

植物学报 ›› 2018, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (1): 139-148.DOI: 10.11983/CBB17014 cstr: 32102.14.CBB17014
• 专题论坛 • 上一篇
帅海威, 孟永杰, 陈锋, 周文冠, 罗晓峰, 杨文钰*( ), 舒凯*(
), 舒凯*( )
)
收稿日期:2017-01-19
接受日期:2017-06-22
出版日期:2018-01-01
发布日期:2018-08-10
通讯作者:
杨文钰,舒凯
基金资助:
Haiwei Shuai, Yongjie Meng, Feng Chen, Wenguan Zhou, Xiaofeng Luo, Wenyu Yang*( ), Kai Shu*(
), Kai Shu*( )
)
Received:2017-01-19
Accepted:2017-06-22
Online:2018-01-01
Published:2018-08-10
Contact:
Wenyu Yang, Kai Shu
摘要: 植物的生长发育与光信号密切相关, 外界光强、光质的变化会改变植物的生长发育状态。在自然或人工生态系统中, 植株个体的光环境往往会被其周围植物所影响, 导致荫蔽胁迫, 其主要表现为光合有效辐射以及红光与远红光比值(R:FR)降低。荫蔽胁迫对植物生长发育的多个时期均有影响, 如抑制种子萌发、促进幼苗下胚轴伸长及促进植物花期提前等, 这对农业生产不利, 会导致作物产量以及品质的降低。植物激素是调控植物生长发育的关键内源因子。大量研究表明, 生长素(IAA)、赤霉素(GA)及油菜素甾醇(BR)等植物激素均参与介导植物的荫蔽胁迫响应。当植物处于荫蔽胁迫时, 光信号的改变会影响植物激素的合成及信号转导。不同植物激素对荫蔽胁迫的响应各不相同, 但其信号通路之间却存在互作关系, 从而形成复杂的网络状调控路径。该文总结了几种主要植物激素(生长素、赤霉素、油菜素甾醇及乙烯)响应荫蔽胁迫的机理, 重点论述了荫蔽胁迫对植物激素合成及信号通路的影响, 以及植物激素调控荫蔽胁迫下植物生长的分子机理, 并对未来潜在的研究热点进行了分析。
帅海威, 孟永杰, 陈锋, 周文冠, 罗晓峰, 杨文钰, 舒凯. 植物荫蔽胁迫的激素信号响应. 植物学报, 2018, 53(1): 139-148.
Haiwei Shuai, Yongjie Meng, Feng Chen, Wenguan Zhou, Xiaofeng Luo, Wenyu Yang, Kai Shu. Phytohormone-mediated Plant Shade Responses. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2018, 53(1): 139-148.
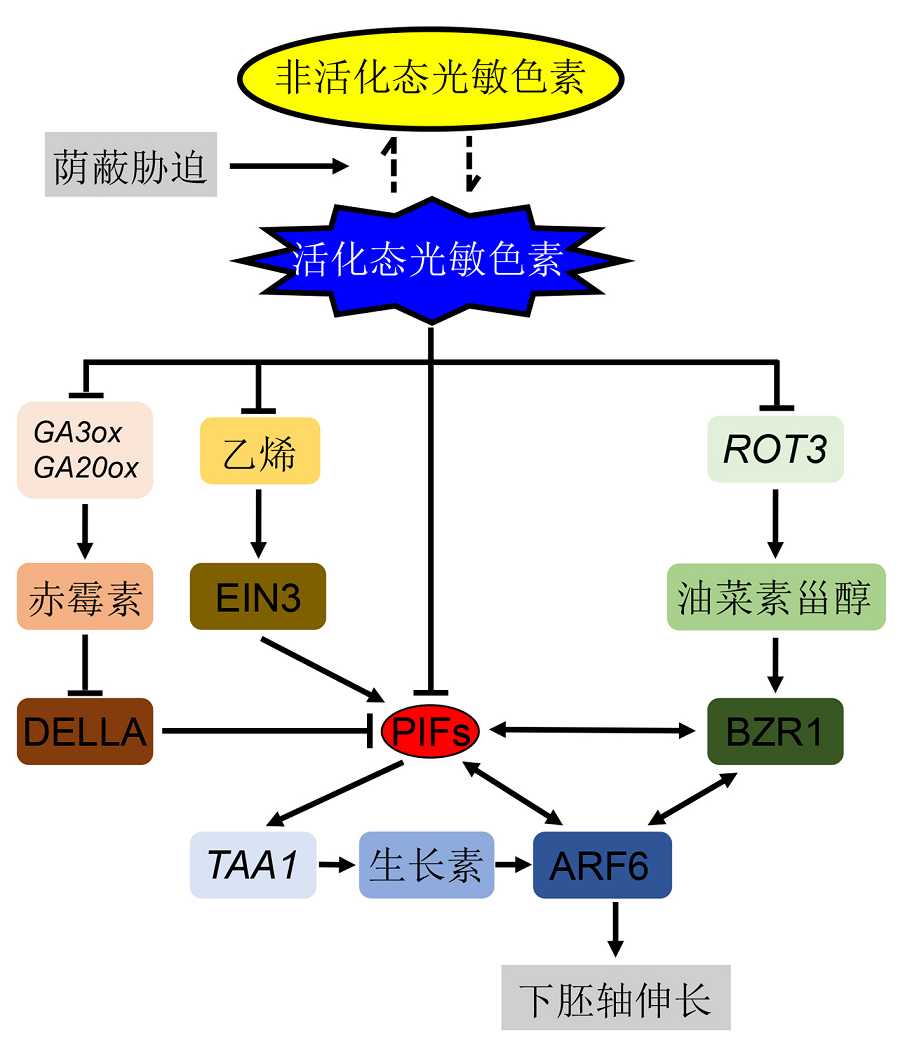
图1 几种重要植物激素响应荫蔽胁迫的信号通路网络荫蔽胁迫下, 光敏色素由活化态Pfr形式转变为非活化态Pr形式, 由此减弱对PIFs的抑制作用。不同植物激素对荫蔽胁迫的响应不同, 但最终都会与PIFs产生互作。在荫蔽胁迫下, 赤霉素(GA)合成基因GA3ox和GA20ox的表达量增加, 进而导致GA含量升高, GA含量的增加又会促进DELLA蛋白的降解, 而DELLA蛋白能抑制PIF4行使功能。油菜素甾醇(BR)合成基因ROT3在荫蔽胁迫下表达量也会增加, 进而促进BR含量的升高, BR的增加能促进BR转录因子基因BZR1的转录, 而BZR1能与PIF4蛋白产生结构上的互作。在荫蔽胁迫下, 乙烯(ETH)的含量也会增加, ETH的增加能促进ETH转录因子基因EIN3的转录, 而EIN3被证明能上调PIF3基因的表达。生长素(IAA)的合成和信号转导均受PIFs的影响, 其中PIF4、PIF5和PIF7对IAA的合成具有促进作用, 且PIF4和PIF5还促进IAA下游转录因子基因ARF6的表达, IAA也是促进下胚轴伸长的主要植物激素。荫蔽胁迫下, 不同信号通路之间存在互作关系。例如, 在调控下胚轴伸长时, PIF4、BZR1和ARF6被证明具有协同作用。
Figure 1 The proposed plant shade response signaling networks mediated by several important phytohormones Phytochrome is transferred from active Pfr to inactive Pr statuses under shade conditions, and this further attenuates the inhibition effect on PIFs. Although the shade response is distinct among different phytohormones, finally the interaction between all phytohormones with PIFs is documented. Under shade conditions, the transcription level of GA biosynthesis genes GA3ox and GA20ox were increased, which further promotes degradation of DELLA and finally inhibits the functions of PIFs. The expression of BR biosynthesis gene ROT3 is also increased under shade conditions, and further enhances BR biosynthesis and promotes BZR1 transcription, and finally the interaction between BZR1 and PIF4 was detected. Similar to GA and BR, ethylene level was also increased under shade conditions. The increase of ethylene then induces EIN3 transcription, and transcription factor EIN3 further enhances the transcription of PIF3. Both auxin biosynthesis and signaling pathways are regulated by PIFs; in detail, PIF4, PIF5 and PIF7 enhance IAA biogenesis, and PIF4 and PIF5 also promote ARF6 expression. So far, auxin is the most important phytohormone mediates plant shade response. In a word, under shade conditions, the crosstalk networks among different phytohormones signaling pathways were documented. For example, the synergy effect of PIF4, BZR1 and ARF6 was detected under shade conditions, with regard to hypocotyl elongation.
| [1] | 刘明雪, 孙梅, 王宇, 李玉花 (2012). 植物UV-B受体及其介导的光信号转导. 植物学报 47, 661-669. |
| [2] | 帅海威, 孟永杰, 罗晓峰, 陈锋, 戚颖, 杨文钰, 舒凯 (2016). 生长素调控种子的休眠与萌发. 遗传 38, 314-322. |
| [3] | 岳晶, 管利萍, 孟思远, 张静, 侯岁稳 (2015). 光敏色素信号通路中磷酸化修饰研究进展. 植物学报 50, 241-254. |
| [4] | Achard P, Liao LL, Jiang CF, Desnos T, Bartlett J, Fu XD, Harberd NP (2007). DELLAs contribute to plant photomorphogenesis. Plant Physiol 143, 1163-1172. |
| [5] | Alabadí D, Gil J, Blázquez MA, García-Mmartínez J (2004). Gibberellins repress photomorphogenesis in darkness. Pl- ant Physiol 134, 1050-1057. |
| [6] | Alvey L, Harberd NP (2005). DELLA proteins: integrators of multiple plant growth regulatory inputs? Physiol Plantarum 123, 153-160. |
| [7] | Boccalandro HE, Ploschuk EL, Yanovsky MJ, Sánchez RA, Gatz C, Casal JJ (2003). Increased phytochrome B alleviates density effects on tuber yield of field potato crops. Plant Physiol 133, 1539-1546. |
| [8] | Botto JF, Sanchez RA, Whitelam GC, Casal JJ (1996). Phytochrome A mediates the promotion of seed germination by very low fluences of light and canopy shade light in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 110, 439-444. |
| [9] | Cagnola JI, Ploschuk E, Benech-Arnold T, Finlayson SA, Casal JJ (2012). Stem transcriptome reveals mechanisms to reduce the energetic cost of shade-avoidance respon- ses in tomato. Plant Physiol 160, 1110-1119. |
| [10] | Casal JJ (2012). Shade avoidance. Arabidopsis Book 10, e157. |
| [11] | Casal JJ (2013). Photoreceptor signaling networks in plant responses to shade. Annu Rev Plant Biol 64, 403-427. |
| [12] | Chaves I, Pokorny R, Byrdin M, Hoang N, Ritz T, Brettel K, Essen LO, van Der Horst GT, Batschauer A, Ahmad M (2011). The cryptochromes: blue light photoreceptors in plants and animals. Annu Rev Plant Biol 62, 335-364. |
| [13] | Christie JM (2007). Phototropin blue-light receptors. Annu Rev Plant Biol 58, 21-45. |
| [14] | Das D, St Onge KR, Voesenek LACJ, Pierik R, Sasidharan R (2016). Ethylene- and shade-induced hypocotyl elongation share transcriptome patterns and functional regulators. Plant Physiol 172, 718-733. |
| [15] | De Lucas M, Davière JM, RodrÍguez-Falcón M, Pontin M, Iglesias-Pedraz JM, Lorrain S, Fankhauser C, Blázquez MA, Titarenko E, Prat S (2008). A molecular framework for light and gibberellin control of cell elongation. Nature 451, 480-484. |
| [16] | de Wit M, Keuskamp DH, Bongers FJ, Hornitschek P, Gommers CMM, Reinen E, Martínez-Cerón C, Fankhauser C, Pierik R (2016). Integration of phytochrome and cryptochrome signals determines plant growth during competition for light.Curr Biol 26, 3320-3326. |
| [17] | de Wit M, Lorrain S, Fankhauser C (2014). Auxin-mediated plant architectural changes in response to shade and high temperature.Physiol Plantarum 151, 13-24. |
| [18] | de Wit M, Spoel SH, Sanchez-Perez GF, Gommers CMM, Pieterse CMJ, Voesenek LACJ, Pierik R (2013). Perception of low red:far-red ratio compromises both salicylic acid- and jasmonic acid-dependent pathogen defences in Arabidopsis. Plant J 75, 90-103. |
| [19] | Devlin PF, Yanovsky MJ, Kay SA (2003). A genomic analy- sis of the shade avoidance response in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 133, 1617-1629. |
| [20] | Djakovic-Petrovic T, de Wit M, Voesenek LACJ, Pierik R (2007). DELLA protein function in growth responses to canopy signals. Plant J 51, 117-126. |
| [21] | Dubois PG, Olsefski GT, Flint-Garcia SA, Setter TL, Hoekenga OA, Brutnell TP (2010). Physiological and genetic characterization of end-of-day far-red light response in maize seedlings. Plant Physiol 154, 173-186. |
| [22] | Evans JR, Poorter H (2001). Photosynthetic acclimation of plants to growth irradiance: the relative importance of specific leaf area and nitrogen partitioning in maximizing carbon gain. Plant Cell Environ 24, 755-767. |
| [23] | Feng SH, Martinez C, Gusmaroli G, Wang Y, Zhou JL, Wang F, Chen LY, Yu L, Iglesias-Pedraz JM, Kircher S, Schäfer E, Fu XD, Fan LM, Deng XW (2008). Coordinated regulation ofArabidopsis thaliana development by light and gibberellins. Nature 451, 475-479. |
| [24] | Finlayson SA, Krishnareddy SR, Kebrom TH, Casal JJ (2010). Phytochrome regulation of branching in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 152, 1914-1927. |
| [25] | Fleet CM, Sun TP (2005). A DELLAcate balance: the role of gibberellin in plant morphogenesis. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8, 77-85. |
| [26] | Franklin KA (2008). Shade avoidance.New Phytol 179, 930-944. |
| [27] | Franklin KA, Davis SJ, Stoddart WM, Vierstra RD, Whitelam GC (2003). Mutant analyses define multiple roles for phytochrome C in Arabidopsis photomorphogenesis. Plant Cell 15, 1981-1989. |
| [28] | Gamage HK (2011). Phenotypic variation in heteroblastic woody species does not contribute to shade survival. AOB Plants doi: 10.1093/aobpla/plr013. |
| [29] | Gong WZ, Qi PF, Du JB, Sun X, Wu XL, Song C, Liu WG, Wu YS, Yu XB, Yong TW, Wang XC, Yang F, Yan YH, Yang WY (2014). Transcriptome analysis of shade- induced inhibition on leaf size in relay intercropped soybean. PLoS One 9, e98465. |
| [30] | Hisamatsu T, King RW, Helliwell CA, Koshioka M (2005). The involvement of gibberellin 20-oxidase genes in phytochrome-regulated petiole elongation of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 138, 1106-1116. |
| [31] | Holmes MG, Smith H (1975). The function of phytochrome in plants growing in the natural environment. Nature 254, 512-514. |
| [32] | Hornitschek P, Kohnen MV, Lorrain S, Rougemont J, Ljung K, López-Vidriero I, Franco-Zorrilla JM, Solano R, Trevisan M, Pradervand S, Xenarios I, Fankhauser C (2012). Phytochrome interacting factors 4 and 5 control seedling growth in changing light conditions by directly controlling auxin signaling. Plant J 71, 699-711. |
| [33] | Jenkins GI (2014). The UV-B photoreceptor UVR8: from structure to physiology. Plant Cell 26, 21-37. |
| [34] | Keuskamp DH, Pollmann S, Voesenek LACJ, Peeters AJM, Pierik R (2010). Auxin transport through PIN- FORMED 3 (PIN3) controls shade avoidance and fitness during competition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107, 22740-22744. |
| [35] | Keuskamp DH, Sasidharan R, Vos I, Peeters AJM, Voe- senek LACJ, Pierik R (2011). Blue-light-mediated shade avoidance requires combined auxin and brassinosteroid action in Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant J 67, 208-217. |
| [36] | Kim GT, Tsukaya H, Uchimiya H (1998). TheROTUNDIFOLIA3 gene of Arabidopsis thaliana encodes a new member of the cytochrome P-450 family that is required for the regulated polar elongation of leaf cells. Gene Dev 12, 2381-2391. |
| [37] | Kurepin LV, Walton LJ, Hayward A, Emery RJ, Pharis RP, Reid DM (2012). Interactions between plant hormones and light quality signaling in regulating the shoot growth ofAra- bidopsis thaliana seedlings. Botany 90, 237-246. |
| [38] | Leivar P, Monte E (2014). PIFs: systems integrators in plant development. Plant Cell 26, 56-78. |
| [39] | Leivar P, Quail PH (2011). PIFs: pivotal components in a cellular signaling hub. Trends Plant Sci 16, 19-28. |
| [40] | Li L, Ljung K, Breton G, Schmitz RJ, Pruneda-Paz J, Cowing-Zitron C, Cole BJ, Ivans LJ, Pedmale UV, Jung HS, Ecker JR, Kay SA, Chory J (2012a). Linking photoreceptor excitation to changes in plant architecture. Gene Dev 26, 785-790. |
| [41] | Li QF, Wang C, Jiang L, Li S, Sun SS, He JX (2012b).An interaction between BZR1 and DELLAs mediates direct signaling crosstalk between brassinosteroids and gibbe- rellins in Arabidopsis. Sci Signal 5, ra72. |
| [42] | Liu X, Zhang H, Zhao Y, Feng Z, Li Q, Yang HQ, Luan S, Li J, He ZH (2013). Auxin controls seed dormancy through stimulation of abscisic acid signaling by inducing ARF- mediated ABI3 activation in Arabidopsis.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110, 15485-15490. |
| [43] | Locascio A, Blázquez MA, AlabadÍ D (2013). Genomic analysis of DELLA protein activity. Plant Cell Physiol 54, 1229-1237. |
| [44] | Lorrain S, Allen T, Duek PD, Whitelam GC, Fankhauser C (2008). Phytochrome-mediated inhibition of shade avoi- dance involves degradation of growth-promoting bHLH transcription factors. Plant J 53, 312-323. |
| [45] | Luccioni LG, Oliverio KA, Yanovsky MJ, Boccalandro HE, Casal JJ (2002). Brassinosteroid mutants uncover fine tuning of phytochrome signaling. Plant Physiol 128, 173-181. |
| [46] | Luo XM, Lin WH, Zhu SW, Zhu JY, Sun Y, Fan XY, Cheng ML, Hao YQ, Oh E, Tian MM, Liu LJ, Zhang M, Xie Q, Chong K, Wang ZY (2010). Integration of light- and brassinosteroid-signaling pathways by a GATA transcription factor in Arabidopsis. Dev Cell 19, 872-883. |
| [47] | Meng C, Chory J (2011). Phytochrome signaling mechanisms and the control of plant development. Trends Cell Biol 21, 664-671. |
| [48] | Mittler R, Blumwald E (2015). The roles of ROS and ABA in systemic acquired acclimation. Plant Cell 27, 64-70. |
| [49] | Morelli G, Ruberti I (2000). Shade avoidance responses. Driving auxin along lateral routes. Plant Physiol 122, 621-626. |
| [50] | Murase K, Hirano Y, Sun TP, Hakoshima T (2008). Gibberellin-induced DELLA recognition by the gibberellin receptor GID1. Nature 456, 459-463. |
| [51] | Nozue K, Harmer SL, Maloof JN (2011). Genomic analysis of circadian clock-, light-, and growth-correlated genes reveals PHYTOCHROME-INTERACTING FACTOR5 as a modulator of auxin signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 156, 357-372. |
| [52] | Nozue K, Tat AV, Devisetty UK, Robinson M, Mumbach MR, Ichihashi Y, Lekkala S, Maloof JN (2015). Shade avoidance components and pathways in adult plants revealed by phenotypic profiling. PLoS Genet 11, e1004953. |
| [53] | Oh E, Zhu JY, Bai MY, Arenhart RA, Sun Y, Wang ZY (2014). Cell elongation is regulated through a central circuit of interacting transcription factors in the Arabidopsis hypocotyl.eLife 3, e03031. |
| [54] | Oh E, Zhu JY, Wang ZY (2012). Interaction between BZR1 and PIF4 integrates brassinosteroid and environmental responses. Nat Cell Biol 14, 802-809. |
| [55] | Pedmale UV, Huang SC, Zander M, Cole BJ, Hetzel J, Ljung K, Reis PAB, Sridevi P, Nito K, Nery JR, Ecker JR, Chory J (2016). Cryptochromes interact directly with PIFs to control plant growth in limiting blue light.Cell 164, 233-245. |
| [56] | Pierik R, Djakovic-Petrovic T, Keuskamp DH, de Wit M, Voesenek LACJ (2009). Auxin and ethylene regulate elongation responses to neighbor proximity signals independent of gibberellin and DELLA proteins in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 149, 1701-1712. |
| [57] | Pigliucci M, Schmitt J (1999). Genes affecting phenotypic plasticity in Arabidopsis: pleiotropic effects and reproductive fitness of photomorphogenic mutants. J Evol Biol 12, 551-562. |
| [58] | Procko C, Burko Y, Jaillais Y, Ljung K, Long JA, Chory J (2016). The epidermis coordinates auxin-induced stem growth in response to shade. Gene Dev 30, 1529-1541. |
| [59] | Procko C, Crenshaw CM, Ljung K, Noel JP, Chory J (2014). Cotyledon-generated auxin is required for shade- induced hypocotyl growth inBrassica rapa. Plant Physiol 165, 1285-1301. |
| [60] | Reddy SK, Holalu SV, Casal JJ, Finlayson SA (2013). Abscisic acid regulates axillary bud outgrowth responses to the ratio of red to far-red light. Plant Physiol 163, 1047-1058. |
| [61] | Reed JW, Foster KR, Morgan PW, Chory J (1996). Phytochrome B affects responsiveness to gibberellins in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 112, 337-342. |
| [62] | Reed JW, Nagpal P, Poole DS, Furuya M, Chory J (1993). Mutations in the gene for the red/far-red light receptor phytochrome B alter cell elongation and physiological responses throughout Arabidopsis development. Plant Cell 5, 147-157. |
| [63] | Reinecke DM, Wickramarathna AD, Ozga JA, Kurepin LV, Jin AL, Good AG, Pharis RP (2013). Gibberellin 3-oxi- dase gene expression patterns influence gibberellin biosynthesis, growth, and development in pea. Plant Physiol 163, 929-945. |
| [64] | Sanchez SE, Cagnola JI, Crepy M, Yanovsky MJ, Casal JJ (2011). Balancing forces in the photoperiodic control of flowering. Photochem Photobiol Sci 10, 451-460. |
| [65] | Schwechheimer C (2008). Understanding gibberellic acid signaling—are we there yet? Curr Opin Plant Biol 11, 9-15. |
| [66] | Shimada A, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Nakatsu T, Nakajima M, Naoe Y, Ohmiya H, Kato H, Matsuoka M (2008). Structural basis for gibberellin recognition by its receptor GID1. Nature 456, 520-523. |
| [67] | Shinomura T, Nagatani A, Hanzawa H, Kubota M, Wata- nabe M, Furuya M (1996). Action spectra for phytochrome A- and B-specific photoinduction of seed germination inArabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93, 8129-8133. |
| [68] | Shu K, Chen Q, Wu YR, Liu RJ, Zhang HW, Wang PF, Li YL, Wang SF, Tang SY, Liu CY, Yang WY, Cao XF, Serino G, Xie Q (2016a). ABI4 mediates antagonistic effects of abscisic acid and gibberellins at transcript and protein levels. Plant J 85, 348-361. |
| [69] | Shu K, Chen Q, Wu YR, Liu RJ, Zhang HW, Wang SF, Tang SY, Yang WY, Xie Q (2016b). ABSCISIC ACID- INSENSITIVE 4 negatively regulates flowering through directly promoting ArabidopsisFLOWERING LOCUS C transcription. J Exp Bot 67, 195-205. |
| [70] | Shu K, Zhang HW, Wang SF, Chen ML, Wu YR, Tang SY, Liu CY, Feng YQ, Cao XF, Xie Q (2013). ABI4 regulates primary seed dormancy by regulating the biogenesis of abscisic acid and gibberellins in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet 9, e1003577. |
| [71] | Smalle J, Haegman M, Kurepa J, Van Montagu M, St- raeten DVD (1997). Ethylene can stimulate Arabidopsis hypocotyl elongation in the light. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94, 2756-2761. |
| [72] | Steindler C, Matteucci A, Sessa G, Weimar T, Ohgishi M, Aoyama T, Morelli G, Ruberti I (1999). Shade avoidance responses are mediated by the ATHB-2 HD-zip protein, a negative regulator of gene expression. Development 126, 4235-4245. |
| [73] | Suetsugu N, Wada M (2013). Evolution of three LOV blue light receptor families in green plants and photosynthetic stramenopiles: phototropin, ZTL/FKF1/LKP2 and aureochrome.Plant Cell Physiol 54, 8-23. |
| [74] | Tao Y, Ferrer JL, Ljung K, Pojer F, Hong F, Long JA, Li L, Moreno JE, Bowman ME, Ivans LJ, Cheng YF, Lim J, Zhao YD, Ballaré CL, Sandberg G, Noel JP, Chory J (2008). Rapid synthesis of auxin via a new tryptophan- dependent pathway is required for shade avoidance in plants. Cell 133, 164-176. |
| [75] | Ugarte CC, Trupkin SA, Ghiglione H, Slafer G, Casal JJ (2010). Low red/far-red ratios delay spike and stem growth in wheat. J Exp Bot 61, 3151-3162. |
| [76] | Vert G, Walcher CL, Chory J, Nemhauser JL (2008). Integration of auxin and brassinosteroid pathways by Auxin Response Factor 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105, 9829-9834. |
| [77] | Woodward AW, Bartel B (2005). Auxin: regulation, action, and interaction. Ann Bot 95, 707-735. |
| [78] | Yamaguchi R, Nakamura M, Mochizuki N, Kay SA, Nagatani A (1999). Light-dependent translocation of a phytochrome B-GFP fusion protein to the nucleus in transgenic Arabidopsis. J Cell Biol 145, 437-445. |
| [79] | Zhang Y, Mayba O, Pfeiffer A, Shi H, Tepperman JM, Speed TP, Quail PH (2013). A quartet of PIF bHLH factors provides a transcriptionally centered signaling hub that regulates seedling morphogenesis through differential expression-patterning of shared target genes in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet 9, e1003244. |
| [80] | Zhao YD (2012). Auxin biosynthesis: a simple two-step pathway converts tryptophan to indole-3-acetic acid in plants. Mol Plant 5, 334-338. |
| [81] | Zhong SW, Shi H, Xue C, Wang L, Xi YP, Li JG, Quail PH, Deng XW, Guo HW (2012). A molecular framework of light-controlled phytohormone action in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol 22, 1530-1535. |
| [1] | 刘旭鹏, 王敏, 韩守安, 朱学慧, 王艳蒙, 潘明启, 张雯. 植物器官脱落调控因素及分子机理研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 472-482. |
| [2] | 陈婷欣, 符敏, 李娜, 杨蕾蕾, 李凌飞, 钟春梅. 铁甲秋海棠DNA甲基转移酶全基因组鉴定及表达分析(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 726-737. |
| [3] | 周玉滢, 陈辉, 刘斯穆. 植物非典型Aux/IAA蛋白应答生长素研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 651-658. |
| [4] | 张悦婧, 桑鹤天, 王涵琦, 石珍珍, 李丽, 王馨, 孙坤, 张继, 冯汉青. 植物对非生物胁迫系统性反应中信号传递的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 122-133. |
| [5] | 孔祥培, 张蒙悦, 丁兆军. 柳暗花明:胞外生长素信号感受的新突破[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 861-865. |
| [6] | 园园, 恩和巴雅尔, 齐艳华. 植物GH3基因家族生物学功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 770-782. |
| [7] | 周淑瑶, 李建明, 毛娟. AtGH3.17调控拟南芥生长素和油菜素甾醇的响应[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 373-384. |
| [8] | 白明义, 彭金荣, 傅向东. 赤霉素和油菜素内酯信号通路双重调控助力小麦新一轮“绿色革命”[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(2): 194-198. |
| [9] | 李季蔓, 靳楠, 胥毛刚, 霍举颂, 陈小云, 胡锋, 刘满强. 不同干旱水平下蚯蚓对番茄抗旱能力的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21488-. |
| [10] | 叶青, 闫晓燕, 陈慧泽, 冯金林, 韩榕. 氮掺杂石墨烯量子点对拟南芥主根生长方向的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(5): 623-634. |
| [11] | 戴琛, 汪瑾, 卢亚萍. 衍生化UPLC-MS法测定酸性植物激素[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(4): 500-507. |
| [12] | 李月, 胡德升, 谭金芳, 梅浩, 王祎, 李慧, 李芳, 韩燕来. 单列毛壳菌通过促进秸秆降解并调控激素响应基因表达促进玉米生长[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(4): 422-433. |
| [13] | 贾利霞, 齐艳华. 生长素代谢、运输及信号转导调控水稻粒型研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(3): 263-275. |
| [14] | 李彬琪, 闫佳慧, 李豪, 辛伟, 田云鹤, 杨贞标, 唐文鑫. 黄瓜卷须缠绕过程中小G蛋白活性变化[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(3): 299-307. |
| [15] | 孟彦彦, 张楠, 熊延. 植物TOR激酶响应上游信号的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 1-11. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||