

植物学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (3): 318-328.DOI: 10.11983/CBB19211 cstr: 32102.14.CBB19211
收稿日期:2019-10-28
接受日期:2020-02-26
出版日期:2020-05-01
发布日期:2020-07-06
通讯作者:
戴思兰
基金资助:
Hong Luo,Xiaohui Wen,Yuanyuan Zhou,Silan Dai( )
)
Received:2019-10-28
Accepted:2020-02-26
Online:2020-05-01
Published:2020-07-06
Contact:
Silan Dai
摘要: 芳香堆心菊(Helenium aromaticum)全株具芳香气味, 且头状花序仅含管状花, 是研究菊科植物花香和花型的良好材料, 但目前尚缺乏对其转基因技术体系的研究。为建立高效的芳香堆心菊离体再生体系, 以叶片、茎段和下胚轴为外植体, 进行25组不同激素及不同浓度配比的不定芽诱导研究。结果表明, 以芳香堆心菊叶片为外植体, 培养基为MS+ 0.2 mg·L-1 NAA+1 mg·L-1 6-BA+0.2 mg·L-1 TDZ, 培养20天后愈伤组织诱导率高达100%, 丛生芽的诱导率为62.10%; 将不定芽接种于1/2MS培养基中进行生根培养, 16天即可生根, 且生根率为63.33%; 生根后继续培养14天现蕾, 开花率达93.33%。此外, 研究表明芳香堆心菊的再生受外植体来源、激素种类和浓度的影响。2,4-D不利于芳香堆心菊不定芽的诱导, 适宜浓度的6-BA和TDZ组合能有效促进芳香堆心菊不定芽的形成。研究初步建立了芳香堆心菊组织培养条件下的离体再生体系, 为建立其遗传转化体系奠定了坚实的基础。研究结果还可用于后续有关菊科植物花香和花型的研究。
罗虹, 温小蕙, 周圆圆, 戴思兰. 芳香堆心菊离体再生体系的建立. 植物学报, 2020, 55(3): 318-328.
Hong Luo, Xiaohui Wen, Yuanyuan Zhou, Silan Dai. Establishment of In Vitro Regeneration System of Helenium aromaticum. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(3): 318-328.
| Treatments | Plant growth regulators (mg·L-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAA | 6-BA | 2,4-D | TDZ | |
| A1 | 0.5 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| A2 | 0.5 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| A3 | 0.5 | 3 | 2 | 0 |
| A4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| A5 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| A6 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| A7 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| A8 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| A9 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 0 |
| B1 | 0.2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| B2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| B3 | 0.2 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| B4 | 0.5 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| B5 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| B6 | 0.2 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| B7 | 0.5 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| C1 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0 | 0.2 |
| C2 | 0.2 | 1 | 0 | 0.2 |
| C3 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 0 | 0.2 |
| C4 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0 | 0.5 |
| C5 | 0.5 | 1 | 0 | 0.5 |
| C6 | 0.1 | 1.5 | 0 | 0.5 |
| C7 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0 | 1 |
| C8 | 0.1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| C9 | 0.2 | 1.5 | 0 | 1 |
表1 芳香堆心菊愈伤组织诱导及不定芽分化培养基
Table 1 Medium for callus induction and adventitious buds differentiation of Helenium aromaticum
| Treatments | Plant growth regulators (mg·L-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAA | 6-BA | 2,4-D | TDZ | |
| A1 | 0.5 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| A2 | 0.5 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| A3 | 0.5 | 3 | 2 | 0 |
| A4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| A5 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| A6 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| A7 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| A8 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| A9 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 0 |
| B1 | 0.2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| B2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| B3 | 0.2 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| B4 | 0.5 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| B5 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| B6 | 0.2 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| B7 | 0.5 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| C1 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0 | 0.2 |
| C2 | 0.2 | 1 | 0 | 0.2 |
| C3 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 0 | 0.2 |
| C4 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0 | 0.5 |
| C5 | 0.5 | 1 | 0 | 0.5 |
| C6 | 0.1 | 1.5 | 0 | 0.5 |
| C7 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0 | 1 |
| C8 | 0.1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| C9 | 0.2 | 1.5 | 0 | 1 |
| Treatments | Plant growth regulators (mg·L-1) |
|---|---|
| NAA | |
| R0 | 0 |
| R1 | 0.1 |
| R2 | 0.2 |
| R3 | 0.3 |
表2 芳香堆心菊生根培养基
Table 2 Medium for root culture of Helenium aromaticum
| Treatments | Plant growth regulators (mg·L-1) |
|---|---|
| NAA | |
| R0 | 0 |
| R1 | 0.1 |
| R2 | 0.2 |
| R3 | 0.3 |
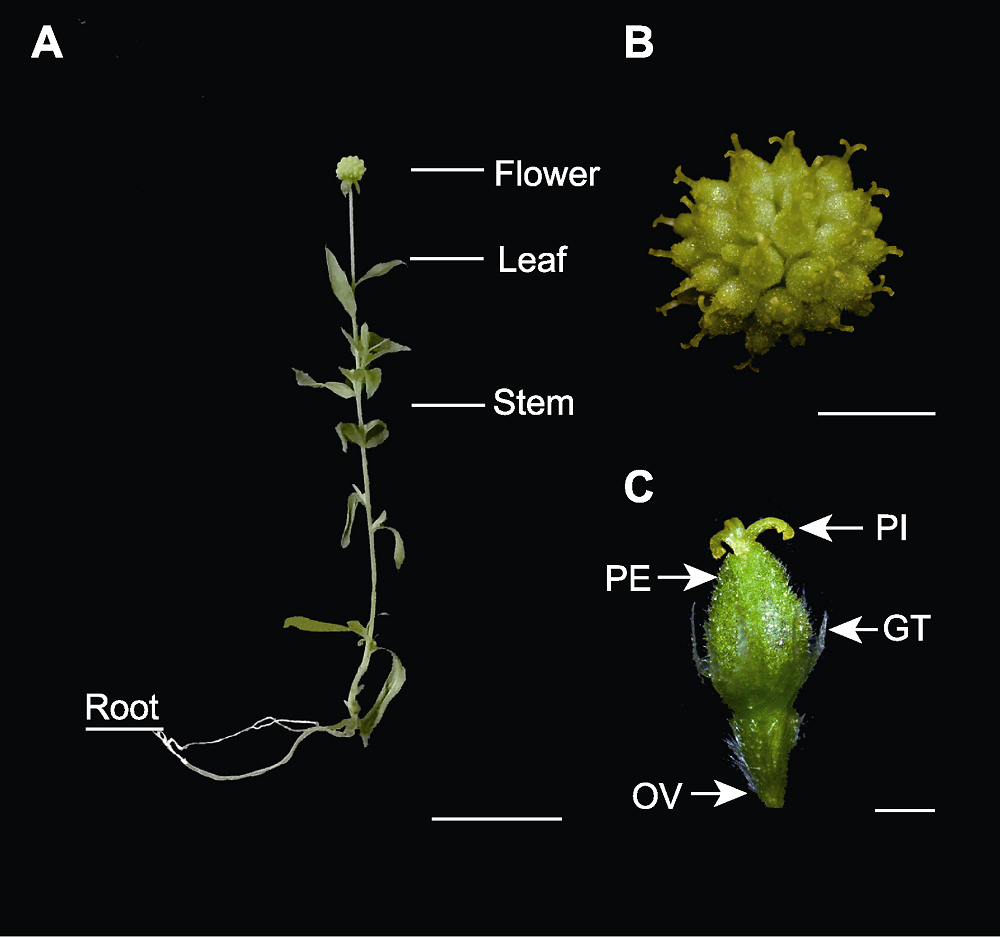
图1 芳香堆心菊整株及花器官形态 (A) 整株(Bar=2 cm); (B) 头状花序(Bar=2 mm); (C) 单个小花(Bar=1 mm)。PE: 花瓣; OV: 子房; PI: 雌蕊; GT: 腺毛
Figure 1 The whole plant and flower morphology of Helenium aromaticum (A) The whole plant (Bar=2 cm); (B) The capitulum (Bar=2 mm); (C) Single flower (Bar=1 mm). PE: Petal; OV: Ovary; PI: Pistil; GT: Glandular trichomes
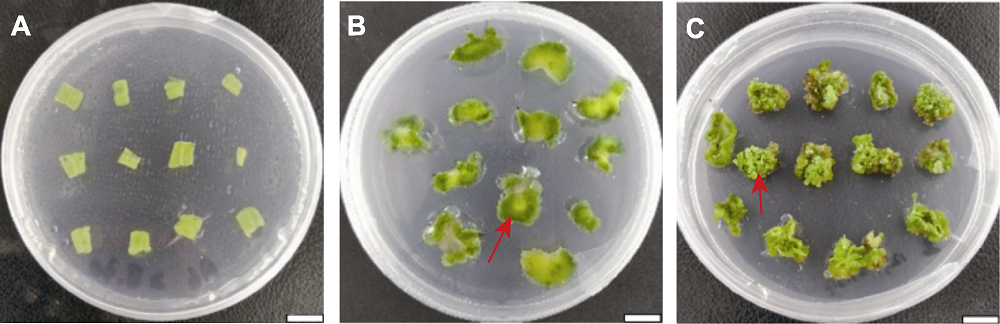
图2 芳香堆心菊叶片愈伤组织诱导及不定芽分化的阶段(C2) (A) 叶片外植体; (B) 愈伤组织(20天, 箭头所示); (C) 不定芽(30天, 箭头所示)。Bars=1 cm。C2同表1。
Figure 2 Several stages of callus induction and adventitious bud differentiation of Helenium aromaticum leaves (C2) (A) Leaf explants; (B) Calli (20 d, shown by arrow); (C) Adventitious buds (30 d, shown by arrow). Bars=1 cm. C2 is the same as Table 1.
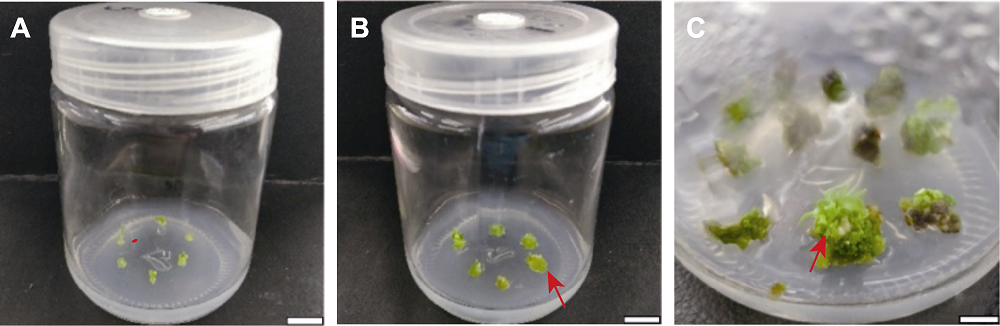
图3 芳香堆心菊茎段愈伤组织诱导及不定芽分化的阶段(B1) (A) 茎段外植体; (B) 愈伤组织(17天, 箭头所示); (C) 不定芽(65天, 箭头所示)。Bars=1 cm。B1同表1。
Figure 3 Several stages of callus induction and adventitious bud differentiation of Helenium aromaticum stem fragments (B1) (A) Stem segment explants; (B) Calli (17 d, shown by arrow); (C) Adventitious buds (65 d, shown by arrow). Bars=1 cm. B1 is the same as Table 1.
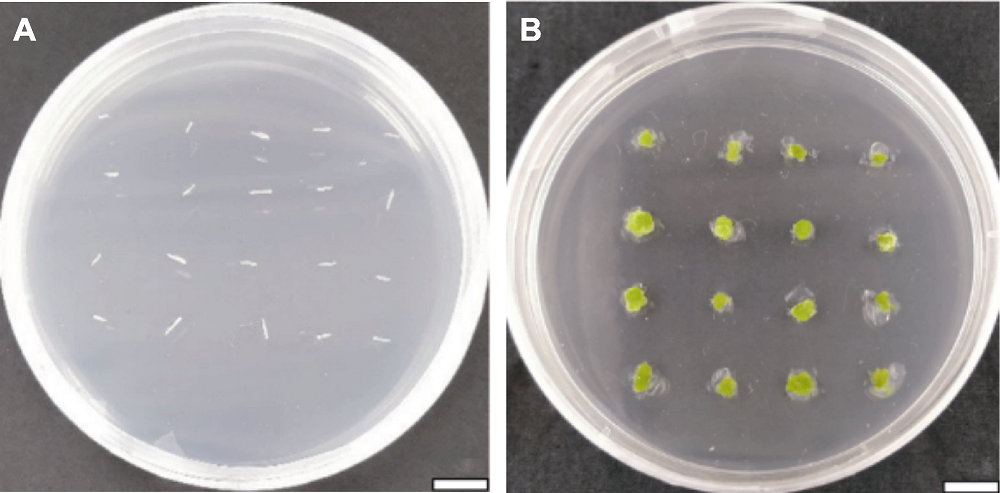
图4 芳香堆心菊下胚轴愈伤组织诱导的阶段(C4) (A) 下胚轴外植体; (B) 愈伤组织(20天)。Bars=1 cm。C4同表1。
Figure 4 Several stages of callus induction of Helenium aromaticum hypocotyls (C4) (A) Hypocotyl explants; (B) Calli (20 d). Bars=1 cm. C4 is the same as Table 1.
| Explant types | Callus induction medium | Adventitious bud differentiation medium | Regeneration rate (%) | Rooting medium |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaf | MS+0.2 mg·L-1 NAA+1 mg·L-1 6-BA+0.2 mg·L-1 TDZ | 62.1 | 1/2MS | |
| Stem segment | MS+0.2 mg·L-1 NAA+1 mg·L-1 6-BA | 9.75 | 1/2MS | |
| Hypocotyl | MS+0.2 mg·L-1 NAA+0.5 mg·L-1 6-BA+0.5 mg·L-1 TDZ | - | - | - |
表3 芳香堆心菊不同外植体再生体系
Table 3 Different explant regeneration systems of Helenium aromaticum
| Explant types | Callus induction medium | Adventitious bud differentiation medium | Regeneration rate (%) | Rooting medium |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaf | MS+0.2 mg·L-1 NAA+1 mg·L-1 6-BA+0.2 mg·L-1 TDZ | 62.1 | 1/2MS | |
| Stem segment | MS+0.2 mg·L-1 NAA+1 mg·L-1 6-BA | 9.75 | 1/2MS | |
| Hypocotyl | MS+0.2 mg·L-1 NAA+0.5 mg·L-1 6-BA+0.5 mg·L-1 TDZ | - | - | - |
| Treatments | Time of rooting (d) | The situation of root and plant | Rate of rooting (%) | Budding time (d) | Rate of flowering (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R0 | 16 | Root system is sparse and slender; the plant is robust with normal stems and leaves, flowering normally | 63.33 | 30 | 93.33 |
| R1 | 10 | The root system is dense and crude, some of which are deformed roots; the plants are dwarf with large leaves | 45.46 | 34 | 86.36 |
| R2 | 13 | The root system is few and short, most of which are deformed roots; the plants dwarf can’t grow with normal leaves | 12.50 | - | 0 |
| R3 | 18 | Root deformity and plants hardly grow taller and leaves weaker | 14.71 | - | 0 |
表4 芳香堆心菊不定芽生根情况
Table 4 Rooting results of adventitious buds of Helenium aromaticum
| Treatments | Time of rooting (d) | The situation of root and plant | Rate of rooting (%) | Budding time (d) | Rate of flowering (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R0 | 16 | Root system is sparse and slender; the plant is robust with normal stems and leaves, flowering normally | 63.33 | 30 | 93.33 |
| R1 | 10 | The root system is dense and crude, some of which are deformed roots; the plants are dwarf with large leaves | 45.46 | 34 | 86.36 |
| R2 | 13 | The root system is few and short, most of which are deformed roots; the plants dwarf can’t grow with normal leaves | 12.50 | - | 0 |
| R3 | 18 | Root deformity and plants hardly grow taller and leaves weaker | 14.71 | - | 0 |
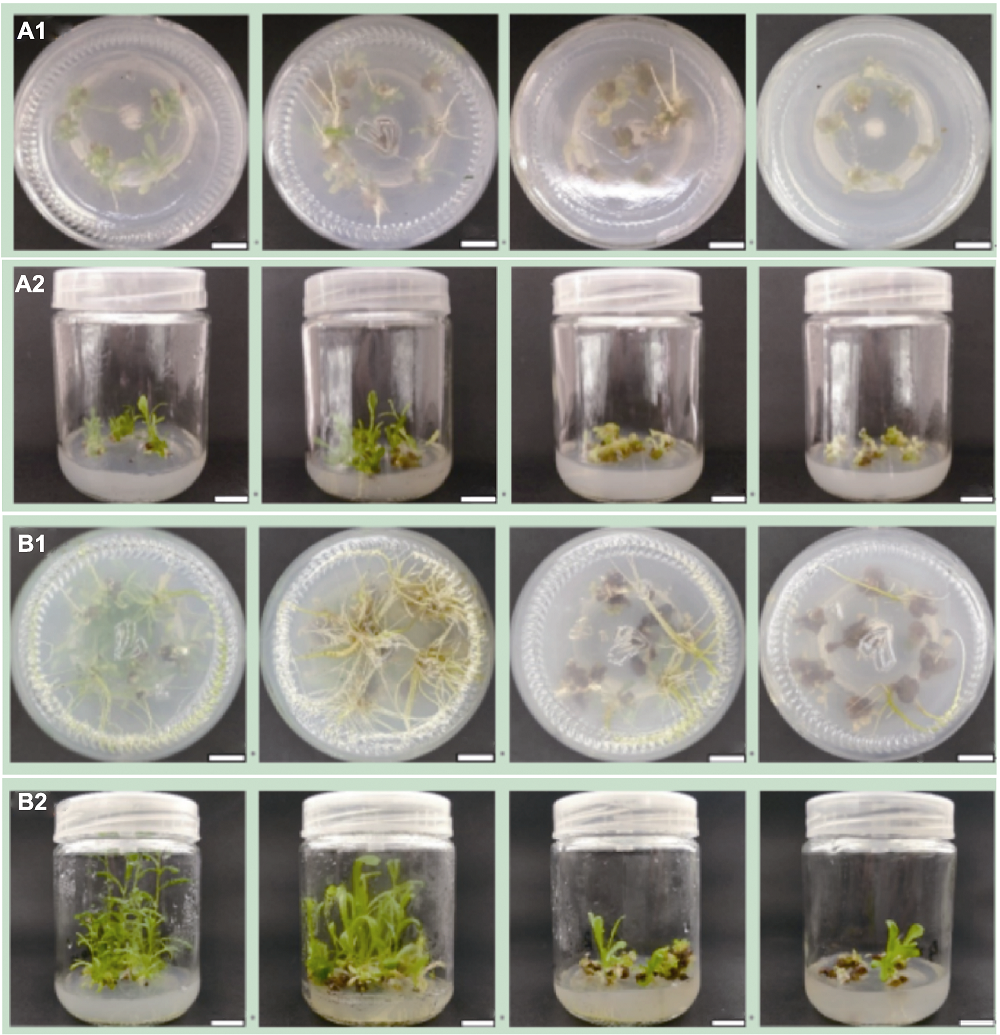
图5 芳香堆心菊不定芽生根及植株状态(从左至右分别为R0、R1、R2和R3) (A1) 生根情况(17天); (A2) 植株状态(17天); (B1) 生根情况(32天); (B2) 植株状态(32天)。Bars=1 cm。R0-R3同表2。
Figure 5 Rooting and plant status of Helenium aromaticum adventitious buds (from left to right are R0, R1, R2, and R3, respectively) (A1) Rooting condition (17 d); (A2) Plant status (17 d); (B1) Rooting condition (32 d); (B2) Plant status (32 d). Bars=1 cm. R0-R3 are the same as Table 2.
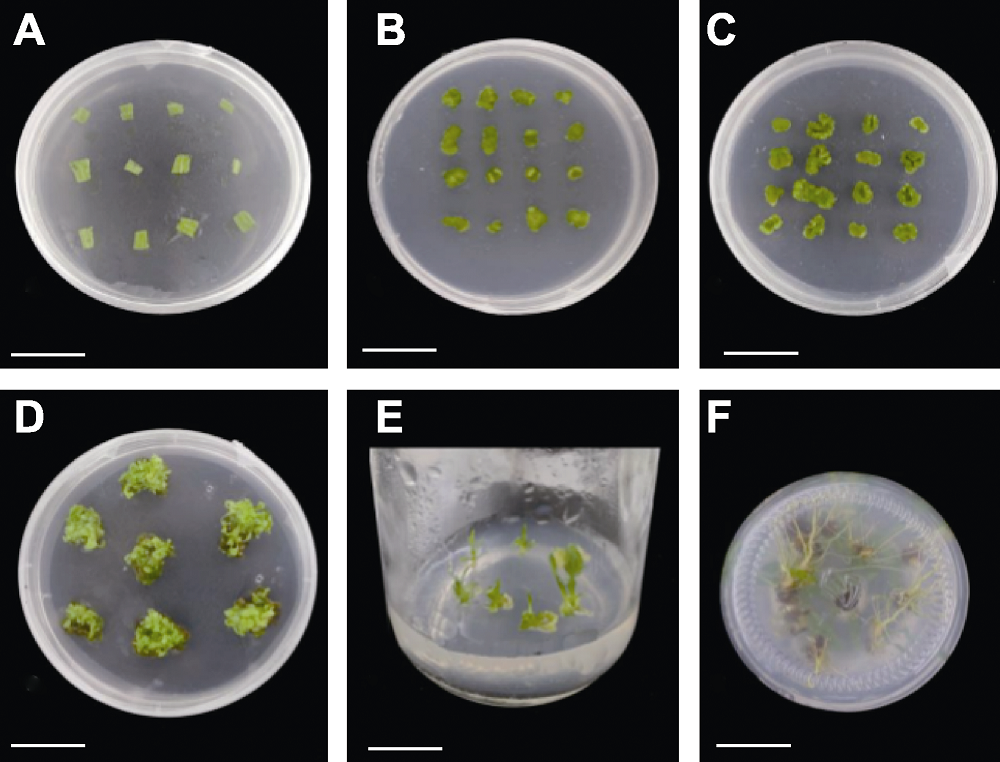
图6 芳香堆心菊叶片离体再生体系的建立 (A) 叶片; (B) 叶片膨大(15天); (C) 叶片的愈伤组织(20天); (D) 愈伤组织分化的不定芽(50天); (E) 不定芽的生根诱导(60天); (F) 生根诱导16天(76天)。Bars=2 cm
Figure 6 Establishment of in vitro regeneration system of Helenium aromaticum leaves (A) The leaf; (B) The leaf swelling (15 d); (C) Calli were induced from leaves (20 d); (D) Adventitious buds could be regenerated from calli (50 d); (E) Inducing rooting (60 d); (F) The adventitious roots induced after 16 days (76 d). Bars=2 cm
| [1] | 包晗, 张芮, 张美玲, 张虹, 陈任 (2018). 甜叶菊叶片外植体再生体系的建立. 北方园艺 42(6), 16-22. |
| [2] | 陈华, 李平, 刘晶, 李银心 (2005). 药蒲公英再生体系的建立和优化. 生物工程学报 21, 244-249. |
| [3] | 陈雪, 张金柱, 潘兵兵, 桑成瑾, 马雪, 杨涛, 车代弟 (2011). 月季愈伤组织的诱导及植株再生. 植物学报 46, 569-574. |
| [4] | 程密密 (2015). 翠菊(Callistephus chinensis (L.) Nees)高频再生体系的建立及多倍体诱导. 硕士论文. 重庆: 西南大学. pp. 17. |
| [5] | 程越 (2014). 菊花脑再生体系建立的研究. 硕士论文. 南京: 南京农业大学. pp. 4. |
| [6] | 丁晓霞 (2018). 菊花组培再生体系研究进展. 辽宁林业科技(4), 64-65, 68. |
| [7] | 冯欢, 易姝利, 谢佳恒, 雷梦琦, 黄萱 (2014). 微型月季愈伤组织诱导及植株再生. 植物学报 49, 595-602. |
| [8] | 付建新, 张超, 王翊, 戴思兰 (2012). 甘菊下胚轴离体再生体系的建立. 北京林业大学学报 34(3), 91-96. |
| [9] | 高亚曼, 李妹芳, 冀芦沙 (2016). 珍珠半夏(Pinellia ternate)高效再生体系的建立及其遗传稳定性检测. 分子植物育种 14, 980-985. |
| [10] | 郝志华, 顾偌铖, 黄洁兰, 武彦博, 田铃 (2017). 常见多肉植物繁育技术的研究进展. 广东蚕业 51(4), 13-16. |
| [11] | 荆甜蕊, 徐思雅, 倪亦飞, 张勇娟, 郭斌, 尉亚辉 (2016). 天山雪莲生物技术研究进展. 基因组学与应用生物学 35, 2201-2210. |
| [12] | 李海萍, 张鲁刚, 张静, 茹磊, 刘学成, 孙希禄 (2011). 萝卜带柄子叶高频再生体系的建立. 植物学报 46, 331-337. |
| [13] | 李金童, 吴雅妮, 丁兵, 齐学军, 张旸, 解莉楠 (2016). 四种露地菊再生体系的建立. 北方园艺 40(19), 119-124. |
| [14] | 刘晨旭, 马欣, 董凤丽, 周蕴薇 (2015). 地被菊‘紫妍’和‘纽9722’的再生体系建立. 草业科学 32, 188-195. |
| [15] | 刘娟旭, 刘玲, 王静, 余义勋 (2008). 大叶相思下胚轴离体培养再生植株的研究. 林业科学研究 21, 403-406. |
| [16] | 刘军, 赵兰勇, 丰震, 张美蓉, 吴银凤 (2004). 菊花叶盘片转基因再生体系的优化选择. 植物学通报 21, 556-558. |
| [17] | 刘萌萌 (2017). 盆栽小菊高频再生体系建立与试管开花研究. 硕士论文. 银川: 宁夏大学. pp. 1. |
| [18] | 罗虹, 温小蕙, 刘影, 蒲娅, 戴思兰 (2018). 芳香堆心菊试管开花及释香机制初探. 见: 张启翔主编. 中国观赏园艺研究进展(2018). 北京: 中国林业出版社. pp. 448-460. |
| [19] | 孙永莲, 戴晓港, 李小平, 陈赢男 (2019). 簸箕柳组培再生体系的建立. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) 43(2), 31-37. |
| [20] | 王碧玉 (2017). 菊花再生及遗传转化体系的研究. 硕士论文. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学. pp. 8. |
| [21] | 王洪霞, 郭尚敬 (2012). TDZ对甜椒不定芽分化的影响. 北方园艺 36(3), 104-106. |
| [22] | 王欢, 刘洋, 苑禹, 李旭, 杜凤国 (2015). 蚂蚱腿子离体快繁技术研究. 植物生理学报 51, 2275-2279. |
| [23] | 王树芸, 吕波, 李坤, 吴佳洁, 付道林 (2012). “济麦”系列品种成熟胚再生体系的优化研究. 分子植物育种 10, 476-484. |
| [24] | 王自布, 莫国秀, 罗会兰, 张德英 (2015). 菊花不同外植体组培快繁及其再生体系的研究. 北方园艺 39(18), 106-109. |
| [25] | 吴志苹, 高亦珂, 范敏, 高耀辉 (2020). 菊花‘金不凋’再生及遗传转化体系的构建. 分子植物育种 18, 150-158. |
| [26] | 咸宏康, 支秋娟, 李卉, 王长泉 (2019). 金樱子(Rosa laevigata Michx.)叶片直接再生不定芽体系的建立. 北方园艺 43(13), 93-100. |
| [27] | 徐术菁 (2016). 东北蒲公英(Taraxacum ohwianum)叶片再生体系建立与优化. 硕士论文. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学. pp. 24. |
| [28] | 徐晓峰, 黄学林 (2003). TDZ: 一种有效的植物生长调节剂. 植物学通报 20, 227-237. |
| [29] | 杨怡帆, 杨清江, 潘峰, 张新利 (2019). 基于主成分分析的不同浓度TDZ处理下‘红地球’葡萄膨大效果的综合评价. 农业科技通讯 (7), 165-168. |
| [30] | 张俊华, 苏振华, 张泽鑫, 李妹芳, 郭尚敬, 曹雪松, 冀芦沙 (2019). 甜椒离体再生体系的构建. 分子植物育种 17, 8208-8214. |
| [31] | 张旭红, 王頔, 梁振旭, 孙美玉, 张金政, 石雷 (2018). 欧洲百合愈伤组织诱导及植株再生体系的建立. 植物学报 53, 840-847. |
| [32] | 张媛, 王康才, 汤兴利 (2008). 杭白菊子叶和下胚轴组织培养技术的研究. 中草药 39, 1721-1723. |
| [33] | 赵喜亭, 蒋丽微, 王苗, 朱玉婷, 张文芳, 李明军 (2016). 怀黄菊间接体胚受体再生体系的建立及CmTGA1的遗传转化. 植物学报 51, 525-532. |
| [34] | 中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会 (1984). 中国植物志, Vol. 74. 北京: 科学出版社. pp. 1. |
| [35] | 左静静, 闫贵云, 安晓宁, 霍利光, 刘少翔 (2017). 正交设计优化北苍术组织培养研究. 中国农学通报 33(11), 21-24. |
| [36] | Alamgir ANM (2017). Medicinal, non-medicinal, biopestici- des, color- and dye-yielding plants; secondary metabolites and drug principles; significance of medicinal plants; use of medicinal plants in the systems of traditional and complementary and alternative medicines (CAMs). In: Alamgir ANM, ed. Therapeutic Use of Medicinal Plants and Their Extracts. Cham Heidelberg: Springer. pp. 61-104. |
| [37] | Barkley TM, Brouillet L, Strother JL (2006). Asteraceae. In: Flora of North America, Vol. 19. New York: Oxford Uni- versity Press. pp. 3-69. |
| [38] | Bierner MW (1978). The taxonomy of Helenium sect. Cephalophora (Asteraceae). Syst Bot 3, 277-298. |
| [39] | Bloszyk E, Samek Z, Toman J, Holub M (1975). Linifolin a and helenalin from Helenium aromaticum. Phytochemistry 14, 1444-1445. |
| [40] | Bush SR, Earle ED, Langhans RW (1976). Plantlets from petal segments, petal epidermis, and shoot tips of the periclinal chimera, Chrysanthemum morifolium ‘Indianapolis’. Am J Bot 63, 729-737. |
| [41] | Chen J, Shen CZ, Guo YP, Rao GY (2018). Patterning the Asteraceae capitulum: duplications and differential expression of the flower symmetry CYC2-like genes. Front Plant Sci 9, 551. |
| [42] | Dewir YH, Nurmansyah, Naidoo Y, Teixeira da Silva JA (2018). Thidiazuron-induced abnormalities in plant tissue cultures. Plant Cell Rep 37, 1451-1470. |
| [43] | Gómez-González S, Ojeda F, Torres-Morales P, Palma JE (2016). Seed pubescence and shape modulate adaptive responses to fire cues. PLoS One 11, e0159655. |
| [44] | Naing AH, Park KI, Mi YC, Lim KB, Kim CK (2016). Optimization of factors affecting efficient shoot regeneration in Chrysanthemum cv. ‘Shinma’. Braz J Bot 39, 975-984. |
| [45] | Renou JP, Brochard P, Jalouzot R (1993). Recovery of transgenic chrysanthemum (Dendranthema grandiflora Tzvelev) after hygromycin resistance selection. Plant Sci 89, 185-197. |
| [46] |
Tanaka K, Kanno Y, Kudo S, Suzuki M (2000). Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in chrysanthemum (Dendranthema grandiflorum ( Ramat.) Kitamura). Plant Cell Rep 19, 946-953.
URL PMID |
| [1] | 李彤, 李楚然, 张芷瑜, 付晓熳, 刘云, 张颖君, 杨力颖, 赵平. 西印度醋栗组培快繁技术初探[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | 李晶晶, 李艳飞, 王安琪, 王佳颖, 邓成燕, 卢敏, 马剑英, 戴思兰. 菊花品种‘万代风光’再生及遗传转化体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [3] | 刘玉泽, 王一菲, 任威蓁, 栗浩, 路斌, 路丙社, 于晓跃. 北美豆梨杂种幼胚挽救及再生体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 800-809. |
| [4] | 冯雯, 王玉国. 栽培薯蓣茎段离体再生体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 792-799. |
| [5] | 曾浩, 李佩芳, 郭至辉, 刘春林, 阮颖. 银扇草再生体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 433-440. |
| [6] | 武晓云, 廖敏凌, 李雪茹, 舒梓淳, 辛佳潼, 张伯晗, 戴思兰. 毛华菊3种瓣型株系再生体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 245-256. |
| [7] | 谢纯刚, 刘哲, 章书声, 胡海涛. 手指柠檬茎段离体再生体系建立[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 926-934. |
| [8] | 廖敏凌, 蒲娅, 武晓云, 马朝峰, 王文奎, 戴思兰. 平潭野菊混合瓣型株系再生体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 449-460. |
| [9] | 逯锦春, 曹丽娜, 佟冠杰, 王鑫颖, 张利英, 喻锌, 李荟芳, 李彦慧. 大花银莲花愈伤组织诱导及再生体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(2): 217-226. |
| [10] | 李孟悦, 刘柳, 刘艳, 张晓曼. 毛报春(Primula × pubescens)腋芽再生组织培养体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(6): 732-739. |
| [11] | 罗钱, 张燕莎, 欧静. 郁金樱愈伤组织诱导及植株再生[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(4): 451-461. |
| [12] | 张冬瑞, 卜志刚, 陈玲玲, 常缨. 香鳞毛蕨的组织培养和快速繁殖体系构建[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(6): 760-767. |
| [13] | 邓莎, 吴艳妮, 吴坤林, 房林, 李琳, 曾宋君. 14种中国典型极小种群野生植物繁育特性和人工繁殖研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(3): 385-400. |
| [14] | 张文婷,何燕红,舒宁,邢景景,刘宝骏,包满珠,刘国锋. 金黄花滇百合植株再生与离体快繁技术体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(6): 773-778. |
| [15] | 徐悦,曹英萍,王玉,付春祥,戴绍军. 发根农杆菌介导的菠菜毛状根遗传转化体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(4): 515-521. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||