

植物学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (5): 773-785.DOI: 10.11983/CBB25034 cstr: 32102.14.CBB25034
王笑1,2,3,4, 徐昌文1,2,3,4, 钱虹萍1,2,3,4, 李思博1,2,3,4, 林金星1,2,3,4, 崔亚宁1,2,3,4,*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-03-03
接受日期:2025-05-07
出版日期:2025-09-10
发布日期:2025-05-14
通讯作者:
*E-mail: 基金资助:
Wang Xiao1,2,3,4, Xu Changwen1,2,3,4, Qian Hongping1,2,3,4, Li Sibo1,2,3,4, Lin Jinxing1,2,3,4, Cui Yaning1,2,3,4,*( )
)
Received:2025-03-03
Accepted:2025-05-07
Online:2025-09-10
Published:2025-05-14
Contact:
*E-mail: 摘要: 植物细胞壁由纤维素、半纤维素、果胶和木质素等成分构成, 是一个动态变化的网络结构, 不仅在植物抵御外界压力和适应环境变化过程中发挥关键防线作用, 还在信号传递过程中作为信息枢纽。当细胞壁受损后, 细胞会感知细胞壁变化并做出早期免疫响应, 如激素变化、壁成分与修饰改变以及抗病次生代谢产物的生成。尽管细胞壁在植物免疫中的重要性已得到广泛认可, 但对于细胞壁损伤引发免疫反应的具体分子机制仍然知之甚少。原位非标记成像技术在植物细胞中的应用逐渐增多, 成为研究细胞壁结构与功能的重要手段。该文综述了植物细胞壁与免疫反应之间的相互作用机制研究进展, 为深入理解植物生命活动规律和提高作物病害抵抗能力提供科学依据; 同时介绍了细胞壁原位非标记成像技术, 为推进细胞壁在免疫反应中的作用研究提供更多技术选择。
王笑, 徐昌文, 钱虹萍, 李思博, 林金星, 崔亚宁. 植物细胞壁参与免疫反应的机制及其原位非标记成像方法. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 773-785.
Wang Xiao, Xu Changwen, Qian Hongping, Li Sibo, Lin Jinxing, Cui Yaning. Mechanisms Involving Plant Cell Walls in the Immune Response and Its In Situ Non-labeled Imaging Technique. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(5): 773-785.
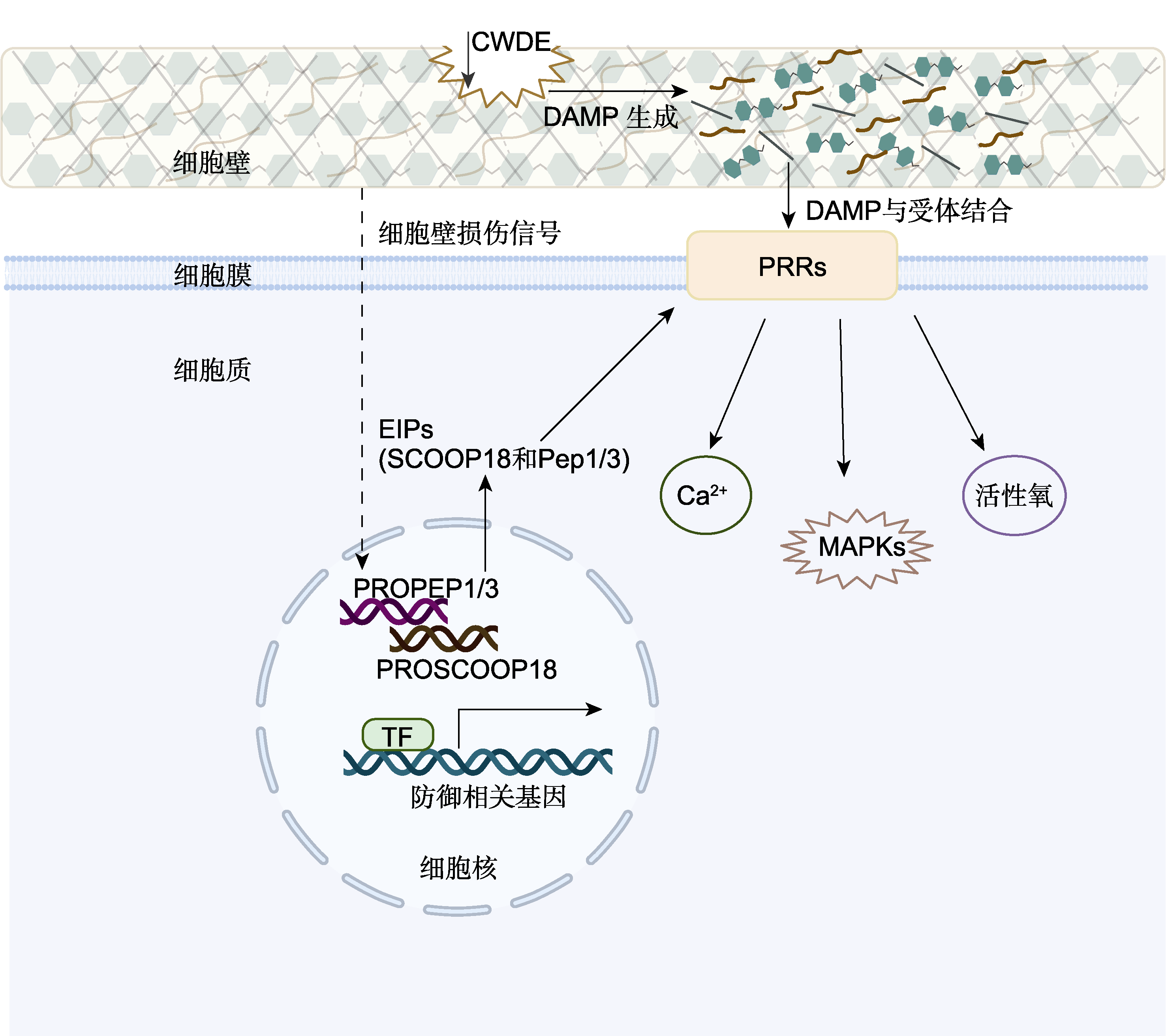
图1 植物细胞壁遭受破坏后, 细胞壁损伤信号转导并激活免疫响应的作用途径 细胞壁降解酶(CWDEs)损伤细胞壁后, 产生损伤相关分子模式(DAMPs), 同时细胞壁完整性维持机制感知细胞壁变化, 促进PROPEP1/3和PROSCOOP18的表达, 诱导内源性免疫肽(EIPs) (如SCOOP18和Pep1/3)的产生, DAMPs和EIPs与细胞表面的模式识别受体(PRRs)结合, 激活下游信号通路, 包括丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPKs)级联信号、活性氧(ROS)和Ca²+等, 激活转录因子(TF)启动防御基因的表达, 最终引发植物的模式触发免疫(PTI)反应增强。实线箭头为已验证的通路, 虚线箭头为推测的通路。
Figure 1 Pathways of action of cell wall damage signaling and activation of immune response after plant cell wall damage Cell wall-degrading enzymes (CWDEs) damage to the cell wall results in the production of damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), while cell wall integrity maintenance mechanisms sense cell wall changes, promote the expression of PROPEP1/3 and PROSCOOP18, and induce the production of endogenous immunopeptides (EIPs) (e.g., SCOOP18 and Pep1/3), and DAMPs and EIPs bind to pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) on the cell surface, activating downstream signaling pathways, including mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), reactive oxygen species (ROS) and Ca²+, etc., which activate transcription factors (TF) to initiate the expression of defense genes, ultimately triggering an enhanced pattern-triggered immunity (PTI) response in plants. The solid lines represent verified pathways, while the dashed line indicates hypothesized pathway that has not yet been verified.
| 基因(编码蛋白) | 作用 | 识别病原体后的变化 | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 纤维素 | CesA (cellulose synthase) | 正向调节纤维素合成 | 下调, 纤维素合成减少 | Wojtasik et al., |
| 半纤维素 | GMT (glucomannan 4β-mannosyltransferase) GGT (galactomannan galactosyltransferase) XXT (xyloglucan xylosyltransferase) XYN (endo-1,4-β-xylanase) | 正向调节半纤维素合成 | 下调, 半纤维素合成减少 | Wojtasik et al., |
| XYLa (1,4-α-xylosidase) GS (α-galactosidase) | 正向调节半纤维素降解 | 上调, 半纤维素降解增多 | ||
| 果胶 | GAE (UDP-glucuronate 4-epimerase) GAUT1/7 (galacturonosyltransferase 1/7) RGXT (rhamnogalacturonan II xylosyltransferase) ARAD (arabinose transferase) PMT (pectin methyltransferase) | 正向调节果胶合成 | 下调, 果胶合成 减少 | Wojtasik et al., |
| PG (polygalacturonase) PaL (pectin lyase) | 正向调节果胶裂解 | 上调, 果胶降解 增多 | ||
| 木质素 | PAL (phenylalanine ammonia lyase) HCT (p-hydroxycinnamoyl CoA: quinate/shikimate p-hydroxycinnamoyl transferase) CCoAOMT (caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase) COMT (caffeic acid/5-hydroxyferulic acid 3/5-O-methyltransferase) SAD (synaptic dehydrogenase) GT (glucosyltransferase) CAD1 (cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase 1) | 正向调节木质素合成 | 上调, 木质素合成增多 | Wojtasik et al., |
| 水杨酸 合成 | ICS1 (isochorismate synthase 1) PAL (phenylalanine ammonia lyase) PAD4 (phytoalexin-deficient 4) EDS1 (enhanced disease susceptibility 1) SAGT1 (salicylic acid glucosyltransferase 1) BSMT1 (benzoic acid and salicylic acid methyltransferase 1) | 与水杨酸(SA)合成相关, 参与植物防御反应 | ICS1、PAD4、EDS1和SAGT1上调/BSMT1下调, SA合成增多 | Silverman et al., |
| 茉莉酸 合成 | VSP1 (vegetative storage protein 1) LOX1 (lipoxygenase 1) MYC2 (myelocytomatosis protein 2) AOC (allene oxide cyclase) | 与茉莉酸(JA)合成相关, 参与植物防御反应 | VSP1、LOX1和AOC上调/MYC2下调, JA合成增多 | Wasternack and Strnad, |
| 乙烯合成 | ACC (1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid synthase) | 与乙烯(ET)合成相关, 参与植物防御反应 | 上调, ET合成增多 | Alonso et al., |
| 抗病次生代谢产物 | PR (pathogenesis-related) PDF (plant defensin) | 与抗病次生代谢产物生成有关 | 上调, 防御素和凝集素合成增多 | Babosha, |
表1 病原体侵染后细胞内细胞壁-免疫相关基因的表达变化
Table 1 Changes in intracellular cell wall-immunity related gene expression after pathogen infection
| 基因(编码蛋白) | 作用 | 识别病原体后的变化 | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 纤维素 | CesA (cellulose synthase) | 正向调节纤维素合成 | 下调, 纤维素合成减少 | Wojtasik et al., |
| 半纤维素 | GMT (glucomannan 4β-mannosyltransferase) GGT (galactomannan galactosyltransferase) XXT (xyloglucan xylosyltransferase) XYN (endo-1,4-β-xylanase) | 正向调节半纤维素合成 | 下调, 半纤维素合成减少 | Wojtasik et al., |
| XYLa (1,4-α-xylosidase) GS (α-galactosidase) | 正向调节半纤维素降解 | 上调, 半纤维素降解增多 | ||
| 果胶 | GAE (UDP-glucuronate 4-epimerase) GAUT1/7 (galacturonosyltransferase 1/7) RGXT (rhamnogalacturonan II xylosyltransferase) ARAD (arabinose transferase) PMT (pectin methyltransferase) | 正向调节果胶合成 | 下调, 果胶合成 减少 | Wojtasik et al., |
| PG (polygalacturonase) PaL (pectin lyase) | 正向调节果胶裂解 | 上调, 果胶降解 增多 | ||
| 木质素 | PAL (phenylalanine ammonia lyase) HCT (p-hydroxycinnamoyl CoA: quinate/shikimate p-hydroxycinnamoyl transferase) CCoAOMT (caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase) COMT (caffeic acid/5-hydroxyferulic acid 3/5-O-methyltransferase) SAD (synaptic dehydrogenase) GT (glucosyltransferase) CAD1 (cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase 1) | 正向调节木质素合成 | 上调, 木质素合成增多 | Wojtasik et al., |
| 水杨酸 合成 | ICS1 (isochorismate synthase 1) PAL (phenylalanine ammonia lyase) PAD4 (phytoalexin-deficient 4) EDS1 (enhanced disease susceptibility 1) SAGT1 (salicylic acid glucosyltransferase 1) BSMT1 (benzoic acid and salicylic acid methyltransferase 1) | 与水杨酸(SA)合成相关, 参与植物防御反应 | ICS1、PAD4、EDS1和SAGT1上调/BSMT1下调, SA合成增多 | Silverman et al., |
| 茉莉酸 合成 | VSP1 (vegetative storage protein 1) LOX1 (lipoxygenase 1) MYC2 (myelocytomatosis protein 2) AOC (allene oxide cyclase) | 与茉莉酸(JA)合成相关, 参与植物防御反应 | VSP1、LOX1和AOC上调/MYC2下调, JA合成增多 | Wasternack and Strnad, |
| 乙烯合成 | ACC (1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid synthase) | 与乙烯(ET)合成相关, 参与植物防御反应 | 上调, ET合成增多 | Alonso et al., |
| 抗病次生代谢产物 | PR (pathogenesis-related) PDF (plant defensin) | 与抗病次生代谢产物生成有关 | 上调, 防御素和凝集素合成增多 | Babosha, |
| 技术 | 优点 | 缺点 | 应用 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 傅里叶红外光谱(Fourier transform infrared, FTIR) | 无损, 可获得多维信息, 适用范围广 | 空间分辨率受限, 水吸收影响成像, 不适合活体成像 | 研究细胞壁成分特性, 研究发育和抗病过程中的成分变化 | Song et al., |
| 共聚焦拉曼光谱成像(confocal Raman microscopy, CRM) | 高光谱和空间分辨率, 非侵入性, 分辨率可达微米级 | 成像速度慢, 拉曼散射效应弱, 荧光背景干扰限制成像质量 | 监测细胞壁成分变化 | Jin et al., et al., 2020; Guo et al., |
| 受激拉曼光谱成像(stimulated Raman scattering, SRS) | 高成像速度, 可进行定量分析, 具有高空间分辨率和高信噪比 | 对待测物质丰度要求高, 设备成本高 | 实时监测高度动态过程中的细胞壁成分与结构变化 | Zhu et al., |
表2 原位非标记成像技术的优缺点及应用
Table 2 Advantages, disadvantages and applications of in situ non-labeled imaging techniques
| 技术 | 优点 | 缺点 | 应用 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 傅里叶红外光谱(Fourier transform infrared, FTIR) | 无损, 可获得多维信息, 适用范围广 | 空间分辨率受限, 水吸收影响成像, 不适合活体成像 | 研究细胞壁成分特性, 研究发育和抗病过程中的成分变化 | Song et al., |
| 共聚焦拉曼光谱成像(confocal Raman microscopy, CRM) | 高光谱和空间分辨率, 非侵入性, 分辨率可达微米级 | 成像速度慢, 拉曼散射效应弱, 荧光背景干扰限制成像质量 | 监测细胞壁成分变化 | Jin et al., et al., 2020; Guo et al., |
| 受激拉曼光谱成像(stimulated Raman scattering, SRS) | 高成像速度, 可进行定量分析, 具有高空间分辨率和高信噪比 | 对待测物质丰度要求高, 设备成本高 | 实时监测高度动态过程中的细胞壁成分与结构变化 | Zhu et al., |
| [1] |
Albersheim P, Anderson AJ (1971). Proteins from plant cell walls inhibit polygalacturonases secreted by plant pathogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 68, 1815-1819.
PMID |
| [2] | Alonso S, Gautam K, Iglesias-Moya J, Martínez C, Jamilena M (2024). Crosstalk between ethylene, jasmonate and ABA in response to salt stress during germination and early plant growth in Cucurbita pepo. Int J Mol Sci 25, 8728. |
| [3] | Azelee NIW, Mahdi HI, Cheng YS, Nordin N, Illias RM, Rahman RA, Shaarani SM, Bhatt P, Yadav S, Chang SW, Ravindran B, Ashokkumar V (2023). Biomass degradation: challenges and strategies in extraction and fractionation of hemicellulose. Fuel 339, 126982. |
| [4] |
Aziz A, Gauthier A, Bézier A, Poinssot B, Joubert JM, Pugin A, Heyraud A, Baillieul F (2007). Elicitor and resistance-inducing activities of β-1,4 cellodextrins in grapevine, comparison with β-1,3 glucans and α-1,4 oligogalacturonides. J Exp Bot 58, 1463-1472.
PMID |
| [5] | Babosha AV (2008). Inducible lectins and plant resistance to pathogens and abiotic stress. Biochemistry 73, 812-825. |
| [6] |
Berglund J, Mikkelsen D, Flanagan BM, Dhital S, Gaunitz S, Henriksson G, Lindström ME, Yakubov GE, Gidley MJ, Vilaplana F (2020). Wood hemicelluloses exert distinct biomechanical contributions to cellulose fibrillar networks. Nat Commun 11, 4692.
DOI PMID |
| [7] | Bot P, Mun BG, Imran QM, Hussain A, Lee SU, Loake G, Yun BW (2019). Differential expression of AtWAKL10 in response to nitric oxide suggests a putative role in biotic and abiotic stress responses. PeerJ 7, e7383. |
| [8] | Bronkhorst J, Kots K, De Jong D, Kasteel M, Van Boxmeer T, Joemmanbaks T, Govers F, van der Gucht J, Ketelaar T, Sprakel J (2022). An actin mechanostat ensures hyphal tip sharpness in Phytophthora infestans to achieve host penetration. Sci Adv 8, eabo0875. |
| [9] |
Brutus A, Sicilia F, Macone A, Cervone F, De Lorenzo G (2010). A domain swap approach reveals a role of the plant wall-associated kinase 1 (WAK1) as a receptor of oligogalacturonides. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107, 9452-9457.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | Bugbee WM (1993). A pectin lyase inhibitor protein from cell walls of sugar beet. Phytopathology 83, 63-68. |
| [11] |
Carpita NC, Gibeaut DM (1993). Structural models of primary cell walls in flowering plants: consistency of molecular structure with the physical properties of the walls during growth. Plant J 3, 1-30.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | Cayrol B, Delteil A, Gobbato E, Kroj T, Morel JB (2016). Three wall-associated kinases required for rice basal immunity form protein complexes in the plasma membrane. Plant Signal Behav 11, e1149676. |
| [13] |
Cervone F, Ausubel FM, De Lorenzo G (2015). Enhancing immunity by engineering DAMPs. Oncotarget 6, 28523-28524.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
Chen J, Xu F, Qiang XN, Liu HB, Wang L, Jiang LL, Li CY, Wang BQ, Luan S, Wu DS, Zhou F, Yu F (2024). Regulated cleavage and translocation of FERONIA control immunity in Arabidopsis roots. Nat Plants 10, 1761-1774.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
Claverie J, Balacey S, Lemaître-Guillier C, Brulé D, Chiltz A, Granet L, Noirot E, Daire X, Darblade B, Héloir MC, Poinssot B (2018). The cell wall-derived xyloglucan is a new DAMP triggering plant immunity in Vitis vinifera and Arabidopsis thaliana. Front Plant Sci 9, 1725.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
Cosgrove DJ (2001). Wall structure and wall loosening. A look backwards and forwards. Plant Physiol 125, 131-134.
PMID |
| [17] | Cosgrove DJ (2024). Structure and growth of plant cell walls. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 25, 340-358. |
| [18] | Cui XM, Ji DC, Chen T, Tian SP (2016). Advances in the studies on molecular mechanism of receptor-like protein kinase FER regulating host plant-pathogen interaction. Chin Bull Bot 56, 339-346. (in Chinese) |
| 崔晓敏, 季东超, 陈彤, 田世平 (2016). 类受体激酶FER调节植物与病原菌相互作用的分子机制. 植物学报 56, 339-346. | |
| [19] | Cui YN, Qian HP, Zhao YX, Li XJ (2020). Intracellular trafficking in pattern recognition receptor-triggered plant immunity. Chin Bull Bot 55, 329-339. (in Chinese) |
|
崔亚宁, 钱虹萍, 赵艳霞, 李晓娟 (2020). 模式识别受体的胞内转运及其在植物免疫中的作用. 植物学报 55, 329-339.
DOI |
|
| [20] | Das S, Bhati V, Dewangan BP, Gangal A, Mishra GP, Dikshit HK, Pawar PAM (2024). Combining Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy and multivariate analysis for chemotyping of cell wall composition in mungbean (Vigna radiata (L.) Wizcek). Plant Methods 20, 135. |
| [21] |
de Azevedo Souza C, Li SD, Lin AZ, Boutrot F, Grossmann G, Zipfel C, Somerville SC (2017). Cellulose-derived oligomers act as damage-associated molecular patterns and trigger defense-like responses. Plant Physiol 173, 2383-2398.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
De Lorenzo G, Ferrari S, Giovannoni M, Mattei B, Cervone F (2019). Cell wall traits that influence plant development, immunity, and bioconversion. Plant J 97, 134-147.
DOI |
| [23] | de Souza WR, Mitchell RAC, Cesarino I (2023). Editorial: the plant cell wall: advances and current perspectives. Front Plant Sci 14, 1235749. |
| [24] |
Delteil A, Gobbato E, Cayrol B, Estevan J, Michel-Romiti C, Dievart A, Kroj T, Morel JB (2016). Several wall-associated kinases participate positively and negatively in basal defense against rice blast fungus. BMC Plant Biol 16, 17.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Diener AC, Ausubel FM (2005). RESISTANCE TO FUSARIUM OXYSPORUM 1, a dominant Arabidopsis disease- resistance gene, is not race specific. Genetics 171, 305-321. |
| [26] |
Dong BX, Liu Y, Huang G, Song AP, Chen SM, Jiang JF, Chen FD, Fang WM (2024). Plant NAC transcription factors in the battle against pathogens. BMC Plant Biol 24, 958.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
Du J, Anderson CT, Xiao CW (2022). Dynamics of pectic homogalacturonan in cellular morphogenesis and adhesion, wall integrity sensing and plant development. Nat Plants 8, 332-340.
DOI PMID |
| [28] | Engelsdorf T, Gigli-Bisceglia N, Veerabagu M, McKenna JF, Vaahtera L, Augstein F, Van der Does D, Zipfel C, Hamann T (2018). The plant cell wall integrity maintenance and immune signaling systems cooperate to control stress responses in Arabidopsis thaliana. Sci Signal 11, eaao3070. |
| [29] |
Ferrari S, Savatin DV, Sicilia F, Gramegna G, Cervone F, De Lorenzo G (2013). Oligogalacturonides: plant damage-associated molecular patterns and regulators of growth and development. Front Plant Sci 4, 49.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
Grantham NJ, Wurman-Rodrich J, Terrett OM, Lyczakowski JJ, Stott K, Iuga D, Simmons TJ, Durand-Tardif M, Brown SP, Dupree R, Busse-Wicher M, Dupree P (2017). An even pattern of xylan substitution is critical for interaction with cellulose in plant cell walls. Nat Plants 3, 859-865.
DOI PMID |
| [31] | Guo YY, Wang SF, Yu KJ, Wang HL, Xu HM, Song CW, Zhao YY, Wen JL, Fu CX, Li Y, Wang SZ, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Cao Y, Shao FJ, Wang XH, Deng X, Chen T, Zhao Q, Li L, Wang GD, Grünhofer P, Schreiber L, Li Y, Song GY, Dixon RA, Lin JX (2023). Manipulating microRNA miR408 enhances both biomass yield and saccharification efficiency in poplar. Nat Commun 14, 4285. |
| [32] | He Q, Zabotina OA, Yu CX (2020). Principal component analysis facilitated fast and noninvasive Raman spectroscopic imaging of plant cell wall pectin distribution and interaction with enzymatic hydrolysis. J Raman Spectrosc 51, 2458-2467. |
| [33] | Jin KX, Liu XG, Jiang ZH, Tian GL, Yang SM, Shang LL, Ma JF (2019). Delignification kinetics and selectivity in poplar cell wall with acidified sodium chlorite. Ind Crops Prod 136, 87-92. |
| [34] |
Kang X, Kirui A, Dickwella Widanage MC, Mentink-Vigier F, Cosgrove DJ, Wang T (2019). Lignin-polysaccharide interactions in plant secondary cell walls revealed by solid-state NMR. Nat Commun 10, 347.
DOI PMID |
| [35] | Ke JJ, Zhu WT, Yuan Y, Du XY, Xu A, Zhang D, Cao S, Chen W, Lin Y, Xie JT, Cheng JS, Fu YP, Jiang DH, Yu X, Li B (2023). Duality of immune recognition by tomato and virulence activity of the Ralstonia solanacearum exo-polygalacturonase PehC. Plant Cell 35, 2552-2569. |
| [36] |
Keegstra K (2010). Plant cell walls. Plant Physiol 154, 483-486.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
Keegstra K, Talmadge KW, Bauer WD, Albersheim P (1973). The structure of plant cell walls: III. A model of the walls of suspension-cultured sycamore cells based on the interconnections of the macromolecular components. Plant Physiol 51, 188-197.
DOI PMID |
| [38] |
Lagaert S, Beliën T, Volckaert G (2009). Plant cell walls: protecting the barrier from degradation by microbial enzymes. Semin Cell Dev Biol 20, 1064-1073.
DOI PMID |
| [39] | Larkan NJ, Ma LS, Haddadi P, Buchwaldt M, Parkin IAP, Djavaheri M, Borhan MH (2020). The Brassica napus wall-associated kinase-like (WAKL) gene Rlm9 provides race-specific blackleg resistance. Plant J 104, 892-900. |
| [40] | Lee HK, Santiago J (2023). Structural insights of cell wall integrity signaling during development and immunity. Curr Opin Plant Biol 76, 102455. |
| [41] | Li DD, Li XM, Wang ZC, Wang HC, Gao JZ, Liu XT, Zhang Z (2024a). Transcription factors RhbZIP17 and RhWRKY30 enhance resistance to Botrytis cinerea by increasing lignin content in rose petals. J Exp Bot 75, 1633-1646. |
| [42] | Li YJ, Shen WW, Zhang X, Cui YN, Zhao YY, Guo YY, Li XJ, Wang SZ, Song GY, Wang P, Ma JF, Lin JX (2024b). Single-cell characterization of major components of plant cell walls in situ by Raman spectroscopy. Sci China Life Sci 67, 1772-1774. |
| [43] | Lin WW, Tang WX, Pan X, Huang AB, Gao XQ, Anderson CT, Yang ZB (2022). Arabidopsis pavement cell morphogenesis requires FERONIA binding to pectin for activation of ROP GTPase signaling. Curr Biol 32, 497-507. |
| [44] | Liu MCJ, Yeh FLJ, Yvon R, Simpson K, Jordan S, Chambers J, Wu HM, Cheung AY (2024). Extracellular pectin-RALF phase separation mediates FERONIA global signaling function. Cell 187, 312-330. |
| [45] |
Malinovsky FG, Fangel JU, Willats WGT (2014). The role of the cell wall in plant immunity. Front Plant Sci 5, 178.
DOI PMID |
| [46] | Man Y, Zhao YY, Ye R, Lin JX, Jing YP (2018). In vivo cytological and chemical analysis of Casparian strips using stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. J Plant Physiol 220, 136-144. |
| [47] |
Molina A, Jordá L, Torres MÁ, Martín-Dacal M, Berlanga DJ, Fernández-Calvo P, Gómez-Rubio E, Martín-Santamaría S (2024). Plant cell wall-mediated disease resistance: current understanding and future perspectives. Mol Plant 17, 699-724.
DOI PMID |
| [48] | Munzert KS, Engelsdorf T (2025). Plant cell wall structure and dynamics in plant-pathogen interactions and pathogen defence. J Exp Bot 76, 228-242. |
| [49] |
Peaucelle A, Braybrook SA, Le Guillou L, Bron E, Kuhlemeier C, Höfte H (2011). Pectin-induced changes in cell wall mechanics underlie organ initiation in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol 21, 1720-1726.
DOI PMID |
| [50] |
Philippe G, Sørensen I, Jiao C, Sun XP, Fei ZJ, Domozych DS, Rose JK (2020). Cutin and suberin: assembly and origins of specialized lipidic cell wall scaffolds. Curr Opin Plant Biol 55, 11-20.
DOI PMID |
| [51] | Rawat S, Ali S, Nayankantha NNC, Chandrashekar N, Mittra B, Grover A (2017). Isolation and expression analysis of defensin gene and its promoter from Brassica juncea. J Plant Dis Prot 124, 591-600. |
| [52] |
Reymond P, Farmer EE (1998). Jasmonate and salicylate as global signals for defense gene expression. Curr Opin Plant Biol 1, 404-411.
DOI PMID |
| [53] | Rongpipi S, Ye D, Gomez ED, Gomez EW (2019). Progress and opportunities in the characterization of cellulose—an important regulator of cell wall growth and mechanics. Front Plant Sci 9, 1894. |
| [54] |
Shine MB, Yang JW, El-Habbak M, Nagyabhyru P, Fu DQ, Navarre D, Ghabrial S, Kachroo P, Kachroo A (2016). Cooperative functioning between phenylalanine ammonia lyase and isochorismate synthase activities contributes to salicylic acid biosynthesis in soybean. New Phytol 212, 627-636.
DOI PMID |
| [55] |
Silverman P, Seskar M, Kanter D, Schweizer P, Metraux JP, Raskin I (1995). Salicylic acid in rice (biosynthesis, conjugation, and possible role). Plant Physiol 108, 633-639.
DOI PMID |
| [56] |
Simmons TJ, Mortimer JC, Bernardinelli OD, Pöppler AC, Brown SP, deAzevedo ER, Dupree R, Dupree P (2016). Folding of xylan onto cellulose fibrils in plant cell walls revealed by solid-state NMR. Nat Commun 7, 13902.
DOI PMID |
| [57] | Song CW, Guo YY, Shen WW, Yao XM, Xu HM, Zhao YY, Li RL, Lin JX (2023). PagUNE12 encodes a basic helix- loop-helix transcription factor that regulates the development of secondary vascular tissue in poplar. Plant Physiol 192, 1046-1062. |
| [58] | Sultana R, Imam Z, Kumar RR, Banu VS, Nahakpam S, Bharti R, Bharadwaj C, Singh AK, Pasala RK, Singh DR, Siddiqui MW (2025). Signaling and defence mechanism of jasmonic and salicylic acid response in pulse crops: role of WRKY transcription factors in stress response. J Plant Growth Regul 44, 5-21. |
| [59] | Sun Y, Wang Y, Zhang XX, Chen ZD, Xia YQ, Wang L, Sun YJ, Zhang MM, Xiao Y, Han ZF, Wang YC, Chai JJ (2022). Plant receptor-like protein activation by a microbial glycoside hydrolase. Nature 610, 335-342. |
| [60] | Tang WX, Lin WW, Zhou X, Guo JZ, Dang X, Li BQ, Lin DS, Yang ZB (2022). Mechano-transduction via the pectin-FERONIA complex activates ROP6 GTPase signaling in Arabidopsis pavement cell morphogenesis. Curr Biol 32, 508-517. |
| [61] |
Wan JX, He M, Hou QQ, Zou LJ, Yang YH, Wei Y, Chen XW (2021). Cell wall associated immunity in plants. Stress Biol 1, 3.
DOI PMID |
| [62] | Wang WB, Fei Y, Wang YJ, Song BB, Li L, Zhang WJ, Cheng HY, Zhang XJ, Chen S, Zhou JM (2023). SHOU4/4L link cell wall cellulose synthesis to pattern-triggered immunity. New Phytol 238, 1620-1635. |
| [63] |
Wang Y, Xu YP, Sun YJ, Wang HB, Qi JM, Wan BW, Ye WW, Lin YC, Shao YY, Dong SM, Tyler BM, Wang YC (2018). Leucine-rich repeat receptor-like gene screen reveals that Nicotiana RXEG1 regulates glycoside hydrolase 12 MAMP detection. Nat Commun 9, 594.
DOI PMID |
| [64] |
Wasternack C, Strnad M (2016). Jasmonate signaling in plant stress responses and development-active and inactive compounds. New Biotechnol 33, 604-613.
DOI PMID |
| [65] | Wildermuth MC, Dewdney J, Wu G, Ausubel FM (2001). Isochorismate synthase is required to synthesize salicylic acid for plant defence. Nature 414, 562-565. |
| [66] |
Wojtasik W, Kulma A, Dymińska L, Hanuza J, Czemplik M, Szopa J (2016). Evaluation of the significance of cell wall polymers in flax infected with a pathogenic strain of Fusarium oxysporum. BMC Plant Biol 16, 75.
DOI PMID |
| [67] | Wormit A, Usadel B (2018). The multifaceted role of pectin methylesterase inhibitors (PMEIs). Int J Mol Sci 19, 2878. |
| [68] | Wu HC, Bulgakov VP, Jinn TL (2018). Pectin methylesterases: cell wall remodeling proteins are required for plant response to heat stress. Front Plant Sci 9, 1612. |
| [69] | Xia YQ, Sun GZ, Xiao JH, He XY, Jiang HB, Zhang ZC, Zhang Q, Li KN, Zhang SC, Shi XC, Wang ZY, Liu L, Zhao Y, Yang YH, Duan KX, Ye WW, Wang YM, Dong SM, Wang Y, Ma ZC, Wang YC (2024). AlphaFold-guided redesign of a plant pectin methylesterase inhibitor for broad-spectrum disease resistance. Mol Plant 17, 1344-1368. |
| [70] |
Xiao Y, Sun GZ, Yu QS, Gao T, Zhu QS, Wang R, Huang SJ, Han ZF, Cervone F, Yin H, Qi TC, Wang YC, Chai JJ (2024). A plant mechanism of hijacking pathogen virulence factors to trigger innate immunity. Science 383, 732-739.
DOI PMID |
| [71] |
Yalpani N, Leon J, Lawton MA, Raskin I (1993). Pathway of salicylic acid biosynthesis in healthy and virus-inoculated tobacco. Plant Physiol 103, 315-321.
DOI PMID |
| [72] | Yang C, Liu R, Pang JH, Ren B, Zhou HB, Wang G, Wang ET, Liu J (2021a). Poaceae-specific cell wall-derived oligosaccharides activate plant immunity via OsCERK1 during Magnaporthe oryzae infection in rice. Nat Commun 12, 2178. |
| [73] | Yang J, Xie MX, Wang XF, Wang GN, Zhang Y, Li ZK, Ma ZY (2021b). Identification of cell wall-associated kinases as important regulators involved in Gossypium hirsutum resistance to Verticillium dahliae. BMC Plant Biol 21, 220. |
| [74] |
Yang K, Qi L, Zhang ZY (2014). Isolation and characterization of a novel wall-associated kinase gene TaWAK5 in wheat (Triticum aestivum). Crop J 2, 255-266.
DOI |
| [75] |
Yang P, Praz C, Li BB, Singla J, Robert CAM, Kessel B, Scheuermann D, Lüthi L, Ouzunova M, Erb M, Krattinger SG, Keller B (2019). Fungal resistance mediated by maize wall-associated kinase ZmWAK-RLK1 correlates with reduced benzoxazinoid content. New Phytol 221, 976-987.
DOI PMID |
| [76] |
Yao XM, Zhang GF, Zhang G, Sun Q, Liu CM, Chu JF, Jing YP, Niu SH, Fu CX, Lew TTS, Lin JX, Li XJ (2024). PagARGOS promotes low-lignin wood formation in poplar. Plant Biotechnol J 22, 2201-2215.
DOI PMID |
| [77] | Zeng YN, Yarbrough JM, Mittal A, Tucker MP, Vinzant TB, Decker SR, Himmel ME (2016). In situ label-free imaging of hemicellulose in plant cell walls using stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. Biotechnol Biofuels 9, 256. |
| [78] | Zhai K, Rhodes J, Zipfel C (2024). A peptide-receptor module links cell wall integrity sensing to pattern-triggered immunity. Nat Plants 10, 1799-1811. |
| [79] | Zhang BC, Gao YH, Zhang LJ, Zhou YH (2021a). The plant cell wall: biosynthesis, construction, and functions. J Integr Plant Biol 63, 251-272. |
| [80] | Zhang DM, Xu ZP, Cao SX, Chen KL, Li SC, Liu XL, Gao CX, Zhang BC, Zhou YH (2018). An uncanonical CCCH- tandem zinc-finger protein represses secondary wall synthesis and controls mechanical strength in rice. Mol Plant 11, 163-174. |
| [81] | Zhang LS, Kars I, Essenstam B, Liebrand TWH, Wagemakers L, Elberse J, Tagkalaki P, Tjoitang D, van den Ackerveken G, van Kan JAL (2014). Fungal endopolygalacturonases are recognized as microbe-associated molecular patterns by the Arabidopsis receptor-like protein RESPONSIVENESS TO BOTRYTIS POLYGALACTURONASES1. . Plant Physiol 164, 352-364. |
| [82] |
Zhang N, Pombo MA, Rosli HG, Martin GB (2020). Tomato wall-associated kinase SLWak1 depends on Fls2/Fls3 to promote apoplastic immune responses to Pseudomonas syringae. Plant Physiol 183, 1869-1882.
DOI PMID |
| [83] | Zhang ZQ, Ma WY, Ren ZY, Wang XX, Zhao JJ, Pei XY, Liu YG, He KL, Zhang F, Huo WQ, Li W, Yang DG, Ma XF (2021b). Characterization and expression analysis of wall-associated kinase (WAK) and WAK-like family in cotton. Int J Biol Macromol 187, 867-879. |
| [84] |
Zhao YY, Man Y, Wen JL, Guo YY, Lin JX (2019). Advances in imaging plant cell walls. Trends Plant Sci 24, 867-878.
DOI PMID |
| [85] | Zhou JG, Mu Q, Wang XY, Zhang J, Yu HZ, Huang TZ, He YX, Dai SJ, Meng XZ (2022). Multilayered synergistic regulation of phytoalexin biosynthesis by ethylene, jasmonate, and MAPK signaling pathways in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 34, 3066-3087. |
| [86] | Zhu JW, Ren WT, Guo F, Wang HK, Yu Y (2024). Revealing spatial distribution and accessibility of cell wall polymers in bamboo through chemical imaging and mild chemical treatments. Carbohydr Polym 339, 122261. |
| [87] | Zhu N, Yang YF, Ji MB, Wu D, Chen KS (2019). Label-free visualization of lignin deposition in loquats using complementary stimulated and spontaneous Raman microscopy. Hortic Res 6, 72. |
| [1] | 肖银燕, 于华, 万里. 植物免疫研究: 机制突破和应用创新[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 693-703. |
| [2] | 徐羽丰, 周冕. 植物免疫的转录后调控[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 704-721. |
| [3] | 刘德水, 岳宁, 刘玉乐. 植物免疫机制新突破[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 669-678. |
| [4] | 江亚楠, 徐雨青, 魏毅铤, 陈钧, 张容菀, 赵蓓蓓, 林宇翔, 饶玉春. 水稻抗病调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 734-748. |
| [5] | 覃磊, 彭志红, 夏石头. 植物NLR免疫受体的识别、免疫激活与信号调控[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 12-23. |
| [6] | 周俭民. 免疫信号轴揭示水稻与病原菌斗争的秘密[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(5): 513-515. |
| [7] | 王伟, 唐定中. 两类免疫受体强强联手筑牢植物免疫防线[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(2): 142-146. |
| [8] | 杨程惠子,唐先宇,李威,夏石头. NLR及其在植物抗病中的调控作用[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(4): 497-504. |
| [9] | 崔亚宁, 钱虹萍, 赵艳霞, 李晓娟. 模式识别受体的胞内转运及其在植物免疫中的作用[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(3): 329-339. |
| [10] | 李伟滔, 贺闽, 陈学伟. ZmFBL41 Chang7-2: 玉米抗纹枯病的关键利器[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(5): 547-549. |
| [11] | 夏石头, 李昕. 开启防御之门: 植物抗病小体[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(3): 288-292. |
| [12] | 闫佳, 刘雅琼, 侯岁稳. 植物抗病蛋白研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(2): 250-263. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||