

植物学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (3): 463-480.DOI: 10.11983/CBB23066 cstr: 32102.14.CBB23066
谢靖雯1,2, 曹晓云1,2, 潘婉琪1,2, 杜灵娟1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-05-22
接受日期:2023-10-24
出版日期:2024-05-10
发布日期:2024-05-10
通讯作者:
杜灵娟, 西北农林科技大学风景园林艺术学院副教授, 博士生导师。2015年4月-2016年4月在美国佐治亚大学园艺系访学。先后主持国家自然科学基金面上项目、陕西省重点研发计划项目、国家自然科学基金青年项目和陕西省基金项目。主要从事园林植物分子育种、园林植物种质资源的调查与评价和园林植物应用研究。发表论文20余篇, 其中SCI论文10余篇; 获得2020年陕西省高等学校科学技术奖一等奖1项(第3参与人)。E-mail: 基金资助:
Jingwen Xie1,2, Xiaoyun Cao1,2, Wanqi Pan1,2, Lingjuan Du1,2,*( )
)
Received:2023-05-22
Accepted:2023-10-24
Online:2024-05-10
Published:2024-05-10
Contact:
E-mail: 摘要: 类黄酮是植物次生代谢过程中产生的多酚类物质, 在植物中广泛存在且功能多样。类黄酮的生物合成发生在内质网的细胞质侧, 但最终积累在液泡腔内。因此, 需要高效的类黄酮转运和积累系统将其从内质网转移至液泡内。几十年来, 关于植物类黄酮转运有诸多研究。目前的研究结果表明, 植物体内存在3种类黄酮转运机制, 包括谷胱甘肽转移酶介导的转运及膜转运蛋白和囊泡介导的转运。该文综述了这3种转运机制以及近年来植物类黄酮转运研究进展, 分析总结了3种不同但具有非排它性机制在功能上的协同作用。虽然类黄酮生物合成途径在许多物种中得到很好的表征, 但是关于其转运研究仍相对缺乏。类黄酮修饰与转运的关系、转运蛋白对底物的特异性和偏好性及类黄酮转运的转录调控仍需深入探索, 以更好地解析类黄酮在植物细胞中的转运和积累机制。
谢靖雯, 曹晓云, 潘婉琪, 杜灵娟. 植物类黄酮转运与积累机制的研究进展. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 463-480.
Jingwen Xie, Xiaoyun Cao, Wanqi Pan, Lingjuan Du. Advances in Plant Flavonoid Transport and Accumulation Mechanism. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(3): 463-480.
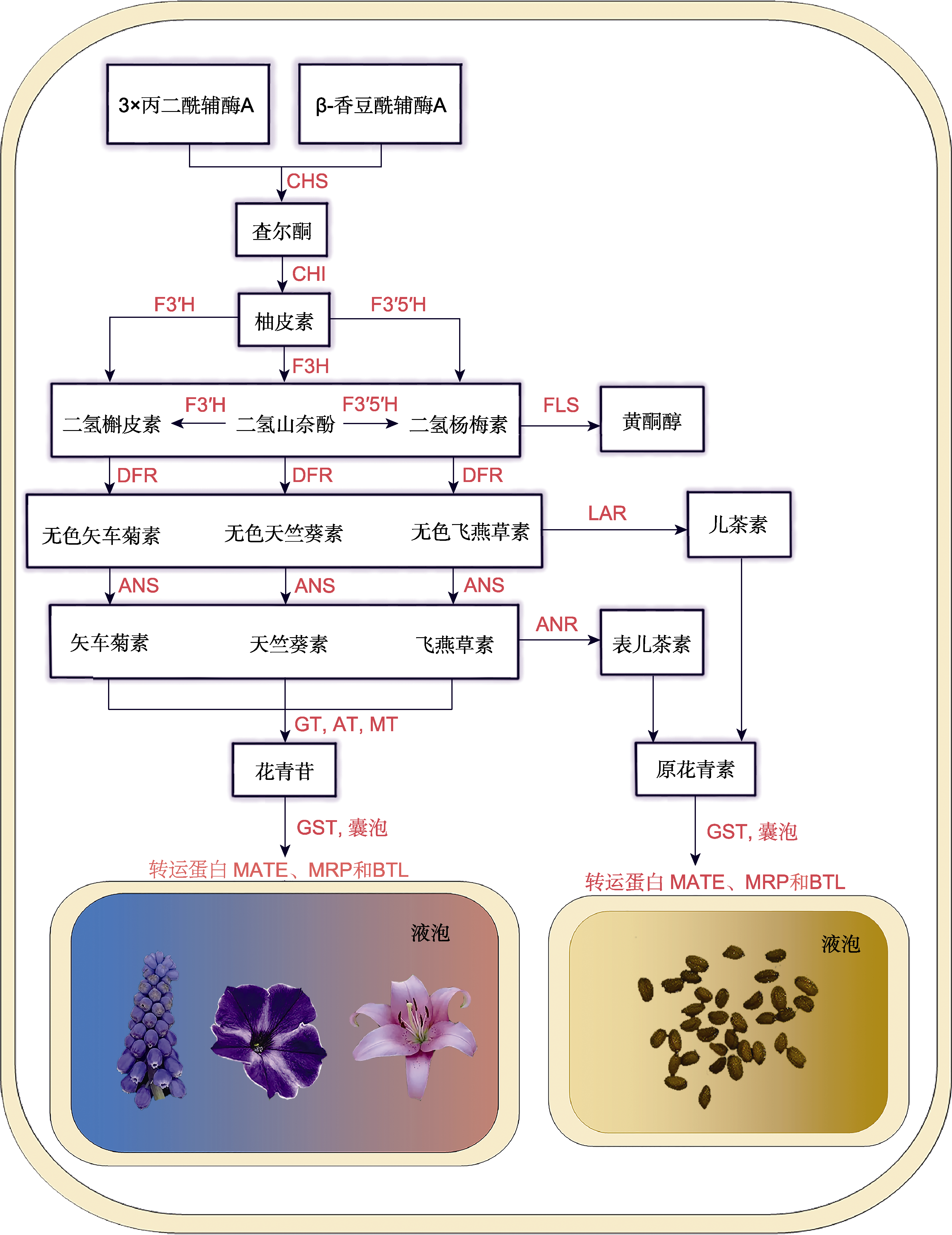
图1 类黄酮的生物合成和转运(改自Koes et al., 2005) 类黄酮生物合成涉及多种结构基因编码酶。CHS: 查尔酮合酶; CHI: 查尔酮异构酶; F3H: 黄烷酮3-羟化酶; F3′H: 黄烷酮3′-羟化酶; F3′5′H: 黄烷酮3′5′-羟化酶; DFR: 二氢黄酮醇4-还原酶; ANS: 花青素合酶; FLS: 黄酮醇合酶; LAR: 原花青素还原酶; ANR: 花青素还原酶; GT: 葡萄糖基转移酶; MT: 甲基转移酶; AT: 酰基转移酶; GST: 谷胱甘肽转移酶; MATE: 多药和毒性化合物排出蛋白; MRP: 多药耐药抗性相关蛋白; BTL: 胆红素易位酶
Figure 1 Biosynthesis and transport of flavonoid (modified from Koes et al., 2005) Flavonoid biosynthesis involves enzymes encoded by various structural genes. CHS: Chalcone synthase; CHI: Chalcone isomerase; F3H: Flavanone 3-hydroxylase; F3′H: Flavanone 3′-hydroxylase; F3′5′H Flavanone 3′5′-hydroxylase; DFR: Dihy- droflavonol reductase; ANS: Anthocyanin synthase; FLS: Flavonol synthase; LAR; Leucoanthocyanidin reductase; ANR: An- thocyanidin reductase; GT: Glycosyltransferases; MT: Methyltransferase; AT: Acyltransferase; GST: Glutathione S-transferase; MATE: Multidrug and toxic compound extrusion; MRP: Multidrug resistance-associated protein; BTL: Bilitranslocase
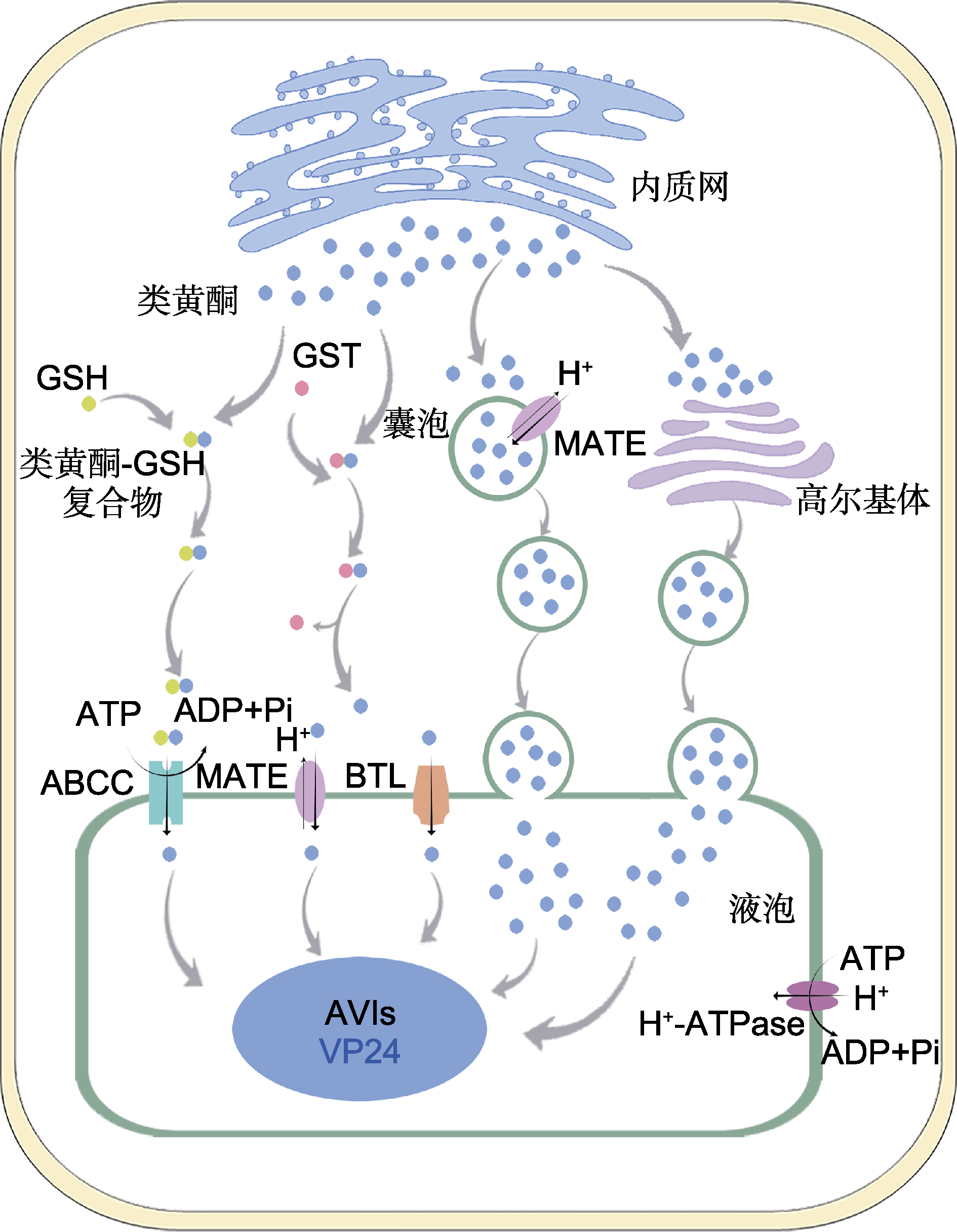
图2 类黄酮的转运与积累机制(改自Kaur et al., 2021) 类黄酮在内质网上生物合成, GST通过催化类黄酮-GSH复合物的形成或直接结合类黄酮, 将其转运至液泡膜。随后液泡膜上的转运蛋白ABCC、MATE和BTL将类黄酮转运至液泡腔内。内质网上合成的类黄酮通过内质网或高尔基体被包裹在囊泡中, 囊泡运输至液泡并与液泡膜融合将类黄酮释放到液泡腔内, 在液泡中类黄酮聚集形成花青苷液泡内涵体(AVIs)。GSH: 谷胱甘肽; ABCC: 多药耐药抗性相关蛋白。GST、MATE和BTL同图1。
Figure 2 Mechanism of flavonoid transport and accumula- tion (modified from Kaur et al., 2021) Flavonoid is synthesized on endoplasmic reticulum, and GST transports it to vacuole membrane by catalyzing the formation of flavonoid-GSH complex or directly binding fla- vonoid. Subsequently, ABCC, MATE and BTL on the vac- uole membrane transport flavonoid into the vacuole. Flavo- noid is wrapped in vesicles through endoplasmic reticulum or Golgi apparatus, and vesicles are transported to vacuoles and fused with vacuole membrane to release flavonoid into vac- uole. In vacuole, flavonoids aggregate to form anthocyanic vacuolar inclusions (AVIs). GSH: Glutathione; ABCC: Mul- tidrug resistance-associated protein. GST, MATE and BTL are the same as shown in Figure 1.
| 物种 | 基因 | GenBank登录号 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 玉米(Zea mays) | Bronze2 | AAA50245 | Marrs et al., |
| 矮牵牛(Petunia hybrida) | PhAN9 | CAA68993 | Alfenito et al., |
| 拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana) | AtTT19 | BAD89984 | Kitamura et al., |
| 葡萄(Vitis vinifera) | VvGST1 | AY156048 | Conn et al., |
| VvGST4 | AY971515 | Pérez-Díaz et al., | |
| 紫苏(Perilla frutescens) | PfGST1 | AB362191 | Yamazaki et al., |
| 仙客来(Cyclamen persicum) | CkmGST3 | AB682678 | Kitamura et al., |
| 香石竹(Dianthus caryophyllus) | FL3/DcGSTF2 | AB688111 | Sasaki et al., |
| 瓜叶菊(Pericallis × hybrida=Senecio cruentus) | ScGST3 | Cui et al., | |
| 中华猕猴桃(Actinidia chinensis) | AcGST1 | MK238757 | Liu et al., |
| 桃(Prunus persica) | PpGST1和Riant | ALE31199 | Cheng et al., |
| PpGST1 | Zhao et al., | ||
| 苹果(Malus pumila=Malus domestica) | MdGSTF6 | Jiang et al., | |
| 番薯(Ipomoea batatas) | IbGSTF4 | MG873448 | Kou et al., |
| 荔枝(Litchi chinensis) | LcGST4 | ALY05893 | Hu et al., |
| 野草莓(Fragaria vesca) | FvRAP | XP_004288578 | Luo et al., |
| 茶(Camellia sinensis) | CsGSTF1 | Wei et al., | |
| 一品红(Euphorbia pulcherrima) | Bract1 | MW718861 | Vilperte et al., |
| 萝卜(Raphanus sativus) | RsGST1 | Lai et al., | |
| RsGSTF12 | Niu et al., | ||
| 百合(Lilium brownii var. viridulum) | LhGST | MK426728 | Cao et al., |
| 陆地棉(Gossypium hirsutum) | GhGSTF12 | Shao et al., | |
| GhTT19 | Chai et al., | ||
| 蒺藜苜蓿(Medicago truncatula) | MtGSTF7 | Wang et al., | |
| 西洋梨(Pyrus communis) | PcGSTF12 | Zhang et al., | |
| 欧洲甜樱桃(Prunus avium) | PavGST1 | Qi et al., | |
| 杨梅(Morella rubra) | MrGST1 | Xue et al., | |
| 牡丹(Paeonia × suffruticosa) | PsGSTF3 | Han et al., |
表1 植物中各种转运类黄酮的谷胱甘肽转移酶
Table 1 List of various GSTs functioning as flavonoid transporters in plants
| 物种 | 基因 | GenBank登录号 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 玉米(Zea mays) | Bronze2 | AAA50245 | Marrs et al., |
| 矮牵牛(Petunia hybrida) | PhAN9 | CAA68993 | Alfenito et al., |
| 拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana) | AtTT19 | BAD89984 | Kitamura et al., |
| 葡萄(Vitis vinifera) | VvGST1 | AY156048 | Conn et al., |
| VvGST4 | AY971515 | Pérez-Díaz et al., | |
| 紫苏(Perilla frutescens) | PfGST1 | AB362191 | Yamazaki et al., |
| 仙客来(Cyclamen persicum) | CkmGST3 | AB682678 | Kitamura et al., |
| 香石竹(Dianthus caryophyllus) | FL3/DcGSTF2 | AB688111 | Sasaki et al., |
| 瓜叶菊(Pericallis × hybrida=Senecio cruentus) | ScGST3 | Cui et al., | |
| 中华猕猴桃(Actinidia chinensis) | AcGST1 | MK238757 | Liu et al., |
| 桃(Prunus persica) | PpGST1和Riant | ALE31199 | Cheng et al., |
| PpGST1 | Zhao et al., | ||
| 苹果(Malus pumila=Malus domestica) | MdGSTF6 | Jiang et al., | |
| 番薯(Ipomoea batatas) | IbGSTF4 | MG873448 | Kou et al., |
| 荔枝(Litchi chinensis) | LcGST4 | ALY05893 | Hu et al., |
| 野草莓(Fragaria vesca) | FvRAP | XP_004288578 | Luo et al., |
| 茶(Camellia sinensis) | CsGSTF1 | Wei et al., | |
| 一品红(Euphorbia pulcherrima) | Bract1 | MW718861 | Vilperte et al., |
| 萝卜(Raphanus sativus) | RsGST1 | Lai et al., | |
| RsGSTF12 | Niu et al., | ||
| 百合(Lilium brownii var. viridulum) | LhGST | MK426728 | Cao et al., |
| 陆地棉(Gossypium hirsutum) | GhGSTF12 | Shao et al., | |
| GhTT19 | Chai et al., | ||
| 蒺藜苜蓿(Medicago truncatula) | MtGSTF7 | Wang et al., | |
| 西洋梨(Pyrus communis) | PcGSTF12 | Zhang et al., | |
| 欧洲甜樱桃(Prunus avium) | PavGST1 | Qi et al., | |
| 杨梅(Morella rubra) | MrGST1 | Xue et al., | |
| 牡丹(Paeonia × suffruticosa) | PsGSTF3 | Han et al., |
| 物种 | 基因 | GenBank登录号 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana) | AtTT12 | AJ294464 | Debeaujon et al., |
| FFT (AtDTX35) | F4JTB3 | Kitamura et al., | |
| 蒺藜苜蓿(Medicago truncatula) | MtMATE1 | ACX37118 | Zhao and Dixon, |
| MtMATE2 | ADV04045 | Zhao et al., | |
| 苹果(Malus pumila=Malus domestica) | MdMATE1 | ADO22709 | Frank et al., |
| MdMATE2 | ADO22711 | Frank et al., | |
| 葡萄(Vitis vinifera) | VvAM1 | ACN91542 | Gomez et al., |
| VvAM3 | ACN88706 | Gomez et al., | |
| 百合(Lilium brownii var. viridulum) | LhDTX35 | MT001433 | Xu et al., |
| 草莓(Fragaria × ananassa) | FaTT12-1 | KY851294 | Chen et al., |
| 陆地棉(Gossypium hirsutum) | GhTT12 | KF240564 | Gao et al., |
| 番茄(Solanum lycopersicum) | SlMATE/MTP77 | AAQ55183 | Mathews et al., |
| 柿(Diospyros kaki) | DkMATE1 | Yang et al., | |
| 鹰嘴豆(Cicer arietinum) | CaMATE1 | Pal et al., | |
| 克里曼丁橘(Citrus clementina) | CitMATE43 | Liu et al., | |
| 矮牵牛(Petunia hybrida) | PhMATE1 | Yuan et al., | |
| 白梨(Pyrus bretschneideri) | PbTT12 | 刘汉婷, | |
| 烟草(Nicotiana tabacum) | NtMATE21 | Gani et al., | |
| NtMATE22 | Gani et al., | ||
| 大豆(Glycine max) | GmMATE1 | Ng et al., | |
| GmMATE4 | Ku et al., |
表2 各种植物中发现的类黄酮MATE转运蛋白
Table 2 List of flavonoid MATE transporters found in various plants
| 物种 | 基因 | GenBank登录号 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana) | AtTT12 | AJ294464 | Debeaujon et al., |
| FFT (AtDTX35) | F4JTB3 | Kitamura et al., | |
| 蒺藜苜蓿(Medicago truncatula) | MtMATE1 | ACX37118 | Zhao and Dixon, |
| MtMATE2 | ADV04045 | Zhao et al., | |
| 苹果(Malus pumila=Malus domestica) | MdMATE1 | ADO22709 | Frank et al., |
| MdMATE2 | ADO22711 | Frank et al., | |
| 葡萄(Vitis vinifera) | VvAM1 | ACN91542 | Gomez et al., |
| VvAM3 | ACN88706 | Gomez et al., | |
| 百合(Lilium brownii var. viridulum) | LhDTX35 | MT001433 | Xu et al., |
| 草莓(Fragaria × ananassa) | FaTT12-1 | KY851294 | Chen et al., |
| 陆地棉(Gossypium hirsutum) | GhTT12 | KF240564 | Gao et al., |
| 番茄(Solanum lycopersicum) | SlMATE/MTP77 | AAQ55183 | Mathews et al., |
| 柿(Diospyros kaki) | DkMATE1 | Yang et al., | |
| 鹰嘴豆(Cicer arietinum) | CaMATE1 | Pal et al., | |
| 克里曼丁橘(Citrus clementina) | CitMATE43 | Liu et al., | |
| 矮牵牛(Petunia hybrida) | PhMATE1 | Yuan et al., | |
| 白梨(Pyrus bretschneideri) | PbTT12 | 刘汉婷, | |
| 烟草(Nicotiana tabacum) | NtMATE21 | Gani et al., | |
| NtMATE22 | Gani et al., | ||
| 大豆(Glycine max) | GmMATE1 | Ng et al., | |
| GmMATE4 | Ku et al., |
| 物种 | 基因 | GenBank登录号 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 玉米(Zea mays) | ZmMRP3 | AY609318 | Goodman et al., |
| ZmMRP4 | BG349642 | Goodman et al., | |
| 拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana) | AtABCC2 | NP_001189675 | Behrens et al., |
| 葡萄(Vitis vinifera) | VvABCC1 | JX245004 | Francisco et al., |
| 水稻(Oryza sativa) | OsMRP15 | LOC_Os06g06440 | Zhu et al., |
| 桃(Prunus persica) | PpABCC1 | Sylvia et al., | |
| 拟南芥(A. thaliana) | AtABCC1、AtABCC2和AtABCC14 | Dean et al., |
表3 各种植物中发现的类黄酮ABCC转运蛋白
Table 3 List of flavonoid ABCC transporters found in various plants
| 物种 | 基因 | GenBank登录号 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 玉米(Zea mays) | ZmMRP3 | AY609318 | Goodman et al., |
| ZmMRP4 | BG349642 | Goodman et al., | |
| 拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana) | AtABCC2 | NP_001189675 | Behrens et al., |
| 葡萄(Vitis vinifera) | VvABCC1 | JX245004 | Francisco et al., |
| 水稻(Oryza sativa) | OsMRP15 | LOC_Os06g06440 | Zhu et al., |
| 桃(Prunus persica) | PpABCC1 | Sylvia et al., | |
| 拟南芥(A. thaliana) | AtABCC1、AtABCC2和AtABCC14 | Dean et al., |
| 物种 | 转录因子 | 靶基因 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 瓜叶菊(Pericallis × hybrida = Senecio cruentus) | ScMYB3 | ScGST3 | Cui et al., |
| 中华猕猴桃(Actinidia chinensis) | AcMYBF110 | AcGST1 | Liu et al., |
| 桃(Prunus persica) | PpMYB10.1 | PpGST1 | Zhao et al., |
| 苹果(Malus pumila = Malus domestica) | MdMYB1 | MdGSTF6 | Jiang et al., |
| 荔枝(Litchi chinensis) | LcMYB1 | LcGST4 | Hu et al., |
| 萝卜(Raphanus sativus) | RsMYB1a | RsGST1 | Lai et al., |
| 百合(Lilium brownii var. viridulum) | LhMYB12-lat | LhGST | Cao et al., |
| 陆地棉(Gossypium hirsutum) | GhPAP1 | GhTT19 | Chai et al., |
| 蒺藜苜蓿(Medicago truncatula) | MtLAP1 | MtGSTF7 | Wang et al., |
| 梨(Pyrus betulaefolia) | PcMYB114 | PcGSTF12 | Zhang et al., |
| 欧洲甜樱桃(Prunus avium) | PavMYB10.1 | PavGST1 | Qi et al., |
| 杨梅(Morella rubra) | MrMYB1.1 | MrGST1 | Xue et al., |
| 柿(Diospyros kaki) | DkMYB4 | DkMATE1 | Yang et al., |
| 苹果(M. pumila = M. domestica) | MdMYB1 | MdMATE-LIKE1 | Hu et al., |
| 白梨(P. bretschneideri) | PbTT2 | PbTT12 | 刘汉婷, |
| 烟草(Nicotiana tabacum) | NtMYB12 | NtMATE21、NtMATE22 | Gani et al., |
| 克里曼丁橘(Citrus clementina) | CitERF32和CitERF33 | CitMATE43 | Liu et al., |
表4 各种植物中发现的类黄酮转录因子及其靶向的转运基因
Table 4 Flavonoid transcription factors and their targeted transport genes found in various plants
| 物种 | 转录因子 | 靶基因 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 瓜叶菊(Pericallis × hybrida = Senecio cruentus) | ScMYB3 | ScGST3 | Cui et al., |
| 中华猕猴桃(Actinidia chinensis) | AcMYBF110 | AcGST1 | Liu et al., |
| 桃(Prunus persica) | PpMYB10.1 | PpGST1 | Zhao et al., |
| 苹果(Malus pumila = Malus domestica) | MdMYB1 | MdGSTF6 | Jiang et al., |
| 荔枝(Litchi chinensis) | LcMYB1 | LcGST4 | Hu et al., |
| 萝卜(Raphanus sativus) | RsMYB1a | RsGST1 | Lai et al., |
| 百合(Lilium brownii var. viridulum) | LhMYB12-lat | LhGST | Cao et al., |
| 陆地棉(Gossypium hirsutum) | GhPAP1 | GhTT19 | Chai et al., |
| 蒺藜苜蓿(Medicago truncatula) | MtLAP1 | MtGSTF7 | Wang et al., |
| 梨(Pyrus betulaefolia) | PcMYB114 | PcGSTF12 | Zhang et al., |
| 欧洲甜樱桃(Prunus avium) | PavMYB10.1 | PavGST1 | Qi et al., |
| 杨梅(Morella rubra) | MrMYB1.1 | MrGST1 | Xue et al., |
| 柿(Diospyros kaki) | DkMYB4 | DkMATE1 | Yang et al., |
| 苹果(M. pumila = M. domestica) | MdMYB1 | MdMATE-LIKE1 | Hu et al., |
| 白梨(P. bretschneideri) | PbTT2 | PbTT12 | 刘汉婷, |
| 烟草(Nicotiana tabacum) | NtMYB12 | NtMATE21、NtMATE22 | Gani et al., |
| 克里曼丁橘(Citrus clementina) | CitERF32和CitERF33 | CitMATE43 | Liu et al., |
| [1] | Agati G, Matteini P, Goti A, Tattini M (2007). Chloro- plast-located flavonoids can scavenge singlet oxygen. New Phytol 174, 77-89. |
| [2] |
Alfenito MR, Souer E, Goodman CD, Buell R, Mol J, Koes R, Walbot V (1998). Functional complementation of an- thocyanin sequestration in the vacuole by widely divergent glutathione S-transferases. Plant Cell 10, 1135-1149.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | Appelhagen I, Nordholt N, Seidel T, Spelt K, Koes R, Quattrochio F, Sagasser M, Weisshaar B (2015). TRANS- PARENT TESTA 13 is a tonoplast P3A-ATPase required for vacuolar deposition of proanthocyanidins in Arabidopsis thaliana seeds. Plant J 82, 840-849. |
| [4] |
Baxter IR, Young JC, Armstrong G, Foster N, Bogen- schutz N, Cordova T, Peer WA, Hazen SP, Murphy AS, Harper JF (2005). A plasma membrane H+-ATPase is required for the formation of proanthocyanidins in the seed coat endothelium of Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102, 2649-2654.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
Behrens CE, Smith KE, Iancu CV, Choe JY, Dean JV (2019). Transport of anthocyanins and other flavonoids by the Arabidopsis ATP-binding cassette transporter AtABCC2. Sci Rep 9, 437.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
Braidot E, Petrussa E, Bertolini A, Peresson C, Ermacora P, Loi N, Terdoslavich M, Passamonti S, Macrì F, Vianello A (2008). Evidence for a putative flavonoid translocator similar to mammalian bilitranslocase in grape berries (Vitis vinifera L.) during ripening. Planta 228, 203-213.
DOI PMID |
| [7] | Buer CS, Muday GK, Djordjevic MA (2007). Flavonoids are differentially taken up and transported long distances in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 145, 478-490. |
| [8] | Cao YW, Xu LF, Xu H, Yang PP, He GR, Tang YC, Qi XY, Song M, Ming J (2021). LhGST is an anthocyanin-related glutathione S-transferase gene in Asiatic hybrid lilies (Lilium spp.). Plant Cell Rep 40, 85-95. |
| [9] | Chai QC, Wang XL, Gao MW, Zhao XC, Chen Y, Zhang C, Jiang H, Wang JB, Wang YC, Zheng MN, Baltaevich AM, Zhao J, Zhao JS (2023). A glutathione S-transferase GhTT19 determines flower petal pigmentation via regu- lating anthocyanin accumulation in cotton. Plant Biotechnol J 21, 433-448. |
| [10] | Chen KL, Du LJ, Liu HL, Liu YL (2019). A novel R2R3-MYB from grape hyacinth, MaMybA, which is dif- ferent from MaAN2, confers intense and magenta antho- cyanin pigmentation in tobacco. BMC Plant Biol 19, 390. |
| [11] | Chen KL, Liu HL, Lou Q, Liu YL (2017). Corrigendum: ectopic expression of the grape hyacinth (Muscari arme- niacum) R2R3-MYB transcription factor gene, MaAN2, in- duces anthocyanin accumulation in tobacco. Front Plant Sci 8, 1722. |
| [12] | Chen S, Wang XJ, Cheng Y, Gao HS, Chen XH (2023). A review of classification, biosynthesis, biological activities and potential applications of flavonoids. Molecules 28, 4982. |
| [13] | Chen SY, Tang YM, Hu YY, Wang Y, Sun B, Wang XR, Tang HR, Chen Q (2018). FaTT12-1, a multidrug and toxin extrusion (MATE) member involved in proanthocya- nidin transport in strawberry fruits. Sci Hortic 231, 158-165. |
| [14] |
Cheng J, Liao L, Zhou H, Gu C, Wang L, Han YP (2015). A small indel mutation in an anthocyanin transporter causes variegated colouration of peach flowers. J Exp Bot 66, 7227-7239.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | Conn S, Curtin C, Bézier A, Franco C, Zhang W (2008). Purification, molecular cloning, and characterization of glutathione S-transferases (GSTs) from pigmented Vitis vinifera L. cell suspension cultures as putative anthocya- nin transport proteins. J Exp Bot 59, 3621-3634. |
| [16] | Conn S, Franco C, Zhang W (2010). Characterization of anthocyanic vacuolar inclusions in Vitis vinifera L. cell sus- pension cultures. Planta 231, 1343-1360. |
| [17] | Conn S, Zhang W, Franco C (2003). Anthocyanic vacuolar inclusions (AVIs) selectively bind acylated anthocyanins in Vitis vinifera L. (grapevine) suspension culture. Biotechnol Lett 25, 835-839. |
| [18] | Cui YM, Fan JW, Lu CF, Ren JS, Qi FT, Huang H, Dai SL (2021). ScGST3 and multiple R2R3-MYB transcription factors function in anthocyanin accumulation in Senecio cruentus. Plant Sci 313, 111094. |
| [19] | Dean JV, Willis M, Shaban L (2022). Transport of acylated anthocyanins by the Arabidopsis ATP-binding cassette transporters AtABCC1, AtABCC2, and AtABCC14. Physiol Plant 174, e13780. |
| [20] |
Debeaujon I, Peeters AJM, Léon-Kloosterziel KM, Koornneef M (2001). The TRANSPARENT TESTA12 gene of Arabidopsis encodes a multidrug secondary transporter- like protein required for flavonoid sequestration in vacuoles of the seed coat endothelium. Plant Cell 13, 853-871.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Feucht W, Treutter D, Polster J (2004). Flavanol binding of nuclei from tree species. Plant Cell Rep 22, 430-436.
PMID |
| [22] | Francisco RM, Regalado A, Ageorges A, Burla BJ, Bassin B, Eisenach C, Zarrouk O, Vialet S, Marlin T, Chaves MM, Martinoia E, Nagya R (2013). ABCC1, an ATP binding cassette protein from grape berry, transports anthocyanidin 3-O-glucosides. Plant Cell 25, 1840-1854. |
| [23] | Frank S, Keck M, Sagasser M, Niehaus K, Weisshaar B, Stracke R (2011). Two differentially expressed MATE factor genes from apple complement the Arabidopsis trans- parent testa12mutant. Plant Biol 13, 42-50. |
| [24] | Gani U, Nautiyal AK, Kundan M, Rout B, Pandey A, Misra P (2022). Two homeologous MATE transporter genes, NtMATE21 and NtMATE22, are involved in the modula- tion of plant growth and flavonol transport in Nicotiana tabacum. J Exp Bot 73, 6186-6206. |
| [25] | Gao JS, Wu N, Shen ZL, Lv K, Qian SH, Guo N, Sun X, Cai YP, Lin Y (2016). Molecular cloning, expression analysis and subcellular localization of a Transparent Testa12 ortholog in brown cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Gene 576, 763-769. |
| [26] | Gaxiola RA, Fink GR, Hirschi KD (2002). Genetic ma- nipulation of vacuolar proton pumps and transporters. Plant Physiol 129, 967-973. |
| [27] | Gomez C, Conejero G, Torregrosa L, Cheynier V, Terrier N, Ageorges A (2011). In vivo grapevine anthocyanin transport involves vesicle-mediated trafficking and the contribution of anthoMATE transporters and GST. Plant J 67, 960-970. |
| [28] |
Gomez C, Terrier N, Torregrosa L, Vialet S, Fournier- Level A, Verries C, Souquet JM, Mazauric JP, Klein M, Cheynier V, Ageorges A (2009). Grapevine MATE-type proteins act as vacuolar H+-dependent acylated anthocyanin transporters. Plant Physiol 150, 402-415.
DOI PMID |
| [29] | Goodman CD, Casati P, Walbot V (2004). A multidrug resistance-associated protein involved in anthocyanin tran- sport in Zea mays. Plant Cell 16, 1812-1826. |
| [30] | Han LL, Zhou L, Zou HZ, Yuan M, Wang Y (2022). PsGSTF3, an anthocyanin-related glutathione S-transferase gene, is essential for petal coloration in tree peony. Int J Mol Sci 23, 1423. |
| [31] | He X, Szewczyk P, Karyakin A, Evin M, Hong WX, Zhang QH, Chang G (2010). Structure of a cation-bound mul- tidrug and toxic compound extrusion transporter. Nature 467, 991-994. |
| [32] |
Hsieh K, Huang AHC (2007). Tapetosomes in Brassica tapetum accumulate endoplasmic reticulum-derived fla- vonoids and alkanes for delivery to the pollen surface. Plant Cell 19, 582-596.
PMID |
| [33] | Hu B, Zhao JT, Lai B, Qin YH, Wang HC, Hu GB (2016a). LcGST4 is an anthocyanin-related glutathione S-transferase gene in Litchi chinensis Sonn. Plant Cell Rep 35, 831-843. |
| [34] | Hu DG, Sun CH, Ma QJ, You CX, Cheng LL, Hao YJ (2016b). MdMYB1 regulates anthocyanin and malate accumulation by directly facilitating their transport into vacuoles in apples. Plant Physiol 170, 1315-1330. |
| [35] |
Hvorup RN, Winnen B, Chang AB, Jiang Y, Zhou XF, Saier MH (2003). The multidrug/oligosaccharidyl-lipid/polysaccharide (MOP) exporter superfamily. Eur J Biochem 270, 799-813.
PMID |
| [36] | Ichino T, Fuji K, Ueda H, Takahashi H, Koumoto Y, Takagi J, Tamura K, Sasaki R, Aoki K, Shimada T, Hara-Nishimura I (2014). GFS9/TT9 contributes to in- tracellular membrane trafficking and flavonoid accumula- tion in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 80, 410-423. |
| [37] | Ishikawa T, Li ZS, Lu YP, Rea PA (1997). The GS-X pump in plant, yeast, and animal cells: structure, function, and gene expression. Biosci Rep 17, 189-207. |
| [38] | Jiang SH, Chen M, He NB, Chen XL, Wang N, Sun QG, Zhang TH, Xu HF, Fang HC, Wang YC, Zhang ZY, Wu SJ, Chen XS (2019). MdGSTF6, activated by MdMYB1, plays an essential role in anthocyanin accumulation in apple. Hortic Res 6, 40. |
| [39] |
Kaur S, Sharma N, Kapoor P, Chunduri V, Pandey AK, Garg M (2021). Spotlight on the overlapping routes and partners for anthocyanin transport in plants. Physiol Plant 171, 868-881.
DOI PMID |
| [40] | Kimble R, Keane KM, Lodge JK, Howatson G (2019). Dietary intake of anthocyanins and risk of cardiovascular disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of pro- spective cohort studies. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 59, 3032-3043. |
| [41] | Kitamura S, Akita Y, Ishizaka H, Narumi I, Tanaka A (2012). Molecular characterization of an anthocyanin-related glutathione S-transferase gene in cyclamen. J Plant Physiol 169, 636-642. |
| [42] | Kitamura S, Matsuda F, Tohge T, Yonekura-Sakakibara K, Yamazaki M, Saito K, Narumi I (2010). Metabolic profiling and cytological analysis of proanthocyanidins in immature seeds of Arabidopsis thaliana flavonoid accu- mulation mutants. Plant J 62, 549-559. |
| [43] |
Kitamura S, Oono Y, Narumi I (2016). Arabidopsis pab1, a mutant with reduced anthocyanins in immature seeds from banyuls, harbors a mutation in the MATE transporter FFT. Plant Mol Biol 90, 7-18.
DOI PMID |
| [44] |
Kitamura S, Shikazono N, Tanaka A (2004). TRANS- PARENT TESTA 19 is involved in the accumulation of both anthocyanins and proanthocyanidins in Arabidopsis. Plant J 37, 104-114.
DOI PMID |
| [45] | Koes R, Verweij W, Quattrocchio F (2005). Flavonoids: a colorful model for the regulation and evolution of bio- chemical pathways. Trends Plant Sci 10, 236-242. |
| [46] | Kou M, Liu YJ, Li ZY, Zhang YG, Tang W, Yan H, Wang X, Chen XG, Su ZX, Arisha MH, Li Q, Ma DF (2019). A novel glutathione S-transferase gene from sweet potato, IbGSTF4, is involved in anthocyanin sequestration. Plant Physiol Biochem 135, 395-403. |
| [47] | Ku YS, Cheng SS, Cheung MY, Niu YC, Liu AL, Chung G, Lam HM (2022). The poly-glutamate motif of GmMATE4 regulates its isoflavone transport activity. Membranes 12, 206. |
| [48] | Kubo H, Nozue M, Kawasaki K, Yasuda H (1995). Intravacuolar spherical bodies in Polygonum cuspidatum. Plant Cell Physiol 36, 1453-1458. |
| [49] |
Kulich I, Pečenková T, Sekereš J, Smetana O, Fendrych M, Foissner I, Höftberger M, Žárský V (2013). Arabi- dopsis exocyst subcomplex containing subunit EXO70B1 is involved in autophagy-related transport to the vacuole. Traffic 14, 1155-1165.
DOI PMID |
| [50] | Lai B, You Y, Zhang LL, Wang QX, Chen FB, Luo GJ, Du LN, Wang HC (2021). Identification and functional characterization of RsGST1, an anthocyanin-related glutathione S-transferase gene in radish. J Plant Physiol 263, 153468. |
| [51] | Le Roy J, Huss B, Creach A, Hawkins S, Neutelings G (2016). Glycosylation is a major regulator of phenylpro- panoid availability and biological activity in plants. Front Plant Sci 7, 735. |
| [52] | Li CX, Yu WJ, Xu JR, Lu XF, Liu YZ (2022). Anthocyanin biosynthesis induced by MYB transcription factors in plants. Int J Mol Sci 23, 11701. |
| [53] | Lin BW, Gong CC, Song HF, Cui YY (2017). Effects of anthocyanins on the prevention and treatment of cancer. Br J Clin Pharmacol 174, 1226-1243. |
| [54] | Liu HT (2020). Functional Analysis of Anthocyanin Trans- porters GSTF12 and TT12 in ‘Red Zaosu’ Pear. Master’s thesis. Yangling: Northwest A&F University. pp. 35-43. (in Chinese) |
| 刘汉婷 (2020). ‘红早酥’梨花青苷转运蛋白GSTF12和TT12的功能分析. 硕士论文. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学. pp. 35-43. | |
| [55] | Liu SC, Li YC, Fang HT, Huang BY, Zhao CN, Sun CD, Li SJ, Chen KS (2022). Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of MATE gene family in citrus fruit (Citrus clementina). Genomics 114, 110446. |
| [56] | Liu YF, Qi YW, Zhang AL, Wu HX, Liu ZD, Ren XL (2019). Molecular cloning and functional characterization of AcGST1, an anthocyanin-related glutathione S-transferase gene in kiwifruit (Actinidia chinensis). Plant Mol Biol 100, 451-465. |
| [57] |
Lu M, Radchenko M, Symersky J, Nie RX, Guo Y (2013). Structural insights into H+-coupled multidrug extrusion by a MATE transporter. Nat Struct Mol Biol 20, 1310-1317.
DOI PMID |
| [58] | Luo HF, Dai C, Li YP, Feng J, Liu ZC, Kang CY (2018). Reduced anthocyanins in petioles codes for a GST an- thocyanin transporter that is essential for the foliage and fruit coloration in strawberry. J Exp Bot 69, 2595-2608. |
| [59] | Marinova K, Pourcel L, Weder B, Schwarz M, Barron D, Routaboul JM, Debeaujon I, Klein M (2007). The Arabidopsis MATE transporter TT12 acts as a vacuolar flavonoid/H+-antiporter active in proanthocyanidin-accumulating cells of the seed coat. Plant Cell 19, 2023-2038. |
| [60] |
Markham KR, Gould KS, Winefield CS, Mitchell KA, Bloor SJ, Boase MR (2000). Anthocyanic vacuolar in- clusions—their nature and significance in flower colouration. Phytochemistry 55, 327-336.
PMID |
| [61] | Marrs KA, Alfenito MR, Lloyd AM, Walbot V (1995). A glutathione-S-transferase involved in vacuolar transfer encoded by the maize gene Bronze-2. Nature 375, 397-400. |
| [62] |
Mathews H, Clendennen SK, Caldwell CG, Liu XL, Connors K, Matheis N, Schuster DK, Menasco DJ, Wagoner W, Lightner J, Wagner DR (2003). Activation tagging in tomato identifies a transcriptional regulator of anthocyanin biosynthesis, modification, and transport. Plant Cell 15, 1689-1703.
DOI PMID |
| [63] |
Mentewab A, Stewart CN (2005). Overexpression of an Arabidopsis thaliana ABC transporter confers kanamycin resistance to transgenic plants. Nat Biotechnol 23, 1177-1180.
PMID |
| [64] |
Mueller LA, Goodman CD, Silady RA, Walbot V (2000). AN9, a petunia glutathione S-transferase required for an- thocyanin sequestration, is a flavonoid-binding protein. Plant Physiol 123, 1561-1570.
DOI PMID |
| [65] |
Mugford ST, Milkowski C (2012). Serine carboxypepti dase-like acyltransferases from plants. Methods Enzymol 516, 279-297.
DOI PMID |
| [66] | Naing AH, Park DY, Park KI, Kim CK (2018). Differential expression of anthocyanin structural genes and transcrip tion factors determines coloration patterns in gerbera flowers. 3 Biotech 8, 393. |
| [67] | Ng MS, Ku YS, Yung WS, Cheng SS, Man CK, Yang L, Song SK, Chung G, Lam HM (2021). MATE-type proteins are responsible for isoflavone transportation and accumulation in soybean seeds. Int J Mol Sci 22, 12017. |
| [68] |
Nishizaki Y, Sasaki N, Yasunaga M, Miyahara T, Okamoto E, Okamoto M, Hirose Y, Ozeki Y (2014). Ide- ntification of the glucosyltransferase gene that supplies the p-hydroxybenzoyl-glucose for 7-polyacylation of ant- hocyanin in delphinium. J Exp Bot 65, 2495-2506.
DOI PMID |
| [69] | Nishizaki Y, Yasunaga M, Okamoto E, Okamoto M, Hi- rose Y, Yamaguchi M, Ozeki Y, Sasaki N (2013). p-hydroxybenzoyl-glucose is a zwitter donor for the bio- synthesis of 7-polyacylated anthocyanin in Delphinium. Plant Cell 25, 4150-4165. |
| [70] | Niu MY, Bao CJ, Chen JH, Zhou W, Zhang YY, Zhang XY, Su NN, Cui J (2022). RsGSTF12contributes to antho- cyanin sequestration in radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Front Plant Sci 13, 870202. |
| [71] | Nozue M, Baba S, Kitamura Y, Xu WX, Kubo H, Nogawa M, Shioiri H, Kojima M (2003). VP24 found in antho- cyanic vacuolar inclusions (AVIs) of sweet potato cells is a member of a metalloprotease family. Biochem Eng J 14, 199-205. |
| [72] | Nozue M, Kubo H, Nishimura M, Katou A, Hattori C, Usuda N, Nagata T, Yasuda H (1993). Characterization of intravacuolar pigmented structures in anthocyanin- containing cells of sweet potato suspension cultures. Plant Cell Physiol 34, 803-808. |
| [73] |
Nozue M, Yamada K, Nakamura T, Kubo H, Kondo M, Nishimura M (1997). Expression of a vacuolar protein (VP24) in anthocyanin-producing cells of sweet potato in suspension culture. Plant Physiol 115, 1065-1072.
PMID |
| [74] |
Nozzolillo C, Ishikura N (1988). An investigation of the intracellular site of anthocyanoplasts using isolated protoplasts and vacuoles. Plant Cell Rep 7, 389-392.
DOI PMID |
| [75] |
Oakley A (2011). Glutathione transferases: a structural perspective. Drug Metab Rev 43, 138-151.
DOI PMID |
| [76] | Pal L, Dwivedi V, Gupta SK, Saxena S, Pandey A, Chat- topadhyay D (2023). Biochemical analysis of anthocya- nin and proanthocyanidin and their regulation in deter- mining chickpea flower and seed coat colour. J Exp Bot 74, 130-148. |
| [77] |
Passamonti S, Cocolo A, Braidot E, Petrussa E, Peresson C, Medic N, Macri F, Vianello A (2005). Cha- racterization of electrogenic bromosulfophthalein transpo- rt in carnation petal microsomes and its inhibition by anti- bodies against bilitranslocase. FEBS J 272, 3282-3296.
PMID |
| [78] |
Pérez-Díaz R, Madrid-Espinoza J, Salinas-Cornejo J, González-Villanueva E, Ruiz-Lara S (2016). Differential roles for VviGST1, VviGST3, and VviGST4 in proantho- cyanidin and anthocyanin transport in Vitis vinífera. Front Plant Sci 7, 1166.
DOI PMID |
| [79] |
Pérez-Díaz R, Ryngajllo M, Pérez-Díaz J, Peña-Cortés H, Casaretto JA, González-Villa-nueva E, Ruiz-Lara S (2014). VvMATE1 and VvMATE2 encode putative proanthocyanidin transporters expressed during berry development in Vitis vinifera L. Plant Cell Rep 33, 1147-1159.
DOI PMID |
| [80] |
Petrussa E, Braidot E, Zancani M, Peresson C, Bertolini A, Patui S, Vianello A (2013). Plant flavonoids-biosynthesis, transport and involvement in stress responses. Int J Mol Sci 14, 14950-14973.
DOI PMID |
| [81] | Pourcel L, Irani NG, Lu YH, Riedl K, Schwartz S, Grote- wold E (2010). The formation of anthocyanic vacuolar inclusions in Arabidopsis thaliana and implications for the sequestration of anthocyanin pigments. Mol Plant 3, 78-90. |
| [82] | Pucker B, Selmar D (2022). Biochemistry and molecular basis of intracellular flavonoid transport in plants. Plants 11, 963. |
| [83] | Putta S, Yarla NS, Eswar Kumar K, Lakkappa DB, Kamal MA, Scotti L, Scotti MT, Ashraf GM, Rao BSB, Sarala Kumari D, Reddy GV, Tarasov VV, Imandi SB, Aliev G (2018). Preventive and therapeutic potentials of antho- cyanins in diabetes and associated complications. Curr Med Chem 25, 5347-5371. |
| [84] | Qi XL, Liu CL, Song LL, Dong YX, Chen L, Li M (2022). A sweet cherry glutathione S-transferase gene, PavGST1, plays a central role in fruit skin coloration. Cells 11, 1170. |
| [85] | Rea PA (1999). MRP subfamily ABC transporters from plants and yeast. J Exp Bot 50, 895-913. |
| [86] | Sasaki N, Nakayama T (2015). Achievements and perspec- tives in biochemistry concerning anthocyanin modification for blue flower coloration. Plant Cell Physiol 56, 28-40. |
| [87] | Sasaki N, Nishizaki Y, Uchida Y, Wakamatsu E, Umemoto N, Momose M, Okamura M, Yoshida H, Yama- guchi M, Nakayama M, Ozeki Y, Itoh Y (2012). Identifi- cation of the glutathione S-transferase gene responsible for flower color intensity in carnations. Plant Biotechnol 29, 223-227. |
| [88] |
Saslowsky DE, Warek U, Winkel BSJ (2005). Nuclear localization of flavonoid enzymes in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 280, 23735-23740.
DOI PMID |
| [89] | Shao DN, Li YJ, Zhu QH, Zhang XY, Liu F, Xue F, Sun J (2021). GhGSTF12, a glutathione S-transferase gene, is essential for anthocyanin accumulation in cotton (Gos- sypium hirsutum L.). Plant Sci 305, 110827. |
| [90] | Sharma S, Chunduri V, Kumar A, Kumar R, Khare P, Kondepudi KK, Bishnoi M, Garg M (2018). Anthocyanin biofortified colored wheat: nutritional and functional characterization. PLoS One 13, e0194367. |
| [91] |
Small CJ, Pecket RC (1982). The ultrastructure of antho- cyanoplasts in red-cabbage. Planta 154, 97-99.
DOI PMID |
| [92] | Smith AP, Nourizadeh SD, Peer WA, Xu JH, Bandyopadhyay A, Murphy AS, Goldsbrough PB (2003). Arabidopsis AtGSTF2 is regulated by ethylene and auxin, and encodes a glutathione S-transferase that interacts with flavonoids. Plant J 36, 433-442. |
| [93] | Song XW, Wei JB, Di SK, Pang YZ (2019). Recent advances in the regulation mechanism of transcription fa- ctors and metabolic engineering of anthocyanins. Chin Bull Bot 54, 133-156. (in Chinese) |
|
宋雪薇, 魏解冰, 狄少康, 庞永珍 (2019). 花青素转录因子调控机制及代谢工程研究进展. 植物学报 54, 133-156.
DOI |
|
| [94] |
Sun Y, Li H, Huang JR (2012). Arabidopsis TT19 functions as a carrier to transport anthocyanin from the cytosol to tonoplasts. Mol Plant 5, 387-400.
DOI PMID |
| [95] | Sylvia C, Sun JL, Zhang YQ, Ntini C, Ogutu C, Zhao Y, Han YP (2023). Genome-wide analysis of ATP Binding Cassette (ABC) transporters in peach (Prunus persica) and identification of a gene PpABCC1involved in antho- cyanin accumulation. Int J Mol Sci 24, 1931. |
| [96] | Takanashi K, Shitan N, Yazaki K (2014). The multidrug and toxic compound extrusion (MATE) family in plants. Plant Biotechnol 31, 417-430. |
| [97] | Thompson EP, Wilkins C, Demidchik V, Davies JM, Glover BJ (2010). An Arabidopsis flavonoid transporter is required for anther dehiscence and pollen development. J Exp Bot 61, 439-451. |
| [98] |
Verweij W, Spelt C, Di Sansebastiano GP, Vermeer J, Reale L, Ferranti F, Koes R, Quattrocchio F (2008). An H+ P-ATPase on the tonoplast determines vacuolar pH and flower colour. Nat Cell Biol 10, 1456-1462.
DOI PMID |
| [99] | Vilperte V, Boehm R, Debener T (2021). A highly mutable GST is essential for bract colouration in Euphorbia pul- cherrima Willd. Ex Klotsch. BMC Genomics 22, 208. |
| [100] | Wagner U, Edwards R, Dixon DP, Mauch F (2002). Probing the diversity of the Arabidopsis glutathione S-transferase gene family. Plant Mol Biol 49, 515-532. |
| [101] | Wang JY, Zhang H, Tian ST, Hao WH, Chen KL, Du LJ (2022a). The R2R3MYB transcription factors MaMYBF and MaMYB1 regulate flavonoid biosynthesis in grape hyacinth. Plant Physiol Biochem 194, 85-95. |
| [102] | Wang RR, Lu N, Liu CG, Dixon RA, Wu Q, Mao YW, Yang YT, Zheng XL, He LL, Zhao BL, Zhang F, Yang SC, Chen HT, Jun JH, Li Y, Liu CN, Liu Y, Chen JH (2022b). MtGSTF7, a TT19-like GST gene, is essential for accu- mulation of anthocyanins, but not proanthocyanins in Medicago truncatula. J Exp Bot 73, 4129-4146. |
| [103] |
Wang SQ, Pan DZ, Lv XJ, Song XM, Qiu ZM, Huang CM, Huang RH, Chen W (2016). Proteomic approach reveals that starch degradation contributes to anthocyanin accumulation in tuberous root of purple sweet potato. J Proteomics 143, 298-305.
DOI PMID |
| [104] | Wang YC, Liu WJ, Jiang HY, Mao ZL, Wang N, Jiang SH, Xu HF, Yang GX, Zhang ZY, Chen XS (2019). The R2R3-MYB transcription factor MdMYB24-like is involved in methyl jasmonate-induced anthocyanin biosynthesis in apple. Plant Physiol Biochem 139, 273-282. |
| [105] | Wei K, Wang LY, Zhang YZ, Ruan L, Li HL, Wu LY, Xu LY, Zhang CC, Zhou XG, Cheng H, Edwards R (2019). A coupled role for CsMYB75 and CsGSTF1 in anthocyanin hyperaccumulation in purple tea. Plant J 97, 825-840. |
| [106] |
Winkel-Shirley B (2001). Flavonoid biosynthesis. A colorful model for genetics, biochemistry, cell biology, and bio- technology. Plant Physiol 126, 485-493.
DOI PMID |
| [107] |
Wolf AE, Dietz KJ, Schröder P (1996). Degradation of glutathione S-conjugates by a carboxypeptidase in the plant vacuole. FEBS Lett 384, 31-34.
PMID |
| [108] | Wu J, Cheng JH, Yang FC (2006). Transcriptional regula- tion of anthocyanin biosynthesis in plants. Chinese Jour- nal of Cell Biology 28, 453-456. (in Chinese) |
| 吴江, 程建徽, 杨夫臣 (2006). 植物花色素苷生物合成的转录调控. 细胞生物学杂志 28, 453-456. | |
| [109] |
Xiong J, Feng JM, Yuan DX, Zhou J, Miao W (2015). Tracing the structural evolution of eukaryotic ATP binding cassette transporter superfamily. Sci Rep 5, 16724.
DOI PMID |
| [110] | Xu H, Yang PP, Cao YW, Tang YC, He GR, Xu LF, Ming J (2020). Cloning and functional characterization of a fla- vonoid transport-related MATE gene in Asiatic hybrid lilies (Lilium spp.). Genes 11, 418. |
| [111] |
Xu WJ, Dubos C, Lepiniec L (2015). Transcriptional control of flavonoid biosynthesis by MYB-bHLH-WDR complexes. Trends Plant Sci 20, 176-185.
DOI PMID |
| [112] | Xue L, Huang XR, Zhang ZH, Lin QH, Zhong QZ, Zhao Y, Gao ZS, Xu CJ (2022). An anthocyanin-related glu- tathione S-transferase, MrGST1, plays an essential role in fruit coloration in Chinese bayberry (Morella rubra). Front Plant Sci 13, 903333. |
| [113] |
Yamazaki M, Shibata M, Nishiyama Y, Springob K, Kita- yama M, Shimada N, Aoki T, Ayabe SI, Saito K (2008). Differential gene expression profiles of red and green forms of Perilla frutescens leading to comprehensive iden- tification of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes. FEBS J 275, 3494-3502.
DOI PMID |
| [114] | Yang SC, Jiang Y, Xu LQ, Shiratake K, Luo ZR, Zhang QL (2016). Molecular cloning and functional characterization of DkMATE1 involved in proanthocyanidin precursor transport in persimmon (Diospyros kaki Thunb.) fruit. Plant Physiol Biochem 108, 241-250. |
| [115] | Yuan JW, Qiu ZJ, Long Y, Liu YZ, Huang JJ, Liu JX, Yu YX (2023). Functional identification of PhMATE1 in flower color formation in petunia. Physiol Plant 175, e13949. |
| [116] | Zhang HB, Wang L, Deroles S, Bennett R, Davies K (2006a). New insight into the structures and formation of anthocyanic vacuolar inclusions in flower petals. BMC Plant Biol 6, 29. |
| [117] | Zhang TR, Zhang HC, Wu RH (2020). Recent advances on blue flower formation. Chin Bull Bot 55, 216-227. (in Chinese) |
|
张泰然, 张和臣, 武荣花 (2020). 蓝色花形成分子机理研究进展. 植物学报 55, 216-227.
DOI |
|
| [118] | Zhang XY, Wang XL, Wang XF, Xia GH, Pan QH, Fan RC, Wu FQ, Yu XC, Zhang DP (2006b). A shift of phloem unloading from symplasmic to apoplasmic pathway is in- volved in developmental onset of ripening in grape berry. Plant Physiol 142, 220-232. |
| [119] |
Zhang Z, Tian CP, Zhang Y, Li CZY, Li X, Yu Q, Wang S, Wang XY, Chen XS, Feng SQ (2020). Transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis provides insights into antho- cyanin and procyanidin accumulation in pear. BMC Plant Biol 20, 129.
DOI PMID |
| [120] |
Zhao J (2015). Flavonoid transport mechanisms: how to go, and with whom. Trends Plant Sci 20, 576-585.
DOI PMID |
| [121] | Zhao J, Dixon RA (2009). MATE transporters facilitate vacuolar uptake of epicatechin 3'-O-glucoside for proan- thocyanidin biosynthesis in Medicago truncatula and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21, 2323-2340. |
| [122] | Zhao J, Dixon RA (2010). The ‘ins’ and ‘outs’ of flavonoid transport. Trends Plant Sci 15, 72-80. |
| [123] | Zhao J, Huhman D, Shadle G, He XZ, Sumner LW, Tang YH, Dixon RA (2011). MATE2 mediates vacuolar se- questration of flavonoid glycosides and glycoside malo- nates in Medicago truncatula. Plant Cell 23, 1536-1555. |
| [124] |
Zhao Y, Dong WQ, Zhu YC, Allan AC, Kui LW, Xu CJ (2020). PpGST1, an anthocyanin-related glutathione S-transferase gene, is essential for fruit coloration in peach. Plant Biotechnol J 18, 1284-1295.
DOI PMID |
| [125] | Zhu QL, Xie XR, Zhang J, Xiang G, Li Y, Wu HB (2013). In silico analysis of a MRP transporter gene reveals its pos- sible role in anthocyanins or flavonoids transport in Oryza sativa. Am J Plant Sci 4, 555-560. |
| [126] | Zhu ZX, Lu YQ (2016). Plant color mutants and the antho- cyanin pathway. Chin Bull Bot 51, 107-119. (in Chinese) |
|
祝志欣, 鲁迎青 (2016). 花青素代谢途径与植物颜色变异. 植物学报 51, 107-119.
DOI |
| [1] | 王鸿梅, 袁蔚, 薛芳, 张召聪, 刘坤, 陈四龙. 植物SWEET基因参与逆境胁迫响应及其调控机制[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | 李柳, 刘庆华, 尹春英. 植物硒生物强化及微生物在其中的应用潜力[J]. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(6): 756-769. |
| [3] | 黄慧梅, 高永康, 台玉莹, 刘超, 曲德杰, 汤锐恒, 王幼宁. 硝酸盐转运蛋白NRT2在植物中的功能及分子机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 783-798. |
| [4] | 胡海涛, 郭龙彪. 植物核黄素的生物合成及其功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(4): 638-655. |
| [5] | 张嘉, 李启东, 李翠, 王庆海, 侯新村, 赵春桥, 李树和, 郭强. 植物MATE转运蛋白研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 461-474. |
| [6] | 孔照胜, 杨文强, 王柏臣, 林荣呈. 豆科饲草碳氮高效固定、转运和同化利用研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(6): 764-773. |
| [7] | 邹青青, 吴含玉, 刘东焕, 姜闯道. 植物光合作用的三维特性研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(2): 250-258. |
| [8] | 尚江源, 淳雁, 李学勇. 水稻穗长基因PAL3的克隆及自然变异分析[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(5): 520-532. |
| [9] | 石添添, 高英, 王欢, 刘君. 细胞核质转运及其受体在植物抗病防御反应中的调控作用[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(4): 480-487. |
| [10] | 李晶,郭亮,崔海信,崔博,刘国强. 纳米农药在植物中的吸收转运研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(4): 513-528. |
| [11] | 崔亚宁, 钱虹萍, 赵艳霞, 李晓娟. 模式识别受体的胞内转运及其在植物免疫中的作用[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(3): 329-339. |
| [12] | 贺祯媚,李东明,齐艳华. 植物ABCB亚家族生物学功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(6): 688-698. |
| [13] | 陈唯,曾晓贤,谢楚萍,田长恩,周玉萍. 植物内源ABA水平的动态调控机制[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(6): 677-687. |
| [14] | 王惠,李谨谨,徐金玉,刘鹏,张海燕. 拟南芥COPT家族蛋白研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(6): 786-796. |
| [15] | 陈颖, 王婷, 华学军. 脯氨酸转运相关基因的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(6): 754-763. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||