

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (4): 611-620.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24113 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24113
• TECHNIQUES AND METHODS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Tong Li1, Churan Li1, Zhiyu Zhang1, Xiaoman Fu1, Yun Liu1, Yingjun Zhang2,*( ), Liying Yang3, Ping Zhao1,*(
), Liying Yang3, Ping Zhao1,*( )
)
Received:2024-07-23
Accepted:2024-12-26
Online:2025-07-10
Published:2024-12-27
Contact:
*E-mail: zhangyj@mail.kib.ac.cn;hypzhao2022@163.com
Tong Li, Churan Li, Zhiyu Zhang, Xiaoman Fu, Yun Liu, Yingjun Zhang, Liying Yang, Ping Zhao. A Preliminary Study on Tissue Culture and Rapid Propagation Technology of Phyllanthus acidus[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(4): 611-620.
| Treatments | 6-BA (mg·L-1) | NAA (mg·L-1) | Number of explants | Adventitious bud induction rate (%) | Growth condition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 90 | 27.78±1.11 b | ++ |
| 2 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 90 | 22.22±4.01 c | ++ |
| 3 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 90 | 20.00±1.92 c | + |
| 4 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 90 | 53.33±7.70 ab | ++ |
| 5 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 90 | 62.22±4.00 a | ++ |
| 6 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 90 | 70.00±15.28 a | + |
| 7 | 2.0 | 0.1 | 90 | 66.67±6.67 a | ++ |
| 8 | 2.0 | 0.2 | 90 | 76.67±14.53 a | +++ |
| 9 | 2.0 | 0.3 | 90 | 75.56±11.60 a | + |
Table 1 Effects of different proportions of plant growth regulators on axillary bud induction of Phyllanthus acidus
| Treatments | 6-BA (mg·L-1) | NAA (mg·L-1) | Number of explants | Adventitious bud induction rate (%) | Growth condition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 90 | 27.78±1.11 b | ++ |
| 2 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 90 | 22.22±4.01 c | ++ |
| 3 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 90 | 20.00±1.92 c | + |
| 4 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 90 | 53.33±7.70 ab | ++ |
| 5 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 90 | 62.22±4.00 a | ++ |
| 6 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 90 | 70.00±15.28 a | + |
| 7 | 2.0 | 0.1 | 90 | 66.67±6.67 a | ++ |
| 8 | 2.0 | 0.2 | 90 | 76.67±14.53 a | +++ |
| 9 | 2.0 | 0.3 | 90 | 75.56±11.60 a | + |
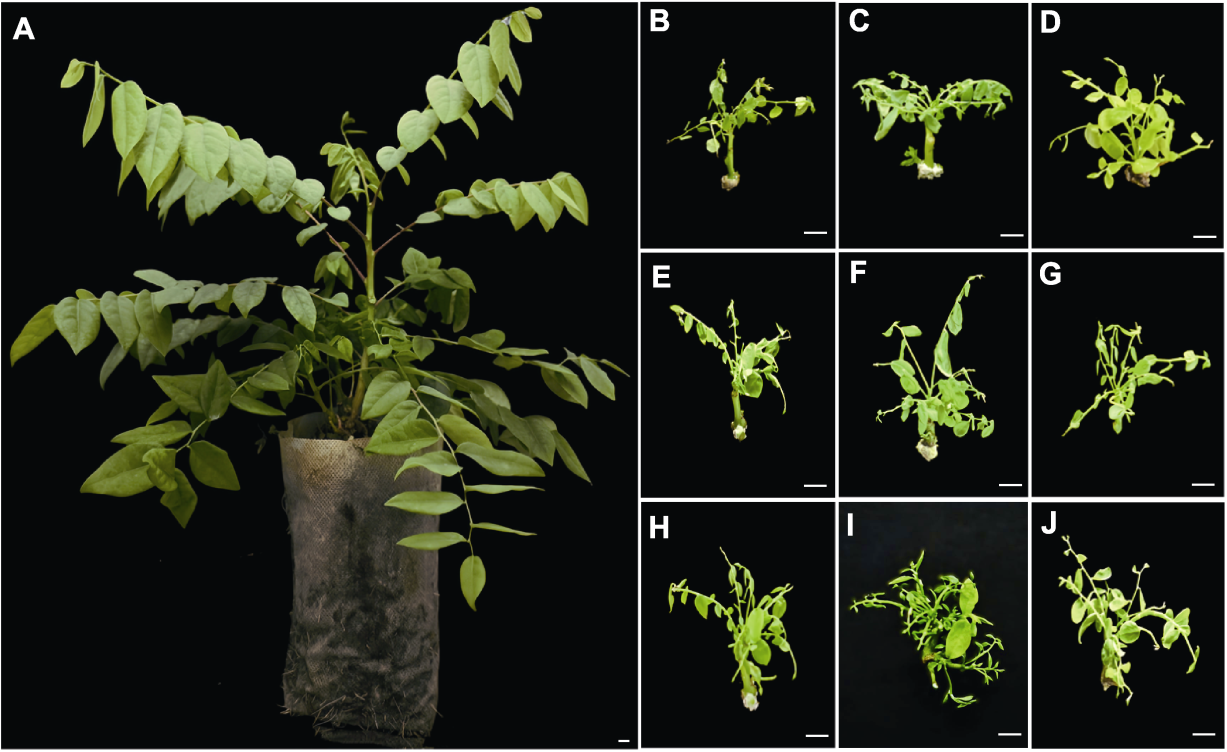

Figure 1 Effects of different plant growth regulator ratios on axillary bud induction of Phyllanthus acidus (A) P. acidus plant; (B)-(D) The growth status of tissue cultured plantlets after 25 days of initial cultivation in different mass concentration ratios of 6-BA and NAA (concentration ratios of 6-BA and NAA in B-J are the same as shown in Table 1). Bars=1 cm
| Treatments | Culture medium | 6-BA (mg·L-1) | NAA (mg·L-1) | Number of explants | Adventitious bud induction rate (%) | Growth condition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MS | 2.0 | 0.2 | 90 | 81.11±2.22 a | +++ |
| 2 | 1/2 MS | 2.0 | 0.2 | 90 | 58.89±2.94 b | + |
| 3 | 1/3 MS | 2.0 | 0.2 | 90 | 52.00±1.17 b | + |
Table 2 Effects of different basic media on axillary bud induction of Phyllanthus acidus
| Treatments | Culture medium | 6-BA (mg·L-1) | NAA (mg·L-1) | Number of explants | Adventitious bud induction rate (%) | Growth condition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MS | 2.0 | 0.2 | 90 | 81.11±2.22 a | +++ |
| 2 | 1/2 MS | 2.0 | 0.2 | 90 | 58.89±2.94 b | + |
| 3 | 1/3 MS | 2.0 | 0.2 | 90 | 52.00±1.17 b | + |

Figure 2 Effects of different basic media on axillary bud induction of Phyllanthus acidus (A) The growth status of tissue cultured plantlets after 25 days of initial cultivation of explants in MS medium; (B) The growth status of tissue cultured plantlets after 25 days of initial cultivation of explants in 1/2 MS medium; (C) The growth status of tissue cultured plantlets after 25 days of initial cultivation of explants in 1/3 MS medium. Bars=1 cm
| Treatments | 6-BA (mg·L-1) | IBA (mg·L-1) | Number of explants | Number of buds after proliferation | Multiplication factor | Plant height (cm) | Growth condition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 90 | 159±0.58 a | 1.77±0.13 a | 2.71±0.06 b | ++ |
| 2 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 90 | 168±1.53 a | 1.86±0.20 a | 3.34±0.07 a | +++ |
| 3 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 90 | 104±0.33 b | 1.16±0.01 b | 2.00±0.06 c | + |
Table 3 Effects of different proportions of plant growth regulators on subgeneration and proliferation of Phyllanthus acidus
| Treatments | 6-BA (mg·L-1) | IBA (mg·L-1) | Number of explants | Number of buds after proliferation | Multiplication factor | Plant height (cm) | Growth condition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 90 | 159±0.58 a | 1.77±0.13 a | 2.71±0.06 b | ++ |
| 2 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 90 | 168±1.53 a | 1.86±0.20 a | 3.34±0.07 a | +++ |
| 3 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 90 | 104±0.33 b | 1.16±0.01 b | 2.00±0.06 c | + |
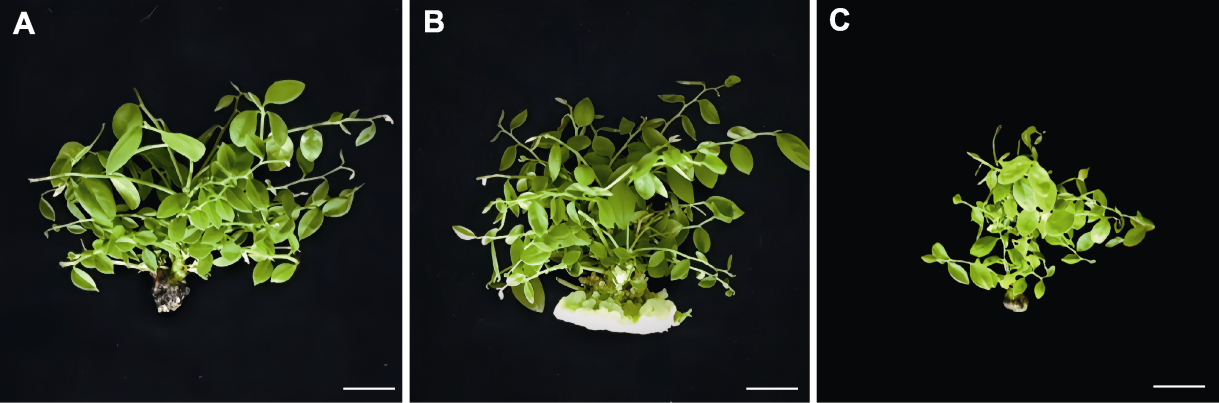

Figure 3 Effects of different proportions of plant growth regulators on subgeneration and proliferation of Phyllanthus acidus (A) The growth status of tissue cultured plantlets after 25 days of subculture proliferation in 1.0 mg·L-1 6-BA+0.1 mg·L-1 IBA medium; (B) The growth status of tissue cultured plantlets after 25 days of subculture proliferation in 1.0 mg·L-1 6-BA+0.2 mg·L-1 IBA medium; (C) The growth status of tissue cultured plantlets after 25 days of subculture proliferation in 1.0 mg·L-1 6-BA+0.3 mg·L-1 IBA medium. Bars=1 cm
| Treatments | NAA (mg·L-1) | IBA (mg·L-1) | Number of explants | Rooting rate (%) | Rooting number (n) | Root length (cm) | Growth condition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.5 | 0 | 30 | 60.00±11.55 ab | 8.40±0.70 a | 0.99±0.06 d | ++ |
| 2 | 1.0 | 0 | 30 | 66.67±6.67 a | 9.00±0.84 a | 1.02±0.05 d | ++ |
| 3 | 1.5 | 0 | 30 | 33.33±8.82 b | 1.50±0.22 d | 0.91±0.06 d | + |
| 4 | 0 | 0.5 | 30 | 76.67±8.82 a | 2.70±0.37 d | 1.87±0.08 c | ++ |
| 5 | 0 | 1.0 | 30 | 70.00±15.28 a | 4.80±4.80 c | 2.70±0.15 b | +++ |
| 6 | 0 | 1.5 | 30 | 83.33±6.67 a | 6.70±0.70 b | 3.70±0.15 a | +++ |
Table 4 Effects of different proportions of plant growth regulators on rooting of Phyllanthus acidus
| Treatments | NAA (mg·L-1) | IBA (mg·L-1) | Number of explants | Rooting rate (%) | Rooting number (n) | Root length (cm) | Growth condition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.5 | 0 | 30 | 60.00±11.55 ab | 8.40±0.70 a | 0.99±0.06 d | ++ |
| 2 | 1.0 | 0 | 30 | 66.67±6.67 a | 9.00±0.84 a | 1.02±0.05 d | ++ |
| 3 | 1.5 | 0 | 30 | 33.33±8.82 b | 1.50±0.22 d | 0.91±0.06 d | + |
| 4 | 0 | 0.5 | 30 | 76.67±8.82 a | 2.70±0.37 d | 1.87±0.08 c | ++ |
| 5 | 0 | 1.0 | 30 | 70.00±15.28 a | 4.80±4.80 c | 2.70±0.15 b | +++ |
| 6 | 0 | 1.5 | 30 | 83.33±6.67 a | 6.70±0.70 b | 3.70±0.15 a | +++ |
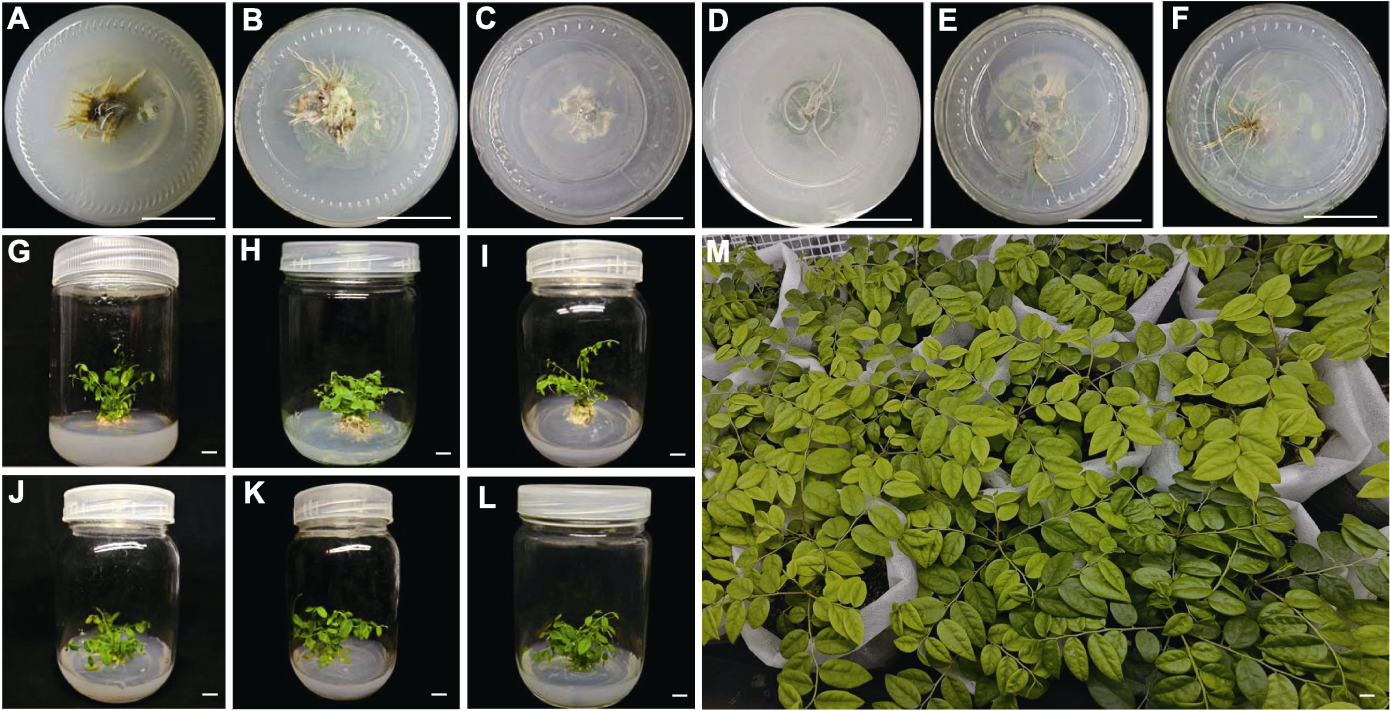
Figure 4 Rooting and transplanting of Phyllanthus acidus plantlet (A)-(F) The growth status of the explants in the lower part of the tissue culture plot after rooting and culture in the medium with different concentrations of NAA and IBA (concentration ratios of NAA and IBA in A-F are the same as shown in Table 4); (G)-(L) Growth status of the explants in the upper part of the tissue culture site after rooting and culture in the medium with different concentrations of NAA and IBA (concentration ratios of NAA and IBA in G-L are the same as shown in Table 4); (M) Transplanting matrix soil with a volume ratio of perlite, peat soil and humus of 1:1:1 (v/v/v), growth after 30 days. Bars=1 cm
| [1] | Ali J, Bantte K, Feyissa T (2017). Protocol optimization for in vitro shoot multiplication of Jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus L.). Afr J Biotechnol 16, 87-90. |
| [2] | Andrianto D, Widianti W, Bintang M (2017). Antioxidant and cytotoxic activity of Phyllanthus acidus fruit extracts. IOP Conf Ser: Earth Environ Sci 58, 012022. |
| [3] | Chakraborty R, Biplab D, Devanna N, Sen S (2012). Antiinflammatory, antinociceptive and antioxidant activities of Phyllanthus acidus L. extracts. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 2, S953-S961. |
| [4] | Chen JY, Deng GX (2024). Key technology of raising seedling by sowing of Phyllanthus acidus. Forest Sci Technol(6), 119-120. (in Chinese) |
| 陈剑英, 邓桂香 (2024). 西印度醋栗播种育苗关键技术. 林业科技通讯 (6), 119-120. | |
| [5] | Geng HC, Zhu HT, Yang WN, Wang D, Yang CR, Zhang YJ (2021). New cytotoxic dichapetalins in the leaves of Phyllanthus acidus: identification, quantitative analysis, and preliminary toxicity assessment. Bioorg Chem 114, 105125. |
| [6] | Gu C (2019). Study on the Chemical Constituents of Phyllanthus acidus from Xishuangbanna. Master’s thesis. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology. pp. 1-89. (in Chinese) |
| 顾晨 (2019). 西双版纳产西印度醋栗化学成分研究. 硕士论文. 昆明: 昆明理工大学. pp. 1-89. | |
| [7] | Hou RG, Ding X, Yang LY, Zhang M, Zhang YJ, Zhao P (2023). α-glucosidase inhibitory activity and safety evaluation of branch and leaf extracts of Phyllanthus acidus. Sci Technol Food Ind 44, 252-259. (in Chinese) |
| 侯润庚, 丁骁, 杨力颖, 张曼, 张颖君, 赵平 (2023). 西印度醋栗枝叶提取物的α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性及安全性评价. 食品工业科技 44, 252-259. | |
| [8] | Huang T, Zhu ZL (2024). Advances in rooting of tissue culture of Nyctaginaceae. Mol Plant Breed 22, 6160-6169. (in Chinese) |
| 黄涛, 祝遵凌 (2024). 紫茉莉科植物组培生根研究进展. 分子植物育种 22, 6160-6169. | |
| [9] | Huang W, Lin LT, Xu CJ, Zheng ZZ, Chen LH, Ming YL (2017). Tissue culture of Phyllanthus urinaria. Subtrop Plant Sci 46, 236-239. (in Chinese) |
|
黄雯, 林亮通, 许传俊, 郑志忠, 陈良华, 明艳林 (2017). 叶下珠组培快繁体系研究. 亚热带植物科学 46, 236-239.
DOI |
|
| [10] | Huang XY, Meng XY, Feng JW, Qiao G, Wu YW (2024). Establishment of in vitro rapid propagation system for Malus hupehensis. South China Fruits 53(4), 175-181. (in Chinese) |
| 黄欣艳, 蒙小玉, 冯建文, 乔光, 吴亚维 (2024). 平邑甜茶离体快繁体系的建立. 中国南方果树 53(4), 175-181. | |
| [11] | Huy DT, Hung NH, Tuyet NTA, Hao BX (2018). Triterpenoids from Phyllanthus acidus (L.) Skeels. Sci Technol Dev J: Nat Sci 2, 71-75. |
| [12] | Jiang LQ, Huan J, Xu ZP, He ZJ, Li WJ (2024). Study on tissue culture and rapid propagation technology of tender stem segments of Olea europaea. J Sichuan Forest Sci Technol 45(4), 20-25. (in Chinese) |
| 姜丽琼, 浣杰, 徐志萍, 何周建, 李文俊 (2024). 油橄榄幼嫩茎段组培快繁技术研究. 四川林业科技 45(4), 20-25. | |
| [13] | Kang M, Zhang MY, Qi XS, Tong NN, Li Y, Shu QY, Liu ZA, Lü CP, Peng LP (2024). Establishment of a fast breeding system for Itoh hybrid ‘He Xie’ in tissue culture. Chin Bull Bot 59, 441-451. (in Chinese) |
|
康敏, 张美莹, 齐秀双, 佟宁宁, 李旸, 舒庆艳, 刘政安, 吕长平, 彭丽平 (2024). 伊藤杂种‘和谐’组培快繁体系的建立. 植物学报 59, 441-451.
DOI |
|
| [14] | Leeya Y, Mulvany MJ, Queiroz EF, Marston A, Hostettmann K, Jansakul C (2010). Hypotensive activity of an n-butanol extract and their purified compounds from leaves of Phyllanthus acidus (L.) Skeels in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 649, 301-313. |
| [15] | Li JH, Ye WY, Zhu PJ, Pang XH, Zhang J, Tang YW, Wei QY (2022). Establishment of a sterile short shoot tissue culture and rapid propagation system for Clerodendranthus spicatus. Chin J Trop Crops 43, 2063-2070. (in Chinese) |
|
李佳慧, 叶维雁, 朱鹏锦, 庞新华, 张继, 唐毓玮, 韦俏宇 (2022). 猫须草无菌短枝组织培养与快速繁殖体系的建立. 热带作物学报 43, 2063-2070.
DOI |
|
| [16] | Li MY, Liu L, Liu Y, Zhang XM (2021). Establishment of tissue culture system for axillary bud regeneration of Primula × pubescens. Chin Bull Bot 56, 732-739. (in Chinese) |
|
李孟悦, 刘柳, 刘艳, 张晓曼 (2021). 毛报春(Primula × pubescens)腋芽再生组织培养体系的建立. 植物学报 56, 732-739.
DOI |
|
| [17] | Liao HQ, Yang XH, Xu F, Yang HX, Chen XY, Xu B (2024). Tissue culture and rapid propagation system of Barthea barthei. Guangxi Forest Sci 53, 501-506. (in Chinese) |
| 廖焕琴, 杨晓慧, 徐放, 杨会肖, 陈新宇, 徐斌 (2024). 棱果花组培快繁体系建立. 广西林业科学 53, 501-506. | |
| [18] | Ling X, Zhang D, Yan XL, Pu SB (2015). Research progress on chemical constituents and physiological activities of Phyllanthus acidus. Chin Wild Plant Resour 34(6), 40-43. (in Chinese) |
| 凌雪, 张迪, 严雪龙, 濮社班 (2015). 西印度醋栗化学成分及活性研究进展. 中国野生植物资源 34(6), 40-43. | |
| [19] | Liu YZ, Wang YF, Ren WZ, Li H, Lu B, Lu BS, Yu XY (2024). Establishment of immature embryo rescue and regeneration system for Pyrus calleryana cv. ‘Cleveland’. Chin Bull Bot 59, 800-809. (in Chinese) |
|
刘玉泽, 王一菲, 任威蓁, 栗浩, 路斌, 路丙社, 于晓跃 (2024). 北美豆梨杂种幼胚挽救及再生体系的建立. 植物学报 59, 800-809.
DOI |
|
| [20] |
Longuefosse JL, Nossin E (1996). Medical ethnobotany survey in Martinique. J Ethnopharmacol 53, 117-142.
PMID |
| [21] | Lu JC, Cao LN, Tong GJ, Wang XY, Zhang LY, Yu X, Li HF, Li YH (2022). Establishment of callus induction and regeneration system of Anemone silvestris. Chin Bull Bot 57, 217-226. (in Chinese) |
|
逯锦春, 曹丽娜, 佟冠杰, 王鑫颖, 张利英, 喻锌, 李荟芳, 李彦慧 (2022). 大花银莲花愈伤组织诱导及再生体系的建立. 植物学报 57, 217-226.
DOI |
|
| [22] | Luo DD, Gu T, Li XW, Duan BZ (2017). Analysis of varieties and standards of Euphorbiaceae medicinal plants used in Dai medicine. Tradit Chin Drug Res Clin Pharmacol 28, 692-698. (in Chinese) |
| 罗丹丹, 顾婷, 李西文, 段宝忠 (2017). 傣医学药用大戟科植物药材品种与标准的现状分析. 中药新药与临床药理 28, 692-698. | |
| [23] | Ma XM, Hu YC, Miao J, Zhang S, Wang JF, Shi SC (2024). Establishment of Lilium ‘Trensor’ in vitro rapid propagation system. Northern Hortic (4), 42-48. (in Chinese) |
| 马秀明, 胡云超, 缪军, 张庶, 王俊峰, 石少川 (2024). 亚洲百合‘穿梭’组培快繁体系的建立. 北方园艺 (4), 42-48. | |
| [24] | Murashige T, Skoog F (1962). A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15, 473-497. |
| [25] | Panda J, Mishra AE (2021). A short review on pharmacological properties of Phyllanthus acidus (L.) Skeels. Int J Bot Stud 6, 403-405. |
| [26] | Pu TL, Jin J, Ma KH, Yuan JM, Luo HY, Zhao QL (2023). Determination and analysis of phenotypic characteristics and nutritional components of Phyllanthus acidus (Linn.) Skeel. Chin J Trop Agric 43(11), 47-51. (in Chinese) |
| 普天磊, 金杰, 马开华, 袁建民, 罗会英, 赵琼玲 (2023). 西印度醋栗表型性状及营养成分测定分析. 热带农业科学 43(11), 47-51. | |
| [27] | Ren LL, Zhang YZ, Huang KL, Wan XC, Zhang ZL, Zhu ML, Wei CL (2023). An efficient system for regenerating adventitious buds in stem segments of tea plants. Chin Bull Bot 58, 308-315. (in Chinese) |
|
任露露, 张有泽, 黄克林, 宛晓春, 张照亮, 朱木兰, 韦朝领 (2023). 茶树茎段不定芽高效发生体系的建立. 植物学报 58, 308-315.
DOI |
|
| [28] | Shimu AS, Miah M, Billah M, Karmakar S, Mohanto SC, Khatun R, Reza MA, Hoque KMF (2021). A comparative study of biological potentiality and EAC cell growth inhibition activity of Phyllanthus acidus (L.) fruit pulp and seed in Bangladesh. Saudi J Biol Sci 28, 2014-2022. |
| [29] | Tan SP, Tan ENY, Lim QY, Nafiah MA (2020). Phyllanthus acidus (L.) Skeels: a review of its traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacological properties. J Ethnopharmacol 253, 112610. |
| [30] | Tang L, Tian SQ (2022). Progress in the application of plant tissue culture technology. Contem Hortic 45(18), 24-26. (in Chinese) |
| 唐链, 田爽琪 (2022). 植物组织培养技术的应用进展. 现代园艺 45(18), 24-26. | |
| [31] | Wang Z, Zhang CL, He SL, Shang WQ, He D, Shen YX, Liu YN, Song YL, Sun YK (2022). Effects of different LED reflecting and lighting methods on the growth of tissue culture seedlings of Gerbera jamesonii. J Henan Agric Sci 51(4), 120-129. (in Chinese) |
| 王政, 张春玲, 何松林, 尚文倩, 贺丹, 申玉晓, 刘艳楠, 宋盈龙, 孙宇科 (2022). LED不同反光及照光方式对非洲菊组培苗生长的影响. 河南农业科学 51(4), 120-129. | |
| [32] | Xie CG, Liu Z, Zhang SS, Hu HT (2023). Establishment of in vitro regeneration system of Citrus australasica. Chin Bull Bot 58, 926-934. (in Chinese) |
|
谢纯刚, 刘哲, 章书声, 胡海涛 (2023). 手指柠檬茎段离体再生体系建立. 植物学报 58, 926-934.
DOI |
|
| [33] | Xu J, Li N, Zhu HT, Yang WN, Wang D, Yang CR, Zhang YJ (2021). Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological activity of Phyllanthus acidus. Guihaia 41, 1784-1793. (in Chinese) |
| 胥佳, 李娜, 朱宏涛, 杨慰农, 王东, 杨崇仁, 张颖君 (2021). 西印度醋栗的化学成分及药理活性研究进展. 广西植物 41, 1784-1793. | |
| [34] | Xu J, Xin Y, Zhu HT, Kong QH, Yang WN, Wang D, Yang CR, Zhang YJ (2023). Flavonoids from the fruits of Phyllanthus acidus (L.) Skeels with anti-α-glucosidase activity. Nat Prod Res 37, 1986-1992. |
| [35] | Zeng C, Mo HP, Pang QL, Lou BH, Deng GZ, Zhang S, Li BL, Su YQ (2024). Induction and in vitro regeneration of Siraitia grosvenorii tubers. South China Fruits 53(5), 95-100. (in Chinese) |
| 曾成, 莫海萍, 庞秋凌, 娄兵海, 邓光宙, 张松, 李伯林, 苏玉卿 (2024). 罗汉果组培块茎诱导及离体再生. 中国南方果树 53(5), 95-100. | |
| [36] | Zhang BH (2023). Research on plant tissue culture technology and its application. Mod Agric Res 29(12), 90-93. (in Chinese) |
| 张宝华 (2023). 植物组织培养技术及应用探究. 现代农业研究 29(12), 90-93. | |
| [37] | Zhang SY, Yao XH, Ren HD, Wang KL (2002). A preliminary study on rapid propagation in vitro of emblic. Forest Res 15, 116-119. (in Chinese) |
| 张守英, 姚小华, 任华东, 王开良 (2002). 余甘子离体快速繁殖技术的初步研究. 林业科学研究 15, 116-119. | |
| [38] | Zhang XB, Lei YN, Chen SC (2018). Effects of different ecological conditions on seed germination of Phyllanthus urinaria. Shaanxi J Agric Sci 64(10), 40-42. (in Chinese) |
| 张小斌, 雷艳妮, 陈书存 (2018). 不同生态条件对叶下珠种子萌发的影响研究. 陕西农业科学 64(10), 40-42. | |
| [39] | Zhu GY, Luo D, Zhao YQ, Xiang ZR, Chen C, Li N, Hao XJ, Ding X, Zhang YJ, Zhao YH (2024). Pacidusin B isolated from Phyllanthus acidus triggers ferroptotic cell death in HT1080 cells. Nat Prod Bioprospect 14, 34. |
| [1] | Ruxin Zhang, Chenrong Li, Tongxin Wang, Jie Li, Tingge Li, Huixian Xu, Meier Li, Ying Zhao, Ting Peng, Jian Wang. Establishment of a Regeneration System for Viola × wittrochiana [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(6): 1-0. |
| [2] | Liru Zhou, Yan Ao, Jing Zhong. Study on Adventitious Bud Induction and Browning Inhibition of Xanthoceras sorbifolium [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(6): 1-0. |
| [3] | Xuemin Cao, Ying Bao, Yuexin Zhang, Ruijie Li, Jianxin Su, Wei Zhang. Tissue Culture, Rapid Propagation and Efficient Transient Expression Systems of Rosa multiflora [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(2): 235-245. |
| [4] | Yuze Liu, Yifei Wang, Weizhen Ren, Hao Li, Bin Lu, Bingshe Lu, Xiaoyue Yu. Establishment of Immature Embryo Rescue and Regeneration System for Pyrus calleryana cv. ‘Cleveland’ [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(5): 800-809. |
| [5] | Wen Feng, Yuguo Wang. Establishment of an In Vitro Regeneration System for Stem Segments of Cultivated Dioscorea polystachya [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(5): 792-799. |
| [6] | Hao Zeng, Peifang Li, Zhihui Guo, Chunlin Liu, Ying Ruan. Establishment of a Regeneration System for Lunaria annua [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(3): 433-440. |
| [7] | Shangwen Zhang, Shiyu Huang, Tianwei Yang, Ting Li, Xiangjun Zhang, Manrong Gao. Establishment of a Tissue Culture and Rapid Propagation System for Erythropalum scandens Based on Orthogonal Test [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(1): 99-109. |
| [8] | Chungang Xie, Zhe Liu, Shusheng Zhang, Haitao Hu. Establishment of In Vitro Regeneration System of Citrus australasica [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(6): 926-934. |
| [9] | Yefei Liu, Haixia Zhao, Xiping Jiang, Rui Qiu, Xinyue Zhou, Yan Zhao, Chunxiang Fu. Establishment of Highly Efficient Tissue Culture and Agrobacterium-mediated Callus Infection Systems for Hordeum brevisubulatum [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(3): 440-448. |
| [10] | Lü Xiuli, Yu Zequn, Chen Xiangbo, Fu Renjie, Miao Shanshan, Du An. Rapid Propagation Technology and Field Production of Hemerocallis fulva cv. ‘Fenmeiren’ [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(3): 350-357. |
| [11] | Jinchun Lu, Lina Cao, Guanjie Tong, Xinying Wang, Liying Zhang, Xin Yu, Huifang Li, Yanhui Li. Establishment of Callus Induction and Regeneration System of Anemone silvestris [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(2): 217-226. |
| [12] | Mengyue Li, Liu Liu, Yan Liu, Xiaoman Zhang. Establishment of Tissue Culture System for Axillary Bud Regeneration of Primula × pubescens [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(6): 732-739. |
| [13] | Yaqian Xiong, Xianbao Deng, Huihui Zhang, Dong Yang, Heng Sun, Juan Liu, Mei Yang. In Vitro Rapid Propagation of Nelumbo nucifera [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(5): 605-613. |
| [14] | Qian Luo, Yansha Zhang, Jing Ou. Callus Induction and Plant Regeneration of Cerasus serrulata var. lannesiana cv. ‘Grandiflora’ [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(4): 451-461. |
| [15] | Hong Luo, Xiaohui Wen, Yuanyuan Zhou, Silan Dai. Establishment of In Vitro Regeneration System of Helenium aromaticum [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(3): 318-328. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||