

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (1): 54-65.DOI: 10.11983/CBB23076 cstr: 32102.14.CBB23076
• EXPERIMENTAL COMMUNICATIONS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yi Song, Hanghang Chen, Xin Cui, Zhifeng Lu, Shipeng Liao, Yangyang Zhang, Xiaokun Li, Rihuan Cong, Tao Ren*( ), Jianwei Lu
), Jianwei Lu
Received:2023-06-11
Accepted:2023-11-02
Online:2024-01-10
Published:2024-01-10
Contact:
*E-mail: Yi Song, Hanghang Chen, Xin Cui, Zhifeng Lu, Shipeng Liao, Yangyang Zhang, Xiaokun Li, Rihuan Cong, Tao Ren, Jianwei Lu. Potassium Nutrient Status-mediated Leaf Growth of Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus) and Its Effect on Phyllosphere Microorganism[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(1): 54-65.
| Treatments | K content (%) | Dry matter weight (g) | Leaf area (cm2) | Specific leaf weight (mg∙cm‒2) | Waxy content (µg∙cm‒2) | Stomatal density (numbers∙cm‒2) | Active protein content (%) | Soluble sugar content (%) | Saccharose content (%) | Fructose content (%) | Starch content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K0 | 0.35 c | 1.09 b | 335 b | 4.2 a | 223 ab | 1630 a | 14.6 a | 8.9 c | 4.3 b | 5.1 c | 16.3 b |
| K30 | 0.61 b | 1.33 b | 382 b | 4.4 a | 306 a | 1449 a | 14.5 a | 15.9 b | 7.3 a | 10.9 b | 20.6 b |
| K180 | 0.92 a | 1.86 a | 508 a | 4.4 a | 188 b | 970 b | 16.3 a | 20.3 a | 9.4 a | 14.2 a | 25.9 a |
Table 1 The phenotypic traits and biochemical parameters of oilseed rape leaves with different K nutrient status
| Treatments | K content (%) | Dry matter weight (g) | Leaf area (cm2) | Specific leaf weight (mg∙cm‒2) | Waxy content (µg∙cm‒2) | Stomatal density (numbers∙cm‒2) | Active protein content (%) | Soluble sugar content (%) | Saccharose content (%) | Fructose content (%) | Starch content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K0 | 0.35 c | 1.09 b | 335 b | 4.2 a | 223 ab | 1630 a | 14.6 a | 8.9 c | 4.3 b | 5.1 c | 16.3 b |
| K30 | 0.61 b | 1.33 b | 382 b | 4.4 a | 306 a | 1449 a | 14.5 a | 15.9 b | 7.3 a | 10.9 b | 20.6 b |
| K180 | 0.92 a | 1.86 a | 508 a | 4.4 a | 188 b | 970 b | 16.3 a | 20.3 a | 9.4 a | 14.2 a | 25.9 a |
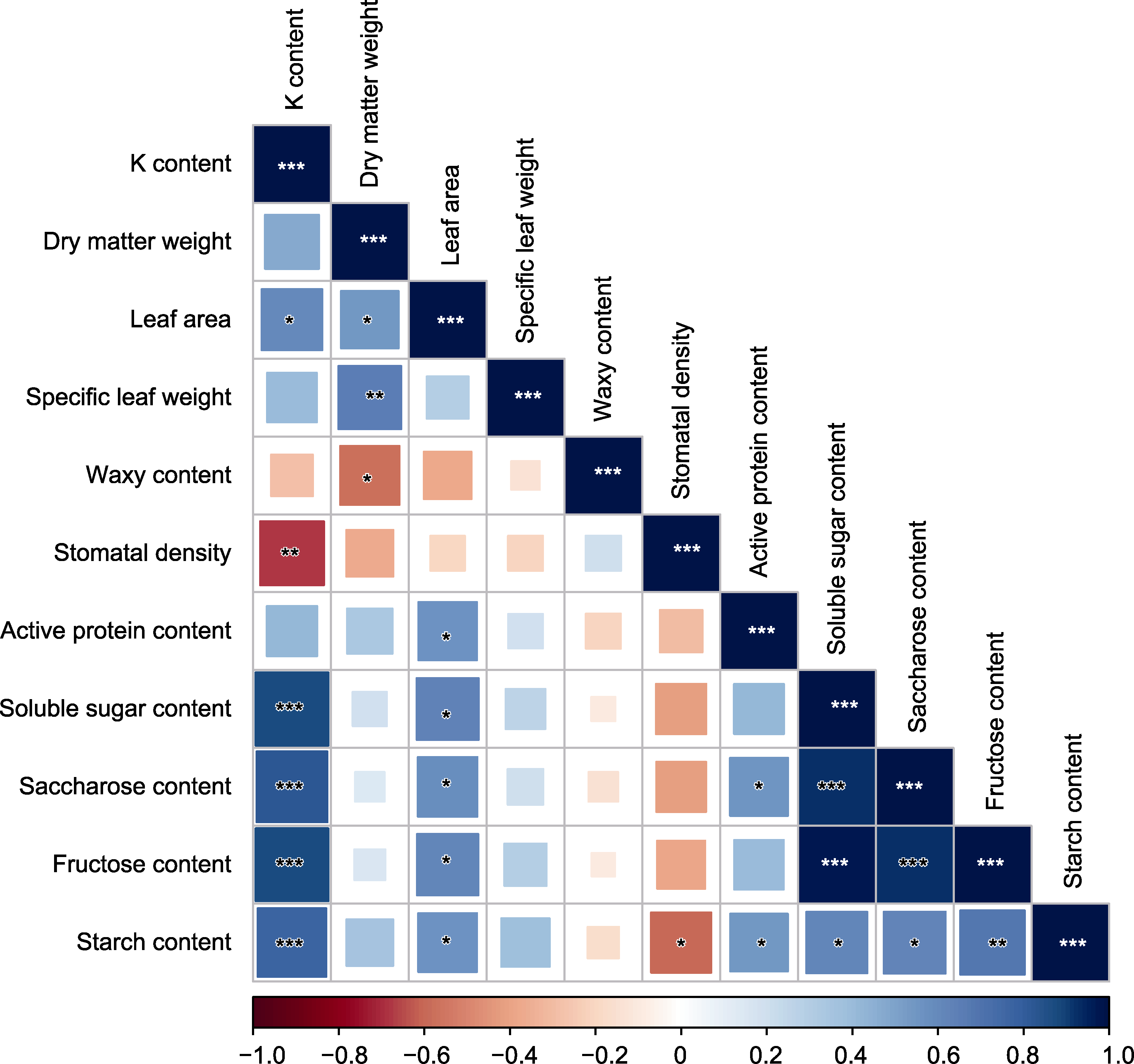
Figure 2 Correlation between leaf phenotypic traits and biochemical parameters under different K nutrient status *, ** and *** indicate significant differences at 0.05, 0.01 and 0.001 levels, respectively.
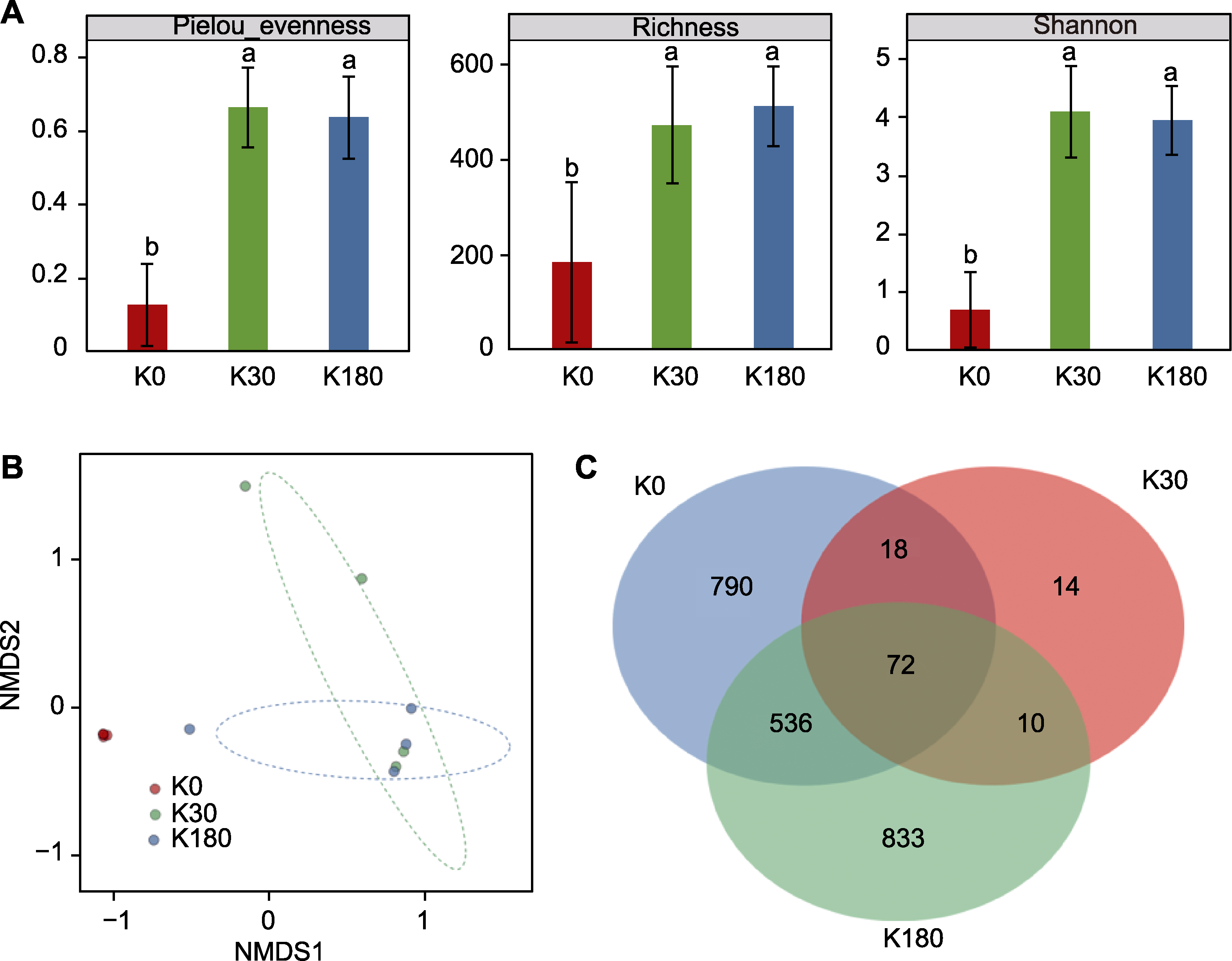
Figure 3 Diversity of phyllospheric bacterial communities in oilseed rape under different K nutrient status (A) Pielou_evenness, Richness and Shannon diversity indices of phyllospheric bacterial communities (different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among treatments (P<0.05)); (B) β-diversity of phyllospheric bacterial communities; (C) Distribution of phyllospheric microbial communities Amplicon Sequence Variants (ASVs). NMDS: Evaluation of rank information for distance values; K0, K30, and K180 are the same as shown in Figure 1.
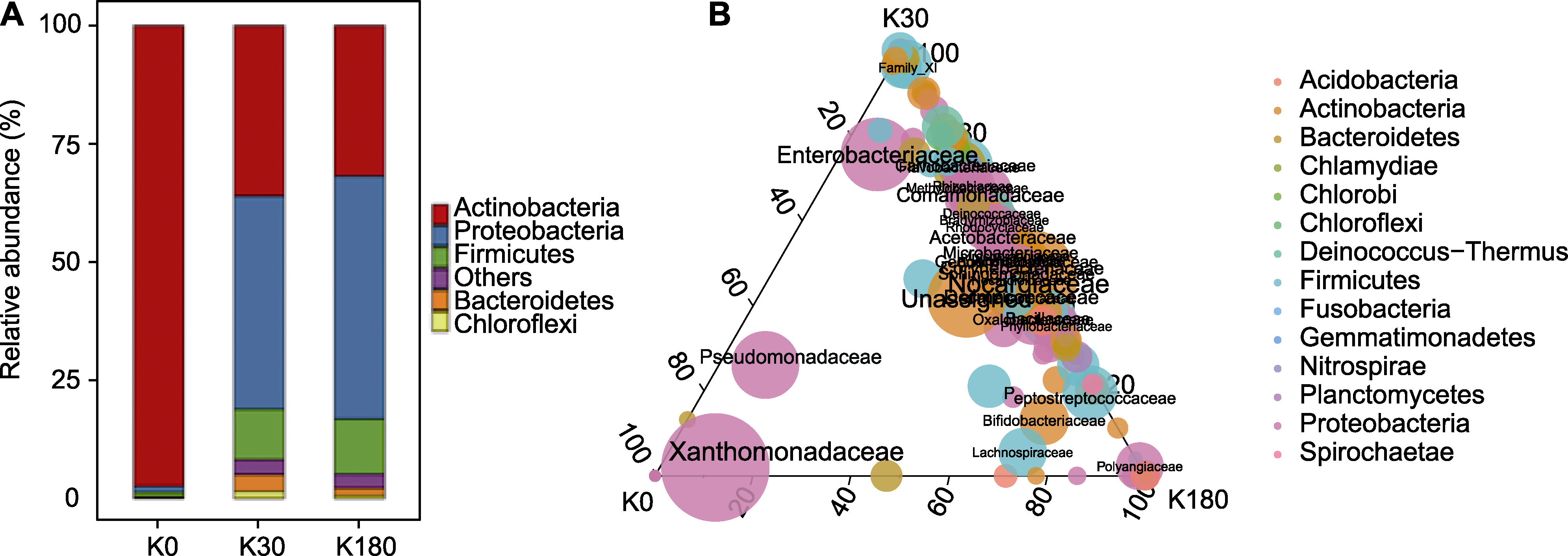
Figure 4 Phyllospheric microbial composition in leaves of oilseed rape under different K nutrient status (A) Phyllospheric microbial composition of oilseed rape at phylum level; (B) Distribution of species at the taxonomic level of families under different K nutrient status (circles and font sizes are mapped based on relative abundance, colored by phylum taxonomic level). K0, K30, and K180 are the same as shown in Figure 1.
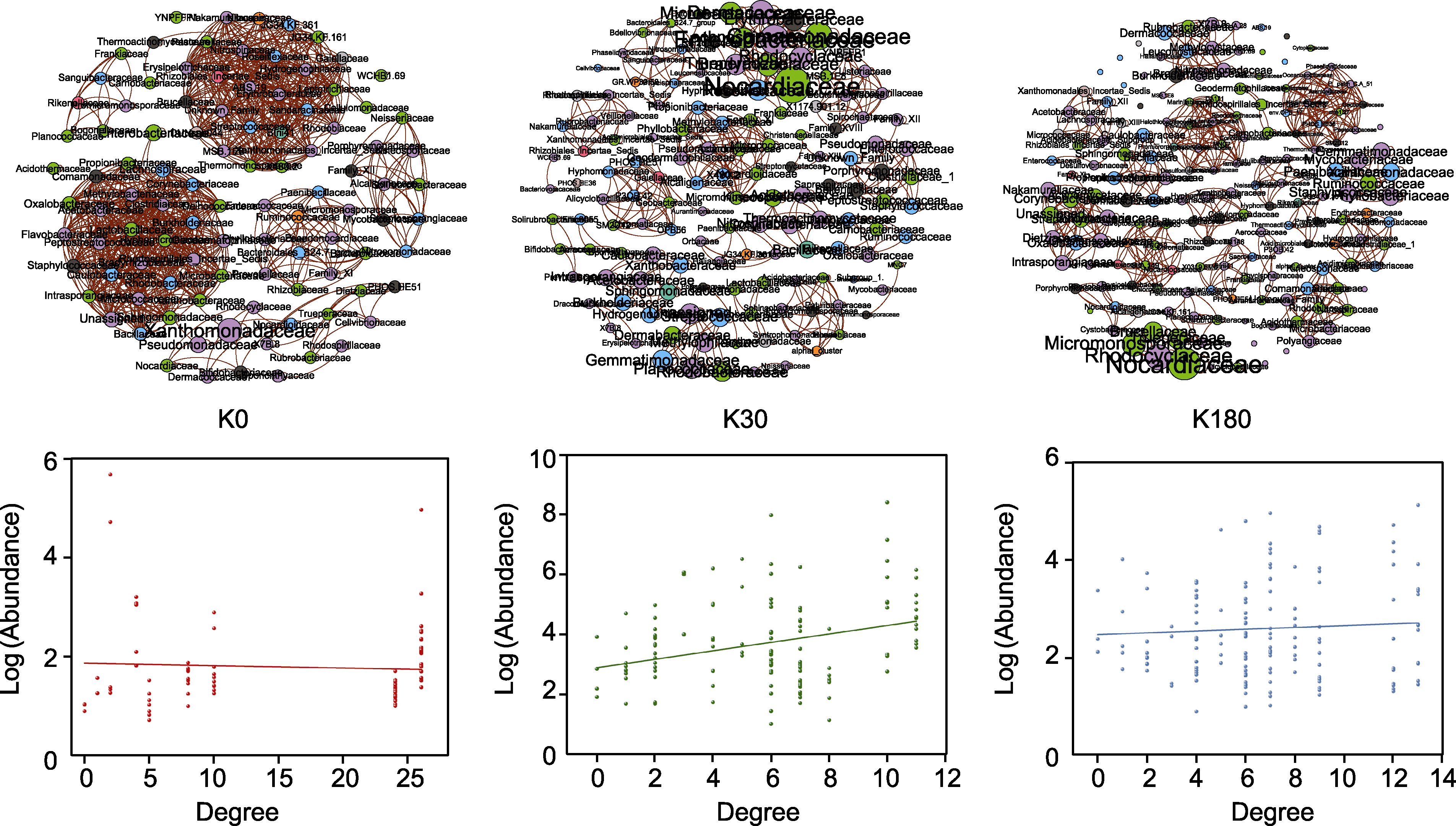
Figure 5 Phyllospheric microbial co-occurrence network and node and node relative abundance relationships for different K nutrient status K0, K30, and K180 are the same as shown in Figure 1.
| Treatments | Nodes | Edges | Network density | Modularity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K0 | 100 | 789 | 0.159 | 0.650 |
| K30 | 138 | 390 | 0.041 | 0.912 |
| K180 | 174 | 536 | 0.036 | 0.915 |
Table 2 Phyllospheric microbial co-occurrence network parameters for different K nutrient status
| Treatments | Nodes | Edges | Network density | Modularity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K0 | 100 | 789 | 0.159 | 0.650 |
| K30 | 138 | 390 | 0.041 | 0.912 |
| K180 | 174 | 536 | 0.036 | 0.915 |
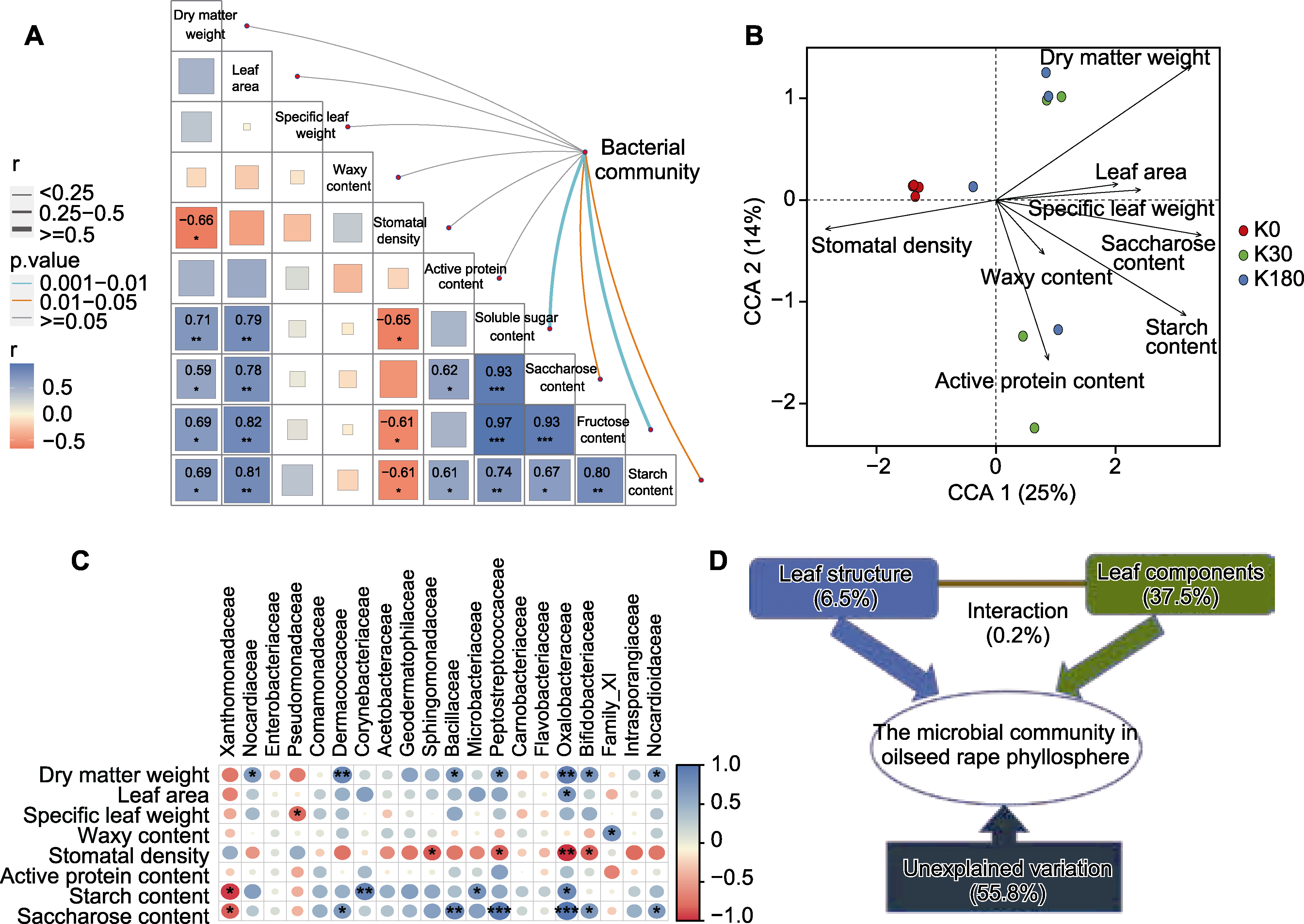
Figure 6 Relationship between leaf traits and phyllospheric microbial composition in oilseed rape under different K nutrient status (A) Mental relationship between leaf phenotypic nutrition and phyllospheric microbial community structure (* P<0.05; ** P<0.01; *** P<0.001); (B) RDA analysis under different potassium nutrient conditions; (C) Correlation analysis between dominant species and leaf phenotypic traits; (D) Relative contributions of leaf structure and leaf fractions to phyllospheric microbial community changes in oilseed rape. CCA: The most important components affect changes in the phyllospheric microbial community; K0, K30, and K180 are the same as shown in Figure 1.
| [1] | 鲍士旦 (2000). 土壤农化分析(第3版). 北京: 中国农业出版社. pp. 103-109. |
| [2] | 高扬 (2014). 小麦叶片表皮蜡质的测定及其对光合和农艺性状的效应分析. 硕士论文. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学. pp. 22-23. |
| [3] | 胡文诗 (2021). 钾营养调控冬油菜叶片光合面积和光合速率的机制. 博士论文. 武汉: 华中农业大学. pp. 34-53. |
| [4] | 姜丹 (2009). 油菜叶际微生物多样性及其对敌敌畏的降解. 硕士论文. 石家庄: 河北科技大学. pp. 42-49. |
| [5] | 刘姗 (2021). 叶际微生物地理分布格局特征及驱动机制. 硕士论文. 杭州: 浙江大学. pp. 31-46. |
| [6] | 龙海, 李一农, 李芳荣, 徐浪 (2010). 植物病原菌黄单胞菌的分类研究进展. 植物保护 36(5), 11-16. |
| [7] | 陆志峰, 鲁剑巍, 潘勇辉, 鲁飘飘, 李小坤, 丛日环, 任涛 (2016). 钾素调控植物光合作用的生理机制. 植物生理学报 52, 1773-1784. |
| [8] | 申长卫 (2017). 施钾影响梨叶片和果实糖合成及分配的生理与分子机制. 博士论文. 南京: 南京农业大学. pp. 49-50. |
| [9] | 苏静, 祝令成, 刘茜, 彭云静, 马百全, 马锋旺, 李明军 (2022). 果实糖代谢与含量调控的研究进展. 果树学报 39, 266-279. |
| [10] |
王宏亮, 郭思义, 王棚涛, 宋纯鹏 (2018). 植物气孔发育机制研究进展. 植物学报 53, 164-174.
DOI |
| [11] |
王凯悦, 陈芳泉, 邵惠芳, 韩丹, 许自成, 黄五星 (2018). 植物角质膜研究进展. 植物学报 53, 556-564.
DOI |
| [12] |
吴一苓, 李芳兰, 胡慧 (2022). 叶脉结构与功能及其对叶片经济谱的影响. 植物学报 57, 388-398.
DOI |
| [13] | 朱新广, 许大全 (2021). 光合作用研究技术. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社. pp. 176-188. |
| [14] | 邹琦 (1995). 植物生理生化实验指导. 北京: 中国农业出版社. pp. 70-72. |
| [15] |
Arnault G, Mony C, Vandenkoornhuyse P (2023). Plant microbiota dysbiosis and the Anna Karenina principle. Trends Plant Sci 28, 18-30.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Breia R, Conde A, Badim H, Fortes AM, Gerós H, Granell A (2021). Plant SWEETs: from sugar transport to plant- pathogen interaction and more unexpected physiological roles. Plant Physiol 186, 836-852.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Chaudhry V, Runge P, Sengupta P, Doehlemann G, Parker JE, Kemen E (2021). Shaping the leaf microbiota: plant-microbe-microbe interactions. J Exp Bot 72, 36-56.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Chen T, Nomura K, Wang XL, Sohrabi R, Xu J, Yao LY, Paasch BC, Ma L, Kremer J, Cheng YT, Zhang L, Wang N, Wang ET, Xin XF, He SY (2020). A plant genetic network for preventing dysbiosis in the phyllosphere. Nature 580, 653-657.
DOI |
| [19] |
Copeland JK, Yuan LJ, Layeghifard M, Wang PW, Guttman DS (2015). Seasonal community succession of the phyllosphere microbiome. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 28, 274-285.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Darlison J, Mogren L, Rosberg AK, Grudén M, Minet A, Liné C, Mieli M, Bengtsson T, Håkansson Å, Uhlig E, Becher PG, Karlsson M, Alsanius BW (2019). Leaf mineral content govern microbial community structure in the phyllosphere of spinach (Spinacia oleracea) and rocket (Diplotaxis tenuifolia). Sci Total Environ 20, 501-512. |
| [21] |
de Bang TC, Husted S, Laursen KH, Persson DP, Schjoerring JK (2021). The molecular-physiological functions of mineral macronutrients and their consequences for deficiency symptoms in plants. New Phytol 229, 2446-2469.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
De Costa DM, Rathnayake RMPS, De Costa WAJM, Kumari WMD, Dissanayake DMN (2006). Variation of phyllosphere microflora of different rice varieties in Sri Lanka and its relationship to leaf anatomical and physiological characters. J Agron Crop Sci 192, 209-220.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Fürnkranz M, Wanek W, Richter A, Abell G, Rasche F, Sessitsch A (2008). Nitrogen fixation by phyllosphere bacteria associated with higher plants and their colonizing epiphytes of a tropical lowland rainforest of Costa Rica. ISME J 2, 561-570.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
Gong TY, Xin XF (2021). Phyllosphere microbiota: community dynamics and its interaction with plant hosts. J Integr Plant Biol 63, 297-304.
DOI |
| [25] |
González-Teuber M, Palma-Onetto V, Aguilera-Sammaritano J, Mithöfer A (2021). Roles of leaf functional traits in fungal endophyte colonization: potential implications for host-pathogen interactions. J Ecol 109, 3972-3987.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Hou WF, Xue XX, Li XK, Khan MR, Yan JY, Ren T, Cong RH, Lu JW (2019). Interactive effects of nitrogen and potassium on: grain yield, nitrogen uptake and nitrogen use efficiency of rice in low potassium fertility soil in China. Field Crops Res 236, 14-23.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Hunter PJ, Hand P, Pink D, Whipps JM, Bending GD (2010). Both leaf properties and microbe-microbe interactions influence within-species variation in bacterial population diversity and structure in the lettuce (Lactuca species) phyllosphere. Appl Environ Microb 76, 8117-8125.
DOI PMID |
| [28] |
Jiang M, Wang ZS, Li XN, Liu SQ, Song FB, Liu FL (2021). Relationship between endophytic microbial diversity and grain quality in wheat exposed to multi-generational CO2 elevation. Sci Total Environ 776, 146029.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Kumar P, Kumar T, Singh S, Tuteja N, Prasad R, Singh J (2020). Potassium: a key modulator for cell homeostasis. J Biotechnol 324, 198-210.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
Laforest-Lapointe I, Messier C, Kembel SW (2016). Host species identity, site and time drive temperate tree phyllosphere bacterial community structure. Microbiome 4, 27.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
Li Y, Zhang ZY, Liu WY, Ke MJ, Qu Q, Zhou ZG, Lu T, Qian HF (2021). Phyllosphere bacterial assemblage is affected by plant genotypes and growth stages. Microbiol Res 248, 126743.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Lu ZF, Ren T, Li J, Hu WS, Zhang JL, Yan JY, Li XK, Cong RH, Guo SW, Lu JW (2020). Nutrition-mediated cell and tissue-level anatomy triggers the covariation of leaf photosynthesis and leaf mass per area. J Exp Bot 71, 6524-6537.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
Mercier J, Lindow SE (2000). Role of leaf surface sugars in colonization of plants by bacterial epiphytes. Appl Environ Microbiol 66, 369-374.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Mo YY, Peng F, Gao XF, Xiao P, Logares R, Jeppesen E, Ren KX, Xue YY, Yang J (2021). Low shifts in salinity determined assembly processes and network stability of microeukaryotic plankton communities in a subtropical urban reservoir. Microbiome 9, 128.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
Niu SQ, Gao Y, Zi HX, Liu Y, Liu XM, Xiong XQ, Yao QQ, Qin ZW, Chen N, Guo L, Yang YZ, Qin P, Lin JZ, Zhu YH (2022). The osmolyte-producing endophyte Streptomyces albidoflavus OsiLf-2 induces drought and salt tolerance in rice via a multi-level mechanism. Crop J 10, 375-386.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Qi SS, Bogdanov A, Cnockaert M, Acar T, Ranty-Roby S, Coenye T, Vandamme P, König GM, Crüsemann M, Carlier A (2021). Induction of antibiotic specialized metabolism by co-culturing in a collection of phyllosphere bacteria. Environ Microbiol 23, 2132-2151.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
Reisberg EE, Hildebrandt U, Riederer M, Hentschel U (2013). Distinct phyllosphere bacterial communities on Arabidopsis wax mutant leaves. PLoS One 8, e78613.
DOI URL |
| [38] | Ren T, Lu JW, Li H, Zou J, Xu HL, Liu XW, Li XK (2013). Potassium-fertilizer management in winter oilseed-rape production in China. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 179, 429-440. |
| [39] |
Ritpitakphong U, Falquet L, Vimoltust A, Berger A, Métraux JP, L'Haridon F (2016). The microbiome of the leaf surface of Arabidopsis protects against a fungal pathogen. New Phytol 210, 1033-1043.
DOI PMID |
| [40] |
Röttjers L, Faust K (2018). From hairballs to hypotheses—biological insights from microbial networks. FEMS Microbiol Rev 42, 761-780.
DOI PMID |
| [41] |
Ryffel F, Helfrich EJN, Kiefer P, Peyriga L, Portais JC, Piel J, Vorholt AJ (2016). Metabolic footprint of epiphytic bacteria on Arabidopsis thaliana leaves. ISME J 10, 632-643.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Sohrabi R, Paasch BC, Liber JA, He SY (2023). Phyllosphere microbiome. Annu Rev Plant Biol 74, 539-568.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Sun AQ, Jiao XY, Chen QL, Wu AL, Zheng Y, Lin YX, He JZ, Hu HW (2021). Microbial communities in crop phyllosphere and root endosphere are more resistant than soil microbiota to fertilization. Soil Biol Biochem 153, 108113.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Tao SQ, Zhang YX, Tian CM, Duplessis S, Zhang NL (2022). Elevated ozone concentration and nitrogen addition increase poplar rust severity by shifting the phyllosphere microbial community. J Fungi 8, 523.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Venkatachalam S, Ranjan K, Prasanna R, Ramakrishnan B, Thapa S, Kanchan A (2016). Diversity and functional traits of culturable microbiome members, including cyanobacteria in the rice phyllosphere. Plant Biol 18, 627-637.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Wagner MR, Lundberg DS, Del Rio TG, Tringe SG, Dangl JL, Mitchell-Olds T (2016). Host genotype and age shape the leaf and root microbiomes of a wild perennial plant. Nat Commun 7, 12151.
DOI PMID |
| [47] |
Waqas M, Yaning C, Iqbal H, Shareef M, Rehman HU, Bilal HM (2021). Synergistic consequences of salinity and potassium deficiency in quinoa: linking with stomatal patterning, ionic relations and oxidative metabolism. Plant Physiol Biochem 159, 17-27.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
Wilson M, Lindow SE (1994). Coexistence among epiphytic bacterial populations mediated through nutritional resource partitioning. Appl Environ Microbiol 60, 4468-4477.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Xiong C, He JZ, Singh BK, Zhu YG, Wang JT, Li PP, Zhang QB, Han LL, Shen JP, Ge AH, Wu CF, Zhang LM (2021a). Rare taxa maintain the stability of crop mycobiomes and ecosystem functions. Environ Microbiol 23, 1907-1924.
DOI URL |
| [50] | Xiong C, Zhu YG, Wang JT, Singh B, Han LL, Shen JP, Li PP, Wang GB, Wu CF, Ge AH, Zhang LM, He JZ (2021b). Host selection shapes crop microbiome assembly and network complexity. New Phytol 229, 1091-1104. |
| [51] |
Zhang JL, Li J, Geng GT, Hu WS, Ren T, Cong RH, Li XK, Lu JW (2020). Combined application of nitrogen and potassium reduces seed yield loss of oilseed rape caused by Sclerotinia stem rot disease. Agron J 112, 5143-5157.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Zhu YG, Xiong C, Wei Z, Chen QL, Ma B, Zhou SYD, Tan JQ, Zhang LM, Cui HL, Duan GL (2022a). Impacts of global change on the phyllosphere microbiome. New Phytol 234, 1977-1986.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
Zhu YX, Han Y, Liu GL, Bian ZR, Yan XY, Li YY, Long HA, Yu GS, Wang Y (2022b). Novel indole-mediated potassium ion import system confers a survival advantage to the Xanthomonadaceae family. ISME J 16, 1717-1729.
DOI URL |
| [1] | Wenqi Zhou, Yuqian Zhou, Yongsheng Li, Haijun He, Yanzhong Yang, Xiaojuan Wang, Xiaorong Lian, Zhongxiang Liu, Zhubing Hu. ZmICE2 Regulates Stomatal Development in Maize [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(6): 866-881. |
| [2] | Ziwen Tang, Dongping Zhang. Research Progress on the Molecular Mechanism of Starch Accumulation in Rice Endosperm [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(4): 612-621. |
| [3] | LI Xu, WU Ting, CHENG Yan, TAN Na-Dan, JIANG Fen, LIU Shi-Zhong, CHU Guo-Wei, MENG Ze, LIU Ju-Xiu. Ecophysiological adaptability of four tree species in the southern subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest to warming [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2020, 44(12): 1203-1214. |
| [4] | Xiaoqing Yang,Xiaoqin Huang,Xiaoyang Han,Tengfei Liu,Xiaowei Yue,Ran Yi. Effect of Exogenous Substances on Cold Tolerance and Key Sucrose Metabolic Gene Expression in Camellia sinensis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(1): 21-30. |
| [5] | Shuhui Zhang,Hong Wang,Wenru Wang,Xuelian Wu,Yuansong Xiao,Futian Peng. Effects of Sucrose on Seedling Growth and Development and SnRK1 Activity in Prunus persica [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(6): 744-752. |
| [6] | Chen-Song HAO, Qing-Kai WANG, Xiao-Ling SUN. Effects of light heterogeneity on leaf anatomical structure in Buchloe dactyloides [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2016, 40(3): 246-254. |
| [7] | Bei-Bei DUAN, Cheng-Zhang ZHAO, Ting XU, Hui-Ling ZHENG, Wei FENG, Ling HAN. Correlation analysis between vein density and stomatal traits of Robinia pseudoacacia in different aspects of Beishan Mountain in Lanzhou [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2016, 40(12): 1289-1297. |
| [8] | Yi Zhang, Dabing Zhang, Man Liu. The Molecular Mechanism of Long-distance Sugar Transport in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2015, 50(1): 107-121. |
| [9] | Liqing Song, Chunmei Hu, Xilin Hou, Lei Shi, Li’an Liu, Jingcheng Yang, Chuangdao Jiang. Relationship Between Photosynthetic Characteristics and Leaf Vein Density in Sorghum bicolor and Perilla frutescens [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2015, 50(1): 100-106. |
| [10] | XIONG Hui, MA Cheng-En, LI Le, ZENG Hui, GUO Da-Li. Stomatal characteristics of ferns and angiosperms and their responses to changing light intensity at different habitats [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2014, 38(8): 868-877. |
| [11] | WANG Wei, CAI Yi-Xia, YANG Jian-Chang, ZHU Qing-Sen. Effects of soil water deficit on physiological causes of rice grain-filling [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2011, 35(2): 195-202. |
| [12] | Bo Huang, Zhaoyu Jiang, Hongxia Qu, Sanmei Ma. The Epidermal Morphology of the Flower of Erythrina corallodendron [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2010, 45(05): 594-603. |
| [13] | Nianwei Qiu Ying Deng. Role of Exogenous Sucrose in Protecting PSII Particles Against Salt Stress and Heat Stress [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2007, 24(04): 484-489. |
| [14] | Jiyan Qi Jianghua Yang Chaorong Tang. Sucrose Transporter Genes and Their Functions in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2007, 24(04): 532-543. |
| [15] | JIANG Guang_Hua, MENG Ya_Li, CHEN Bing_Lin, BIAN Hai_Yun, ZHOU Zhi_Guo. EFFECTS OF LOW TEMPERATURE ON PHYSIOLOGICAL MECHANISMS OF COTTON FIBER STRENGTH FORMING PROCESS [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2006, 30(2): 335-343. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||