

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2020, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (4): 397-402.DOI: 10.11983/CBB20099 cstr: 32102.14.CBB20099
• COMMENTARIES • Next Articles
Ruifeng Yao1,*( ),Daoxin Xie2,*(
),Daoxin Xie2,*( )
)
Received:2020-05-28
Accepted:2020-06-02
Online:2020-07-01
Published:2020-06-11
Contact:
Ruifeng Yao,Daoxin Xie
Ruifeng Yao,Daoxin Xie. New Insight into Strigolactone Signaling[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(4): 397-402.
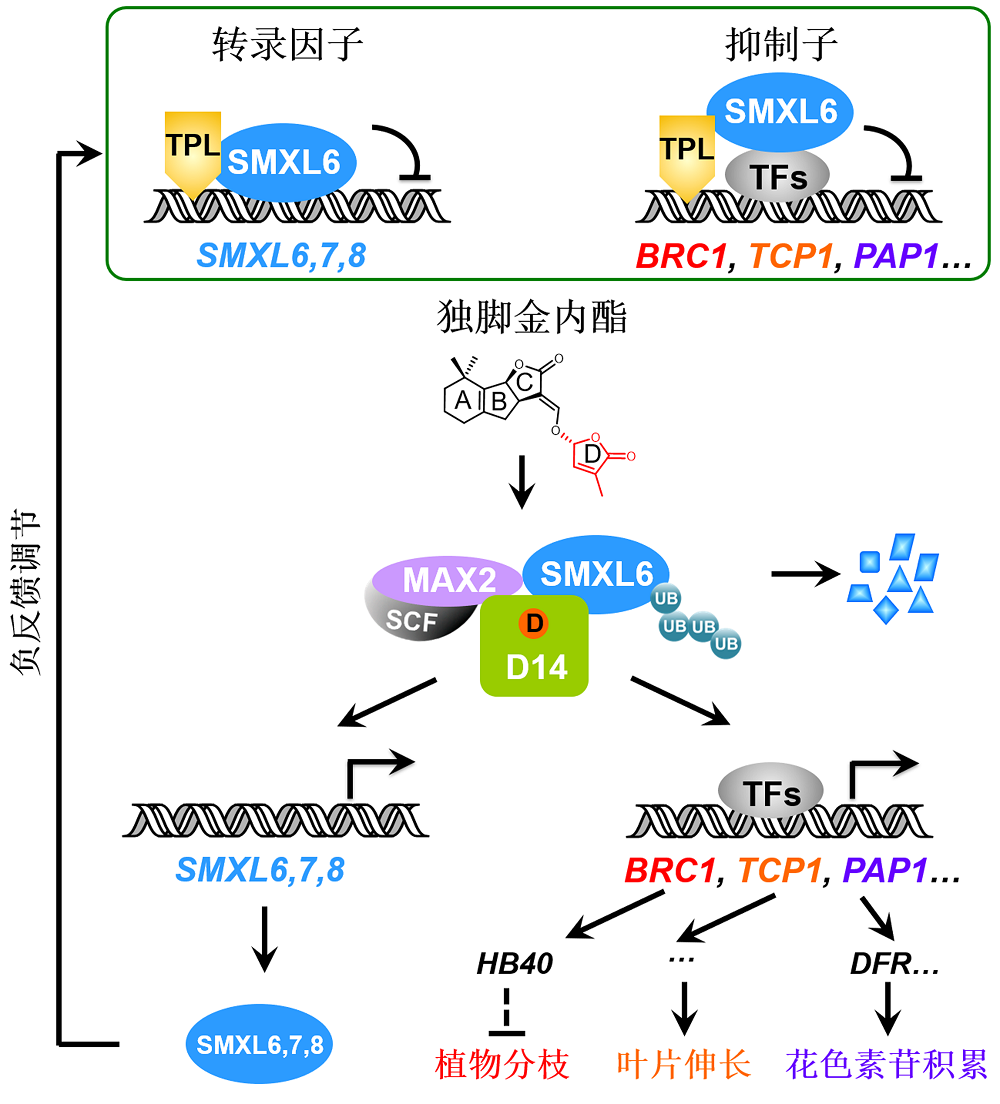
Figure 1 Working model for the dual-function repressors SMXL6,7,8 in strigolactone signaling SMXL6,7,8 in the strigolactone signaling pathway act as novel repressors with dual functions: SMXL6,7,8 act as repressors that recruit TPL co-repressor proteins and bind transcription factors to inhibit their transcriptional activity, thereby suppressing expression of strigolactone (SL)-responsive genes; meanwhile, SMXL6,7,8 also serve as transcription factors that directly bind and inhibit the promoters of SMXL6,7,8 genes. SL is perceived by D14 to trigger formation of SMXL6,7,8-D14-MAX2 complex and further induce SMXL6,7,8 degradation via the ubiquitination-proteasome pathway. The SL-induced SMXL6,7,8 degradation releases transcription factors to activate expression of the SL-responsive genes such as BRC1, TCP1 and PAP1 essential for plant branching, leaf elongation, and anthocyanin biosynthesis, respectively. Such SMXL6,7,8 degradation also de- represses the SMXL6,7,8 suppression on the SMXL6,7,8 promoters to activate the expression of SMXL6,7,8 genes, which forms a negative feedback regulation loop that maintains the homeostasis of SL pathway. SCF: Skp1-Cullin-F- box; UB: Ubiquitin
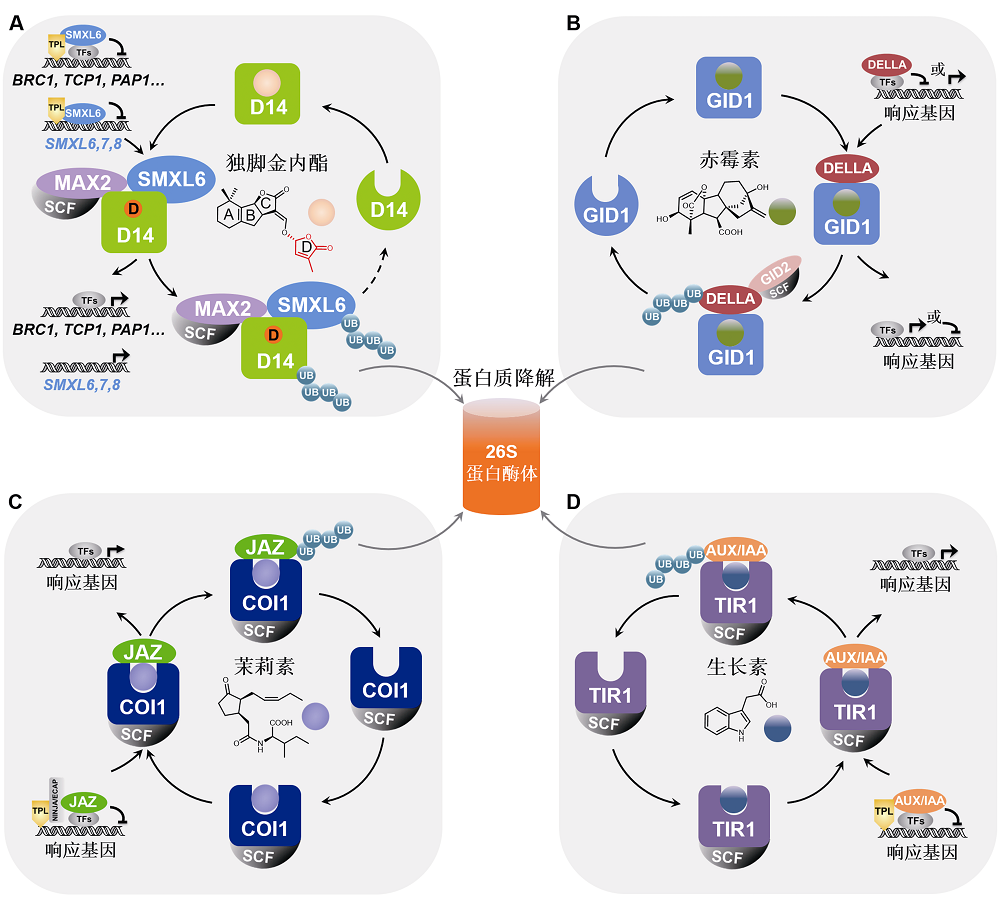
Figure 2 Comparison of the repressor proteins in strigolactone, gibberellin, jasmonate and auxin signaling pathways The repressor proteins D53/SMXL, DELLA, JAZ, and AUX/IAA in the signaling pathways of strigolactone (A), gibberellin (B), jasmonate (C) and auxin (D) bind and inhibit downstream transcription factors, thereby suppressing the expression of hormone-responsive genes. Hormone molecule is recognized by corresponding receptor protein and activates the signal transduction chain to induce the degradation of the repressor protein via ubiquitination-proteasome pathway, then triggering response gene expression and related biological processes. Moreover, the repressor proteins SMXL6,7,8 in strigolactone (SL) signaling pathway can also directly bind and inhibit the promoter of SMXL6,7,8 gene as transcription factors. SL induces the degradation of SMXL6,7,8 to release its repression on the SMXL6,7,8 promoters to activate the expression of SMXL6,7,8 genes, forming a negative feedback regulation loop (A) essential for the homeostasis of SL pathway.
| [1] | 黎家, 李传友 (2019). 新中国成立70年来植物激素研究进展. 中国科学: 生命科学 49, 1227-1281. |
| [2] |
Bürger M, Chory J (2020). The many models of strigolactone signaling. Trends Plant Sci 25, 395-405.
DOI URL PMID |
| [3] |
de Saint Germain A, Clavé G, Badet-Denisot MA, Pillot JP, Cornu D, Le Caer JP, Burger M, Pelissier F, Retailleau P, Turnbull C, Bonhomme S, Chory J, Rameau C, Boyer FD (2016). A histidine covalent receptor and butenolide complex mediates strigolactone perception. Nat Chem Biol 12, 787-794.
DOI URL PMID |
| [4] |
Duan J, Yu H, Yuan K, Liao Z, Meng X, Jing Y, Liu G, Chu J, Li J (2019). Strigolactone promotes cytokinin degradation through transcriptional activation of CYTOKININ OXIDASE/DEHYDROGENASE 9 in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116, 14319-14324.
DOI URL PMID |
| [5] |
Fang Z, Ji Y, Hu J, Guo R, Sun S, Wang X (2020). Strigolactones and brassinosteroids antagonistically regulate the stability of the D53-OsBZR1 complex to determine FC1 expression in rice tillering. Mol Plant 13, 586-597.
URL PMID |
| [6] |
Gomez-Roldan V, Fermas S, Brewer PB, Puech-Pages V, Dun EA, Pillot JP, Letisse F, Matusova R, Danoun S, Portais JC, Bouwmeester H, Bécard G, Beveridge CA, Rameau C, Rochange SF (2008). Strigolactone inhibition of shoot branching. Nature 455, 189-194.
DOI URL PMID |
| [7] |
Hamiaux C, Drummond RSM, Janssen BJ, Ledger SE, Cooney JM, Newcomb RD, Snowden KC (2012). DAD2 is an α/β hydrolase likely to be involved in the perception of the plant branching hormone, strigolactone. Curr Biol 22, 2032-2036.
DOI URL PMID |
| [8] |
Hu J, Ji Y, Hu X, Sun S, Wang X (2020). BES1 functions as the co-regulator of D53-like SMXLs to inhibit BRC1 expression in strigolactone-regulated shoot branching in Arabidopsis. Plant Commun 1, 100014.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Jiang L, Liu X, Xiong G, Liu H, Chen F, Wang L, Meng X, Liu G, Yu H, Yuan Y, Yi W, Zhao L, Ma H, He Y, Wu Z, Melcher K, Qian Q, Xu H, Wang Y, Li J (2013). DWARF 53 acts as a repressor of strigolactone signaling in rice. Nature 504, 401-405.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Ma H, Duan J, Ke J, He Y, Gu X, Xu TH, Yu H, Wang Y, Brunzelle JS, Jiang Y, Rothbart SB, Xu H, Li J, Melcher K (2017). A D53 repression motif induces oligomerization of TOPLESS corepressors and promotes assembly of a corepressor-nucleosome complex. Sci Adv 3, e1601217.
DOI URL PMID |
| [11] |
Seto Y, Yasui R, Kameoka H, Tamiru M, Cao MM, Terauchi R, Sakurada A, Hirano R, Kisugi T, Hanada A, Umehara M, Seo E, Akiyama K, Burke J, Takeda-Kamiya N, Li WQ, Hirano Y, Hakoshima T, Mashiguchi K, Noel JP, Kyozuka J, Yamaguchi S (2019). Strigolactone perception and deactivation by a hydrolase receptor DWARF14. Nat Commun 10, 191.
DOI URL PMID |
| [12] |
Shabek N, Ticchiarelli F, Mao HB, Hinds TR, Leyser O, Zheng N (2018). Structural plasticity of D3-D14 ubiquitin ligase in strigolactone signaling. Nature 563, 652-656.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] |
Song X, Lu Z, Yu H, Shao G, Xiong J, Meng X, Jing Y, Liu G, Xiong G, Duan J, Yao X, Liu C, Li H, Wang Y, Li J (2017). IPA1 functions as a downstream transcription factor repressed by D53 in strigolactone signaling in rice. Cell Res 27, 1128-1141.
URL PMID |
| [14] |
Stanga JP, Smith SM, Briggs WR, Nelson DC (2013). SUPPRESSOR OF MORE AXILLARY GROWTH2 1 controls seed germination and seedling development in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 163, 318-330.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Umehara M, Hanada A, Yoshida S, Akiyama K, Arite T, Takeda-Kamiya N, Magome H, Kamiya Y, Shirasu K, Yoneyama K, Kyozuka J, Yamaguchi S (2008). Inhibition of shoot branching by new terpenoid plant hormones. Nature 455, 195-200.
URL PMID |
| [16] |
Uraguchi D, Kuwata K, Hijikata Y, Yamaguchi R, Imaizumi H, Am S, Rakers C, Mori N, Akiyama K, Irle S, McCourt P, Kinoshita T, Ooi T, Tsuchiya Y (2018). A femtomolar-range suicide germination stimulant for the parasitic plant Striga hermonthica. Science 362, 1301-1305.
URL PMID |
| [17] | Wang B, Wang Y, Li J (2017). Strigolactones. In: Li JY, Li CY, Smith SM, eds. Hormone Metabolism and Signaling in Plants. London: Academic Press. pp. 327-359. |
| [18] |
Wang L, Wang B, Jiang L, Liu X, Li X, Lu Z, Meng X, Wang Y, Smith SM, Li J (2015). Strigolactone signaling in Arabidopsis regulates shoot development by targeting D53-like SMXL repressor proteins for ubiquitination and degradation. Plant Cell 27, 3128-3142.
DOI URL PMID |
| [19] |
Wang L, Wang B, Yu H, Guo H, Lin T, Kou L, Wang A, Shao N, Ma H, Xiong G, Li X, Yang J, Chu J, Li J (2020a). Transcriptional regulation of strigolactone signaling in Arabidopsis. Nature 583, 277-281.
DOI URL PMID |
| [20] |
Wang L, Xu Q, Yu H, Ma H, Li X, Yang J, Chu J, Xie Q, Wang Y, Smith SM, Li J, Xiong G, Wang B (2020b). Strigolactone and karrikin signaling pathways elicit ubiquitination and proteolysis of SMXL2 to regulate hypocotyl elongation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 32, 2251-2270.
DOI URL PMID |
| [21] |
Waters MT, Gutjahr C, Bennett T, Nelson DC (2017). Strigolactone signaling and evolution. Annu Rev Plant Biol 68, 291-322.
DOI URL PMID |
| [22] |
Xie Y, Liu Y, Ma M, Zhou Q, Zhao Y, Zhao B, Wang B, Wei H, Wang H (2020). Arabidopsis FHY3 and FAR1 integrate light and strigolactone signaling to regulate branching. Nat Commun 11, 1955.
URL PMID |
| [23] | Yao R, Ming Z, Yan L, Li S, Wang F, Ma S, Yu C, Yang M, Chen L, Chen L, Li Y, Yan C, Miao D, Sun Z, Yan J, Sun Y, Wang L, Chu J, Fan S, He W, Deng H, Nan F, Li J, Rao Z, Lou Z, Xie D (2016). DWARF14 is a non-canonical hormone receptor for strigolactone. Nature 536, 469-473. |
| [24] |
Yao R, Wang F, Ming Z, Du X, Chen L, Wang Y, Zhang W, Deng H, Xie D (2017). ShHTL7 is a non-canonical receptor for strigolactones in root parasitic weeds. Cell Res 27, 838-841.
DOI URL PMID |
| [25] |
Yao R, Wang L, Li Y, Chen L, Li S, Du X, Wang B, Yan J, Li J, Xie D (2018). Rice DWARF14 acts as an unconventional hormone receptor for strigolactone. J Exp Bot 69, 2355-2365.
DOI URL PMID |
| [26] |
Zhao LH, Zhou XE, Wu ZS, Yi W, Xu Y, Li SL, Xu TH, Liu Y, Chen RZ, Kovach A, Kang YY, Hou L, He YZ, Xie C, Song WL, Zhong DF, Xu YC, Wang YH, Li JY, Zhang CH, Melcher K, Xu HE (2013). Crystal structures of two phytohormone signal-transducing α/β hydrolases: karrikin-signaling KAI2 and strigolactone-signaling DWARF14. Cell Res 23, 436-439.
DOI URL PMID |
| [27] |
Zhou F, Lin Q, Zhu L, Ren Y, Zhou K, Shabek N, Wu F, Mao H, Dong W, Gan L, Ma W, Gao H, Chen J, Yang C, Wang D, Tan J, Zhang X, Guo X, Wang J, Jiang L, Liu X, Chen W, Chu J, Yan C, Ueno K, Ito S, Asami T, Cheng Z, Wang J, Lei C, Zhai H, Wu C, Wang H, Zheng N, Wan J (2013). D14-SCFD3-dependent degradation of D53 regulates strigolactone signaling. Nature 504, 406-410.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Zwanenburg B, Blanco-Ania D (2018). Strigolactones: new plant hormones in the spotlight. J Exp Bot 69, 2205-2218.
DOI URL PMID |
| [1] | Chen Pengxiang, Wang Bo, Wang Zijun, Han Rong. The Regulatory Roles of the Transcription Factors in Plant's Response to UV-B Radiation [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(3): 449-459. |
| [2] | Liu Xupeng, Wang Min, Han Shou'an, Zhu Xuehui, Wang Yanmeng, Pan Mingqi, Zhang Wen. Research Progress on Factors and Molecular Mechanisms Regulating Plant Organ Abscission [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(3): 472-482. |
| [3] | Ruifeng Yao, Daoxin Xie. Activation and Termination of Strigolactone Signal Perception in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(6): 873-877. |
| [4] | Tingxin Chen, Min Fu, Na Li, Leilei Yang, Lingfei Li, Chunmei Zhong. Identification and Expression Analysis of DNA Methyltransferase in Begonia masoniana [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(5): 726-737. |
| [5] | Wen Chen, Yingying Zhou, Ping Luo, Yongyi Cui. Molecular Mechanism of Petal Doubling of Flower in Angiosperm [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(2): 257-277. |
| [6] | Xinhai Zeng, Rui Chen, Yu Shi, Chaoyue Gai, Kai Fan, Zhaowei Li. Research Advances in Biological Functions of Plant SPL Transcription Factors [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(6): 982-997. |
| [7] | Yu Miao, Ruan Chengjiang, Ding Jian, Li Jingbin, Lu Shunguang, Wen Xiufeng. Hrh-miRn458 Regulates Oil Biosynthesis of Sea Buckthorn via Targeting Transcription Factor WRI1 [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(5): 635-648. |
| [8] | Li Yue, Hu Desheng, Tan Jinfang, Mei Hao, Wang Yi, Li Hui, Li Fang, Han Yanlai. Chaetomium uniseriatum Promotes Maize Growth by Accelerating Straw Degradation and Regulating the Expression of Hormone Responsive Genes [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(4): 422-433. |
| [9] | Yanyan Meng, Nan Zhang, Yan Xiong. Novel Links in the Plant Target of Rapamycin Signaling Networks [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(1): 1-11. |
| [10] | Jingwen Wang, Xingjun Wang, Changle Ma, Pengcheng Li. A Review on the Mechanism of Ribosome Stress Response in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(1): 80-89. |
| [11] | Dong Liu. Managing Both Internal and Foreign Affairs—A PHR-centered Gene Network Regulates Plant-mycorrhizal Symbiosis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(6): 647-650. |
| [12] | Tianxingzi Wang, Zheng Zhu, Yue Chen, Yuqing Liu, Gaowei Yan, Shan Xu, Tong Zhang, Jinjiao Ma, Shijuan Dou, Liyun Li, Guozhen Liu. Rice OsWRKY42 is a Novel Element in Xa21-mediated Resistance Pathway Against Bacterial Leaf Blight [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(6): 687-698. |
| [13] | Xiaoting Zhao, Kaitao Mao, Jiahui Xu, Chuan Zheng, Xiaofeng Luo, Kai Shu. Protein Phosphorylation and Its Regulatory Roles in Seed Dormancy and Germination [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(4): 488-499. |
| [14] | Kaicheng Kang, Xiqiang Niu, Xianzhong Huang, Nengbing Hu, Yihu Sui, Kaijing Zhang, Hao Ai. Genome-wide Identification and Comparative Evolutionary Analysis of the R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor Gene Family in Pepper [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(3): 315-329. |
| [15] | Qilu Yu, Jiangzhe Zhao, Xiaoxian Zhu, Kewei Zhang. Regulation of Rice Growth by Root-secreted Phytohormones [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(2): 175-182. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||