

植物学报 ›› 2018, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (4): 487-501.DOI: 10.11983/CBB17082 cstr: 32102.14.CBB17082
郭书磊1,2, 张君1, 齐建双1, 岳润清1, 韩小花1, 燕树锋1, 卢彩霞1, 傅晓雷1, 陈娜娜1, 库丽霞2,*( ), 铁双贵1,*(
), 铁双贵1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2017-04-13
接受日期:2017-10-25
出版日期:2018-07-01
发布日期:2018-09-11
通讯作者:
库丽霞,铁双贵
作者简介:† 共同第一作者。
基金资助:
Guo Shulei1,2, Zhang Jun1, Qi Jianshuang1, Yue Runqing1, Han Xiaohua1, Yan Shufeng1, Lu Caixia1, Fu Xiaolei1, Chen Nana1, Ku Lixia2,*( ), Tie Shuanggui1,*(
), Tie Shuanggui1,*( )
)
Received:2017-04-13
Accepted:2017-10-25
Online:2018-07-01
Published:2018-09-11
Contact:
Ku Lixia,Tie Shuanggui
About author:† These authors contributed equally to this paper
摘要: 叶长、叶宽、叶面积及叶夹角不仅影响玉米(Zea mays)光合效率, 也是株型的重要构成因素。通过对620个叶形QTL进行整合, 构建不同遗传背景下的叶形QTL整合图谱, 利用元分析发掘出22个叶长、22个叶宽、12个叶面积以及17个叶夹角mQTL; 进一步运用生物信息学手段, 确定44个与叶片发育密切相关的候选基因。分析发现, 仅有NAL7-like、YABBY6- like和GRF2等13个基因位于mQTL区间内, 而玉米中已克隆的KNOTTED1、AN3/GIF1、rgd1/lbl1、mwp1及SRL2-like、HYL1-like和CYCB2;4-like等水稻(Oryza sativa)和拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)叶形同源基因位于未被整合的QTL内; 对44个候选基因在叶片长、宽、厚发育过程中基部-末端、中央-边缘、远轴-近轴的调控机理进行归纳分析, 发现玉米中仅有少数几个候选基因被报道, 揭示了叶形发育的部分分子机理。因此, 对玉米叶形相关mQTL/QTL及基因进行全面深入的分析, 不仅有助于增加对其遗传结构的了解, 发掘更多候选基因, 阐明叶形发育和形成的分子机制, 还可为耐密理想株型的分子标记辅助选择提供依据。
郭书磊, 张君, 齐建双, 岳润清, 韩小花, 燕树锋, 卢彩霞, 傅晓雷, 陈娜娜, 库丽霞, 铁双贵. 玉米叶形相关性状的Meta-QTL及候选基因分析. 植物学报, 2018, 53(4): 487-501.
Guo Shulei, Zhang Jun, Qi Jianshuang, Yue Runqing, Han Xiaohua, Yan Shufeng, Lu Caixia, Fu Xiaolei, Chen Nana, Ku Lixia, Tie Shuanggui. Analysis of Meta-quantitative Trait Loci and Their Candidate Genes Related to Leaf Shape in Maize. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2018, 53(4): 487-501.
| Parents | Type of Pop. | Pop. size | No. of QTL for LL | No. of QTL for LW | No. of QTL for LAr | No. of QTL for LA | No./type of marker | Analysis method | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B73×G79 | F2:3 | 214 | — | — | 7 | — | 185/RFLP | IM | Agrama et al., 1999 |
| B73×Mo17 | RIL | 180 | — | — | — | 9 | 192/SSR | CIM | Mickelson et al., 2002 |
| H21×Mo17 | F2:3 | 120 | — | — | — | 7 | 102/SSR | CIM | 于永涛等, 2006 |
| Zi330×K36 | F2:3 | 114 | — | — | — | 2 | 90/SSR | CIM | 于永涛等, 2006 |
| Ye478×Dan340 | F2:3 | 397 | — | — | — | 6 | 138/SSR | CIM | 路明等, 2007 |
| Mo17×Huangzao4 | RIL | 239 | 4 | 2 | 5 | — | 98/SSR | CIM | 郑祖平等, 2007 |
| Ye478×Wu312 | RIL | 218 | — | — | 7 | — | 184/SSR | ICIM | 刘建超等, 2010 |
| Yu82×Shen137 | F2:3 | 229 | 3 | 4 | 13 | 3 | 222/SSR | CIM | Ku et al., 2010, 2012a |
| Yu82×Yu87-1 | F2:3 | 256 | 5 | 5 | — | 5 | 216/SSR | CIM | Ku et al., 2012b |
| B73/Mo17 etc. | NAM | 4892 | 36 | 34 | — | 30 | 203000/SNP | GWAS | Tian et al., 2011 |
| N6×BT-1 | RIL | 250 | — | — | 6 | — | 207/SSR | CIM | 李贤唐等, 2011 |
| Y105×Y106 | F2 | 189 | 5 | 7 | 6 | 8 | 215/SSR | ICIM | 郭莹, 2012 |
| Y114×Y115 | F2 | 189 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 204/SSR | ICIM | 郭莹, 2012 |
| Ye478×Wu312 | RIL | 218 | 14 | 7 | 9 | — | 184/SSR | CIM | Cai et al., 2012 |
| Yu82×D132 | F2:3 | 245 | — | — | 18 | — | 204/SSR | CIM | Ku et al., 2012 |
| B73×1212 | RIL | 325 | 67 | 62 | — | — | 208/SSR | ICIM | 唐登国, 2013 |
| B73×Mo17 | RIL | 93 | 1 | 2 | — | 3 | IBM2 map | CIM | Wassom, 2013 |
| CY5×YL106 | F2:3 | 144 | — | — | — | 8 | 212/SSR | CIM | 刘正等, 2014 |
| Z58/87-1// PH6WC/Zi330 | CP | 228 | — | — | — | 13 | 225/SSR | IM | 张姿丽等, 2014b |
| T4×T19 | F2:3 | 232 | — | — | 4 | — | 81/SSR | CIM | 张姿丽等, 2014a |
| Yu82×Yu87-1 | RIL | 208 | — | 18 | — | — | 1370/SNP | CIM | Guo et al., 2015 |
| Yu82×Shen137 | RIL | 197 | — | 9 | — | — | 1411/SNP | CIM | Guo et al., 2015 |
| Zong3×Yu87-1 | RIL | 223 | — | 10 | — | — | 1479/SNP | CIM | Guo et al., 2015 |
| Yu537A×Shen137 | RIL | 212 | — | 9 | — | — | 1371/SNP | CIM | Guo et al., 2015 |
| B73×Mo17 | DH | 221 | 9 | 17 | 16 | 12 | 5935/bin markers | ICIM | 张志腾, 2015 |
| Xu178×K12 | RIL | 150 | — | — | — | 34 | 191/SSR | CIM | 常立国等, 2016 |
| M1-7×SYF | F2 | 259 | — | — | 36 | — | 218/SSR | CIM | 安允权等, 2016 |
| Yu82×D132 | RIL | 234 | 5 | 7 | 4 | — | 1226/SNP | CIM | Wei et al., 2016 |
表1 玉米叶形相关QTL信息整合
Table 1 Summary of the QTL of leaf shape in maize reported previously
| Parents | Type of Pop. | Pop. size | No. of QTL for LL | No. of QTL for LW | No. of QTL for LAr | No. of QTL for LA | No./type of marker | Analysis method | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B73×G79 | F2:3 | 214 | — | — | 7 | — | 185/RFLP | IM | Agrama et al., 1999 |
| B73×Mo17 | RIL | 180 | — | — | — | 9 | 192/SSR | CIM | Mickelson et al., 2002 |
| H21×Mo17 | F2:3 | 120 | — | — | — | 7 | 102/SSR | CIM | 于永涛等, 2006 |
| Zi330×K36 | F2:3 | 114 | — | — | — | 2 | 90/SSR | CIM | 于永涛等, 2006 |
| Ye478×Dan340 | F2:3 | 397 | — | — | — | 6 | 138/SSR | CIM | 路明等, 2007 |
| Mo17×Huangzao4 | RIL | 239 | 4 | 2 | 5 | — | 98/SSR | CIM | 郑祖平等, 2007 |
| Ye478×Wu312 | RIL | 218 | — | — | 7 | — | 184/SSR | ICIM | 刘建超等, 2010 |
| Yu82×Shen137 | F2:3 | 229 | 3 | 4 | 13 | 3 | 222/SSR | CIM | Ku et al., 2010, 2012a |
| Yu82×Yu87-1 | F2:3 | 256 | 5 | 5 | — | 5 | 216/SSR | CIM | Ku et al., 2012b |
| B73/Mo17 etc. | NAM | 4892 | 36 | 34 | — | 30 | 203000/SNP | GWAS | Tian et al., 2011 |
| N6×BT-1 | RIL | 250 | — | — | 6 | — | 207/SSR | CIM | 李贤唐等, 2011 |
| Y105×Y106 | F2 | 189 | 5 | 7 | 6 | 8 | 215/SSR | ICIM | 郭莹, 2012 |
| Y114×Y115 | F2 | 189 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 204/SSR | ICIM | 郭莹, 2012 |
| Ye478×Wu312 | RIL | 218 | 14 | 7 | 9 | — | 184/SSR | CIM | Cai et al., 2012 |
| Yu82×D132 | F2:3 | 245 | — | — | 18 | — | 204/SSR | CIM | Ku et al., 2012 |
| B73×1212 | RIL | 325 | 67 | 62 | — | — | 208/SSR | ICIM | 唐登国, 2013 |
| B73×Mo17 | RIL | 93 | 1 | 2 | — | 3 | IBM2 map | CIM | Wassom, 2013 |
| CY5×YL106 | F2:3 | 144 | — | — | — | 8 | 212/SSR | CIM | 刘正等, 2014 |
| Z58/87-1// PH6WC/Zi330 | CP | 228 | — | — | — | 13 | 225/SSR | IM | 张姿丽等, 2014b |
| T4×T19 | F2:3 | 232 | — | — | 4 | — | 81/SSR | CIM | 张姿丽等, 2014a |
| Yu82×Yu87-1 | RIL | 208 | — | 18 | — | — | 1370/SNP | CIM | Guo et al., 2015 |
| Yu82×Shen137 | RIL | 197 | — | 9 | — | — | 1411/SNP | CIM | Guo et al., 2015 |
| Zong3×Yu87-1 | RIL | 223 | — | 10 | — | — | 1479/SNP | CIM | Guo et al., 2015 |
| Yu537A×Shen137 | RIL | 212 | — | 9 | — | — | 1371/SNP | CIM | Guo et al., 2015 |
| B73×Mo17 | DH | 221 | 9 | 17 | 16 | 12 | 5935/bin markers | ICIM | 张志腾, 2015 |
| Xu178×K12 | RIL | 150 | — | — | — | 34 | 191/SSR | CIM | 常立国等, 2016 |
| M1-7×SYF | F2 | 259 | — | — | 36 | — | 218/SSR | CIM | 安允权等, 2016 |
| Yu82×D132 | RIL | 234 | 5 | 7 | 4 | — | 1226/SNP | CIM | Wei et al., 2016 |
| Bin | mQTL/QTL | CI (cM) | Candidate gene | Annotation | Homologous gene | E-value | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.02 | mQTLW1-1 | 153.8-158.3 | GRMZM2G480386 | NAL7-like | Os03g0162000/YUCCA7 | 0 | Fujino et al., 2008 |
| 1.04 | q12SevLW1 | 270.6-286.2 | GRMZM2G011483 | SRL2-like | Os03g19520/SRL2 | 0 | Liu et al., 2016 |
| 1.05 | mQTLW1-2 | 485.9-505.6 | GRMZM2G141955 | YABBY6-like | Os12g42610/YAB6 | 3E-88 | Toriba et al., 2007; Zhang et al., 2009 |
| GRMZM2G003509 | PHB-like | AT2G34710/AtHB14 | 0 | Kim et al., 2003; Mallory et al., 2004 | |||
| 1.09 | mQTLW1-3 | 820.6-845.5 | GRMZM2G018414 | GRF8 | AT4G37740/AtGRF2 | 4E-37 | Debernardi et al., 2014 |
| 1.10 | q4LWm139 | 873.7-902.1 | GRMZM2G017087 | KNOTTED1 | AT4G08150/KN1 | 2E-114 | Ramirez et al., 2009 |
| GRMZM2G178261 | GRF1-like | AT2G22840/AtGRF1 | 2E-66 | Kim et al., 2003 | |||
| GRMZM2G180246 | AN3/GIF1 | AT5G28640/AtAN3/GIF1 | 1E-36 | Nelissen et al., 2015 | |||
| 1.11 | q4LLm155 | 941.6-1022.3 | GRMZM2G135447 | OSH43-like | Os03g0771500/OsH43 | 4E-99 | Sentoku et al., 2000 |
| 2.02 | q3LAr2a | 67.5-79.7 | GRMZM2G174784 | AP2-like | AT4G36920/AP2 | 7E-102 | Würschum et al., 2006; Mlotshwa et al., 2006 |
| 2.02 | mQTLW2-1 | 118.3-147.8 | GRMZM2G102346 | NAL1-like | Os04g52479/NAL1 | 0 | Kubo et al., 2017 |
| GRMZM2G041223 | GRF6 | AT3G13960/AtGRF5 | 1E-36 | Horiguchi et al., 2006; Debernardi et al., 2014 | |||
| 2.06 | q4RLAr2 | 355.7-374.4 | GRMZM2G444808 | HYL1-like | AT1G09700/HYL1 | 6E-56 | Liu et al., 2011 |
| 2.06 | q8SecLW2 | 370.0-381.6 | GRMZM2G083972 | LNG2-like | AT3G02170/LNG2 | 6E-57 | Lee et al., 2006 |
| GRMZM2G161382 | CYCD3;3-like | AT3G50070/CYCD3;3 | 5E-56 | Dewitte et al., 2007 | |||
| 2.07 | q7LL2b | 450.0-461.9 | GRMZM2G004619 | GRF4 | AT4G37740/AtGRF2 | 5E-28 | Kim et al., 2003 |
| 2.10 | q12LAr2 | 713.1-732.4 | GRMZM2G146688 | ANT-like | AT4G37750/ANT | 1E-131 | Mizukami and Fis- cher, 2000 |
| 3.02 | q4LWm309 | 69.6-90.3 | GRMZM2G143235 | ROT3-like | AT4G36380/ROT3 | 1E-176 | Kim et al., 1998 |
| 3.06 | mQTLW3-2 | 368.5-390.3 | GRMZM2G118250 | AS2-like | AT1G65620/AS2 | 1E-66 | Iwakawa et al., 2007 |
| 3.08 | q4LWm410 | 613.6-653.7 | GRMZM2G437460 | ARF3-like | AT2G33860/ARF3/ETT | 1E-169 | Kelley et al., 2012 |
| 4.04 | q13NLW4 | 220.5-230.6 | GRMZM2G402653 | OSH1-like | Os03g0727000/OsH1 | 1E-75 | Matsuoka et al., 1993 |
| 4.06 | mQTLW4 | 373.7-399.4 | GRMZM2G124566 | GRF9-like | AT2G36400/AtGRF3 | 1E-36 | Kim et al., 2003 |
| 4.08 | q7LL4 | 429.5-451.0 | GRMZM2G075117 | CYCD3;1-like | AT4G34160/CYCD3;1 | 4E-47 | Dewitte et al., 2007 |
| GRMZM2G105335 | GRF3 | AT3G13960/AtGRF5 | 8E-49 | Horiguchi et al., 2006; Debernardi et al., 2014 | |||
| 5.03 | q4LWm602 | 268.8-295.0 | GRMZM2G361518 | AGO10-like | AT5G43810/AGO10/ZLL | 0 | Zhu et al., 2011; Roodbarkelari et al., 2015 |
| 5.03 | q4LLm605 | 280.1-296.1 | GRMZM2G171349 | COW1-like | AT4G34580/COW1 | 3E-66 | Woo et al., 2007 |
| 5.06 | q4LLm661 | 500.7-521.1 | GRMZM2G034876 | GRF1 | AT3G13960/AtGRF5 | 1E-47 | Horiguchi et al., 2006; Debernardi et al., 2014 |
| 5.07 | mQTLW5-3 | 556.7-578.5 | GRMZM5G893117 | GRF9 | AT3G13960/AtGRF5 | 1E-27 | Horiguchi et al., 2006; Debernardi et al., 2014 |
| 6.01 | q8FirLW6-1 | 82.3-93.9 | GRMZM2G122537 | PRS1-like | AT2G28610/PRS1 | 6E-29 | Matsumoto and Ok- ada, 2001; Nakata et al., 2012 |
| GRMZM2G020187 | rgd1/lbl1 | AT5G23570/SGS3 | 1E-157 | Dotto et al., 2014 | |||
| mQTL/QTL | CI (cM) | Candidate gene | Annotation | Homologous gene | E-value | Reference | |
| 6.01 | mQTLAr6 | 92.8-108.9 | GRMZM2G098594 | GRF14 | AT3G13960/AtGRF5 | 1E-36 | Horiguchi et al., 2006; Debernardi et al., 2014 |
| 6.02 | q7PLL6 | 123.0-144.8 | GRMZM2G073671 | CYCB2;3-like | AT1G20610/CYCB2;3 | 1E-144 | Eloy et al., 2011 |
| GRMZM2G157820 | CLF-like | AT2G23380/CLF | 0 | Menges et al., 2005; Schatlowski et al., 2010 | |||
| 6.04 | q4LWm706 | 158.2-205.1 | GRMZM5G850129 | GRF7 | AT3G13960/AtGRF5 | 4E-41 | Horiguchi et al., 2006; Debernardi et al., 2014 |
| 7.00 | q4LWm762 | 8.0-93.0 | GRMZM2G028041 | OSH15-like | Os07g0129700/OsH15 | 1.E-168 | Nagasaki et al., 2001 |
| GRMZM2G019200 | DRL1-like | Os11g0312782/DRL1 | 0 | Jun et al., 2015 | |||
| 7.02 | q12EigLW7 | 200.7-217.9 | GRMZM2G107377 | CYCD3;2-like | AT5G67260/CYCD3;2 | 8E-49 | Dewitte et al., 2007 |
| 7.02 | q12FirLW7 | 229.3-246.3 | GRMZM2G082264 | mwp1 | Os09g23200/SLL1/Kan1 | 2E-170 | Candela et al., 2008 |
| 7.03 | q3LW7 | 380.6-498.2 | GRMZM2G096709 | GRF10 | AT4G37740/AtGRF2 | 4E-29 | Kim et al., 2003; Deb- ernardi et al., 2014 |
| 8.08 | q3LW8 | 599.1-603.8 | GRMZM5G874163 | ARF4-like | AT5G60450/ARF4 | 7E-120 | Pekker et al., 2005; Hunter et al., 2006 |
| 9.03 | mQTLW9 | 206.1-230.6 | GRMZM2G119359 | GRF12 | AT2G06200/AtGRF6 | 1E-30 | Kim et al., 2003; Liang et al., 2014 |
| GRMZM5G870176 | NRL-like | Os12g36890/CSLD4 | 0 | Hu et al., 2010 | |||
| 10.04 | mQTLW10 | 295.6-327.3 | GRMZM2G078641 | GRF2 | GRAT3G13960/AtGRF7 | 3E-156 | Horiguchi et al., 2006; Debernardi et al., 2014 |
| 10.06 | q1HNLAr10 | 367.0-383.9 | GRMZM2G061287 | CYCB2;4-like | AT1G76310/CYCB2;4 | 9E-148 | Menges et al., 2005; Eloy et al., 2011 |
表2 mQTL/QTL区域内的玉米叶形候选基因
Table 2 Candidate genes for maize leaf shape of mQTL/QTL
| Bin | mQTL/QTL | CI (cM) | Candidate gene | Annotation | Homologous gene | E-value | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.02 | mQTLW1-1 | 153.8-158.3 | GRMZM2G480386 | NAL7-like | Os03g0162000/YUCCA7 | 0 | Fujino et al., 2008 |
| 1.04 | q12SevLW1 | 270.6-286.2 | GRMZM2G011483 | SRL2-like | Os03g19520/SRL2 | 0 | Liu et al., 2016 |
| 1.05 | mQTLW1-2 | 485.9-505.6 | GRMZM2G141955 | YABBY6-like | Os12g42610/YAB6 | 3E-88 | Toriba et al., 2007; Zhang et al., 2009 |
| GRMZM2G003509 | PHB-like | AT2G34710/AtHB14 | 0 | Kim et al., 2003; Mallory et al., 2004 | |||
| 1.09 | mQTLW1-3 | 820.6-845.5 | GRMZM2G018414 | GRF8 | AT4G37740/AtGRF2 | 4E-37 | Debernardi et al., 2014 |
| 1.10 | q4LWm139 | 873.7-902.1 | GRMZM2G017087 | KNOTTED1 | AT4G08150/KN1 | 2E-114 | Ramirez et al., 2009 |
| GRMZM2G178261 | GRF1-like | AT2G22840/AtGRF1 | 2E-66 | Kim et al., 2003 | |||
| GRMZM2G180246 | AN3/GIF1 | AT5G28640/AtAN3/GIF1 | 1E-36 | Nelissen et al., 2015 | |||
| 1.11 | q4LLm155 | 941.6-1022.3 | GRMZM2G135447 | OSH43-like | Os03g0771500/OsH43 | 4E-99 | Sentoku et al., 2000 |
| 2.02 | q3LAr2a | 67.5-79.7 | GRMZM2G174784 | AP2-like | AT4G36920/AP2 | 7E-102 | Würschum et al., 2006; Mlotshwa et al., 2006 |
| 2.02 | mQTLW2-1 | 118.3-147.8 | GRMZM2G102346 | NAL1-like | Os04g52479/NAL1 | 0 | Kubo et al., 2017 |
| GRMZM2G041223 | GRF6 | AT3G13960/AtGRF5 | 1E-36 | Horiguchi et al., 2006; Debernardi et al., 2014 | |||
| 2.06 | q4RLAr2 | 355.7-374.4 | GRMZM2G444808 | HYL1-like | AT1G09700/HYL1 | 6E-56 | Liu et al., 2011 |
| 2.06 | q8SecLW2 | 370.0-381.6 | GRMZM2G083972 | LNG2-like | AT3G02170/LNG2 | 6E-57 | Lee et al., 2006 |
| GRMZM2G161382 | CYCD3;3-like | AT3G50070/CYCD3;3 | 5E-56 | Dewitte et al., 2007 | |||
| 2.07 | q7LL2b | 450.0-461.9 | GRMZM2G004619 | GRF4 | AT4G37740/AtGRF2 | 5E-28 | Kim et al., 2003 |
| 2.10 | q12LAr2 | 713.1-732.4 | GRMZM2G146688 | ANT-like | AT4G37750/ANT | 1E-131 | Mizukami and Fis- cher, 2000 |
| 3.02 | q4LWm309 | 69.6-90.3 | GRMZM2G143235 | ROT3-like | AT4G36380/ROT3 | 1E-176 | Kim et al., 1998 |
| 3.06 | mQTLW3-2 | 368.5-390.3 | GRMZM2G118250 | AS2-like | AT1G65620/AS2 | 1E-66 | Iwakawa et al., 2007 |
| 3.08 | q4LWm410 | 613.6-653.7 | GRMZM2G437460 | ARF3-like | AT2G33860/ARF3/ETT | 1E-169 | Kelley et al., 2012 |
| 4.04 | q13NLW4 | 220.5-230.6 | GRMZM2G402653 | OSH1-like | Os03g0727000/OsH1 | 1E-75 | Matsuoka et al., 1993 |
| 4.06 | mQTLW4 | 373.7-399.4 | GRMZM2G124566 | GRF9-like | AT2G36400/AtGRF3 | 1E-36 | Kim et al., 2003 |
| 4.08 | q7LL4 | 429.5-451.0 | GRMZM2G075117 | CYCD3;1-like | AT4G34160/CYCD3;1 | 4E-47 | Dewitte et al., 2007 |
| GRMZM2G105335 | GRF3 | AT3G13960/AtGRF5 | 8E-49 | Horiguchi et al., 2006; Debernardi et al., 2014 | |||
| 5.03 | q4LWm602 | 268.8-295.0 | GRMZM2G361518 | AGO10-like | AT5G43810/AGO10/ZLL | 0 | Zhu et al., 2011; Roodbarkelari et al., 2015 |
| 5.03 | q4LLm605 | 280.1-296.1 | GRMZM2G171349 | COW1-like | AT4G34580/COW1 | 3E-66 | Woo et al., 2007 |
| 5.06 | q4LLm661 | 500.7-521.1 | GRMZM2G034876 | GRF1 | AT3G13960/AtGRF5 | 1E-47 | Horiguchi et al., 2006; Debernardi et al., 2014 |
| 5.07 | mQTLW5-3 | 556.7-578.5 | GRMZM5G893117 | GRF9 | AT3G13960/AtGRF5 | 1E-27 | Horiguchi et al., 2006; Debernardi et al., 2014 |
| 6.01 | q8FirLW6-1 | 82.3-93.9 | GRMZM2G122537 | PRS1-like | AT2G28610/PRS1 | 6E-29 | Matsumoto and Ok- ada, 2001; Nakata et al., 2012 |
| GRMZM2G020187 | rgd1/lbl1 | AT5G23570/SGS3 | 1E-157 | Dotto et al., 2014 | |||
| mQTL/QTL | CI (cM) | Candidate gene | Annotation | Homologous gene | E-value | Reference | |
| 6.01 | mQTLAr6 | 92.8-108.9 | GRMZM2G098594 | GRF14 | AT3G13960/AtGRF5 | 1E-36 | Horiguchi et al., 2006; Debernardi et al., 2014 |
| 6.02 | q7PLL6 | 123.0-144.8 | GRMZM2G073671 | CYCB2;3-like | AT1G20610/CYCB2;3 | 1E-144 | Eloy et al., 2011 |
| GRMZM2G157820 | CLF-like | AT2G23380/CLF | 0 | Menges et al., 2005; Schatlowski et al., 2010 | |||
| 6.04 | q4LWm706 | 158.2-205.1 | GRMZM5G850129 | GRF7 | AT3G13960/AtGRF5 | 4E-41 | Horiguchi et al., 2006; Debernardi et al., 2014 |
| 7.00 | q4LWm762 | 8.0-93.0 | GRMZM2G028041 | OSH15-like | Os07g0129700/OsH15 | 1.E-168 | Nagasaki et al., 2001 |
| GRMZM2G019200 | DRL1-like | Os11g0312782/DRL1 | 0 | Jun et al., 2015 | |||
| 7.02 | q12EigLW7 | 200.7-217.9 | GRMZM2G107377 | CYCD3;2-like | AT5G67260/CYCD3;2 | 8E-49 | Dewitte et al., 2007 |
| 7.02 | q12FirLW7 | 229.3-246.3 | GRMZM2G082264 | mwp1 | Os09g23200/SLL1/Kan1 | 2E-170 | Candela et al., 2008 |
| 7.03 | q3LW7 | 380.6-498.2 | GRMZM2G096709 | GRF10 | AT4G37740/AtGRF2 | 4E-29 | Kim et al., 2003; Deb- ernardi et al., 2014 |
| 8.08 | q3LW8 | 599.1-603.8 | GRMZM5G874163 | ARF4-like | AT5G60450/ARF4 | 7E-120 | Pekker et al., 2005; Hunter et al., 2006 |
| 9.03 | mQTLW9 | 206.1-230.6 | GRMZM2G119359 | GRF12 | AT2G06200/AtGRF6 | 1E-30 | Kim et al., 2003; Liang et al., 2014 |
| GRMZM5G870176 | NRL-like | Os12g36890/CSLD4 | 0 | Hu et al., 2010 | |||
| 10.04 | mQTLW10 | 295.6-327.3 | GRMZM2G078641 | GRF2 | GRAT3G13960/AtGRF7 | 3E-156 | Horiguchi et al., 2006; Debernardi et al., 2014 |
| 10.06 | q1HNLAr10 | 367.0-383.9 | GRMZM2G061287 | CYCB2;4-like | AT1G76310/CYCB2;4 | 9E-148 | Menges et al., 2005; Eloy et al., 2011 |

图1 整合图谱中叶形相关mQTL在玉米各染色体上的分布Chr: 染色体。染色体上红色区域为mQTL重叠部分所在染色体的位置; 染色体左侧为整合后mQTL的名称及位置分布; 染色体右侧为整合图谱中的标记及遗传图距(cM)。
Figure 1 Distribution of leaf shape mQTL on maize chromosomes in the integrated mapChr: Chromosome. The red region is the identified location of the overlaps of mQTL on the chromosome; The position distribution and the name for mQTL are listed in the left of chromosome; Marker name and genetic distance (cM) are listed in the right of chromosome.
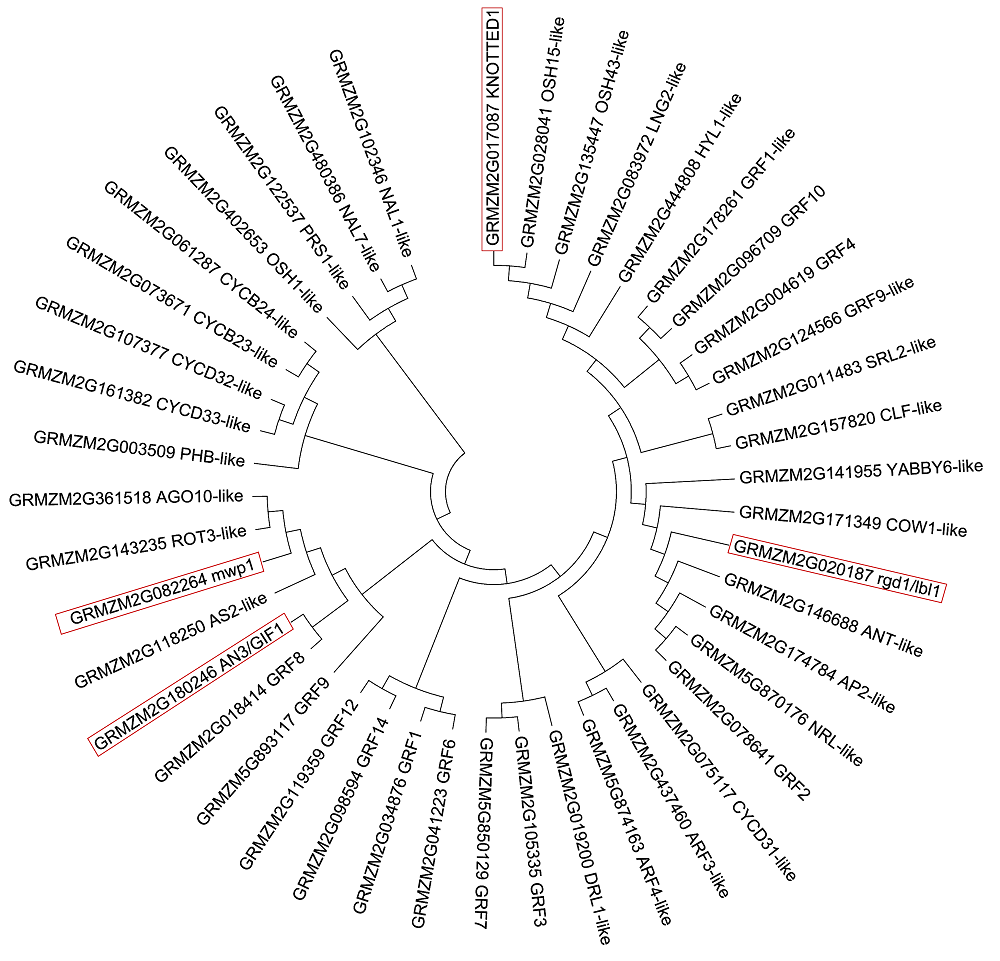
图2 玉米44个叶形候选基因的氨基酸序列聚类进化树方框标注的为玉米中已克隆且功能已知的叶形候选基因蛋白功能
Figure 2 Phylogenetic trees of amino acid sequences of 44 candidate genes related to leaf shape of maizeFunction of candidate genes which have been known and cloned related to maize leaf shape are highlighted in the box
| 42 | Lee YK, Kim GT, Kim IJ, Park J, Kwak SS, Choi G, Chung WI (2006). LONGIFOLIA1 and LONGIFOLIA2, two homologous genes, regulate longitudinal cell elongation in Arabidopsis. Development 133, 4305-4314. |
| 43 | Liang G, He H, Li Y, Wang F, Yu DQ (2014). Molecular mechanism of microRNA396 mediating pistil development in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol 164, 249-258. |
| 44 | Liu XF, Li M, Liu K, Tang D, Sun MF, Li YF, Shen Y, Du GJ, Cheng ZK (2016). Semi-Rolled Leaf 2 modulates rice leaf rolling by regulating abaxial side cell differentiation. J Exp Bot 67, 2139-2150. |
| 45 | Liu ZY, Jia LG, Wang H, He YK (2011). HYL1 regulates the balance between adaxial and abaxial identity for leaf flattening via miRNA-mediated pathways.J Exp Bot 62, 4367-6381. |
| 46 | Luan WJ, Liu YQ, Zhang FX, Song YL, Wang ZY, Peng YK, Sun ZX (2011). OsCD1 encodes a putative member of the cellulose synthase-like D sub-family and is essential for rice plant architecture and growth. Plant Biotechnol J 9, 513-524. |
| 47 | Mallory AC, Reinhart BJ, Jones-Rhoades MW, Tang GL, Zamore PD, Barton MK, Bartel DP (2004). MicroRNA control of PHABULOSA in leaf development: importance of pairing to the microRNA 5′ region.EMBO J 23, 3356-3364. |
| 48 | Matsumoto N, Okada K (2001). A homeobox gene, PRES- SED FLOWER, regulates lateral axis-dependent deve- lopment of Arabidopsis flowers. Genes Dev 15, 3355-3364. |
| 49 | Matsuoka M, Ichikawa H, Saito A, Tada Y, Fujimura T, Kano-Murakami Y (1993). Expression of a rice homeobox gene causes altered morphology of transgenic plants.Plant Cell 5, 1039-1048. |
| 50 | Menges M, de Jager SM, Gruissem W, Murray JAH (2005). Global analysis of the core cell cycle regulators of Arabidopsis identifies novel genes, reveals multiple and highly specific profiles of expression and provides a coherent model for plant cell cycle control.Plant J 41, 546-566. |
| 51 | Mickelson SM, Stuber CS, Senior L, Kaeppler SM (2002). Quantitative trait loci controlling leaf and tassel traits in a B73 × Mo17 population of maize.Crop Sci 42, 1902-1909. |
| 52 | Mizukami Y, Fischer RL (2000). Plant organ size control: AINTEGUMENTA regulates growth and cell numbers during organogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97, 942-947. |
| 53 | Mlotshwa S, Yang ZY, Kim YJ, Chen XM (2006). Floral patterning defects induced by Arabidopsis APETALA2 and microRNA172 expression in Nicotiana benthamiana.Plant Mol Biol 61, 781-793. |
| 54 | Nagasaki H, Sakamoto T, Sato Y, Matsuoka M (2001). Functional analysis of the conserved domains of a rice KNOX homeodomain protein, OSH15.Plant Cell 13, 2085-2098. |
| 55 | Nakata M, Matsumoto N, Tsugeki R, Rikirsch E, Laux T, Okada K (2012). Roles of the middle domain-specific WUSCHEL-RELATED HOMEOBOX genes in early development of leaves in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24, 519-535. |
| 56 | Nardmann J, Ji JB, Werr W, Scanlon MJ (2004). The maize duplicate genes narrow sheath 1 and narrow sheath 2 encode a conserved homeobox gene function in a lateral domain of shoot apical meristems. Development 131, 2827-2839. |
| 57 | Nelissen H, Eeckhout D, Demuynck K, Persiau G, Walton A, Van Bel M, Vervoort M, Candaele J, de Block J, Aes- aert S, Van Lijsebettens M, Goormachtig S, Vandepoele K, Van Leene J, Muszynski M, Gevaert K, Inzé D, De Jaeger G (2015). Dynamic changes in ANGUSTIFOLIA3 complex composition reveal a growth regulatory mechanism in the maize leaf.Plant Cell 27, 1605-1619. |
| 58 | Pekker I, Alvarez JP, Eshed Y (2005). Auxin response factors mediate Arabidopsis organ asymmetry via modulation of KANADI activity.Plant Cell 17, 2899-2910. |
| 59 | Qi J, Qian Q, Bu QY, Li SY, Chen Q, Sun JQ, Liang WX, Zhou YH, Chu CC, Li XG, Ren FG, Palme K, Zhao BR, Chen JF, Chen MS, Li CY (2008). Mutation of the rice Narrow leaf1 gene, which encodes a novel protein, affects vein patterning and polar auxin transport. Plant Physiol 147, 1947-1959. |
| 60 | Ramirez J, Bolduc N, Lisch D, Hake S (2009). Distal expression of knotted1 in maize leaves leads to reestablishment of proximal/distal patterning and leaf dissection.Plant Physiol 151, 1878-1888. |
| 61 | Reymond M, Muller B, Tardieu F (2004). Dealing with the genotype×environment interaction via a modelling approach: a comparison of QTLs of maize leaf length or width with QTLs of model parameters.J Exp Bot 55, 2461-2472. |
| 62 | Roodbarkelari F, Du F, Truernit E, Laux T (2015). ZLL/ AGO10 maintains shoot meristem stem cells during Arabidopsis embryogenesis by down-regulating ARF2- mediated auxin response.BMC Biol 13, 74. |
| 63 | Scanlon MJ, Chen KD, McKnight CC (2000). The narrow sheath duplicate genes: sectors of dual aneuploidy reveal ancestrally conserved gene functions during maize leaf development. Genetics 155, 1379-1389. |
| 64 | Schatlowski N, Stahl Y, Hohenstatt ML, Goodrich J, Schubert D (2010). The CURLY LEAF interacting protein BLISTER controls expression of polycomb-group target genes and cellular differentiation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 22, 2291-2305. |
| 65 | Sentoku N, Sato Y, Matsuoka M (2000). Overexpression of rice OSH genes induces ectopic shoots on leaf sheaths of transgenic rice plants. Dev Biol 220, 358-364. |
| 66 | Tian F, Bradbury PJ, Brown PJ, Hung H, Sun Q, Flint-Garcia S, Rocheford TR, McMullen MD, Holland JB, Buckler ES (2011). Genome-wide association study of leaf architecture in the maize nested association mapping population.Nat Genet 43, 159-162. |
| 67 | Timmermans MC, Schultes NP, Jankovsky JP, Nelson T (1998). Leaf bladeless 1 is required for dorsoventrality of lateral organs in maize. Development 125, 2813-2823. |
| 68 | Toriba T, Harada K, Takamura A, Nakamura H, Ichikawa H, Suzaki T, Hirano HY (2007). Molecular characterization the YABBY gene family in Oryza sativa and expression analysis of OsYABBY1. Mol Genet Genom 277, 457-468. |
| 69 | Vercruyssen L, Verkest A, Gonzalez N, Heyndrickx KS, Eeckhout D, Han SK, Jégu T, Archacki R, Van Leene J, Andriankaja M, De Bodt S, Abeel T, Coppens F, Dhondt S, De Milde L, Vermeersch M, Maleux K, Gevaert K, Jerzmanowski A, Benhamed M, Wagner D, Vandepoele K, De Jaeger G, Inzé D (2014). ANGUSTIFOLIA3 binds to SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complexes to regulate transcription during Arabidopsis leaf development.Plant Cell 26, 210-229. |
| 70 | Wassom JJ (2013). Quantitative trait loci for leaf angle, leaf width, leaf length, and plant height in a maize (Zea mays L.) B73 × Mo17 population. Maydica 58, 318-321. |
| 71 | Wei XM, Wang XB, Guo SL, Zhou JL, Shi Y, Wang HT, Dou DD, Song XH, Li GH, Ku LX, Chen YH (2016). Epistatic and QTL × environment interaction effects on leaf area-associated traits in maize.Plant Breed 135, 671-676. |
| 72 | Woo YM, Park HJ, Su’udi M, Yang JI, Park JJ, Back K, Park YM, An G (2007). Constitutively wilted 1, a member of the rice YUCCA gene family, is required for maintaining water homeostasis and an appropriate root to shoot ratio. Plant Mol Biol 65, 125-136. |
| 73 | Wu L, Zhang DF, Xue M, Qian JJ, He Y, Wang SC (2014). Overexpression of the maize GRF10, an endogenous truncated growth-regulating factor protein, leads to reduction in leaf size and plant height.J Integr Plant Biol 56, 1053-1063. |
| 74 | Würschum T, Groß-Hardt R, Laux T (2006). APETALA2 regulates the stem cell niche in the Arabidopsis shoot meristem. Plant Cell 18, 295-307. |
| 75 | Yoshikawa T, Eiguchi M, Hibara KI, Ito JI, Nagato Y (2013). Rice SLENDER LEAF 1 gene encodes cellulose synthase-like D4 and is specifically expressed in M-phase cells to regulate cell proliferation. J Exp Bot 64, 2049-2061. |
| 76 | Zhang DF, Li B, Jia GQ, Zhang TF, Dai JR, Li JS, Wang SC (2008). Isolation and characterization of genes encoding GRF transcription factors and GIF transcriptional coactivators in Maize (Zea mays L.). Plant Sci 175, 809-817. |
| 77 | Zhang GH, Xu Q, Zhu XD, Qian Q, Xue HW (2009). SHALLOT-LIKE1 is a KANADI transcription factor that modulates rice leaf rolling by regulating leaf abaxial cell development.Plant Cell 21, 719-735. |
| 1 | 安允权, 张君, 席章营, 李明娜, 李沛, 王顺喜, 张莹莹, 陈彦惠, 吴连成 (2016). 玉米不同叶位叶面积的QTL定位. 分子植物育种 14, 2113-2120. |
| 2 | 常立国, 何坤辉, 刘建超, 薛吉全 (2016). 不同环境条件下玉米叶夹角的QTL定位. 玉米科学 24(4), 49-55. |
| 3 | 郭莹 (2012). 利用不同F2群体定位玉米株型性状的QTL. 硕士论文. 重庆: 西南大学. pp. 45-47. |
| 4 | 鞠培娜, 方云霞, 邹国兴, 彭友林, 孙川, 胡江, 董国军, 曾大力, 郭龙彪, 张光恒, 高振宇, 钱前 (2010). 一个新的水稻叶形突变体(tll1)的遗传分析与精细定位. 植物学报 45, 654-661. |
| 5 | 李贤唐, 丁俊强, 王瑞霞, 吴建宇 (2011). 玉米株型相关性状的QTL定位与分析. 江苏农业科学 39(2), 21-25. |
| 6 | 刘建超, 褚群, 蔡红光, 米国华, 陈范骏 (2010). 玉米SSR连锁图谱构建及叶面积的QTL定位. 遗传 32, 625-631. |
| 7 | 刘正, 余婷婷, 梅秀鹏, 陈淅宁, 王国强, 王久光, 刘朝显, 王旭, 蔡一林 (2014). 玉米穗上叶夹角和叶间距的QTL定位. 农业生物技术学报 22, 177-187. |
| 8 | 路明, 周芳, 谢传晓, 李明顺, 徐云碧, Warburton M, 张世煌 (2007). 玉米杂交种掖单13号的SSR连锁图谱构建与叶夹角和叶向值的QTL定位与分析. 遗传 29, 1131-1138. |
| 9 | 唐登国 (2013). 玉米叶宽和叶长性状的QTL定位与分析. 硕士论文. 雅安: 四川农业大学. pp. 29-43. |
| 10 | 于永涛, 张吉民, 石云素, 宋燕春, 王天宇, 黎裕 (2006). 利用不同群体对玉米株高和叶片夹角的QTL分析. 玉米科学 14(2), 88-92. |
| 11 | 袁园园, 王丽, 赵盼盼, 王林嵩 (2016). 棉花类结瘤素MtN21基因家族生物信息学分析. 植物学报 51, 515-524. |
| 12 | 张姿丽, 蒋锋, 刘鹏飞, 陈青春, 张媛, 王晓明 (2014a). 甜玉米穗位叶面积QTL定位. 湖北农业科学 53, 1502-1505. |
| 13 | 张姿丽, 刘鹏飞, 蒋锋, 陈青春, 张媛, 王晓明, 王汉宁 (2014b). 基于四交群体的玉米叶夹角和叶向值QTL定位分析. 中国农业大学学报 19(4), 7-16. |
| 14 | 张志腾 (2015). 玉米叶型相关性状QTL定位与分析. 硕士论文. 雅安: 四川农业大学. pp. 21-23. |
| 15 | 郑祖平, 黄玉碧, 田孟良, 谭振波 (2007). 不同供氮水平下玉米株型相关性状的QTLs定位和上位性效应分析. 玉米科学 15(2), 14-18. |
| 16 | Agrama HAS, Zakaria AG, Said FB, Tuinstra M (1999). Identification of quantitative trait loci for nitrogen use efficiency in maize.Mol Breed 5, 187-195. |
| 17 | Cai HG, Chu Q, Yuan LX, Liu JC, Chen XH, Chen FJ, Mi GH, Zhang FS (2012). Identification of quantitative trait loci for leaf area and chlorophyll content in maize ( Zea mays) under low nitrogen and low phosphorus supply. Mol Breed 30, 251-266. |
| 18 | Candaele J, Demuynck K, Mosoti D, Beemster GTS, Inzé D, Nelissen H (2014). Differential methylation during maize leaf growth targets developmentally regulated ge- nes.Plant Physiol 164, 1350-1364. |
| 19 | Candela H, Johnston R, Gerhold A, Foster T, Hake S (2008). The Milkweed pod1 gene encodes a KANADI protein that is required for abaxial/adaxial patterning in maize leaves. Plant Cell 20, 2073-2087. |
| 20 | Darvasi A, Soller M (1997). A simple method to calculate resolving power and confidence interval of QTL map location.Behav Genet 27, 125-132. |
| 21 | Debernardi JM, Mecchia MA, Vercruyssen L, Smaczniak C, Kaufmann K, Inze D, Rodriguez RE, Palatnik JF (2014). Post-transcriptional control of GRF transcription factors by microRNA miR396 and GIF co-activator affects leaf size and longevity.Plant J 79, 413-426. |
| 22 | Dewitte W, Scofield S, Alcasabas AA, Maughan SC, Menges M, Braun N, Collins C, Nieuwland J, Prinsen E, Sundaresan V, Murray JAH (2007). Arabidopsis CYCD3 D-type cyclins link cell proliferation and endocycles and are rate-limiting for cytokinin responses.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104, 14537-14542. |
| 23 | Ding ZQ, Lin ZF, Li Q, Wu H, Xiang CY, Wang JF (2015). DNL1, encodes cellulose synthase-like D4, is a major QTL for plant height and leaf width in rice(Oryza sativa L.). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 457, 133-140. |
| 24 | Dotto MC, Petsch KA, Aukerman MJ, Beatty M, Hammell M, Timmermans MC (2014). Genome-wide analysis of leaf bladeless1-regulated and phased small RNAs underscores the importance of the TAS3 ta-siRNA pathway to maize development. PLoS Genet 10, e1004826. |
| 25 | Eloy NB, de Freitas Lima M, Van Damme D, Vanhaeren H, Gonzalez N, de Milde L, Hemerly AS, Beemster GTS, Inzé D, Ferreira PCG (2011). The APC/C subunit 10 plays an essential role in cell proliferation during leaf development. Plant J 68, 351-363. |
| 26 | Facette MR, Shen ZX, Björnsdóttir FR, Briggs SP, Smith LG (2013). Parallel proteomic and phosphoproteomic ana- lyses of successive stages of maize leaf development.Plant Cell 25, 2798-2812. |
| 27 | Fujino K, Matsuda Y, Ozawa K, Nishimura T, Koshiba T, Fraaije MW, Sekiguchi H (2008). NARROW LEAF 7 controls leaf shape mediated by auxin in rice. Mol Genet Genom 279, 499-507. |
| 28 | Goffinet B, Gerber S (2000). Quantitative trait loci: a meta- analysis.Genetics 155, 463-473. |
| 29 | Guo SL, Ku LX, Qi JS, Tian ZQ, Han T, Zhang LK, Su HH, Ren ZZ, Chen YH (2015). Genetic analysis and major quantitative trait locus mapping of leaf widths at different positions in multiple populations.PLoS One 10, e0119095. |
| 30 | Horiguchi G, Ferjani A, Fujikura U, Tsukaya H (2006). Coordination of cell proliferation and cell expansion in the control of leaf size in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Plant Res 119, 37-42. |
| 31 | Hu J, Zhu L, Zeng DL, Gao ZY, Guo LB, Fang YX, Zhang GH, Dong GJ, Yan MX, Liu J, Qian Q (2010). Identification and characterization of NARROW AND ROLLED LEAF 1, a novel gene regulating leaf morphology and plant architecture in rice. Plant Mol Biol 73, 283-292. |
| 32 | Hunter C, Willmann MR, Wu G, Yoshikawa M, de la Luz Gutiérrez-Nava M, Poethig SR (2006). Trans-acting siRNA-mediated repression of ETTIN and ARF4 regulates heteroblasty in Arabidopsis.Development 133, 2973-2981. |
| 33 | Iwakawa H, Iwasaki M, Kojima S, Ueno Y, Soma T, Tanaka H, Semiarti E, Machida Y, Machida C (2007). Expression of the ASYMMETRIC LEAVES 2 gene in the adaxial domain of Arabidopsis leaves represses cell proliferation in this domain and is critical for the development of properly expanded leaves. Plant J 51, 173-184. |
| 34 | Jun SE, Cho KH, Hwang JY, Abdel-Fattah W, Hammermeister A, Schaffrath R, Bowman JL, Kim GT (2015). Comparative analysis of the conserved functions of Arabidopsis DRL1 and yeast KTI12.Mol Cells 38, 243-250. |
| 35 | Kelley DR, Arreola A, Gallagher TL, Gasser CS (2012). ETTIN (ARF3) physically interacts with KANADI proteins to form a functional complex essential for integument deve- lopment and polarity determination in Arabidopsis.Deve- lopment 139, 1105-1109. |
| 36 | Kim GT, Tsukaya H, Uchimiya H (1998). The ROTUNDIFOLIA3 gene of Arabidopsis thaliana encodes a new member of the cytochrome P450 family that is required for the regulated polar elongation of leaf cells. Genes Dev 12, 2381-2391. |
| 37 | Kim JH, Choi D, Kende H (2003). The AtGRF family of putative transcription factors is involved in leaf and cotyledon growth in Arabidopsis.Plant J 36, 94-104. |
| 38 | Ku LX, Zhang J, Guo SL, Liu HY, Zhao RF, Chen YH (2012a). Integrated multiple population analysis of leaf architecture traits in maize (Zea mays L.). J Exp Bot 63, 261-274. |
| 39 | Ku LX, Zhang J, Zhang JC, Guo SL, Liu HY, Zhao RF, Yan QX, Chen YH (2012b). Genetic dissection of leaf area by jointing two F2:3 populations in maize (Zea mays L.). Plant Breed 131, 591-599. |
| 78 | Zhu HL, Hu FQ, Wang RH, Zhou X, Sze SH, Liou LW, Barefoot A, Dickman M, Zhang XR (2011). Arabidopsis Argonaute10 specifically sequesters miR166/165 to regulate shoot apical meristem development.Cell 145, 242-256. |
| 40 | Ku LX, Zhao WM, Zhang J, Wu LC, Wang CL, Wang PA, Zhang WQ, Chen YH (2010). Quantitative trait loci mapping of leaf angle and leaf orientation value in maize (Zea mays L.). Theor Appl Genet 121, 951-959. |
| 41 | Kubo FC, Yasui Y, Kumamaru T, Sato Y, Hirano HY (2017). Genetic analysis of rice mutants responsible for narrow leaf phenotype and reduced vein number.Genes Genet Syst 91, 235-240. |
| [1] | 吴锁伟, 安学丽, 万向元. 玉米雄性不育机理及其在工程核不育制种中的应用[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 932-949. |
| [2] | 郑名敏, 黄强, 张鹏, 刘孝伟, 赵卓凡, 易洪杨, 荣廷昭, 曹墨菊. 玉米细胞质雄性不育及育性恢复研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 999-1006. |
| [3] | 杜庆国, 李文学. lncRNA调控玉米生长发育和非生物胁迫研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 950-962. |
| [4] | 王子阳, 刘升学, 杨志蕊, 秦峰. 玉米抗旱性的遗传解析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 883-902. |
| [5] | 张强, 赵振宇, 李平华. 基因编辑技术在玉米中的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 978-998. |
| [6] | 王涛, 冯敬磊, 张翠. 高温胁迫影响玉米生长发育的分子机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 963-977. |
| [7] | 杨娟, 赵月磊, 陈晓远, 王宝宝, 王海洋. 玉米开花期调控机理及育种应用[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 912-931. |
| [8] | 闫恒宇, 李朝霞, 李玉斌. 高温对玉米生长的影响及中国耐高温玉米筛选研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 1007-1023. |
| [9] | 杨文丽, 李钊, 刘志铭, 张志华, 杨今胜, 吕艳杰, 王永军. 不同熟期玉米叶片衰老特性及其对叶际细菌的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 1024-1040. |
| [10] | 李园, 范开建, 安泰, 李聪, 蒋俊霞, 牛皓, 曾伟伟, 衡燕芳, 李虎, 付俊杰, 李慧慧, 黎亮. 玉米自然群体自交系农艺性状的多环境全基因组预测初探[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 1041-1053. |
| [11] | 程可心, 杜尧, 李凯航, 王浩臣, 杨艳, 金一, 何晓青. 玉米与叶际微生物组的互作遗传机制[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(2): 215-228. |
| [12] | 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 朱哲楠, 张芷宁, 汪理海, 陈钧, 李三峰, 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 钟芊芊, 殷文晶, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻穗部性状QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 217-230. |
| [13] | 朱宝, 赵江哲, 张可伟, 黄鹏. 水稻细胞分裂素氧化酶9参与调控水稻叶夹角发育[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 10-21. |
| [14] | 于熙婷, 黄学辉. 现代玉米起源新见解——两类大刍草的混血[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 857-860. |
| [15] | 周文期, 周玉乾, 李永生, 何海军, 杨彦忠, 王晓娟, 连晓荣, 刘忠祥, 胡筑兵. 玉米ZmICE2基因调控气孔发育[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 866-881. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||