

植物学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (2): 182-191.DOI: 10.11983/CBB19169 cstr: 32102.14.CBB19169
收稿日期:2019-08-28
接受日期:2019-11-28
出版日期:2020-03-01
发布日期:2020-02-12
通讯作者:
顾彪
基金资助:
Hua Zhao1,Guangda Shao1,2,Wenxin Gao1,2,Biao Gu1,2,*( )
)
Received:2019-08-28
Accepted:2019-11-28
Online:2020-03-01
Published:2020-02-12
Contact:
Biao Gu
摘要: 基因瞬时表达是植物中研究目标基因功能的常用手段。在模式植物拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)中, 相比原生质体和农杆菌介导的基因异源表达技术, 利用粒子轰击进行基因瞬时表达一直鲜有报道。其主要原因是拟南芥叶型相对较小、基因枪操作相对烦琐以及基因表达效率差异较大。该研究通过优化双管基因枪系统, 在营养生长旺盛的拟南芥莲座叶中实现GFP和GUS基因高效表达。同时, 通过GUS报告基因明确了坏死诱导因子BAX、Avh238和ATR13/Rpp13激发拟南芥细胞坏死的表型。但在本氏烟(Nicotiana benthamiana)中明显诱导细胞坏死的Avrblb1/RB基因对, 在拟南芥中却丧失了诱导细胞坏死的活性。由于双管基因枪系统每次轰击时设置平行对照, 可有效降低转化实验中的样本变异度, 为拟南芥及其突变体研究中准确评价基因功能和高通量筛选目标基因提供新的技术参考。
赵华,邵广达,高文鑫,顾彪. 双管基因枪介导的基因瞬时表达技术在拟南芥中的应用. 植物学报, 2020, 55(2): 182-191.
Hua Zhao,Guangda Shao,Wenxin Gao,Biao Gu. The Application of Double-barreled Particle Bombardment for Transient Gene Expression in Arabidopsis. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(2): 182-191.
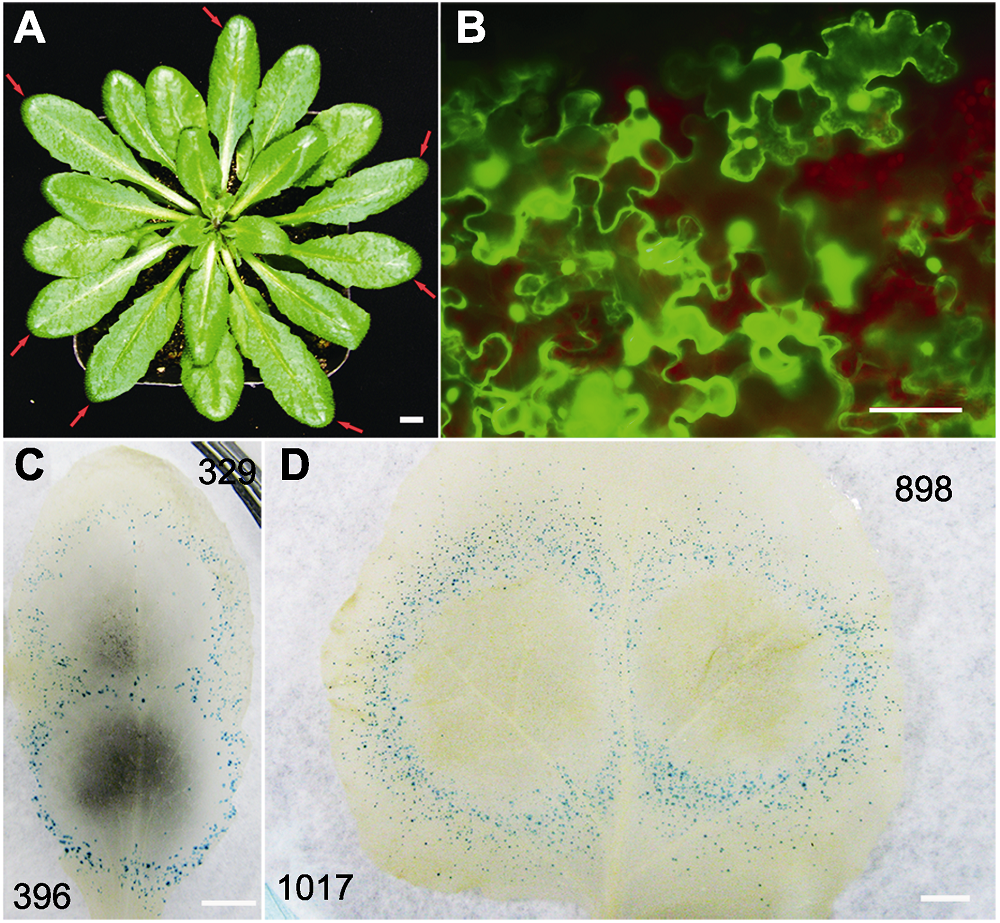

图1 利用双管基因枪在拟南芥和本氏烟叶片中瞬时表达GFP和GUS报告基因 (A) 用于基因瞬时表达的拟南芥植株, 红色箭头所示为选用的莲座叶(Bar=5 mm); (B) 拟南芥叶片中GFP报告基因荧光显微观察(Bar=50 μm); (C), (D) 分别为拟南芥和本氏烟叶片中GUS报告基因的表达情况。黑色数字代表统计的GUS蓝斑数量(Bars=5 mm)。
Figure 1 Transient expression of GFP and GUS reporter genes in Arabidopsis thaliana and Nicotiana benthamiana leaves via double-barreled particle bombardment (A) The rosette leaves (red arrow pointed) of A. thaliana were selected for transient gene expression (Bar=5 mm); (B) Observation of green fluorescent reporter gene (GFP) with fluorescent microscopy (Bar=50 μm); (C), (D) Transient expression of GUS in A. thaliana and N. benthamiana leaves, respectively. Numbers of GUS positive spots are indicated in black numbers (Bars=5 mm).
| Primer name | Forward primer (5'-3') | Reverse primer (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| GFP | CTAGCCCCGGGATGGTGAGCAAGGGCGAG | CTGAGGTACCTTACTTGTACAGCTCGTC |
| GUS | CTAGCCCCGGGATGGTAGATCTGAGGAACC | CTGAGGTACCTCACACGTGATGGTGATGG |
| BAX | CTAGCCCCGGGATGGACGGGTCCGGGGAG | GTGCAGGATCCCTGGAAGAAGATGGGCTGA |
| Avh238 | CTAGCCCCGGGATGGAGGCGAAGCTCTTG | GTGCAGGATCCGTTGGCCAAGCCTGTGTAG |
| Avrblb1 | CTAGCCCCGGGATGGTTTCATCCAATCTCAAC | GTGCAGGTACCCTAGCTAGGGCCAACGTTTTTATC |
| RB | CTAGCCCCGGGATGGCTGAAGCTTTCATTCAAG | GTGCAGGATCCTTAAATATATATATTCACATTAG |
| ATR13 | CTAGCCCCGGGATGAATCTGCTCCACGCCCATG | GTGCAGGATCCTTACTGACTGGCAACGGCAGTC |
| Rpp13 | CTAGCCCCGGGATGGTAGATGCGATCACGGAG | GTGCAGGATCCCTAAACGCTCGCAATCGGTTTG |
| qRB | GAGAAGAGCAATTCCCTGTGC | GTTAGGTGCTGCAATCCCTCTG |
| qUBC9 | CATCGGATAGCCCTTATTCTG | TGGAACACCTTCGTCCTAAAA |
表1 PCR和qRT-PCR引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences of PCR and qRT-PCR
| Primer name | Forward primer (5'-3') | Reverse primer (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| GFP | CTAGCCCCGGGATGGTGAGCAAGGGCGAG | CTGAGGTACCTTACTTGTACAGCTCGTC |
| GUS | CTAGCCCCGGGATGGTAGATCTGAGGAACC | CTGAGGTACCTCACACGTGATGGTGATGG |
| BAX | CTAGCCCCGGGATGGACGGGTCCGGGGAG | GTGCAGGATCCCTGGAAGAAGATGGGCTGA |
| Avh238 | CTAGCCCCGGGATGGAGGCGAAGCTCTTG | GTGCAGGATCCGTTGGCCAAGCCTGTGTAG |
| Avrblb1 | CTAGCCCCGGGATGGTTTCATCCAATCTCAAC | GTGCAGGTACCCTAGCTAGGGCCAACGTTTTTATC |
| RB | CTAGCCCCGGGATGGCTGAAGCTTTCATTCAAG | GTGCAGGATCCTTAAATATATATATTCACATTAG |
| ATR13 | CTAGCCCCGGGATGAATCTGCTCCACGCCCATG | GTGCAGGATCCTTACTGACTGGCAACGGCAGTC |
| Rpp13 | CTAGCCCCGGGATGGTAGATGCGATCACGGAG | GTGCAGGATCCCTAAACGCTCGCAATCGGTTTG |
| qRB | GAGAAGAGCAATTCCCTGTGC | GTTAGGTGCTGCAATCCCTCTG |
| qUBC9 | CATCGGATAGCCCTTATTCTG | TGGAACACCTTCGTCCTAAAA |
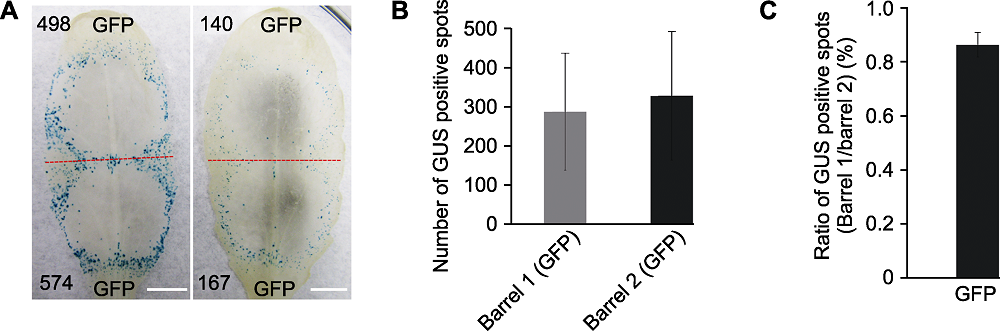
图2 不同拟南芥植株莲座叶中瞬时表达GUS报告基因的效率 (A) 不同莲座叶中双管基因枪介导GFP/GUS混合报告基因瞬时表达, 红色虚线划分轰击后双管基因枪2个枪孔形成的GUS蓝斑, 黑色数字代表形成的GUS蓝斑数量(Bars=5 mm); (B) 统计分析20片莲座叶中叶尖(Barrel 1)和叶柄(Barrel 2)产生GUS蓝斑的数量(误差线表示±标准差, P>0.1); (C) 将图B中的数据, 按照相同叶片Barrel 1和Barrel 2产生GUS蓝斑数量的比率进行统计分析(误差线表示±标准差)。每次选取2株拟南芥的10个叶片进行测试, 实验重复2次。将Barrel 1与Barrel 2产生GUS蓝斑数量进行对数转换后用威尔科克森符号轶和确定统计差异。
Figure 2 The efficiency of transient expression of GUS gene in different rosette leaves of Arabidopsis thaliana (A) Co-bombardment of GFP/GUS gene mixture in different rosette leaves, the red dotted line separates two positions produced by double-barreled particle bombardment, numbers of GUS blue spots are indicated in black numbers (Bars=5 mm); (B) Statistic analysis of GUS spots counted from the tip of leaf blade (Barrel 1) and petiole (Barrel 2) (error bar represents ± SD, P>0.1); (C) Ratios of GUS spot numbers in Barrel 1 and Barrel 2 of the same leaf (error bar represents ± SD). Ten rosette leaves from two A. thaliana plants were tested and the test was repeated twice. Statistical analysis by Wilcoxon rank sum test using log ratios of GUS spot numbers in Barrel 1 and Barrel 2.
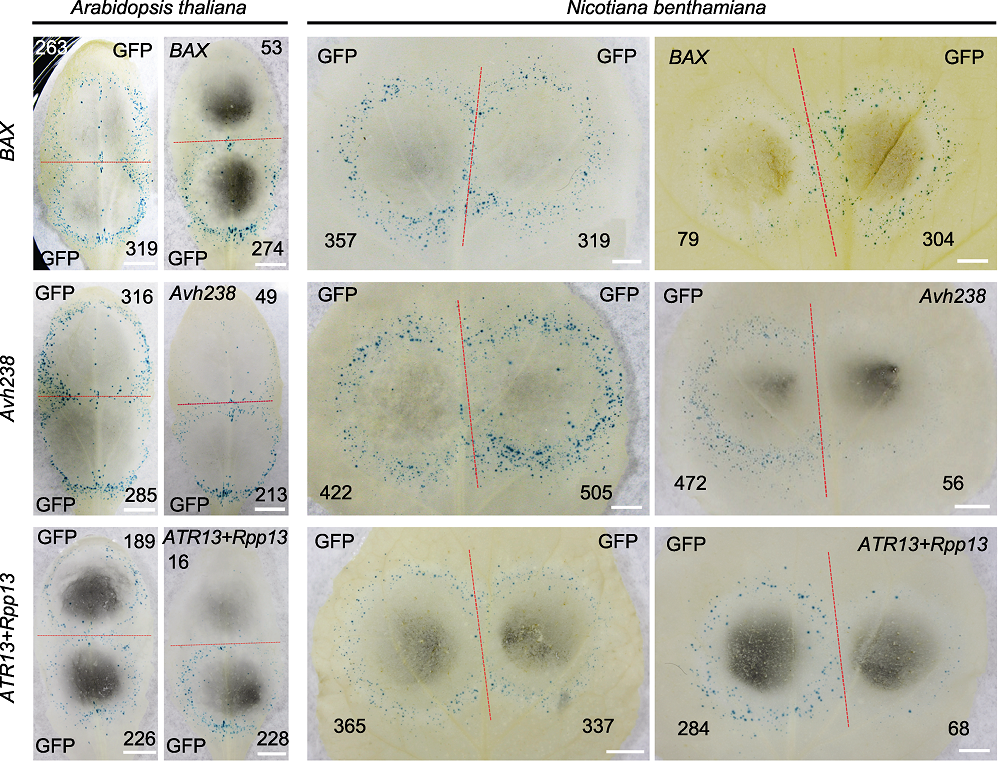
图3 拟南芥和本氏烟叶片中的病原菌效应基因致死活性检测 =利用双管基因枪在拟南芥和本氏烟叶片上瞬时表达哺乳动物细胞凋亡因子BAX、大豆疫霉菌RxLR效应基因Avh238以及拟南芥霜霉菌效应基因ATR13和拟南芥抗病基因Rpp13后, GUS蓝斑指示的细胞坏死情况, GFP为对照。红色虚线划分轰击后双管基因枪2个枪孔形成的GUS蓝斑, 黑色数字代表形成的GUS蓝斑数量(Bars=5 mm)。
Figure 3 Cell death induction by various pathogen effectors in Arabidopsis thaliana and Nicotiana benthamiana leaves Mammalian apoptosis inducer BAX, RxLR effector gene Avh238 of Phytophthora sojae, effector gene ATR13 of Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis and disease resistance gene Rpp13 of A. thaliana gene pairs were transiently expressed in leaves of A. thaliana and N. benthamiana by double-barreled particle bombardment, cell necrosis was indicated by GUS blue spots, with GFP as control. The red dotted line separates two positions produced by co-bombardment, numbers of GUS spots are indicated in black numbers (Bars=5 mm).
| BAX ± SD | Avh238 ± SD | ATR13/Rpp13 ± SD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GFP/GFP | BAX/GFP | GFP/GFP | Avh238/GFP | ATR13 + Rpp13/GFP | |
| Arabidopsis thaliana | 0.92±0.13 | 0.23±0.13* | 0.84±0.17 | 0.94±0.15 | 0.22±0.08* |
| Nicotiana benthamiana | 1.05±0.23 | 0.13±0.07* | 0.92±0.21 | 0.94±0.10 | 0.22±0.05* |
表2 在拟南芥和本氏烟叶片中测试BAX、Avh238和ATR13/Rpp13诱导细胞坏死的活性
Table 2 Measurement of cell death induction activities by BAX, Avh238 and ATR13/Rpp13 in Arabidopsis thaliana and Nicotiana benthamiana
| BAX ± SD | Avh238 ± SD | ATR13/Rpp13 ± SD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GFP/GFP | BAX/GFP | GFP/GFP | Avh238/GFP | ATR13 + Rpp13/GFP | |
| Arabidopsis thaliana | 0.92±0.13 | 0.23±0.13* | 0.84±0.17 | 0.94±0.15 | 0.22±0.08* |
| Nicotiana benthamiana | 1.05±0.23 | 0.13±0.07* | 0.92±0.21 | 0.94±0.10 | 0.22±0.05* |
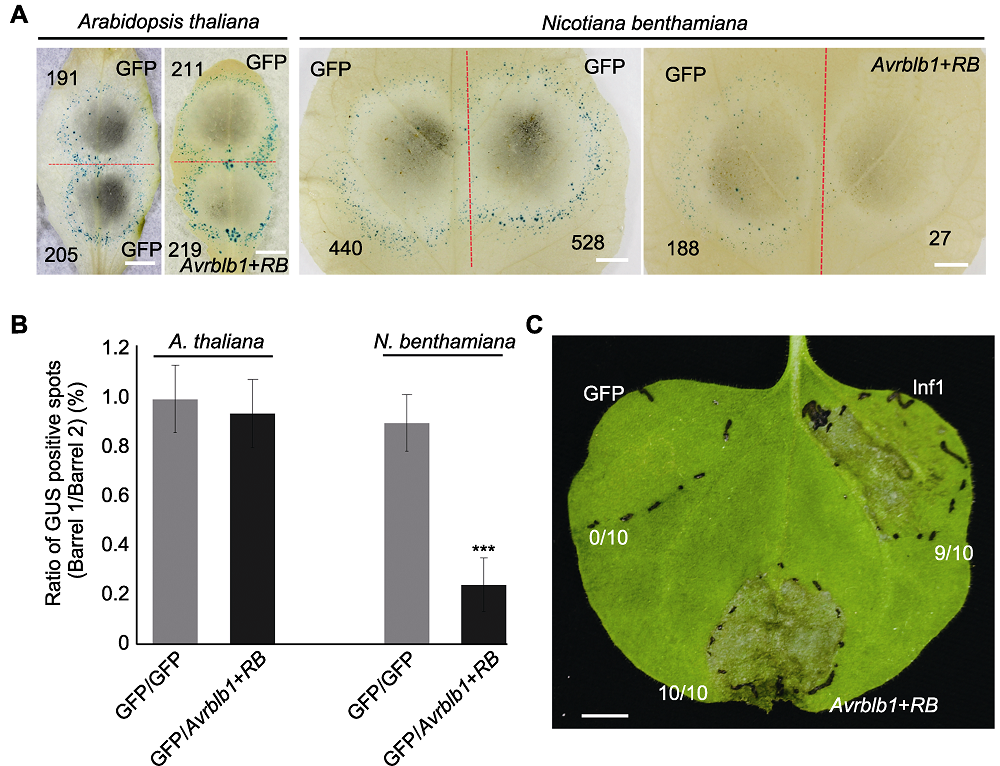
图4 拟南芥和本氏烟叶片中致病疫霉效应基因Avrblb1和马铃薯抗病基因RB致死活性检测 (A) 拟南芥和本氏烟中双管基因枪介导Avrblb1/Rpp13基因对瞬时表达, GFP为对照, 红色虚线划分轰击后双管基因枪2个枪孔形成的GUS蓝斑, 黑色数字指示GUS蓝斑数量(Bars=5 mm); (B) GUS蓝斑比率(拟南芥和本氏烟各10个叶片, 实验重复2次, 误差线表示±标准差)。处理与对照产生GUS斑数进行对数转换后用威尔科克森符号轶和确定统计差异, ***表示差异极显著(P<0.001); (C) 本氏烟叶片中农杆菌介导Avrblb1/RB瞬时表达, GFP为阴性对照, PAMP分子Inf1为阳性对照, 注射4天后拍照。每个处理重复注射10次(Bar=5 mm)。
Figure 4 Cell death induction triggered by Avrblb1 of Phytophthora infestans and RB of Solanum tuberosum in Arabidopsis thaliana and Nicotiana benthamiana leaves (A) Co-bombardment mediated transient expression of Avrblb1/Rpp13 gene pair in A. thaliana and N. benthamiana leaves, the red dotted line separates two positions produced by co-bombardment, numbers of GUS spots are indicated in black numbers (Bars=5 mm); (B) Ratio of GUS positive spots (ten leaves from each plant were tested, and the test was repeated twice, error bar represents ± SD). P values for treatments and the control were calculated from the log ratios using the Wilcoxon rank sum test, *** indicates extremely significant differences (P<0.001); (C) Agrobacterium-mediated transient expression of Avrblb1/RB in N. benthamiana leaves, GFP and Inf1 were used as negative and positive control, respectively. Pictures were taken 4 days post infiltration, each treatment contains 10 replicates (Bar=5 mm).
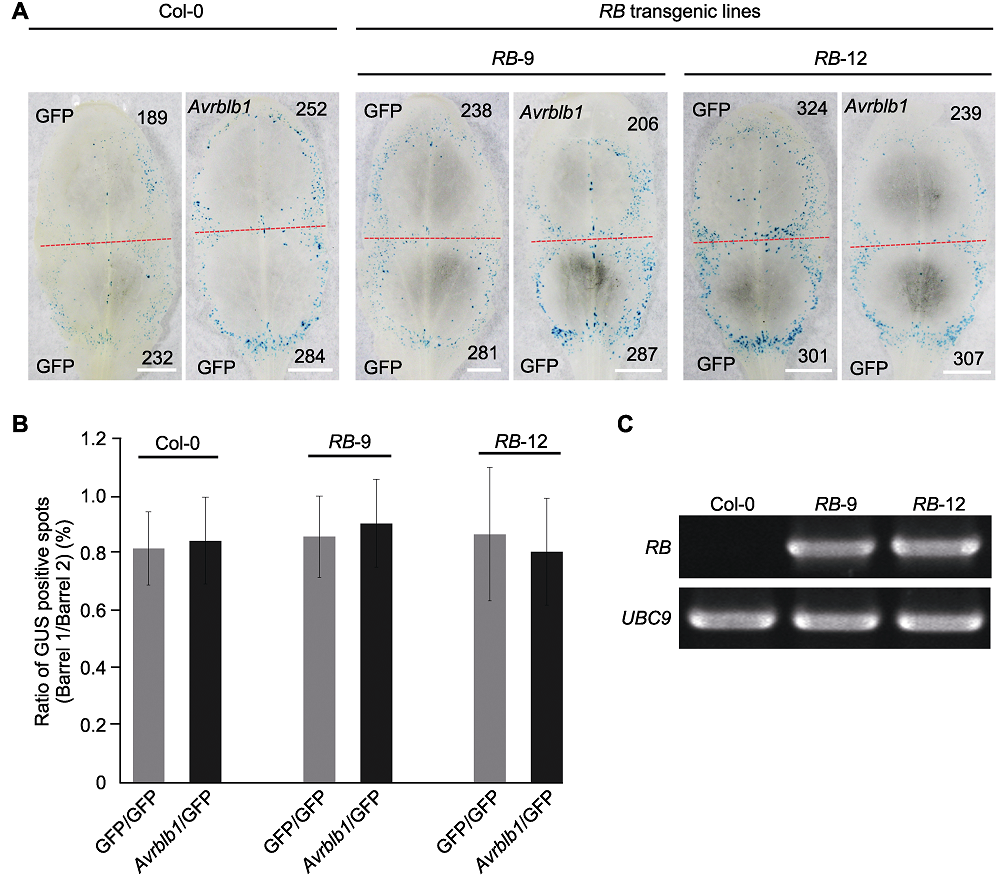
图5 拟南芥RB转基因株系RB-9和RB-12中效应基因Avrblb1致死活性检测 (A) 在拟南芥RB转基因株系RB-9和RB-12中瞬时表达Avrblb1后GUS报告基因表达分析, GFP为对照(红色虚线划分轰击后双管基因枪2个枪孔形成的GUS蓝斑, 黑色数字指示GUS蓝斑数量(Bars=5 mm)); (B) 在拟南芥RB转基因株系中瞬时表达Avrblb1基因后的GUS蓝斑数量统计(拟南芥和本氏烟各10片叶, 实验重复2次, 处理与对照产生GUS斑数进行对数转换后用威尔科克森符号轶和确定统计差异(误差线表示±标准差, P>0.1)); (C) 利用RT-PCR检测拟南芥RB转基因株系RB-9和RB-12中RB基因的表达, UBC9为内参基因。
Figure 5 Measurement of cell death induction by effector gene Avrblb1 in Arabidopsis transgenic line RB-9 and RB-12 (A) Co-bombardment mediated transient expression of Avrblb1 in transgenic lines RB-9 and RB-12, with GFP as control (the red dotted line separates two positions produced by co-bombardment, numbers of GUS spots are indicated in black numbers (Bars=5 mm)); (B) The diagram showed that transient expression of Avrblb1 in RB transgenic lines (ten leaves of each plant were tested, and the test was repeated twice, P values for treatments and the control were calculated from the log ratios using the Wilcoxon rank sum test (error bar represents ± SD, P>0.1)); (C) The RT-PCR detection of RB expressed in transgenic line RB-9 and RB-12, UBC9 was used as the reference gene.
| [1] | Champouret N, Bouwmeester K, Rietman H, van der Lee T, Maliepaard C, Heupink A, van de Vondervoort PJI, Jacobsen E, Visser RGF, van der Vossen EAG, Govers F, Vleeshouwers VGAA ( 2009). Phytophthora infestans isolates lacking class I ipiO variants are virulent on Rpi-blb1 potato. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 22, 1535-1545. |
| [2] | Coll NS, Vercammen D, Smidler A, Clover C, Van Breusegem F, Dangl JF, Epple P ( 2010). Arabidopsis type I metacaspases control cell death. Science 330, 1393-1397. |
| [3] | Dong SM, Yin WX, Kong GH, Yang XY, Qutob D, Chen QH, Kale SD, Sui YY, Zhang ZG, Dou DL, Zheng XB, Gijzen M, Tyler BM, Wang YC ( 2011). Phytophthora sojae avirulence effector Avr3b is a secreted NADH and ADP-ribose pyrophosphorylase that modulates plant immunity. PLoS Pathog 7, e1002353. |
| [4] | Dou DL, Kale SD, Wang XL, Chen YB, Wang QQ, Wang X, Jiang RHY, Arredondo FD, Anderson RG, Thakur PB, McDowell JM, Wang YC, Tyler BM ( 2008). Conserved C-terminal motifs required for avirulence and suppression of cell death by Phytophthora sojae effector Avr1b. Plant Cell 20, 1118-1133. |
| [5] | Gu B, Kale SD, Wang QH, Wang DH, Pan QN, Cao H, Meng YL, Kang ZS, Tyler BM, Shan WX ( 2011). Rust secreted protein Ps87 is conserved in diverse fungal pathogens and contains a RXLR-like motif sufficient for translocation into plant cells. PLoS One 6, e27217. |
| [6] | Kale SD, Tyler BM ( 2011). Assaying effector function in Planta using double-barreled particle bombardment. In: McDowell J, ed. Plant Immunity. Methods in Molecular Biology (Methods and Protocols), Vol. 712. New York: Humana Press. pp. 153-172. |
| [7] | Koornneef M, Meinke D ( 2010). The development of Arabidopsis as a model plant. Plant J 61, 909-921. |
| [8] | Mangano S, Gonzalez CD, Petruccelli S ( 2014). Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transient transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana leaves. In: Sanchez-Serrano JJ, Salinas J, eds. Arabidopsis Protocols, Methods in Molecular Biology (Methods and Protocols), Vol. 1062. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press. pp. 165-173. |
| [9] | Sohn KH, Lei R, Nemri A, Jones JDG ( 2007). The downy mildew effector proteins ATR1 and ATR13 promote disease susceptibility in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 19, 4077-4090. |
| [10] | Tsuda K, Qi YP, Nguyen LV, Bethke G, Tsuda Y, Glazebrook J, Katagiri F ( 2012). An efficient Agrobacterium-mediated transient transformation of Arabidopsis. Plant J 69, 713-719. |
| [11] | Ueki S, Lacroix B, Krichevsky A, Lazarowitz SG, Citovsky V ( 2009). Functional transient genetic transformation of Arabidopsis leaves by biolistic bombardment. Nat Protoc 4, 71-77. |
| [12] | Wang QQ, Han CZ, Ferreira AO, Yu XL, Ye WW, Tripathy S, Kale SD, Gu B, Sheng YT, Sui YY, Wang XL, Zhang ZG, Cheng BP, Dong SM, Shan WX, Zheng XB, Dou DL, Tyler BM, Wang YC ( 2011a). Transcriptional programming and functional interactions within the Phytophthora sojae RXLR effector repertoire. Plant Cell 23, 2064-2086. |
| [13] | Wang XJ, Tang CL, Zhang HC, Xu JR, Liu B, Lv J, Han DJ, Huang LL, Kang ZS ( 2011b). TaDAD2, a negative regulator of programmed cell death, is important for the interaction between wheat and the stripe rust fungus. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 24, 79-90. |
| [14] | Weigel D, Glazebrook J ( 2011). Arabidopsis: a Laboratory Manual. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. pp. 119-140. |
| [15] | Yang B, Wang QQ, Jing MF, Guo BD, Wu JW, Wang HN, Wang Y, Lin L, Wang Y, Ye WW, Dong SM, Wang YC ( 2017). Distinct regions of the Phytophthora essential effector Avh238 determine its function in cell death activation and plant immunity suppression. New Phytol 214, 361-375. |
| [16] | Yoo SD, Cho YH, Sheen J ( 2007). Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplasts: a versatile cell system for transient gene expression analysis. Nat Protoc 2, 1565-1572. |
| [1] | 刘雨函, 曹启江, 张诗晗, 李益慧, 王菁, 谭晓萌, 刘筱儒, 王显玲. 拟南芥AtFTCD-L参与根系响应土壤紧实度的机制研究[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | 曹雪敏, 包颖, 张悦新, 李瑞杰, 苏健馨, 张蔚. 野蔷薇组培快繁和高效瞬时表达体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 235-245. |
| [3] | 景艳军, 林荣呈. 蓝光受体CRY2化身“暗黑舞者”[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 878-882. |
| [4] | 罗燕, 刘奇源, 吕元兵, 吴越, 田耀宇, 安田, 李振华. 拟南芥光敏色素突变体种子萌发的光温敏感性[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 752-762. |
| [5] | 杨继轩, 王雪霏, 顾红雅. 西藏野生拟南芥开花时间变异的遗传基础[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 373-382. |
| [6] | 陈艳晓, 李亚萍, 周晋军, 解丽霞, 彭永彬, 孙伟, 和亚男, 蒋聪慧, 王增兰, 郑崇珂, 谢先芝. 拟南芥光敏色素B氨基酸位点突变对其结构与功能的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 481-494. |
| [7] | 方妍力, 田传玉, 苏如意, 刘亚培, 王春连, 陈析丰, 郭威, 纪志远. 水稻抗细菌性条斑病基因挖掘与初定位[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 1-9. |
| [8] | 田传玉, 方妍力, 沈晴, 王宏杰, 陈析丰, 郭威, 赵开军, 王春连, 纪志远. 2019-2021年我国南方稻区白叶枯病菌的毒力与遗传多样性调查研究[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 743-749. |
| [9] | 王钢, 王二涛. “卫青不败由天幸”——WeiTsing的广谱抗根肿病机理被揭示[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 356-358. |
| [10] | 杨永青, 郭岩. 植物细胞质外体pH感受机制的解析[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(4): 409-411. |
| [11] | 支添添, 周舟, 韩成云, 任春梅. PAD4突变加速拟南芥酪氨酸降解缺陷突变体sscd1的程序性细胞死亡[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(3): 288-298. |
| [12] | 李艳艳, 齐艳华. 植物Aux/IAA基因家族生物学功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 30-41. |
| [13] | 王田幸子, 朱峥, 陈悦, 刘玉晴, 燕高伟, 徐珊, 张彤, 马金姣, 窦世娟, 李莉云, 刘国振. 水稻OsWRKY42是Xa21介导的抗白叶枯病途径新元件[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(6): 687-698. |
| [14] | 李秋信, 迟伟, 季代丽. CURT1调控类囊体膜弯曲的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(4): 462-469. |
| [15] | 车永梅, 孙艳君, 卢松冲, 侯丽霞, 范欣欣, 刘新. AtMYB77促进NO合成参与调控干旱胁迫下拟南芥侧根发育[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(4): 404-413. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||