

植物学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (1): 81-92.DOI: 10.11983/CBB18012 cstr: 32102.14.CBB18012
收稿日期:2018-01-12
接受日期:2018-03-13
出版日期:2019-01-01
发布日期:2019-07-31
通讯作者:
陈彤
基金资助:
Danying Ma,Dongchao Ji,Yong Xu,Tong Chen( ),Shiping Tian
),Shiping Tian
Received:2018-01-12
Accepted:2018-03-13
Online:2019-01-01
Published:2019-07-31
Contact:
Tong Chen
摘要: 真核生物通过双层膜结构包裹细胞内受损的蛋白、细胞器或外源物质, 经溶酶体(或液泡)将内含物降解并进行循环利用, 这种高度保守的生物学过程称为自噬。活性氧是细胞有氧代谢的副产物, 作为一种信号分子广泛参与不同生物学过程的调控。研究表明, 真核生物中自噬与活性氧之间存在密切联系。该文结合近年的研究进展, 对植物细胞中活性氧的种类及作用和自噬的分子机制等进行概述, 旨在探讨活性氧对自噬的调控作用。
马丹颖,季东超,徐勇,陈彤,田世平. 活性氧调控植物细胞自噬的研究进展. 植物学报, 2019, 54(1): 81-92.
Danying Ma,Dongchao Ji,Yong Xu,Tong Chen,Shiping Tian. Advances in the Regulation on Autophagy by Reactive Oxygen Species in Plant Cells. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(1): 81-92.
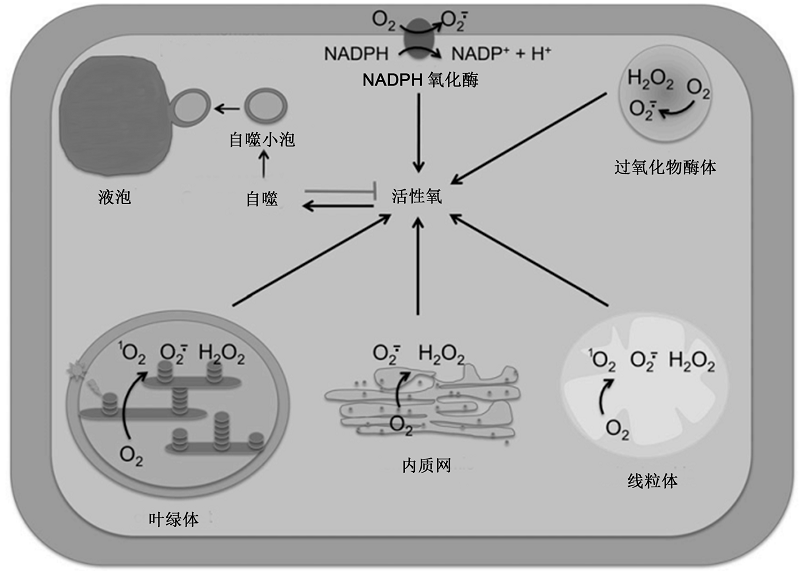
图1 植物细胞中不同来源的活性氧调控自噬(改自Pérez-Pérez et al., 2012b) 定位于质膜的NADPH氧化酶, 以及叶绿体、线粒体、过氧化物酶体和内质网等细胞器均能产生活性氧。过量的活性氧会诱导细胞自噬, 以减少活性氧的产生并清除细胞受损组分。NADPH: 烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸磷酸; O2: 氧分子; O2·-: 超氧阴离子; H2O2: 过氧化氢; 1O2: 单线态氧
Figure 1 Different reactive oxygen species (ROS) sources control autophagy in plant cells (modified from Pérez-Pérez et al., 2012b) ROS can be generated by plasma membrane-localized NOX and different organelles, including chloroplast, mitochondria, peroxisome, and endoplasmic reticulum. Excess ROS then induce autophagy, which contributes to down-regulate ROS production and remove damaged cellular components. NADPH: Reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; O2: Dioxygen; O2·-: Superoxide anion; H2O2: Hydrogen peroxide; 1O2: Singlet oxygen
| 1 |
蔡霞, 方晓艾, 田兰婷, 赵雪艳 ( 2016). 显微镜技术在植物细胞自噬研究中的应用. 电子显微学报 35, 180-185.
DOI URL |
| 2 |
黄晓, 李发强 ( 2016). 细胞自噬在植物细胞程序性死亡中的作用. 植物学报 51, 859-862.
DOI URL |
| 3 |
景红娟, 周广舟, 谭晓荣, 平康康, 任雪建 ( 2012). 活性氧对植物自噬调控的研究进展. 植物学报 47, 534-542.
DOI URL |
| 4 |
林植芳, 刘楠 ( 2012). 活性氧调控植物生长发育的研究进展. 植物学报 47, 74-86.
DOI URL |
| 5 | 刘洋, 张静, 王秋玲, 侯岁稳 ( 2018). 植物细胞自噬研究进展. 植物学报 53, 5-16. |
| 6 | 任晨霞, 龚清秋 ( 2014). 细胞自噬在植物碳氮营养中作用的研究进展. 中国细胞生物学学报 36, 407-414. |
| 7 | 王燕, 刘玉乐 ( 2010). 植物细胞自噬研究进展. 中国细胞生物学学报 32, 677-689. |
| 8 |
杨小龙, 李漾漾, 刘玉凤, 齐明芳, 李天来 ( 2017). 植物细胞选择性自噬研究进展. 园艺学报 44, 2015-2028.
DOI URL |
| 9 |
Ahmad P, Jaleel CA, Salem MA, Nabi G, Sharma S ( 2010). Roles of enzymatic and nonenzymatic antioxidants in plants during abiotic stress. Crit Rev Biotechnol 30, 161-175.
DOI URL PMID |
| 10 |
Alers S, Löffler AS, Wesselborg S, Stork B ( 2012). Role of AMPK-mTOR-Ulk1/2 in the regulation of autophagy: cross talk, shortcuts, and feedbacks. Mol Cell Biol 32, 2-11.
DOI URL PMID |
| 11 | Alexander A, Cai SL, Kim J, Nanez A, Sahin M, MacLean KH, Inoki K, Guan KL, Shen JJ, Person MD, Kusewitt D, Mills GB, Kastan MB, Walker CL ( 2010). ATM signals to TSC2 in the cytoplasm to regulate mTORC1 in response to ROS. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107, 4153-4158. |
| 12 | Apel K, Hirt H ( 2004). Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55, 373-399. |
| 13 | Asada K ( 2006). Production and scavenging of reactive oxy- gen species in chloroplasts and their functions. Plant Phy- siol 141, 391-396. |
| 14 |
Ashford TP, Porter KR ( 1962). Cytoplasmic components in hepatic cell lysosomes. Cell Biol 12, 198-202.
DOI URL PMID |
| 15 | Bassham DC ( 2007). Plant autophagy—more than a starvation response. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10, 587-593. |
| 16 |
Bernales S, McDonald KL, Walter P ( 2006). Autophagy counterbalances endoplasmic reticulum expansion during the unfolded protein response. PLoS Biol 4, e423.
DOI URL PMID |
| 17 |
Bienert GP, Chaumont F ( 2014). Aquaporin-facilitated transmembrane diffusion of hydrogen peroxide. Biochim Biophys Acta 1840, 1596-1604.
DOI URL PMID |
| 18 | Blagosklonny MV ( 2008). Aging: ROS or TOR. Cell Cycle 7, 3344-3354. |
| 19 | Buchanan BB, Balmer Y ( 2005). Redox regulation: a broadening horizon. Annu Rev Plant Biol 56, 187-220. |
| 20 |
Budanov AV ( 2011). Stress-responsive sestrins link p53 with redox regulation and mammalian target of rapamycin signaling. Antioxid Redox Signal 15, 1679-1690.
DOI URL PMID |
| 21 |
Chaouch S, Queval G, Noctor G ( 2012). AtRbohF is a crucial modulator of defence-associated metabolism and a key actor in the interplay between intracellular oxidative stress and pathogenesis responses in Arabidopsis. Plant J 69, 613-627.
DOI URL PMID |
| 22 |
Chung T, Phillips AR, Vierstra RD ( 2010). ATG8 lipidation and ATG8-mediated autophagy in Arabidopsis require ATG12 expressed from the differentially controlled ATG- 12A and ATG12B loci.Plant J 62, 483-493.
DOI URL PMID |
| 23 | Chung T, Suttangkakul A, Vierstra RD ( 2009). The ATG autophagic conjugation system in maize: ATG transcripts and abundance of the ATG8-lipid adduct are regulated by development and nutrient availability. Plant Physiol 149, 220-234. |
| 24 |
Coll NS, Smidler A, Puigvert M, Popa C, Valls M, Dangl JL ( 2014). The plant metacaspase AtMC1 in pathogen-trig- gered programmed cell death and aging: functional linkage with autophagy. Cell Death Differ 21, 1399-1408.
DOI URL PMID |
| 25 |
Dames SA, Mulet JM, Rathgeb-Szabo K, Hall MN, Grzesiek S ( 2005). The solution structure of the FATC domain of the protein kinase target of rapamycin suggests a role for redox-dependent structural and cellular stability. J Biol Chem 280, 20558-20564.
DOI URL PMID |
| 26 |
del Río LA ( 2011). Peroxisomes as a cellular source of reactive nitrogen species signal molecules. Arch Biochem Bio- phys 506, 1-11.
DOI URL PMID |
| 27 |
del Río LA, Corpas FJ, Sandalio LM, Palma JM, Gómez M, Barroso JB ( 2002). Reactive oxygen species, antioxidant systems and nitric oxide in peroxisomes. J Exp Bot 53, 1255-1272.
DOI URL PMID |
| 28 |
Dewaele M, Maes H, Agostinis P ( 2010). ROS-mediated mechanisms of autophagy stimulation and their relevance in cancer therapy. Autophagy 6, 838-854.
DOI URL PMID |
| 29 |
Díaz-Troya S, Pérez-Pérez ME, Pérez-Martín M, Moes S, Jeno P, Florencio FJ, Crespo JL ( 2011). Inhibition of protein synthesis by TOR inactivation revealed a conserved regulatory mechanism of the BiP chaperone in Chlamydomonas.Plant Physiol 157, 730-741.
DOI URL PMID |
| 30 | Finkel T ( 2011). Signal transduction by reactive oxygen species. J Cell Biol 194, 7-15. |
| 31 |
Foyer CH, Bloom AJ, Queval G, Noctor G ( 2009). Photorespiratory metabolism: genes, mutants, energetics, and redox signaling. Annu Rev Plant Biol 60, 455-484.
DOI URL PMID |
| 32 | Foyer CH, Noctor G ( 2003). Redox sensing and signaling associated with reactive oxygen in chloroplasts, peroxi- somes and mitochondria. Physiol Plant 119, 355-364. |
| 33 |
Gechev TS, Van Breusegem F, Stone JM, Denev I, Laloi C ( 2006). Reactive oxygen species as signals that modulate plant stress responses and programmed cell death. BioEssays 28, 1091-1101.
DOI URL PMID |
| 34 |
Han SJ, Wang Y, Zheng XJ, Jia Q, Zhao JP, Bai F, Hong YG, Liu YL ( 2015). Cytoplastic glyceraldehyde-3-phosph- ate dehydrogenases interact with ATG3 to negatively regulate autophagy and immunity in Nicotiana benthamia- na.Plant Cell 27, 1316-1331.
DOI URL PMID |
| 35 |
Han SJ, Yu BJ, Wang Y, Liu YL ( 2011). Role of plant autophagy in stress response. Protein & Cell 2, 784-791.
DOI URL PMID |
| 36 |
Hayward AP, Dinesh-Kumar SP ( 2011). What can plant autophagy do for an innate immune response? Annu Rev Phytopathol 49, 557-576.
DOI URL PMID |
| 37 |
He CC, Klionsky DJ ( 2009). Regulation mechanisms and signaling pathways of autophagy. Annu Rev Genet 43, 67-93.
DOI URL PMID |
| 38 |
Henry E, Fung N, Liu J, Drakakaki G, Coaker G ( 2015). Beyond glycolysis: GAPDHs are multi-functional enzymes involved in regulation of ROS, autophagy, and plant immune responses. PLoS Genet 11, e1005199.
DOI URL PMID |
| 39 |
Hofius D, Li L, Hafrén A, Coll NS ( 2017). Autophagy as an emerging arena for plant-pathogen interactions. Curr Opin Plant Biol 38, 117-123.
DOI URL PMID |
| 40 |
Hofius D, Munch D, Bressendorff S, Mundy J, Petersen M ( 2011). Role of autophagy in disease resistance and hypersensitive response-associated cell death. Cell Death Differ 18, 1257-1262.
DOI URL PMID |
| 41 |
Hosokawa N, Hara T, Kaizuka T, Kishi C, Takamura A, Miura Y, Iemura SI, Natsume T, Takehana K, Yamada N, Guan JL, Oshiro N, Mizushima N ( 2009). Nutrient-dependent mTORC1 association with the ULK1-Atg13- FIP200 complex required for autophagy. Mol Biol Cell 20, 1981-1991.
DOI URL |
| 42 |
Ishida H, Yoshimoto K, Izumi M, Reisen D, Yano Y, Makino A, Ohsumi Y, Hanson MR, Mae T ( 2008). Mobilization of Rubisco and stroma-localized fluorescent proteins of chloroplasts to the vacuole by an ATG gene-dependent autophagic process.Plant Physiol 148, 142-155.
DOI URL |
| 43 |
Izumi M, Ishida H, Nakamura S, Hidema J ( 2017). Entire photodamaged chloroplasts are transported to the central vacuole by autophagy. Plant Cell 29, 377-394.
DOI URL PMID |
| 44 |
Izumi M, Wada S, Makino A, Ishida H ( 2010). The autophagic degradation of chloroplasts via Rubisco-containing bodies is specifically linked to leaf carbon status but not nitrogen status in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 154, 1196-1209.
DOI URL |
| 45 | Kamada Y, Funakoshi T, Shintani T, Nagano K, Ohsumi M, Ohsumi Y ( 2000). Tor-mediated induction of autophagy via an Apg1 protein kinase complex. J Cell Biol 150, 1507-1513. |
| 46 |
Kihara A, Noda T, Ishihara N, Ohsumi Y ( 2001). Two distinct Vps34 phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complexes function in autophagy and carboxypeptidase Y sorting in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Cell Biol 152, 519-530.
DOI URL |
| 47 |
Kirisako T, Ichimura Y, Okada H, Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Yoshimori T, Ohsumi M, Takao T, Noda T, Ohsumi Y ( 2000). The reversible modification regulates the membrane-binding state of Apg8/Aut7 essential for autophagy and the cytoplasm to vacuole targeting pathway. J Cell Biol 151, 263-276.
DOI URL PMID |
| 48 |
Kissová I, Deffieu M, Manon S, Camougrand N ( 2004). Uth1p is involved in the autophagic degradation of mitochondria. J Biol Chem 279, 39068-39074.
DOI URL PMID |
| 49 |
Kwon SI, Cho HJ, Jung JH, Yoshimoto K, Shirasu K, Park OK ( 2010 a). The Rab GTPase RabG3b functions in auto- phagy and contributes to tracheary element differentiation in Arabidopsis. Plant J 64, 151-164.
DOI URL PMID |
| 50 |
Kwon SI, Cho HJ, Park OK ( 2010 b). Role of Arabidopsis RabG3b and autophagy in tracheary element differentiation. Autophagy 6, 1187-1189.
DOI URL PMID |
| 51 | Ledford HK, Chin BL, Niyogi KK ( 2007). Acclimation to singlet oxygen stress in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.Eukaryot Cell 6, 919-930. |
| 52 |
Lenz HD, Haller E, Melzer E, Kober K, Wurster K, Stahl M, Bassham DC, Vierstra RD, Parker JE, Bautor J, Molina A, Escudero V, Shindo T, van der Hoorn RA, Gust AA, Nürnberger T ( 2011). Autophagy differentially controls plant basal immunity to biotrophic and necrotrophic patho- gens. Plant J 66, 818-830.
DOI URL PMID |
| 53 |
Levine B, Klionsky DJ ( 2017). Autophagy wins the 2016 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine: breakthroughs in baker’s yeast fuel advances in biomedical research. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114, 201-205.
DOI URL PMID |
| 54 |
Liu YL, Schiff M, Czymmek K, Tallóczy Z, Levine B, Dinesh-Kumar SP ( 2005). Autophagy regulates programmed cell death during the plant innate immune response. Cell 121, 567-577.
DOI URL PMID |
| 55 |
Liu YM, Bassham DC ( 2012). Autophagy: pathways for self-eating in plant cells. Annu Rev Plant Biol 63, 215-237.
DOI URL PMID |
| 56 | Liu YM, Burgos JS, Deng Y, Srivastava R, Howell SH, Bassham DC ( 2012). Degradation of the endoplasmic reticulum by autophagy during endoplasmic reticulum stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24, 4635-4651. |
| 57 | Liu YM, Xiong Y, Bassham DC ( 2009). Autophagy is required for tolerance of drought and salt stress in plants. Autophagy 5, 954-963. |
| 58 | Malhotra JD, Kaufman RJ ( 2007). Endoplasmic reticulum stress and oxidative stress: a vicious cycle or a double-edged sword? Antioxid Redox Signal 9, 2277-2293. |
| 59 |
Meijer WH, van der Klei IJ, Veenhuis M, Kiel JAKW ( 2007). ATG genes involved in non-selective autophagy are conserved from yeast to man, but the selective Cvt and pexo- phagy pathways also require organism-specific genes. Autophagy 3, 106-116.
DOI URL PMID |
| 60 |
Minina EA, Moschou PN, Vetukuri RR, Sanchez-Vera V, Cardoso C, Liu QS, Elander PH, Dalman K, Beganovic M, Yilmaz JL, Marmon S, Shabala L, Suarez MF, Ljung K, Novák O, Shabala S, Stymne S, Hofius D, Bozhkov PV ( 2018). Transcriptional stimulation of rate-limiting components of the autophagic pathway improves plant fitness. J Exp Bot 69, 1415-1432.
DOI URL PMID |
| 61 |
Mizushima N ( 2010). The role of the Atg1/ULK1 complex in autophagy regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 22, 132-139.
DOI URL PMID |
| 62 |
Mizushima N, Yoshimori T, Ohsumi Y ( 2011). The role of Atg proteins in autophagosome formation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 27, 107-132.
DOI URL PMID |
| 63 | Møller IM ( 2001). Plant mitochondria and oxidative stress: electron transport, NADPH turnover and metabolism of reactive oxygen species. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 52, 561-591. |
| 64 | Moreau M, Azzopardi M, Clément G, Dobrenel T, Marchive C, Renne C, Martin-Magniette ML, Taconnat L, Renou JP, Robaglia C, Meyer C ( 2012). Mutations in the Arabidopsis homolog of LST8/GβL, a partner of the target of rapamycin kinase, impair plant growth, flowering, and metabolic adaptation to long days. Plant Cell 24, 463-481. |
| 65 | Nakatogawa H, Suzuki K, Kamada Y, Ohsumi Y ( 2009). Dynamics and diversity in autophagy mechanisms: lessons from yeast. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10, 458-467. |
| 66 |
Okamoto K, Kondo-Okamoto N, Ohsumi Y ( 2009). Mitochondria-anchored receptor Atg32 mediates degradation of mitochondria via selective autophagy. Dev Cell 17, 87-97.
DOI URL PMID |
| 67 | Pérez-Pérez ME, Couso I, Crespo JL ( 2012 a). Carotenoid deficiency triggers autophagy in the model green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.Autophagy 8, 376-388. |
| 68 | Pérez-Pérez ME, Florencio FJ, Crespo JL ( 2010). Inhibition of target of rapamycin signaling and stress activate autophagy in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.Plant Physiol 152, 1874-1888. |
| 69 | Pérez-Pérez ME, Lemaire SD, Crespo JL ( 2012 b). Reactive oxygen species and autophagy in plants and algae. Plant Physiol 160, 156-164. |
| 70 | Pu YT, Luo XJ, Bassham DC ( 2017). TOR-dependent and - independent pathways regulate autophagy in Arabidopsis thaliana.Front Plant Sci 8, 1204. |
| 71 |
Qi H, Xia FN, Xie LJ, Yu LJ, Chen QF, Zhuang XH, Wang Q, Li FQ, Jiang LW, Xie Q, Xiao S ( 2017). TRAF family proteins regulate autophagy dynamics by modulating AU- TOPHAGY PROTEIN6 stability in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 29, 890-911.
DOI URL PMID |
| 72 |
Rahal A, Kumar A, Singh V, Yadav B, Tiwari R, Chakraborty S, Dhama K ( 2014). Oxidative stress, prooxidants, and antioxidants: the interplay. Biomed Res Int 2014, 761264.
DOI URL PMID |
| 73 |
Ren MZ, Qiu SQ, Venglat P, Xiang DQ, Feng L, Selvaraj G, Datla R ( 2011). Target of rapamycin regulates development and ribosomal RNA expression through kinase domain in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 155, 1367-1382.
DOI URL PMID |
| 74 |
Reumann S, Voitsekhovskaja O, Lillo C ( 2010). From signal transduction to autophagy of plant cell organelles: lessons from yeast and mammals and plant-specific features. Protoplasma 247, 233-256.
DOI URL PMID |
| 75 |
Robaglia C, Thomas M, Meyer C ( 2012). Sensing nutrient and energy status by SnRK1 and TOR kinases. Curr Opin Plant Biol 15, 301-307.
DOI URL PMID |
| 76 |
Rutkowski DT, Kaufman RJ ( 2007). That which does not kill me makes me stronger: adapting to chronic ER stress. Trends Biochem Sci 32, 469-476.
DOI URL PMID |
| 77 | Santos CX, Tanaka LY, Wosniak J Jr, Laurindo FRM ( 2009). Mechanisms and implications of reactive oxygen species generation during the unfolded protein response: roles of endoplasmic reticulum oxidoreductases, mitochondrial electron transport, and NADPH oxidase. Antioxid Redox Signal 11, 2409-2427. |
| 78 |
Schafer FQ, Wang HP, Kelley EE, Cueno KL, Martin SM, Buettner GR ( 2002). Comparing beta-carotene, vitamin E and nitric oxide as membrane antioxidants. Biol Chem 383, 671-681.
DOI URL PMID |
| 79 |
Scheler C, Durner J, Astier J ( 2013). Nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species in plant biotic interactions. Curr Opin Plant Biol 16, 534-539.
DOI URL PMID |
| 80 | Scherz-Shouval R, Shvets E, Fass E, Shorer H, Gil L, Elazar Z ( 2007). Reactive oxygen species are essential for autophagy and specifically regulate the activity of Atg4. EMBO J 26, 1749-1760. |
| 81 |
Schieke SM, Finkel T ( 2006). Mitochondrial signaling, TOR, and life span. Biol Chem 387, 1357-1361.
DOI URL PMID |
| 82 |
Shibata M, Oikawa K, Yoshimoto K, Kondo M, Mano S, Yamada K, Hayashi M, Sakamoto W, Ohsumi Y, Nishimura M ( 2013). Highly oxidized peroxisomes are selectively degraded via autophagy in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25, 4967-4983.
DOI URL PMID |
| 83 | Shin JH, Yoshimoto K, Ohsumi Y, Jeon JS, An G ( 2009). OsATG10b, an autophagosome component, is needed for cell survival against oxidative stresses in rice. Mol Cells 27, 67-74. |
| 84 | Soto-Burgos J, Bassham DC ( 2017) SnRK1 activates autophagy via the TOR signaling pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana.PLoS One 12, e0182591. |
| 85 |
Sun X, Wang P, Jia X, Huo LQ, Che RM, Ma FW ( 2018). Improvement of drought tolerance by overexpressing Md- ATG18a is mediated by modified antioxidant system and activated autophagy in transgenic apple.Plant Biotechnol J 16, 545-557.
DOI URL PMID |
| 86 |
Suttangkakul A, Li FQ, Chung T, Vierstra RD ( 2011). The ATG1/ATG13 protein kinase complex is both a regulator and a target of autophagic recycling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 23, 3761-3779.
DOI URL PMID |
| 87 |
Suzuki N, Miller G, Morales J, Shulaev V, Torres MA, Mittler R ( 2011). Respiratory burst oxidases: the engines of ROS signaling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14, 691-699.
DOI URL PMID |
| 88 | Swanson S, Gilroy S ( 2010). ROS in plant development. Physiol Plant 138, 384-392. |
| 89 |
Tal R, Winter G, Ecker N, Klionsky DJ, Abeliovich H ( 2007). Aup1p, a yeast mitochondrial protein phosphatase homolog, is required for efficient stationary phase mitophagy and cell survival. J Biol Chem 282, 5617-5624.
DOI URL PMID |
| 90 |
Thompson AR, Vierstra RD ( 2005). Autophagic recycling: lessons from yeast help define the process in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8, 165-173.
DOI URL PMID |
| 91 | Tolkovsky AM ( 2009). Mitophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1793, 1508-1515. |
| 92 | Tsugane K, Kobayashi K, Niwa Y, Ohba Y, Wada K, Kobayashi H ( 1999). A recessive Arabidopsis mutant that grows photoautotrophically under salt stress shows enhanced active oxygen detoxification. Plant Cell 11, 1195-1206. |
| 93 |
Ungermann C, Langosch D ( 2005). Functions of SNAREs in intracellular membrane fusion and lipid bilayer mixing. J Cell Sci 118, 3819-3828.
DOI URL PMID |
| 94 |
Üstün S, Hafrén A, Hofius D ( 2017). Autophagy as a mediator of life and death in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 40, 122-130.
DOI URL PMID |
| 95 | van Dongen JT, Licausi F ( 2015). Oxygen sensing and signaling. Annu Rev Plant Biol 66, 345-367. |
| 96 |
Wada S, Ishida H, Izumi M, Yoshimoto K, Ohsumi Y, Mae T, Makino A ( 2009). Autophagy plays a role in chloroplast degradation during senescence in individually darkened leaves. Plant Physiol 149, 885-893.
DOI URL |
| 97 | Wang CW, Klionsky DJ ( 2003). The molecular mechanism of autophagy. Mol Med 9, 65-76. |
| 98 | Wang Y, Liu YL ( 2013). Autophagic degradation of leaf starch in plants. Autophagy 9, 1247-1248. |
| 99 | Wang Y, Yu BJ, Zhao JP, Guo JB, Li Y, Han SJ, Huang L, Du YM, Hong YG, Tang DZ, Liu YL ( 2013). Autophagy contributes to leaf starch degradation. Plant Cell 25, 1383-1399. |
| 100 |
Wang Y, Zheng XY, Yu BJ, Han SJ, Guo JB, Tang HP, Yu AYL, Deng HT, Hong YG, Liu YL ( 2015). Disruption of microtubules in plants suppresses macroautophagy and triggers starch excess-associated chloroplast autophagy. Autophagy 11, 2259-2274.
DOI URL PMID |
| 101 |
Xia KF, Liu T, Ouyang J, Wang R, Fan T, Zhang MY ( 2011). Genome-wide identification, classification, and expression analysis of autophagy-associated gene homologues in rice ( Oryza sativa L.).DNA Res 18, 363-377.
DOI URL PMID |
| 102 |
Xiong Y, Contento AL, Bassham DC ( 2007 a). Disruption of autophagy results in constitutive oxidative stress in Ara- bidopsis. Autophagy 3, 257-258.
DOI URL PMID |
| 103 |
Xiong Y, Contento AL, Nguyen PQ, Bassham DC ( 2007 b). Degradation of oxidized proteins by autophagy during oxidative stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 143, 291-299.
DOI URL PMID |
| 104 |
Xiong Y, McCormack M, Li L, Hall Q, Xiang CB, Sheen J ( 2013). Glucose-TOR signaling reprograms the transcriptome and activates meristems. Nature 496, 181-186.
DOI URL PMID |
| 105 |
Xiong Y, Sheen J ( 2014). The role of target of rapamycin signaling networks in plant growth and metabolism. Plant Physiol 164, 499-512.
DOI URL PMID |
| 106 |
Xu GY, Wang SS, Han SJ, Xie K, Wang Y, Li JL, Liu YL ( 2017). Plant Bax Inhibitor-1 interacts with ATG6 to regulate autophagy and programmed cell death. Autophagy 13, 1161-1175.
DOI URL PMID |
| 107 |
Yorimitsu T, Nair U, Yang ZF, Klionsky DJ ( 2006). Endoplasmic reticulum stress triggers autophagy. J Biol Chem 281, 30299-30304.
DOI URL PMID |
| 108 |
Yoshimoto K, Hanaoka H, Sato S, Kato T, Tabata S, Noda T, Ohsumi Y ( 2004). Processing of ATG8s, ubiquitin-like proteins, and their deconjugation by ATG4s are essential for plant autophagy. Plant Cell 16, 2967-2983.
DOI URL PMID |
| 109 | Yoshimoto K, Jikumaru Y, Kamiya Y, Kusano M, Consonni C, Panstruga R, Ohsumi Y, Shirasu K ( 2009). Autophagy negatively regulates cell death by controlling NPR1-dependent salicylic acid signaling during senescence and the innate immune response in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21, 2914-2927. |
| 110 |
Yoshimoto K, Takano Y, Sakai Y ( 2010). Autophagy in plants and phytopathogens. FEBS Lett 584, 1350-1358.
DOI URL PMID |
| 111 |
Zhang DY, Wang W, Sun XJ, Xu DQ, Wang CY, Zhang Q, Wang HF, Luo WW, Chen Y, Chen HY, Liu ZX ( 2016). AMPK regulates autophagy by phosphorylating BECN1 at threonine 388. Autophagy 12, 1447-1459.
DOI URL PMID |
| 112 |
Zhou XM, Zhao P, Wang W, Zou J, Cheng TH, Peng XB, Sun MX ( 2015). A comprehensive, genome-wide analysis of autophagy-related genes identified in tobacco suggests a central role of autophagy in plant response to various environmental cues. DNA Res 22, 245-257.
DOI URL PMID |
| [1] | 王鸿梅, 袁蔚, 薛芳, 张召聪, 刘坤, 陈四龙. 植物SWEET基因参与逆境胁迫响应及其调控机制[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | 王子韵, 吕燕文, 肖钰, 吴超, 胡新生. 植物基因表达调控与进化机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [3] | 周婧, 高飞. 植物缺铁诱导型香豆素合成及其在铁吸收中的功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 460-471. |
| [4] | 熊良林, 梁国鲁, 郭启高, 景丹龙. 基因可变剪接调控植物响应非生物胁迫研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 435-448. |
| [5] | 刘志祥, 谢华, 张慧, 黄晓磊. 表皮碳氢化合物在社会性昆虫中的功能多样性及其调控[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24302-. |
| [6] | 李巧峡, 李有龙, 李纪纲, 陈晨龙, 孙坤. 光周期调控维西堇菜与裂叶堇菜开放花和闭锁花的发育[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 23484-. |
| [7] | 范雪兰, 落艳娇, 徐超群, 郭宝林. 淫羊藿类黄酮生物合成相关基因研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 834-846. |
| [8] | 陈雯, 周颖盈, 罗平, 崔永一. 被子植物花朵重瓣化分子调控机制[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 257-277. |
| [9] | 夏婧, 饶玉春, 曹丹芸, 王逸, 柳林昕, 徐雅婷, 牟望舒, 薛大伟. 水稻中乙烯生物合成关键酶OsACS和OsACO调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 291-301. |
| [10] | 张悦婧, 桑鹤天, 王涵琦, 石珍珍, 李丽, 王馨, 孙坤, 张继, 冯汉青. 植物对非生物胁迫系统性反应中信号传递的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 122-133. |
| [11] | 朱璐, 袁冲, 刘义飞. 植物次生代谢产物生物合成基因簇研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 134-143. |
| [12] | 董小云, 魏家萍, 崔俊美, 武泽峰, 郑国强, 李辉, 王莹, 田海燕, 刘自刚. 植物抗冻蛋白研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 966-981. |
| [13] | 苏鲁方, 王萍, 李顺, 蔡燕, 郭丹丹, 刘琴, 刘小云. 植物sirtuin蛋白家族研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 998-1007. |
| [14] | 戴若惠, 钱心妤, 孙静蕾, 芦涛, 贾绮玮, 陆天麒, 路梅, 饶玉春. 水稻叶色调控机制及相关基因研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 799-812. |
| [15] | 刘裕强, 万建民. 寄主监控昆虫唾液蛋白平衡植物抗性与生长发育[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 353-355. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||