

植物学报 ›› 2015, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (2): 255-262.DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1259.2015.00255 cstr: 32102.14.SP.J.1259.2015.00255
王鹤飞1,2, 李雪1, 董玲丽2, 张俊成2, 赵茂林2, 邢国珍1, 王道文2,*( ), 郑文明1,*(
), 郑文明1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2014-03-14
接受日期:2014-04-16
出版日期:2015-03-01
发布日期:2015-04-10
通讯作者:
王道文,郑文明
作者简介:? 共同第一作者
基金资助:Hefei Wang1, 2, Xue Li1, Lingli Dong2, Juncheng Zhang2, Maolin Zhao2, Guozhen Xing1, Daowen Wang2, *, Wenming Zheng1, *
Received:2014-03-14
Accepted:2014-04-16
Online:2015-03-01
Published:2015-04-10
Contact:
Wang Daowen,Zheng Wenming
About author:? These authors contributed equally to this paper
摘要: 受体样蛋白激酶及其衍生蛋白(受体样胞内激酶和受体样蛋白)在调控植物生长、发育和不良环境反应等过程中发挥重要作用。该文简要介绍了近年来获得的对植物受体样蛋白激酶及其衍生蛋白的主要认识, 着重总结了小麦(Triticum aestivum)受体样蛋白激酶及其衍生蛋白的研究进展与不足, 并展望了该领域的发展趋势, 对在小麦中进一步有效开展受体样蛋白激酶及其衍生蛋白的结构和功能研究具参考意义。
王鹤飞, 李雪, 董玲丽, 张俊成, 赵茂林, 邢国珍, 王道文, 郑文明. 小麦受体样蛋白激酶及其衍生蛋白的研究进展. 植物学报, 2015, 50(2): 255-262.
Hefei Wang, Xue Li, Lingli Dong, Juncheng Zhang, Maolin Zhao, Guozhen Xing, Daowen Wang, Wenming Zheng. Progress and Prospects in the Research on Wheat Receptor-like Kinases and Derivative Proteins. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2015, 50(2): 255-262.
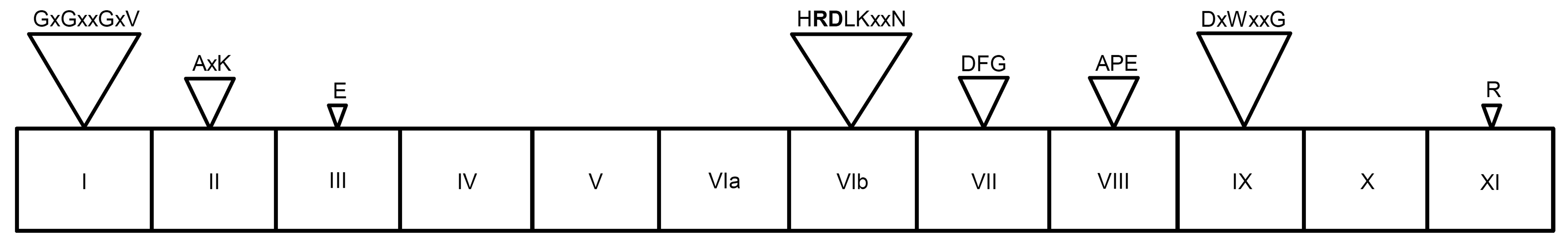
图1 典型的植物RLK蛋白激酶域一级结构示意图(Stone and Walker, 1995; Dardick and Ronald, 2006) 罗马数字标注12个亚区, 在一些亚区中含有相对保守的氨基酸基序或残基。在保守的基序中, x代表可变化的氨基酸位置。在亚区VIb含有的保守基序中, RD序列(黑体标注)的变化用于划分RD、non-RD和RD-minus三类RLK蛋白
Figure 1 A diagram illustrating the 12 subdomains (indicated by Roman numerals) in the kinase domain of typical RLKs (Stone and Walker, 1995; Dardick and Ronald, 2006) The conserved amino acid motifs or residues identified in some of the subdomains are depicted. In the depicted motifs, the letter x marks the residue that is not conserved. The RD element (shown in bold) present in the motif HRDLKxxN of subdomain VIb has been used for dividing typical RLKs into RD, non-RD and RD-minus classes
| 名称 | 一级 结构 | 激酶域 类型 | 调控(参与)的性状 | 功能验证方法 | 激酶域 活性 | 基因分离方法 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TaRLK-R1, R2, R3 | RLK | Non-RD | 调控R基因介导的小麦对条锈病菌的专化抗性 | 病毒诱导基因沉默(VIGS) | TaRLK-R3具有自身磷酸化活性 | 同源基因克隆 | Zhou et al., 2007 |
| TaSERK1, 2, 3 | RLK | RD | TaSERK1和TaSERK2可能参与小麦体细胞胚发育,TaSERK3可能参与小麦油菜素内酯信号传递 | 未验证 | 待确定 | 同源基因克隆 | Singla et al., 2008 |
| WKS1 (Yr36) | RLCK | Non-RD | 控制温度依赖性的、小麦对条锈病菌的广谱抗性 | 缺失突变体、转基因 | 具有丝/苏氨酸激酶活性 | 图位克隆 | Fu et al., 2009 |
| TaRPK1-2G | RLCK | RD | 受白粉病菌和茉莉酸甲酯处理诱导,参与小麦对白粉病菌的抗性 | VIGS | 待确定 | 同源基因克隆 | Qin et al., 2012 |
| WELP | RLK | RD | 受脱水、高盐、高温胁迫诱导,可能参与小麦对非生物逆境的耐性 | 未验证 | 待确定 | 同源基因克隆 | Zheng et al., 2012 |
| TaER1, 2 | RLK | RD | 在幼嫩组织和器官中表达量较高,受多种环境胁迫诱导,可能参与小麦生长发育以及胁迫耐性的调控 | 未验证 | 待确定 | 同源基因克隆 | Huang et al., 2013 |
| RLP1.1 | RLP | - | 调控小麦对条锈病菌的过敏抗性 | VIGS、转基因 | - | 同源基因克隆 | Jiang et al., 2013 |
| TaCRK1 | RLK | RD | 受小麦纹枯病菌诱导,但表达降低后不影响植株的抗性 | VIGS | 待确定 | 同源基因克隆 | Yang et al., 2013 |
| CERK1 | RLK | RD | 与CEBiP互作,激活真菌几丁质诱导的防御反应,调控小麦对真菌的抗性 | VIGS | 待确定 | 同源基因克隆 | Lee et al., 2014 |
| CEBiP | RLP | - | 与CERK1互作,激活真菌几丁质诱导的防御反应,调控小麦对真菌的抗性 | VIGS | - | 同源基因克隆 | Lee et al., 2014 |
表1 小麦中已得到较多研究的RLK、RLCK和RLP蛋白
Table 1 A list of the RLK, RLCK and RLP proteins that have been studied in more detail in wheat
| 名称 | 一级 结构 | 激酶域 类型 | 调控(参与)的性状 | 功能验证方法 | 激酶域 活性 | 基因分离方法 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TaRLK-R1, R2, R3 | RLK | Non-RD | 调控R基因介导的小麦对条锈病菌的专化抗性 | 病毒诱导基因沉默(VIGS) | TaRLK-R3具有自身磷酸化活性 | 同源基因克隆 | Zhou et al., 2007 |
| TaSERK1, 2, 3 | RLK | RD | TaSERK1和TaSERK2可能参与小麦体细胞胚发育,TaSERK3可能参与小麦油菜素内酯信号传递 | 未验证 | 待确定 | 同源基因克隆 | Singla et al., 2008 |
| WKS1 (Yr36) | RLCK | Non-RD | 控制温度依赖性的、小麦对条锈病菌的广谱抗性 | 缺失突变体、转基因 | 具有丝/苏氨酸激酶活性 | 图位克隆 | Fu et al., 2009 |
| TaRPK1-2G | RLCK | RD | 受白粉病菌和茉莉酸甲酯处理诱导,参与小麦对白粉病菌的抗性 | VIGS | 待确定 | 同源基因克隆 | Qin et al., 2012 |
| WELP | RLK | RD | 受脱水、高盐、高温胁迫诱导,可能参与小麦对非生物逆境的耐性 | 未验证 | 待确定 | 同源基因克隆 | Zheng et al., 2012 |
| TaER1, 2 | RLK | RD | 在幼嫩组织和器官中表达量较高,受多种环境胁迫诱导,可能参与小麦生长发育以及胁迫耐性的调控 | 未验证 | 待确定 | 同源基因克隆 | Huang et al., 2013 |
| RLP1.1 | RLP | - | 调控小麦对条锈病菌的过敏抗性 | VIGS、转基因 | - | 同源基因克隆 | Jiang et al., 2013 |
| TaCRK1 | RLK | RD | 受小麦纹枯病菌诱导,但表达降低后不影响植株的抗性 | VIGS | 待确定 | 同源基因克隆 | Yang et al., 2013 |
| CERK1 | RLK | RD | 与CEBiP互作,激活真菌几丁质诱导的防御反应,调控小麦对真菌的抗性 | VIGS | 待确定 | 同源基因克隆 | Lee et al., 2014 |
| CEBiP | RLP | - | 与CERK1互作,激活真菌几丁质诱导的防御反应,调控小麦对真菌的抗性 | VIGS | - | 同源基因克隆 | Lee et al., 2014 |
| 1 | Afzal AJ, Lightfoot DA (2007). Soybean disease resistance protein RHG1-LRR domain expressed, purified and refolded from Escherichia coli inclusion bodies: preparation for a functional analysis.Protein Expr Purif 53, 346-355. |
| 2 | Afzal AJ, Wood AJ, Lightfoot DA (2008). Plant receptor-like serine threonine kinases: roles in signaling and plant defense.Mol Plant Microbe Interact 21, 507-517. |
| 3 | Altenbach SB, Vensel WH, DuPont FM (2010). Integration of transcriptomic and proteomic data from a single wheat cultivar provides new tools for understanding the roles of individual alpha gliadin proteins in flour quality and celiac disease.J Cereal Sci 52, 143-151. |
| 4 | Antolín-Llovera M, Ried MK, Binder A, Parniske M (2012). Receptor kinase signaling pathways in plant-microbe interactions.Annu Rev Phytopathol 50, 451-473. |
| 5 | Brenchley R, Spannagl M, Pfeifer M, Barker GLA, D'Amore R, Allen AM, McKenzie N, Kramer M, Kerhornou A, Bolser D, Kay S, Waite D, Trick M, Bancroft I, Gu Y, Huo NX, Luo MC, Sehgal S, Gill B, Kianian S, Anderson O, Kersey P, Dvorak J, McCombie WR, Hall A, Mayer KFX, Edwards KJ, Bevan MW, Hall N (2012). Analysis of the bread wheat genome using whole-genome shotgun sequencing.Nature 491, 705-710. |
| 6 | Castells E, Casacuberta JM (2007). Signaling through kinase-defective domains: the prevalence of atypical receptor-like kinases in plants.J Exp Bot 58, 3503-3511. |
| 7 | Chevalier D, Batoux M, Fulton L, Pfister K, Yadav RK, Schellenberg M, Schneitz K (2005). STRUBBELIG defines a receptor kinase-mediated signaling pathway regulating organ development in Arabidopsis.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102, 9074-9079. |
| 8 | Dardick C, Ronald P (2006). Plant and animal pathogen recognition receptors signal through non-RD kinases.PLoS Pathog 2, e2. |
| 9 | Dardick C, Chen J, Richter T, Ouyang S, Ronald P (2007). The rice kinase database. A phylogenomic database for the rice kinome.Plant Physiol 143, 579-586. |
| 10 | Dardick C, Schwessinger B, Ronald P (2012). Non-ar- ginine-aspartate (non-RD) kinases are associated with innate immune receptors that recognize conserved microbial signatures.Curr Opin Plant Biol 15, 358-366. |
| 11 | De Smet, Voß U, Jurgens G, Beeckman T (2009). Receptor-like kinases shape the plant.Nat Cell Biol 11, 1166-1173. |
| 12 | Fu DL, Uauy C, Distelfeld A, Blechl A, Epstein L, Chen XM, Sela H, Fahima T, Dubcovsky J (2009). A kinase-START gene confers temperature-dependent resistance to wheat stripe rust. Science 323, 1357-1360. |
| 13 | Gish LA, Clark SE (2011). The RLK/Pelle family of kinases.Plant J 66, 117-127. |
| 14 | He Y, Jones HD, Chen S, Chen XM, Wang DW, Li KX, Wang DS, Xia LQ (2010). Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. var. durum cv. ‘Stewart’) with improved efficiency.J Exp Bot 61, 1567-1581. |
| 15 | Huang LZ, Yasir TA, Phillips AL, Hu YG (2013). Isolation and characterization of ERECTA genes and their expression patterns in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).Aust J Crop Sci 7, 381-390. |
| 16 | Idänheimo N, Gauthier A, Salojärvi J, Siligato R, Brosché M, Kollist H, Mähönen AP, Kangasjärvi J, Wrzaczek M (2014). The Arabidopsis thaliana cysteine-rich receptor-like kinases CRK6 and CRK7 protect against apoplastic oxidative stress.Biochem Biophys Res Commun 445, 457-462. |
| 17 | Jeong S, Trotochaud AE, Clark SE (1999). The Arabidopsis CLAVATA2 gene encodes a receptor-like protein required for the stability of the CLAVATA1 receptor-like kinase.Plant Cell 11, 1925-1934. |
| 18 | Jia JZ, Zhao SC, Kong XY, Li YR, Zhao GY, He WM, Appels R, Pfeifer M, Tao Y, Zhang XY, Jing RL, Zhang C, Ma YZ, Gao LF, Gao C, Spannagl M, Mayer KFX, Li D, Pan SK, Zheng FY, Hu Q, Xia XC, Li JW, Liang QS, Chen J, Wicker T, Gou CY, Kuang HH, He GY, Luo YD, Keller B, Xia QJ, Lu P, Wang JY, Zou HF, Zhang RZ, Xu JY, Gao JL, Middleton C, Quan ZW, Liu GM, Wang J, International Wheat Genome Sequencing Consortium, Yang HM, Liu X, He ZH, Mao L, Wang J (2013). Aegilops tauschii draft genome sequence reveals a gene repertoire for wheat adaptation.Nature 496, 91-95. |
| 19 | Jiang ZN, Ge S, Xing LP, Han DJ, Kang ZS, Zhang GQ, Wang XJ, Wang X, Chen PD, Cao AZ (2013). RLP1.1, a novel wheat receptor-like protein gene, is involved in the defence response against Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici.J Exp Bot 64, 3735-3746. |
| 20 | Johnson LN, Nobel MEM, Owen DJ (1996). Active and inactive protein kinases: structural basis for regulation.Cell 85, 149-158. |
| 21 | Lee WS, Rudd JJ, Hammond-Kosack KE, Kanyuka K (2014). Mycosphaerella graminicola LysM effector-me- diated stealth pathogenesis subverts recognition through both CERK1 and CEBiP homologues in wheat.Mol Plant Microbe Interact 27, 236-243. |
| 22 | Lehti-Shiu MD, Zou C, Hanada K, Shiu SH (2009). Evolutionary history and stress regulation of plant receptor-like kinase/pelle genes.Plant Physiol 150, 12-26. |
| 23 | Lehti-Shiu MD, Shiu SH (2012). Diversity, classification and function of the plant protein kinase superfamily.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 367, 2619-2639. |
| 24 | Lehti-Shiu MD, Zou C, Shiu SH (2012). Origin, diversity, expansion history, and functional evolution of the plant receptor-like kinase/pelle family. In: Tax F, Kemmerling B, eds. Signaling and Communication in Plants 13. Berlin: Springer-Verlag. pp. 1-22. |
| 25 | Lin WW, Li B, Lu DP, Chen SX, Zhu N, He P, Shan LB (2014). Tyrosine phosphorylation of protein kinase complex BAK1/BIK1 mediates Arabidopsis innate immunity.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, 3632-3637. |
| 26 | Ling HQ, Zhao SC, Liu DC, Wang JY, Sun H, Zhang C, Fan HJ, Li D, Dong LL, Tao Y, Gao C, Wu HL, Li YW, Cui Y, Guo XS, Zheng SS, Wang B, Yu K, Liang QS, Yang WL, Lou XY, Chen J, Feng MJ, Jian JB, Zhang XF, Luo GB, Jiang Y, Liu JJ, Wang ZB, Sha YH, Zhang BR, Wu HJ, Tang DZ, Shen QH, Xue PY, Zou SH, Wang XJ, Liu X, Wang FM, Yang YP, An XL, Dong ZY, Zhang KP, Zhang XQ, Luo MC, Dvorak J, Tong YP, Wang J, Yang HM, Li ZS, Wang DW, Zhang AM, Wang J (2013). Draft genome of the wheat A-genome progenitor Triticum urartu.Nature 496, 87-90. |
| 27 | Llompart B, Castells E, Río A, Roca R, Ferrando A, Stiefel V, Puigdomènech P, Casacuberta JM (2003). The direct activation of MIK, a germinal center kinase (GCK)-like kinase, by MARK, a maize atypical receptor kinase, suggests a new mechanism for signaling through kinase-dead receptors.J Biol Chem 278, 48105-48111. |
| 28 | Marshall A, Aalen RB, Audenaert D, Beeckman T, Broadley MR, Butenko MA, Caño-Delgado AI, de Vries S, Dresselhaus T, Felix G, Graham NS, Foulkes J, Granier C, Greb T, Grossniklaus U, Hammond JP, Heidstra R, Hodgman C, Hothorn M, Inzé D, Østergaard L, Russinova E, Simon R, Skirycz A, Stahl Y, Zipfel C, De Smet I (2012). Tackling drought stress: receptor-like kinases present new approaches.Plant Cell 24, 2262-2278. |
| 29 | Müller R, Bleckmann A, Simon R (2008). The receptor kinase CORYNE of Arabidopsis transmits the stem cell-limiting signal CLAVATA3 independently of CLA- VATA1.Plant Cell 20, 934-946. |
| 30 | Muschietti J, Eyal Y, McCormick S (1998). Pollen tube localization implies a role in pollen-pistil interactions for the tomato receptor-like protein kinases LePRK1 and LePRK2.Plant Cell 103, 319-330. |
| 31 | Osakabe Y, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K, Tran LSP (2013). Sensing the environment: key roles of membrane-localized kinases in plant perception and response to abiotic stress.J Exp Bot 64, 445-458. |
| 32 | Paterson AH, Bowers JE, Bruggmann R, Dubchak I, Grimwood J, Gundlach H, Haberer G, Hellsten U, Mitros T, Poliakov A, Schmutz J, Spannagl M, Tang HB, Wang XY, Wicker T, Bharti AK, Chapman J, Feltus FA, Gowik U, Grigoriev IV, Lyons E, Maher CA, Martis M, Narechania A, Otillar RP, Penning BW, Salamov AA, Wang Y, Zhang LF, Carpita NC, Freeling M, Gingle AR, Hash CT, Keller B, Klein P, Kresovich S, McCann MC, Ming R, Peterson DG, Mehboob-ur-Rahman, Ware D, Westhoff P, Mayer KF, Messing J, Rokhsar DS (2009). The Sorghum bicolor genome and the diversification of grasses.Nature 457, 551-556. |
| 33 | Prince DC, Drurey C, Zipfel C, Hogenhout S (2014). The leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase BRASSINOSTEROID INSENSITIVE1-ASSOCIATED KINASE 1 and the cytochrome P450 PHYTOALEXIN DEFICIENT3 contribute to innate immunity to aphids in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol 164, 2207-2219. |
| 34 | Sanabria NM, Huang JC, Dubery IA (2010). Self/non-self perception in plants in innate immunity and defense. Self/nonself 1, 40-54. |
| 35 | Schnable PS, Ware D, Fulton RS, Stein JC, Wei FS, Pasternak S, Liang CZ, Zhang JW, Fulton L, Graves TA, Minx P, Reily AD, Courtney L, Kruchowski SS, Tomlinson C, Strong C, Delehaunty K, Fronick C, Courtney B, Rock SM, Belter E, Du FY, Kim K, Abbott RM, Cotton M, Levy A, Marchetto P, Ochoa K, Jackson SM, Gillam B, Chen WZ, Yan L, Higginbotham J, Cardenas M, Waligorski J, Applebaum E, Phelps L, Falcone J, Kanchi K, Thane T, Scimone A, Thane N, Henke J, Wang T, Ruppert J, Shah N, Rotter K, Hodges J, Ingenthron E, Cordes M, Kohlberg S, Sgro J, Delgado B, Mead K, Chinwalla A, Leonard S, Crouse K, Collura K, Kudrna D, Currie J, He R, Angelova A, Rajasekar S, Mueller T, Lomeli R, Scara G, Ko A, Delaney K, Wissotski M, Lopez G, Campos D, Braidotti M, Ashley E, Golser W, Kim H, Lee S, Lin J, Dujmic Z, Kim W, Talag J, Zuccolo A, Fan C, Sebastian A, Kramer M, Spiegel L, Nascimento L, Zutavern T, Miller B, Ambroise C, Muller S, Spooner W, Narechania A, Ren L, Wei S, Kumari S, Faga B, Levy MJ, McMahan L, Van Buren P, Vaughn MW, Ying K, Yeh CT, Emrich SJ, Jia Y, Kalyanaraman A, Hsia AP, Barbazuk WB, Baucom RS, Brutnell TP, Carpita NC, Chaparro C, Chia JM, Deragon JM, Estill JC, Fu Y, Jeddeloh JA, Han Y, Lee H, Li P, Lisch DR, Liu S, Liu Z, Nagel DH, McCann MC, SanMiguel P, Myers AM, Nettleton D, Nguyen J, Penning BW, Ponnala L, Schneider KL, Schwartz DC, Sharma A, Soderlund C, Springer NM, Sun Q, Wang H, Waterman M, Westerman R, Wolfgruber TK, Yang LX, Yu Y, Zhang LF, Zhou SG, Zhu QH, Bennetzen JL, Dawe RK, Jiang JM, Jiang N, Presting GG, Wessler SR, Aluru S, Martienssen RA, Clifton SW, McCombie WR, Wing RA, Wilson RK (2009). The B73 maize genome: complexity, diversity, and dynamics.Science 326, 1112-1115. |
| 36 | Shan QW, Wang YP, Li J, Zhang Y, Chen KL, Liang Z, Zhang K, Liu JX, Xi JJ, Qiu JL, Gao CX (2013). Targeted genome modification of crop plants using a CRISPR-Cas system.Nat Biotechnol 31, 686-688. |
| 37 | Shimizu T, Nakano T, Takamizawa D, Desaki Y, Ishii- Minami N, Nishizawa Y, Minami E, Okada K, Yamane H, Kaku H, Shibuya N (2010). Two LysM receptor molecules, CEBiP and OsCERK1, cooperatively regulate chitin elicitor signaling in rice. Plant J 64, 204-214. |
| 38 | Shiu SH, Bleecker AB (2003). Expansion of the receptor-like kinase/Pelle gene family and receptor-like proteins in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol 132, 530-543. |
| 39 | Singla B, Khurana JP, Khurana P (2008). Characterization of three somatic embryogenesis receptor kinase genes from wheat, Triticum aestivum.Plant Cell Rep 27, 833-843. |
| 40 | Stone JM, Walker JC (1995). Plant protein kinase families and signal transduction.Plant Physiol 108, 451-457. |
| 41 | Tang WQ, Kim TW, Oses-Prieto JA, Sun Y, Deng ZP, Zhu SW, Wang RJ, Burlingame AL, Wang ZY (2008). BSKs mediate signal transduction from the receptor kinase BRI1 in Arabidopsis.Science 321, 557-560. |
| 42 | The International Brachypodium Initiative (2010). Genome sequencing and analysis of the model grass Brachypodium distachyon.Nature 463, 763-768. |
| 43 | The International Barley Genome Sequencing Consortium (2012). A physical, genetic and functional sequence assembly of the barley genome.Nature 491, 711-716. |
| 44 | Upadhyay SK, Kumar J, Alok A, Tuli R (2013). RNA- guided genome editing for target gene mutations in wh- eat.G3 3, 2233-2238. |
| 45 | Weil CF (2009). TILLING in grass species.Plant Physiol 149, 158-164. |
| 46 | Yang K, Rong W, Qi L, Li JR, Wei XN, Zhang ZY (2013). Isolation and characterization of a novel wheat cysteine-rich receptor-like kinase gene induced by Rhizoctonia cerealis.Sci Rep 3, 3021. |
| 47 | Yuan C, Li C, Yan LJ, Jackson AO, Liu ZY, Han CG, Yu JL, Li DW (2011). A high throughput barley stripe mosaic virus vector for virus induced gene silencing in monocots and dicots.PLoS One 6, e26468. |
| 48 | Zheng WJ, Xu ZS, Chen M, Li LC, Chai SC, Ma YZ (2012). Isolation and characterization of receptor-like protein kinase WELP1 in wheat.Afr J Microbiol Res 6, 2410-2418. |
| 49 | Zhou HB, Li SF, Deng ZY, Wang XP, Chen T, Zhang JS, Chen SY, Ling HQ, Zhang AM, Wang DW, Zhang XQ (2007). Molecular analysis of three new receptor-like kinase genes from hexaploid wheat and evidence for their participation in the wheat hypersensitive response to stripe rust fungus infection.Plant J 52, 420-434. |
| [1] | 马亮, 杨永青, 郭岩. “后绿色革命”基因——助力培育“气候智能”作物新品种[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 489-498. |
| [2] | 许庭旸, 刘雨辰, 王万鹏, 苏航, 苏昆龙, 吴振映, 吕明, 李福利, 王小山, 付春祥. 喷施不同植物生长调节剂对盐碱地小麦生长发育的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 354-362. |
| [3] | 周玉滢, 陈辉, 刘斯穆. 植物非典型Aux/IAA蛋白应答生长素研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 651-658. |
| [4] | 刘笑, 杜琬莹, 张云秀, 唐成名, 李华伟, 夏海勇, 樊守金, 孔令安. NO3-缓解小麦根部NH4+毒性机理(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 397-413. |
| [5] | 武棒棒, 郝宇琼, 杨淑斌, 黄雨茜, 关攀锋, 郑兴卫, 赵佳佳, 乔玲, 李晓华, 刘维仲, 郑军. 山西小麦籽粒叶黄素含量变异及遗传特性分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(4): 535-547. |
| [6] | 白明义, 彭金荣, 傅向东. 赤霉素和油菜素内酯信号通路双重调控助力小麦新一轮“绿色革命”[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(2): 194-198. |
| [7] | 李聪, 齐立娟, 谷晓峰, 李继刚. 植物光信号途径重要新调控因子TZP的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(5): 579-587. |
| [8] | 孔令让. 另辟蹊径破解小麦条锈病的基因密码[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(4): 405-408. |
| [9] | 贾利霞, 齐艳华. 生长素代谢、运输及信号转导调控水稻粒型研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(3): 263-275. |
| [10] | 支添添, 周舟, 韩成云, 任春梅. PAD4突变加速拟南芥酪氨酸降解缺陷突变体sscd1的程序性细胞死亡[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(3): 288-298. |
| [11] | 熊淑萍, 曹文博, 曹锐, 张志勇, 付新露, 徐赛俊, 潘虎强, 王小纯, 马新明. 水平结构配置对冬小麦冠层垂直结构、微环境及产量的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2022, 46(2): 188-196. |
| [12] | 孙佳欢, 刘冬, 朱家祺, 张书宁, 高梅香. 小麦-玉米轮作农田土壤螨多样性空间分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22292-. |
| [13] | 崔晓敏, 季东超, 陈彤, 田世平. 类受体激酶FER调节植物与病原菌相互作用的分子机制[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(3): 339-346. |
| [14] | 宋松泉, 刘军, 杨华, 张文虎, 张琪, 高家东. 细胞分裂素调控种子发育、休眠与萌发的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(2): 218-231. |
| [15] | 杨程惠子,唐先宇,李威,夏石头. NLR及其在植物抗病中的调控作用[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(4): 497-504. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||