

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2021, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (1): 6-9.DOI: 10.11983/CBB20190 cstr: 32102.14.CBB20190
• COMMENTARIES • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2020-11-25
Accepted:2021-01-05
Online:2021-01-01
Published:2021-01-15
Contact:
Tongda Xu
Rongfeng Huang, Tongda Xu. Auxin Regulates the Lateral Root Development Through MAPK-mediated VLCFAs Biosynthesis[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(1): 6-9.
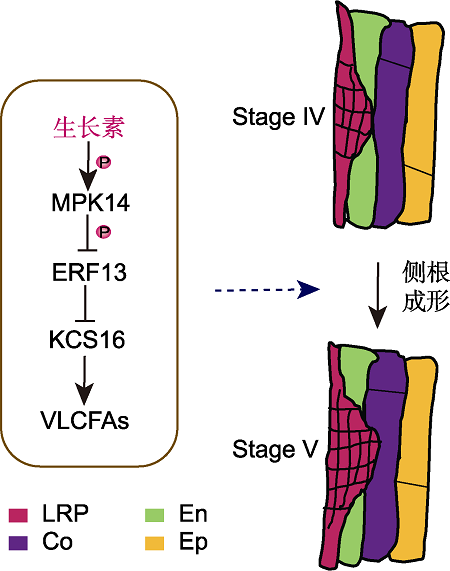
Figure 1 A working model of MPK14-mediated auxin signaling to control lateral root development LRP: Lateral root primordium; En: Endodermis; Co: Cortex; Ep: Epidermis
| [1] | 黎家, 李传友 (2019). 新中国成立70年来植物激素研究进展. 中国科学: 生命科学 49, 1227-1281. |
| [2] |
Atta R, Laurens L, Boucheron-Dubuisson E, Guivarc'h A, Carnero E, Giraudat-Pautot V, Rech P, Chriqui D (2009). Pluripotency of Arabidopsis xylem pericycle underlies shoot regeneration from root and hypocotyl explants grown in vitro. Plant J 57, 626-644.
URL PMID |
| [3] |
Bach L, Faure JD (2010). Role of very-long-chain fatty acids in plant development, when chain length does matter. Comptes Rendus Biologies 333, 361-370.
URL PMID |
| [4] | Bach L, Gissot L, Marion J, Tellier F, Moreau P, Satiat-Jeunemaître B, Palauqui JC, Napier JA, Faure JD (2011). Very-long-chain fatty acids are required for cell plate formation during cytokinesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Cell Sci 124, 3223-3234. |
| [5] |
Che P, Lall S, Howell SH (2007). Developmental steps in acquiring competence for shoot development in Arabidopsis tissue culture. Planta 226, 1183-1194.
URL PMID |
| [6] | De Rybel B, Vassileva V, Parizot B, Demeulenaere M, Grunewald W, Audenaert D, Van Campenhout J, Overvoorde P, Jansen L, Vanneste S, Möller B, Wilson M, Holman T, Van Isterdael G, Brunoud G, Vuylsteke M, Vernoux T, De Veylder L, Inzé D, Weijers D, Bennett MJ, Beeckman T (2010). A novel aux/IAA28 signaling cascade activates GATA23-dependent specification of lateral root founder cell identity. Curr Biol 20, 1697-1706. |
| [7] | Goh T, Kasahara H, Mimura T, Kamiya Y, Fukaki H (2012). Multiple AUX/IAA-ARF modules regulate lateral root formation: the role of Arabidopsis SHY2/IAA3 -mediated auxin signaling. Philos Trans Roy Soc B: Biol Sci 367, 1461-1468. |
| [8] | Hamann T, Benkova E, Baurle I, Kientz M, Jürgens G (2002). The Arabidopsis BODENLOS gene encodes an auxin response protein inhibiting MONOPTEROS-mediated embryo patterning. Genes Dev 16, 1610-1615. |
| [9] | He YX, Meng XZ (2020). MAPK signaling: emerging roles in lateral root formation. Trends Plant Sci 25, 126-129. |
| [10] | Huang RF, Zheng R, He J, Zhou ZM, Wang JC, Xiong Y, Xu TD (2019). Noncanonical auxin signaling regulates cell division pattern during lateral root development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116, 21285-21290. |
| [11] | Lavenus J, Goh T, Roberts I, Guyomarc'h S, Lucas M, De Smet I, Fukaki H, Beeckman T, Bennett M, Laplaze L (2013). Lateral root development in Arabidopsis: fifty shades of auxin. Trends Plant Sci 18, 450-458. |
| [12] |
Lee HW, Kim NY, Lee DJ, Kim J (2009). LBD18/ ASL20 regulates lateral root formation in combination with LBD16/ASL18 downstream of ARF7 and ARF19 in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 151, 1377-1389.
URL PMID |
| [13] | Lv BS, Wei KJ, Hu KQ, Tian T, Zhang F, Yu ZP, Zhang DJ, Su YH, Sang YL, Zhang XS, Ding ZJ (2021). MPK14- mediated auxin signaling controls lateral root development via ERF13-regulated very-long-chain fatty acid biosynthesis. Mol Plant 14, 285-297. |
| [14] | Malamy JE, Benfey PN (1997). Organization and cell differentiation in lateral roots of Arabidopsis thaliana. Development 124, 33-44. |
| [15] |
Nakagami H, Pitzschke A, Hirt H (2005). Emerging MAP kinase pathways in plant stress signaling. Trends Plant Sci 10, 339-346.
URL PMID |
| [16] |
Péret B, De Rybel B, Casimiro I, Benková E, Swarup R, Laplaze L, Beeckman T, Bennett MJ (2009). Arabidopsis lateral root development: an emerging story. Trends Plant Sci 14, 399-408.
URL PMID |
| [17] |
Pitzschke A, Schikora A, Hirt H (2009). MAPK cascade signaling networks in plant defence. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12, 421-426.
URL PMID |
| [18] | Qin YM, Hu CY, Pang Y, Kastaniotis AJ, Hiltunen JK, Zhu YX (2007). Saturated very-long-chain fatty acids promote cotton fiber and Arabidopsis cell elongation by activating ethylene biosynthesis. Plant Cell 19, 3692-3704. |
| [19] | Roudier F, Gissot L, Beaudoin F, Haslam R, Michaelson L, Marion J, Molino D, Lima A, Bach L, Morin H, Tellier F, Palauqui JC, Bellec Y, Renne C, Miquel M, DaCosta M, Vignard J, Rochat C, Markham JE, Moreau P, Napier J, Faure JD (2010). Very-long-chain fatty acids are involved in polar auxin transport and developmental patterning in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 22, 364-375. |
| [20] | Seo PJ, Park CM (2011). Cuticular wax biosynthesis as a way of inducing drought resistance. Plant Signal Behav 6, 1043-1045. |
| [21] |
Shang BS, Xu CY, Zhang XX, Cao HF, Xin W, Hu YX (2016). Very-long-chain fatty acids restrict regeneration capacity by confining pericycle competence for callus formation in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113, 5101-5106.
DOI URL PMID |
| [22] |
Smirnova A, Leide J, Riederer M (2013). Deficiency in a very-long-chain fatty acid β-ketoacyl-coenzyme a synthase of tomato impairs microgametogenesis and causes floral organ fusion. Plant Physiol 161, 196-209.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Sugimoto K, Jiao YL, Meyerowitz EM (2010). Arabidopsis regeneration from multiple tissues occurs via a root development pathway. Dev Cell 18, 463-471.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Xu J, Zhang SQ (2015). Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in signaling plant growth and development. Trends Plant Sci 20, 56-64. |
| [25] | Zhu QK, Shao YM, Ge ST, Zhang MM, Zhang TS, Hu XT, Liu YD, Walker J, Zhang SQ, Xu J (2019). A MAPK cascade downstream of IDA-HAE/HSL2 ligand-receptor pair in lateral root emergence. Nat Plants 5, 414-423. |
| [1] | Yuying Zhou, Hui Chen, Simu Liu. Research Progress on Auxin Responsive Non-canonical Aux/IAA Proteins in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(4): 651-658. |
| [2] | Xiangpei Kong, Mengyue Zhang, Zhaojun Ding. There Is a Way Out-new Breakthroughs in Extracellular Auxin Sensing [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(6): 861-865. |
| [3] | Yuan Yuan, Enhebayaer, Qi Yanhua. Research Advances in Biological Functions of GH3 Gene Family in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(5): 770-782. |
| [4] | Shuyao Zhou, Jianming Li, Juan Mao. AtGH3.17-mediated Regulation of Auxin and Brassinosteroid Response in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(3): 373-384. |
| [5] | Ye Qing, Yan Xiaoyan, Chen Huize, Feng Jinlin, Han Rong. Effect of Nitrogen-doped Graphene Quantum Dots on Growth Direction of Primary Root in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(5): 623-634. |
| [6] | Binqi Li, Jiahui Yan, Hao Li, Wei Xin, Yunhe Tian, Zhenbiao Yang, Wenxin Tang. Changes of Small GTPases Activity During Cucumber Tendril Winding [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(3): 299-307. |
| [7] | Lixia Jia, Yanhua Qi. Advances in the Regulation of Rice (Oryza sativa) Grain Shape by Auxin Metabolism, Transport and Signal Transduction [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(3): 263-275. |
| [8] | Jingwen Wang, Xingjun Wang, Changle Ma, Pengcheng Li. A Review on the Mechanism of Ribosome Stress Response in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(1): 80-89. |
| [9] | Yanyan Li, Yanhua Qi. Advances in Biological Functions of Aux/IAA Gene Family in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(1): 30-41. |
| [10] | Yongmei Che, Yanjun Sun, Songchong Lu, Lixia Hou, Xinxin Fan, Xin Liu. AtMYB77 Involves in Lateral Root Development via Regulating Nitric Oxide Biosynthesis under Drought Stress in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(4): 404-413. |
| [11] | Yuqing Lin, Yanhua Qi. Advances in Auxin Efflux Carrier PIN Proteins [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(2): 151-165. |
| [12] | Yuting Yao,Jiaqi Ma,Xiaoli Feng,Jianwei Pan,Chao Wang. A Role of Arabidopsis Phosphoinositide Kinase, FAB1, in Root Hair Growth [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(2): 126-136. |
| [13] | Zhenmei He,Dongming Li,Yanhua Qi. Advances in Biofunctions of the ABCB Subfamily in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(6): 688-698. |
| [14] | Shuhui Zhang,Hong Wang,Wenru Wang,Xuelian Wu,Yuansong Xiao,Futian Peng. Effects of Sucrose on Seedling Growth and Development and SnRK1 Activity in Prunus persica [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(6): 744-752. |
| [15] | Kongqin Hu, Zhaojun Ding. A TIR1-independent Auxin Signaling Module [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(3): 293-295. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
