

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2021, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (3): 284-295.DOI: 10.11983/CBB20200 cstr: 32102.14.CBB20200
Previous Articles Next Articles
Jianhua Jiang1, Xiaojing Dang1, Wenhao Yao2, Mengzhu Hu2, Yuting Wang2, Changmin Hu1, Ying Zhang1, Dezheng Wang1,*( )
)
Received:2020-12-09
Accepted:2021-03-01
Online:2021-05-01
Published:2021-04-30
Contact:
Dezheng Wang
About author:First author contact:† These authors contributed equally to this paper
Jianhua Jiang, Xiaojing Dang, Wenhao Yao, Mengzhu Hu, Yuting Wang, Changmin Hu, Ying Zhang, Dezheng Wang. Genetic Analysis of Four Stigma Traits with Genic Male Sterile Line in Rice (Oryza sativa)[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(3): 284-295.
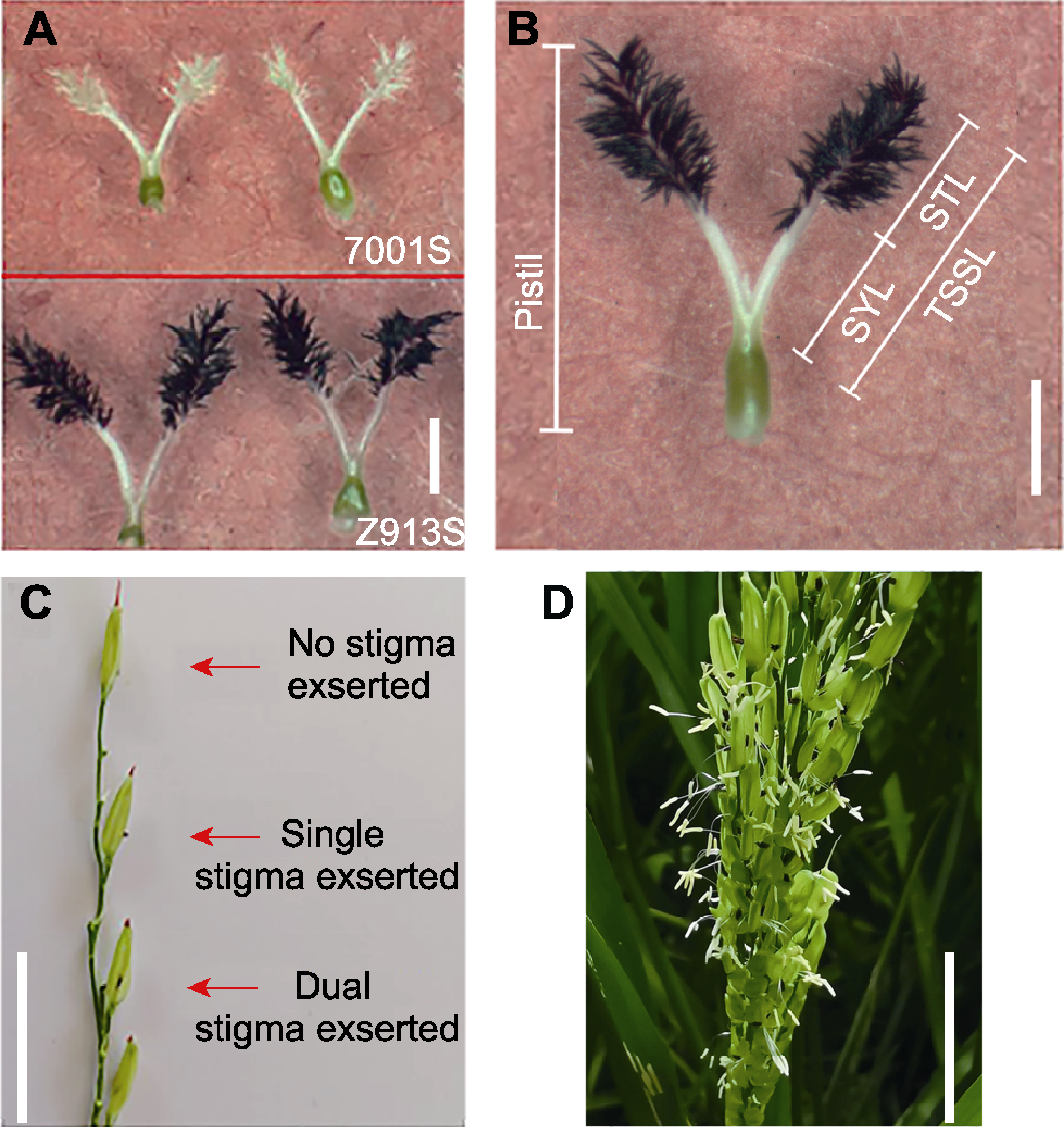
Figure 1 Phenotypes of pistil and stigma of 7001S and Z913S (A) Stigma morphology of 7001S and Z913S; (B) Names of rice pistil parts defined in this study (STL: Stigma length; SYL: Style length; TSSL: The sum of stigma and style length); (C) Phenotype of single, dual, and no stigma exsertion in a spikelet; (D) Phenotype of exserted stigma in Z913S. (A), (B) Bars=1 mm; (C), (D) Bars=1 cm
| Traits | Stigma length | Style length | The sum of stigma and style length | Percentage of exserted stigma |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stigma length | - | 0.432** | 0.897** | 0.298** |
| Style length | 0.526** | - | 0.847** | 0.320** |
| The sum of stigma and style length | 0.792** | 0.893** | - | 0.365** |
| Percentage of exserted stigma | 0.386** | 0.274** | 0.383** | - |
Table 1 Correlation coefficients among four stigma traits of rice
| Traits | Stigma length | Style length | The sum of stigma and style length | Percentage of exserted stigma |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stigma length | - | 0.432** | 0.897** | 0.298** |
| Style length | 0.526** | - | 0.847** | 0.320** |
| The sum of stigma and style length | 0.792** | 0.893** | - | 0.365** |
| Percentage of exserted stigma | 0.386** | 0.274** | 0.383** | - |
| Trait | Environment | Parent | F1 | F2/F2:3 population | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7001S | Z913S | Range | Means±standar-d deviation | Coefficient of variation (%) | Heritability (%) | Skewness | Kurtosis | |||
| Stigma length | E1 | 0.915 | 1.571** | 1.237 | 0.782-1.666 | 1.145±0.143 | 12.48 | 82.85 | 0.54 | 0.88 |
| E2 | 0.915 | 1.511** | 1.204 | 0.690-1.560 | 1.122±0.148 | 13.24 | 82.37 | 0.11 | 0.23 | |
| Style length | E1 | 0.721 | 0.931** | 0.852 | 0.468-1.160 | 0.782±0.119 | 15.20 | 84.38 | 0.69 | 0.36 |
| E2 | 0.600 | 0.924** | 0.790 | 0.394-1.283 | 0.786±0.201 | 15.62 | 82.66 | 0.11 | -0.86 | |
| The sum of stigma and style length | E1 | 1.636 | 2.502** | 2.089 | 1.406-2.617 | 1.927±0.229 | 11.88 | 91.73 | 0.63 | 0.30 |
| E2 | 1.521 | 2.434** | 1.994 | 1.218-2.618 | 1.907±0.297 | 15.58 | 92.54 | 0.14 | -0.50 | |
| Percentage of exserted stigma | E1 | 14.82 | 51.00** | 37.88 | 3.24-78.52 | 30.64±15.22 | 49.68 | 86.80 | 0.76 | 0.47 |
| E2 | 22.83 | 50.37** | 38.21 | 2.33-80.79 | 40.44±18.01 | 44.53 | 90.63 | 0.10 | -0.76 | |
Table 2 Description of stigma traits of the F2 and F2:3 populations and 7001S/Z913S of rice
| Trait | Environment | Parent | F1 | F2/F2:3 population | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7001S | Z913S | Range | Means±standar-d deviation | Coefficient of variation (%) | Heritability (%) | Skewness | Kurtosis | |||
| Stigma length | E1 | 0.915 | 1.571** | 1.237 | 0.782-1.666 | 1.145±0.143 | 12.48 | 82.85 | 0.54 | 0.88 |
| E2 | 0.915 | 1.511** | 1.204 | 0.690-1.560 | 1.122±0.148 | 13.24 | 82.37 | 0.11 | 0.23 | |
| Style length | E1 | 0.721 | 0.931** | 0.852 | 0.468-1.160 | 0.782±0.119 | 15.20 | 84.38 | 0.69 | 0.36 |
| E2 | 0.600 | 0.924** | 0.790 | 0.394-1.283 | 0.786±0.201 | 15.62 | 82.66 | 0.11 | -0.86 | |
| The sum of stigma and style length | E1 | 1.636 | 2.502** | 2.089 | 1.406-2.617 | 1.927±0.229 | 11.88 | 91.73 | 0.63 | 0.30 |
| E2 | 1.521 | 2.434** | 1.994 | 1.218-2.618 | 1.907±0.297 | 15.58 | 92.54 | 0.14 | -0.50 | |
| Percentage of exserted stigma | E1 | 14.82 | 51.00** | 37.88 | 3.24-78.52 | 30.64±15.22 | 49.68 | 86.80 | 0.76 | 0.47 |
| E2 | 22.83 | 50.37** | 38.21 | 2.33-80.79 | 40.44±18.01 | 44.53 | 90.63 | 0.10 | -0.76 | |
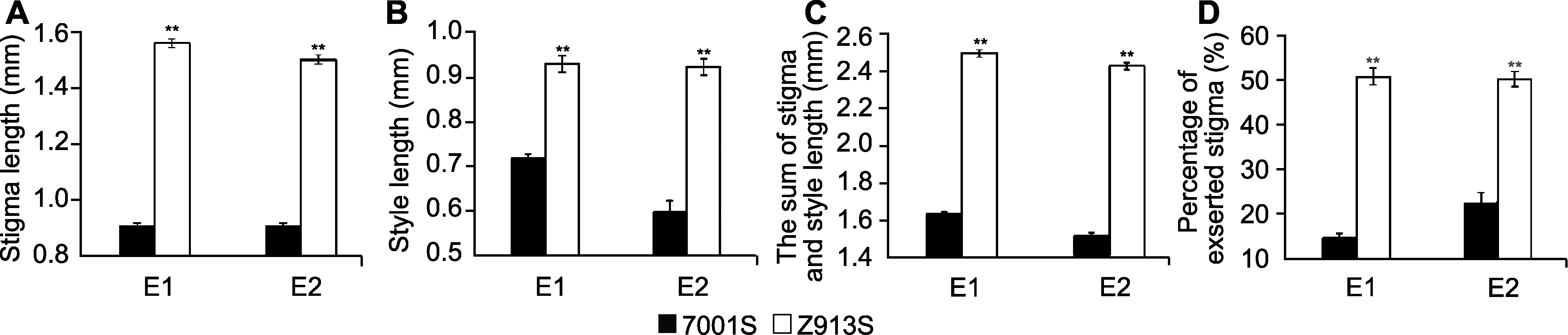
Figure 3 Phenotypic evaluations of four stigma traits in two environments of rice 7001S and Z913S (A) Stigma length; (B) Style length; (C) The sum of stigma and style length; (D) Percentage of exserted stigma. ** indicate significant differences at 1% level.
| Traits | Source of variation | Degrees of freedom | Sum of squares | Mean square | F value | F0.05 | F0.01 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stigma length | Genotypes | 2 | 6.34 | 3.17 | 876.00** | 3.10 | 4.85 |
| Environments | 1 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 6.83* | 3.95 | 6.93 | |
| Genotype × Environment | 2 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1.51 | 3.10 | 4.85 | |
| Style length | Genotypes | 2 | 1.10 | 0.55 | 86.84** | 3.10 | 4.85 |
| Environments | 1 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 12.93** | 3.95 | 6.93 | |
| Genotype × Environment | 2 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 3.19 | 3.10 | 4.85 | |
| The sum of stigma and style length | Genotypes | 2 | 12.67 | 6.33 | 1174.95** | 3.10 | 4.85 |
| Environments | 1 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 36.45** | 3.95 | 6.93 | |
| Genotype × Environment | 2 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.86 | 3.10 | 4.85 | |
| Percentage of exserted stigma | Genotypes | 2 | 16677.93 | 8338.96 | 278.09** | 3.10 | 4.85 |
| Environments | 1 | 136.20 | 136.20 | 4.54* | 3.95 | 6.93 | |
| Genotype × Environment | 2 | 327.42 | 163.71 | 5.46** | 3.10 | 4.85 |
Table 3 Joint analysis of variance for four stigma traits of rice 7001S, Z913S, and 7001S/Z913S F1
| Traits | Source of variation | Degrees of freedom | Sum of squares | Mean square | F value | F0.05 | F0.01 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stigma length | Genotypes | 2 | 6.34 | 3.17 | 876.00** | 3.10 | 4.85 |
| Environments | 1 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 6.83* | 3.95 | 6.93 | |
| Genotype × Environment | 2 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1.51 | 3.10 | 4.85 | |
| Style length | Genotypes | 2 | 1.10 | 0.55 | 86.84** | 3.10 | 4.85 |
| Environments | 1 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 12.93** | 3.95 | 6.93 | |
| Genotype × Environment | 2 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 3.19 | 3.10 | 4.85 | |
| The sum of stigma and style length | Genotypes | 2 | 12.67 | 6.33 | 1174.95** | 3.10 | 4.85 |
| Environments | 1 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 36.45** | 3.95 | 6.93 | |
| Genotype × Environment | 2 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.86 | 3.10 | 4.85 | |
| Percentage of exserted stigma | Genotypes | 2 | 16677.93 | 8338.96 | 278.09** | 3.10 | 4.85 |
| Environments | 1 | 136.20 | 136.20 | 4.54* | 3.95 | 6.93 | |
| Genotype × Environment | 2 | 327.42 | 163.71 | 5.46** | 3.10 | 4.85 |
| Trait | Environment | Candidate model | MLV value | AIC value | Test of goodness-of-fita |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stigma length | E1 | PG-ADI | 246.62 | -481.23 | 0/0/0/0/0 |
| MX1-AD-ADI | 251.95 | -487.89 | 0/0/0/0/0 | ||
| MX2-ADI-ADI | 257.05 | -490.09 | 0/0/0/0/0 | ||
| MX2-ADI-AD | 256.33 | -494.66 | 0/0/0/0/0 | ||
| E2 | PG-ADI | 210.90 | -409.81 | 0/0/0/1/0 | |
| MX1-AD-ADI | 210.90 | -407.80 | 0/0/0/1/0 | ||
| MX2-ADI-AD | 211.65 | -397.30 | 0/0/0/0/0 | ||
| MX2-AD-AD | 207.63 | -397.25 | 0/0/0/0/0 | ||
| Style length | E1 | MX2-ADI-ADI | 322.90 | -621.79 | 0/0/2/0/0 |
| MX2-ADI-AD | 322.69 | -627.37 | 0/0/2/0/0 | ||
| MX2-AD-AD | 316.56 | -623.12 | 0/1/1/1/0 | ||
| MX2-EEAD-AD | 313.03 | -622.05 | 0/1/1/1/0 | ||
| E2 | 1MG-A | 107.98 | -211.96 | 1/1/0/1/0 | |
| 2MG-AD | 111.92 | -211.84 | 0/0/0/0/0 | ||
| 2MG-A | 111.21 | -214.41 | 0/0/0/0/0 | ||
| MX1-A-AD | 112.06 | -214.11 | 0/0/0/0/0 | ||
| The sum of stigma and style length | E1 | 2MG-ADI | 90.19 | -158.38 | 0/0/0/1/0 |
| MX1-AD-ADI | 92.18 | -168.37 | 0/0/0/1/0 | ||
| MX2-ADI-ADI | 97.25 | -170.51 | 0/0/0/1/0 | ||
| MX2-ADI-AD | 95.63 | -173.27 | 0/0/0/1/0 | ||
| E2 | 2MG-EEAD | -12.03 | 32.05 | 0/0/1/0/0 | |
| MX1-A-AD | -11.29 | 32.59 | 1/1/1/1/0 | ||
| MX2-AD-AD | -2.11 | 22.23 | 0/0/0/0/0 | ||
| MX2-EEAD-AD | -7.10 | 26.19 | 0/0/0/0/0 | ||
| Percentage of exserted stigma | E1 | MX2-ADI-ADI | -1538.19 | 3100.38 | 0/0/2/0/0 |
| MX2-ADI-AD | -1538.18 | 3094.36 | 0/0/2/0/0 | ||
| MX2-AD-AD | -1540.16 | 3090.32 | 0/0/2/0/0 | ||
| MX2-EEAD-AD | -1545.89 | 3095.79 | 0/0/1/0/0 | ||
| E2 | 2MG-AD | -1425.36 | 2862.71 | 0/0/2/0/0 | |
| 2MG-A | -1426.26 | 2860.51 | 0/0/2/1/0 | ||
| MX1-AD-AD | -1423.53 | 2861.07 | 0/0/2/0/0 | ||
| MX1-AEND-AD | -1425.67 | 2861.34 | 0/0/2/0/0 |
Table 4 Max log likelihood value (MLV) and Akaike’s Information Criterion (AIC) values of candidate models calculated with IECM method for four stigma related traits of rice
| Trait | Environment | Candidate model | MLV value | AIC value | Test of goodness-of-fita |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stigma length | E1 | PG-ADI | 246.62 | -481.23 | 0/0/0/0/0 |
| MX1-AD-ADI | 251.95 | -487.89 | 0/0/0/0/0 | ||
| MX2-ADI-ADI | 257.05 | -490.09 | 0/0/0/0/0 | ||
| MX2-ADI-AD | 256.33 | -494.66 | 0/0/0/0/0 | ||
| E2 | PG-ADI | 210.90 | -409.81 | 0/0/0/1/0 | |
| MX1-AD-ADI | 210.90 | -407.80 | 0/0/0/1/0 | ||
| MX2-ADI-AD | 211.65 | -397.30 | 0/0/0/0/0 | ||
| MX2-AD-AD | 207.63 | -397.25 | 0/0/0/0/0 | ||
| Style length | E1 | MX2-ADI-ADI | 322.90 | -621.79 | 0/0/2/0/0 |
| MX2-ADI-AD | 322.69 | -627.37 | 0/0/2/0/0 | ||
| MX2-AD-AD | 316.56 | -623.12 | 0/1/1/1/0 | ||
| MX2-EEAD-AD | 313.03 | -622.05 | 0/1/1/1/0 | ||
| E2 | 1MG-A | 107.98 | -211.96 | 1/1/0/1/0 | |
| 2MG-AD | 111.92 | -211.84 | 0/0/0/0/0 | ||
| 2MG-A | 111.21 | -214.41 | 0/0/0/0/0 | ||
| MX1-A-AD | 112.06 | -214.11 | 0/0/0/0/0 | ||
| The sum of stigma and style length | E1 | 2MG-ADI | 90.19 | -158.38 | 0/0/0/1/0 |
| MX1-AD-ADI | 92.18 | -168.37 | 0/0/0/1/0 | ||
| MX2-ADI-ADI | 97.25 | -170.51 | 0/0/0/1/0 | ||
| MX2-ADI-AD | 95.63 | -173.27 | 0/0/0/1/0 | ||
| E2 | 2MG-EEAD | -12.03 | 32.05 | 0/0/1/0/0 | |
| MX1-A-AD | -11.29 | 32.59 | 1/1/1/1/0 | ||
| MX2-AD-AD | -2.11 | 22.23 | 0/0/0/0/0 | ||
| MX2-EEAD-AD | -7.10 | 26.19 | 0/0/0/0/0 | ||
| Percentage of exserted stigma | E1 | MX2-ADI-ADI | -1538.19 | 3100.38 | 0/0/2/0/0 |
| MX2-ADI-AD | -1538.18 | 3094.36 | 0/0/2/0/0 | ||
| MX2-AD-AD | -1540.16 | 3090.32 | 0/0/2/0/0 | ||
| MX2-EEAD-AD | -1545.89 | 3095.79 | 0/0/1/0/0 | ||
| E2 | 2MG-AD | -1425.36 | 2862.71 | 0/0/2/0/0 | |
| 2MG-A | -1426.26 | 2860.51 | 0/0/2/1/0 | ||
| MX1-AD-AD | -1423.53 | 2861.07 | 0/0/2/0/0 | ||
| MX1-AEND-AD | -1425.67 | 2861.34 | 0/0/2/0/0 |
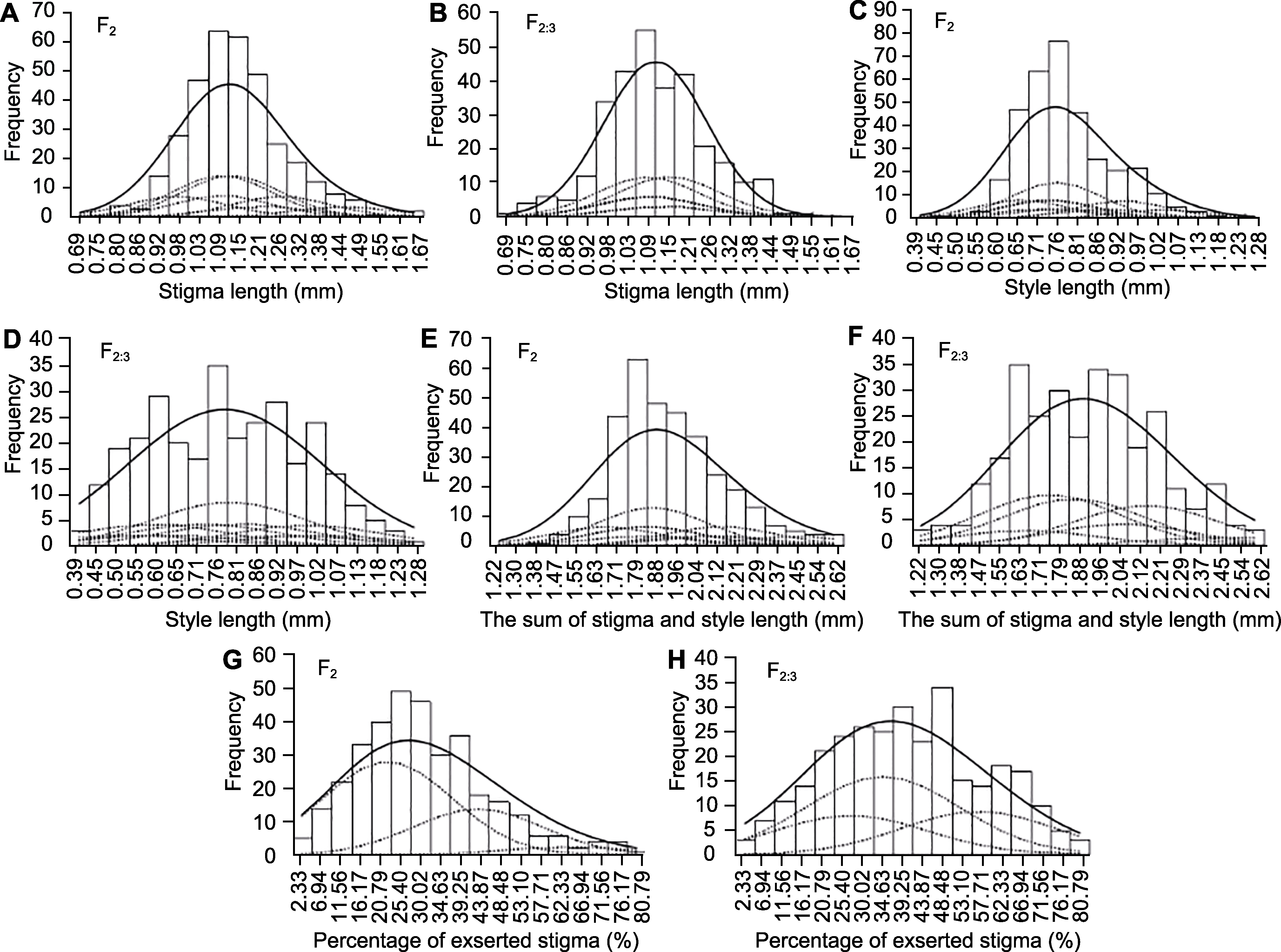
Figure 4 Frequency distribution, fitted mixed distribution and its component distribution for four stigma traits of F2 and F2:3 populations in the cross of rice 7001S/Z913S (A), (B) Distribution in F2 and F2:3 populations of stigma length; (C), (D) Distribution in F2 and F2:3 populations of style length; (E), (F) Distribution in F2 and F2:3 populations of the sum of stigma and style length; (G), (H) Distribution in F2 and F2:3 populations of percentage of exserted stigma
| Genetic parameter | Trait | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stigma length | Style length | The sum of stigma and style length | Percentage of exserted stigma | |||||
| E1 | E2 | E1 | E2 | E1 | E2 | E1 | E2 | |
| MX2-ADI- AD | MX2-ADI- AD | MX2-ADI- AD | 2MG-AD | MX2-ADI- AD | MX2-EEAD-AD | MX2-EEAD-AD | MX1-AEND-AD | |
| Univalent parameter | ||||||||
| da(d) | 0.06 | 0.002 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.14 | -0.26 | -10.61 | -17.87 |
| db | 0.06 | 0.001 | 0.03 | -0.20 | 0.02 | - | - | - |
| ha(h) | -0.12 | -0.05 | -0.12 | 0.04 | -0.29 | - | - | - |
| hb | -0.10 | -0.05 | -0.06 | -0.005 | -0.21 | - | - | - |
| i | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.05 | - | 0.17 | - | - | - |
| jab | 0.09 | 0.002 | 0.02 | - | 0.10 | - | - | - |
| jba | -0.06 | 0.001 | -0.02 | - | -0.01 | - | - | - |
| l | 0.13 | 0.36 | 0.08 | - | 0.24 | - | - | - |
| [d] | -0.45 | -0.30 | -0.24 | - | -0.59 | 0.06 | 3.01 | -10.51 |
| [h] | 0.20 | -0.24 | 0.17 | - | 0.45 | 0.54 | 24.67 | 0.14 |
| Bivalent parameter | ||||||||
| σ2p | 0.020 | 0.022 | 0.014 | 0.040 | 0.053 | 0.089 | 232.04 | 325.28 |
| σ2mg | 0.013 | 0.014 | 0.010 | 0.033 | 0.039 | 0.082 | 155.72 | 216.11 |
| σ2pg | 0.005 | 0.005 | - | - | 0.010 | - | 40.91 | 80.75 |
| h2mg (%) | 65.00 | 63.64 | 71.43 | 82.50 | 73.58 | 92.13 | 67.11 | 66.44 |
| h2pg (%) | 25.00 | 22.73 | - | - | 18.87 | - | 17.63 | 24.82 |
Table 5 Estimates of genetic parameters for four stigma traits of rice
| Genetic parameter | Trait | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stigma length | Style length | The sum of stigma and style length | Percentage of exserted stigma | |||||
| E1 | E2 | E1 | E2 | E1 | E2 | E1 | E2 | |
| MX2-ADI- AD | MX2-ADI- AD | MX2-ADI- AD | 2MG-AD | MX2-ADI- AD | MX2-EEAD-AD | MX2-EEAD-AD | MX1-AEND-AD | |
| Univalent parameter | ||||||||
| da(d) | 0.06 | 0.002 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.14 | -0.26 | -10.61 | -17.87 |
| db | 0.06 | 0.001 | 0.03 | -0.20 | 0.02 | - | - | - |
| ha(h) | -0.12 | -0.05 | -0.12 | 0.04 | -0.29 | - | - | - |
| hb | -0.10 | -0.05 | -0.06 | -0.005 | -0.21 | - | - | - |
| i | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.05 | - | 0.17 | - | - | - |
| jab | 0.09 | 0.002 | 0.02 | - | 0.10 | - | - | - |
| jba | -0.06 | 0.001 | -0.02 | - | -0.01 | - | - | - |
| l | 0.13 | 0.36 | 0.08 | - | 0.24 | - | - | - |
| [d] | -0.45 | -0.30 | -0.24 | - | -0.59 | 0.06 | 3.01 | -10.51 |
| [h] | 0.20 | -0.24 | 0.17 | - | 0.45 | 0.54 | 24.67 | 0.14 |
| Bivalent parameter | ||||||||
| σ2p | 0.020 | 0.022 | 0.014 | 0.040 | 0.053 | 0.089 | 232.04 | 325.28 |
| σ2mg | 0.013 | 0.014 | 0.010 | 0.033 | 0.039 | 0.082 | 155.72 | 216.11 |
| σ2pg | 0.005 | 0.005 | - | - | 0.010 | - | 40.91 | 80.75 |
| h2mg (%) | 65.00 | 63.64 | 71.43 | 82.50 | 73.58 | 92.13 | 67.11 | 66.44 |
| h2pg (%) | 25.00 | 22.73 | - | - | 18.87 | - | 17.63 | 24.82 |
| 1 | 曹黎明, 程灿, 周继华, 储黄伟, 牛付安, 袁勤 (2018). 上海杂交粳稻产业发展与展望. 中国种业 ( 9), 19-22. |
| 2 | 曹锡文, 刘兵, 章元明 (2013). 植物数量性状分离分析Windows软件包SEA的研制. 南京农业大学学报 36(6), 1-6. |
| 3 | 陈兰, 张红, 张启武, 江建华, 王洋, 陈杰丽, 洪德林 (2012). 水稻6个异交相关性状的SSR关联分析. 南京农业大学学报 35(2), 1-9. |
| 4 | 冯常辉, 张友昌, 王孝刚, 张教海, 夏松波, 韩光明, 别墅, 秦鸿德 (2020). 陆地棉现蕾期和开花期性状的遗传分析. 分子植物育种 18, 4747-4753. |
| 5 | 冯云超, 晏庆九, 张芳魁, 霍仕平, 向振凡, 羊炼, 张兴端 (2019). 玉米果穗露顶主基因+多基因遗传模型及遗传效应. 华北农学报 34(S1), 22-28. |
| 6 | 盖钧镒 (2000). 试验统计方法. 北京: 中国农业出版社. pp. 99- 126, 157-189. |
| 7 | 计慎敏, 张大兵 (2007). 水稻花器官特征决定以及数量控制的分子机制. 植物学通报 24, 284-292. |
| 8 |
江建华, 洪德林, 郭媛, 张启武 (2009). 粳稻穗角与谷粒性状的相关性及谷粒性状遗传分析. 植物学报 44, 167-177.
DOI |
| 9 | 江建华, 吴爽, 景春雨, 王德正 (2017). 高异交率水稻籼型温敏核不育系Z913S的选育. 安徽农业科学 45(27), 33-34, 37. |
| 10 | 李成荃, 许克农, 王守海, 罗彦长, 王德正 (1994). 粳型水稻光敏核不育系7001S的育性与利用研究. 安徽农业科学 22, 11-15. |
| 11 | 李威, 圣忠华, 朱子亮, 魏祥进, 石磊, 邬亚文, 唐绍清, 王建龙, 胡培松 (2017). 粳稻柱头外露率QTL定位. 中国水稻科学 31, 23-30. |
| 12 | 廖佩言, 刘景西, 何平, 汪文清 (1986). 水稻花器性状对异交结实影响的初步分析. 农业科学导报 ( 1), 1-5. |
| 13 | 刘强明 (2015). 水稻异交相关性状的QTL遗传剖析与柱头长度QTL qSTL3. 1的精细定位. 博士论文. 南京: 南京农业大学. pp. 21-42. |
| 14 | 罗伟雄, 李明, 陈军, 罗琼 (2011). 一个新的水稻花器官突变体的鉴定和基因定位. 植物学报 46, 506-513. |
| 15 | 牛付安, 刘健, 郭媛, 陈兰, 江建华, 洪德林 (2012). 4个环境下稳定表达的控制粳稻穗角性状的新位点. 中国水稻科学 26, 409-416. |
| 16 | 田露申, 牛应泽, 余青青, 郭世星, 柳丽 (2009). 甘蓝型油菜白花性状的主基因+多基因遗传分析. 中国农业科学 42, 3987-3995. |
| 17 | 吴爽, 江建华, 汤修竹, 王德正 (2015). 水稻温敏核不育系广茉S的异交特性研究. 杂交水稻 30(3), 35-38. |
| 18 | 解松峰, 吉万全, 王长有, 胡卫国, 李俊, 张耀元, 师晓曦, 张俊杰, 张宏, 陈春环 (2019). 小麦穗部性状的主基因+多基因混合遗传模型分析. 中国农业科学 52, 4437-4452. |
| 19 | 杨保汉 (1997). 不育系柱头外露率及其结实率研究. 杂交水稻 12(1), 13-15. |
| 20 | 杨振玉, 李志彬, 东丽, 朱崴, 蔡卓, 曲丽君, 华泽田 (2016). 中国杂交粳稻发展与展望. 科学通报 61, 3770-3777. |
| 21 | 尹成, 李平波, 高冠军, 张庆路, 罗利军, 何予卿 (2014). 水稻柱头外露率QTL定位. 分子植物育种 12, 43-49. |
| 22 | 袁隆平 (2010). 发展杂交水稻保障粮食安全. 杂交水稻 25(S1), 1-2. |
| 23 |
Bakti C, Tanaka J (2019). Detection of dominant QTLs for stigma exsertion ratio in rice derived from Oryza rufipogon accession ‘W0120’. Breed Sci 69, 143-150.
DOI URL |
| 24 | Dang XJ, Liu EB, Liang YF, Liu QM, Breria CM, Hong DL (2016). QTL detection and elite alleles mining for stigma traits in Oryza sativa by association mapping. Front Plant Sci 7, 1188. |
| 25 |
Dang XJ, Yang Y, Zhang YQ, Chen XG, Fan ZL, Liu QM, Ji J, Li DL, Li YH, Fang BJ, Wu ZX, Liu EB, Hu XX, Zhu SS, She D, Wang H, Li YL, Chen SQ, Wu YF, Hong DL (2020). OsSYL2 AA, an allele identified by gene-based association, increases style length in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant J 104, 1491-1503.
DOI URL |
| 26 |
Hu SP, Zhou Y, Zhang L, Zhu XD, Wang ZG, Li L, Luo LJ, Zhou QM (2009). QTL analysis of floral traits of rice (Oryza sativa L.) under well-watered and drought stress conditions. Genes Genomics 31, 173-181.
DOI URL |
| 27 |
Li PB, Feng FC, Zhang QL, Chao Y, Gao GJ, He YQ (2014). Genetic mapping and validation of quantitative trait loci for stigma exsertion rate in rice. Mol Breed 34, 2131-2138.
DOI URL |
| 28 |
Li SC, Li WB, Huang B, Cao XM, Zhou XY, Ye SM, Li CB, Gao FY, Zou T, Xie KL, Ren Y, Ai P, Tang TF, Li XM, Deng QM, Wang SQ, Zheng AP, Zhu J, Liu HN, Wang LX, Li P (2013). Natural variation in PTB1 regulates rice seed setting rate by controlling pollen tube growth. Nat Commun 4, 2793.
DOI URL |
| 29 |
Liu QM, Qin JC, Li TW, Liu EB, Fan DJ, Edzesi WM, Liu JH, Jiang JH, Liu XL, Xiao LJ, Liu LL, Hong DL (2015). Fine mapping and candidate gene analysis of qSTL3, a stigma length-conditioning locus in rice(Oryza sativa L.). PLoS One 10, e0127938.
DOI URL |
| 30 |
Liu Y, Zhang AN, Wang FM, Kong DY, Li MS, Bi JG, Zhang FY, Wang JH, Luo XX, Pan ZQ, Yu XQ, Liu GL, Luo LJ (2019). Fine mapping a quantitative trait locus, qSER-7, that controls stigma exsertion rate in rice(Oryza sativa L.). Rice 12, 46.
DOI PMID |
| 31 |
Marathi B, Ramos J, Hechanova SL, Oane RH, Jena KK (2015). SNP genotyping and characterization of pistil traits revealing a distinct phylogenetic relationship among the species of Oryza. Euphytica 201, 131-148.
DOI URL |
| 32 |
Miyata M, Yamamoto T, Komori T, Nitta N (2007). Marker- assisted selection and evaluation of the QTL for stigma exsertion under japonica rice genetic background. Theor Appl Genet 114, 539-548.
PMID |
| 33 |
Qian Q, Guo LB, Smith SM, Li JY (2016). Breeding high-yield superior quality hybrid super rice by rational design. Natl Sci Rev 3, 283-294.
DOI URL |
| 34 | Rahman MH, Yu P, Zhang YX, Sun LP, Wu WX, Shen XH, Zhan XD, Chen DB, Cao LY, Cheng SH (2016). Quantitative trait loci mapping of the stigma exertion rate and spikelet number per panicle in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Genet Mol Res 15, gmr15048432. |
| 35 |
Rahman MH, Zhang YX, Zhang KQ, Rahman MS, Barman HN, Riaz A, Chen YY, Wu WX, Zhan XD, Cao LY, Cheng SH (2017). Genetic dissection of the major quantitative trait locus (qSE11), and its validation as the major influence on the rate of stigma exsertion in rice(Oryza sativa L.). Front Plant Sci 8, 1818.
DOI URL |
| 36 |
Sasaki A, Ashikari M, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Itoh H, Nishimura A, Swapan D, Ishiyama K, Saito T, Kobayashi M, Khush GS, Kitano H, Matsuoka M (2002). Green revolution: a mutant gibberellin-synthesis gene in rice. Nature 416, 701-702.
PMID |
| 37 |
Takano-Kai N, Doi K, Yoshimura A(2011). GS3 participates in stigma exsertion as well as seed length in rice. Breed Sci 61, 244-250.
DOI URL |
| 38 |
Uga Y, Fukuta Y, Cai HW, Iwata H, Ohsawa R, Morishima H, Fujimura T (2003). Mapping QTLs influencing rice floral morphology using recombinant inbred lines derived from a cross between Oryza sativa L. and Oryza rufipogon Griff. Theor Appl Genet 107, 218-226.
PMID |
| 39 |
Uga Y, Siangliw M, Nagamine T, Ohsawa R, Fujimura T, Fukuta Y (2010). Comparative mapping of QTLs determining glume, pistil and stamen sizes in cultivated rice ( Oryza sativa L.). Plant Breed 129, 657-669.
DOI URL |
| 40 |
Virmani SS, Athwal DS (1973). Genetic variability in floral characteristics influencing outcrossing in Oryza sativa L. Crop Sci 13, 66-67.
DOI URL |
| 41 |
Wang SK, Wu K, Yuan QB, Liu XY, Liu ZB, Lin XY, Zeng RZ, Zhu HT, Dong GJ, Qian Q, Zhang GQ, Fu XD (2012). Control of grain size, shape and quality by OsSPL16 in rice. Nat Genet 44, 950-955.
DOI URL |
| 42 |
Xing YZ, Tang WJ, Xue WY, Xu CG, Zhang QF (2008). Fine mapping of a major quantitative trait loci, qSSP7, controlling the number of spikelets per panicle as a single Mendelian factor in rice. Theor Appl Genet 116, 789-796.
DOI PMID |
| 43 |
Xiong LX, Liu KD, Dai XK, Xu CG, Zhang Q (1999). Identification of genetic factors controlling domestication-related traits of rice using an F2 population of a cross between Oryza sativa and O. rufipogon. Theor Appl Genet 98, 243-251.
DOI URL |
| 44 |
Xue WY, Xing YZ, Weng XY, Zhao Y, Tang WJ, Wang L, Zhou HJ, Yu SB, Xu CG, Li XH, Zhang QF (2008). Na- tural variation in Ghd7 is an important regulator of heading date and yield potential in rice. Nat Genet 40, 761-767.
DOI URL |
| 45 |
Yan WG, Li Y, Agrama HA, Luo DG, Gao FY, Lu XJ, Ren GJ (2009). Association mapping of stigma and spikelet characteristics in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Breed 24, 277-292.
DOI URL |
| 46 |
Yu XQ, Mei HW, Luo LJ, Liu GL, Liu HY, Zou GH, Hu SP, Li MS, Wu JH (2006). Dissection of additive, epistatic effect and Q×E interaction of quantitative trait loci influencing stigma exsertion under water stress in rice. Acta Genet Sin 33, 542-550.
DOI URL |
| 47 |
Zhang KQ, Zhang YX, Wu WX, Zhan XD, Bakr Anis G, Rahman MH, Hong YB, Riaz A, Zhu AK, Cao YR, Sun LP, Yang ZF, Yang QQ, Cao LY, Cheng SH (2018). qSE7 is a major quantitative trait locus (QTL) influencing stigma exsertion rate in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Sci Rep 8, 14523.
DOI URL |
| 48 |
Zheng AP, Lin RM, Zhang DH, Qin PG, Xu LZ, Ai P, Ding L, Wang YR, Chen Y, Liu Y, Sun ZG, Feng HT, Liang XX, Fu RT, Tang CQ, Li Q, Zhang J, Xie ZL, Deng QM, Li SC, Wang SQ, Zhu J, Wang LX, Liu HN, Li P (2013). The evolution and pathogenic mechanisms of the rice sheath blight pathogen. Nat Commun 4, 1424.
DOI URL |
| 49 |
Zhou F, Lin QB, Zhu LH, Ren YL, Zhou KN, Shabek N, Wu FQ, Mao HB, Dong W, Gan L, Ma WW, Gao H, Chen J, Yang C, Wang D, Tan JJ, Zhang X, Guo XP, Wang JL, Jiang L, Liu X, Chen WQ, Chu JF, Yan CY, Ueno K, Ito S, Asami T, Cheng ZJ, Wang J, Lei CL, Zhai HQ, Wu CY, Wang HY, Zheng N, Wan JM (2013). D14-SCF D3- dependent degradation of D53 regulates strigolactone signaling . Nature 504, 406-410.
DOI URL |
| 50 |
Zhou H, Li PB, Xie WB, Hussain S, Li YB, Xia D, Zhao H, Sun SY, Chen JX, Ye H, Hou J, Zhao D, Gao GJ, Zhang QL, Wang GW, Lian XM, Xiao JH, Yu SB, Li XH, He YQ (2017). Genome-wide association analyses reveal the genetic basis of stigma exsertion in rice. Mol Plant 10, 634-644.
DOI PMID |
| [1] |
Juan Cui, Xiaoyu Yu, Yuejiao Yu, Chengwei Liang, Jian Sun, Wenfu Chen.
Analysis of Texture Factors and Genetic Basis Influencing the Differences in Eating Quality between Northeast China and Japanese Japonica Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | Zhao Ling, Guan Ju, Liang Wenhua, Zhang Yong, Lu Kai, Zhao Chunfang, Li Yusheng, Zhang Yadong. Mapping of QTLs for Heat Tolerance at the Seedling Stage in Rice Based on a High-density Bin Map [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(3): 342-353. |
| [3] | Xinyu Li, Yue Gu, Feifei Xu, Jinsong Bao. Research Progress on Post-translational Modifications of Starch Biosynthesis-related Proteins in Rice Endosperm [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(2): 256-270. |
| [4] | Jianguo Li, Yi Zhang, Wenjun Zhang. Iron Plaque Formation and Its Effects on Phosphorus Absorption in Rice Roots [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(1): 132-143. |
| [5] | Ruifeng Yao, Daoxin Xie. Activation and Termination of Strigolactone Signal Perception in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(6): 873-877. |
| [6] | Jinjin Lian, Luyao Tang, Yinuo Zhang, Jiaxing Zheng, Chaoyu Zhu, Yuhan Ye, Yuexing Wang, Wennan Shang, Zhenghao Fu, Xinxuan Xu, Richeng Wu, Mei Lu, Changchun Wang, Yuchun Rao. Genetic Locus Mining and Candidate Gene Analysis of Antioxidant Traits in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(5): 738-751. |
| [7] | Jiahui Huang, Huimin Yang, Xinyu Chen, Chaoyu Zhu, Yanan Jiang, Chengxiang Hu, Jinjin Lian, Tao Lu, Mei Lu, Weilin Zhang, Yuchun Rao. Response Mechanism of Rice Mutant pe-1 to Low Light Stress [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(4): 574-584. |
| [8] | Jianmin Zhou. A Combat Vehicle with a Smart Brake [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(3): 343-346. |
| [9] | Chaoyu Zhu, Chengxiang Hu, Zhenan Zhu, Zhining Zhang, Lihai Wang, Jun Chen, Sanfeng Li, Jinjin Lian, Luyao Tang, Qianqian Zhong, Wenjing Yin, Yuexing Wang, Yuchun Rao. Mapping of QTLs Associated with Rice Panicle Traits and Candidate Gene Analysis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(2): 217-230. |
| [10] | Yanli Fang, Chuanyu Tian, Ruyi Su, Yapei Liu, Chunlian Wang, Xifeng Chen, Wei Guo, Zhiyuan Ji. Mining and Preliminary Mapping of Rice Resistance Genes Against Bacterial Leaf Streak [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(1): 1-9. |
| [11] | Bao Zhu, Jiangzhe Zhao, Kewei Zhang, Peng Huang. OsCKX9 is Involved in Regulating the Rice Lamina Joint Development and Leaf Angle [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(1): 10-21. |
| [12] | Qingduo Li, Dongmei Li. Analysis for the prevalence of global bat-borne Bartonella [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 23166-. |
| [13] | Tian Chuanyu, Fang Yanli, Shen Qing, Wang Hongjie, Chen Xifeng, Guo Wei, Zhao Kaijun, Wang Chunlian, Ji Zhiyuan. Genotypic Diversity and Pathogenisity of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae Isolated from Southern China in 2019-2021 [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(5): 743-749. |
| [14] | Dai Ruohui, Qian Xinyu, Sun Jinglei, Lu Tao, Jia Qiwei, Lu Tianqi, Lu Mei, Rao Yuchun. Research Progress on the Mechanisms of Leaf Color Regulation and Related Genes in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(5): 799-812. |
| [15] | Jiayi Jin, Yiting Luo, Huimin Yang, Tao Lu, Hanfei Ye, Jiyi Xie, Kexin Wang, Qianyu Chen, Yuan Fang, Yuexing Wang, Yuchun Rao. QTL Mapping and Expression Analysis on Candidate Genes Related to Chlorophyll Content in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(3): 394-403. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||