

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (5): 846-853.DOI: 10.11983/CBB25102 cstr: 32102.14.CBB25102
• TECHNIQUE AND METHOD • Previous Articles
Received:2025-06-04
Accepted:2025-07-08
Online:2025-09-10
Published:2025-07-08
Contact:
*E-mail: spyan@mail.hzau.edu.cn
Shi Shixi, Yan Shunping. Optimization of an High-performance Liquid Chromatography Method for the Determination of Salicylic Acid[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(5): 846-853.
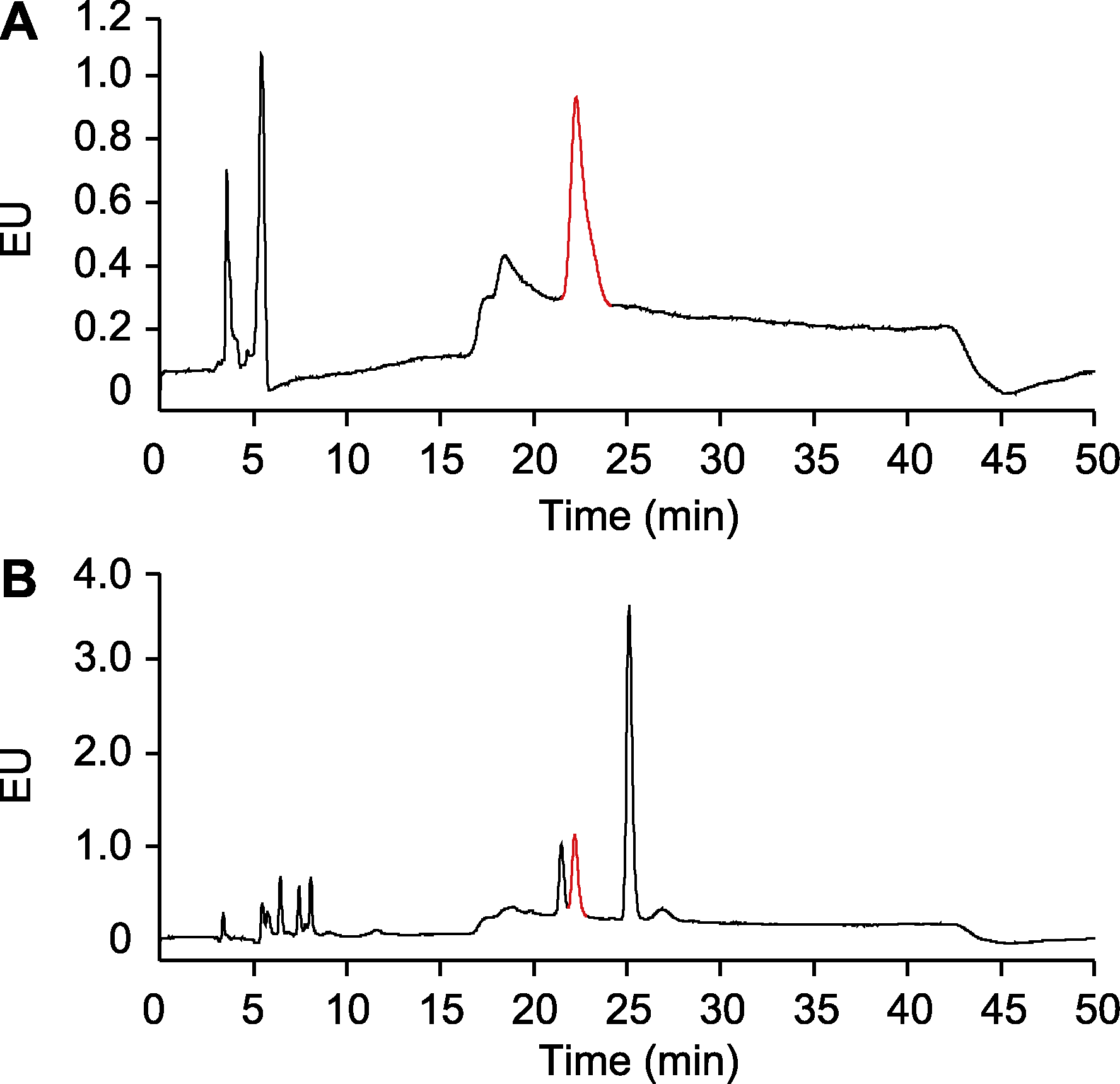
Figure 1 Detection of salicylic acid (SA) using methods reported in Zhang et al., 2017 (A) 0.1 μg·mL-1 SA standard sample; (B) The sample is free SA in Arabidopsis without Psm ES4326 infection. EU: Emission units. The peaks labeled in red indicate SA.
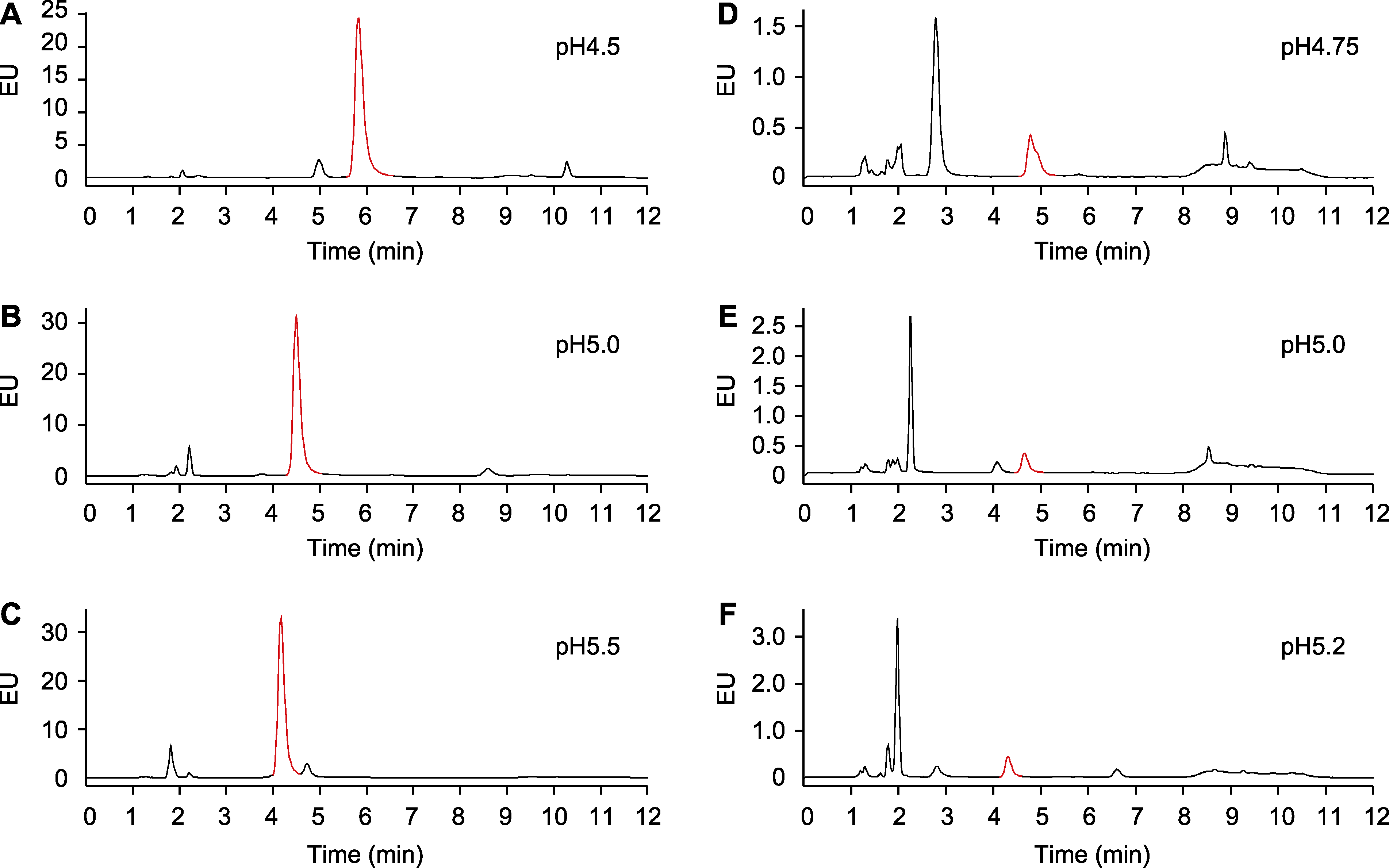
Figure 2 Effects of pH of the mobile phase on salicylic acid (SA) separation (A)-(C) The samples are total SA extracted from Arabidopsis treated with Psm ES4326 for 24 h; (D)-(F) The samples are total SA in Arabidopsis without Psm ES4326 infection. EU is the same as shown in Figure 1. The peaks labeled in red indicate SA.
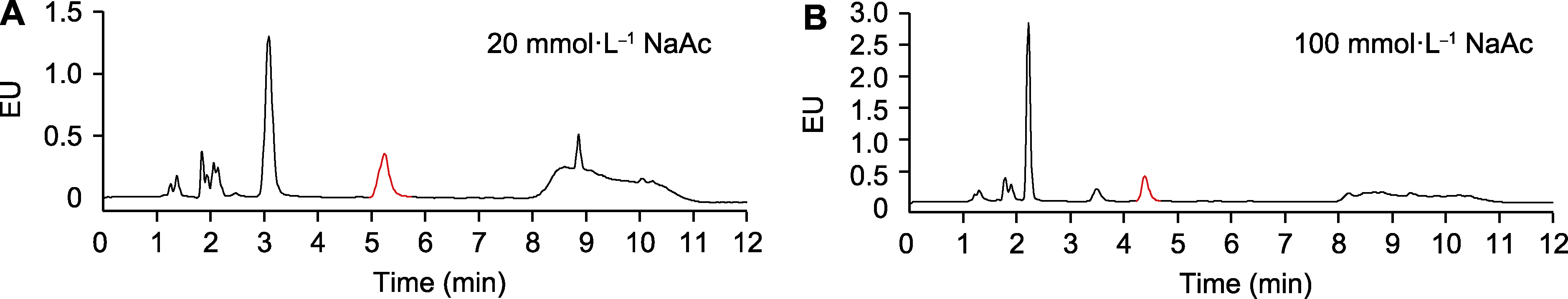
Figure 3 Effects of the concentration of sodium acetate in the mobile phase on salicylic acid (SA) separation (A) 20 mmol∙L-1 NaAc; (B) 100 mmol∙L-1 NaAc. The samples are total SA in Arabidopsis without Psm ES4326 infection. EU is the same as shown in Figure 1. The peaks labeled in red indicate SA.
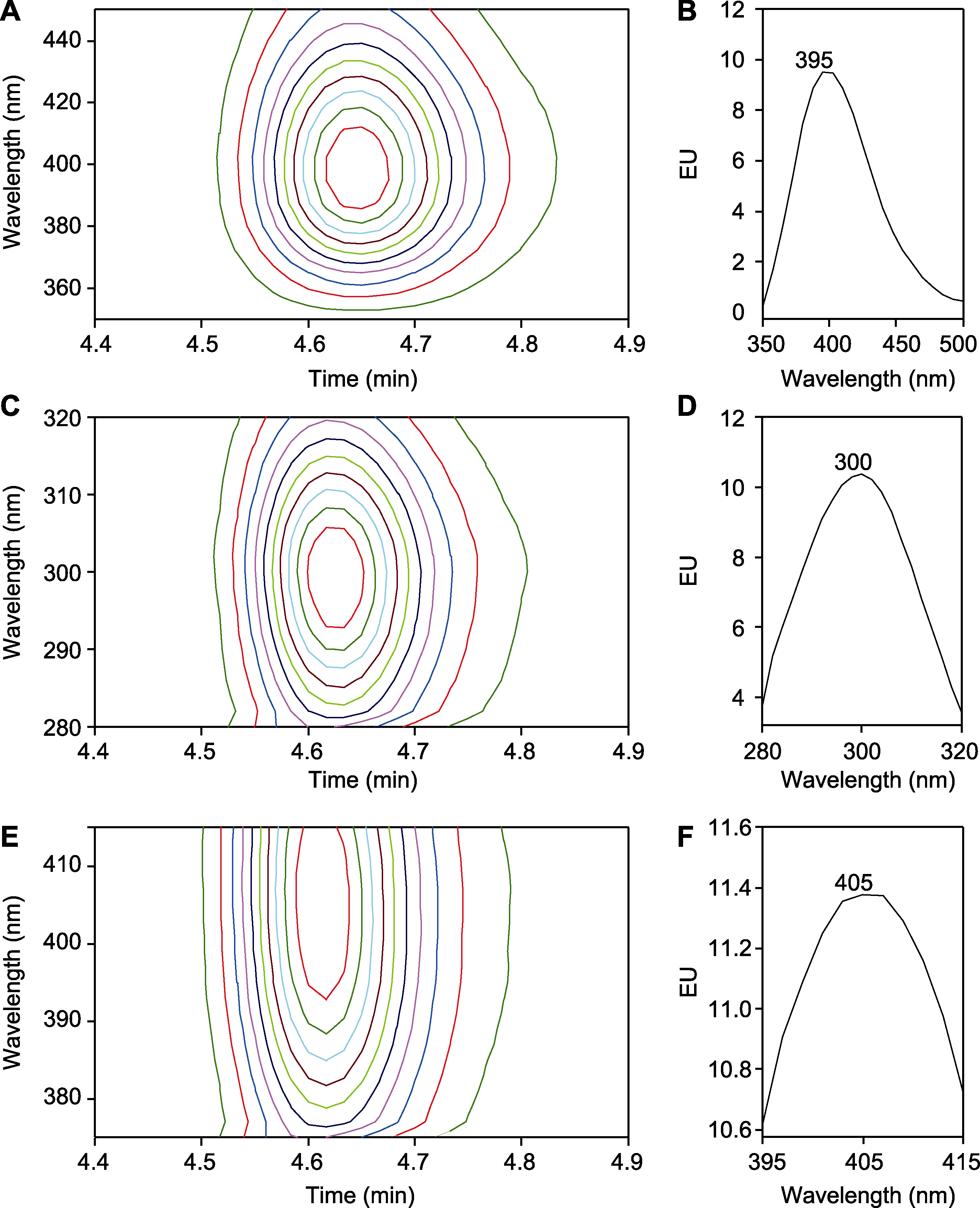
Figure 4 Optimization of detection wavelength for salicylic acid (SA) (A), (B) The excitation wavelength is 296 nm and the emission wavelength is 350-450 nm; (C), (D) The excitation wavelength is 280-320 nm and the emission wavelength is 395 nm; (E), (F) The excitation wavelength is 300 nm and the emission wavelength is 375-415 nm. (A), (C), (E) Two-dimensional signal plots; (B), (D), (F) Fluorescence wavelength-fluorescence energy integration plots. All samples are 1 µg∙mL-1 SA standards. EU is the same as shown in Figure 1.
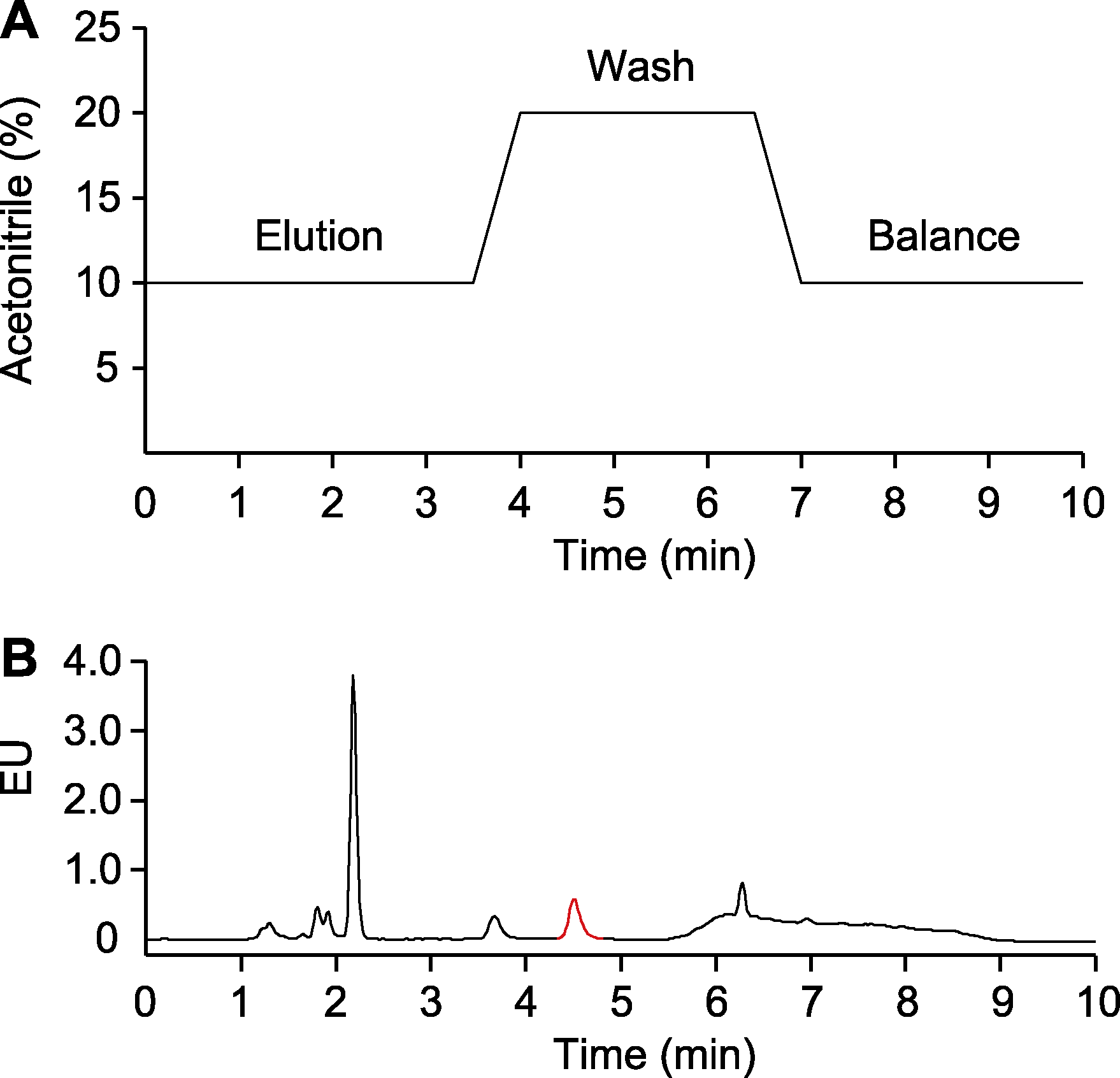
Figure 5 Optimization of salicylic acid (SA) detection procedure (A) Graph of detection procedure; (B) Detection results. The samples are total SA in Arabidopsis without Psm ES4326 infection. EU is the same as shown in Figure 1. The peak labeled in red indicates SA.
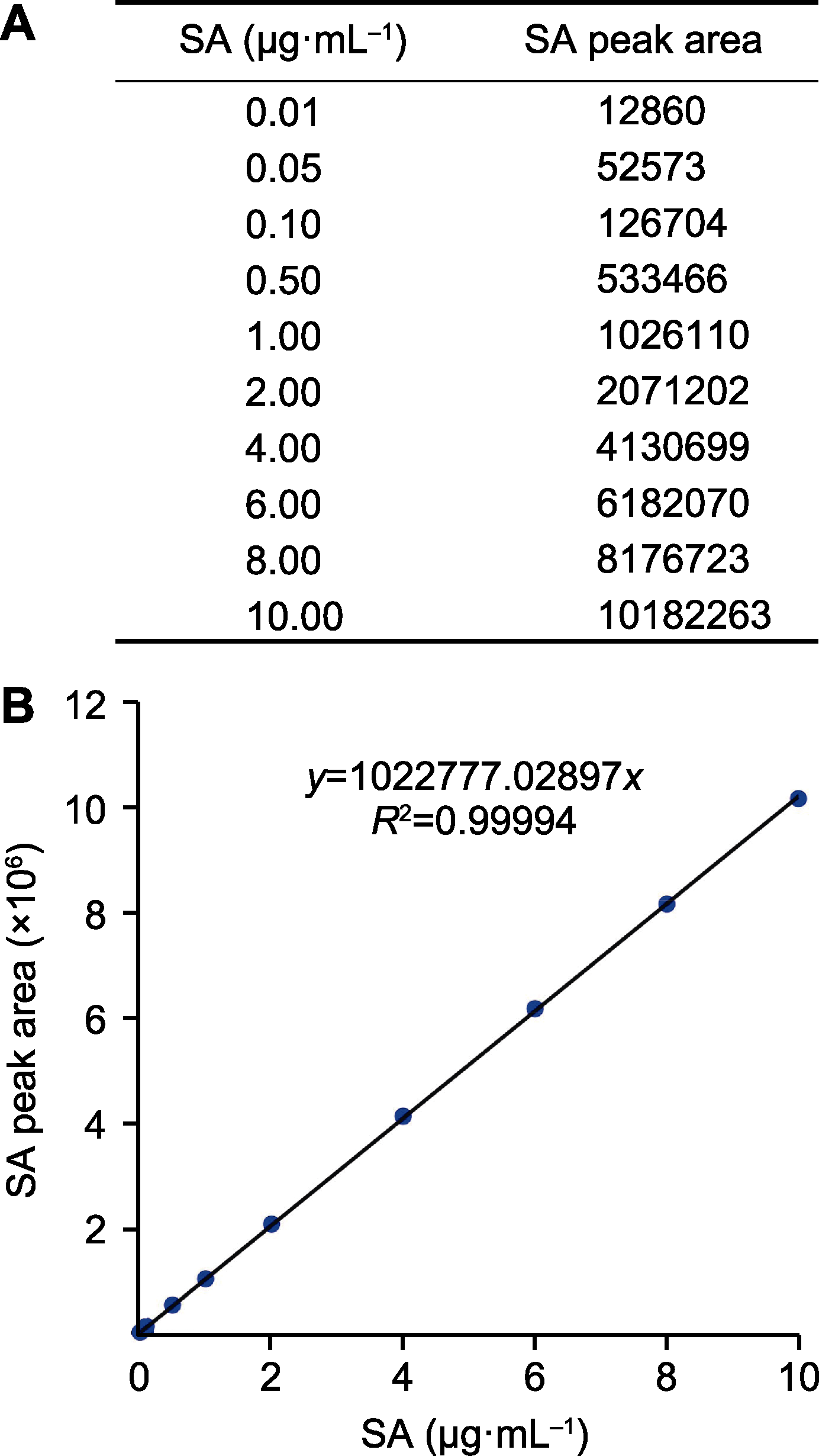
Figure 6 Salicylic acid (SA) standard curve (A) Peak areas corresponding to different concentrations of SA standards; (B) The standard curve (with an intercept of 0, R2 indicates the coefficient of determination)
| [1] | Aboul-Soud MAM, Cook K, Loake GJ (2004). Measurement of salicylic acid by a high-performance liquid chromatography procedure based on ion-exchange. Chromatographia 59, 129-133. |
| [2] |
Balcke GU, Handrick V, Bergau N, Fichtner M, Henning A, Stellmach H, Tissier A, Hause B, Frolov A (2012). An UPLC-MS/MS method for highly sensitive high-throughput analysis of phytohormones in plant tissues. Plant Methods 8, 47.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | Cao H, Bowling SA, Gordon AS, Dong XN (1994). Characterization of an Arabidopsis mutant that is nonresponsive to inducers of systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 6, 1583-1592. |
| [4] | Defraia CT, Schmelz EA, Mou ZL (2008). A rapid biosensor-based method for quantification of free and glucose- conjugated salicylic acid. Plant Methods 4, 28. |
| [5] |
Delaney TP, Uknes S, Vernooij B, Friedrich L, Weymann K, Negrotto D, Gaffney T, Gut-Rella M, Kessmann H, Ward E, Ryals J (1994). A central role of salicylic acid in plant disease resistance. Science 266, 1247-1250.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
Ding YL, Sun TJ, Ao K, Peng YJ, Zhang YX, Li X, Zhang YL (2018). Opposite roles of salicylic acid receptors NPR1 and NPR3/NPR4 in transcriptional regulation of plant immunity. Cell 173, 1454-1467.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
Fu ZQ, Dong XN (2013). Systemic acquired resistance: turning local infection into global defense. Annu Rev Plant Biol 64, 839-863.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | Fu ZQ, Yan SP, Saleh A, Wang W, Ruble J, Oka N, Mohan R, Spoel SH, Tada Y, Zheng N, Dong XN (2012). NPR3 and NPR4 are receptors for the immune signal salicylic acid in plants. Nature 486, 228-232. |
| [9] |
Gaffney T, Friedrich L, Vernooij B, Negrotto D, Nye G, Uknes S, Ward E, Kessmann H, Ryals J (1993). Requirement of salicylic acid for the induction of systemic acquired resistance. Science 261, 754-756.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
Huang WE, Wang H, Zheng HJ, Huang LF, Singer AC, Thompson I, Whiteley AS (2005). Chromosomally located gene fusions constructed in Acinetobacter sp. ADP1 for the detection of salicylate. Environ Microbiol 7, 1339-1348.
PMID |
| [11] | Kumar S, Zavaliev R, Wu QL, Zhou Y, Cheng J, Dillard L, Powers J, Withers J, Zhao JS, Guan ZQ, Borgnia MJ, Bartesaghi A, Dong XN, Zhou P (2022). Structural basis of NPR1 in activating plant immunity. Nature 605, 561-566. |
| [12] | Lim EK, Doucet CJ, Li Y, Elias L, Worrall D, Spencer SP, Ross J, Bowles DJ (2002). The activity of Arabidopsis glycosyltransferases toward salicylic acid, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, and other benzoates. J Biol Chem 277, 586-592. |
| [13] |
Marek G, Carver R, Ding YZ, Sathyanarayan D, Zhang XD, Mou ZZ (2010). A high-throughput method for isolation of salicylic acid metabolic mutants. Plant Methods 6, 21.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | Mishra S, Roychowdhury R, Ray S, Hada A, Kumar A, Sarker U, Aftab T, Das R (2024). Salicylic acid (SA)-mediated plant immunity against biotic stresses: an insight on molecular components and signaling mechanism. Plant Stress 11, 100427. |
| [15] |
Nawrath C, Métraux JP (1999). Salicylic acid induction- deficient mutants of Arabidopsis express PR-2 and PR-5 and accumulate high levels of camalexin after pathogen inoculation. Plant Cell 11, 1393-1404.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
Raskin I, Turner IM, Melander WR (1989). Regulation of heat production in the inflorescences of an Arum lily by endogenous salicylic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86, 2214-2218.
PMID |
| [17] |
Schmelz EA, Engelberth J, Alborn HT, O’Donnell P, Sammons M, Toshima H, Tumlinson JH (2003). Simultaneous analysis of phytohormones, phytotoxins, and volatile organic compounds in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100, 10552-10557.
DOI PMID |
| [18] | Snyder LR, Kirkland JJ, Dolan JW (陈小明, 唐雅妍译) (2012). 现代液相色谱技术导论(第3版). 北京: 人民卫生出版社. pp. 126-131. |
| [19] | Song JT (2006). Induction of a salicylic acid glucosyltransferase, AtSGT1, is an early disease response in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Cells 22, 233-238. |
| [20] |
Yan SP, Dong XN (2014). Perception of the plant immune signal salicylic acid. Curr Opin Plant Biol 20, 64-68.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | Ye C, Yao LB, Jin Y, Gao R, Tan Q, Li XY, Zhang YJ, Chen XF, Ma BJ, Zhang W, Zhang KW (2025). Establishment and application of a high-throughput screening method for salicylic acid metabolic mutants in rice. Chin Bull Bot 60, 586-596. (in Chinese) |
|
叶灿, 姚林波, 金莹, 高蓉, 谭琪, 李旭映, 张艳军, 陈析丰, 马伯军, 章薇, 张可伟 (2025). 水稻水杨酸代谢突变体高通量筛选方法的建立与应用. 植物学报 60, 586-596.
DOI |
|
| [22] | Yu XD, Cui XY, Wu C, Shi SX, Yan SP (2022). Salicylic acid inhibits gibberellin signaling through receptor interactions. Mol Plant 15, 1759-1771. |
| [23] |
Yu XD, Xu YR, Yan SP (2021). Salicylic acid and ethylene coordinately promote leaf senescence. J Integr Plant Biol 63, 823-827.
DOI |
| [24] | Zhang YJ, Zhao L, Zhao JZ, Li YJ, Wang JB, Guo R, Gan SS, Liu CJ, Zhang KW (2017). S5H/DMR6 encodes a salicylic acid 5-hydroxylase that fine-tunes salicylic acid homeostasis. Plant Physiol 175, 1082-1093. |
| [1] | Xiao Yinyan, Yu Hua, Wan Li. Plant Immunity Study: Mechanism Breakthroughs and Application Innovations [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(5): 693-703. |
| [2] | Wu Yujun, Li Yingju, Luo Qiaoyu, Ma Yonggui. Light-regulated Plant Immunity: The Regulatory Network From Light Signaling Pathways to Immune Responses [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(5): 786-803. |
| [3] | Su Silin, Tang Xianyu, Chen Yi, Wang Ting, Xia Shitou. Transcriptional Regulation of Systemic Acquired Resistance in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(5): 722-733. |
| [4] | Liu Deshui, Yue Ning, Liu Yule. Emerging Innovation in Plant Immunity [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(5): 669-678. |
| [5] | Jiang Yanan, Xu Yuqing, Wei Yiting, Chen Jun, Zhang Rongwan, Zhao Beibei, Lin Yuxiang, Rao Yuchun. Research Progress on the Regulatory Mechanism of Rice Disease Resistance [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(5): 734-748. |
| [6] | Zhu Xiaobo, Wang Liyin, Chen Xuewei. Salicylic Acid-mediated Plant Immune Responses: From Metabolism and Perception to Immune Activation [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(5): 679-692. |
| [7] | Can Ye, Linbo Yao, Ying Jin, Rong Gao, Qi Tan, Xuying Li, Yanjun Zhang, Xifeng Chen, Bojun Ma, Wei Zhang, Kewei Zhang. Establishment and Application of a High-throughput Screening Method for Salicylic Acid Metabolic Mutants in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(4): 586-596. |
| [8] | Yang Li, Qu Xitong, Chen Zihang, Zou Tingting, Wang Quanhua, Wang Xiaoli. Identification of the Spinach AT-hook Gene Family and Analysis of Expression Profiles [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(3): 377-392. |
| [9] | Jianmin Zhou. A Combat Vehicle with a Smart Brake [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(3): 343-346. |
| [10] | Jiaxin Chen, Hao Mei, Caixiang Huang, Zongyuan Liang, Yitong Quan, Dongpeng Li, Buweimaieryemu·Saimaiti , Xinxin Li, Hong Liao. A Highly Efficient Method to Generate Chimeric Soybean Plant with Transgenic Hairy Roots [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(1): 89-98. |
| [11] | Yuan Yuan, Enhebayaer, Qi Yanhua. Research Advances in Biological Functions of GH3 Gene Family in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(5): 770-782. |
| [12] | Nan Wu, Lei Qin, Kan Cui, Haiou Li, Zhongsong Liu, Shitou Xia. Cloning of Brassica napus EXA1 Gene and Its Regulation on Plant Disease Resistance [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(3): 385-393. |
| [13] | Jian-Min Zhou. A Ca2+-ROS Signaling Axis in Rice Provides Clues to Rice-pathogen Coevolution and Crop Improvements [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(5): 513-515. |
| [14] | Tiantian Shi, Ying Gao, Huan Wang, Jun Liu. Nucleo-cytoplasmic Transport and Transport Receptors in Plant Disease Resistance Defense Response [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(4): 480-487. |
| [15] | Jianfei Liu, Yan Liu, Kejian Liu, Yang Chi, Zhifa Huo, Yonghong Huo, Xiangling You. Optimization of the Regeneration System from Somatic Embryogenesis in Larix olgensis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(5): 605-612. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
