

植物学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (1): 114-131.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24144 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24144
收稿日期:2024-09-19
接受日期:2024-10-30
出版日期:2025-01-10
发布日期:2024-10-31
通讯作者:
* 胡海涛, E-mail: haitao-hu@zjnu.cn;基金资助:
Haitao Hu*( ), Yue Wu, Ling Yang*(
), Yue Wu, Ling Yang*( )
)
Received:2024-09-19
Accepted:2024-10-30
Online:2025-01-10
Published:2024-10-31
Contact:
* E-mail: 摘要: 烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸(NAD+)和烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸磷酸(NADP+)是植物核心能量代谢、生长发育以及胁迫应答的整合者, 可直接或间接影响多种关键的细胞功能。作为细胞代谢的基石, 胞内NAD(P)+稳态对于维持植物正常能量代谢、生长发育和胁迫应答至关重要。NAD(P)+的合成受损或缺乏将引发植物细胞代谢紊乱和一系列缺陷表型, 严重时甚至导致植物死亡。目前, 植物中NAD(P)+的合成途径及其关键酶已比较明确, 但其在植物体内的稳态调控以及协调植物生长与胁迫应答的机制尚不清楚。因此, 研究植物细胞内NAD(P)+稳态的调节机制及其平衡植物生长与胁迫应答的分子机理具有重要意义。该文综述了植物NAD(P)+的生物合成代谢途径, 重点阐述了NAD(P)+参与调节植物生长发育和胁迫应答过程, 并展望了植物NAD(P)+的研究前景。
胡海涛, 武越, 杨玲. 植物NAD(P)+的生物合成及其生物学功能研究进展. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 114-131.
Haitao Hu, Yue Wu, Ling Yang. Research Progress on the NAD(P)+ Biosynthesis and Function in Plants. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(1): 114-131.
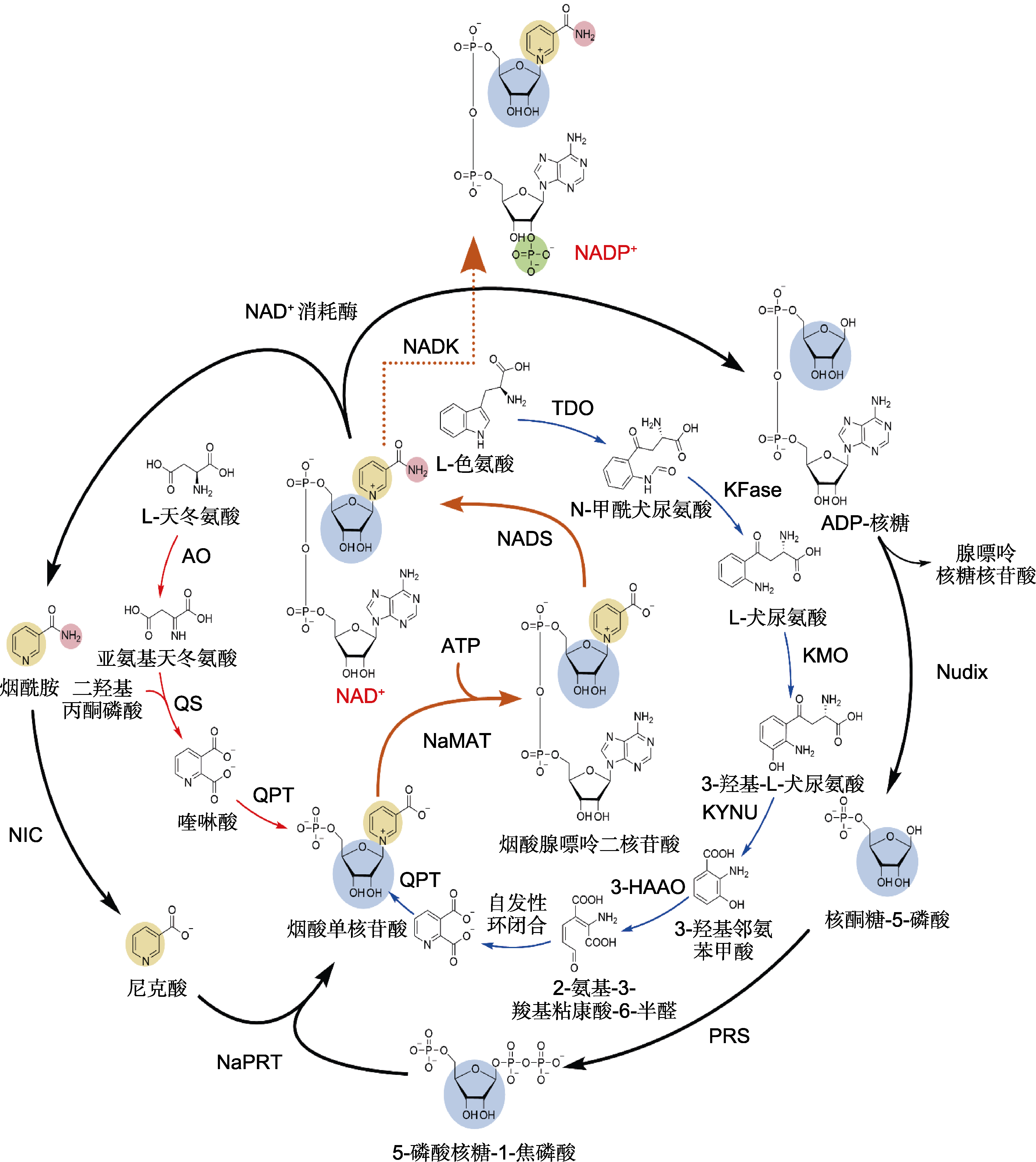
图2 植物NAD(P)+生物合成途径 植物及细菌中NAD(P)+的从头合成途径(红色箭头)、补救途径(黑色箭头)及这2种合成途径共有步骤(橘黄色箭头)。AO: 天冬氨酸氧化酶; QS: 喹啉酸合酶; QPT: 喹啉酸磷酸核糖转移酶; NaMAT: 烟酸单核苷酸腺苷酸转移酶; NADS: NAD+合成酶; NADK: NAD+激酶; NIC: 尼克酰胺脱氨酶; NaPRT: 尼克酸磷酸核糖转移酶; Nudix: 核苷二磷酸衍生物水解酶; PRS: 5-磷酸核糖-1-焦磷酸合成酶。哺乳动物和真菌中NAD(P)+的从头合成途径(蓝色箭头)。TDO: 色氨酸-2,3-双加氧酶; KFase: 犬尿氨酸甲酰胺酶; KMO: 犬尿氨酸-3-单加氧酶; KYNU: 犬尿氨酸酶; 3-HAAO: 3-羟基邻氨基苯甲酸3,4-双加氧酶
Figure 2 NAD(P)+ biosynthesis pathways in plants The de novo biosynthesis pathway (red arrows) and the salvage pathway (black arrows) of NAD(P)+ in plants and bacteria, and steps that are shared by these two synthesis pathways (orange arrows). AO: Aspartate oxidase; QS: Quinolinate synthase; QPT: Quinolinate phosphoribosyltransferase; NaMAT: Nicotinate mononucleotide adenylyltransferase; NADS: NAD+ synthetase; NADK: NAD+ kinase; NIC: Nicotinamidase; NaPRT: Nicotinate phosphoribosyltransferase; Nudix: Nudix hydrolase; PRS: 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate synthetase. The de novo biosynthesis pathway of NAD(P)+ in mammals and fungi (blue arrows). TDO: Tryptophan-2,3-dioxygenase; KFase: Kynurenine formamidase; KMO: Kynurenine-3-monooxygenase; KYNU: Kynureninase; 3-HAAO: 3-hydroxyanthranilate 3,4-dioxygenase
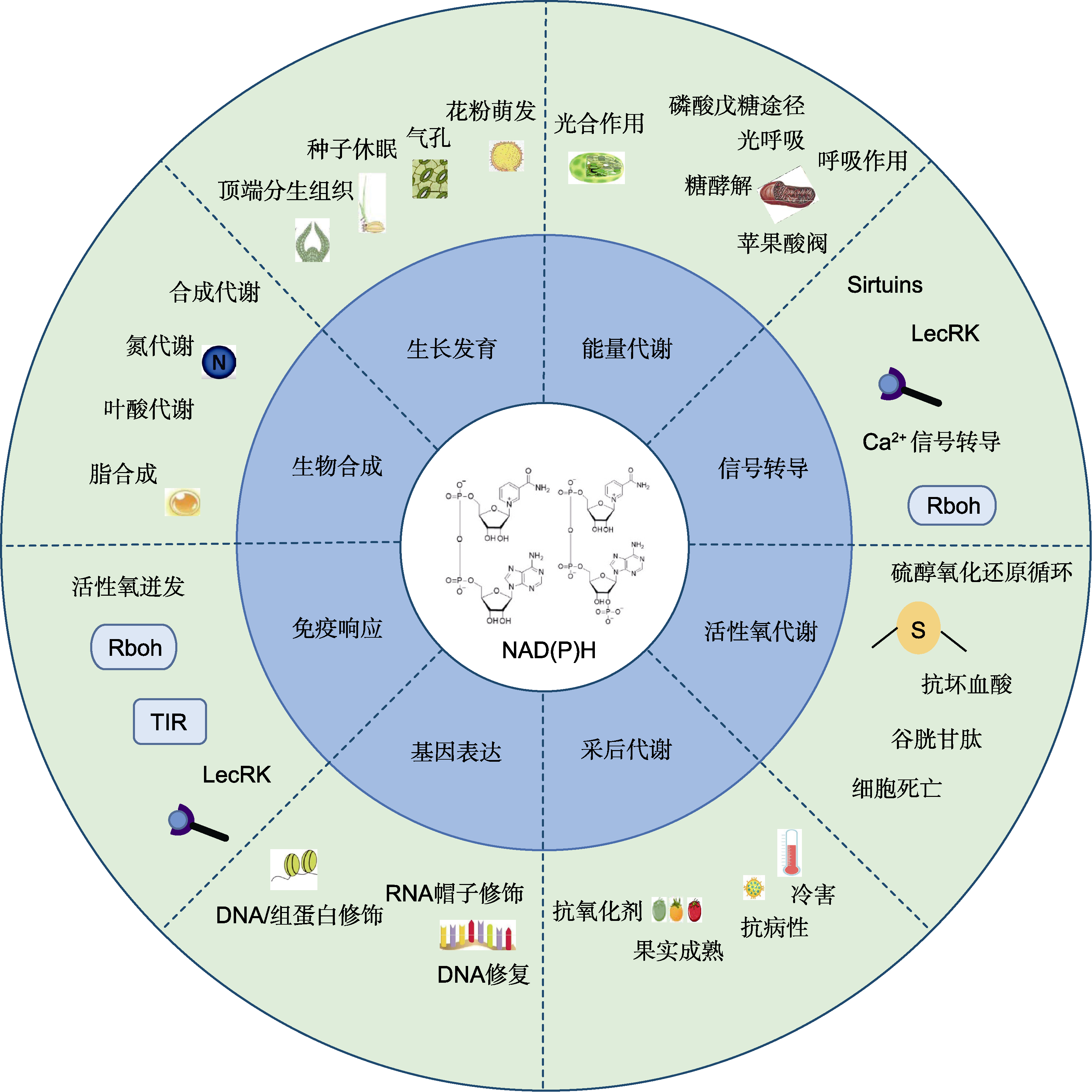
图3 植物中NAD(P)+的生物学功能(Smith et al., 2021) NAD(P)+参与调节植物中各种生物学过程, 包括生长发育、能量代谢、信号转导、活性氧代谢、采后代谢、基因表达、免疫反应与生物合成等。LecRK: 凝集素受体激酶; TIR: Toll/白细胞介素-1受体; Rboh: 呼吸爆发氧化酶同源物
Figure 3 Biological functions of NAD(P)+ in plants (Smith et al., 2021) NAD(P)+ are involved in many aspects of plant biological processes, including growth and development, energy metabolism, signal transduction, reactive oxygen species metabolism, post-harvest metabolism, gene expression, immune response and biosynthesis. LecRK: Lectin receptor kinase; TIR: Toll/interleukin-1 receptor; Rboh: Respiratory burst oxidase homologue
| [1] | Aghdam MS, Palma JM, Corpas FJ (2020). NADPH as a quality footprinting in horticultural crops marketability. Trends Food Sci Technol 103, 152-161. |
| [2] | Ahmad Z, Bashir K, Matsui A, Tanaka M, Sasaki R, Oikawa A, Hirai MY, Chaomurilege, Zu YH, Kawai-Yamada M, Rashid B, Husnain T, Seki M (2021). Overexpression of nicotinamidase 3 (NIC3) gene and the exogenous application of nicotinic acid (NA) enhance drought tolerance and increase biomass in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 107,63-84. |
| [3] |
Alferez FM, Gerberich KM, Li JL, Zhang YP, Graham JH, Mou ZL (2018). Exogenous nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide induces resistance to citrus canker in citrus. Front Plant Sci 9, 1472.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Alipour S, Wojciechowska N, Stolarska E, Bilska K, Kalemba EM (2020). NAD(P)-driven redox status contributes to desiccation tolerance in Acer seeds. Plant Cell Physiol 61, 1158-1167.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | Barreto P, Koltun A, Nonato J, Yassitepe J, de Godoy Maia I, Arruda P (2022). Metabolism and signaling of plant mitochondria in adaptation to environmental stresses. Int J Mol Sci 23, 11176. |
| [6] | Berrin JG, Pierrugues O, Brutesco C, Alonso B, Montillet JL, Roby D, Kazmaier M (2005). Stress induces the expression of AtNADK-1, a gene encoding a NAD(H) kinase in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Genet Genomics 273, 10-19. |
| [7] |
Briggs AG, Bent AF (2011). Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation in plants. Trends Plant Sci 16, 372-380.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | Carol RJ, Takeda S, Linstead P, Durrant MC, Kakesova H, Derbyshire P, Drea S, Zarsky V, Dolan L (2005). A RhoGDP dissociation inhibitor spatially regulates growth in root hair cells. Nature 438, 1013-1016. |
| [9] | Chai MF, Chen QJ, An R, Chen YM, Chen J, Wang XC (2005). NADK2, an Arabidopsis chloroplastic NAD kinase, plays a vital role in both chlorophyll synthesis and chloroplast protection. Plant Mol Biol 59, 553-564. |
| [10] |
Colinas M, Shaw HV, Loubéry S, Kaufmann M, Moulin M, Fitzpatrick TB (2014). A pathway for repair of NAD(P)H in plants. J Biol Chem 289, 14692-14706.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | de Souza Chaves I, Feitosa-Araújo E, Florian A, Medeiros DB, da Fonseca-Pereira P, Charton L, Heyneke E, Apfata JAC, Pires MV, Mettler-Altmann T, Araújo WL, Neuhaus HE, Palmieri F, Obata T, Weber APM, Linka N, Fernie AR, Nunes-Nesi A (2019). The mitochondrial NAD+ transporter (NDT1) plays important roles in cellular NAD+ homeostasis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 100, 487-504. |
| [12] | Dong HJ, Wang XF, Tan C, Gao L, Cui J, Liu L, Mo BX, Xing YZ, Yu Y, Chen XM (2022). NAD+-capped RNAs are widespread in rice (Oryza sativa) and spatiotemporally modulated during development. Sci China Life Sci 65, 2121-2124. |
| [13] |
Dubiella U, Seybold H, Durian G, Komander E, Lassig R, Witte CP, Schulze WX, Romeis T (2013). Calcium-dependent protein kinase/NADPH oxidase activation circuit is required for rapid defense signal propagation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110, 8744-8749.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | Durand M, Brehaut V, Clement G, Kelemen Z, Macé J, Feil R, Duville G, Launay-Avon A, Roux CPL, Lunn JE, Roudier F, Krapp A (2023). The Arabidopsis transcription factor NLP2 regulates early nitrate responses and integrates nitrate assimilation with energy and carbon skeleton supply. Plant Cell 35, 1429-1454. |
| [15] | Feitosa-Araujo E, da Fonseca-Pereira P, Knorr LS, Schwarzländer M, Nunes-Nesi A (2022). NAD meets ABA: connecting cellular metabolism and hormone signaling. Trends Plant Sci 27, 16-28. |
| [16] | Feitosa-Araujo E, da Fonseca-Pereira P, Pena MM, Medeiros DB, Perez de Souza L, Yoshida T, Weber APM, Araújo WL, Fernie AR, Schwarzländer M, Nunes- Nesi A (2020). Changes in intracellular NAD status affect stomatal development in an abscisic acid-dependent manner. Plant J 104, 1149-1168. |
| [17] | Feng BM, Liu CL, de Oliveira MVV, Intorne AC, Li B, Babilonia K, de Souza Filho GA, Shan LB, He P (2015). Protein poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation regulates Arabidopsis immune gene expression and defense responses. PLoS Genet 11, e1004936. |
| [18] |
Fukuda Y, Ishiyama C, Kawai-Yamada M, Hashida SN (2023). Adjustment of light-responsive NADP dynamics in chloroplasts by stromal pH. Nat Commun 14, 7148.
DOI PMID |
| [19] | Gakière B, Hao JF, de Bont L, Pétriacq P, Nunes-Nesi A, Fernie AR (2018). NAD+ biosynthesis and signaling in plants. Crit Rev Plant Sci 37, 259-307. |
| [20] | Gu ZY, Pan WY, Chen W, Lian QC, Wu Q, Lv ZY, Cheng X, Ge XC (2019). New perspectives on the plant PARP family: Arabidopsis PARP3 is inactive, and PARP1 exhibits predominant poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase activity in response to DNA damage. BMC Plant Biol 19, 364. |
| [21] | Hao JF, Pétriacq P, de Bont L, Hodges M, Gakière B (2018). Characterization of L-aspartate oxidase from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Sci 271, 133-142. |
| [22] | Hashida SN, Itami T, Takahara K, Hirabayashi T, Uchimiya H, Kawai-Yamada M (2016). Increased rate of NAD metabolism shortens plant longevity by accelerating developmental senescence in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 57, 2427-2439. |
| [23] | Hashida SN, Itami T, Takahashi H, Takahara K, Nagano M, Kawai-Yamada M, Shoji K, Goto F, Yoshihara T, Uchimiya H (2010). Nicotinate/nicotinamide mononucleotide adenyltransferase-mediated regulation of NAD biosynthesis protects guard cells from reactive oxygen species in ABA-mediated stomatal movement in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 61, 3813-3825. |
| [24] | Hashida SN, Kawai-Yamada M, Uchimiya H (2013a). NAD+ accumulation as a metabolic off switch for orthodox pollen. Plant Signal Behav 8, e23937. |
| [25] | Hashida SN, Takahashi H, Kawai-Yamada M, Uchimiya H (2007). Arabidopsis thaliana nicotinate/nicotinamide mononucleotide adenyltransferase (AtNMNAT) is required for pollen tube growth. Plant J 49, 694-703. |
| [26] | Hashida SN, Takahashi H, Takahara K, Kawai-Yamada M, Kitazaki K, Shoji K, Goto F, Yoshihara T, Uchimiya H (2013b). NAD+ accumulation during pollen maturation in Arabidopsis regulating onset of germination. Mol Plant 6, 216-225. |
| [27] | Hashida SN, Takahashi H, Uchimiya H (2009). The role of NAD biosynthesis in plant development and stress responses. Ann Bot 103, 819-824. |
| [28] | He HJ, Zhang YZ, Wen BB, Meng XG, Wang N, Sun MY, Zhang R, Zhao XH, Tan QP, Xiao W, Li DM, Fu XL, Chen XD, Li L (2022). PpNUDX8, a peach NUDIX hydrolase, plays a negative regulator in response to drought stress. Front Plant Sci 12, 831883. |
| [29] | Hong YC, Wang Z, Shi HZ, Yao JJ, Liu X, Wang FX, Zeng L, Xie Z, Zhu JK (2020). Reciprocal regulation between nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide metabolism and abscisic acid and stress response pathways in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet 16, e1008892. |
| [30] | Hong YC, Yu ZJ, Zhou Q, Chen CY, Hao YQ, Wang Z, Zhu JK, Guo HW, Huang AC (2024). NAD+ deficiency primes defense metabolism via 1O2-escalated jasmonate biosynthesis in plants. Nat Commun 15, 6652. |
| [31] | Huang LM, Sun QW, Qin FJ, Li C, Zhao Y, Zhou DX (2007). Down-regulation of a SILENT INFORMATION RE- GULATOR2-related histone deacetylase gene, OsSRT1, induces DNA fragmentation and cell death in rice. Plant Physiol 144, 1508-1519. |
| [32] | Huang Y, Liu QC, Jibrin M, Mou ZL, Dufault N, Li YC, Zhang SA (2023). Evaluating nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide for its effects on halo blight of snap bean. Plant Dis 107, 675-681. |
| [33] |
Hunt L, Gray JE (2009). The relationship between pyridine nucleotides and seed dormancy. New Phytol 181, 62-70.
DOI PMID |
| [34] | Ishikawa K, Ogawa T, Hirosue E, Nakayama Y, Harada K, Fukusaki E, Yoshimura K, Shigeoka S (2009). Modulation of the poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation reaction via the Arabidopsis ADP-ribose/NADH pyrophosphohydrolase, AtNUDX7, is involved in the response to oxidative stress. Plant Physiol 151, 741-754. |
| [35] |
Ishikawa K, Yoshimura K, Harada K, Fukusaki E, Ogawa T, Tamoi M, Shigeoka S (2010). AtNUDX6, an ADP-ribose/ NADH pyrophosphohydrolase in Arabidopsis, positively regulates NPR1-dependent salicylic acid signaling. Plant Physiol 152, 2000-2012.
DOI PMID |
| [36] | Jethva J, Lichtenauer S, Schmidt-Schippers R, Steffen- Heins A, Poschet G, Wirtz M, van Dongen JT, Eirich J, Finkemeier I, Bilger W, Schwarzländer M, Sauter M (2023). Mitochondrial alternative NADH dehydrogenases NDA1 and NDA2 promote survival of reoxygenation st- ress in Arabidopsis by safeguarding photosynthesis and limiting ROS generation. New Phytol 238, 96-112. |
| [37] | Ji DL, Li QX, Guo YJ, An WJ, Manavski N, Meurer J, Chi W (2022). NADP+ supply adjusts the synthesis of photosystem I in Arabidopsis chloroplasts. Plant Physiol 189, 2128-2143. |
| [38] | Jia AL, Huang SJ, Ma SC, Chang XY, Han ZF, Chai JJ (2023). TIR-catalyzed nucleotide signaling molecules in plant defense. Curr Opin Plant Biol 73, 102334. |
| [39] |
Kadota Y, Sklenar J, Derbyshire P, Stransfeld L, Asai S, Ntoukakis V, Jones JDG, Shirasu K, Menke F, Jones A, Zipfel C (2014). Direct regulation of the NADPH oxidase RBOHD by the PRR-associated kinase BIK1 during plant immunity. Mol Cell 54, 43-55.
DOI PMID |
| [40] | Katoh A, Uenohara K, Akita M, Hashimoto T (2006). Early steps in the biosynthesis of NAD in Arabidopsis start with aspartate and occur in the plastid. Plant Physiol 141, 851-857. |
| [41] | Kaya H, Nakajima R, Iwano M, Kanaoka MM, Kimura S, Takeda S, Kawarazaki T, Senzaki E, Hamamura Y, Higashiyama T, Takayama S, Abe M, Kuchitsu K (2014). Ca2+-activated reactive oxygen species production by Arabidopsis RbohH and RbohJ is essential for proper pollen tube tip growth. Plant Cell 26, 1069-1080. |
| [42] | Kaya H, Takeda S, Kobayashi MJ, Kimura S, Iizuka A, Imai A, Hishinuma H, Kawarazaki T, Mori K, Yamamoto Y, Murakami Y, Nakauchi A, Abe M, Kuchitsu K (2019). Comparative analysis of the reactive oxygen species-producing enzymatic activity of Arabidopsis NADPH oxidases. Plant J 98, 291-300. |
| [43] | Khan S, Pandey SS, Jyotshna, Shanker K, Khan F, Rahman LU (2017). Cloning and functional characterization of quinolinic acid phosphoribosyl transferase (QPT) gene of Nicotiana tabacum. Physiol Plant 160, 253-265. |
| [44] |
Kong L, Feng BM, Yan Y, Zhang C, Kim JH, Xu LH, Rack JGM, Wang Y, Jang JC, Ahel I, Shan LB, He P (2021). Noncanonical mono(ADP-ribosyl)ation of zinc finger SZF proteins counteracts ubiquitination for protein homeostasis in plant immunity. Mol Cell 81, 4591-4604.
DOI PMID |
| [45] | Le XH, Lee CP, Millar AH (2021). The mitochondrial pyruvate carrier (MPC) complex mediates one of three pyruvate-supplying pathways that sustain Arabidopsis respiratory metabolism. Plant Cell 33, 2776-2793. |
| [46] | Li BB, Wang X, Tai L, Ma TT, Shalmani A, Liu WT, Li WQ, Chen KM (2018). NAD kinases: metabolic targets controlling redox co-enzymes and reducing power partitioning in plant stress and development. Front Plant Sci 9, 379. |
| [47] | Li Q, Zhou MX, Chhajed S, Yu FH, Chen SX, Zhang YP, Mou ZL (2023). N-hydroxypipecolic acid triggers systemic acquired resistance through extracellular NAD(P). Nat Com- mun 14, 6848. |
| [48] | Li W, Zhang FX, Chang YW, Zhao T, Schranz ME, Wang GD (2015). Nicotinate O-glucosylation is an evolutionarily metabolic trait important for seed germination under stress conditions in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 27, 1907-1924. |
| [49] | Li W, Zhang FX, Wu RR, Jia LJ, Li GS, Guo YL, Liu CM, Wang GD (2017). A novel N-methyltransferase in Arabidopsis appears to feed a conserved pathway for nicotinate detoxification among land plants and is associated with lignin biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 174, 1492-1504. |
| [50] | Li WY, Wang X, Li R, Li WQ, Chen KM (2014). Genome-wide analysis of the NADK gene family in plants. PLoS One 9, e101051. |
| [51] | Lindén P, Keech O, Stenlund H, Gardeström P, Moritz T (2016). Reduced mitochondrial malate dehydrogenase activity has a strong effect on photorespiratory metabolism as revealed by 13C labeling. J Exp Bot 67, 3123-3135. |
| [52] | Liu XY, Wei W, Zhu WJ, Su LF, Xiong ZY, Zhou M, Zheng Y, Zhou DX (2017). Histone deacetylase AtSRT1 links metabolic flux and stress response in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 10, 1510-1522. |
| [53] | Ma MZ, Liu YF, Bai CM, Yong JWH (2021). The significance of chloroplast NAD(P)H dehydrogenase complex and its dependent cyclic electron transport in photosynthesis. Front Plant Sci 12, 661863. |
| [54] | Maruta T, Ogawa T, Tsujimura M, Ikemoto K, Yoshida T, Takahashi H, Yoshimura K, Shigeoka S (2016). Loss- of-function of an Arabidopsis NADPH pyrophosphohydrolase, AtNUDX19, impacts on the pyridine nucleotides status and confers photooxidative stress tolerance. Sci Rep 6, 37432. |
| [55] | Miwa A, Sawada Y, Tamaoki D, Yokota Hirai M, Kimura M, Sato K, Nishiuchi T (2017). Nicotinamide mononucleotide and related metabolites induce disease resistance against fungal phytopathogens in Arabidopsis and barley. Sci Rep 7, 6389. |
| [56] | Mou ZL (2017). Extracellular pyridine nucleotides as immune elicitors in Arabidopsis. Plant Signal Behav 12, e1388977. |
| [57] | Müller K, Carstens AC, Linkies A, Torres MA, Leubner-Metzger G (2009). The NADPH-oxidase AtrbohB plays a role in Arabidopsis seed after-ripening. New Phytol 184, 885-897. |
| [58] | Munk SHN, Merchut-Maya JM, Adelantado Rubio A, Hall A, Pappas G, Milletti G, Lee M, Johnsen LG, Guldberg P, Bartek J, Maya-Mendoza A (2023). NAD+ regulates nucleotide metabolism and genomic DNA replication. Nat Cell Biol 25, 1774-1786. |
| [59] | Ogawa T, Ishikawa K, Harada K, Fukusaki E, Yoshimura K, Shigeoka S (2009). Overexpression of an ADP-ribose pyrophosphatase, AtNUDX2, confers enhanced tolerance to oxidative stress in Arabidopsis plants. Plant J 57, 289-301. |
| [60] | Ogawa T, Muramoto K, Takada R, Nakagawa S, Shigeoka S, Yoshimura K (2016). Modulation of NADH Levels by Arabidopsis nudix hydrolases, AtNUDX6 and 7, and the respective proteins themselves play distinct roles in the regulation of various cellular responses involved in biotic/abiotic stresses. Plant Cell Physiol 57, 1295-1308. |
| [61] | Palmieri F, Rieder B, Ventrella A, Blanco E, Do PT, Nunes-Nesi A, Trauth AU, Fiermonte G, Tjaden J, Agrimi G, Kirchberger S, Paradies E, Fernie AR, Neuhaus HE (2009). Molecular identification and functional characterization of Arabidopsis thaliana mitochondrial and chloroplastic NAD+ carrier proteins. J Biol Chem 284, 31249-31259. |
| [62] | Pétriacq P, de Bont L, Hager J, Didierlaurent L, Mauve C, Guérard F, Noctor G, Pelletier S, Renou JP, Tcherkez G, Gakière B (2012). Inducible NAD overproduction in Arabidopsis alters metabolic pools and gene expression correlated with increased salicylate content and resistance to Pst-AvrRpm1. Plant J 70, 650-665. |
| [63] |
Pétriacq P, Ton J, Patrit O, Tcherkez G, Gakière B (2016). NAD acts as an integral regulator of multiple defense layers. Plant Physiol 172, 1465-1479.
PMID |
| [64] | Regmi H, Abdelsamad N, DiGennaro P, Desaeger J (2021). Potential of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) for management of root-knot nematode in tomato. J Nematol 53, 1-11. |
| [65] | Saito M, Konishi M, Miyagi A, Sakuraba Y, Kawai-Yamada M, Yanagisawa S (2022). Arabidopsis nitrate-induced aspartate oxidase gene expression is necessary to maintain metabolic balance under nitrogen nutrient fluctuation. Commun Biol 5, 432. |
| [66] |
Schippers JHM, Foyer CH, van Dongen JT (2016). Redox regulation in shoot growth, SAM maintenance and flowering. Curr Opin Plant Biol 29, 121-128.
DOI PMID |
| [67] |
Smith EN, Schwarzländer M, Ratcliffe RG, Kruger NJ (2021). Shining a light on NAD- and NADP-based metabolism in plants. Trends Plant Sci 26, 1072-1086.
DOI PMID |
| [68] | Song W, Liu L, Yu DL, Bernardy H, Jirschitzka J, Huang SJ, Jia AL, Jemielniak W, Acker J, Laessle H, Wang JL, Shen QC, Chen WJ, Li PL, Parker JE, Han ZF, Schulze-Lefert P, Chai JJ (2024). Substrate-induced condensation activates plant TIR domain proteins. Nature 627, 847-853. |
| [69] | Spechenkova N, Kalinina NO, Zavriev SK, Love AJ, Taliansky M (2023). ADP-ribosylation and antiviral resistance in plants. Viruses 15, 241. |
| [70] | Steinbeck J, Fuchs P, Negroni YL, Elsässer M, Lich- tenauer S, Stockdreher Y, Feitosa-Araujo E, Kroll JB, Niemeier JO, Humberg C, Smith EN, Mai M, Nunes- Nesi A, Meyer AJ, Zottini M, Morgan B, Wagner S, Schwarzländer M (2020). In vivo NADH/NAD+ biosensing reveals the dynamics of cytosolic redox metabolism in plants. Plant Cell 32, 3324-3345. |
| [71] | Su LF, Wang P, Li S, Cai Y, Guo DD, Liu Q, Liu XY (2023). Research progress in sirtuin protein family in plants. Chin Bull Bot 58, 998-1007. (in Chinese) |
|
苏鲁方, 王萍, 李顺, 蔡燕, 郭丹丹, 刘琴, 刘小云 (2023). 植物sirtuin蛋白家族研究进展. 植物学报 58, 998-1007.
DOI |
|
| [72] | Sun X, Han GL, Meng Z, Lin L, Sui N (2019). Roles of malic enzymes in plant development and stress responses. Plant Signal Behav 14, e1644596. |
| [73] | Suzuki S, Tanaka D, Miyagi A, Takahara K, Kono M, Chaomurilege, Noguchi K, Ishikawa T, Nagano M, Yamaguchi M, Kawai-Yamada M (2023). Loss of peroxisomal NAD kinase 3 (NADK3) affects photorespiration metabolism in Arabidopsis. J Plant Physiol 283, 153950. |
| [74] |
Sweetman C, Waterman CD, Rainbird BM, Smith PMC, Jenkins CD, Day DA, Soole KL (2019). AtNDB2 is the main external NADH dehydrogenase in mitochondria and is important for tolerance to environmental stress. Plant Physiol 181, 774-788.
DOI PMID |
| [75] | Tian HN, Wu ZS, Chen SY, Ao K, Huang WJ, Yaghmaiean H, Sun TJ, Xu F, Zhang YJ, Wang SC, Li X, Zhang YL (2021). Activation of TIR signaling boosts pattern-triggered immunity. Nature 598, 500-503. |
| [76] |
Wallström SV, Florez-Sarasa I, Araújo WL, Escobar MA, Geisler DA, Aidemark M, Lager I, Fernie AR, Ribas- Carbó M, Rasmusson AG (2014). Suppression of NDA-type alternative mitochondrial NAD(P)H dehydrogenases in Arabidopsis thaliana modifies growth and metabolism, but not high light stimulation of mitochondrial electron transport. Plant Cell Physiol 55, 881-896.
DOI PMID |
| [77] |
Wan L, Essuman K, Anderson RG, Sasaki Y, Monteiro F, Chung EH, Nishimura EO, DiAntonio A, Milbrandt J, Dangl JL, Nishimura MT (2019). TIR domains of plant immune receptors are NAD+-cleaving enzymes that promote cell death. Science 365, 799-803.
DOI PMID |
| [78] | Wang CG, Huang XE, Li Q, Zhang YP, Li JL, Mou ZL (2019a). Extracellular pyridine nucleotides trigger plant systemic immunity through a lectin receptor kinase/BAK1 complex. Nat Commun 10, 4810. |
| [79] | Wang CZ, Gao F, Wu JG, Dai JL, Wei CH, Li Y (2010). Arabidopsis putative deacetylase AtSRT2 regulates basal defense by suppressing PAD4, EDS5 and SID2 expression. Plant Cell Physiol 51, 1291-1299. |
| [80] | Wang GD, Pichersky E (2007). Nicotinamidase participates in the salvage pathway of NAD biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J 49, 1020-1029. |
| [81] | Wang P, Su LF, Cao L, Hu HB, Wan HP, Wu CH, Zheng Y, Bao C, Liu XY (2024a). AtSRT1 regulates flowering by regulating flowering integrators and energy signals in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol Biochem 213, 108841. |
| [82] |
Wang X, Li BB, Ma TT, Sun LY, Tai L, Hu CH, Liu WT, Li WQ, Chen KM (2020). The NAD kinase OsNADK1 affects the intracellular redox balance and enhances the tolerance of rice to drought. BMC Plant Biol 20, 11.
DOI PMID |
| [83] | Wang XF, Yu DL, Yu JC, Hu H, Hang RL, Amador Z, Chen Q, Chai JJ, Chen XM (2024b). Toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domain-containing proteins have NAD-RNA decapping activity. Nat Commun 15, 2261. |
| [84] | Wang Y, Li SF, Zhao YH, You CJ, Le B, Gong ZZ, Mo BX, Xia YJ, Chen XM (2019b). NAD+-capped RNAs are widespread in the Arabidopsis transcriptome and can probably be translated. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116, 12094-12102. |
| [85] | Wang YF, Liu C, Qin YY, Du YY, Song C, Kang ZS, Guo J, Guo J (2024c). Stripe rust effector Pst03724 modulates host immunity by inhibiting NAD kinase activation by a calmodulin. Plant Physiol 195, 1624-1641. |
| [86] | Wei M, Zhuang Y, Li H, Li PH, Huo HQ, Shu D, Huang WZ, Wang SH (2020). The cloning and characterization of hypersensitive to salt stress mutant, affected in quinolinate synthase, highlights the involvement of NAD in stress-induced accumulation of ABA and proline. Plant J 102, 85-98. |
| [87] | Wu BY, Li P, Hong XF, Xu CH, Wang R, Liang Y (2022). The receptor-like cytosolic kinase RIPK activates NADP- malic enzyme 2 to generate NADPH for fueling ROS production. Mol Plant 15, 887-903. |
| [88] | Wu LW, Ren DY, Hu SK, Li GM, Dong GJ, Jiang L, Hu XM, Ye WJ, Cui YT, Zhu L, Hu J, Zhang GH, Gao ZY, Zeng DL, Qian Q, Guo LB (2016). Down-regulation of a nicotinate phosphoribosyltransferase gene, OsNaPRT1, leads to withered leaf tips. Plant Physiol 171, 1085-1098. |
| [89] | Wu RR, Zhang FX, Liu LY, Li W, Pichersky E, Wang GD (2018). MeNA, controlled by reversible methylation of nicotinate, is an NAD precursor that undergoes long-distance transport in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 11, 1264-1277. |
| [90] |
Zeng X, Li YF, Mahalingam R (2014). Arabidopsis nudix hydrolase 7 plays a role in seed germination. Planta 239, 1015-1025.
DOI PMID |
| [91] |
Zhang H, Zhao Y, Zhou DX (2017). Rice NAD+-dependent histone deacetylase OsSRT1 represses glycolysis and regulates the moonlighting function of GAPDH as a transcriptional activator of glycolytic genes. Nucleic Acids Res 45, 12241-12255.
DOI PMID |
| [92] | Zhang QQ, Tian SL, Chen GY, Tang QM, Zhang YJ, Fleming AJ, Zhu XG, Wang P (2024). Regulatory NADH dehydrogenase-like complex optimizes C4 photosynthetic carbon flow and cellular redox in maize. New Phytol 241, 82-101. |
| [93] | Zhang XD, Mou ZL (2009). Extracellular pyridine nucleotides induce PR gene expression and disease resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant J 57, 302-312. |
| [94] | Zhang XD, Mou ZL (2012). Expression of the human NAD(P)-metabolizing ectoenzyme CD38 compromises sy- stemic acquired resistance in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant Mi- crobe In 25, 1209-1218. |
| [95] | Zhao YN, Luo LL, Xu JS, Xin PY, Guo HY, Wu J, Bai L, Wang GD, Chu JF, Zuo JR, Yu H, Huang X, Li JY (2018). Malate transported from chloroplast to mitochondrion triggers production of ROS and PCD in Arabidopsis thaliana. Cell Res 28, 448-461. |
| [96] |
Zhao YN, Yu H, Zhou JM, Smith SM, Li JY (2020). Malate circulation: linking chloroplast metabolism to mitochondrial ROS. Trends Plant Sci 25, 446-454.
DOI PMID |
| [97] | Zheng WP (2020). Review: the plant sirtuins. Plant Sci 293, 110434. |
| [1] | 周婧, 高飞. 植物缺铁诱导型香豆素合成及其在铁吸收中的功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 460-471. |
| [2] | 李新宇, 谷月, 徐非非, 包劲松. 水稻胚乳淀粉合成相关蛋白的翻译后修饰研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 256-270. |
| [3] | 范雪兰, 落艳娇, 徐超群, 郭宝林. 淫羊藿类黄酮生物合成相关基因研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 834-846. |
| [4] | 夏婧, 饶玉春, 曹丹芸, 王逸, 柳林昕, 徐雅婷, 牟望舒, 薛大伟. 水稻中乙烯生物合成关键酶OsACS和OsACO调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 291-301. |
| [5] | 刘潇潇, 巩迪, 高天鹏, 殷俐娜, 王仕稳. 植物类囊体主要膜脂及其生物合成[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 144-155. |
| [6] | 朱璐, 袁冲, 刘义飞. 植物次生代谢产物生物合成基因簇研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 134-143. |
| [7] | 胡海涛, 郭龙彪. 植物核黄素的生物合成及其功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(4): 638-655. |
| [8] | 郭彦君, 陈枫, 罗敬文, 曾为, 许文亮. 植物细胞壁木聚糖的生物合成及其应用[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(2): 316-334. |
| [9] | 李艳艳, 齐艳华. 植物Aux/IAA基因家族生物学功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 30-41. |
| [10] | 刘德帅, 姚磊, 徐伟荣, 冯美, 姚文孔. 褪黑素参与植物抗逆功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 111-126. |
| [11] | 刘佩佩, 张耿, 李晓娟. 植物果胶的生物合成与功能[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(2): 191-200. |
| [12] | 张雨, 赵明洁, 张蔚. 植物次生细胞壁生物合成的转录调控网络[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(3): 351-368. |
| [13] | 董燕梅, 张文颖, 凌正一, 李靖锐, 白红彤, 李慧, 石雷. 转录因子调控植物萜类化合物生物合成研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(3): 340-350. |
| [14] | 贺祯媚,李东明,齐艳华. 植物ABCB亚家族生物学功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(6): 688-698. |
| [15] | 魏铭,王鑫伟,陈博,宋程威,杜亮,肖建伟,林金星. 植物紫色酸性磷酸酶基因家族功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(1): 93-101. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||