

植物学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (2): 183-190.DOI: 10.11983/CBB20177 cstr: 32102.14.CBB20177
赵菲1, 党刘毅2, 魏敏惠1, 刘春莹1, 冷伟1,*( ), 尚琛晶1,3,*(
), 尚琛晶1,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-11-01
接受日期:2021-03-01
出版日期:2021-03-01
发布日期:2021-03-17
通讯作者:
冷伟,尚琛晶
作者简介:cjshang@szu.edu.cn基金资助:
Fei Zhao1, Liuyi Dang2, Minhui Wei1, Chunying Liu1, Wei Leng1,*( ), Chenjing Shang1,3,*(
), Chenjing Shang1,3,*( )
)
Received:2020-11-01
Accepted:2021-03-01
Online:2021-03-01
Published:2021-03-17
Contact:
Wei Leng,Chenjing Shang
摘要: 凝集素是一类具有特异性糖结合活性的蛋白质, 通常具有1个或多个非催化的糖结合结构域。凝集素在植物对病原菌的防御反应中发挥重要作用。由于其抗细菌、真菌、病毒和昆虫等的活性, 凝集素在农业和生物医药领域都具有很大的应用潜力。作为最小的凝集素家族之一, 苋科凝集素的研究较少。该文通过对重要经济作物黄瓜(Cucumis sativus)的基因组进行分析, 对16种苋科凝集素基因在黄瓜基因组中的分布和位置进行研究, 并分析相关基因的外显子/内含子组成。进一步通过启动子分析, 阐明了苋科凝集素基因对非生物胁迫的响应情况。最后, 通过实时荧光定量PCR, 检测了黄瓜中4种苋科凝集素基因对低温、高盐、干旱和ABA处理的响应情况。研究结果可为揭示苋科凝集素的生理功能及其在植物胁迫响应中的作用提供参考。
赵菲, 党刘毅, 魏敏惠, 刘春莹, 冷伟, 尚琛晶. 黄瓜苋科凝集素基因的表达分析与逆境调控. 植物学报, 2021, 56(2): 183-190.
Fei Zhao, Liuyi Dang, Minhui Wei, Chunying Liu, Wei Leng, Chenjing Shang. Expression of Amaranthin-like Lectins Gene and Responses to Abiotic Stresses in Cucumber. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(2): 183-190.
| Primer name | Forward primer (5'-3') | Reverse primer (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| CACS | TGGGAAGATTCTTA- TGAAGTGC | CTCGTCAAATTT- ACACATTGGT |
| PP2A | CAACAGGTGATATT- GGATTATGAT | GCCAGCTCATCC- TCATATAAG |
| AAT4 | TTCGTACACGCAAC- GAGA | TGAAGAGGGTAA- GGCTTG |
| NAAT1 | GAGGAGCTGTGAAA- GGAGCA | CCCTCCACGACA- GTTCCAAT |
| AAT9 | CAGAAACAGCGAAC- CAGAGC | AACTTCATCCCCA- CCGAGTT |
| AAT14 | GGGAATAGAGACGA- TCCGAACT | GCGCAGAAGGCA- GTGTTT |
表1 实时荧光定量PCR引物列表
Table 1 Primer list for qRT-PCR
| Primer name | Forward primer (5'-3') | Reverse primer (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| CACS | TGGGAAGATTCTTA- TGAAGTGC | CTCGTCAAATTT- ACACATTGGT |
| PP2A | CAACAGGTGATATT- GGATTATGAT | GCCAGCTCATCC- TCATATAAG |
| AAT4 | TTCGTACACGCAAC- GAGA | TGAAGAGGGTAA- GGCTTG |
| NAAT1 | GAGGAGCTGTGAAA- GGAGCA | CCCTCCACGACA- GTTCCAAT |
| AAT9 | CAGAAACAGCGAAC- CAGAGC | AACTTCATCCCCA- CCGAGTT |
| AAT14 | GGGAATAGAGACGA- TCCGAACT | GCGCAGAAGGCA- GTGTTT |
| Gene | Start position | End position | Orientation | Gene | Start position | End position | Orientation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CucsaAAT1 | 5496646 | 5495195 | Reverse | CucsaAAT9 | 5654159 | 5656355 | Forward |
| CucsaAAT2 | 5583941 | 5582553 | Reverse | CucsaAAT10 | 5681664 | 5683484 | Forward |
| CucsaAAT3 | 5590531 | 5589140 | Reverse | CucsaAAT11 | 5691672 | 5690257 | Reverse |
| CucsaAAT4 | 5596447 | 5595167 | Reverse | CucsaAAT12 | 7077986 | 7075008 | Reverse |
| CucsaAAT5 | 5605793 | 5607184 | Forward | CucsaAAT13 | 7083801 | 7085207 | Forward |
| CucsaAAT6 | 5619299 | 5621364 | Forward | CucsaAAT14 | 7090825 | 7094963 | Forward |
| CucsaAAT7 | 5630016 | 5631894 | Forward | CucsaNAAT1 | 5648115 | 5646235 | Reverse |
| CucsaAAT8 | 5636899 | 5638943 | Forward | CucsaNAAT2 | 5670107 | 5668263 | Reverse |
表2 黄瓜中苋科凝集素基因及其在6号染色体上的位置
Table 2 Amaranthin-like genes in cucumber and their locations on chromosome 6
| Gene | Start position | End position | Orientation | Gene | Start position | End position | Orientation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CucsaAAT1 | 5496646 | 5495195 | Reverse | CucsaAAT9 | 5654159 | 5656355 | Forward |
| CucsaAAT2 | 5583941 | 5582553 | Reverse | CucsaAAT10 | 5681664 | 5683484 | Forward |
| CucsaAAT3 | 5590531 | 5589140 | Reverse | CucsaAAT11 | 5691672 | 5690257 | Reverse |
| CucsaAAT4 | 5596447 | 5595167 | Reverse | CucsaAAT12 | 7077986 | 7075008 | Reverse |
| CucsaAAT5 | 5605793 | 5607184 | Forward | CucsaAAT13 | 7083801 | 7085207 | Forward |
| CucsaAAT6 | 5619299 | 5621364 | Forward | CucsaAAT14 | 7090825 | 7094963 | Forward |
| CucsaAAT7 | 5630016 | 5631894 | Forward | CucsaNAAT1 | 5648115 | 5646235 | Reverse |
| CucsaAAT8 | 5636899 | 5638943 | Forward | CucsaNAAT2 | 5670107 | 5668263 | Reverse |
| Protein | Domain architecture | No. of amino acids | Protein size (kDa) | Theoretical pI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CucsaAAT1 | AAT | 484 | 54.9 | 8.3 |
| CucsaAAT2 | AAT | 463 | 53.6 | 7.9 |
| CucsaAAT3 | AAT | 463 | 53.5 | 8.0 |
| CucsaAAT4 | AAT | 466 | 53.7 | 8.2 |
| CucsaAAT5 | AAT | 463 | 53.3 | 7.5 |
| CucsaAAT6 | AAT | 464 | 53.4 | 7.5 |
| CucsaAAT7 | AAT | 471 | 53.5 | 5.1 |
| CucsaAAT8 | AAT | 475 | 54.7 | 8.3 |
| CucsaAAT9 | AAT | 474 | 55.0 | 6.7 |
| CucsaAAT10 | AAT | 476 | 54.9 | 5.7 |
| CucsaAAT11 | AAT | 482 | 55.4 | 7.0 |
| CucsaAAT12 | AAT | 502 | 57.6 | 9.0 |
| CucsaAAT13 | AAT | 468 | 53.9 | 7.7 |
| CucsaAAT14 | AAT | 505 | 58.2 | 6.8 |
| CucsaNAAT1 | NAAT | 626 | 70.4 | 5.1 |
| CucsaNAAT2 | NAAT | 614 | 69.4 | 4.9 |
表3 黄瓜中苋科凝集素蛋白的理化性质
Table 3 Physiochemical properties of amaranthin-like proteins in cucumber
| Protein | Domain architecture | No. of amino acids | Protein size (kDa) | Theoretical pI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CucsaAAT1 | AAT | 484 | 54.9 | 8.3 |
| CucsaAAT2 | AAT | 463 | 53.6 | 7.9 |
| CucsaAAT3 | AAT | 463 | 53.5 | 8.0 |
| CucsaAAT4 | AAT | 466 | 53.7 | 8.2 |
| CucsaAAT5 | AAT | 463 | 53.3 | 7.5 |
| CucsaAAT6 | AAT | 464 | 53.4 | 7.5 |
| CucsaAAT7 | AAT | 471 | 53.5 | 5.1 |
| CucsaAAT8 | AAT | 475 | 54.7 | 8.3 |
| CucsaAAT9 | AAT | 474 | 55.0 | 6.7 |
| CucsaAAT10 | AAT | 476 | 54.9 | 5.7 |
| CucsaAAT11 | AAT | 482 | 55.4 | 7.0 |
| CucsaAAT12 | AAT | 502 | 57.6 | 9.0 |
| CucsaAAT13 | AAT | 468 | 53.9 | 7.7 |
| CucsaAAT14 | AAT | 505 | 58.2 | 6.8 |
| CucsaNAAT1 | NAAT | 626 | 70.4 | 5.1 |
| CucsaNAAT2 | NAAT | 614 | 69.4 | 4.9 |
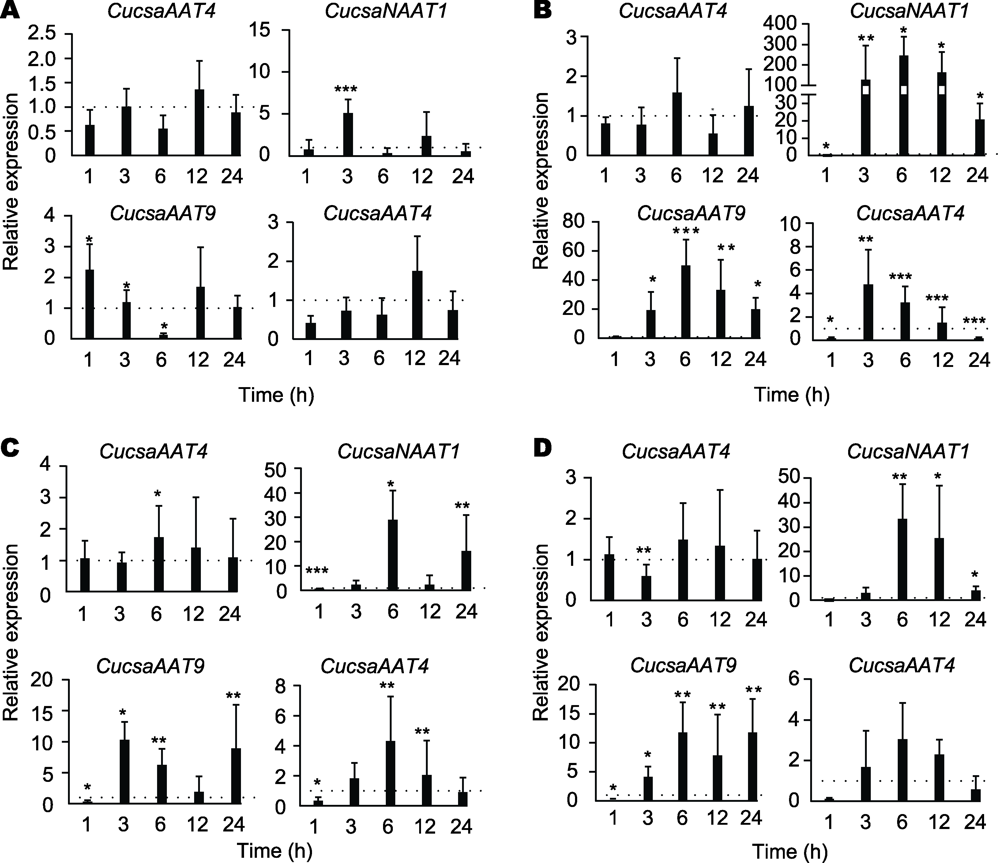
图4 不同胁迫处理后黄瓜苋科凝集素基因的表达水平 (A)低温处理; (B)高盐处理;(C)干旱处理; (D)脱落酸处理。柱状图代表了2次生物学重复的平均值和标准偏差, 每个重复中包含实验组与对照组各4株植物; 星号表示处理组与对照组之间的统计学显著性(* P<0.05, ** P<0.01, ***P<0.001)。
Figure 4 Relative expression levels for amaranthin-like genes in cucumber plants subjected to different abiotic stress conditions (A)Cold treatment; (B) Salt treatment; (C) Drought treatment;(D) ABA treatment. Bars represent means and standard errors from two independent biological replicates, each replicate containing a pool of 4 plants for stress-treated groups as well as control groups. Asterisks indicate statistically signi?cant differences compared to the plants with mock treatments (* P<0.05,** P<0.01, ***P<0.001).
| [1] | 王梦龙, 彭小群, 陈竹锋, 唐晓艳 (2020). 植物凝集素类受体蛋白激酶研究进展. 植物学报 55,96-105. |
| [2] | 王志斌, 张秀梅, 郭三堆 (2000). 在转基因植物中利用植物凝集素防治害虫的研究. 植物学通报 17,108-113. |
| [3] | 曾日中, 黎瑜 (1998). 橡胶蛋白—一种与胶乳凝固有关的具有抗真菌活性的植物凝集素. 植物学通报 15(增刊),24-28. |
| [4] | Al Atalah B, Fouquaert E, Van Damme EJM (2013). Promoter analysis for three types of EUL-related rice lectins in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol Rep 31, 1315- 1324. |
| [5] | Chen SC, Jin WJ, Liu AR, Zhang SJ, Liu DL, Wang FH, Lin XM, He CX (2013). Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) increase growth and secondary metabolism in cucumber subjected to low temperature stress. Sci Hortic 160,222-229. |
| [6] | Dang LY, Rougé P, Van Damme EJM (2017). Amaranthin-like proteins with aerolysin domains in plants. Front Plant Sci 8,1368. |
| [7] | Dang LY, Van Damme EJM (2016). Genome-wide identification and domain organization of lectin domains in cucumber. Plant Physiol Biochem 108,165-176. |
| [8] | Faruque K, Begam R, Deyholos MK (2015). The amaranthin-like lectin (LuALL) genes of flax: a unique gene family with members inducible by defence hormones. Plant Mol Biol Rep 33,731-741. |
| [9] | Ghazarian H, Idoni B, Oppenheimer SB (2011). A glycobiology review: carbohydrates, lectins and implications in cancer therapeutics. Acta Histochem 113,236-247. |
| [10] | Higo K, Ugawa Y, Iwamoto M, Korenaga T (1999). Plant cis-acting regulatory DNA elements (PLACE) database: 1999. Nucleic Acids Res 27,297-300. |
| [11] | Huang SW, Li RQ, Zhang ZH, Li L, Gu XF, Fan W, Lucas WJ, Wang XW, Xie BY, Ni PX, Ren YY, Zhu HM, Li J, Lin K, Jin WW, Fei ZJ, Li GC, Staub J, Kilian A, van der Vossen EAG, Wu Y, Guo J, He J, Jia ZQ, Ren Y, Tian G, Lu Y, Ruan J, Qian WB, Wang MW, Huang QF, Li B, Xuan ZL, Cao JJ, Asan, Wu ZG, Zhang JB, Cai QL, Bai YQ, Zhao BW, Han YH, Li Y, Li XF, Wang SH, Shi QX, Liu SQ, Cho WK, Kim JY, Xu Y, Heller-Uszynska K, Miao H, Cheng ZC, Zhang SP, Wu J, Yang YH, Kang HX, Li M, Liang HQ, Ren XL, Shi ZB, Wen M, Jian M, Yang HL, Zhang GJ, Yang ZT, Chen R, Liu SF, Li JW, Ma LJ, Liu H, Zhou Y, Zhao J, Fang XD, Li GQ, Fang L, Li YR, Liu DY, Zheng HK, Zhang Y, Qin N, Li Z, Yang GH, Yang S, Bolund L, Kristiansen K, Zheng HC, Li SC, Zhang XQ, Yang HM, Wang J, Sun RF, Zhang BX, Jiang SZ, Wang J, Du YC, Li SG (2009). The genome of the cucumber, Cucumis sativus L. Nat Genet 41, 1275- 1281. |
| [12] | Li YM, Li SH, He XR, Jiang WL, Zhang DL, Liu BB, Li QM (2020). CO2 enrichment enhanced drought resistance by regulating growth, hydraulic conductivity and phytohormone contents in the root of cucumber seedlings. Plant Physiol Biochem 152,62-71. |
| [13] | Migocka M, Papierniak A (2011). Identification of suitable reference genes for studying gene expression in cucumber plants subjected to abiotic stress and growth regulators. Mol Breed 28,343-357. |
| [14] | Pfaffl MW, Horgan GW, Dempfle L (2002). Relative expression software tool (REST) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 30,e36. |
| [15] | Shang CJ, Dang LY, Van Damme EJM (2017). Plant AB toxins with lectin domains. In: Gopalakrishnakone P, Carlini RC, Ligabue-Braun R, eds. Plant Toxins. Dordrecht: Springer. pp.1-14. |
| [16] | Szczesny P, Iacovache I, Muszewska A, Ginalski K, van der Goot FG, Grynberg M (2011). Extending the aerolysin family: from bacteria to vertebrates. PLoS One 6,e20349. |
| [17] | Tsaneva M, Van Damme EJM (2020). 130 years of plant lectin research. Glycoconj J 37,533-551. |
| [18] | Tuteja N (2007). Abscisic acid and abiotic stress signaling. Plant Signal Behav 2,135-138. |
| [19] | Van Holle S, Van Damme EJM (2019). Messages from the past: new insights in plant lectin evolution. Front Plant Sci 10,36. |
| [20] | Wang J, Pan CT, Wang Y, Ye L, Wu J, Chen LF, Zou T, Lu G (2015). Genome-wide identification of MAPK, MAPKK, and MAPKKK gene families and transcriptional profiling analysis during development and stress response in cucumber. BMC Genomics 16,386. |
| [21] | Yan SS, Che G, Ding L, Chen ZJ, Liu XF, Wang HY, Zhao WS, Ning K, Zhao JY, Tesfamichael K, Wang Q, Zhang XL (2016). Different cucumber CsYUC genes regulate response to abiotic stresses and flower development. Sci Rep 6,20760. |
| [22] | Zhu YX, Jia JH, Yang L, Xia YC, Zhang HL, Jia JB, Zhou R, Nie PY, Yin JL, Ma DF, Liu LC (2019). Identification of cucumber circular RNAs responsive to salt stress. BMC Plant Biol 19,164. |
| [1] | 熊良林, 梁国鲁, 郭启高, 景丹龙. 基因可变剪接调控植物响应非生物胁迫研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 435-448. |
| [2] | 杜庆国, 李文学. lncRNA调控玉米生长发育和非生物胁迫研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 950-962. |
| [3] | 宋想, 王璐瑶, 富博晓, 李双达, 魏媛媛, 洪艳, 戴思兰. 高等植物启动子元件鉴定与合成研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 691-708. |
| [4] | 周文杰, 张文瀚, 贾玮, 许自成, 黄五星. 植物miRNA响应非生物胁迫研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 810-833. |
| [5] | 仲昭暄, 张冬瑞, 李璐, 苏颖, 王黛宁, 王泽冉, 刘洋, 常缨. 香鳞毛蕨dfr-miR160a和靶基因DfARF10的生物信息学及表达模式分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 22-33. |
| [6] | 张悦婧, 桑鹤天, 王涵琦, 石珍珍, 李丽, 王馨, 孙坤, 张继, 冯汉青. 植物对非生物胁迫系统性反应中信号传递的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 122-133. |
| [7] | 许亚楠, 闫家榕, 孙鑫, 王晓梅, 刘玉凤, 孙周平, 齐明芳, 李天来, 王峰. 红光和远红光在调控植物生长发育及应答非生物胁迫中的作用[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(4): 622-637. |
| [8] | 张嘉, 李启东, 李翠, 王庆海, 侯新村, 赵春桥, 李树和, 郭强. 植物MATE转运蛋白研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 461-474. |
| [9] | 任晓童, 张冉冉, 魏绍巍, 罗晓峰, 徐佳慧, 舒凯. 种子际微生物研究展望[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 499-509. |
| [10] | 吴霖升, 张永光, 章钊颖, 张小康, 吴云飞. 日光诱导叶绿素荧光遥感及其在陆地生态系统监测中的应用[J]. 植物生态学报, 2022, 46(10): 1167-1199. |
| [11] | 谢玲玲, 王金龙, 伍国强. 植物CBL-CIPK信号系统响应非生物胁迫的调控机制[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(5): 614-626. |
| [12] | 肖银燕, 袁伟娜, 刘静, 孟建, 盛奇明, 谭烨欢, 徐春香. 木葡聚糖及其在植物抗逆过程中的功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(6): 777-787. |
| [13] | 洪林,杨蕾,杨海健,王武. AP2/ERF转录因子调控植物非生物胁迫响应研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(4): 481-496. |
| [14] | 凡惠金, 金康鸣, 卓仁英, 乔桂荣. 毛竹不同截短U3启动子的克隆及表达分析[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(3): 299-307. |
| [15] | 王梦龙,彭小群,陈竹锋,唐晓艳. 植物凝集素类受体蛋白激酶研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(1): 96-105. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||