

植物学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (4): 486-496.DOI: 10.11983/CBB18139 cstr: 32102.14.CBB18139
范业赓1,丘立杭1,黄杏1,周慧文1,甘崇琨2,李杨瑞1,杨荣仲1,吴建明1,*( ),陈荣发1,*(
),陈荣发1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2018-06-19
接受日期:2018-12-10
出版日期:2019-07-01
发布日期:2020-01-08
通讯作者:
吴建明,陈荣发
基金资助:
Yegeng Fan1,Lihang Qiu1,Xing Huang1,Huiwen Zhou1,Chongkun Gan2,Yangrui Li1,Rongzhong Yang1,Jianming Wu1,*( ),Rongfa Chen1,*(
),Rongfa Chen1,*( )
)
Received:2018-06-19
Accepted:2018-12-10
Online:2019-07-01
Published:2020-01-08
Contact:
Jianming Wu,Rongfa Chen
摘要: 以甘蔗(Saccharum officinarum)优良品种桂糖42号(GT42)为研究材料, 分别于未伸长期(9-10叶龄以前) (Ls1)、伸长初期(12-13叶龄) (Ls2)和伸长盛期(15-16叶龄) (Ls3)取甘蔗第2片真叶(自顶部起)对应的节间组织, 测定其赤霉素(GA)、生长素(IAA)、油菜素甾醇(BR)、细胞分裂素(CTK)、乙烯(ETH)和脱落酸(ABA)的含量, 并通过实时荧光定量PCR (qRT-PCR)分析赤霉素合成途径关键基因GA20氧化酶基因(GA20-Oxidase1)、赤霉素受体基因(GID1)和DELLA蛋白编码基因(GAI)的差异表达。结果表明, 在甘蔗伸长期间, GA和IAA含量呈现上升趋势, CTK和ABA含量呈下降趋势, ETH含量先上升后下降, BR含量则变化不明显; GA20-Oxidase1和GID1的表达呈上升趋势, 而GAI的表达则呈下降趋势, 这与相关植物激素的变化基本一致。综上, 甘蔗节间伸长过程主要与GA和IAA相关, 其次为CTK和ABA, 而ETH受到IAA的调控影响节间伸长; 植物激素间通过相互作用调控GA20-Oxidase1、GID1和GAI的表达, 影响GA含量和GA的信号转导过程, 进而影响甘蔗节间的伸长。该研究揭示了甘蔗节间伸长过程中赤霉素生物合成途径和信号转导关键基因的差异表达及植物激素含量的动态变化规律。
范业赓,丘立杭,黄杏,周慧文,甘崇琨,李杨瑞,杨荣仲,吴建明,陈荣发. 甘蔗节间伸长过程赤霉素生物合成关键基因的表达及相关植物激素动态变化. 植物学报, 2019, 54(4): 486-496.
Yegeng Fan,Lihang Qiu,Xing Huang,Huiwen Zhou,Chongkun Gan,Yangrui Li,Rongzhong Yang,Jianming Wu,Rongfa Chen. Expression Analysis of Key Genes in Gibberellin Biosynthesis and Related Phytohormonal Dynamics During Sugarcane Internode Elongation. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(4): 486-496.
| Genes | Sequences of primers (5'-3') | Tm (°C) | Product length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25S rRNA | F: CGAATACGAACCGTGAAAGC | 58.4 | 164 |
| R: ACAATGATAGGAAGAGCCGACA | 59.0 | ||
| GA20-Oxidase1 | F: CCGTCGTGGACTACTTCG | 54.0 | 205 |
| R: CACGGCGGGTAGTAGTTGAG | 58.3 | ||
| GID1 | F: GGTCATCCTCTTCTTCCACGG | 60.8 | 119 |
| R: AGTTGACGGACACCACGACG | 61.3 | ||
| GAI | F: GCGACGACAAGGATGAGGA | 58.8 | 186 |
| R: TGAAGCGGTCAAGGAATGTG | 59.2 |
表1 实时荧光定量PCR引物序列
Table 1 Primers for real-time quantitative PCR
| Genes | Sequences of primers (5'-3') | Tm (°C) | Product length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25S rRNA | F: CGAATACGAACCGTGAAAGC | 58.4 | 164 |
| R: ACAATGATAGGAAGAGCCGACA | 59.0 | ||
| GA20-Oxidase1 | F: CCGTCGTGGACTACTTCG | 54.0 | 205 |
| R: CACGGCGGGTAGTAGTTGAG | 58.3 | ||
| GID1 | F: GGTCATCCTCTTCTTCCACGG | 60.8 | 119 |
| R: AGTTGACGGACACCACGACG | 61.3 | ||
| GAI | F: GCGACGACAAGGATGAGGA | 58.8 | 186 |
| R: TGAAGCGGTCAAGGAATGTG | 59.2 |
| Period | Plant height (cm) | Elongation rate (cm·d-1) | Internode number | Average internode length (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ls1 | 39.38±1.10 | 0.44±0.01 | 4±1 | 6.09±0.28 |
| Ls2 | 68.37±1.25** | 0.97±0.07** | 7±1** | 8.05±0.18** |
| Ls3 | 147.13±0.85** | 2.63±0.06** | 12±1** | 11.43±0.07** |
表2 不同时期甘蔗的伸长情况(平均值±标准差)
Table 2 The elongation of sugarcane at different stages (means±SD)
| Period | Plant height (cm) | Elongation rate (cm·d-1) | Internode number | Average internode length (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ls1 | 39.38±1.10 | 0.44±0.01 | 4±1 | 6.09±0.28 |
| Ls2 | 68.37±1.25** | 0.97±0.07** | 7±1** | 8.05±0.18** |
| Ls3 | 147.13±0.85** | 2.63±0.06** | 12±1** | 11.43±0.07** |
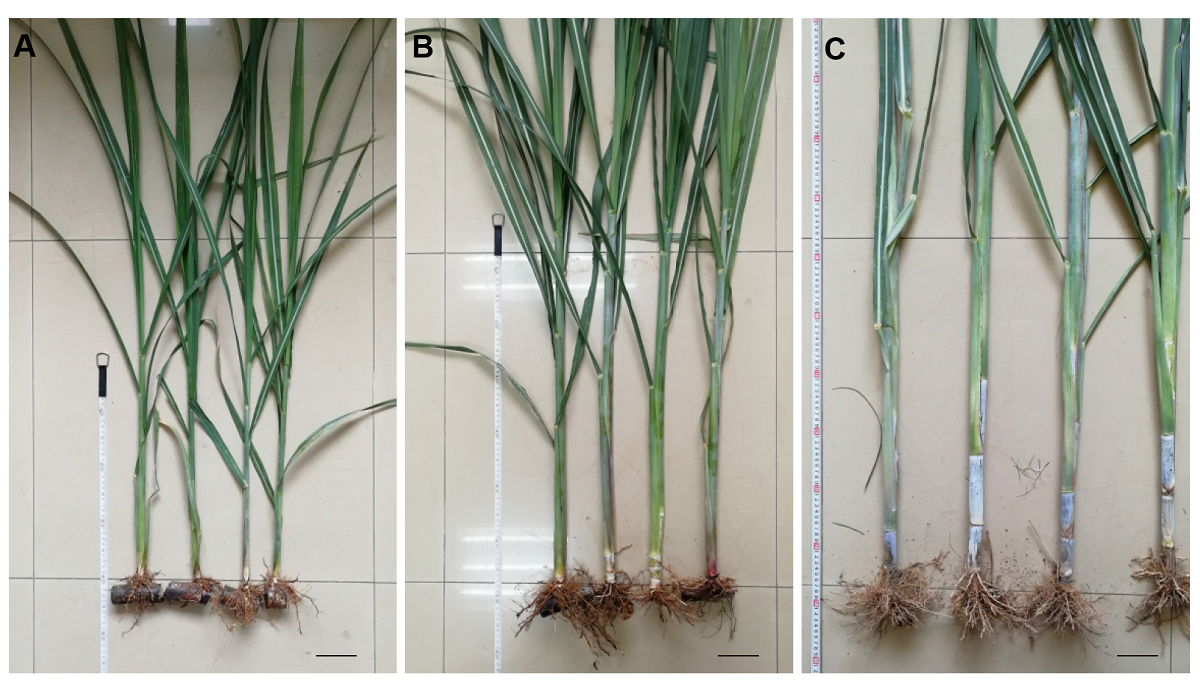

图1 不同时期甘蔗节间生长的差异 (A) 未伸长期(Ls1)甘蔗株高; (B) 伸长初期(Ls2)甘蔗株高; (C) 伸长盛期(Ls3)甘蔗株高。Bars=10 cm
Figure 1 Changes of sugarcane elongation at different stages (A) The sugarcane plant height of non-elongation stage (Ls1); (B) The sugarcane plant height of early elongation stage (Ls2); (C) The sugarcane plant height of elongation stage (Ls3). Bars=10 cm
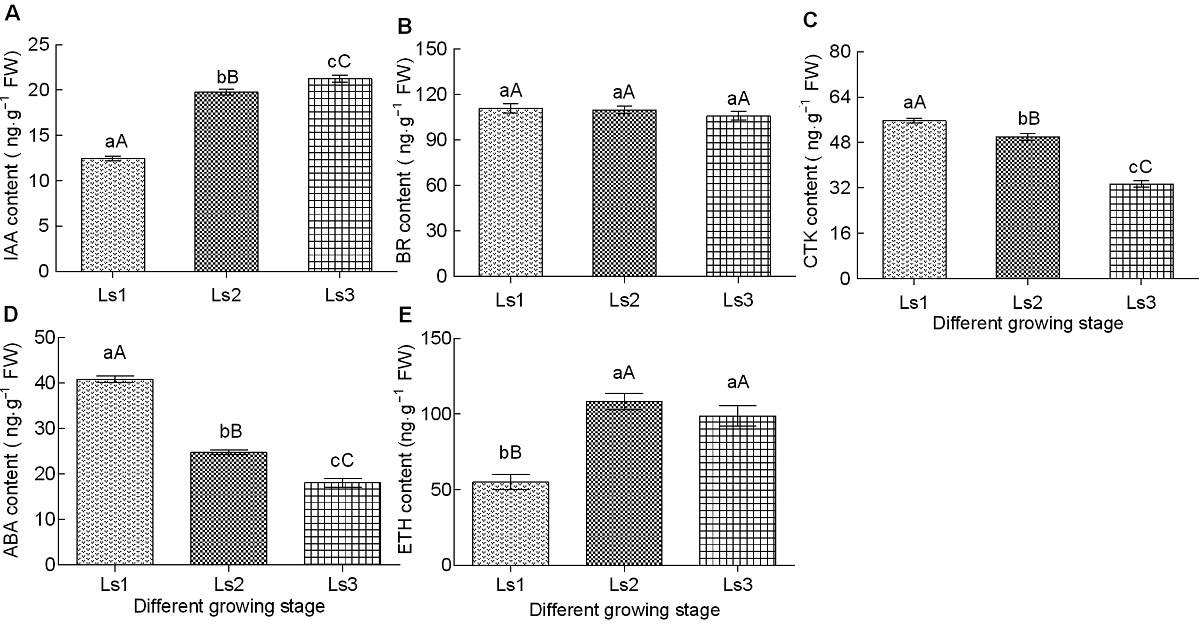
图2 不同伸长时期甘蔗节间植物激素含量变化 (A) 生长素(IAA); (B) 油菜素甾醇(BR); (C) 细胞分裂素(CTK); (D) 脱落酸(ABA); (E) 乙烯(ETH)。不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05), 不同大写字母表示差异极显著(P<0.01)。Ls1-Ls3同表2。
Figure 2 Changes of endogenous hormone contents in sugarcane internode during different elongation stages (A) Indole acetic acid (IAA); (B) Brassinosteroids (BR); (C) Cytokinin (CTK); (D) Abscisic acid (ABA); (E) Ethylene (ETH). The different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05), and the different capital letters indicate extremely significant differences (P<0.01). Ls1-Ls3 see Table 2.
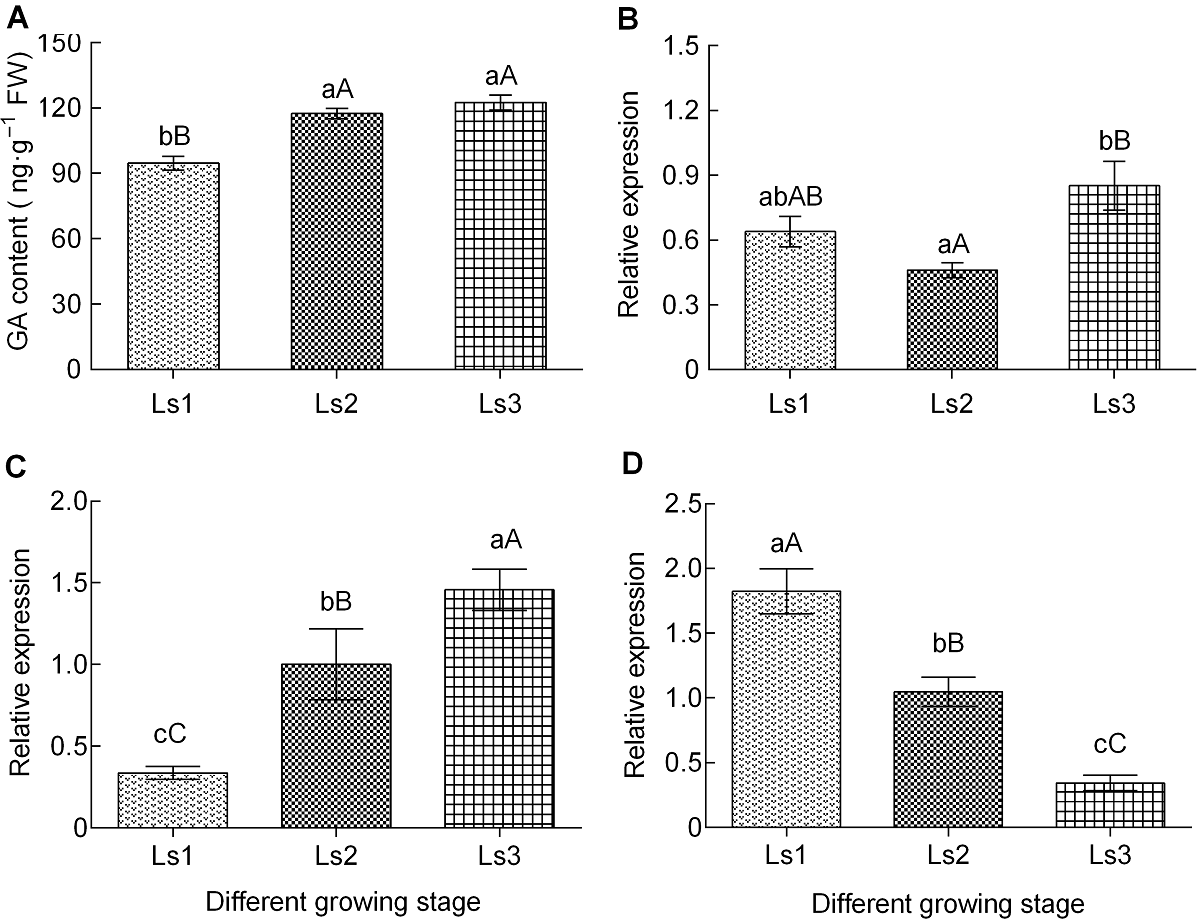
图3 甘蔗节间伸长过程中赤霉素含量变化及其合成途径关键基因的差异表达 (A) 赤霉素(GA)含量; (B) GA20-Oxidase1的表达量; (C) GID1的表达量; (D) GAI的表达量。不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05), 不同大写字母表示差异极显著(P<0.01)。Ls1-Ls3同表2。
Figure 3 The changes of gibberellin content and genes differential expression of synthetic pathways during sugarcane internode elongation (A) The content of gibberellic acid (GA); (B) The expression level of GA20-Oxidase1; (C) The expression level of GID1; (D) The expression level of GAI. The different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05), and the different capital letters indicate extremely significant differences (P<0.01). Ls1-Ls3 see Table 2.
| [1] | 陈登举, 高培军, 吴兴波, 高岩, 温国胜, 王玉魁, 高荣孚, 张汝民 ( 2013). 毛竹茎秆叶绿体超微结构及其发射荧光光谱特征. 植物学报 48, 635-642. |
| [2] | 陈明辉, 黄杏, 谢晓娜, 杨丽涛, 李杨瑞, 陈保善 ( 2013). 宿根矮化病菌对甘蔗生长和内源激素的影响. 华中农业学报 32(3), 57-61. |
| [3] | 陈宇杰, 刘飞, 梁菲菲, 石君, 赵焕梦 ( 2017). 蓖麻DELLA蛋白家族GAI基因克隆、表达及生物信息学分析. 内蒙古民族大学学报(自然科学版) 32, 320-327. |
| [4] | 刁家连, 何钟佩 ( 1998). 冬小麦茎秆生长过程中内源激素动态的系统研究. 中国农业大学学报 3(增刊), 16-20. |
| [5] | 丁兴萃 ( 1997). 毛竹笋体生长发育过程中内源激素的动态分析. 竹子研究汇刊 16(2), 53-62. |
| [6] | 董静, 尹梦回, 杨帆, 赵娟, 覃珊, 侯磊, 罗明, 裴炎, 肖月华 ( 2009). 棉花赤霉素不敏感矮化GID1同源基因的克隆和表达分析. 作物学报 35, 1822-1830. |
| [7] | 杜维, 丁健, 阮成江 ( 2018). 沙棘果实发育过程中内源激素水平的动态变化. 植物学报 53, 219-226. |
| [8] | 段娜, 贾玉奎, 徐军, 陈海玲, 孙鹏 ( 2015). 植物内源激素研究进展. 中国农学通报 31(2), 159-165. |
| [9] | 方楷, 杨光耀, 杨清培, 黄俊宝, 施建敏, 于芬 ( 2011). 毛竹成竹过程中内源激素动态变化. 江西农业大学学报 33, 1107-1111. |
| [10] | 冯丹, 陈贵林 ( 2011). 独脚金内酯调控侧枝发育的研究进展. 生态学杂志 30, 349-356. |
| [11] | 冯孟杰, 徐恒, 张华, 朱英 ( 2015). 茉莉素调控植物生长发育的研究进展. 植物生理学报 51, 407-412. |
| [12] | 甘小洪, 丁雨龙 ( 2004). 毛竹茎秆纤维发育过程的超微结构观察. 植物学通报 21, 180-188. |
| [13] | 甘小洪, 唐翠彬, 温中斌, 丁雨龙 ( 2013). 寿竹笋的营养成分研究. 天然产物研究与开发 25, 494-499. |
| [14] | 郭光生, 曾炳山, 范春节, 裘珍飞 ( 2018). 外施GA3对巨桉木质部发育的影响. 分子植物育种 16, 602-606. |
| [15] | 季兰, 杨仁崔 ( 2002). 水稻茎伸长生长与植物激素. 植物学通报 19, 109-115. |
| [16] | 江雪, 楼崇, 袁娜, 岳晋军, 顾小平 ( 2016). 外源GA3对毛竹实生苗新分蘖竹株秆形与竹材纤维质量的影响. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) 40(2), 121-126. |
| [17] | 姜勇, 胡尚连, 曹颖, 卢学琴, 黄艳, 徐刚 ( 2017). 外源GA3对毛竹实生苗茎秆生长及CesA基因表达的影响. 植物研究 37, 744-750. |
| [18] | 李欢庆, 李桂玲, 崔香环, 安国勇, 宋纯鹏 ( 2008). 茉莉酸甲酯抑制拟南芥根伸长生长电生理学机制. 广西植物 28, 414-419. |
| [19] | 李惠民, 李宏亮, 高吉仁 ( 2010). 水杨酸对黄瓜种子萌发和胚根伸长的影响及其与乙烯的关系. 西安工程大学学报 24, 773-775. |
| [20] | 黎舒佳, 高谨, 李家洋, 王永红 ( 2015). 独脚金内酯调控水稻分蘖的研究进展. 植物学报 50, 539-548. |
| [21] | 李霞, 郭振华 ( 2014). 麻竹节间伸长过程的初步研究. 植物分类与资源学报 36, 22-28. |
| [22] | 李兴亮, 郭献平, 沈元月, 曹庆芹, 冯永庆, 秦岭 ( 2011). 板栗赤霉素缺陷型短雄花序芽变的初步鉴定及CmGID1基因的表达分析. 园艺学报 38, 1251-1258. |
| [23] | 刘芳, 袁华招, 沈欣杰, 廖雄, 李天红 ( 2013). 外源GA3和PP333对甜樱桃新梢生长及赤霉素代谢关键基因表达的影响. 核农学报 27, 272-278. |
| [24] | 阙友雄, 许莉萍, 徐景升, 张积森, 张木清, 陈如凯 ( 2009). 甘蔗基因表达定量PCR分析中内参基因的选择. 热带作物学报 30, 274-278. |
| [25] | 王利军, 战吉成, 黄卫东 ( 2002). 水杨酸与植物抗逆性. 植物生理学通讯 38, 619-624. |
| [26] | 王伦旺, 廖江雄, 谭芳, 唐仕云, 黄家雍, 李翔, 杨荣仲, 李杨瑞, 黄海荣, 经艳, 邓宇驰 ( 2015). 高产高糖抗倒伏甘蔗新品种桂糖42号的选育及高产栽培技术. 南方农业学报 46, 1361-1366. |
| [27] | 魏强, 丁雨龙 ( 2017). 矢竹地下茎转录组测序及节间生长相关基因表达分析. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) 41(5), 42-48. |
| [28] | 卫晓轶, 张明才, 张燕, 李召虎, 段留生 ( 2011). 乙烯利对不同基因型玉米节间伸长和内源激素的影响. 农药学学报 13, 475-479. |
| [29] | 吴建明, 李杨瑞, 王爱勤, 杨柳, 杨丽涛 ( 2010 a). 赤霉素处理对甘蔗节间伸长及产质量的影响. 中国糖料 ( 4), 24-26. |
| [30] | 吴建明, 李杨瑞, 王爱勤, 杨柳, 杨丽涛 ( 2010 b). 赤霉素诱导甘蔗节间伸长的效应与相关酶活性的关系. 西北植物学报 30, 962-967. |
| [31] | 吴建明, 李杨瑞, 杨柳, 王爱勤, 杨丽涛 ( 2009). 赤霉素诱导甘蔗节间伸长与内源激素变化的关系. 热带作物学报 30, 1452-1457. |
| [32] | 吴良如, 萧江华 ( 1998). 大小年毛竹林中内源激素节律变化特征的研究. 竹子研究汇刊 17, 24-30. |
| [33] | 肖辉海 ( 2008). 长穗颈温敏核不育水稻穗颈节间伸长与内源激素的关系. 植物生理学通讯 44, 656-660. |
| [34] | 肖辉海, 郝小花, 王文龙 ( 2011). 温度对温敏核不育水稻eui突变体最上节间伸长的影响. 植物学报 46, 138-146. |
| [35] | 许婷婷, 杨光耀, 杨清培, 于芬 ( 2016). 厚壁毛竹快速高生长期竹秆ATP酶超微细胞化学定位. 西北植物学报 36, 1566-1574. |
| [36] | 徐有明, 郝培应, 费本华 ( 2008). 竹笋形态发育构建过程中解剖结构及化学成分的动态变化. 东北林业大学学报 36(4), 8-11, 16. |
| [37] | 杨晓婉, 郑国琦, 杨涓, 许兴, 卢迪, 杨乐 ( 2014). 宁夏枸杞果实内源激素的变化及其与细胞壁成分和相关酶的关系. 植物学报 49, 30-40. |
| [38] | 杨奕, 董文渊, 邱月群, 李雯, 杨佳俊, 韩妍 ( 2015). 筇竹笋生长过程中营养成分的变化. 东北林业大学学报 43, 80-82, 87. |
| [39] | 张春玲 ( 2014). 毛竹笋-竹生长发育过程系统分析与生长素相关基因研究. 博士论文. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院. pp. 42-68. |
| [40] | 张珂 ( 2014). 玉米节间伸长过程中相关基因甲基化及表达分析. 硕士论文. 武汉: 华中农业大学. pp. 37-38. |
| [41] | 张同祯, 李永生, 李玥, 姚海梅, 赵娟, 王婵, 赵阳, 王汉宁, 方永丰, 胡晋 ( 2016). 多胺氧化酶(PAO)调控光诱导玉米中胚轴伸长的生理机制. 作物学报 42, 734-742. |
| [42] | 张莹, 田埂, 路慧萍, 冉洪, 胡陶, 郭起荣 ( 2015). 厚壁毛竹六个节气笋芽发育的转录组分析. 江西农业大学学报 37, 466-474. |
| [43] | Abeles FB, Morgan PW, Saltveit ME ( 1992). Ethylene in Plant Biology. San Diego: Academic Press. pp. 123-135. |
| [44] | Ayano M, Kani T, Kojima M, Sakakibara H, Kitaoka T, Kuroha T, Angeles-Shim RB, Kitano H, Nagai K, Ashikari M ( 2014). Gibberellin biosynthesis and signal transduction is essential for internode elongation in deepwater rice. Plant Cell Environ 37, 2313-2324. |
| [45] | Choi YH, Yoshizawa K, Kobayashi M, Sakurai A ( 1995). Distribution of endogenous gibberellins in vegetative shoots of rice. Plant Cell Physiol 36, 997-1001. |
| [46] | Coles JP, Phillips AL, Croker SJ, García-Lepe R, Lewis MJ, Hedden P ( 1999). Modification of gibberellin production and plant development in Arabidopsis by sense and antisense expression of gibberellin 20-oxidase genes. Plant J 17, 547-556. |
| [47] | Cui K, He CY, Zhang JG, Duan AG, Zeng YF ( 2012). Temporal and spatial profiling of internode elongation-associated protein expression in rapidly growing culms of bamboo. J Proteome Res 11, 2492-2507. |
| [48] | Cutler AJ, Krochko JE ( 1999). Formation and breakdown of ABA. Trends Plant Sci 4, 472-478. |
| [49] | De Lucas M, Davière JM, Rodríguez-Falcón M, Pontin M, Iglesias-Pedraz JM, Lorrain S, Fankhauser C, Blázquez MA, Titarenko E, Prat S ( 2008). A molecular framework for light and gibberellin control of cell elongation. Nature 451, 480-484. |
| [50] | Eriksson ME, Hoffman D, Kaduk M, Mauriat M, Moritz T ( 2015). Transgenic hybrid aspen trees with increased gibberellin (GA) concentrations suggest that GA acts in parallel with FLOWERING LOCUS T2 to control shoot elongation. New Phytol 205, 1288-1295. |
| [51] | Feng SH, Martinez C, Gusmaroli G, Wang Y, Zhou JL, Wang F, Chen LY, Yu L, Iglesias-Pedraz JM, Kircher S, Schäfer E, Fu XD, Fan LM, Deng XW ( 2008). Coordinated regulation of Arabidopsis thaliana development by light and gibberellins. Nature 451, 475-479. |
| [52] | Gao J, Zhang Y, Zhang CL, Qi FY, Li XP, Mu SH, Peng ZH ( 2014). Characterization of the floral transcriptome of Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) at different flowering developmental stages by transcriptome sequencing and RNA-seq analysis. PLoS One 9, e98910. |
| [53] | Gao XH, Huang XZ, Xiao SL, Fu XD ( 2008). Evolutionarily conserved DELLA-mediated gibberellin signaling in plants. J Integr Plant Biol 50, 825-834. |
| [54] | Hattori Y, Nagai K, Furukawa S, Song XJ, Kawano R, Sakakibara H, Wu JZ, Matsumoto T, Yoshimura A, Kitano H, Matsuoka M, Mori H, Ashikari M ( 2009). The ethylene response factors SNORKEL1 and SNORKEL2 allow rice to adapt to deep water. Nature 460, 1026-1030. |
| [55] | He CY, Cui K, Zhang JG, Duan AG, Zeng YF ( 2013). Next-generation sequencing-based mRNA and microRNA expression profiling analysis revealed pathways involved in the rapid growth of developing culms in Moso bamboo. BMC Plant Biol 13, 119. |
| [56] | Hedden P, Phillips AL ( 2000). Gibberellin metabolism: new insights revealed by the genes. Trends Plant Sci 5, 523-530. |
| [57] | Kende H, van der Knaap E, Cho HT ( 1998). Deepwater rice: a model plant to study stem elongation. Plant Physiol 118, 1105-1110. |
| [58] | Lawit SJ, Wych HM, Xu DP, Kundu S, Tomes DT ( 2010). Maize DELLA proteins dwarf plant8 and dwarf plant9 as modulators of plant development. Plant Cell Physiol 51, 1854-1868. |
| [59] | Lee S, Cheng H, King KE, Wang W, He YW, Hussain A, Lo J, Harberd NP, Peng JR ( 2002). Gibberellin regulates Arabidopsis seed germination via RGL2, a GAI/RGA-like gene whose expression is up-regulated following imbibition. Genes Dev 16, 646-658. |
| [60] | Li LF, Zhang WB, Zhang LL, Li N, Peng JZ, Wang YQ, Zhong CM, Yang YP, Sun SL, Liang S, Wang XJ ( 2015). Transcriptomic insights into antagonistic effects of gibberellin and abscisic acid on petal growth in Gerbera hybrida. Front Plant Sci 6, 168. |
| [61] | Magome H, Nomura T, Hanada A, Takeda-Kamiya N, Ohnishi T, Shinma Y, Katsumata T, Kawaide H, Kamiya Y, Yamaguchi S ( 2013). CYP714B1 and CYP 714B2 encode gibberellin 13-oxidases that reduce gibberellin activity in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110, 1947-1952. |
| [62] | Mauriat M, Moritz T ( 2009). Analyses of GA20ox- and GID1-over-expressing aspen suggest that gibberellins play two distinct roles in wood formation. Plant J 58, 989-1003. |
| [63] | Peng JR, Carol PO, Richards DE, King KE, Cowling RJ, Murphy GP, Harberd NP ( 1997). The Arabidopsis GAI gene defines a signaling pathway that negatively regulates gibberellin responses. Genes Dev 11, 3194-3205. |
| [64] | Peng ZH, Zhang CL, Zhang Y, Hu T, Mu SH, Li XP, Gao J ( 2013). Transcriptome sequencing and analysis of the fast growing shoots of Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). PLoS One 8, e78944. |
| [65] | Pierik R, Cuppens MLC, Voesenek LACJ, Visser EJW ( 2004). Interactions between ethylene and gibberellins in phytochrome-mediated shade avoidance responses in tobacco. Plant Physiol 136, 2928-2936. |
| [66] | Pierik R, Visser EJW, De Kroon H, Voesenek LACJ ( 2003). Ethylene is required in tobacco to successfully compete with proximate neighbours. Plant Cell Environ 26, 1229-1234. |
| [67] | Qin XQ, Zeevaart JAD ( 2002). Overexpression of a 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase gene in Nicotiana plumbaginifolia increases abscisic acid and phaseic acid levels and enhances drought tolerance. Plant Physiol 128, 544-551. |
| [68] | Rieu I, Ruiz-Rivero O, Fernandez-Garcia N, Griffiths J, Powers SJ, Gong F, Linhartova T, Eriksson S, Nilsson O, Thomas SG, Phillips AL, Hedden P ( 2008). The gibberellin biosynthetic genes AtGA20ox1 and AtGA20- ox2 act, partially redundantly, to promote growth and development throughout the Arabidopsis life cycle. Plant J 53, 488-504. |
| [69] | Ross JJ, O’Neill DP, Smith JJ, Kerckhoffs LHJ, Elliot RC ( 2000). Evidence that auxin promotes gibberellin A1 biosynthesis in pea. Plant J 21, 547-552. |
| [70] | Takatsuka H, Umeda M ( 2014). Hormonal control of cell division and elongation along differentiation trajectories in roots. J Exp Bot 65, 2633-2643. |
| [71] | Thomas GS, Hedden P ( 2018). Gibberellin metabolism and signal transduction. In: Hedden P, Thomas SG, eds. Annual Plant Reviews. Washington: John Wiley & Sons. pp. 147-184. |
| [72] | Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Ashikari M, Nakajima M, Itoh H, Katoh E, Kobayashi M, Chow TY, Hsing YI, Kitano H, Yamaguchi I, Matsuoka M ( 2005). Gibberellin insensitive Dwarf 1 encodes a soluble receptor for gibberellin. Nature 437, 693-698. |
| [73] | Voorend W, Nelissen H, Vanholme R, De Vliegher A, Van Breusegem F, Boerjan W, Roldán-Ruiz I, Muylle H, Inzé D ( 2016). Overexpression of GA20-OXIDASE1 impacts plant height, biomass allocation and saccharification efficiency in maize. Plant Biotechnol J 14, 997-1007. |
| [74] | Wang HY, Cui K, He CY, Zeng YF, Liao SX, Zhang JG ( 2015). Endogenous hormonal equilibrium linked to bamboo culm development. Genet Mol Res 14, 11312-11323. |
| [75] | Wang YJ, Deng DX ( 2014). Molecular basis and evolutionary pattern of GA-GID1-DELLA regulatory module. Mol Genet Genomics 289, 1-9. |
| [76] | Xiao YH, Ye YF, Feng Y, Li XB, Luo M, Hou L, Luo XY, Li DM, Pei Y ( 2006). Functional expression of the cotton gibberellic acid oxidase homologous gene GhGA20ox1 in tobacco. J Plant Physiol Mol Biol 32, 563-569. |
| [1] | 刘旭鹏, 王敏, 韩守安, 朱学慧, 王艳蒙, 潘明启, 张雯. 植物器官脱落调控因素及分子机理研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 472-482. |
| [2] | 陆珍, 谢光杰, Qaisar KHAN, 覃英, 黄毓燕, 郭道君, 杨婷婷, 杨丽涛, 邢永秀, 李杨瑞, 王震. 伯克霍尔德菌通过改善生理适应性及调节铝响应基因的表达增强甘蔗对铝胁迫的耐受性[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(3): 475-487. |
| [3] | 陈婷欣, 符敏, 李娜, 杨蕾蕾, 李凌飞, 钟春梅. 铁甲秋海棠DNA甲基转移酶全基因组鉴定及表达分析(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 726-737. |
| [4] | 段政勇, 丁敏, 王宇卓, 丁艺冰, 陈凌, 王瑞云, 乔治军. 糜子SBP基因家族全基因组鉴定及表达分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 231-244. |
| [5] | 张悦婧, 桑鹤天, 王涵琦, 石珍珍, 李丽, 王馨, 孙坤, 张继, 冯汉青. 植物对非生物胁迫系统性反应中信号传递的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 122-133. |
| [6] | 白明义, 彭金荣, 傅向东. 赤霉素和油菜素内酯信号通路双重调控助力小麦新一轮“绿色革命”[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(2): 194-198. |
| [7] | 李季蔓, 靳楠, 胥毛刚, 霍举颂, 陈小云, 胡锋, 刘满强. 不同干旱水平下蚯蚓对番茄抗旱能力的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21488-. |
| [8] | 李月, 胡德升, 谭金芳, 梅浩, 王祎, 李慧, 李芳, 韩燕来. 单列毛壳菌通过促进秸秆降解并调控激素响应基因表达促进玉米生长[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(4): 422-433. |
| [9] | 戴琛, 汪瑾, 卢亚萍. 衍生化UPLC-MS法测定酸性植物激素[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(4): 500-507. |
| [10] | 孟彦彦, 张楠, 熊延. 植物TOR激酶响应上游信号的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 1-11. |
| [11] | 赵晓亭, 毛凯涛, 徐佳慧, 郑钏, 罗晓峰, 舒凯. 蛋白质磷酸化修饰与种子休眠及萌发调控[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(4): 488-499. |
| [12] | 俞启璐, 赵江哲, 朱晓仙, 张可伟. 水稻根分泌激素调节生长速度[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(2): 175-182. |
| [13] | 谢露露, 崔青青, 董春娟, 尚庆茂. 植物嫁接愈合分子机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(5): 634-643. |
| [14] | 姚瑞枫,谢道昕. 独脚金内酯信号途径的新发现——抑制子也是转录因子[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(4): 397-402. |
| [15] | 徐佳慧, 代宇佳, 罗晓峰, 舒凯, 谭伟明. 植物激素研究中的化学生物学思路与应用[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(3): 369-381. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||