

植物学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (6): 1007-1023.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24104 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24104
所属专题: 玉米生物学与分子设计(2024年59卷6期)
收稿日期:2024-07-15
接受日期:2024-10-30
出版日期:2024-11-10
发布日期:2024-10-31
通讯作者:
*李玉斌, 青岛农业大学农学院教授, 博士生导师。入选中国农业科学院“青年英才计划”A类引进人才。其研究团队在Proc Natl Acad Sci USA、Plant Cell、Plant Physiol和Genetics等主流期刊上发表研究论文30篇。以玉米为研究对象, 针对全球气候变暖导致的夏季高温玉米主产区生产的极度危害, 通过遗传学、基因组学与生物育种学多途径解析玉米耐高温的遗传机理及重要农艺表现, 利用生物育种技术创制玉米耐热新种质, 为培育耐高温玉米提供重要的种质储备和基础遗传材料。E-mail: yubinli@qau.edu.cn
基金资助:
Hengyu Yan, Zhaoxia Li, Yubin Li*( )
)
Received:2024-07-15
Accepted:2024-10-30
Online:2024-11-10
Published:2024-10-31
Contact:
*E-mail: yubinli@qau.edu.cn
摘要: 气候变化导致的全球平均气温上升严重威胁粮食安全生产, 其中作为全球三大主粮作物之一的玉米(Zea mays)所受影响极为显著。高温在玉米生长发育的多个阶段均产生重要影响, 生殖生长阶段的高温对玉米尤为不利, 能显著降低其产量。该文系统综述了高温对玉米生长的影响, 包括萌发期、苗期、营养生长中后期、开花期和灌浆期, 详尽梳理了玉米响应高温胁迫的主要分子机制(包括热激响应和未折叠蛋白反应等), 总结了我国在耐高温玉米选育方面的最新进展, 通过人工模拟高温处理和田间自然高温筛选, 鉴定出一批耐高温的杂交种和自交系。同时, 在展望未来重要研究策略中, 提出利用表型组学、全基因组关联分析和全基因组选择育种等新技术手段, 结合智能化农业管理措施, 培育高耐热性玉米品种, 以应对气候变化带来的高温挑战, 保障全球粮食安全。
闫恒宇, 李朝霞, 李玉斌. 高温对玉米生长的影响及中国耐高温玉米筛选研究进展. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 1007-1023.
Hengyu Yan, Zhaoxia Li, Yubin Li. Research Progress on Heat Stress Impact on Maize Growth and Heat-Tolerant Maize Screening in China. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(6): 1007-1023.
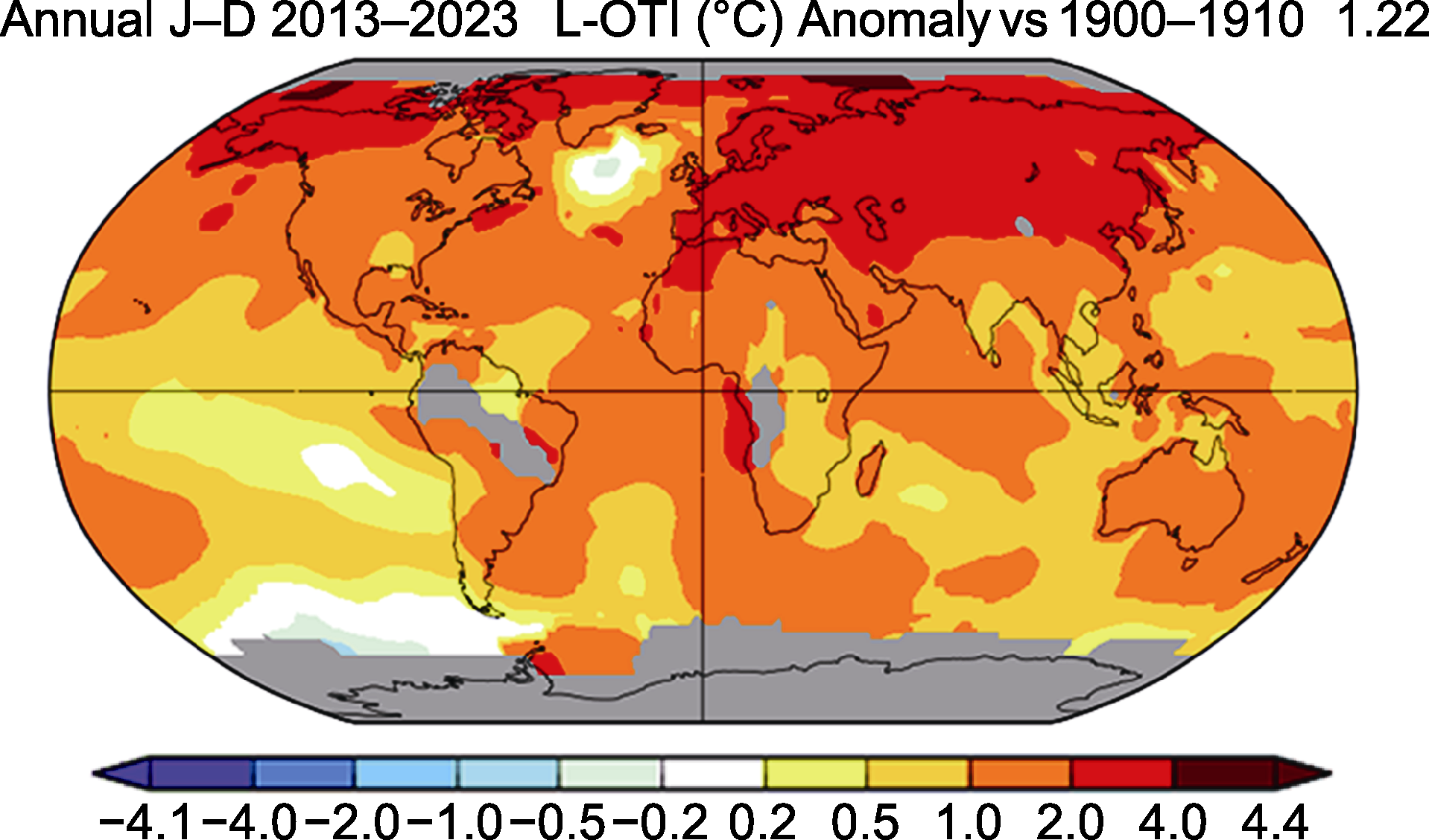
图1 全球平均地表温度在2013-2023年间相比1900-1910年的平均值变化 右上角数字表示全球温度变化的平均值, 数据来源于NASA (https://data.giss.nasa.gov/gistemp/)。L-OTI: 陆地-海洋温度指数
Figure 1 Changes in global average surface temperature from 2013-2023 compared to the average from 1900-1910 The number in the top right corner indicating the average global temperature change, data source: NASA (https://data.giss.nasa.gov/gistemp/). L-OTI: Land-ocean Temperature Index
| 年份 | 高温时期 | 耐高温评价指标 | 增温方式 | 耐高温杂交种 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 花期 | 产量、百粒重、穗长、穗粗和结实率 | 大棚增温, 增温后日平均温度和日平均最高温分别比对照高2.5-3.6°C和2.6-4.7°C | 起源9号、良硕88、黎乐66、奥玉116和伟科702 | 于康珂等, |
| 2019 | 小穗分化期和抽雄期 | 株高、穗位高和产量相关性状 | 田间自然高温, 2017年山东乐陵持续高温, 小穗分化期平均气温在32°C以上, 最高温度38.6°C | 明科玉77、德发5号、青农11、正大12、裕丰303、金海13和裕丰105 | 孙武等, |
| 2019 | 雌雄间隔期、雄穗分枝数、空秆率、畸形穗率、苞叶过短株率、果穗长和秃尖长 | 田间自然高温, 2018年6-8月平均气温27.6°C, 极端高温达37°C, 且极端高温天数比往年偏多 | C1210、郑原玉432、瑞华玉288、京农科738、隆平259、硕秋518、MC708、登海187和先玉1466 | 任仰涛等, | |
| 2020 | 抽雄吐丝期和开花散粉期 | 花粉活力 | 田间人工大棚: 抽雄吐丝期, 白天进行高温处理, 日最高温度不超过40°C; 人工气候室盆栽: 开花散粉期的9-16点, 设置30、35和40°C的温度梯度 | 郑单309 | 贾良良等, |
| 2020 | 大喇叭口后期 | 雌雄间隔期、株高、穗位高、穗长、穗粗、穗粒数、穗粒重和耐高温系数 | 智能温室的高温处理: 高温处理(36- 41°C)从大喇叭口后期到灌浆期5天, 温度为38-41°C的天数不少于7天 | 漯玉336、阳光98和豫丰3358耐高温能力强; 郑单958和阳光99的耐高温能力次之 | 吴伟华等, |
| 2022 | 大喇叭口期 | 籽粒产量、穗粒数、结实率、穗长、穗粗、雄穗主轴着生小穗长度和雄穗分枝长度 | 大棚增温: 持续高温处理7天, 昼夜温度控制在38/28°C (12小时光照/12小时黑暗) | 登海111、强盛339、鲁单9088、登海605、德瑞88和登海533 | 朱亚迪等, |
| 2023 | 花期 | 产量、Fv/Fm、叶面积指数和花粉活力 | 大棚增温方式(平均温度约为35°C)和延迟播种田间自然增温方式(平均温度约为36°C) | 苏玉糯2号、中糯2号和苏玉糯901 | 宋旭东等, |
表1 玉米杂交种耐高温评价进展
Table 1 Progress in evaluating heat tolerance of maize hybrids
| 年份 | 高温时期 | 耐高温评价指标 | 增温方式 | 耐高温杂交种 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 花期 | 产量、百粒重、穗长、穗粗和结实率 | 大棚增温, 增温后日平均温度和日平均最高温分别比对照高2.5-3.6°C和2.6-4.7°C | 起源9号、良硕88、黎乐66、奥玉116和伟科702 | 于康珂等, |
| 2019 | 小穗分化期和抽雄期 | 株高、穗位高和产量相关性状 | 田间自然高温, 2017年山东乐陵持续高温, 小穗分化期平均气温在32°C以上, 最高温度38.6°C | 明科玉77、德发5号、青农11、正大12、裕丰303、金海13和裕丰105 | 孙武等, |
| 2019 | 雌雄间隔期、雄穗分枝数、空秆率、畸形穗率、苞叶过短株率、果穗长和秃尖长 | 田间自然高温, 2018年6-8月平均气温27.6°C, 极端高温达37°C, 且极端高温天数比往年偏多 | C1210、郑原玉432、瑞华玉288、京农科738、隆平259、硕秋518、MC708、登海187和先玉1466 | 任仰涛等, | |
| 2020 | 抽雄吐丝期和开花散粉期 | 花粉活力 | 田间人工大棚: 抽雄吐丝期, 白天进行高温处理, 日最高温度不超过40°C; 人工气候室盆栽: 开花散粉期的9-16点, 设置30、35和40°C的温度梯度 | 郑单309 | 贾良良等, |
| 2020 | 大喇叭口后期 | 雌雄间隔期、株高、穗位高、穗长、穗粗、穗粒数、穗粒重和耐高温系数 | 智能温室的高温处理: 高温处理(36- 41°C)从大喇叭口后期到灌浆期5天, 温度为38-41°C的天数不少于7天 | 漯玉336、阳光98和豫丰3358耐高温能力强; 郑单958和阳光99的耐高温能力次之 | 吴伟华等, |
| 2022 | 大喇叭口期 | 籽粒产量、穗粒数、结实率、穗长、穗粗、雄穗主轴着生小穗长度和雄穗分枝长度 | 大棚增温: 持续高温处理7天, 昼夜温度控制在38/28°C (12小时光照/12小时黑暗) | 登海111、强盛339、鲁单9088、登海605、德瑞88和登海533 | 朱亚迪等, |
| 2023 | 花期 | 产量、Fv/Fm、叶面积指数和花粉活力 | 大棚增温方式(平均温度约为35°C)和延迟播种田间自然增温方式(平均温度约为36°C) | 苏玉糯2号、中糯2号和苏玉糯901 | 宋旭东等, |
| 年份 | 高温时期 | 耐高温评价指标 | 增温方式 | 耐高温自交系 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2004 | 花期 | 雄穗上着生小花的数目、花粉败育程度和花丝伸长 | 田间自然高温: 7月35°C且持续8天以上 | 特耐型: 运系5081和稷土60; 高耐型: 武314、运系98-2、91-367-1、Mg27和870115 | 王安乐等, |
| 2019 | 花期 | 空秆率和结实率 | 田间自然高温: 花期最高气温≥35°C, 最低温度≥27°C | 耐极端高温材料: PHN82; 中等耐热材料: PH5AD、B792、517M、9058、L201、M03、MM501D、BD0753和337 | 贺正华等, |
| 2019 | 花期 | 叶片灼烧程度 | 田间自然高温: 2017年开花期, ≥35°C的天气多达17天; 2018年开花期, ≥35°C的天气多达19天 | L403 | 曾威, |
| 2019 | 灌浆期 | 产量热稳定性和千粒重热感指数 | 人工模拟高温: 高温处理组平均温度为40.91°C, 正常组的平均温度为32.61°C | PH6WC、PHB1M、海014、武314和九禾6929 | 李铭东等, |
| 2019 | 拔节期至散粉期 | 花粉粒活性、叶绿素和丙二醛含量及叶绿素荧光参数 | 田间自然高温: 供试材料拔节期至散粉期处于自然>32°C高温环境 | PH4CV、15YC18、YZA3、YZA1和PB80 | 姚启伦等, |
| 2020 | 花期 | 空秆率、穗位系数、单株籽粒产量以及雌雄间隔 | 田间自然高温: 开花期连续3天气温超过33°C | SML11、SML69、SML79、鲜玉糯4号选系、SML48、SML225、紫糯、SWL01、SML354、SML425、沪玉糯3号选系、SML454、SML490、SML498、黄糯、Golden Bantam、h2113、SML1258、SML1543和SML1551 | 关媛等, |
| 2021 | 花期 | 株高、穗位高、果穗空秆率、果穗结实率、相对结实率以及部分穗部性状和籽粒产量 | 田间自然高温: 2019年7月, 高温>30°C的天数有28天; 高温>35°C的天数有21天。2020年7月, 高温>30°C的天数有30天; 高温>35°C的天数有20天; 2020年7月17-27日, 高温>40°C的天数有8天 | 极强耐高温材料: GW5F、GW4F、GW7F和PH6WC | 杨杰等, |
| 2022 | 苗期: 幼苗生长至三叶一心 | 幼苗生长至三叶一心期经38-40°C高温处理后存活天数 | 人工模拟高温: 38-40°C高温处理 | Zheng58、14HF2006、14HF1899和14HF2118 | 倪燕林, |
| 2022 | 花期 | 花粉活力 | 人工模拟高温: 40°C胁迫处理30、50和70分钟 | 603、LH196、齐319、785、LH93、L139、4N506、PHWG5、604、KZ123、沈135、武202、LH209、779和PHPR5 | 贾腾蛟等, |
| 2022 | 花期 | 叶片高温半致死温度 | 大棚增温: 苗期白天棚内最高温度为42°C, 其它时间自然降温, 取第6片真叶; 白天棚内最高温度为40°C, 其它时间自然降温, 取大喇叭口期穗位叶 | B29和PH4CV | 邢凌云, |
| 2022 | 苗期和 花期 | 苗期耐热性: 第2片叶在热胁迫下萎蔫长度; 花期耐热性: 花粉活力以及结实率 | 智能温室高温: 苗期45°C; 花期39°C | 苗期耐高温材料: CIMBL41、Chang7-2和Dan340; 花期耐高温材料: CIMBL43、CIMBL107、CIMBL84和M153 | 胡俊杰, |
表2 玉米耐高温自交系筛选进展
Table 2 Progress in screening heat-tolerant maize inbred lines
| 年份 | 高温时期 | 耐高温评价指标 | 增温方式 | 耐高温自交系 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2004 | 花期 | 雄穗上着生小花的数目、花粉败育程度和花丝伸长 | 田间自然高温: 7月35°C且持续8天以上 | 特耐型: 运系5081和稷土60; 高耐型: 武314、运系98-2、91-367-1、Mg27和870115 | 王安乐等, |
| 2019 | 花期 | 空秆率和结实率 | 田间自然高温: 花期最高气温≥35°C, 最低温度≥27°C | 耐极端高温材料: PHN82; 中等耐热材料: PH5AD、B792、517M、9058、L201、M03、MM501D、BD0753和337 | 贺正华等, |
| 2019 | 花期 | 叶片灼烧程度 | 田间自然高温: 2017年开花期, ≥35°C的天气多达17天; 2018年开花期, ≥35°C的天气多达19天 | L403 | 曾威, |
| 2019 | 灌浆期 | 产量热稳定性和千粒重热感指数 | 人工模拟高温: 高温处理组平均温度为40.91°C, 正常组的平均温度为32.61°C | PH6WC、PHB1M、海014、武314和九禾6929 | 李铭东等, |
| 2019 | 拔节期至散粉期 | 花粉粒活性、叶绿素和丙二醛含量及叶绿素荧光参数 | 田间自然高温: 供试材料拔节期至散粉期处于自然>32°C高温环境 | PH4CV、15YC18、YZA3、YZA1和PB80 | 姚启伦等, |
| 2020 | 花期 | 空秆率、穗位系数、单株籽粒产量以及雌雄间隔 | 田间自然高温: 开花期连续3天气温超过33°C | SML11、SML69、SML79、鲜玉糯4号选系、SML48、SML225、紫糯、SWL01、SML354、SML425、沪玉糯3号选系、SML454、SML490、SML498、黄糯、Golden Bantam、h2113、SML1258、SML1543和SML1551 | 关媛等, |
| 2021 | 花期 | 株高、穗位高、果穗空秆率、果穗结实率、相对结实率以及部分穗部性状和籽粒产量 | 田间自然高温: 2019年7月, 高温>30°C的天数有28天; 高温>35°C的天数有21天。2020年7月, 高温>30°C的天数有30天; 高温>35°C的天数有20天; 2020年7月17-27日, 高温>40°C的天数有8天 | 极强耐高温材料: GW5F、GW4F、GW7F和PH6WC | 杨杰等, |
| 2022 | 苗期: 幼苗生长至三叶一心 | 幼苗生长至三叶一心期经38-40°C高温处理后存活天数 | 人工模拟高温: 38-40°C高温处理 | Zheng58、14HF2006、14HF1899和14HF2118 | 倪燕林, |
| 2022 | 花期 | 花粉活力 | 人工模拟高温: 40°C胁迫处理30、50和70分钟 | 603、LH196、齐319、785、LH93、L139、4N506、PHWG5、604、KZ123、沈135、武202、LH209、779和PHPR5 | 贾腾蛟等, |
| 2022 | 花期 | 叶片高温半致死温度 | 大棚增温: 苗期白天棚内最高温度为42°C, 其它时间自然降温, 取第6片真叶; 白天棚内最高温度为40°C, 其它时间自然降温, 取大喇叭口期穗位叶 | B29和PH4CV | 邢凌云, |
| 2022 | 苗期和 花期 | 苗期耐热性: 第2片叶在热胁迫下萎蔫长度; 花期耐热性: 花粉活力以及结实率 | 智能温室高温: 苗期45°C; 花期39°C | 苗期耐高温材料: CIMBL41、Chang7-2和Dan340; 花期耐高温材料: CIMBL43、CIMBL107、CIMBL84和M153 | 胡俊杰, |
| [1] |
Adhikari B, Gayral M, Herath V, Bedsole CO, Kumar S, Ball H, Atallah O, Shaw B, Pajerowska-Mukhtar KM, Verchot J (2024). bZIP60 and Bax inhibitor 1 contribute IRE1-dependent and independent roles to potexvirus infection. New Phytol 243, 1172-1189.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | Akman Z (2009). Comparison of high temperature tolerance in maize, rice and sorghum seeds by plant growth regulators. J Anim Vet Adv 8, 358-361. |
| [3] | Barlow KM, Christy BP, O’Leary GJ, Riffkin PA, Nuttall JG (2015). Simulating the impact of extreme heat and frost events on wheat crop production: a review. Field Crops Res 171, 109-119. |
| [4] | Barton DA, Cantrill LC, Law AMK, Phillips CG, Sutton BG, Overall RL (2014). Chilling to zero degrees disrupts pollen formation but not meiotic microtubule arrays in Triticum aestivum L. Plant Cell Environ 37, 2781-2794. |
| [5] |
Begcy K, Nosenko T, Zhou LZ, Fragner L, Weckwerth W, Dresselhaus T (2019). Male sterility in maize after transient heat stress during the tetrad stage of pollen development. Plant Physiol 181, 683-700.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
Borrás L, Vitantonio-Mazzini LN (2018). Maize reproductive development and kernel set under limited plant growth environments. J Exp Bot 69, 3235-3243.
DOI PMID |
| [7] | Charng YY, Liu HC, Liu NY, Chi WT, Wang CN, Chang SH, Wang TT (2007). A heat-inducible transcription factor, HsfA2, is required for extension of acquired thermotolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 143, 251-262. |
| [8] |
Chaturvedi P, Wiese AJ, Ghatak A, Záveská Drábková L, Weckwerth W, Honys D (2021). Heat stress response mechanisms in pollen development. New Phytol 231, 571-585.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | Chen YN, Brandizzi F (2012). AtIRE1A/AtIRE1B and AGB1 independently control two essential unfolded protein response pathways in Arabidopsis. Plant J 69, 266-277. |
| [10] | Chung U, Gbegbelegbe S, Shiferaw B, Robertson R, Yun JI, Tesfaye K, Hoogenboom G, Sonder K (2014). Modeling the effect of a heat wave on maize production in the USA and its implications on food security in the developing world. Weather Clim Extrem 5-6, 67-77. |
| [11] | Cicchino M, Edreira JIR, Otegui ME (2010). Heat stress during late vegetative growth of maize: effects on phenology and assessment of optimum temperature. Crop Sci 50, 1431-1437. |
| [12] |
Crafts-Brandner SJ, Salvucci ME (2002). Sensitivity of photosynthesis in a C4 plant, maize, to heat stress. Plant Physiol 129, 1773-1780.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Deng Y, Srivastava R, Howell SH (2013). Protein kinase and ribonuclease domains of IRE1 confer stress tolerance, vegetative growth, and reproductive development in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110, 19633-19638.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
Diogo R Jr, de Resende Von Pinho EV, Pinto RT, Zhang LR, Condori-Apfata JA, Pereira PA, Vilela DR (2023). Maize heat shock proteins—prospection, validation, categorization and in silico analysis of the different ZmHSP families. Stress Biol 3, 37.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | Djalovic I, Kundu S, Bahuguna RN, Pareek A, Raza A, Singla-Pareek SL, Prasad PVV, Varshney RK (2024). Maize and heat stress: physiological, genetic, and molecular insights. Plant Genome 17, e20378. |
| [16] |
Djanaguiraman M, Narayanan S, Erdayani E, Prasad PVV (2020). Effects of high temperature stress during anthesis and grain filling periods on photosynthesis, lipids and grain yield in wheat. BMC Plant Biol 20, 268.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | Dresselhaus T, Lausser A, Márton ML (2011). Using maize as a model to study pollen tube growth and guidance, cross-incompatibility and sperm delivery in grasses. Ann Bot 108, 727-737. |
| [18] | El-Sappah AH, Rather SA, Wani SH, Elrys AS, Bilal M, Huang QL, Dar ZA, Elashtokhy MMA, Soaud N, Koul M, Mir RR, Yan K, Li J, El-Tarabily KA, Abbas M (2022). Heat stress-mediated constraints in maize (Zea mays) production: challenges and solutions. Front Plant Sci 13, 879366. |
| [19] | Farooq M, Bramley H, Palta JA, Siddique KHM (2011). Heat stress in wheat during reproductive and grain-filling phases. Crit Rev Plant Sci 30, 491-507. |
| [20] | Firon N, Shaked R, Peet MM, Pharr DM, Zamski E, Rosenfeld K, Althan L, Pressman E (2006). Pollen grains of heat tolerant tomato cultivars retain higher carbohydrate concentration under heat stress conditions. Sci Hortic 109, 212-217. |
| [21] | Gourdji SM, Sibley AM, Lobell DB (2013). Global crop exposure to critical high temperatures in the reproductive period: historical trends and future projections. Environ Res Lett 8, 024041. |
| [22] | Guan Y, Dang DD, Wang H, Das RR, Pan GL, Jeffers DP, Ruan YY, Zheng HJ (2020). Study on the identification of heat tolerance of inbred lines in sweet corn and waxy corn. Acta Agric Shanghai 36(6), 28-32. (in Chinese) |
| 关媛, 党冬冬, 王慧, Das RR, 潘广磊, Jeffers DP, 阮燕晔, 郑洪建 (2020). 甜、糯玉米自交系耐热性鉴定研究. 上海农业学报 36(6), 28-32. | |
| [23] | Hasheminejad SM, Alizadeh O, Amiri B, Barzegari M, Bayat ME (2017). The effects of drought and heat stress on some physiological and agronomic characteristics of new hybrids of corn in the north of Khuzestan Province (Iran). EurAsian J BioSci 11, 47-51. |
| [24] | Hawker JS, Jenner CF (1993). High temperature affects the activity of enzymes in the committed pathway of starch synthesis in developing wheat endosperm. Func Plant Biol 20, 197-209. |
| [25] | He ZH, Yang YY, Zhang SL, Huang YQ (2019). Dissection of the heat response tolerance for 80 maize inbred lines. Hubei Agric Sci 58(5), 12-15. (in Chinese) |
| 贺正华, 杨园园, 张士龙, 黄益勤 (2019). 80份玉米种质耐热性鉴定研究. 湖北农业科学 58(5), 12-15. | |
| [26] |
Howell SH (2013). Endoplasmic reticulum stress responses in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 64, 477-499.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | Howell SH (2021). Evolution of the unfolded protein response in plants. Plant Cell Environ 44, 2625-2635. |
| [28] | Hu JJ (2022). Establishment and Application of Maize Heat Resistance Evaluation System. Master’s thesis. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University. pp. 19-25. (in Chinese) |
| 胡俊杰 (2022). 玉米耐热性评价体系的建立和应用. 硕士论文. 武汉: 华中农业大学. pp. 19-25. | |
| [29] | Iloh AC, Omatta G, Ogbadu GH, Onyenekwe PC (2014). Effects of elevated temperature on seed germination and seedling growth on three cereal crops in Nigeria. Sci Res Essays 9, 806-813. |
| [30] | Jia LL, Huang SH, Liu XT, Yang YM, Sun YM (2020). Effect of high temperature during flowering on pollen vigor and yield of different summer maize cultivars. Jiangsu Agric Sci 48(18), 92-95. (in Chinese) |
| 贾良良, 黄少辉, 刘学彤, 杨云马, 孙彦铭 (2020). 花期高温对不同夏玉米品种花粉活力和产量的影响. 江苏农业科学 48(18), 92-95. | |
| [31] | Jia TJ, Wang H, Wang LF, Cao YY, Li JJ, Yang JW, Li HY (2022). Rapid determination and estimation of pollen viability under simulated high temperature stress in maize inbred population. J Maize Sci 30(2), 91-95. (in Chinese) |
| 贾腾蛟, 王浩, 王利锋, 曹言勇, 李晶晶, 杨继伟, 李会勇 (2022). 模拟高温胁迫下玉米自交系群体花粉活力的快速测定及评估. 玉米科学 30(2), 91-95. | |
| [32] | Jiang LY, Hu WJ, Qian YX, Ren QY, Zhang J (2021). Genome-wide identification, classification and expression analysis of the Hsf and Hsp70 gene families in maize. Gene 770, 145348. |
| [33] | Jones RJ, Schreiber BMN, Roessler JA (1996). Kernel sink capacity in maize: genotypic and maternal regulation. Crop Sci 36, 301-306. |
| [34] |
Kan Y, Lin HX (2022). A research progress of thermo-perception and thermo-responses in rice. Chin J Nat 44, 411-421. (in Chinese)
DOI |
| 阚义, 林鸿宣 (2022). 水稻高温感知及响应机制的研究进展. 自然杂志 44, 411-421. | |
| [35] |
Kan Y, Mu XR, Zhang H, Gao J, Shan JX, Ye WW, Lin HX (2022). TT2 controls rice thermotolerance through SCT1- dependent alteration of wax biosynthesis. Nat Plants 8, 53-67.
DOI PMID |
| [36] | Kim JS, Mochida K, Shinozaki K (2022). ER stress and the unfolded protein response: homeostatic regulation coordinate plant survival and growth. Plants (Basel) 11, 3197. |
| [37] | Kim SY, Hong CB, Lee I (2001). Heat shock stress causes stage-specific male sterility in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Plant Res 114, 301-307. |
| [38] |
Kotak S, Larkindale J, Lee U, von Koskull-Döring P, Vierling E, Scharf KD (2007). Complexity of the heat stress response in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10, 310-316.
DOI PMID |
| [39] | Kurtyka R, Burdach Z, Karcz W (2011). Temperature dependence of growth in maize seedlings and excised coleoptile segments. Pol J Environ Stud 20, 1221-1225. |
| [40] | Li JF (2023). Analysis of the occurrence degree of high temperature and heat damage to summer corn in Huaibei area in 2022 and preventive measures. Modern Agric Technol (10), 34-37. (in Chinese) |
| 李景峰 (2023). 2022年淮北地区夏玉米高温热害发生程度分析及预防对策. 现代农业科技 (10), 34-37. | |
| [41] | Li MD, Liang XL, Abula A, Han DX, Yang J, Xi HJ, Shang JX, Teng YX, Yang XJ, Li ZF, Wang YJ (2019). Analysis and evaluation of the heat resistance of maize inbred lines at grain filling stage. Xinjiang Agric Sci 56, 1382-1387. (in Chinese) |
|
李铭东, 梁晓玲, 阿不来提·阿布拉, 韩登旭, 杨杰, 郗浩江, 商佳鑫, 滕元旭, 杨新军, 李召锋, 王业建 (2019). 玉米自交系灌浆期耐热性评价. 新疆农业科学 56, 1382-1387.
DOI |
|
| [42] | Li T, Zhang XP, Liu Q, Liu J, Chen YQ, Sui P (2022a). Yield penalty of maize (Zea mays L.) under heat stress in different growth stages: a review. J Integr Agric 21, 2465-2476. |
| [43] | Li XM, Chao DY, Wu Y, Huang XH, Chen K, Cui LG, Su L, Ye WW, Chen H, Chen HC, Dong NQ, Guo T, Shi M, Feng Q, Zhang P, Han B, Shan JX, Gao JP, Lin HX (2015). Natural alleles of a proteasome α2 subunit gene contribute to thermotolerance and adaptation of African rice. Nat Genet 47, 827-833. |
| [44] | Li YL, Li YY, Su Q, Wu YL, Zhang R, Li YW, Ma YZ, Ma HH, Guo XP, Zhu LF, Min L, Zhang XL (2022b). High temperature induces male sterility via MYB66-MYB4-Casein kinase I signaling in cotton. Plant Physiol 189, 2091-2109. |
| [45] | Li Z, Li ZR, Ji YL, Wang CY, Wang SF, Shi YT, Le J, Zhang M (2024). The heat shock factor 20-HSF4-cellulose synthase A2 module regulates heat stress tolerance in maize. Plant Cell 36, 2652-2667. |
| [46] | Li ZX, Howell SH (2021a). Heat stress responses and thermotolerance in maize. Int J Mol Sci 22, 948. |
| [47] | Li ZX, Howell SH (2021b). Review: the two faces of IRE1 and their role in protecting plants from stress. Plant Sci 303, 110758. |
| [48] | Li ZX, Tang J, Bassham DC, Howell SH (2021). Daily temperature cycles promote alternative splicing of RNAs encoding SR45a, a splicing regulator in maize. Plant Physiol 186, 1318-1335. |
| [49] | Li ZX, Tang J, Srivastava R, Bassham DC, Howell SH (2020). The transcription factor bZIP60 links the unfolded protein response to the heat stress response in maize. Plant Cell 32, 3559-3575. |
| [50] | Li ZX, Zhang JR (2022). Effects of raised ambient temperature on the local and systemic adaptions of maize. Plants 11, 755. |
| [51] | Liu JJ, Sun N, Liu M, Liu JC, Du BJ, Wang XJ, Qi XT (2013). An autoregulatory loop controlling Arabidopsis HsfA2 expression: role of heat shock-induced alternative splicing. Plant Physiol 162, 512-521. |
| [52] | Liu MY, Zhou YH, Sun JX, Mao F, Yao Q, Li BL, Wang YY, Gao YB, Dong X, Liao SH, Wang P, Huang SB (2023a). From the floret to the canopy: high temperature tolerance during flowering. Plant Commun 4, 100629. |
| [53] | Liu P, Yin BZ, Gu LM, Zhang SY, Ren JH, Wang YD, Duan WW, Zhen WC (2023b). Heat stress affects tassel development and reduces the kernel number of summer maize. Front Plant Sci 14, 1186921. |
| [54] | Liu XH, Lyu YS, Yang WP, Yang ZT, Lu SJ, Liu JX (2020). A membrane-associated NAC transcription factor OsNTL3 is involved in thermotolerance in rice. Plant Biotechnol J 18, 1317-1329. |
| [55] | Lizaso JI, Ruiz-Ramos M, Rodríguez L, Gabaldon-Leal C, Oliveira JA, Lorite IJ, Sánchez D, García E, Rodríguez A (2018). Impact of high temperatures in maize: phenology and yield components. Field Crops Res 216, 129-140. |
| [56] |
Lohani N, Singh MB, Bhalla PL (2020). High temperature susceptibility of sexual reproduction in crop plants. J Exp Bot 71, 555-568.
DOI PMID |
| [57] | Ma YZ, Min L, Wang JD, Li YY, Wu YL, Hu Q, Ding YH, Wang MJ, Liang YJ, Gong ZL, Xie S, Su XJ, Wang CZ, Zhao YL, Fang QD, Li YL, Chi HB, Chen M, Khan AH, Lindsey K, Zhu LF, Li XY, Zhang XL (2021). A combination of genome-wide and transcriptome-wide association studies reveals genetic elements leading to male sterility during high temperature stress in cotton. New Phytol 231, 165-181. |
| [58] | McNellie JP, Chen JP, Li XR, Yu JM (2018). Genetic mapping of foliar and tassel heat stress tolerance in maize. Crop Sci 58, 2484-2493. |
| [59] |
Meehl GA, Tebaldi C (2004). More intense, more frequent, and longer lasting heat waves in the 21st century. Science 305, 994-997.
DOI PMID |
| [60] | Meng AJ, Wen DX, Zhang CQ (2022). Dynamic changes in seed germination under low-temperature stress in maize. Int J Mol Sci 23, 5495. |
| [61] | Monjardino P, Smith AG, Jones RJ (2005). Heat stress effects on protein accumulation of maize endosperm. Crop Sci 45, 1203-1210. |
| [62] | Mueller SM, Messina CD, Vyn TJ (2019). The role of the exponential and linear phases of maize (Zea mays L.) ear growth for determination of kernel number and kernel weight. Eur J Agron 111, 125939. |
| [63] | Oliver SN, Van Dongen JT, Alfred SC, Mamun EA, Zhao XC, Saini HS, Fernandes SF, Blanchard CL, Sutton BG, Geigenberger P, Dennis ES, Dolferus R (2005). Cold-induced repression of the rice anther-specific cell wall invertase gene OSINV4 is correlated with sucrose accumulation and pollen sterility. Plant Cell Environ 28, 1534-1551. |
| [64] | Ni YL (2022). Effects of high temperature stress on growth and rhizosphere environmental of maize seedlings stress. Master's thesis. Wuhan: Yangtze University. pp. 8-10. |
| 倪燕林 (2022). 高温胁迫对玉米幼苗生长及根际环境的影响. 硕士论文. 武汉: 长江大学. pp. 8-10. | |
| [65] | Parish RW, Li SF (2010). Death of a tapetum: a programme of developmental altruism. Plant Sci 178, 73-89. |
| [66] |
Pastor-Cantizano N, Ko DK, Angelos E, Pu YT, Brandizzi F (2020). Functional diversification of ER stress responses in Arabidopsis. Trends Biochem Sci 45, 123-136.
DOI PMID |
| [67] |
Perkins-Kirkpatrick SE, Lewis SC (2020). Increasing trends in regional heatwaves. Nat Commun 11, 3357.
DOI PMID |
| [68] | Rattalino Edreira JI, Budakli Carpici E, Sammarro D, Otegui ME (2011). Heat stress effects around flowering on kernel set of temperate and tropical maize hybrids. Field Crops Res 123, 62-73. |
| [69] | Ren YT, Jin YG, Li HH, Li ZF, Yang YL, Zhao QB, Chang DW, Man XY, Song HF, Xia ZH (2019). Screening of high temperature stress resistance of 29 new maize varieties in Huaibei area of Jiangsu province. China Seed Ind (6), 38-42. (in Chinese) |
| 任仰涛, 金彦刚, 李辉晖, 李珍富, 杨永乐, 赵其兵, 常东伟, 满锡玉, 宋红芳, 夏中华 (2019). 江苏淮北地区29个玉米新品种耐高温胁迫筛选. 中国种业 (6), 38-42. | |
| [70] |
Riley GJP (1981). Effects of high temperature on the germination of maize (Zea mays L.). Planta 151, 68-74.
DOI PMID |
| [71] | Rosmaina, Utami D, Aryanti E, Zulfahmi (2021). Impact of heat stress on germination and seedling growth of chili pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). IOP Conf Ser: Earth Environ Sci 637, 012032. |
| [72] | Sánchez B, Rasmussen A, Porter JR (2014). Temperatures and the growth and development of maize and rice: a review. Glob Chang Biol 20, 408-417. |
| [73] |
Sehgal A, Sita K, Siddique KHM, Kumar R, Bhogireddy S, Varshney RK, Hanumantha Rao B, Nair RM, Prasad PVV, Nayyar H (2018). Drought or/and heat-stress effects on seed filling in food crops: impacts on functional biochemistry, seed yields, and nutritional quality. Front Plant Sci 9, 1705.
DOI PMID |
| [74] |
Shi JX, Cui MH, Yang L, Kim YJ, Zhang DB (2015). Genetic and biochemical mechanisms of pollen wall development. Trends Plant Sci 20, 741-753.
DOI PMID |
| [75] | Shi YH, Mosser DD, Morimoto RI (1998). Molecularchaperones as HSF1-specific transcriptional repressors. Genes Dev 12, 654-666. |
| [76] | Siebers MH, Slattery RA, Yendrek CR, Locke AM, Drag D, Ainsworth EA, Bernacchi CJ, Ort DR (2017). Simulated heat waves during maize reproductive stages alter reproductive growth but have no lasting effect when applied during vegetative stages. Agric Ecosyst Environ 240, 162-170. |
| [77] | Singh I, Debnath S, Gautam A, Yadava P (2020). Characterization of contrasting genotypes reveals general physiological and molecular mechanisms of heat-stress adaptation in maize (Zea mays L.). Physiol Mol Biol Plants 26, 921-929. |
| [78] | Snider JL, Oosterhuis DM, Loka DA, Kawakami EM (2011). High temperature limits in vivo pollen tube growth rates by altering diurnal carbohydrate balance in field- grown Gossypium hirsutum pistils. J Plant Physiol 168, 1168-1175. |
| [79] |
Song XD, Zhu GL, Zhang SY, Zhang HM, Zhou GF, Zhang ZL, Mao YX, Lu HH, Chen GQ, Shi ML, Xue L, Zhou GS, Hao DR (2024). Identification of heat tolerance of waxy maizes at flowering stage and screening of evaluation indexes in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River region. Acta Agron Sin 50, 172-186. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
宋旭东, 朱广龙, 张舒钰, 章慧敏, 周广飞, 张振良, 冒宇翔, 陆虎华, 陈国清, 石明亮, 薛林, 周桂生, 郝德荣 (2024). 长江中下游地区糯玉米花期耐热性鉴定及评价指标筛选. 作物学报 50, 172-186.
DOI |
|
| [80] | Song ZT, Zhang LL, Han JJ, Zhou M, Liu JX (2021). Histone H3K4 methyltransferases SDG25 and ATX1 maintain heat-stress gene expression during recovery in Arabidopsis. Plant J 105, 1326-1338. |
| [81] | Sun W, Han SH, Liu JM, Yang JH, Jiang W, Duan MT (2019). Response of maize cultivars to high temperature stress at spikelet differentiation stage and tasseling stage. Chin Agric Sci Bull 35(17), 12-19. (in Chinese) |
|
孙武, 韩淑华, 刘建民, 杨甲海, 姜雯, 段梅堂 (2019). 不同玉米品种在小穗分化期和抽雄期对高温胁迫的响应差异. 中国农学通报 35(17), 12-19.
DOI |
|
| [82] | Sun YJ, Wang Q, Shao QW, Xin ZM, Xiao HJ, Cheng J (2023). Research advances on the effect of high temperature stress on plant photosynthesis. Chin Bull Bot 58, 486-498. (in Chinese) |
|
孙永江, 王琪, 邵琪雯, 辛智鸣, 肖辉杰, 程瑾 (2023). 高温胁迫对植物光合作用的影响研究进展. 植物学报 58, 486-498.
DOI |
|
| [83] | Talukder ASMHM, McDonald GK, Gill GS (2014). Effect of short-term heat stress prior to flowering and early grain set on the grain yield of wheat. Field Crops Res 160, 54-63. |
| [84] | Wang AL, Chen ZH, Zhao DF (2004). A preliminary report on identification and screen of maize inbred line materials tolerant to high temperature. J Maize Sci 12(4), 29-30. (in Chinese) |
| 王安乐, 陈朝辉, 赵德法 (2004). 玉米自交系材料耐高温特性鉴定筛选初报. 玉米科学 12(4), 29-30. | |
| [85] | Wang N, Liu Q, Ming B, Shang WX, Zhao XF, Wang XQ, Wang J, Zhang JL, Luo ZK, Liao Y (2022). Impacts of heat stress around flowering on growth and development dynamic of maize (Zea mays L.) ear and yield formation. Plants (Basel) 11, 3515. |
| [86] | Wang T, Feng JL, Zhang C (2024). Research progress on the molecular mechanisms underlying the impact of heat stress on maize growth and development. Chin Bull Bot 59, 963-977. (in Chinese) |
|
王涛, 冯敬磊, 张翠 (2024). 高温胁迫影响玉米生长发育的分子机制研究进展. 植物学报 59, 963-977.
DOI |
|
| [87] | Wang YY, Liu XL, Hou XF, Sheng DC, Dong X, Gao YB, Wang P, Huang SB (2021). Maximum lethal temperature for flowering and seed set in maize with contrasting male and female flower sensitivities. J Agron Crop Sci 207, 679-689. |
| [88] | Wang YY, Tao HB, Tian BJ, Sheng DC, Xu CC, Zhou HM, Huang SB, Wang P (2019). Flowering dynamics, pollen, and pistil contribution to grain yield in response to high temperature during maize flowering. Environ Exp Bot 158, 80-88. |
| [89] |
Wang YY, Tao HB, Zhang P, Hou XF, Sheng DC, Tian BJ, Wang P, Huang SB (2020). Reduction in seed set upon exposure to high night temperature during flowering in maize. Physiol Plant 169, 73-82.
DOI PMID |
| [90] | Waqas MA, Wang XK, Zafar SA, Noor MA, Hussain HA, Nawaz MA, Farooq M (2021). Thermal stresses in maize: effects and management strategies. Plants 10, 293. |
| [91] | Wei SJ, Ma LG (2023). Comprehensive insight into tapetum- mediated pollen development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Cells 12, 247. |
| [92] | Wu H, Becraft PW, Dannenhoffer JM (2022). Maize endosperm development: tissues, cells, molecular regulation and grain quality improvement. Front Plant Sci 13, 852082. |
| [93] | Wu WH, Liu JY, Yuan LZ, Yan HX, Fu JF, Zhao YQ, Wang HQ, Zhang YJ, Wang R, Li T, Liu K (2020). Effects of high temperature at florescence stage on the yield and major agronomic characters of different maize varieties. J Anhui Agric Sci 48(6), 33-36. (in Chinese) |
| 吴伟华, 柳家友, 袁刘正, 闫海霞, 付家锋, 赵月强, 王会强, 张云杰, 王蕊, 李腾, 刘康 (2020). 花期高温对不同玉米品种主要农艺形状和产量的影响. 安徽农业科学 48(6), 33-36. | |
| [94] | Xie WX (2023). Observed and Projected Changes in Heat Waves with Different Severities and Types over China. PhD dissertation. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology. pp. 24-53. (in Chinese) |
| 谢文欣 (2023). 中国不同强度和类型高温热浪的变化及其预估. 博士论文. 南京: 南京信息工程大学. pp. 24-53. | |
| [95] | Xing LY (2022). Identification of Heat Tolerance, Analysis of Leaf Transcriptome and Metabolome and QTL Mapping of the Related Traits under High Temperature Stress in Maize. Master’s thesis. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University. pp. 10-20. (in Chinese) |
| 邢凌云 (2022). 玉米耐热性鉴定、高温胁迫下叶片转录组和代谢组分析及相关性状的QTL定位. 硕士论文. 郑州: 河南农业大学. pp. 10-20. | |
| [96] | Xu F, Wang B, He C, Liu DL, Feng PY, Yao N, Zhang RH Xu ST, Xue JQ, Feng H, Yu Q, He JQ (2021). Optimizing sowing date and planting density can mitigate the impacts of future climate on maize yield: a case study in the Guanzhong plain of China. Agronomy 11, 1452. |
| [97] |
Xue XF, Du SY, Jiao FC, Xi MH, Wang AG, Xu HC, Jiao QQ, Zhang X, Jiang H, Chen JT, Wang M (2021). The regulatory network behind maize seed germination: effects of temperature, water, phytohormones, and nutrients. Crop J 9, 718-724.
DOI |
| [98] | Yan HL, Wang CH, Liu K, Tian XH (2021). Detrimental effects of heat stress on grain weight and quality in rice (Oryza sativa L.) are aggravated by decreased relative humidity. PeerJ 9, e11218. |
| [99] |
Yan ZH, Liu DY, Jia XC, Yang Q, Chen YB, Dong PF, Wang Q (2021). Maize tassel development, physiological traits and yield under heat and drought stress during flowering stage. Sci Agric Sin 54, 3592-3608. (in Chinese)
DOI PMID |
|
闫振华, 刘东尧, 贾绪存, 杨琴, 陈艺博, 董朋飞, 王群 (2021). 花期高温干旱对玉米雄穗发育、生理特性和产量影响. 中国农业科学 54, 3592-3608.
DOI |
|
| [100] | Yang C, Luo AN, Lu HP, Davis SJ, Liu JX (2024). Diurnal regulation of alternative splicing associated with thermotolerance in rice by two glycine-rich RNA-binding proteins. Sci Bull 69, 59-71. |
| [101] | Yang DD, Xu HC, Liu Y, Li MZ, Ali M, Xu XY, Lu G (2021). RNA N6-methyladenosine responds to low-temperature stress in tomato anthers. Front Plant Sci 12, 687826. |
| [102] |
Yang H, Gu XT, Ding MQ, Lu WP, Lu DL (2018). Heat stress during grain filling affects activities of enzymes involved in grain protein and starch synthesis in waxy maize. Sci Rep 8, 15665.
DOI PMID |
| [103] | Yang H, Huang TQ, Ding MQ, Lu DL, Lu WP (2017). High temperature during grain filling impacts on leaf senescence in waxy maize. Agron J 109, 906-916. |
| [104] | Yang H, Liu C, Wang ZF, Hu XL, Wang T (2019). Advances in the regulatory mechanisms of pollen response to heat stress in crops. Chin Bull Bot 54, 157-167. (in Chinese) |
|
杨浩, 刘晨, 王志飞, 胡秀丽, 王台 (2019). 作物花粉高温应答机制研究进展. 植物学报 54, 157-167.
DOI |
|
| [105] | Yang J, Han DX, Abula A, Liang XL, Wang Y, Xu ML (2021). Identification and evaluation of heat tolerance of maize inbred lines during flowering under natural high temperature in Xinjiang. Acta Bot Boreal-Occident Sin 41, 1380-1390. (in Chinese) |
| 杨杰, 韩登旭, 阿布来提·阿布拉, 梁晓玲, 王莹, 徐明良 (2021). 新疆自然高温环境下玉米自交系开花期耐热性鉴定与评价. 西北植物学报 41, 1380-1390. | |
| [106] | Yao QL, Chen FB, Li WB, Fang P (2019). Screening for physiological indexes of maize inbred lines under heat stress. J Maize Sci 27(6), 84-88. (in Chinese) |
| 姚启伦, 陈发波, 李文博, 方平 (2019). 玉米自交系耐热生理指标筛选研究. 玉米科学 27(6), 84-88. | |
| [107] |
Yoshida T, Ohama N, Nakajima J, Kidokoro S, Mizoi J, Nakashima K, Maruyama K, Kim JM, Seki M, Todaka D, Osakabe Y, Sakuma Y, Schöffl F, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2011). Arabidopsis HsfA1 transcription factors function as the main positive regulators in heat shock-responsive gene expression. Mol Genet Genomics 286, 321-332.
DOI PMID |
| [108] | Yu KK, Liu Y, Li YM, Sun NN, Zhan J, You DL, Niu L, Li CH, Liu TX (2016). Screening and comprehensive evaluation of heat-tolerance of maize hybrids in flowering stage. J Maize Sci 24(2), 62-71. (in Chinese) |
| 于康珂, 刘源, 李亚明, 孙宁宁, 詹静, 尤东玲, 牛丽, 李潮海, 刘天学 (2016). 玉米花期耐高温品种的筛选与综合评价. 玉米科学 24(2), 62-71. | |
| [109] | Zeng W (2019). Construction of High-Density Genetic Map and Analysis of Genetic Basis of High Temperature Tolerance at Flowering in Maize. PhD dissertation. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University. pp. 16-35. (in Chinese) |
| 曾威 (2019). 玉米高密度遗传图谱构建与花期高温抗性的遗传基础解析. 博士论文. 合肥: 安徽农业大学. pp. 16-35. | |
| [110] |
Zhang H, Zhou JF, Kan Y, Shan JX, Ye WW, Dong NQ, Guo T, Xiang YH, Yang YB, Li YC, Zhao HY, Yu HX, Lu ZQ, Guo SQ, Lei JJ, Liao B, Mu XR, Cao YJ, Yu JJ, Lin YS, Lin HX (2022). A genetic module at one locus in rice protects chloroplasts to enhance thermotolerance. Science 376, 1293-1300.
DOI PMID |
| [111] |
Zhang HN, Li GL, Fu C, Duan SN, Hu D, Guo XL (2020). Genome-wide identification, transcriptome analysis and alternative splicing events of Hsf family genes in maize. Sci Rep 10, 8073.
DOI PMID |
| [112] | Zhang SS, Yang HX, Ding L, Song ZT, Ma H, Chang F, Liu JX (2017). Tissue-specific transcriptomics reveals an important role of the unfolded protein response in maintaining fertility upon heat stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 29, 1007-1023. |
| [113] | Zhang YH, Xu ZG, Li J, Wang R (2021a). Optimum planting density improves resource use efficiency and yield stability of rainfed maize in semiarid climate. Front Plant Sci 12, 752606. |
| [114] | Zhang ZB, Hu MH, Xu WW, Wang Y, Huang K, Zhang C, Wen J (2021b). Understanding the molecular mechanism of anther development under abiotic stresses. Plant Mol Biol 105, 1-10. |
| [115] | Zhao C, Liu B, Piao S, Wang XH, Lobell DB, Huang Y, Huang MT, Yao YT, Bassu S, Ciais P, Durand JL, Elliott J, Ewert F, Janssens IA, Li T, Lin ED, Liu Q, Martre P, Müller C, Peng SS, Peñuelas J, Ruane AC, Wallach D, Wang T, Wu DH, Liu Z, Zhu Y, Zhu ZC, Asseng S (2017). Temperature increase reduces global yields of major crops in four independent estimates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114, 9326-9331. |
| [116] | Zhu YD, Wang HQ, Wang HZ, Ren H, Lü JH, Zhao B, Zhang JW, Ren BZ, Yin FW, Liu P (2022). Evaluation and identification index of heat tolerance in different summer maize varieties at V12 stage. Acta Agron Sin 48, 3130-3143. (in Chinese) |
|
朱亚迪, 王慧琴, 王洪章, 任昊, 吕建华, 赵斌, 张吉旺, 任佰朝, 殷复伟, 刘鹏 (2022). 不同夏玉米品种大喇叭口期耐热性评价和鉴定指标筛选. 作物学报 48, 3130-3143.
DOI |
| [1] | 李青洋, 刘翠, 何李, 彭姗, 马嘉吟, 胡子祎, 刘宏波. 甘蓝型油菜BnaA02.CPSF6基因的克隆及功能分析(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 62-73. |
| [2] | 王亚萍, 包文泉, 白玉娥. 单细胞转录组学在植物生长发育及胁迫响应中的应用进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 101-113. |
| [3] | 李园, 范开建, 安泰, 李聪, 蒋俊霞, 牛皓, 曾伟伟, 衡燕芳, 李虎, 付俊杰, 李慧慧, 黎亮. 玉米自然群体自交系农艺性状的多环境全基因组预测初探[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 1041-1053. |
| [4] | 张强, 赵振宇, 李平华. 基因编辑技术在玉米中的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 978-998. |
| [5] | 王涛, 冯敬磊, 张翠. 高温胁迫影响玉米生长发育的分子机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 963-977. |
| [6] | 杨娟, 赵月磊, 陈晓远, 王宝宝, 王海洋. 玉米开花期调控机理及育种应用[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 912-931. |
| [7] | 杜庆国, 李文学. lncRNA调控玉米生长发育和非生物胁迫研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 950-962. |
| [8] | 王子阳, 刘升学, 杨志蕊, 秦峰. 玉米抗旱性的遗传解析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 883-902. |
| [9] | 吴锁伟, 安学丽, 万向元. 玉米雄性不育机理及其在工程核不育制种中的应用[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 932-949. |
| [10] | 郑名敏, 黄强, 张鹏, 刘孝伟, 赵卓凡, 易洪杨, 荣廷昭, 曹墨菊. 玉米细胞质雄性不育及育性恢复研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 999-1006. |
| [11] | 杨文丽, 李钊, 刘志铭, 张志华, 杨今胜, 吕艳杰, 王永军. 不同熟期玉米叶片衰老特性及其对叶际细菌的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 1024-1040. |
| [12] | 路笃贤, 张严妍, 刘艳, 李岩竣, 左新秀, 林金星, 崔亚宁. 非编码RNA在植物生长发育及逆境响应中的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 709-725. |
| [13] | 程可心, 杜尧, 李凯航, 王浩臣, 杨艳, 金一, 何晓青. 玉米与叶际微生物组的互作遗传机制[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(2): 215-228. |
| [14] | 周文期, 周玉乾, 李永生, 何海军, 杨彦忠, 王晓娟, 连晓荣, 刘忠祥, 胡筑兵. 玉米ZmICE2基因调控气孔发育[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 866-881. |
| [15] | 于熙婷, 黄学辉. 现代玉米起源新见解——两类大刍草的混血[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 857-860. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||