

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (3): 385-393.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22077 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22077
• EXPERIMENTAL COMMUNICATIONS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Nan Wu1, Lei Qin1, Kan Cui1, Haiou Li1, Zhongsong Liu2, Shitou Xia1( )
)
Received:2022-04-17
Accepted:2022-07-03
Online:2023-05-01
Published:2023-05-17
Contact:
*E-mail: xstone0505@hunau.edu.cn
Nan Wu, Lei Qin, Kan Cui, Haiou Li, Zhongsong Liu, Shitou Xia. Cloning of Brassica napus EXA1 Gene and Its Regulation on Plant Disease Resistance[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(3): 385-393.
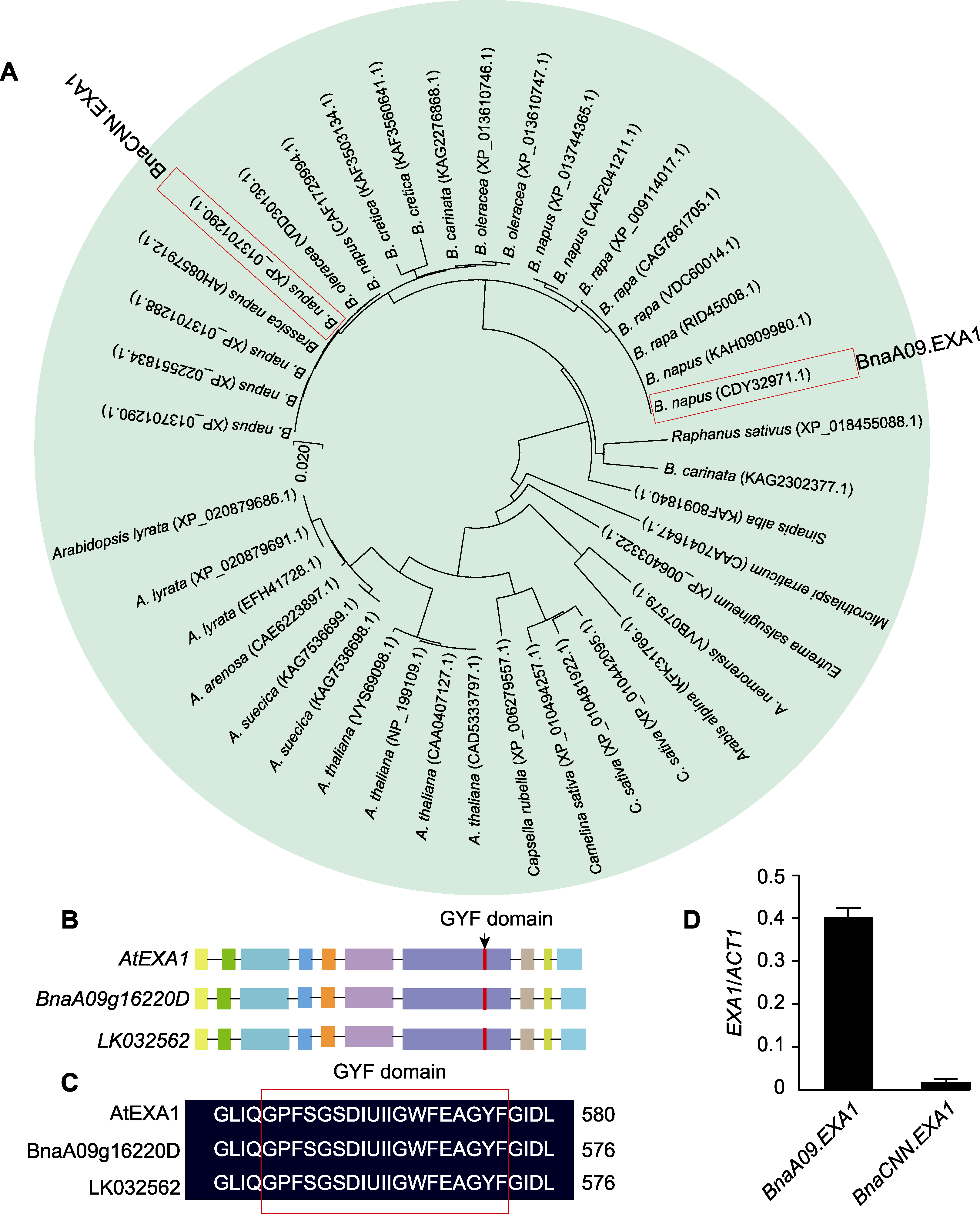
Figure 1 Sequence analysis of BnaEXA1 (A) Phylogenetic analysis of EXA1 in Brassicaceae; (B) Comparison of the derived genome sequences of AtEXA1 and BnaEXA1 (the rectangle represents the exon and the black line represents the intron); (C) Schematic structures of BnaEXA1 (red box indicates GYF domain); (D) Expression analysis of BnaEXA1 in XY-15
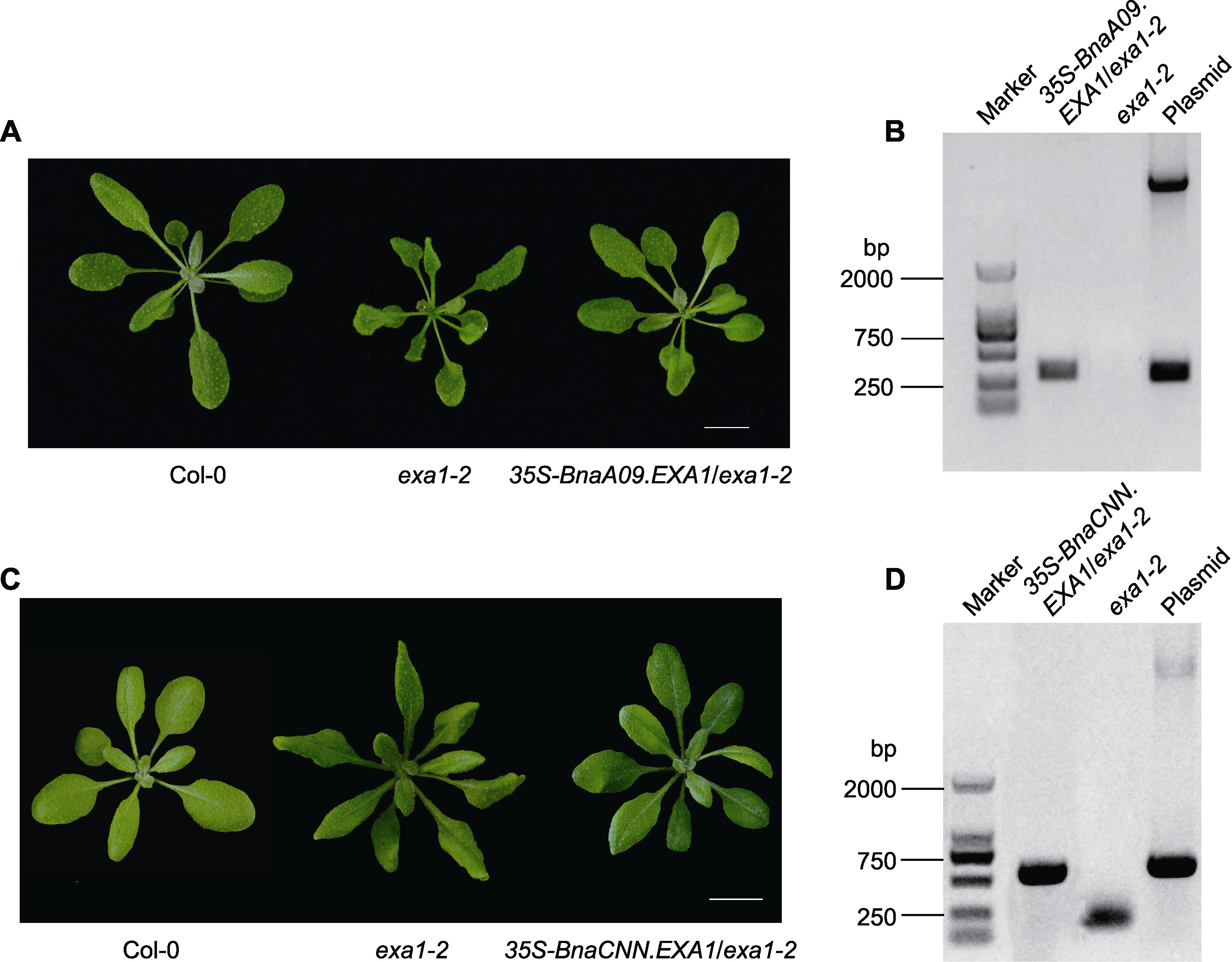
Figure 2 Morphological phenotype and detection of BnaEXA1 transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana (A), (C) Morphological phenotypes of 4-week-old Col-0, exa1-2 and BnaEXA1 transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana plants were used for analysis; (B), (D) Identification of BnaEXA1 transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana plants by PCR; Marker: DNA marker; Negative control: exa1-2 mutant; Positive control: Plasmid (35S-BnaA09.EXA1 and 35S-BnaCNN.EXA1 expression vectors). Bars=1 cm
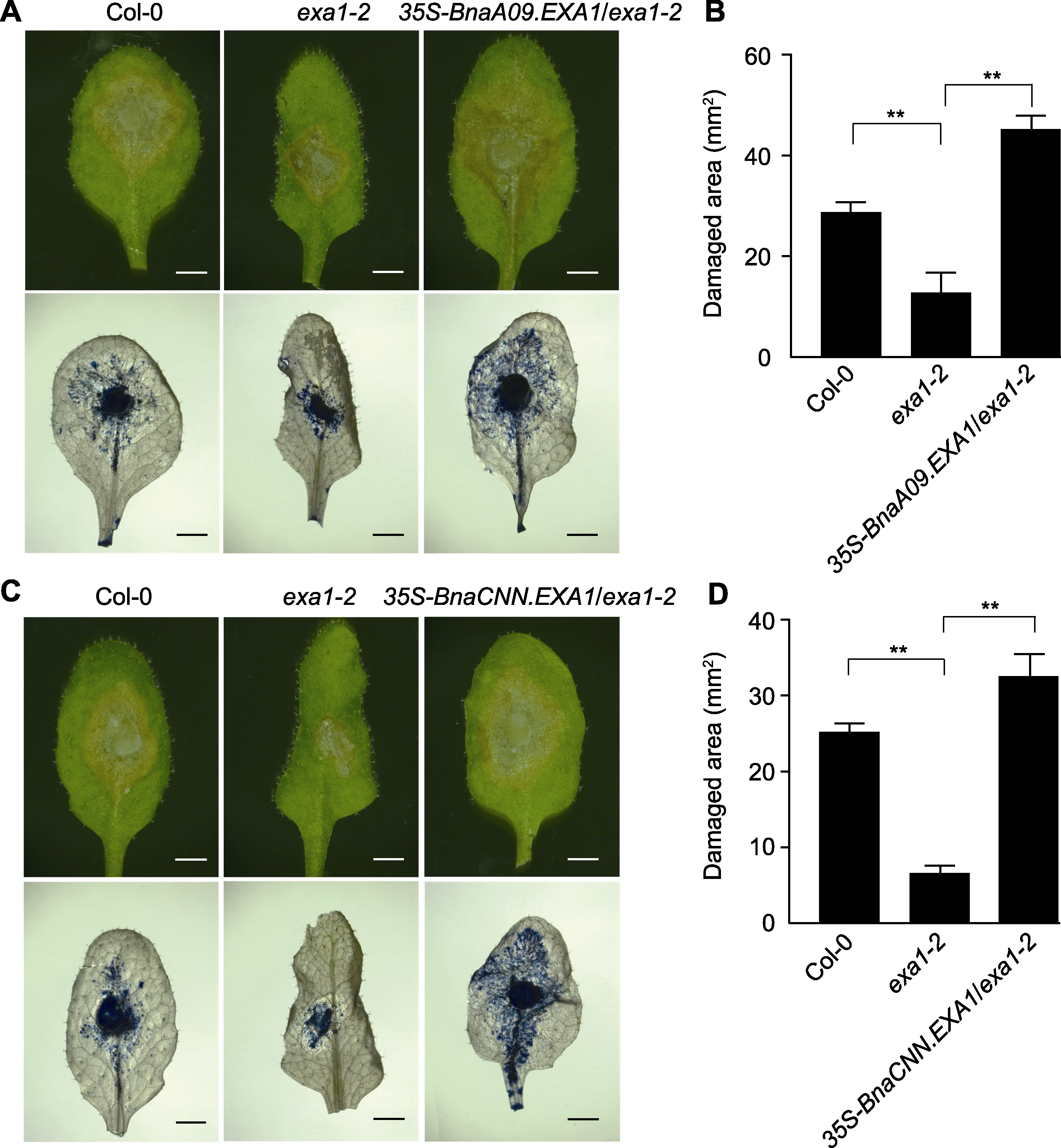
Figure 3 Disease resistance phenotype of BnaEXA1 transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana lineages after Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in-fection (A), (C) Disease resistance phenotype and trypan blue staining of Col-0, exa1-2 and BnaEXA1 transgenic A. thaliana plants infected by S. sclerotiorum (bars=1 cm); (B), (D) Damage area of Col-0, exa1-2 and BnaEXA1 transgenic A. thaliana lineages infected by S. sclerotiorum. ** P<0.01
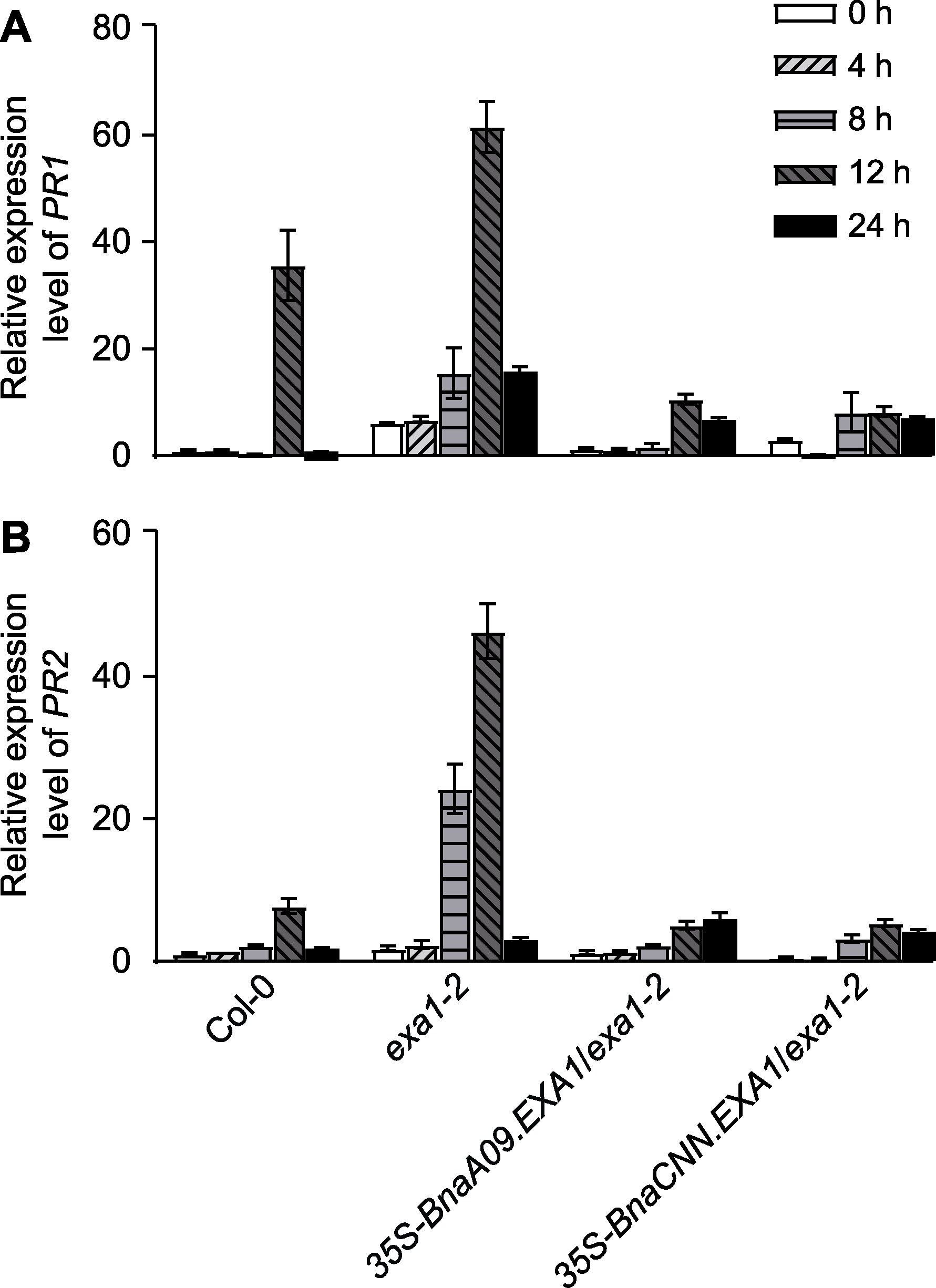
Figure 4 PR gene expression induced by Sclerotinia scle- rotiorum PR1 (A) and PR2 (B) gene expression levels in Col-0, ex-a1-2 and BnaEXA1 transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana linea-ges after 0, 4, 8, 12, and 24 hours of infection by S. scle-rotiorum
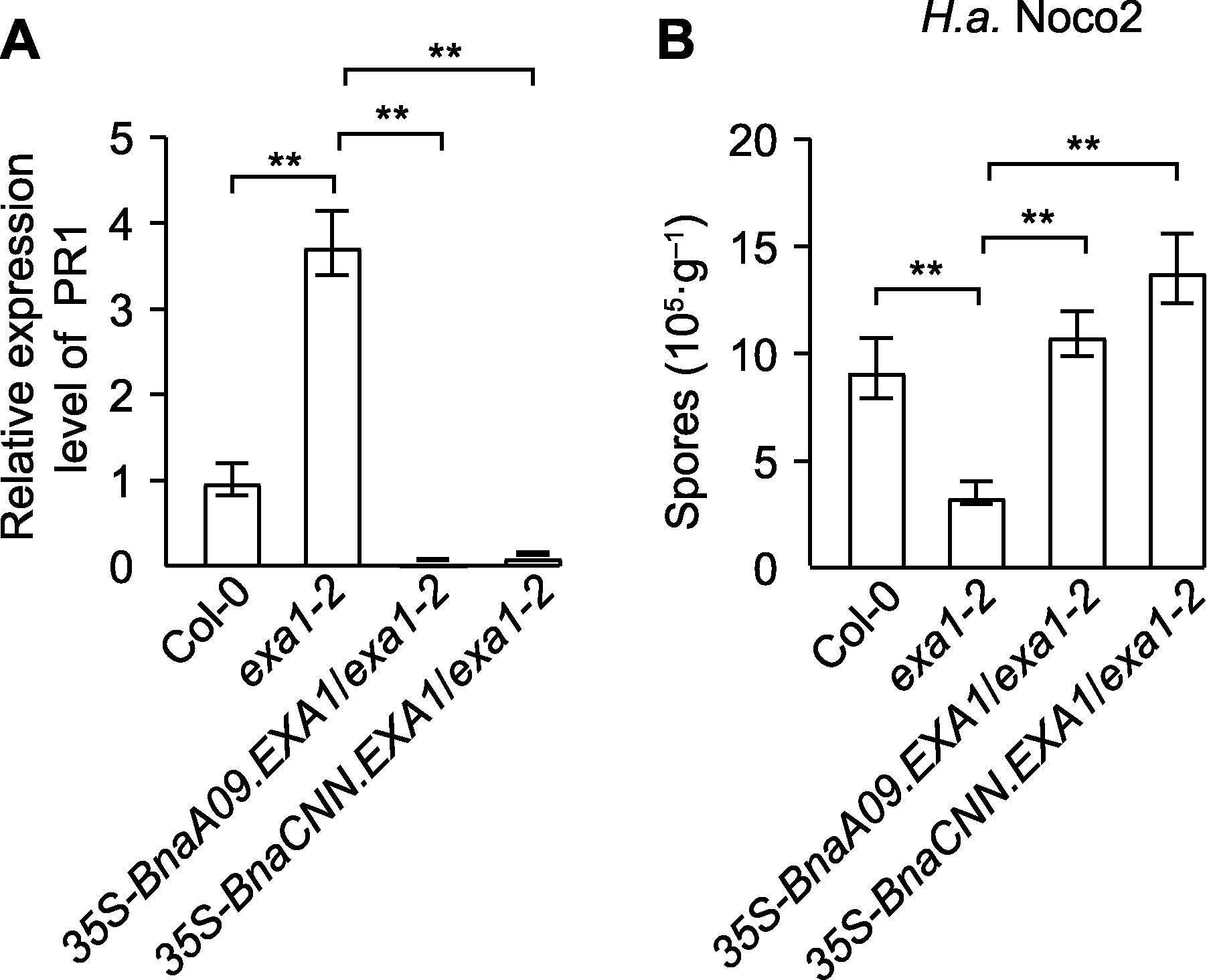
Figure 5 Disease resistance phenotype of BnaEXA1 trans- genic Arabidopsis thaliana lineages (A) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of PR1 expressions in Col-0, exa1-2 and BnaEXA1 transgenic A. thaliana plant-s; (B) Identification of resistance of Col-0, exa1-2 and BnaEXA1 transgenic A. thaliana lineages to H.a. (Hyalo-peronospora arabidopsidis) Noco2. ** P<0.01
| [1] | 费维新, 李强生, 吴新杰, 侯树敏, 陈凤祥, 王文相, 胡宝成 (2002). 利用栽培措施控制油菜菌核病的研究. 中国油料作物学报 24(3), 47-49. |
| [2] | 王爱荣 (2006). 核盘菌与拟南芥互作的分子机制研究. 博士论文. 福州: 福建农林大学. pp. 1-106. |
| [3] | Amselem J, Cuomo CA, van Kan JAL, Viaud M, Benito EP, Couloux A, Coutinho PM, de Vries RP, Dyer PS, Fillinger S, Fournier E, Gout L, Hahn M, Kohn L, Lapalu N, Plummer KM, Pradier JM, Quévillon E, Sharon A, Simon A, ten Have A, Tudzynski B, Tudzynski P, Wincker P, Andrew M, Anthouard V, Beever RE, Beffa R, Benoit I, Bouzid O, Brault B, Chen ZH, Choquer M, Collémare J, Cotton P, Danchin EG, Da Silva C, Gautier A, Giraud C, Giraud T, Gonzalez C, Grossetete S, Güldener U, Henrissat B, Howlett BJ, Kodira C, Kretschmer M, Lappartient A, Leroch M, Levis C, Mauceli E, Neuvéglise C, Oeser B, Pearson M, Poulain J, Poussereau N, Quesneville H, Rascle C, Schumacher J, Ségurens B, Sexton A, Silva E, Sirven C, Soanes DM, Talbot NJ, Templeton M, Yandava C, Yarden O, Zeng QD, Rollins JA, Lebrun MH, Dickman M(2011). Genomic analysis of the necrotrophic fungal pathogens Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and Botrytis cinerea. PLoS Genet 7, e1002230. |
| [4] |
Ash MR, Faelber K, Kosslick D, Albert GI, Roske Y, Kofler M, Schuemann M, Krause E, Freund C (2010). Conserved ß-hairpin recognition by the GYF domains of Smy2 and GIGYF2 in mRNA surveillance and vesicular transport complexes. Structure 18, 944-954.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Barbetti MJ, Banga SK, Fu TD, Li YC, Singh D, Liu SY, Ge XT, Banga SS (2014). Comparative genotype reactions to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum within breeding populations of Brassica napus and B. juncea from India and China. Euphytica 197, 47-59.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Dai FM, Xu T, Wolf GA, He ZH (2006). Physiological and molecular features of the pathosystem Arabidopsis thaliana L.-Sclerotinia sclerotiorum Libert. J Integr Plant Biol 48, 44-52.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Giovannone B, Tsiaras WG, de la Monte S, Klysik J, Lautier C, Karashchuk G, Goldwurm S, Smith RJ (2009). GIGYF2 gene disruption in mice results in neurodegeneration and altered insulin-like growth factor signaling. Hum Mol Genet 18, 4629-4639.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
Guo XM, Stotz HU (2007). Defense against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in Arabidopsis is dependent on jasmonic acid, salicylic acid, and ethylene signaling. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 20, 1384-1395.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Hale VA, Guiney EL, Goldberg LY, Haduong JH, Kwartler CS, Scangos KW, Goutte C (2012). Notch signaling is antagonized by SAO-1, a novel GYF-domain protein that interacts with the E3 ubiquitin ligase SEL-10 in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 190, 1043-1057.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Hashimoto M, Neriya Y, Keima T, Iwabuchi N, Koinuma H, Hagiwara-Komoda Y, Ishikawa K, Himeno M, Maejima K, Yamaji Y, Namba S (2016). EXA1, a GYF domain protein, is responsible for loss-of-susceptibility to Plantago asiatica mosaic virus in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 88, 120-131.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Kofler M, Motzny K, Freund C (2005). GYF domain proteomics reveals interaction sites in known and novel target proteins. Mol Cell Proteomics 4, 1797-1811.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Letunic I, Doerks T, Bork P (2015). SMART: recent updates, new developments and status in 2015. Nucleic Acids Res 43, D257-D260.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Li S, Li X, Zhou YJ (2018). Ribosomal protein L18 is an essential factor that promote rice stripe virus accumulation in small brown planthopper. Virus Res 247, 15-20.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | Matsui H, Nomura Y, Egusa M, Hamada T, Hyon GS, Kaminaka H, Watanabe Y, Ueda T, Trujillo M, Shirasu K, Nakagami H (2017). The GYF domain protein PSIG1 dampens the induction of cell death during plant-pathogen interactions. PLoS Genet 13, e1007037. |
| [15] | Rowe HC, Walley JW, Corwin J, Chan EKF, Dehesh K, Kliebenstein DJ (2010). Deficiencies in jasmonate-mediated plant defense reveal quantitative variation in Botrytis cinerea pathogenesis. PLoS Pathog 6, e1000861. |
| [16] |
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011). MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28, 2731-2739.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | Wu ZS, Huang S, Zhang XB, Wu D, Xia ST, Li X (2017). Regulation of plant immune receptor accumulation through translational repression by a glycine-tyrosine-phenylalanine (GYF) domain protein. eLife 6, e23684. |
| [1] | Qingyang Li, Cui Liu, Li He, Shan Peng, Jiayin Ma, Ziyi Hu, Hongbo Liu. Cloning and Functional Analysis of the BnaA02.CPSF6 Gene from Brassica napus [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(1): 62-73. |
| [2] | Liuqing Yang, Jin Wang, Jingli Yan, Qinqin Chen, Haokun Cheng, Chun Li, Peiyu Zhao, Bo Yang, Yuanqing Jiang. Analysis of Expression Characteristics and Identification of Interaction Proteins of BnaABF2 Transcription Factor in Brassica napus [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(1): 49-61. |
| [3] | Jianmin Zhou. A Combat Vehicle with a Smart Brake [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(3): 343-346. |
| [4] | Yi Song, Hanghang Chen, Xin Cui, Zhifeng Lu, Shipeng Liao, Yangyang Zhang, Xiaokun Li, Rihuan Cong, Tao Ren, Jianwei Lu. Potassium Nutrient Status-mediated Leaf Growth of Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus) and Its Effect on Phyllosphere Microorganism [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(1): 54-65. |
| [5] | Zhang Yingchuan, Wu Xiaomingyu, Tao Baolong, Chen Li, Lu Haiqin, Zhao Lun, Wen Jing, Yi Bin, Tu Jinxing, Fu Tingdong, Shen Jinxiong. Bna-miR43 Mediates the Response of Drought Tolerance in Brassica napus [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(5): 701-711. |
| [6] | Jian-Min Zhou. A Ca2+-ROS Signaling Axis in Rice Provides Clues to Rice-pathogen Coevolution and Crop Improvements [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(5): 513-515. |
| [7] | Tiantian Shi, Ying Gao, Huan Wang, Jun Liu. Nucleo-cytoplasmic Transport and Transport Receptors in Plant Disease Resistance Defense Response [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(4): 480-487. |
| [8] | Jian-Min Zhou. Fighting Fusarium Head Blight in Wheat—a Remedy from Afar [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(2): 123-125. |
| [9] | Min Song,Yao Zhang,Liying Wang,Xiangyong Peng. Genome-wide Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of Zinc Finger Homeodomain Family Genes in Brassica napus [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(6): 699-710. |
| [10] | Na Zhang,Xiuxia Liu,Xuesen Chen,Shujing Wu. Identifying Genes Responsive to Jasmonates in Apple Based on Transcriptome Analysis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(6): 733-743. |
| [11] | Yan Jia, Liu Yaqiong, Hou Suiwen. Recent Advances in Disease Resistance Proteins in Plant Immunity [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2018, 53(2): 250-263. |
| [12] | Gao Huhu, Zhang Yunxiao, Hu Shengwu, Guo Yuan. Genome-wide Survey and Phylogenetic Analysis of MADS-box Gene Family in Brassica napus [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2017, 52(6): 699-712. |
| [13] | Liu Kaige, Qi Shuanghui, Duan Shaowei, Li Dong, Jin Changyu, Gao Chenhao, Liu Mingxun Chen Xuanxia. Functional Analysis of Brassica napus BnTTG1-1 Gene [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2017, 52(6): 713-722. |
| [14] | Jia Ledong, Li Shimeng, Xu Daixiang, Qu Cunmin, Li Jiana, Wang Rui. Bioinformatics Analysis of BnMYB80 Genes in Brassica napus [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2016, 51(5): 620-630. |
| [15] | Zhen Liu, Xia Liu, Jianzhong Liu. The Roles of Protein S-nitrosylation in Plant Cell Death and Disease Resistance [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2016, 51(1): 130-143. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||