

植物学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (1): 46-57.DOI: 10.11983/CBB18045 cstr: 32102.14.CBB18045
收稿日期:2018-02-12
接受日期:2018-05-21
出版日期:2019-01-01
发布日期:2019-07-31
通讯作者:
徐凡
基金资助:
Shengnan Cui1,2,Yihan Zhang1,Fan Xu1,*( )
)
Received:2018-02-12
Accepted:2018-05-21
Online:2019-01-01
Published:2019-07-31
Contact:
Fan Xu
摘要: 蛋白磷酸酶催化的蛋白质可逆磷酸化反应是叶片衰老的关键环节。该研究筛选并克隆了1个新的参与水稻(Oryza sativa)叶片衰老调控的PP2C基因OsSAPP3。研究表明, OsSAPP3的启动子在ProOsSAPP3-GUS转基因拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)的莲座叶中有活性, 并且活性以依赖叶龄方式增加。利用CaMV 35S启动子驱动组成型异源过表达OsSAPP3导致转基因拟南芥无法正常生长。用可诱导型启动子GVG系统驱动OsSAPP3异源过表达导致转基因拟南芥出现莲座叶变小、数量增加、叶片早衰及抽薹开花提前等早衰表型。外源诱导OsSAPP3基因异源过表达后, 利用实时荧光定量PCR检测到SAG12、WRKY6和NAC2等衰老标志基因显著上调表达。研究结果表明, OsSAPP3是参与水稻叶片衰老的正向调控因子。
崔胜男,张艺函,徐凡. 异源过表达水稻OsSAPP3基因促进拟南芥叶片衰老. 植物学报, 2019, 54(1): 46-57.
Shengnan Cui,Yihan Zhang,Fan Xu. Heterologous Overexpression of Rice OsSAPP3 Gene Promotes Leaf Senescence in Transgenic Arabidopsis. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(1): 46-57.
| Primer name | Primer sequence (5'-3') | Annotation |
|---|---|---|
| CDSOsSAPP3-F | CCCGGGATGCTATCTGCTGCGATGGAATACTT | PCR |
| CDSOsSAPP3-R | GAACTCTATGTAGGAACTGAGAATGGAGCAAGG | PCR |
| cGVG-SAPP3-F | GTCGACATGCTATCTGCTGCGATGGAATAC | PCR |
| cGVG-SAPP3-R | ATCGATCTATGTAGGAACTGAGAATGGAGCAA | PCR |
| ProOsSAPP3-F | AAGCTTTCATATCCGTTGTTCCGTAGCG | PCR |
| ProOsSAPP3-R | TCTAGACCTTCATCTCCGACACCTCCC | PCR |
表1 引物序列
Table 1 Sequences of primers
| Primer name | Primer sequence (5'-3') | Annotation |
|---|---|---|
| CDSOsSAPP3-F | CCCGGGATGCTATCTGCTGCGATGGAATACTT | PCR |
| CDSOsSAPP3-R | GAACTCTATGTAGGAACTGAGAATGGAGCAAGG | PCR |
| cGVG-SAPP3-F | GTCGACATGCTATCTGCTGCGATGGAATAC | PCR |
| cGVG-SAPP3-R | ATCGATCTATGTAGGAACTGAGAATGGAGCAA | PCR |
| ProOsSAPP3-F | AAGCTTTCATATCCGTTGTTCCGTAGCG | PCR |
| ProOsSAPP3-R | TCTAGACCTTCATCTCCGACACCTCCC | PCR |
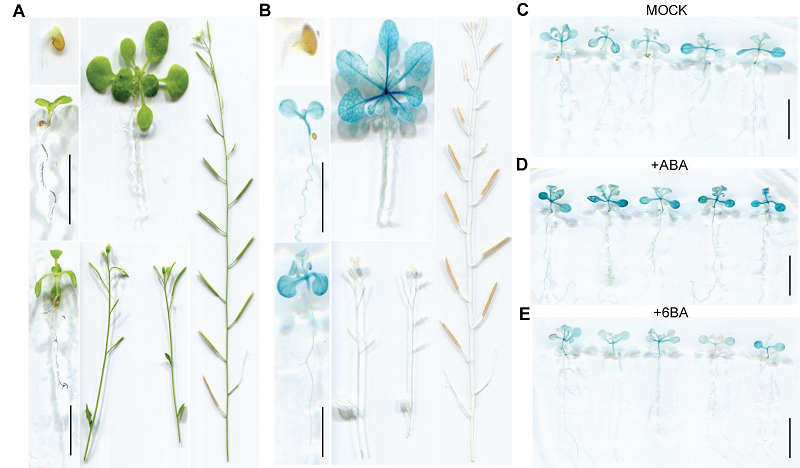
图1 ProOsSAPP3-GUS转基因拟南芥不同发育时期GUS组织化学染色 (A) 染色前的转基因拟南芥, 从上到下, 从左到右, 依次为Stage 0.5、Stage 1.02、Stage 1.04、Stage 1.10、Stage 6.0、Stage 6.9; (B) 染色后的转基因拟南芥, 从上到下, 从左到右苗龄同染色前; (C) 经MOCK溶液(激素溶剂)处理的转基因拟南芥; (D) 经10 μmol?L-1 ABA溶液处理的转基因拟南芥; (E) 经10 μmol?L-1 6-BA溶液处理的转基因拟南芥。Bars=5 mm
Figure 1 GUS histochemical staining of ProOsSAPP3-GUS transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana at different developmental stages (A) From top to bottom, from left to right, the transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana before stain: Stage 0.5, Stage 1.02, Stage 1.04, Stage 1.10, Stage 6.0, Stage 6.9; (B) From top to bottom, from left to right, the transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana was stained in turn, and the seedling age was identical to that before staining; (C) Transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana treated with MOCK solution (hormone solvent); (D) Transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana treated with 10 μmol?L-1 ABA solution; (E) Transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana treated with 10 μmol?L-1 6-BA solution. Bars=5 mm

图2 组成型异源过表达OsSAPP3基因导致转基因拟南芥生长发育异常 (A) 35S-OsSAPP3转基因与野生型拟南芥的基因表达水平; (B) WT为野生型拟南芥植株; 35S-OsSAPP3为35S-OsSAPP3转基因拟南芥株系; 图左上为营养土中生长14天的幼苗, 图左下为营养土中生长21天的植株, 图右为营养土中培养75天的植株。图中数据为平均值±标准差, n=10, 实验经3次生物学重复。** P<0.01。Bars=1 cm
Figure 2 Heterologous expression of OsSAPP3 gene lead to abnormal growth and development of transgenic Arabidopsis (A) 35S-OsSAPP3 transgenic Arabidopsis and wild-type Arabidopsis gene expression levels; (B) Wild-type Arabidopsis plant (WT) and 35S-OsSAPP3 transgenic Arabidopsis line (35S-OsSAPP3). The top left panel was the 14-day-old seedling growing in the nutrient soil, the bottom left is the 21-day-old plant growing in the nutrient soil, and the right panel was the plants cultured in nutrient soil for 25 days. Values are means±SD of one representative biological replicate (n=10) out of three, ** P<0.01. Bars=1 cm
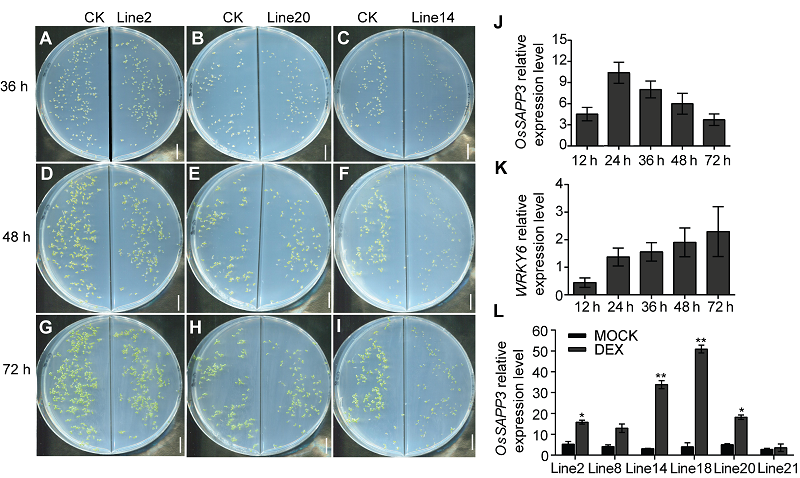
图3 外源诱导OsSAPP3异源过表达导致转基因拟南芥无法正常萌发 (A)-(C) DEX诱导36小时, 各转基因种子与对照种子萌发情况; (D)-(F) DEX诱导48小时, 各转基因种子与对照种子萌发情况; (G)-(I) DEX诱导72小时, 各转基因种子与对照种子萌发情况; (J) 外源诱导不同时长, OsSAPP3基因的表达变化情况; (K) 外源诱导不同时长, WRKY6基因的表达变化情况; (L) GVG-OsSAPP3转基因拟南芥纯合株系的基因表达水平。数据为平均值±标准差, n=10, 实验经3次生物学重复。* P<0.05, ** P<0.01。Bars=1 cm
Figure 3 Exogenously induced OsSAPP3 heterologous over expression resulted in the inability of germination of transgenic Arabidopsis (A)-(C) DEX induced 36 h, the germination of transgenic and control seeds; (D)-(F) DEX induced 48 h, the germination of transgenic and control seeds; (G)-(I) DEX induced 72 h, the germination of transgenic and control seeds; (J) The expression of OsSAPP3 induced by exogenous factors at different times; (K) Exogenous induction of WRKY6 expression changes at different times; (L) Gene expression levels of GVG-OsSAPP3 transgenic Arabidopsis homozygous lines. Values are means±SD of one representative biological replicate (n=10) out of three. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01. Bars=1 cm
| Number of rosette leavesa | 5% significant level | 1% very significant level | Rosette leaf sizeb | 5% significant level | 1% very significant level | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 9.4 | c | A | 2.84 | d | C |
| Line2 | 10.2 | bc | A | 2.3 | ab | BC |
| Line20 | 11.8 | abc | A | 1.9 | bc | AB |
| Line14 | 12.6 | ab | A | 1.5 | cd | A |
Table 2 Phenotypic data of Arabidopsis GVG-OsSAPP3 transgenic lines and control (CK)
| Number of rosette leavesa | 5% significant level | 1% very significant level | Rosette leaf sizeb | 5% significant level | 1% very significant level | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 9.4 | c | A | 2.84 | d | C |
| Line2 | 10.2 | bc | A | 2.3 | ab | BC |
| Line20 | 11.8 | abc | A | 1.9 | bc | AB |
| Line14 | 12.6 | ab | A | 1.5 | cd | A |
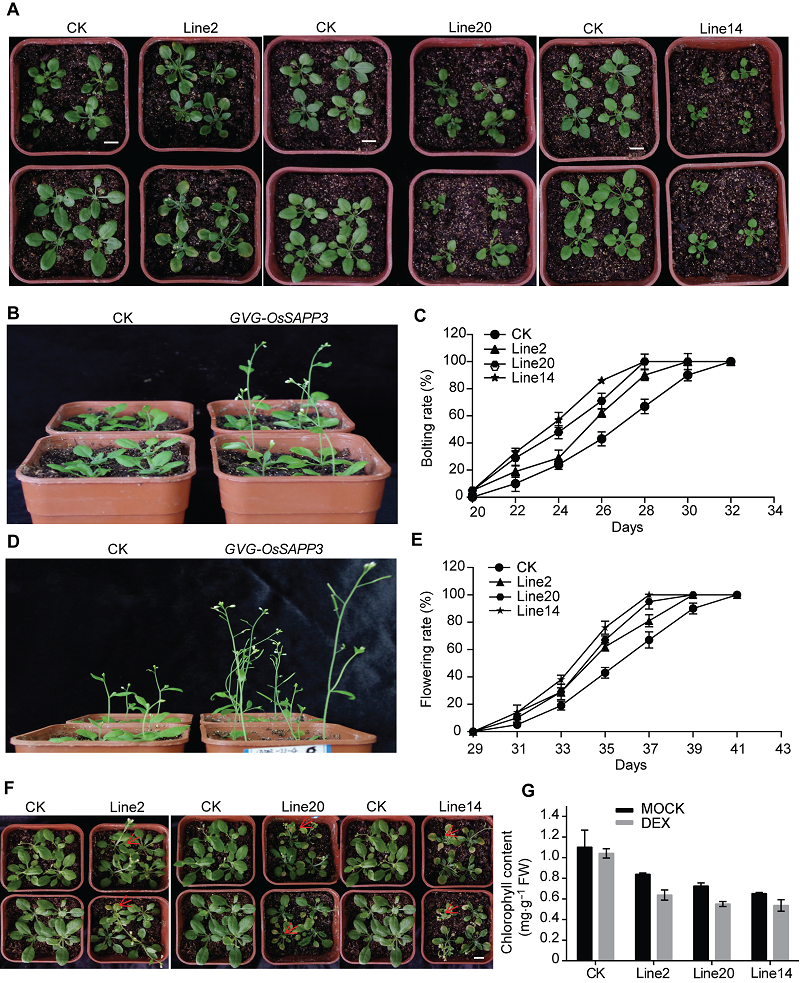
图4 外源诱导OsSAPP3基因异源过表达促进转基因拟南芥成熟苗提前衰老 (A) 喷施处理5天后的转化对照(CK)和GVG-OsSAPP3转基因拟南芥; (B) 苗龄24天的CK和GVG-OsSAPP3转基因拟南芥的代表植株; (C) CK和GVG-OsSAPP3转基因拟南芥的抽薹进程; (D) 苗龄34天的CK和GVG-OsSAPP3转基因拟南芥植株; (E) CK和GVG-OsSAPP3转基因拟南芥的开花进程; (F) 喷施处理后21天的CK和GVG-OsSAPP3转基因拟南芥; (G) 苗龄26天的CK和GVG-OsSAPP3转基因拟南芥第4、5和6片叶的叶绿素含量。数据为平均值±标准差, n=10, 实验经3次生物学重复。Bars=1 cm
Figure 4 Exogenous-induced OsSAPP3 heterologous over expression promotes premature aging of transgenic Arabidopsis mature seedlings (A) Arabidopsis control (CK) and GVG-OsSAPP3 transgenic Arabidopsis after spray treatment for 5 days; (B) 24-day-old CK and GVG-OsSAPP3 transgenic Arabidopsis plants; (C) The CK and GVG-OsSAPP3 transgenic Arabidopsis bolting process; (D) 34-day-old CK and GVG-OsSAPP3 transgenic Arabidopsis plants; (E) The CK and GVG-OsSAPP3 transgenic Arabidopsis flowering process; (F) CK and GVG-OsSAPP3 transgenic Arabidopsis after spray treatment for 21 days; (G) The chlorophyll contents of the fourth, fifth and sixth leaf of 26-day-old CK and GVG-OsSAPP3 transgenic Arabidopsis. Values are means±SD of one representative biological replicate (n=10) out of three. Bars=1 cm
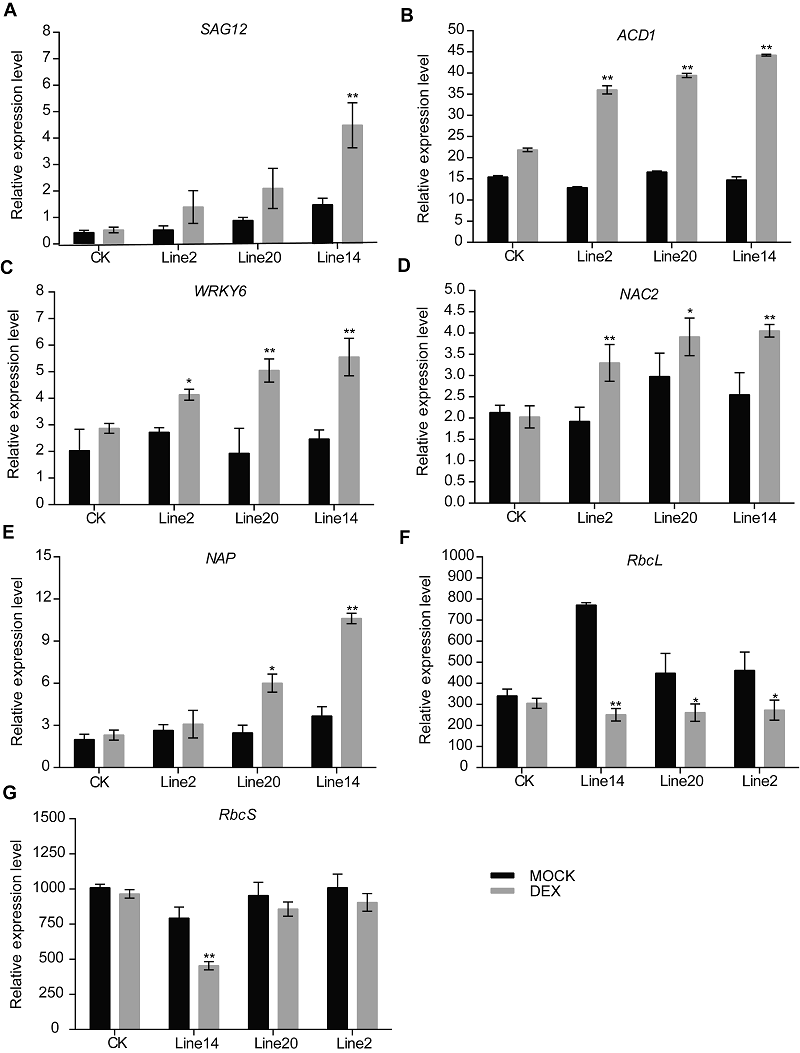
图5 30 μmol?L-1 DEX与MOCK溶液处理24小时后, 转化对照(CK)和GVG-OsSAPP3转基因拟南芥第5和6片叶的衰老标志基因表达变化
Figure 5 Changes of senescence marker gene expression in the fifth and sixth leaves of control (CK) and GVG-OsSAPP3 transgenic Arabidopsis after 30 μmol?L-1 DEX and MOCK solution treatment for 24 hoursValues are means±SD of one representative biological replicate (n=10) out of three. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01.
| 1 | 李合生 (2000). 植物生理生化实验原理和技术. 北京: 高等教育出版社. pp. 134-137. |
| 2 |
牟少亮, 李秀娟, 官德义, 赖燕, 何水林 ( 2011). 水稻蛋白磷酸酶ABI2基因启动子的克隆和功能分析. 热带作物学报 32, 2293-2297.
DOI URL |
| 3 | 孙高阳, 吴向远, 叶琳琳, 孟淑君, 阎鹏帅, 汤继华, 郭战勇 ( 2017). 玉米衰老相关基因在2个杂交种及其亲本中的表达分析. 河南农业大学学报 2, 140-148. |
| 4 |
翁华, 冉亮, 魏群 ( 2003). 植物蛋白磷酸酶及其在植物抗逆中的作用. 植物学报 20, 609-615.
DOI URL |
| 5 | 肖冬, 崔燕娇, 王宁宁 ( 2014). 叶片衰老过程中的蛋白激酶和蛋白磷酸酶. 植物生理学报 50, 1267-1273. |
| 6 | 徐凡 ( 2012). GmSARK和AtSARK基因调控叶片衰老分子机制的研究. 博士论文. 天津: 南开大学. pp. 1-12. |
| 7 |
徐凡, 李鹏丽, 安宝燕, 苑玲玲, 孟涛, 岳慧琴, 王宁宁 ( 2010). 大豆诱导型启动子驱动类受体蛋白激酶GmSARK转基因植物分析. 植物学报 45, 149-156.
DOI URL |
| 8 |
徐娜, 徐江民, 蒋玲欢, 饶玉春 ( 2017). 水稻叶片早衰成因及分子机理研究进展. 植物学报 52, 102-112.
DOI URL |
| 9 |
杨同文, 李成伟 ( 2014). 植物叶片衰老的表观遗传调控. 植物学报 49, 729-737.
DOI URL |
| 10 |
郑建敏, 张涛, 郑家奎 ( 2009). 水稻叶片衰老相关基因的研究进展. 基因组学与应用生物学 28, 1010-1019.
DOI URL |
| 11 |
Aoyama T, Chua NH ( 1997). A glucocorticoid-mediated transcriptional induction system in transgenic plants. Plant J 11, 605-612.
DOI URL PMID |
| 12 |
Bhatnagar N, Min MK, Choi EH, Kim N, Moon SJ, Yoon I, Kwon T, Junq KH, Kim BG ( 2017). The protein phosphatase 2C clade a protein OsPP2C51 positively regulates seed germination by directly inactivating OsbZIP10.Plant Mol Biol 93, 389-401.
DOI URL PMID |
| 13 |
Boyes DC, Zayed AM, Ascenzi R, McCaskill AJ, Hoffman NE, Davis KR, Görlach J ( 2001). Growth stage-based phenotypic analysis of Arabidopsis: a model for high throughput functional genomics in plants. Plant Cell 13, 1499-1510.
DOI URL PMID |
| 14 |
Buchanan-Wollaston V, Page T, Harrison E, Breeze E, Lim PO, Nam HG, Lin JF, Wu SH, Swidzinski J, Ishizaki K, Leaver CJ ( 2005). Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals significant differences in gene expression and signaling pathways between developmental and dark/ starvation-induced senescence in Arabidopsis. Plant J 42, 567-585.
DOI URL PMID |
| 15 |
Castro PH, Lilay GH, Muñoz-Mérida A, Schjoerring JK, Azevedo H, Assunção AGL ( 2017). Phylogenetic analysis of F-bZIP transcription factors indicates conservation of the zinc deficiency response across land plants. Sci Rep 7, 3806.
DOI URL PMID |
| 16 |
Chen C, Yu Y, Ding XD, Liu BD, Duanmu H, Zhu D, Sun XL, Cao L, Zaib-Un-Nisa, Li Q, Zhu YM ( 2018). Genome-wide analysis and expression profiling of PP2C clade D under saline and alkali stresses in wild soybean and Arabidopsis. Protoplasma 255, 643-654.
DOI URL PMID |
| 17 |
Jiang YJ, Liang G, Yang SZ, Yu DQ ( 2014). Arabidopsis WRKY57 functions as a node of convergence for jasmonic acid- and auxin-mediated signaling in jasmonic acid- induced leaf senescence. Plant Cell 26, 230-245.
DOI URL PMID |
| 18 |
Lim PO, Hong GN ( 2007). Aging and senescence of the leaf organ. J Plant Biol 50, 291-300.
DOI URL |
| 19 |
Lim PO, Woo HR, Hong GN ( 2003). Molecular genetics of leaf senescence in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci 8, 272-278.
DOI URL PMID |
| 20 |
Liu D, Gong QQ, Ma YY, Li PL, Li JP, Yang SH, Yuan LL, Yu YQ, Pan DD, Xu F, Wang NN ( 2010). cpSecA, a thylakoid protein translocase subunit, is essential for photosynthetic development in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 61, 1655-1669.
DOI URL PMID |
| 21 |
Liu L, Xu W, Hu XS, Liu HJ, Lin YJ ( 2016). W-box and G-box elements play important roles in early senescence of rice flag leaf. Sci Rep 6, 20881.
DOI URL PMID |
| 22 | Menges M, Hennig L, Gruissem W, Murray JAH ( 2002). Cell cycle-regulated gene expression in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 277, 41987-42002. |
| 23 |
Quirino BF, Noh YS, Himelblau E, Amasino RM ( 2000). Molecular aspects of leaf senescence. Trends Plant Sci 5, 278-282.
DOI URL PMID |
| 24 |
Robatzek S, Somssich IE ( 2002). Targets of AtWRKY6 regulation during plant senescence and pathogen defense.Genes Dev 16, 1139-1149.
DOI URL PMID |
| 25 | Sakuraba Y, Schelbert S, Park SY, Han SH, Lee BD, Andrès CB, Kessler F, Hörtensteiner S, Paek NC ( 2012). STAY-GREEN and chlorophyll catabolic enzymes interact at light-harvesting complex ii for chlorophyll detoxification during leaf senescence in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24, 507-518. |
| 26 |
Schweighofer A, Kazanaviciute V, Scheikl E, Teige M, Doczi R, Hirt H, Schwanninger M, Kant M, Schuurink R, Mauch F, Buchala A, Cardinale F, Meskiene I ( 2007). The PP2C-type phosphatase AP2C1, which negatively regulates MPK4 and MPK6, modulates innate immunity, jasmonic acid, and ethylene levels in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 19, 2213-2224.
DOI URL PMID |
| 27 |
Shen XJ, Guo X, Zhao D, Zhang Q, Jiang YZ, Wang YT, Peng X, Wei Y, Zhai ZF, Zhao W, Li TH ( 2017). Cloning and expression profiling of the PacSnRK2 and PacPP2C gene families during fruit development, ABA treatment, and dehydration stress in sweet cherry.Plant Physiol Biochem 119, 275-285.
DOI URL PMID |
| 28 |
Wang CL, Lu GQ, Hao YQ, Guo HM, Guo Y, Zhao J, Cheng HM ( 2017). ABP9, a maize bZIP transcription factor, enhances tolerance to salt and drought in transgenic cotton. Planta 246, 453-469.
DOI URL PMID |
| 29 |
Wang FB, Liu JC, Chen MX, Zhou LJ, Li ZW, Zhao Q, Pan G, Zaidi SHR, Cheng FM ( 2016). Involvement of abscisic acid in PSII photodamage and D1 protein turnover for light-induced premature senescence of rice flag leaves. PLoS One 11, e0161203.
DOI URL PMID |
| 30 |
Xiao D, Cui YJ, Xu F, Xu XX, Gao GX, Wang YX, Guo ZX, Wang D, Wang NN ( 2015). Senescence-suppressed protein phosphatase directly interacts with the cytoplasmic domain of senescence-associated receptor-like kinase and negatively regulates leaf senescence in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 169, 1275-1291.
DOI URL PMID |
| 31 |
Xu F, Meng T, Li PL, Yu YQ, Cui YJ, Wang YX, Gong QQ, Wang NN ( 2011). A soybean dual-specificity kinase, GmSARK, and its Arabidopsis homolog, AtSARK, regulate leaf senescence through synergistic actions of auxin and ethylene. Plant Physiol 157, 2131-2153.
DOI URL PMID |
| 32 |
Xue TT, Wang D, Zhang SZ, Ehlting J, Ni F, Jakab S, Zheng CC, Zhong Y ( 2008). Genome-wide and expression analysis of protein phosphatase 2C in rice and Ara- bidopsis. BMC Genomics 9, 550.
DOI URL PMID |
| 33 | Zhang KW, Gan SS ( 2012). An abscisic acid-AtNAP transcription factor-SAG113 protein phosphatase 2C regulatory chain for controlling dehydration in senescing Arabidopsis leaves. Plant Physiol 158, 961-969. |
| 34 |
Zhao Y, Chan ZL, Gao JH, Xing L, Cao MJ, Yu CM, Hu YL, You J, Shi HT, Zhu YF, Gong YH, Mu ZX, Wang HQ, Deng X, Wang PC, Bressan RA, Zhu JK ( 2016). ABA receptor PYL9 promotes drought resistance and leaf senescence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113, 1949-1954.
DOI URL PMID |
| [1] | 刘雨函, 曹启江, 张诗晗, 李益慧, 王菁, 谭晓萌, 刘筱儒, 王显玲. 拟南芥AtFTCD-L参与根系响应土壤紧实度的机制研究[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | 杨文丽, 李钊, 刘志铭, 张志华, 杨今胜, 吕艳杰, 王永军. 不同熟期玉米叶片衰老特性及其对叶际细菌的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 1024-1040. |
| [3] | 景艳军, 林荣呈. 蓝光受体CRY2化身“暗黑舞者”[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 878-882. |
| [4] | 罗燕, 刘奇源, 吕元兵, 吴越, 田耀宇, 安田, 李振华. 拟南芥光敏色素突变体种子萌发的光温敏感性[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 752-762. |
| [5] | 陈艳晓, 李亚萍, 周晋军, 解丽霞, 彭永彬, 孙伟, 和亚男, 蒋聪慧, 王增兰, 郑崇珂, 谢先芝. 拟南芥光敏色素B氨基酸位点突变对其结构与功能的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 481-494. |
| [6] | 杨继轩, 王雪霏, 顾红雅. 西藏野生拟南芥开花时间变异的遗传基础[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 373-382. |
| [7] | 王钢, 王二涛. “卫青不败由天幸”——WeiTsing的广谱抗根肿病机理被揭示[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 356-358. |
| [8] | 杨永青, 郭岩. 植物细胞质外体pH感受机制的解析[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(4): 409-411. |
| [9] | 支添添, 周舟, 韩成云, 任春梅. PAD4突变加速拟南芥酪氨酸降解缺陷突变体sscd1的程序性细胞死亡[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(3): 288-298. |
| [10] | 李艳艳, 齐艳华. 植物Aux/IAA基因家族生物学功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 30-41. |
| [11] | 李秋信, 迟伟, 季代丽. CURT1调控类囊体膜弯曲的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(4): 462-469. |
| [12] | 车永梅, 孙艳君, 卢松冲, 侯丽霞, 范欣欣, 刘新. AtMYB77促进NO合成参与调控干旱胁迫下拟南芥侧根发育[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(4): 404-413. |
| [13] | 王婷, 羊欢欢, 赵弘巍, JosefVoglmeir, 刘丽. 蛋白质N-糖基化在拟南芥生长周期中的变化规律及去糖基化对根发育的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(3): 262-274. |
| [14] | 林雨晴, 齐艳华. 生长素输出载体PIN家族研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(2): 151-165. |
| [15] | 马龙, 李桂林, 李师鹏, 蒋苏. 根尖整体透明技术改良[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(5): 596-604. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||