27-8G-N-R | GGGGAAATTCGAGCTCTCAAATCAC- TTGACGATTCT |
| D27family-6G-N-F | GCTGTACAAGACTAGTATGGCAGCA- GCCCTGCCCAT |
| D27family-6G-N-R | GGGGAAATTCGAGCTCCTATGTCTG-AAGTTTGGGGC |
| D27family-3G-N-F | GCTGTACAAGACTAGTATGGCGACG- CCGCTCGCGAC |
| D27family-3G-N-R | GGGGAAATTCGAGCTCTCAAACTTG-GGGGCAACCGA |
| QRT-8G-F | ATGAAACGAAGCTACTACACGA |
| QRT-8G-R | CAGATTGTCGAACCAGTTGTC |
| QRT-6G-F | GATGGGGGAGAAGACGGAGTA |
| QRT-6G-R | TTCTTCTTCTTCTCCAACTCCG |
| QRT-3G-F | CGCCTCTATTGCTTGTCCTATA |
| QRT-3G-R | AACTGAACATGTGCCCATTAAC |
| Culin-F | TATGGGTCATCAACAGCTTGTC |
| Culin-R | GTAGTCCCTCGTGATGAGATCC |
| Gene ID | Species | Primary structure | GRAVY | Subcellular location | Secondary structure | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length of amino acids | Molecular weight (kDa) | Theoretical PI | Instability index (II) | Alpha helix | Beta bridge | Exten- ded strand | Ran- dom coil | ||||
| AT4G01995 | Arabidopsis thaliana | 258.00 | 28636.56 | 7.97 | 38.48 | 0.030 | Chloroplast | 0.34 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.49 |
| AT1G03055 | A. thaliana | 264.00 | 29795.14 | 8.94 | 53.39 | -0.358 | Chloroplast | 0.35 | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0.46 |
| AT1G64680 | A. thaliana | 250.00 | 28162.63 | 8.52 | 51.89 | -0.333 | Chloroplast | 0.33 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.52 |
| BdiBd21-2.2G0489400 | Brachypodium distachyon | 268.00 | 29298.93 | 8.28 | 56.92 | -0.093 | Chloroplast | 0.34 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.51 |
| BdiBd21-4.4G0220000 | B. distachyon | 277.00 | 30715.66 | 8.76 | 52.53 | -0.091 | Chloroplast | 0.34 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.54 |
| BdiBd21-3.3G0180800 | B. distachyon | 275.00 | 30152.06 | 9.16 | 58.90 | -0.147 | Chloroplast | 0.33 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.53 |
| Seita.6G088800 | Setaria italica | 271.00 | 30429.45 | 8.93 | 54.85 | -0.380 | Chloroplast | 0.37 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.52 |
| Seita.3G050900 | S. italica | 277.00 | 30185.83 | 8.66 | 58.84 | -0.170 | Chloroplast | 0.32 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.51 |
| Seita.8G168400 | S. italica | 277.00 | 30185.83 | 8.66 | 58.84 | -0.170 | Chloroplast | 0.36 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.48 |
| LOC_Os08g02210 | Oryza sativa | 261.00 | 28906.58 | 8.88 | 49.96 | -0.244 | Chloroplast | 0.35 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.50 |
| LOC_Os05g04090 | O. sativa | 118.00 | 13355.34 | 5.85 | 56.27 | -0.186 | Cytoplasm | 0.23 | 0.04 | 0.17 | 0.56 |
| LOC_Os05g04070 | O. sativa | 270.00 | 29343.02 | 7.94 | 58.60 | -0.047 | Chloroplast | 0.31 | 0.04 | 0.13 | 0.51 |
| LOC_Os11g37650 | O. sativa | 365.00 | 40864.68 | 8.52 | 55.08 | 0.024 | Chloroplast | 0.34 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 0.45 |
| Sobic.009G030800 | Sorghum bicolor | 277.00 | 30225.93 | 8.51 | 64.68 | -0.182 | Chloroplast | 0.31 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.55 |
| Sobic.005G168200 | So. bicolor | 292.00 | 32325.36 | 8.72 | 54.69 | -0.216 | Chloroplast | 0.37 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.47 |
| Sobic.007G016600 | So. bicolor | 369.00 | 30202.19 | 8.79 | 62.57 | -0.383 | Chloroplast | 0.33 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.54 |
| Sevir.6G087800 | Setaria viridis | 271.00 | 30483.49 | 8.83 | 55.49 | -0.403 | Chloroplast | 0.38 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.49 |
| Sevir.8G177900 | Se. viridis | 289.00 | 32243.38 | 8.82 | 54.93 | -0.187 | Chloroplast | 0.36 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.48 |
| Sevir.3G051400 | Se. viridis | 277.00 | 30185.83 | 8.66 | 58.84 | -0.170 | Chloroplast | 0.32 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.51 |
| Zm00008a034103 | Zea mays | 202.00 | 22824.65 | 9.31 | 65.45 | -0.249 | Chloroplast | 0.34 | 0.04 | 0.18 | 0.44 |
| Zm00008a023158 | Z. mays | 155.00 | 17878.49 | 8.22 | 56.01 | -0.370 | Chloroplast | 0.46 | 0.07 | 0.14 | 0.33 |
| Zm00008a023504 | Z. mays | 235.00 | 26224.37 | 8.93 | 67.47 | -0.340 | Chloroplast | 0.36 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.49 |
| HORVU1Hr1G015940 | Hordeum vulgare | 307.00 | 33309.59 | 9.29 | 65.88 | -0.191 | Chloroplast | 0.34 | 0.04 | 0.10 | 0.52 |
| HORVU7Hr1G076030 | H. vulgare | 294.00 | 33156.27 | 8.63 | 65.27 | -0.413 | Chloroplast | 0.34 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.49 |
| HORVU7Hr1G096970 | H. vulgare | 275.00 | 30372.12 | 8.89 | 74.47 | -0.130 | Chloroplast | 0.38 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.45 |
Table 2 Characteristics of D27s genes from different plant species
| Gene ID | Species | Primary structure | GRAVY | Subcellular location | Secondary structure | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length of amino acids | Molecular weight (kDa) | Theoretical PI | Instability index (II) | Alpha helix | Beta bridge | Exten- ded strand | Ran- dom coil | ||||
| AT4G01995 | Arabidopsis thaliana | 258.00 | 28636.56 | 7.97 | 38.48 | 0.030 | Chloroplast | 0.34 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.49 |
| AT1G03055 | A. thaliana | 264.00 | 29795.14 | 8.94 | 53.39 | -0.358 | Chloroplast | 0.35 | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0.46 |
| AT1G64680 | A. thaliana | 250.00 | 28162.63 | 8.52 | 51.89 | -0.333 | Chloroplast | 0.33 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.52 |
| BdiBd21-2.2G0489400 | Brachypodium distachyon | 268.00 | 29298.93 | 8.28 | 56.92 | -0.093 | Chloroplast | 0.34 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.51 |
| BdiBd21-4.4G0220000 | B. distachyon | 277.00 | 30715.66 | 8.76 | 52.53 | -0.091 | Chloroplast | 0.34 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.54 |
| BdiBd21-3.3G0180800 | B. distachyon | 275.00 | 30152.06 | 9.16 | 58.90 | -0.147 | Chloroplast | 0.33 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.53 |
| Seita.6G088800 | Setaria italica | 271.00 | 30429.45 | 8.93 | 54.85 | -0.380 | Chloroplast | 0.37 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.52 |
| Seita.3G050900 | S. italica | 277.00 | 30185.83 | 8.66 | 58.84 | -0.170 | Chloroplast | 0.32 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.51 |
| Seita.8G168400 | S. italica | 277.00 | 30185.83 | 8.66 | 58.84 | -0.170 | Chloroplast | 0.36 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.48 |
| LOC_Os08g02210 | Oryza sativa | 261.00 | 28906.58 | 8.88 | 49.96 | -0.244 | Chloroplast | 0.35 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.50 |
| LOC_Os05g04090 | O. sativa | 118.00 | 13355.34 | 5.85 | 56.27 | -0.186 | Cytoplasm | 0.23 | 0.04 | 0.17 | 0.56 |
| LOC_Os05g04070 | O. sativa | 270.00 | 29343.02 | 7.94 | 58.60 | -0.047 | Chloroplast | 0.31 | 0.04 | 0.13 | 0.51 |
| LOC_Os11g37650 | O. sativa | 365.00 | 40864.68 | 8.52 | 55.08 | 0.024 | Chloroplast | 0.34 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 0.45 |
| Sobic.009G030800 | Sorghum bicolor | 277.00 | 30225.93 | 8.51 | 64.68 | -0.182 | Chloroplast | 0.31 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.55 |
| Sobic.005G168200 | So. bicolor | 292.00 | 32325.36 | 8.72 | 54.69 | -0.216 | Chloroplast | 0.37 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.47 |
| Sobic.007G016600 | So. bicolor | 369.00 | 30202.19 | 8.79 | 62.57 | -0.383 | Chloroplast | 0.33 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.54 |
| Sevir.6G087800 | Setaria viridis | 271.00 | 30483.49 | 8.83 | 55.49 | -0.403 | Chloroplast | 0.38 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.49 |
| Sevir.8G177900 | Se. viridis | 289.00 | 32243.38 | 8.82 | 54.93 | -0.187 | Chloroplast | 0.36 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.48 |
| Sevir.3G051400 | Se. viridis | 277.00 | 30185.83 | 8.66 | 58.84 | -0.170 | Chloroplast | 0.32 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.51 |
| Zm00008a034103 | Zea mays | 202.00 | 22824.65 | 9.31 | 65.45 | -0.249 | Chloroplast | 0.34 | 0.04 | 0.18 | 0.44 |
| Zm00008a023158 | Z. mays | 155.00 | 17878.49 | 8.22 | 56.01 | -0.370 | Chloroplast | 0.46 | 0.07 | 0.14 | 0.33 |
| Zm00008a023504 | Z. mays | 235.00 | 26224.37 | 8.93 | 67.47 | -0.340 | Chloroplast | 0.36 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.49 |
| HORVU1Hr1G015940 | Hordeum vulgare | 307.00 | 33309.59 | 9.29 | 65.88 | -0.191 | Chloroplast | 0.34 | 0.04 | 0.10 | 0.52 |
| HORVU7Hr1G076030 | H. vulgare | 294.00 | 33156.27 | 8.63 | 65.27 | -0.413 | Chloroplast | 0.34 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.49 |
| HORVU7Hr1G096970 | H. vulgare | 275.00 | 30372.12 | 8.89 | 74.47 | -0.130 | Chloroplast | 0.38 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.45 |
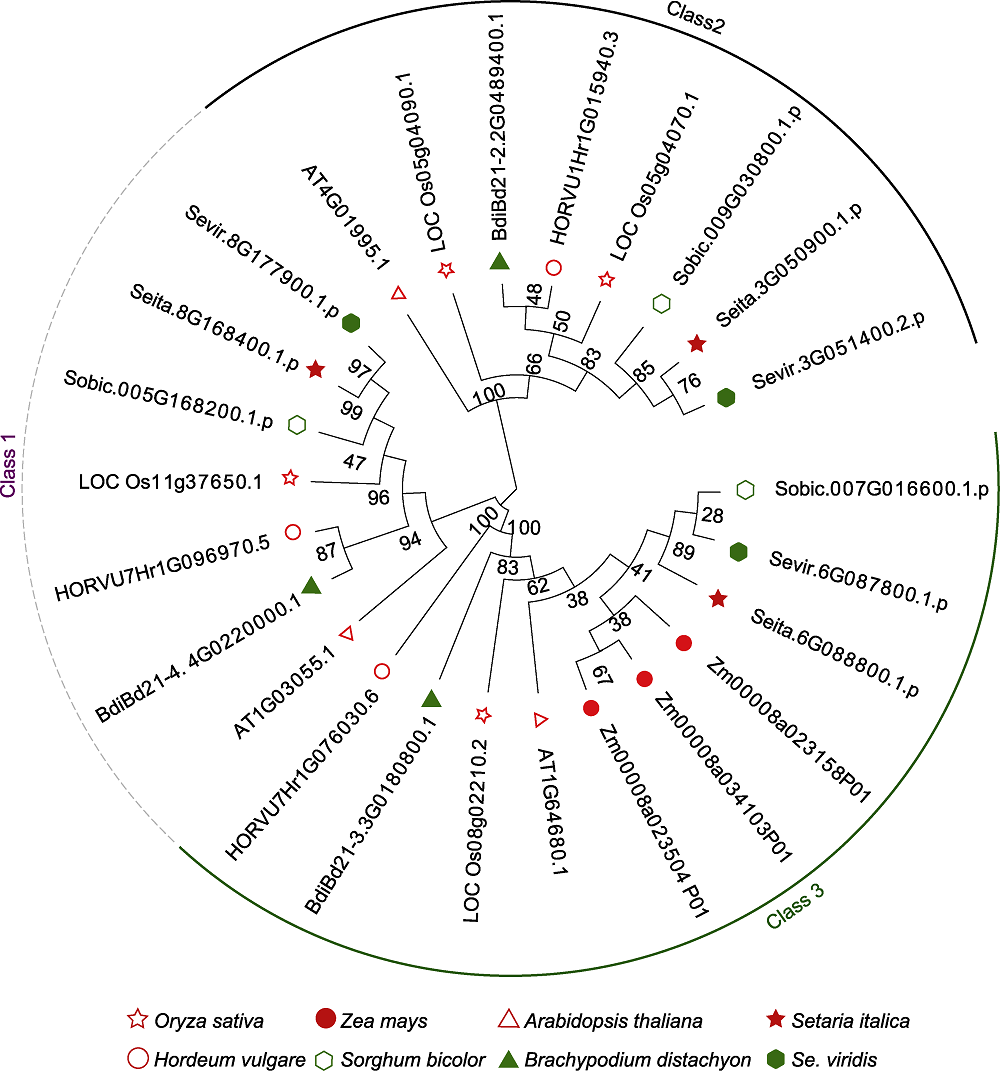
Figure 1 Phylogenetic trees of D27s genes in different crops The phylogenetic tree was constructed by using amino acid sequences of D27 proteins from 8 crop species, and the neighbor-joining method.
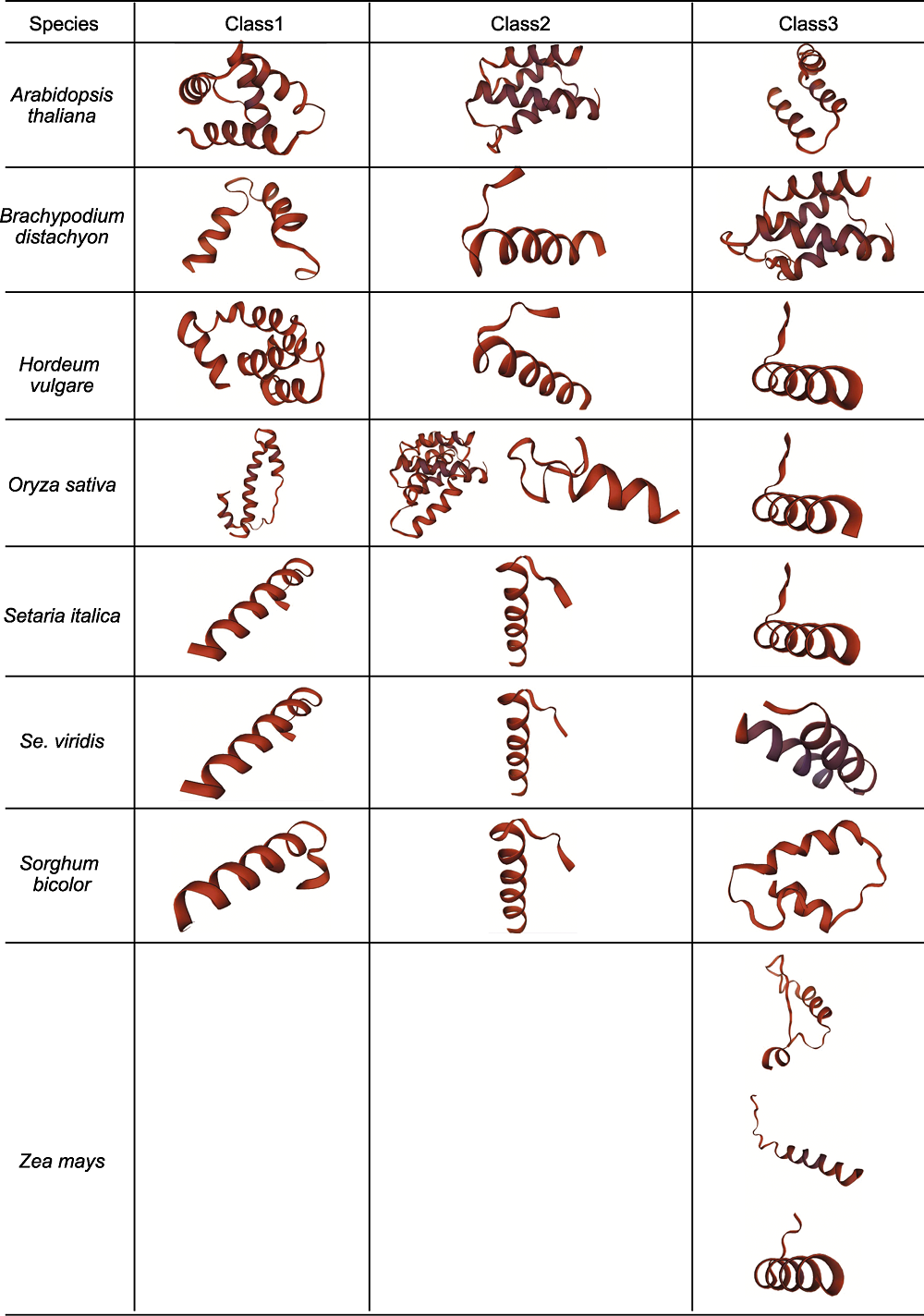
Figure 2 Tertiary structure of D27s in different species The tertiary structure of D27s in Arabidopsis thaliana, Brachypodium distachyon, Hordeum vulgare, Oryza sativa, Setaria italica, Se. viridis, Sorghum bicolor and Zea mays are visualized according to the phylogenetic tree. Class1, Class2 and Class3 correspond to the first, second and third clades of the phylogenetic tree, respectively.
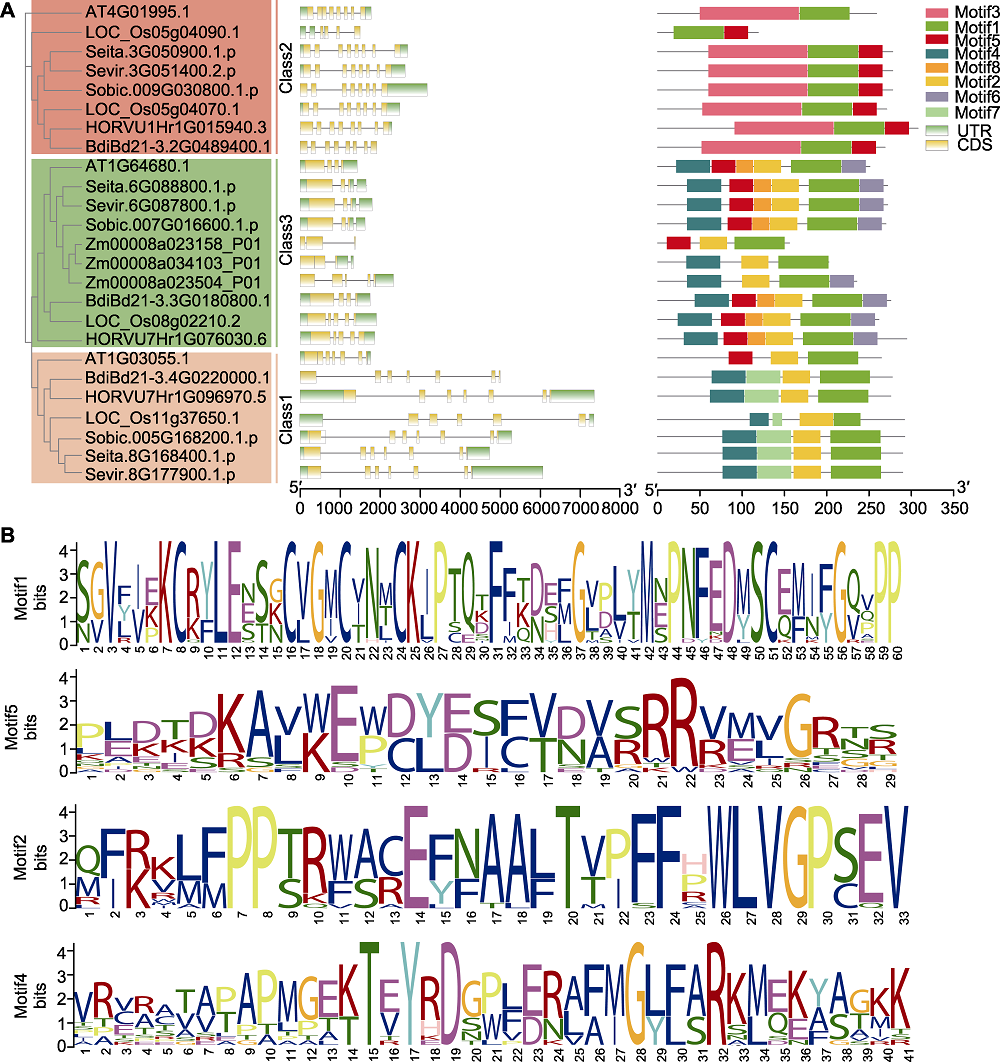
Figure 3 A gene structures of D27s genes and conserved motifs in the D27s (A) Analysis of D27s gene structure and D27 protein conserved domains (based on evolutionary tree (left), 25 D27s genes were analyzed for gene structure (middle) and protein conserved domains (right); horizontal lines in the middle represent introns, different colors in the right part represent different conserved domains; the lower scale represents gene or protein length); (B) The conservative motif logo generated by comparison of amino acid sequences of 25 D27s members. UTR: Untranslated region; CDS: Coding sequence
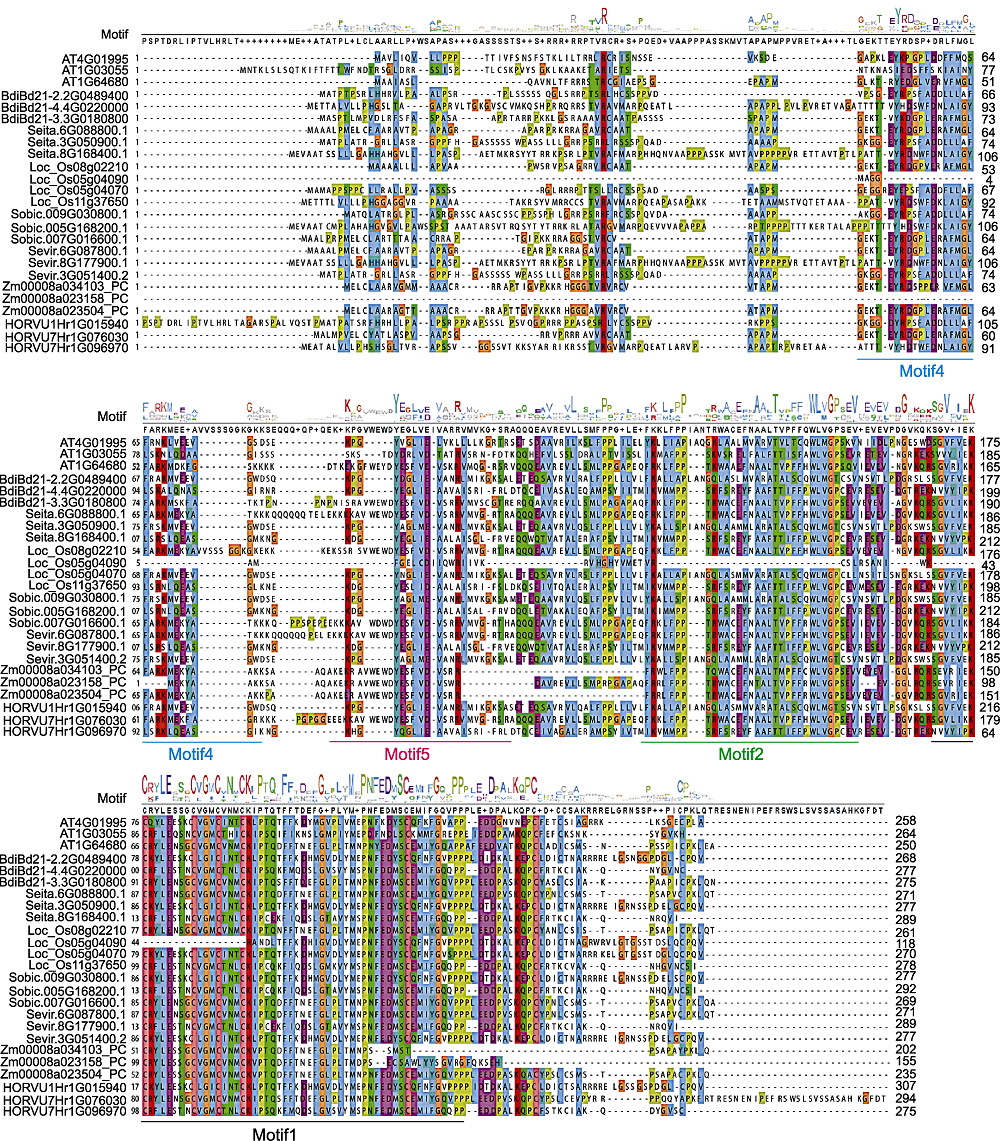
Figure 4 Alignment of amino acid sequences of D27s from 8 different species Motif1, motif2, motif4 and motif5 are found in 25 D27s sequences of 8 species, and motif1 is marked in black; motif2 is marked in green; motif4 is marked in blue; motif5 is marked in red.
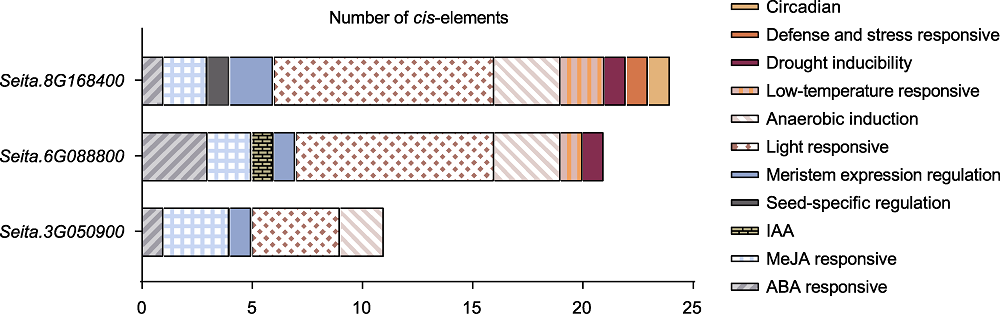
Figure 5 Prediction of D27s cis-element Diagram of cis-acting elements in the 2 000 bp upstream promoter regions of foxtail millet D27 genes. Rectangular boxes with different colors represent different cis-elements.
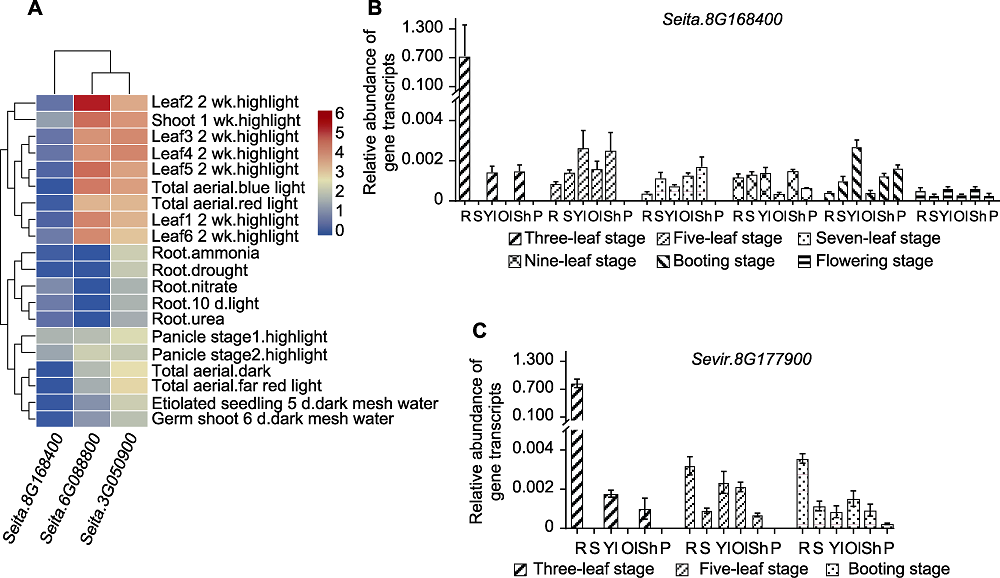
Figure 6 Expression of D27s genes throughout the reproductive period in different tiller materials (A) Expression patterns of D27s genes in different tissues of Yugu1; (B) Expression of SiD27-1 in different tissues of less tiller material Yugu1 reproductive period; (C) Expression of SvD27-1 in different tissues of multi-tiller material A10 reproductive period. R stand for root, S stand for stem, Yl stand for young leaf, Ol stand for old leaf, Sh stand for leaf sheath, and P stand for spike.
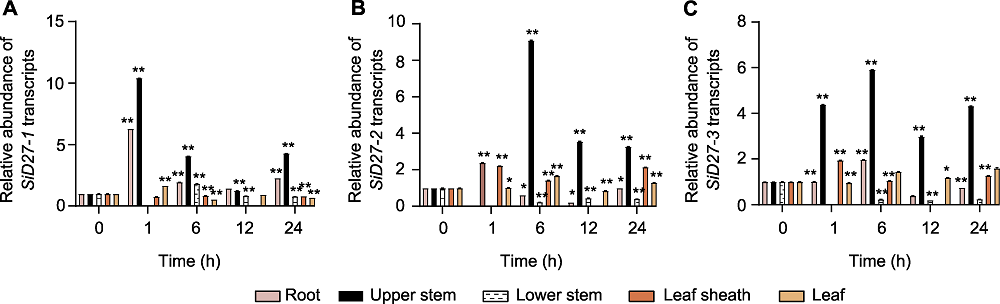
Figure 7 Responsive pattern of D27s in different tissues under phosphorus (P) deficiency treatment (A) Seita.8G168400 (SiD27-1); (B) Seita.6G088800 (SiD27-2); (C) Seita.3G050900 (SiD27-3). * P<0.05; ** P<0.01
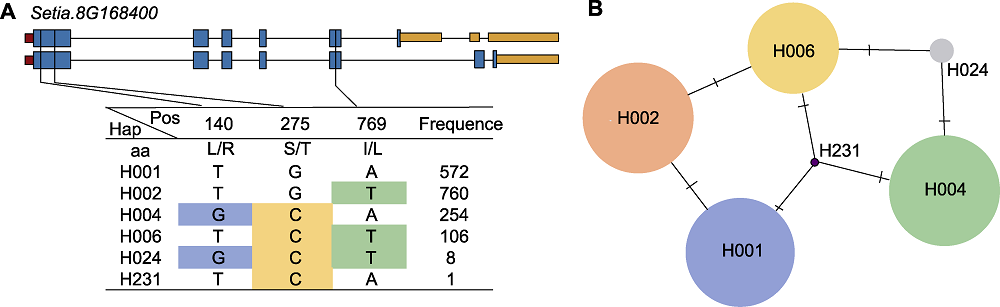
Figure 9 Sequence polymorphism analysis of SiD27-1 (A) The gene structure of SiD27-1 and its haplotypes; (B) Haplotype variation analysis (circle size indicate the number of varieties in each Hap; traverse lines represent the extent of variation between two Haps)
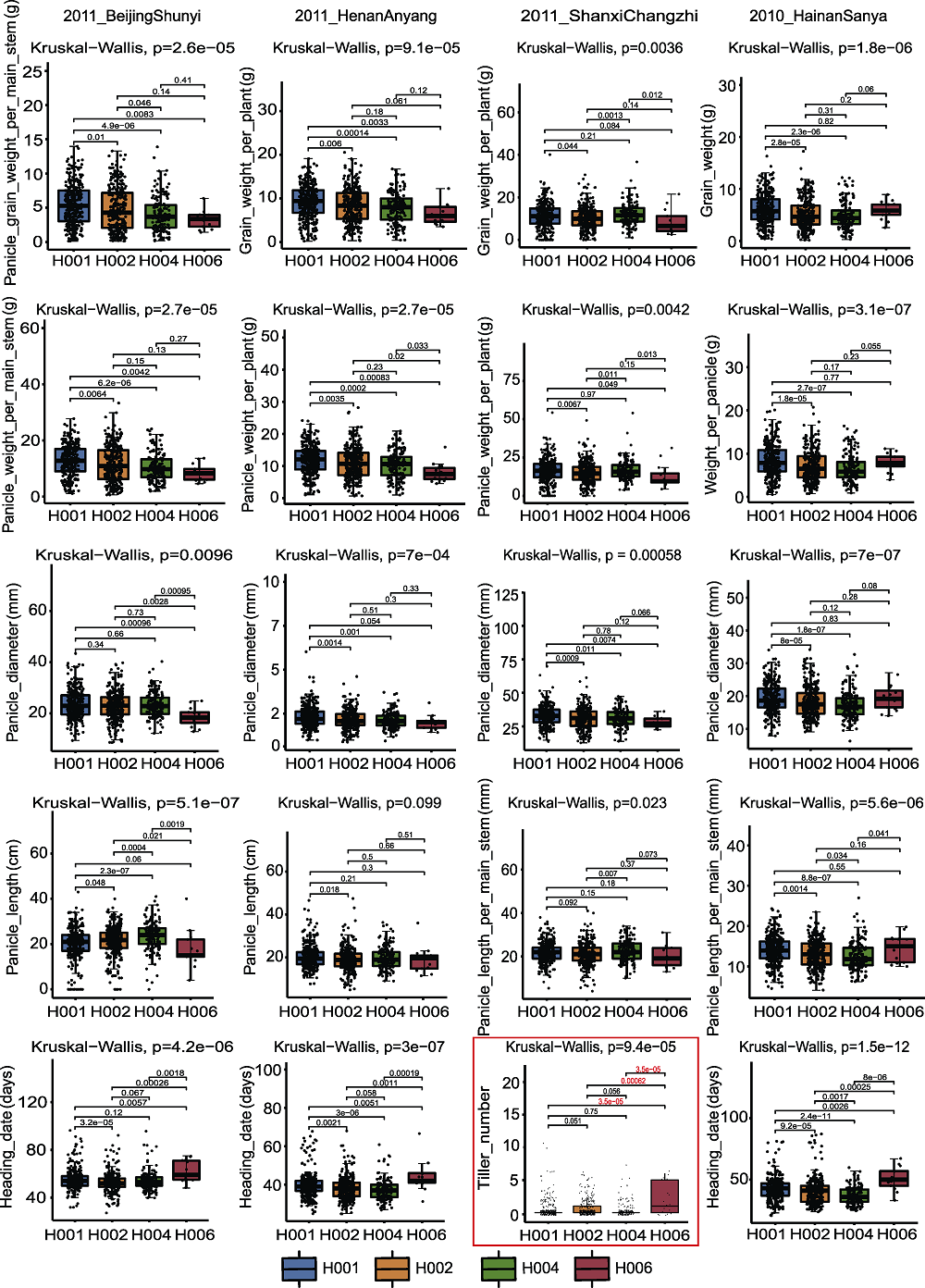
Figure 10 Box plot of SiD27-1 associated with phenotypic data in different years The red box represent the association analysis between SiD27-1 genotype and tiller phenotype
| [1] |
常金科, 黎家 (2017). 独脚金内酯信号感知揭示配体-受体作用新机制. 植物学报 52, 123-127.
DOI |
| [2] |
刁现民 (2019). 禾谷类杂粮作物耐逆和栽培技术研究新进展. 中国农业科学 52, 3943-3949.
DOI |
| [3] | 贾冠清, 刁现民 (2017). 谷子(Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv.)作为功能基因组研究模式植物的发展现状及趋势. 生命科学 29, 292-301. |
| [4] | 黎家 (2018). 植物激素——植物学研究永恒的话题. 生物技术通报 34, 5-6. |
| [5] |
黎舒佳, 高谨, 李家洋, 王永红 (2015). 独脚金内酯调控水稻分蘖的研究进展. 植物学报 50, 539-548.
DOI |
| [6] | 李学勇, 钱前, 李家洋 (2003). 水稻分蘖的分子机理研究. 中国科学院院刊 18, 274-276. |
| [7] | 刘艳, 彭晓丹, 李洋 (2016). 几种水培液对香根草生长情况的影响. 农技服务 33, 23-25. |
| [8] | 王闵霞, 彭鹏, 龙海馨, 王平, 白玉路, 李学勇 (2014). 独脚金内酯途径相关基因的研究进展. 分子植物育种 12, 603-609. |
| [9] |
吴转娣, 刘新龙, 刘家勇, 昝逢刚, 李旭娟, 刘洪博, 林秀琴, 陈学宽, 苏火生, 赵培方, 吴才文 (2017). 甘蔗独脚金内酯生物合成关键基因ScD27的克隆与表达分析. 作物学报 43, 31-41.
DOI |
| [10] | 许智宏, 李家洋 (2006). 中国植物激素研究: 过去, 现在和未来. 植物学报 23, 433. |
| [11] |
Abuauf H, Haider I, Jia KP, Ablazov A, Mi JN, Blilou I, Al-Babili S (2018). The Arabidopsis DWARF27 gene encodes an all-trans-/9-cis-β-carotene isomerase and is induced by auxin, abscisic acid and phosphate deficiency. Plant Sci 277, 33-42.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Bailey TL, Williams N, Misleh C, Li WW (2006). MEME: discovering and analyzing DNA and protein sequence motifs. Nucleic Acids Res 34, W369-W373.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Brewer PB, Dun EA, Ferguson BJ, Rameau C, Beveridge CA (2009). Strigolactone acts downstream of auxin to regulate bud outgrowth in pea and Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 150, 482-493.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Chen CJ, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas HR, Frank MH, He YH, Xia R (2020). TBtools: an integrative toolkit de- veloped for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol Plant 13, 1194-1202.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Cook CE, Whichard LP, Turner B, Wall ME, Egley GH (1966). Germination of witchweed (Striga lutea Lour.): isolation and properties of a potent stimulant. Science 154, 1189-1190.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
Fang ZM, Ji YY, Hu J, Guo RK, Sun SY, Wang XL (2020). Strigolactones and brassinosteroids antagonistically regu- late the stability of the D53-OsBZR1 complex to determi- ne FC1 expression in rice tillering. Mol Plant 13, 586-597.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Gao HB, Wang WG, Wang YH, Liang Y (2019). Molecular mechanisms underlying plant architecture and its environ- mental plasticity in rice. Mol Breeding 39, 167.
DOI |
| [18] |
Gomez-Roldan V, Fermas S, Brewer PB, Puech-Pagès V, Dun EA, Pillot JP, Letisse F, Matusova R, Danoun S, Portais JC, Bouwmeester H, Bécard G, Beveridge CA, Rameau C, Rochange S (2008). Strigolactone inhibition of shoot branching. Nature 455, 189-194.
DOI |
| [19] |
Hammond JP, White PJ (2011). Sugar signaling in root responses to low phosphorus availability. Plant Physiol 156, 1033-1040.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | Ito S, Ito K, Abeta N, Takahashi R, Sasaki Y, Yajima S (2016). Effects of strigolactone signaling on Arabidopsis growth under nitrogen deficient stress condition. Plant Signaling Behav 11, e1126031. |
| [21] |
Kebrom TH, Mullet JE (2016). Transcriptome profiling of tiller buds provides new insights into PhyB regulation of tillering and indeterminate growth in sorghum. Plant Physiol 170, 2232-2250.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | Koltai H, Beveridge CA (2013). Strigolactones and the coordinated development of shoot and root. In: Baluška F, ed. Long-Distance Systemic Signaling and Communication in Plants. Berlin: Springer. pp. 189-204. |
| [23] |
Koltai H, Cohen M, Chesin O, Mayzlish-Gati E, Bécard G, Puech V, Dor BB, Resnick N, Wininger S, Kapulnik Y (2011). Light is a positive regulator of strigolactone levels in tomato roots. J Plant Physiol 168, 1993-1996.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Kronzucker HJ, Kirk GJD, Siddiqi MY, Glass ADM (1998). Effects of hypoxia on 13NH4+ fluxes in rice roots: kinetics and compartmental analysis. Plant Physiol 116, 581-587.
PMID |
| [25] | Lescot M, Déhais P, Thijs G, Marchal K, Moreau Y, Van De Peer Y, Rouzé P, Rombauts S (2002). PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 30, 325-327. |
| [26] |
Li B, Du X, Fei YY, Wang FQ, Xu Y, Li X, Li WQ, Chen ZH, Fan FJ, Wang J, Tao YJ, Jiang YJ, Zhu QH, Yang J (2021). Efficient breeding of early-maturing rice cultivar by editing PHYC via CRISPR/Cas9. Rice 14, 86.
DOI |
| [27] |
Liao ZG, Yu H, Duan JB, Yuan K, Yu CJ, Meng XB, Kou LQ, Chen MJ, Jing YH, Liu GF, Smith SM, Li JY (2019). SLR1 inhibits MOC1 degradation to coordinate tiller number and plant height in rice. Nat Commun 10, 2738.
DOI PMID |
| [28] |
Lin H, Wang RX, Qian Q, Yan MX, Meng XB, Fu ZM, Yan CY, Jiang B, Su Z, Li JY, Wang YH (2009). DWARF27, an iron-containing protein required for the biosynthesis of strigolactones, regulates rice tiller bud outgrowth. Plant Cell 21, 1512-1525.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
López-Ráez JA, Charnikhova T, Gómez-Roldán V, Mausova R, Kohlen W, De Vos R, Verstappen F, Puech- Pages V, Bécard G, Mulder P, Bouwmeester H (2008). Tomato strigolactones are derived from carotenoids and their biosynthesis is promoted by phosphate starvation. New Phytol 178, 863-874.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
Marro N, Lidoy J, Chico MÁ, Rial C, García J, Varela RM, Macías FA, Pozo MJ, Janoušková M, López-Ráez JA (2022). Strigolactones: new players in the nitrogen-phosphorus signaling interplay. Plant Cell Environ 45, 512-527.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Matusova R, Rani K, Verstappen FWA, Franssen MCR, Beale MH, Bouwmeester HJ (2005). The strigolactone germination stimulants of the plant-parasitic Striga and Orobanche spp. are derived from the carotenoid pathway. Plant Physiol 139, 920-934.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Minh BQ, Schmidt HA, Chernomor O, Schrempf D, Woodhams MD, Von Haeseler A, Lanfear R (2020). IQ- TREE 2: new models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol Biol Evol 37, 1530-1534.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Umehara M, Hanada A, Magome H, Takeda-Kamiya N, Yamaguchi S (2010). Contribution of strigolactones to the inhibition of tiller bud outgrowth under phosphate defici- ency in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 51, 1118-1126.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Umehara M, Hanada A, Yoshida S, Akiyama K, Arite T, Takeda-Kamiya N, Magome H, Kamiya Y, Shirasu K, Yoneyama K, Kyozuka J, Yamaguchi S (2008). Inhibition of shoot branching by new terpenoid plant hormones. Nature 455, 195-200.
DOI |
| [35] |
Wang B, Smith SM, Li JY (2018). Genetic regulation of shoot architecture. Annu Rev Plant Biol 69, 437-468.
DOI PMID |
| [36] |
Wang YX, Shang LG, Yu H, Zeng LJ, Hu J, Ni S, Rao YC, Li SF, Chu JF, Meng XB, Wang L, Hu P, Yan JJ, Kang SJ, Qu MH, Lin H, Wang T, Wang Q, Hu XM, Chen HQ, Wang B, Gao ZY, Guo LB, Zeng DL, Zhu XD, Xiong GS, Li JY, Qian Q (2020). A strigolactone biosynthesis gene contributed to the green revolution in rice. Mol Plant 13, 923-932.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
Waters MT, Brewer PB, Bussell JD, Smith SM, Beveridge CA (2012). The Arabidopsis ortholog of rice DWARF27 acts upstream of MAX1 in the control of plant development by strigolactones. Plant Physiol 159, 1073-1085.
DOI PMID |
| [38] |
Wen C, Zhao QC, Nie J, Liu GQ, Shen L, Cheng CX, Xi L, Ma N, Zhao LJ (2016). Physiological controls of chrysanthemum DgD27 gene expression in regulation of shoot branching. Plant Cell Rep 35, 1053-1070.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Yoneyama K, Yoneyama K, Takeuchi Y, Sekimoto H (2007). Phosphorus deficiency in red clover promotes exudation of orobanchol, the signal for mycorrhizal symbionts and germination stimulant for root parasites. Planta 225, 1031-1038.
PMID |
| [40] |
Zhang L, Yu H, Ma B, Liu GF, Wang JJ, Wang JM, Gao RC, Li JJ, Liu JY, Xu J, Zhang YY, Li Q, Huang XH, Xu JL, Li JM, Qian Q, Han B, He ZH, Li JY (2017). A natural tandem array alleviates epigenetic repression of IPA1 and leads to superior yielding rice. Nat Commun 8, 14798.
DOI |
| [41] |
Zhao B, Wu TT, Ma SS, Jiang DJ, Bie XM, Sui N, Zhang XS, Wang F (2020). TaD27-B gene controls the tiller number in hexaploid wheat. Plant Biotechnol J 18, 513-525.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | Chen Pengxiang, Wang Bo, Wang Zijun, Han Rong. The Regulatory Roles of the Transcription Factors in Plant's Response to UV-B Radiation [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(3): 449-459. |
| [2] | Wen Chen, Yingying Zhou, Ping Luo, Yongyi Cui. Molecular Mechanism of Petal Doubling of Flower in Angiosperm [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(2): 257-277. |
| [3] | Xinhai Zeng, Rui Chen, Yu Shi, Chaoyue Gai, Kai Fan, Zhaowei Li. Research Advances in Biological Functions of Plant SPL Transcription Factors [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(6): 982-997. |
| [4] | Tian Chuanyu, Fang Yanli, Shen Qing, Wang Hongjie, Chen Xifeng, Guo Wei, Zhao Kaijun, Wang Chunlian, Ji Zhiyuan. Genotypic Diversity and Pathogenisity of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae Isolated from Southern China in 2019-2021 [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(5): 743-749. |
| [5] | Rong Sun, Yulu Yang, Yajun Li, Hui Zhang, Xukai Li. Genome-wide Identification and Analysis of PLATZ Transcription Factor Gene Family in Foxtail Millet [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(4): 548-559. |
| [6] | Qi Wang, Yanli Xu, Peng Yan, Haosheng Dong, Wei Zhang, Lin Lu, Zhiqiang Dong. Effects of PAC on Soil Nitrogen Supply and Leaf Antioxidant Properties in Foxtail Millet at Anthesis Stage [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(1): 90-107. |
| [7] | Yu Miao, Ruan Chengjiang, Ding Jian, Li Jingbin, Lu Shunguang, Wen Xiufeng. Hrh-miRn458 Regulates Oil Biosynthesis of Sea Buckthorn via Targeting Transcription Factor WRI1 [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(5): 635-648. |
| [8] | Jingwen Wang, Xingjun Wang, Changle Ma, Pengcheng Li. A Review on the Mechanism of Ribosome Stress Response in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(1): 80-89. |
| [9] | Yi Qin, Yanshuang Liu, Liuliu Qiu, Min Zhou, Xiaoshan Du, Shaojun Dai, Meihong Sun. Advance in Molecular Mechanism of MBF1 Regulating Plant Heat Response and Development [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(1): 56-68. |
| [10] | Wenjing Zhang, Xiaomeng Yang, Kan Gao, Xinyi Wei, Xuetong Shi, Ruixuan Wang, Fengxia Wu, Juqing Kang. Analysis on the Evolution and Transcription Activation Activity of ABI4 in Brassicaceae [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(6): 676-686. |
| [11] | Tianxingzi Wang, Zheng Zhu, Yue Chen, Yuqing Liu, Gaowei Yan, Shan Xu, Tong Zhang, Jinjiao Ma, Shijuan Dou, Liyun Li, Guozhen Liu. Rice OsWRKY42 is a Novel Element in Xa21-mediated Resistance Pathway Against Bacterial Leaf Blight [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(6): 687-698. |
| [12] | Dong Liu. Managing Both Internal and Foreign Affairs—A PHR-centered Gene Network Regulates Plant-mycorrhizal Symbiosis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(6): 647-650. |
| [13] | Kaicheng Kang, Xiqiang Niu, Xianzhong Huang, Nengbing Hu, Yihu Sui, Kaijing Zhang, Hao Ai. Genome-wide Identification and Comparative Evolutionary Analysis of the R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor Gene Family in Pepper [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(3): 315-329. |
| [14] | Xibao Li, Minyi Lai, Shan Liang, Xiaojing Wang, Caiji Gao, Chao Yang. Function and Transcriptional Regulation of Autophagy-related Genes in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(2): 201-217. |
| [15] | Yan Wang, Bowei Jia, Mingzhe Sun, Xiaoli Sun. Advances in Molecular Mechanisms of Stress Tolerance in Wild Soybean [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(1): 104-115. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||