

植物学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (3): 340-350.DOI: 10.11983/CBB19186 cstr: 32102.14.CBB19186
董燕梅1,2,张文颖1,2,凌正一1,2,李靖锐1,2,白红彤1,李慧1,*( ),石雷1,*(
),石雷1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2019-09-19
接受日期:2020-02-17
出版日期:2020-05-01
发布日期:2020-07-06
通讯作者:
李慧,石雷
基金资助:
Yanmei Dong1,2,Wenying Zhang1,2,Zhengyi Ling1,2,Jingrui Li1,2,Hongtong Bai1,Hui Li1,*( ),Lei Shi1,*(
),Lei Shi1,*( )
)
Received:2019-09-19
Accepted:2020-02-17
Online:2020-05-01
Published:2020-07-06
Contact:
Hui Li,Lei Shi
摘要: 萜类化合物是植物次生代谢物中结构和数量最多的一类化合物, 它们在植物体内以及植物与环境和其它生命体的相互作用中发挥重要作用。转录因子通过调控代谢通路中基因的转录起始来调节次生代谢物质的产量。目前, 研究发现参与萜类合成的转录因子家族主要有6个, 包括AP2/ERF、bHLH、MYB、NAC、WRKY和bZIP。该文主要对其家族的结构特点、调控模式以及研究进展进行综述, 以期进一步丰富萜烯合成的网络调控, 为植物萜类相关的分子育种、优质栽培和病虫害生物防治等提供新的思路与方法。
董燕梅, 张文颖, 凌正一, 李靖锐, 白红彤, 李慧, 石雷. 转录因子调控植物萜类化合物生物合成研究进展. 植物学报, 2020, 55(3): 340-350.
Yanmei Dong, Wenying Zhang, Zhengyi Ling, Jingrui Li, Hongtong Bai, Hui Li, Lei Shi. Advances in Transcription Factors Regulating Plant Terpenoids Biosynthesis. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(3): 340-350.
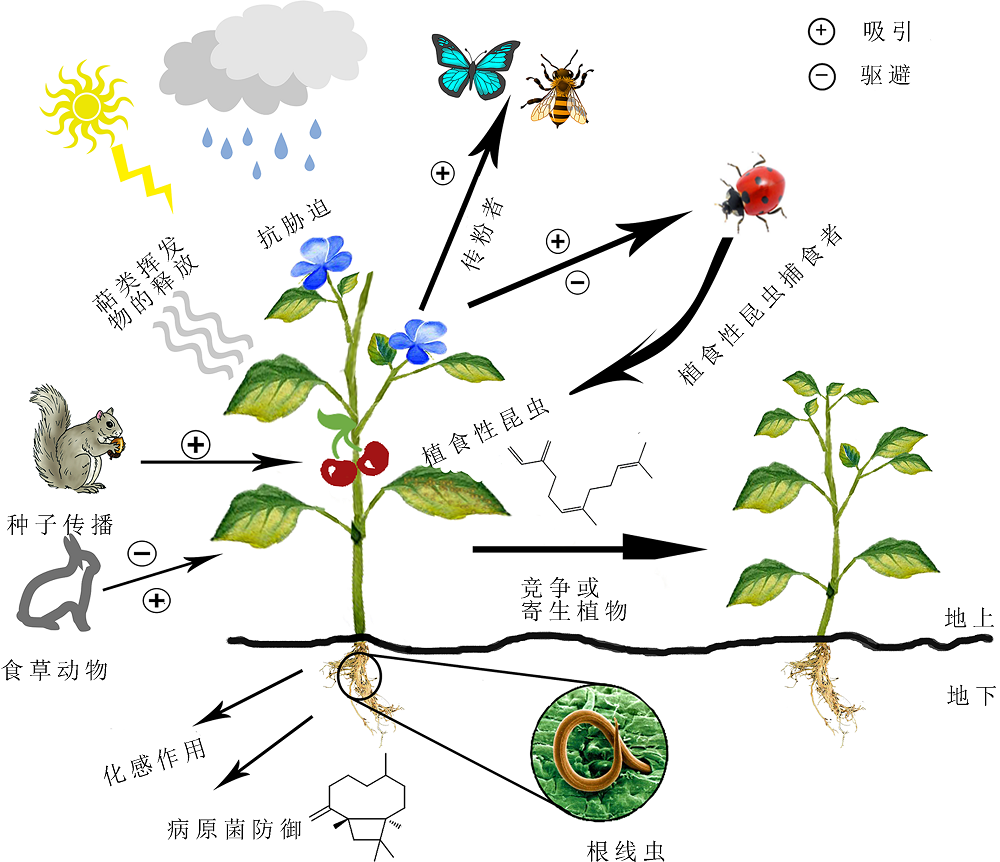
图1 挥发物介导的植物与周围环境的相互作用(改自Abbas et al., 2017)
Figure 1 A summary of volatile-mediated interactions between plants and their surrounding environment (modified from Abbas et al., 2017)
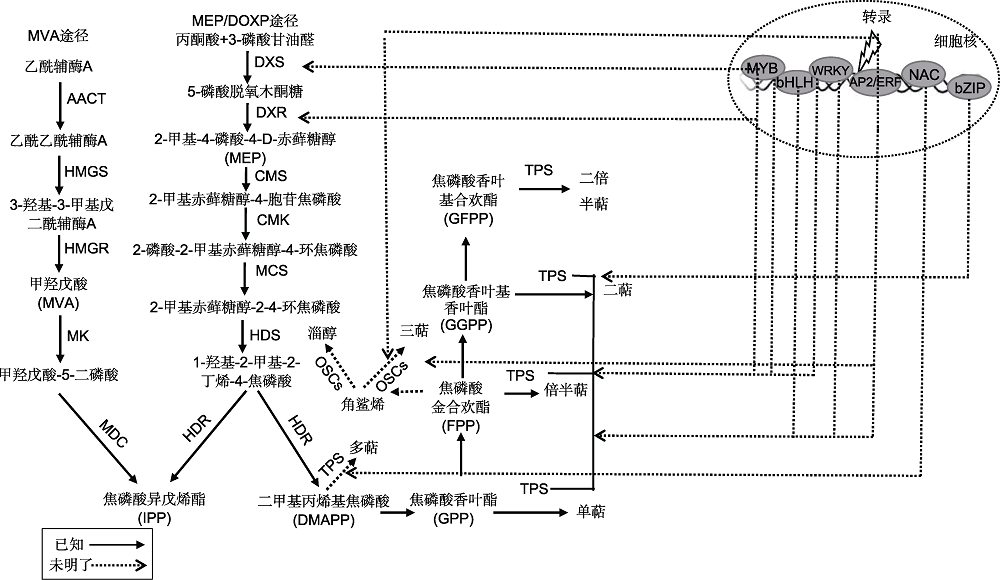
图2 植物萜类化合物的生物合成途径(图中相近的转录因子可互作共同行使生物功能) AACT: 乙酰乙酰辅酶A硫解酶; HMGS: 3-羟基-3-甲基戊二酰辅酶A合酶; HMGR: 羟甲基戊二酰辅酶A还原酶; MK: 甲羟戊酸激酶; MDC: 甲羟戊酸5-二磷酸脱羧酶; DXS: 1-脱氧-D-木酮糖-5-磷酸合酶; DXR: 1-脱氧-D-木酮糖-5-磷酸还原酶; CMS: 4-二磷酸胞苷- 2-C-甲基-D-赤藓醇合酶; CMK: 4-二磷酸胞苷-2-C-甲基-D-赤藓糖激酶; MCS: 2-C-甲基-D-赤藓糖-2,4-环二磷酸合酶; HDS: 1-羟基- 2-甲基-2-(E)-丁烯基-4-二磷酸合酶; HDR: 1-羟基-2-甲基-2-(E)-丁烯基-4-焦磷酸还原酶; TPS: 萜类合酶总称; OSCs: 氧化鲨烯环化酶
Figure 2 Biosynthetic pathways of terpenoids in plants (close transcription factors could interact with each other to perform biological functions) AACT: Acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase; HMGS: 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase; HMGR: 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase; MK: Mevalonate kinase; MDC: Mevalonate diphosphate decarboxylase; DXS: 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase; DXR: 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductase; CMS: 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol synthase; CMK: 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase; MCS: 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol-2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase; HDS: 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl-4-diphosphate synthase; HDR: 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl-4-pyrophosphate reductase; TPS: Terpenoid synthases; OSCs: Oxidosqualene cyclase
| 类型 | 植物 | TFs名称 | 登录号 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP2/ERF | 青蒿(Artemisia annua) | AaERF1 | AEQ93554.1 | |
| AaERF2 | AEQ93555.1 | |||
| TAR1 | EZ159016.1 | |||
| AaORA | AGB07586.1 | |||
| 黄瓜(Cucumis sativus) | CsERF | AAV66332.1 | ||
| bHLH | 青蒿(A. annua) | AabHLH1 | A0A3S9XA60 | |
| 拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana) | AtMYC2 | AT1G32640 | ||
| PIF5 | AT3G59060 | |||
| 丹参(Salvia miltiorrhiza) | SmMYC2a | KJ945636.1 | ||
| 蝴蝶兰(Phalaenopsis amabilis) | bHLH4 | AVZ23987.1 | ||
| 乌拉尔甘草(Glycyrrhiza uralensis) | bHLH3 | A0A2Z6BDF1 | ||
| 白桦(Betula platyphylla) | bHLH9 | A0A1X9RU20 | ||
| MYB | 拟南芥(A. thaliana) | MYB61 | AT1G09540 | |
| PAP1 | AT4G04020 | |||
| AtMYB21 | AT3G27810 | |||
| AtMYB24 | AT5G40350 | |||
| 留兰香(Mentha spicata) | MsMYB | AQR58379.1 | ||
| 白桦(B. platyphylla) | BpMYB21 | XP_018851905.1 | ||
| BpMYB61 | KT344120 | |||
| NAC | 青蒿(A. annua) | AaNAC1 | AQU15092.1 | |
| 番茄(Solanum lycopersicum) | SlNAC4 | AGH20612.1 | ||
| 软枣猕猴桃(Actinidia arguta) | NAC3 | KF319052 | ||
| bZIP | 青蒿(A. annua) | HY5 | JAT51023.1 | |
| bZIP1 | PWA69369.1 | |||
| 水稻(Oryza sativa) | TGAP1 | AK073715 | ||
| 其它 | 留兰香(M. spicata) | MsYABBY5 | AT2G26580 | |
| 青蒿(A. annua) | EIN3 | PWA84782.1 | ||
| 软枣猕猴桃(A. arguta) | AaEIL1 | KF319041 |
表1 植物中已分离和鉴定的参与调控萜类代谢合成途径的转录因子
Table 1 Transcription factors involved in the regulation of the terpenoids biosynthetic pathway identified in some plant species
| 类型 | 植物 | TFs名称 | 登录号 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP2/ERF | 青蒿(Artemisia annua) | AaERF1 | AEQ93554.1 | |
| AaERF2 | AEQ93555.1 | |||
| TAR1 | EZ159016.1 | |||
| AaORA | AGB07586.1 | |||
| 黄瓜(Cucumis sativus) | CsERF | AAV66332.1 | ||
| bHLH | 青蒿(A. annua) | AabHLH1 | A0A3S9XA60 | |
| 拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana) | AtMYC2 | AT1G32640 | ||
| PIF5 | AT3G59060 | |||
| 丹参(Salvia miltiorrhiza) | SmMYC2a | KJ945636.1 | ||
| 蝴蝶兰(Phalaenopsis amabilis) | bHLH4 | AVZ23987.1 | ||
| 乌拉尔甘草(Glycyrrhiza uralensis) | bHLH3 | A0A2Z6BDF1 | ||
| 白桦(Betula platyphylla) | bHLH9 | A0A1X9RU20 | ||
| MYB | 拟南芥(A. thaliana) | MYB61 | AT1G09540 | |
| PAP1 | AT4G04020 | |||
| AtMYB21 | AT3G27810 | |||
| AtMYB24 | AT5G40350 | |||
| 留兰香(Mentha spicata) | MsMYB | AQR58379.1 | ||
| 白桦(B. platyphylla) | BpMYB21 | XP_018851905.1 | ||
| BpMYB61 | KT344120 | |||
| NAC | 青蒿(A. annua) | AaNAC1 | AQU15092.1 | |
| 番茄(Solanum lycopersicum) | SlNAC4 | AGH20612.1 | ||
| 软枣猕猴桃(Actinidia arguta) | NAC3 | KF319052 | ||
| bZIP | 青蒿(A. annua) | HY5 | JAT51023.1 | |
| bZIP1 | PWA69369.1 | |||
| 水稻(Oryza sativa) | TGAP1 | AK073715 | ||
| 其它 | 留兰香(M. spicata) | MsYABBY5 | AT2G26580 | |
| 青蒿(A. annua) | EIN3 | PWA84782.1 | ||
| 软枣猕猴桃(A. arguta) | AaEIL1 | KF319041 |
| [1] | 郭倩倩, 周文彬 (2019). 植物响应联合胁迫机制的研究进展. 植物学报 54, 662-673. |
| [2] | 李慧, 白红彤, 王晓, 姜闯道, 张金政, 石雷 (2011). 椒样薄荷、薄荷和苏格兰留兰香精油与抗生素的协同抑菌功能. 植物学报 46, 37-43. |
| [3] | 李笑, 成玉富, 杨旭 (2017). 茄科植物WRKY转录因子的研究进展. 园艺学报 44, 170-178. |
| [4] | 李欣, 李影, 曲子越, 孙璐, 王思瑶, 詹亚光, 尹静 (2017). bHLH转录因子在茉莉酸信号诱导植物次生产物合成中的作用及分子机制. 植物生理学报 53, 1-8. |
| [5] | 刘强, 张贵友, 陈受宜 (2000). 植物转录因子的结构与调控作用. 科学通报 45, 1465-1474. |
| [6] | 牟玉兰, 闫浩, 龚黎黎 (2018). 萜类化合物的研究概况. 化工管理 (11), 12-13. |
| [7] | 苏文炳, 蒋园园, 白昀鹭, 甘小清, 刘月学, 林顺权 (2019). 转录因子调控植物萜类化合物生物合成研究进展. 农业生物技术学报 27, 919-926. |
| [8] | 孙俊聪, 侯柄竹, 陈晓亚, 唐克轩, 黎胜红, 尚轶, 崔光红, 段礼新, 黄三文, 漆小泉 (2019). 新中国成立70年来我国植物代谢领域的重要进展. 中国科学: 生命科学 49, 1213-1226. |
| [9] | 孙璐 (2018). 白桦BpMYB21和BpMYB61基因的克隆、表达特性及功能研究. 硕士论文. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学. pp. 4-6, 71-72. |
| [10] | 唐彪, 胡增辉, 冷平生 (2018). 不同花期‘西伯利亚’百合花瓣单萜合成途径转录组分析. 植物科学学报 36, 252-263. |
| [11] | 魏海超, 刘媛, 豆明珠, 杨素欣, 冯献忠 (2015). 大豆AP2/ERF基因家族的分子进化分析. 植物生理学报 51, 1706-1718. |
| [12] | 岳跃冲, 范燕萍 (2011). 植物萜类合成酶及其代谢调控的研究进展. 园艺学报 38, 379-388. |
| [13] | 张慧敏, 张雷, 马永硕, 尚轶, 王深浩, 杨清, 黄三文 (2014). 调控黄瓜苦味基因Bi的AP2/ERF家族转录因子. 园艺学报 41, 672-680. |
| [14] | 张凯伦, 罗祖良, 郭玉华, 石宏武, 马小军 (2017). bHLH转录因子调控药用植物萜类化合物生物合成的研究进展. 中国现代中药 19, 142-147. |
| [15] | 张全琪, 朱家红, 倪燕妹, 张治礼 (2011). 植物bHLH转录因子的结构特点及其生物学功能. 热带亚热带植物学报 19, 84-90. |
| [16] | 张雪松, 裴建军, 赵林果, 汤锋, 房仙颖, 解静聪 (2016). 不同品种桂花转录组分析及桂花精油成分差异的初步探讨. 天然产物研究与开发 28, 529-535. |
| [17] | 赵英 (2019). 丹参SmMYB36基因对萜类和苯丙烷代谢途径调控的研究. 硕士论文. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学. pp. 1-6, 53-54. |
| [18] | Abbas F, Ke YG, Yu RC, Yue YC, Amanullah S, Jahangir MM, Fan YR (2017). Volatile terpenoids: multiple functions, biosynthesis, modulation and manipulation by genetic engineering. Planta 246, 803-816. |
| [19] |
Albert NW, Lewis DH, Zhang HB, Schwinn KE, Jameson PE, Davies KM (2011). Members of an R2R3-MYB transcription factor family in Petunia are developmentally and environmentally regulated to control complex floral and vegetative pigmentation patterning. Plant J 65, 771-784.
URL PMID |
| [20] | Ben-Yehoshua S, Rodov V, Nafussi B, Feng XQ, Yen J, Koltai T, Nelkenbaum U (2008). Involvement of limonene hydroperoxides formed after oil gland injury in the induction of defense response against Penicillium digitatum in lemon fruit. J Agric Food Chem 56, 1889-1895. |
| [21] |
Brandt W, Bräuer L, Günnewich N, Kufka J, Rausch F, Schulze D, Schulze E, Weber R, Zakharova S, Wessjohann L (2009). Molecular and structural basis of metabolic diversity mediated by prenyldiphosphate converting enzymes. Phytochemistry 70, 1758-1775.
URL PMID |
| [22] |
Caputi L, Aprea E (2011). Use of terpenoids as natural flavouring compounds in food industry. Recent Pat Food Nutr Agric 3, 9-16.
URL PMID |
| [23] | Chappell J (2003). Biochemistry and molecular biology of the isoprenoid biosynthetic pathway in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 46, 521-547. |
| [24] | Chuang YC, Hung YC, Tsai WC, Chen WH, Chen HH (2018). PbbHLH4 regulates floral monoterpene biosynthesis in Phalaenopsis orchids. J Exp Bot 69, 4363-4377. |
| [25] | De Geyter N, Gholami A, Goormachtig S, Goossens A (2012). Transcriptional machineries in jasmonate-elicited plant secondary metabolism. Trends Plant Sci 17, 349-359. |
| [26] | Ding K, Pei TL, Bai ZQ, Jia YY, Ma PD, Liang ZS (2017). SmMYB36, a novel R2R3-MYB transcription factor, enhances tanshinone accumulation and decreases phenolic acid content in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots. Sci Rep 7, 5104. |
| [27] | Duval M, Hsieh TF, Kim SY, Thomas TL (2002). Molecular characterization of AtNAM: a member of the Arabidopsis NAC domain superfamily. Plant Mol Biol 50, 237-248. |
| [28] |
Eulgem T, Rushton PJ, Robatzek S, Somssich IE (2000). The WRKY superfamily of plant transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci 5, 199-206.
URL PMID |
| [29] |
Gershenzon J, Dudareva N (2007). The function of terpene natural products in the natural world. Nat Chem Biol 3, 408-414.
DOI URL PMID |
| [30] |
Hong GJ, Xue XY, Mao YB, Wang LJ, Chen XY (2012). Arabidopsis MYC2 interacts with DELLA proteins in regulating sesquiterpene synthase gene expression. Plant Cell 24, 2635-2648.
DOI URL PMID |
| [31] | Hurst HC (1994). Transcription factors 1: bZIP proteins. Protein Profile 1, 123-168. |
| [32] |
Ji YP, Xiao JW, Shen YL, Ma D, Li ZQ, Pu GB, Li X, Huang LL, Liu BY, Ye HC, Wang H (2014). Cloning and characterization of AabHLH1, a bHLH transcription factor that positively regulates artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua. Plant Cell Physiol 55, 1592-1604.
DOI URL PMID |
| [33] | Jiang WM, Fu XQ, Pan QF, Tang YL, Shen Q, Lv ZY, Yan TX, Shi P, Li L, Zhang LD, Wang GF, Sun XF, Tang KX (2016). Overexpression of AaWRKY1 leads to an enhanced content of artemisinin in Artemisia annua. BioMed Res Int 2016,7314971. |
| [34] |
Li H, Li JR, Dong YM, Hao HP, Ling ZY, Bai HT, Wang HF, Cui HX, Shi L (2019). Time-series transcriptome provides insights into the gene regulation network involved in the volatile terpenoid metabolism during the flower development of lavender. BMC Plant Biol 19, 313.
URL PMID |
| [35] |
Li X, Xu YY, Shen SL, Yin XR, Klee H, Zhang B, Chen KS (2017). Transcription factor CitERF71 activates the terpene synthase gene CitTPS16 involved in the synthesis of E-geraniol in sweet orange fruit. J Exp Bot 68, 4929-4938.
DOI URL PMID |
| [36] |
Lu X, Zhang L, Zhang FY, Jiang WM, Shen Q, Zhang LD, Lv ZY, Wang GF, Tang KX (2013). AaORA, a trichome- specific AP2/ERF transcription factor of Artemisia annua, is a positive regulator in the artemisinin biosynthetic pathway and in disease resistance to Botrytis cinerea. New Phytol 198, 1191-1202.
URL PMID |
| [37] |
Lv ZY, Wang S, Zhang FY, Chen LX, Hao XL, Pan QF, Fu XQ, Li L, Sun XF, Tang KX (2016). Overexpression of a novel NAC domain-containing transcription factor gene (AaNAC1) enhances the content of artemisinin and increases tolerance to drought and Botrytis cinerea in Artemisia annua. Plant Cell Physiol 57, 1961-1971.
URL PMID |
| [38] |
Mannen K, Matsumoto T, Takahashi S, Yamaguchi Y, Tsukagoshi M, Sano R, Suzuki H, Sakurai N, Shibata D, Koyama T, Nakayama T (2014). Coordinated transcriptional regulation of isopentenyl diphosphate biosynthetic pathway enzymes in plastids by phytochrome-interacting factor 5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 443, 768-774.
URL PMID |
| [39] |
Matías-Hernández L, Jiang WM, Yang K, Tang KX, Brodelius PE, Pelaz S (2017). AaMYB1 and its orthologue AtMYB61 affect terpene metabolism and trichome development in Artemisia annua and Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 90, 520-534.
DOI URL PMID |
| [40] | Miyamoto K, Matsumoto T, Okada A, Komiyama K, Chujo T, Yoshikawa H, Nojiri H, Yamane H, Okada K (2014). Identification of target genes of the bZIP transcription factor OsTGAP1, whose overexpression causes elicitor-induced hyperaccumulation of diterpenoid phytoalexins in rice cells. PLoS One 9, e105823. |
| [41] |
Miyamoto K, Nishizawa Y, Minami E, Nojiri H, Yamane H, Okada K (2015). Overexpression of the bZIP transcription factor OsbZIP79 suppresses the production of diterpenoid phytoalexin in rice cells. J Plant Physiol 173, 19-27.
DOI URL PMID |
| [42] |
Moses T, Pollier J, Thevelein JM, Goossens A (2013). Bioengineering of plant (tri)terpenoids: from metabolic engineering of plants to synthetic biology in vivo and in vitro. New Phytol 200, 27-43.
DOI URL PMID |
| [43] |
Nieuwenhuizen NJ, Chen XY, Wang MY, Matich AJ, Perez RL, Allan AC, Green SA, Atkinson RG (2015). Natural variation in monoterpene synthesis in kiwifruit: transcriptional regulation of terpene synthases by NAC and ETHYLENE-INSENSITIVE3-Like transcription factors. Plant Physiol 167, 1243-1258.
URL PMID |
| [44] |
Okada A, Okada K, Miyamoto K, Koga J, Shibuya N, Nojiri H, Yamane H (2009). OsTGAP1, a bZIP transcription factor, coordinately regulates the inductive production of diterpenoid phytoalexins in rice. J Biol Chem 284, 26510-26518.
URL PMID |
| [45] | Olsen AN, Ernst HA, Leggio LL, Skriver K (2005). NAC transcription factors: structurally distinct, functionally diverse. Trends Plant Sci 10, 79-87. |
| [46] |
Ooka H, Satoh K, Doi K, Nagata T, Otomo Y, Murakami K, Matsubara K, Osato N, Kawai J, Carninci P, Hayashizaki Y, Suzuki K, Kojima K, Takahara Y, Yamamoto K, Kikuchi S (2003). Comprehensive analysis of NAC family genes in Oryza sativa and Arabidopsis thaliana. DNA Res 10, 239-247.
URL PMID |
| [47] |
Paz-Ares J, Ghosal D, Wienand U, Peterson PA, Saedler H (1987). The regulatory c1 locus of Zea mays encodes a protein with homology to MYB proto-oncogene products and with structural similarities to transcriptional activators. EMBO J 6, 3553-3558.
URL PMID |
| [48] |
Qi TC, Huang H, Wu DW, Yan JB, Qi YJ, Song SS, Xie DX (2014). Arabidopsis DELLA and JAZ proteins bind the WD-repeat/bHLH/MYB complex to modulate gibberellin and jasmonate signaling synergy. Plant Cell 26, 1118-1133.
DOI URL PMID |
| [49] | Reddy VA, Wang Q, Dhar N, Kumar N, Venkatesh PN, Rajan C, Panicker D, Sridhar V, Mao HZ, Sarojam R (2017). Spearmint R2R3-MYB transcription factor MsMYB negatively regulates monoterpene production and suppresses the expression of geranyl diphosphate synthase large subunit (MsGPPS. LSU). Plant Biotechnol J 15, 1105-1119. |
| [50] | Reeves PH, Ellis CM, Ploense SE, Wu MF, Yadav V, Tholl D, Chételat A, Haupt I, Kennerley BJ, Hodgens C, Farmer EE, Nagpal P, Reed JW (2012). A regulatory network for coordinated flower maturation. PLoS Genet 8, e1002506. |
| [51] |
Roberts SC (2007). Production and engineering of terpenoids in plant cell culture. Nat Chem Biol 3, 387-395.
DOI URL PMID |
| [52] |
Rushton DL, Tripathi P, Rabara RC, Lin J, Ringler P, Boken AK, Langum TJ, Smidt L, Boomsma DD, Emme NJ, Chen XF, Finer JJ, Shen QJ, Rushton PJ (2012). WRKY transcription factors: key components in abscisic acid signaling. Plant Biotechnol J 10, 2-11.
URL PMID |
| [53] |
Rushton PJ, Somssich IE, Ringler P, Shen QJ (2010). WRKY transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci 15, 247-258.
URL PMID |
| [54] | Sakuma Y, Liu Q, Dubouzet JG, Abe H, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2002). DNA-binding specificity of the ERF/AP2 domain of Arabidopsis DREBs, transcription factors involved in dehydration- and cold-inducible gene expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 290, 998-1009. |
| [55] |
Schwab W, Davidovich-Rikanati R, Lewinsohn E (2008). Biosynthesis of plant-derived flavor compounds. Plant J 54, 712-732.
DOI URL PMID |
| [56] |
Shang Y, Ma YS, Zhou Y, Zhang HM, Duan LX, Chen HM, Zeng JG, Zhou Q, Wang SH, Gu WJ, Liu M, Ren JW, Gu XF, Zhang SP, Wang Y, Yasukawa K, Bouwmeester HJ, Qi XQ, Zhang ZH, Lucas WJ, Huang SW (2014). Biosynthesis, regulation, and domestication of bitterness in cucumber. Science 346, 1084-1088.
DOI URL PMID |
| [57] |
Shen SL, Yin XR, Zhang B, Xie XL, Jiang Q, Grierson D, Chen KS (2016). CitAP2.10 activation of the terpene synthase CsTPS1 is associated with the synthesis of (+)-valencene in ‘Newhall’ orange. J Exp Bot 67, 4105-4115.
DOI URL PMID |
| [58] | Shi M, Zhou W, Zhang JL, Huang SX, Wang HZ, Kai GY (2016). Methyl jasmonate induction of tanshinone biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots is mediated by JASMONATE ZIM-DOMAIN repressor proteins. Sci Rep 6, 20919. |
| [59] |
Spyropoulou EA, Haring MA, Schuurink RC (2014a). Expression of terpenoids 1, a glandular trichome-specific transcription factor from tomato that activates the terpene synthase 5 promoter. Plant Mol Biol 84, 345-357.
URL PMID |
| [60] | Spyropoulou EA, Haring MA, Schuurink RC (2014b). RNA sequencing on Solanum lycopersicum trichomes identifies transcription factors that activate terpene synthase promoters. BMC Genomics 15, 402. |
| [61] |
Suttipanta N, Pattanaik S, Kulshrestha M, Patra B, Singh SK, Yuan L (2011). The transcription factor CrWRKY1 positively regulates the terpenoid indole alkaloid biosynthesis in Catharanthus roseus. Plant Physiol 157, 2081-2093.
DOI URL PMID |
| [62] | Tamura K, Yoshida K, Hiraoka Y, Sakaguchi D, Chikugo A, Mochida K, Kojoma M, Mitsuda N, Saito K, Muranaka T, Seki H (2018). The basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor GubHLH3 positively regulates soyasaponin biosynthetic genes in Glycyrrhiza uralensis. Plant Cell Physiol 59, 783-796. |
| [63] | Tan HX, Xiao L, Gao SH, Li Q, Chen JF, Xiao Y, Ji Q, Chen RB, Chen WS, Zhang L (2015). TRICHOME and ARTEMISININ REGULATOR 1 is required for trichome development and artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua. Mol Plant 8, 1396-1411. |
| [64] | Tang YL, Li L, Yan TX, Fu XQ, Shi P, Shen Q, Sun XF, Tang KX (2018). AaEIN3 mediates the downregulation of artemisinin biosynthesis by ethylene signaling through promoting leaf senescence in Artemisia annua. Front Plant Sci 9, 413. |
| [65] |
Vranová E, Coman D, Gruissem W (2012). Structure and dynamics of the isoprenoid pathway network. Mol Plant 5, 318-333.
DOI URL PMID |
| [66] | Wang Q, Reddy VA, Panicker D, Mao HZ, Kumar N, Venkatesh PN, Chua NH, Sarojam R (2016). Metabolic engineering of terpene biosynthesis in plants using a trichome-specific transcription factor MsYABBY5 from spearmint (Mentha spicata). Plant Biotechnol J 14, 1619-1632. |
| [67] |
Wei CL, Yang H, Wang SB, Zhao J, Liu C, Gao LP, Xia EH, Lu Y, Tai YL, She GB, Sun J, Cao HS, Tong W, Gao Q, Li YY, Deng WW, Jiang XL, Wang WZ, Chen Q, Zhang SH, Li HJ, Wu JL, Wang P, Li PH, Shi CY, Zheng FY, Jian JB, Huang B, Shan D, Shi MM, Fang CB, Yue Y, Li FD, Li DX, Wei S, Han B, Jiang CJ, Yin Y, Xia T, Zhang ZZ, Bennetzen JL, Zhao SC, Wan XC (2018). Draft genome sequence of Camellia sinensis var. sinensis provides insights into the evolution of the tea genome and tea quality. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115, E4151-E4158.
DOI URL PMID |
| [68] |
Xu YH, Wang JW, Wang S, Wang JY, Chen XY (2004). Characterization of GaWRKY1, a cotton transcription factor that regulates the sesquiterpene synthase gene (+)-δ-cadinene synthase-A1. Plant Physiol 135, 507-515.
DOI URL PMID |
| [69] |
Xu YY, Zhu CQ, Xu CJ, Sun J, Grierson D, Zhang B, Chen KS (2019). Integration of metabolite profiling and transcriptome analysis reveals genes related to volatile terpenoid metabolism in finger citron (C. medica var. sarcodactylis). Molecules 24, 2564.
DOI URL |
| [70] | Yamamura C, Mizutani E, Okada K, Nakagawa H, Fukushima S, Tanaka A, Maeda S, Kamakura T, Yamane H, Takatsuji H, Mori M (2015). Diterpenoid phytoalexin factor, a bHLH transcription factor, plays a central role in the biosynthesis of diterpenoid phytoalexins in rice. Plant J 84, 1100-1113. |
| [71] |
Yamane H (2013). Biosynthesis of phytoalexins and regulatory mechanisms of it in rice. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 77, 1141-1148.
DOI URL PMID |
| [72] |
Yin J, Li X, Zhan YG, Li Y, Qu ZY, Sun L, Wang SY, Yang J, Xiao JL (2017). Cloning and expression of BpMYC4 and BpbHLH9 genes and the role of BpbHLH9 in triterpenoid synthesis in birch. BMC Plant Biol 17, 214.
URL PMID |
| [73] |
Yu ZX, Li JX, Yang CQ, Hu WL, Wang LJ, Chen XY (2012). Jasmonate-responsive AP2/ERF transcription factors AaERF1 and AaERF2 positively regulate artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua L. Mol Plant 5, 353-365.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
Zhang FY, Fu XQ, Lv ZY, Lu X, Shen Q, Zhang L, Zhu MM, Wang GF, Sun XF, Liao ZH, Tang KX (2015). A basic leucine zipper transcription factor, AabZIP1, connects abscisic acid signaling with artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua. Mol Plant 8, 163-175.
DOI URL PMID |
| [75] |
Zhang FY, Xiang LE, Yu Q, Zhang HX, Zhang TX, Zeng JL, Geng C, Li L, Fu XQ, Shen Q, Yang CX, Lan XZ, Chen M, Tang KX, Liao ZH (2018). ARTEMISININ BIOSYNTHESIS PROMOTING KINASE 1 positively regulates artemisinin biosynthesis through phosphorylating AabZIP1. J Exp Bot 69, 1109-1123.
DOI URL PMID |
| [76] |
Zhang JX, Zhou LB, Zheng XY, Zhang JJ, Yang L, Tan RH, Zhao SJ (2017). Overexpression of SmMYB9b enhances tanshinone concentration in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots. Plant Cell Rep 36, 1297-1309.
DOI URL PMID |
| [77] |
Zhang YJ, Wang LJ (2005). The WRKY transcription factor superfamily: its origin in eukaryotes and expansion in plants. BMC Evol Biol 5, 1.
DOI URL PMID |
| [78] |
Zhou F, Sun TH, Zhao L, Pan XW, Lu S (2015). The bZIP transcription factor HY5 interacts with the promoter of the monoterpene synthase gene QH6 in modulating its rhythmic expression. Front Plant Sci 6, 304.
DOI URL PMID |
| [79] |
Zhou Y, Ma YS, Zeng JG, Duan LX, Xue XF, Wang HS, Lin T, Liu ZQ, Zeng KW, Zhong Y, Zhang S, Hu Q, Liu M, Zhang HM, Reed J, Moses T, Liu XY, Huang P, Qing ZX, Liu XB, Tu PF, Kuang HH, Zhang ZH, Osbourn A, Ro DK, Shang Y, Huang SW (2016). Convergence and divergence of bitterness biosynthesis and regulation in Cucurbitaceae. Nat Plants 2, 16183.
DOI URL PMID |
| [80] |
Zhou YY, Zhou X, Li Q, Chen JF, Xiao Y, Zhang L, Chen WS (2017). Molecular cloning, bioinformatics analysis, and transcriptional profiling of JAZ1 and JAZ2 from Salvia miltiorrhiza. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 64, 27-34.
DOI URL PMID |
| [81] |
Zhu MK, Chen GP, Zhou S, Tu Y, Wang Y, Dong TT, Hu ZL (2014). A new tomato NAC (NAM/ATAF1/2/CUC2) transcription factor, SlNAC4, functions as a positive regulator of fruit ripening and carotenoid accumulation. Plant Cell Physiol 55, 119-135.
DOI URL PMID |
| [82] | Zhuang J, Peng RH, Cheng ZM, Zhang J, Cai B, Zhang Z, Gao F, Zhu B, Fu XY, Jin XF, Chen JM, Qiao YS, Xiong AS, Yao QH (2009). Genome-wide analysis of the putative ap2/erf family genes in Vitis vinifera. Sci Hortic 123, 73-81. |
| [83] |
Zvi MMB, Shklarman E, Masci T, Kalev H, Debener T, Shafir S, Ovadis M, Vainstein A (2012). PAP1 transcription factor enhances production of phenylpropanoid and terpenoid scent compounds in rose flowers. New Phytol 195, 335-345.
DOI URL PMID |
| [1] | 周婧, 高飞. 植物缺铁诱导型香豆素合成及其在铁吸收中的功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 460-471. |
| [2] | 陈鹏翔, 王波, 王子俊, 韩榕. 转录因子在植物响应UV-B辐射中的调控作用[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 449-459. |
| [3] | 李新宇, 谷月, 徐非非, 包劲松. 水稻胚乳淀粉合成相关蛋白的翻译后修饰研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 256-270. |
| [4] | 胡海涛, 武越, 杨玲. 植物NAD(P)+的生物合成及其生物学功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 114-131. |
| [5] | 范雪兰, 落艳娇, 徐超群, 郭宝林. 淫羊藿类黄酮生物合成相关基因研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 834-846. |
| [6] | 夏婧, 饶玉春, 曹丹芸, 王逸, 柳林昕, 徐雅婷, 牟望舒, 薛大伟. 水稻中乙烯生物合成关键酶OsACS和OsACO调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 291-301. |
| [7] | 陈雯, 周颖盈, 罗平, 崔永一. 被子植物花朵重瓣化分子调控机制[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 257-277. |
| [8] | 刘潇潇, 巩迪, 高天鹏, 殷俐娜, 王仕稳. 植物类囊体主要膜脂及其生物合成[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 144-155. |
| [9] | 朱璐, 袁冲, 刘义飞. 植物次生代谢产物生物合成基因簇研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 134-143. |
| [10] | 曾鑫海, 陈锐, 师宇, 盖超越, 范凯, 李兆伟. 植物SPL转录因子的生物功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 982-997. |
| [11] | 胡海涛, 郭龙彪. 植物核黄素的生物合成及其功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(4): 638-655. |
| [12] | 郭彦君, 陈枫, 罗敬文, 曾为, 许文亮. 植物细胞壁木聚糖的生物合成及其应用[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(2): 316-334. |
| [13] | 于淼, 阮成江, 丁健, 李景滨, 卢顺光, 温秀凤. 沙棘hrh-miRn458靶向转录因子WRI1调控油脂合成[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(5): 635-648. |
| [14] | 秦怡, 刘艳爽, 仇柳柳, 周敏, 杜小杉, 戴绍军, 孙美红. MBF1调控植物热应答与生长发育分子机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 56-68. |
| [15] | 刘德帅, 姚磊, 徐伟荣, 冯美, 姚文孔. 褪黑素参与植物抗逆功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 111-126. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||